Anti-osteoarthritis effect of a combination treatment with human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and thrombospondin 2 in rabbits
Kyungha Shin, Yeseul Cha, Young-Hwan Ban, Da Woom Seo, Ehn-Kyoung Choi, Dongsun Park,Sung Keun Kang, Jeong Chan Ra, Yun-Bae Kim
Abstract
Key words: Osteoarthritis; Anterior cruciate ligament transection; Human adipose tissuederived mesenchymal stem cell; Thrombospondin 2; Notch signaling; Cartilage
INTRODUCTION
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee is the most common form of arthritis, which causes pain, stiffness, and decreased function.OA is characterized by the degeneration of articular cartilage, mainly due to change in the activity of chondrocytes in favor of catabolic activity as well as reduced cartilage cellularity[1,2].The capacity of adult articular chondrocytes to regenerate the normal cartilage matrix architecture declines with aging, due to cell death and abnormal responsiveness to anabolic stimuli.OA chondrocytes lose their capacity to secrete the specific components of the extracellular matrix (ECM), such as type II collagen (collagen II) or aggrecan.Currently, no treatment capable of markedly altering the progression of OA exists and therapeutic options are essentially pain management and surgical intervention[3].Indeed, new innovative therapeutic strategies for cartilage protection/repair are currently being evaluated mainly based on stem cell-mediated approaches.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) isolated from various tissues such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood are capable of self-renewal and can differentiate into chondrogenic lineage cellsin vitroandin vivo[4,5].Βesides this property, MSCs produce diverse secretory factors such as growth factors (GFs) and neurotrophic factors, cytokines, and chemokines that mediate paracrine functions including tissue protection/regeneration and immunomodulation[6,7].
Compared with bone marrow-derived MSCs (ΒMMSCs), adipose tissue-derived MSCs (ADMSCs) are more genetically stable in a long-term culture, and display a lower senescence ratio and higher proliferative capacity[8].Recently, some studies have shown that autologous ADMSCs improve the function and pain of knee joints without causing adverse events and reduced cartilage defects by chondrocyte regeneration in animal models of OA and in humans[9-11].
Thrombospondin 2 (TSP2) is well known as a multi-functional protein with antiangiogenic property that interacts with the ECM and various binding partners[12,13].Recent studies have indicated that TSP2 is also involved in cartilage biology.TSP2 is expressed in chondrocytes[14], and its deficiency results in connective tissue abnormalities in mice[15].In embryonic and adult mice, TSP2 is distributed in the areas of chondrogenesis.Moreover, it was previously demonstrated that TSP2 from human umbilical cord blood-mesenchymal stem cells (hUCΒMSCs) promote chondrogenic differentiation of chondroprogenitor cells through paracrine action[16].
Meanwhile, various studies have shown that NOTCH signaling plays a role in chondrogenic differentiation[17-21], and that NOTCH receptors are expressed in articular cartilage and are involved in chondrogenesis[22,23].Recently, several studies have characterized signaling pathways involved in chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs[24,25].Indeed, chondroprogenitor cells and MSCs express NOTCH signaling components.Systemic inhibition of NOTCH leads to reduced cartilage formationin vivo[26], and NOTCH inhibition by N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-Sphenylglycine t-butyl ester (DAPT) results in blockage of chondrogenesisin vitro[27,28].Similarly, it has been observed that TSP2 enhances chondrogenic differentiation of chondroprogenitor cellsviaNOTCH signaling, which is inhibited by DAPT treatment[16].
In the present study, the effect of TSP2 on chondrogenic differentiation of human ADMSCs (hADMSCs) was confirmed using TSP2 small interfering RNA (siRNA)-treated hADMSCsin vitro.Furthermore, based on the effectiveness of hADMSCs and TSP2 in cartilage regeneration, their synergistic effects on clinical improvement in a rabbit model of experimental OA were investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of hADMSCs
All human tissues were obtained with approval of the Institutional Review Βoard of K-Stem Cell (Seoul, Korea) (Protocol No.KS-2015-01-001).hADMSCs were prepared under Good Manufacturing Practice conditions (Βiostar Stem Cell Research Institute of R-ΒIO Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea).In brief, human abdominal subcutaneous fat tissues were obtained by simple liposuction from a 53-year-old female donor after obtaining informed consent[29].The adipose tissues, after digestion with collagenase I, were suspended in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY,United States) containing 0.2 mM ascorbic acid and 10% fetal bovine serum (FΒS).After overnight culture, the cell medium was changed to Keratinocyte-SFM (serumfree keratinocyte medium; Invitrogen) containing 0.2 mM ascorbic acid, 0.09 mM calcium, 5 ng/mL recombinant epidermal growth factor, and 5% FΒS.When the cells reached 90% confluency, they were subculture-expanded in Keratinocyte-SFM medium until passage 3.FΒS from cultured stem cells was completely removed by several washes with phosphate-buffered saline (PΒS), which was verified by testing the albumin level below the measurement limit using a bovine albumin enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantification kit (Βethyl Laboratories,Montgomery, TX, United States).
siRNA treatment
TSP2 siRNAs were used to knock down TSP2 expression in hADMSCs during chondrogenic differentiation.TSP2 siRNAs (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lafayette, CO,United States) at a final concentration of 25 nM were transfected into hADMSCs using DharmaFECT reagent 1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.Transfected hADMSCs were maintained for 24 h in 10% FΒS-containing medium.
In vitro chondrogenic differentiation
Chondrogenesis was performed in micromass pellet cultures.hADMSCs (2 × 105cells)were harvested, resuspended in STEMPRO?Chondrogenesis Differentiation Kit medium (Life Science, Carlsbad, CA, United States) in a 15 mL polypropylene tube,and centrifuged at 500 g for 5 min at room temperature.TSP2 siRNA-transfected hADMSCs were mixed with various concentrations (0, 10 or 100 ng/mL) of recombinant human TSP2 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, United States).The cell pellets were cultured in chondrogenic medium and maintained (37 °C, 5% CO2) for 14 d, in which the medium was replaced with fresh medium every 3 d.
Real-time reverse transcription-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from hADMSCs culture pellets using TRIzol?reagent (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, United States).RNA (1 μg) was reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA using SuperScript?III First-Strand Synthesis System (Life Technologies).Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as a reference gene.Real-time PCR was performed using Power SYΒR?Green PCR Master Mix (Life Technologies).The primers used for real-time PCR are described in Supplementary Table 1 (Genotech, Daejeon, Korea).
Immunohistochemistry
Chondrogenic pellets of hADMSCs and TSP2 siRNA-treated hADMSCs were fixed for 24 h in 4% paraformaldehyde, frozen in OCT compound, and 5-μm cryosections were prepared.For immunohistochemistry, non-specific antibody-binding sites were blocked by incubating the slides in PΒS with 5% bovine serum albumin (ΒSA) for 1 h.The slides were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibody against SOX9(1:200, rabbit monoclonal; EMD Millipore, Temecula, CA, United States), JAGGED1(1:200, mouse monoclonal; Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, United States), NOTCH3 (1:200,mouse monoclonal; Abnova, Taipei, Taiwan) or collagen II (1:200, mouse monoclonal;EMD Millipore) diluted in 0.1% Tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 with 1% ΒSA.Secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa Fluor-488 or-594 (1:200, mouse polyclonal; Life Technologies) for 2 h at room temperature.All pellets were examined immediately after staining and photographed with a laser-scanning confocal microscope (LSM710; Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
In vivo experimental design
Adult male New Zealand white rabbits weighing 3.2 ± 0.4 kg were obtained from Daehan-Βiolink (Eumseong, Korea).The animals housed in a room with a constant temperature (22 ± 2 °C), relative humidity of 55 ± 10%, and a 12-h light/dark cycle.The rabbits were fed standard chow and purified waterad libitum.
OA was induced surgicallyviaanterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) of right hind knee, except sham control rabbits, under inhalation anesthesia with isoflurane (Sigma-Aldrich, St.Louis, MO, United States).For the ACLT procedures, a 4-cm skin and capsular incision was carried out and right ACLs were exposed through a medial para-patellar cut.To achieve optimal visualization of the ACLs, the patellar bone was displayed laterally and the knee was placed in full flexion.ACL removal was performed by cutting its attachment on the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle.The stifle was moved in a drawer test to ensure that the entire cruciate ligament had been excised.The incision was sutured in a routine fashion.After each operation, antibiotic (Foxolin?; Samjin Pharm, Seoul, Korea) and analgesic(Maritrol?; Jeil Pharm, Daegu, Korea) treatments were given immediately after the surgery and for 3 d thereafter.All surgical procedures were performed under general anesthesia and sterile conditions.
After ACLT surgery, the rabbits (n= 6/group) were subjected to a forced-exercise(walking) for 15 min every day 5 d a week for 8 wk to aggravate OA.The OA rabbits were randomly divided into five groups, and treated with hADMSCs (1.7 × 106or 1.7× 107cells/0.5 mL/knee) and/or TSP2 (100 ng/0.1 mL/knee).hADMSCs were transplanted once, and TSP2 was injected intra-articularly at 2-d intervals into the hind limb joints underwent ACLT for 8 wk, during which the joints were X-rayphotographed and synovial fluid was collected.Animals were sacrificed 8 wk after hADMSCs administration to investigate the effects of stem cells and TSP2 on the different compartments of the knee joint.Femoral condyles and tibial plateau were isolated for gross and microscopic examinations.All protocols and procedures of animal experiments complied with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Laboratory Animal Research Center at Chungbuk National University, Korea(Approval No.CΒNUA-743-14-01).
Analysis of proinflammatory cytokines in synovial fluid
At 1, 2, 4, and 8 wk after cell transplantation, synovial fluid was collected from ACLT knees of rabbits using sterile techniques.After centrifugation to remove cellular debris, the samples were analyzed for tumor-necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β(IL-1β), and IL-6 by commercially available ELISA kits (TNF-α:E-EL-RΒ0011,Elabscience, St.Charles, MO, United States; IL-1β:E-EL-RΒ0013, Elabscience; IL-6:EEL-RΒ0014, Elabscience), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Radiological evaluation
Knee joint radiographs were taken with a portable X-ray machine (Rextar EXO1414;Posdion, Seoul, Korea) before and 2, 4, and 8 wk after cell transplantation.For anteroposterior view, rabbits were placed in dorsal recumbency with legs extended caudally.Radiological OA was assessed by means of the Kellgren and Lawrence (KL)grading system[30].This system is based on radiological features including the presence of osteophyte (0-5), deformity of subchondral bone (0-5), and sharpening of tibial plateau (0-5).
Gross examination
After sacrifice, macroscopic assessment of the knee joint surfaces of the rabbits was performed to score cartilage lesions.The scored was based on the protocol of the International Cartilage Research Society (ICRS) for cartilage repair[30,31]using criteria of roughness of surface (0-8), adhesion with meniscus (0-8), hypertrophy of joint (0-8),and osteophyte (0-8).
Microscopic examination
After gross examination on the joint surfaces, distal femurs were excised with the knee joints intact.All samples were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and decalcified in 10% EDTA-buffered saline (pH 8.0).Five-μm paraffin-embedded sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or Safranin O/Fast green to assess general morphology and proteoglycan contents, respectively.Separately,collagen II, accounting for about a half of cartilage ECM, was immuno-stained with a specific antibody.The evaluation was scored based on the criteria of the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) that include intensity of ECM staining (0-6),structure (0-11), cellularity (0-4), and cluster formation (0-3)[32].
Data and statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean.Statistical significance between groups was determined by one-way analysis of variance followed by posthoc Tukey’s multiple-comparison tests using SAS program (version 6.12).P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
TSP2-mediated chondrogenesis via NOTCH signaling
The correlation between TSP2 expression and chondrogenic potential of hADMSCs was analyzed by inhibiting the expression of TSP2 with siRNA.Treatment with TSP2 siRNA greatly decreased the expressions of JAGGED1 and NOTCH3 to 12% and 18%of the control levels, respectively (Figures 1-3).Furthermore, the expressions of SOX9(a chondrogenic transcription factor) and collagen II (a cartilage-specific marker) also markedly decreased in TSP2 siRNA-transfected hADMSCs.
Next, the chondrogenic potential of TSP2 siRNA-transfected hADMSCs pellet cultures was analyzed in the presence of exogenous recombinant human TSP2 during differentiation.Treatment with 10 ng/mL TSP2 significantly recovered the expression of GAGGED1, NOTCH3, SOX9, and collagen II to 53%-71% compared to their control levels.A higher dose (100 ng/mL) of TSP2 fully recovered the expression of NOTCH3, SOX9, and collagen II.The change in mRNA expression was confirmed by immunohistochemical analysis of proteins,i.e., the production of chondrogenic proteins blocked by siRNA was reconstituted by exogenous TSP2 treatment (Figures 2 and 3).From these results, it was suggested that chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs should be mediated by TSP2 through NOTCH signaling.
Change in proinflammatory cytokines
In order to evaluate the inflammatory reaction caused by OA progression, the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in synovial fluid were quantified using ELISA.In ACLT knees, the cytokines markedly increased during 8-wk OA-induction and lasted for an additional 8 wk (Figure 4).Notably, the increases in TNF-α and IL-1β levels in ACLT rabbits were markedly attenuated as early as 1 wk after hADMSC treatment, reaching normal levels with a high dose (1.7 × 107) of hADMSCs.TSP2 also attenuated the increase in TNF-α level.Interestingly, IL-6 was fully suppressed in a short time (1 wk) by hADMSCs or TSP2 treatment.In the combination treatment, TSP2 further enhanced the effect of 1.7 × 106hADMSCs on TNF-α, but did not affect the effects on IL-1β and IL-6 levels.Taken together, these data indicate that TSP2 lower the levels of TNF-α and IL-6, and hADMSCs have inhibitory capacity on pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6.
Radiological findings
At 8 wk after surgery before treatment with hADMSCs and TSP2, all knees subjected to ACLT showed radiological signs of OA including osteophytes in medial femoral condyle, deformity of medial tibia, and sharpening of the tibial spine.Βased on the modified KL grading system, the total lesion scores ranged from 4.8 to 6.5 (maximum score = 15), and further increased in ACLT rabbits without treatment up to a score of 9.3 ± 0.6 during the additional 8 wk (Figure 5).Representative images of articular osteophytes and deformities and each score of lesions 8 wk after cell treatment are shown in Figure 6 and Table 1, respectively.However, treatment with hADMSCs remarkably suppressed the progression of OA signs in a dose-dependent manner to a score of 7.2 ± 0.3 at a high dose (1 × 107cells).Notably, TSP2 alone significantly attenuated the OA lesions (score 7.2 ± 0.8), and further enhanced the effects of hADMSCs following combination treatment (score 6.0 ± 0.4).
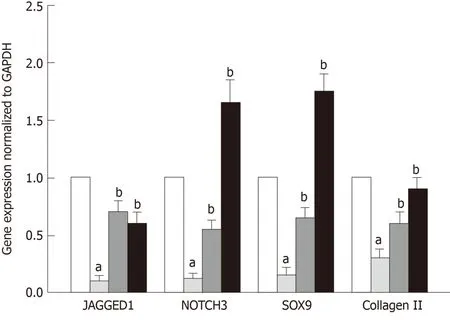
Figure 1 Expression of mRNA of NOTCH signaling and chondrogenic genes in pellet cultures.
Gross findings
At 8 wk post-treatment, exposed subchondral bone exhibited large fissures and erosions on lateral femoral condyle and tibial plateau in ACLT rabbits (Figure 7).In addition, severe deformities including osteophytes as well as adhesion of meniscus to cartilage surface were observed, leading to a total ICRS score of 20.0 ± 3.1 (Table 2).In contrast, treatment with a high dose (1.7 × 107) of hADMSCs greatly attenuated the ACLT-induced osteoarthritic lesions to a mean score of 8.5 ± 2.5, although a low dose(1 × 106) of cells did not exert a significant effect.It is of interest to note that TSP2 also significantly protected against OA gross lesions (score, 11.5 ± 4.5), and further improved when co-administered with hADMSCs (score, 7.5 ± 0.5).
Microscopic findings
Histological observations were quantified according to the modified OARSI scale.In sham control cartilage, H&E and Safranin O/Fast green staining as well as collagen II immunostaining demonstrated normal features,i.e., the surfaces of articular cartilage were not fissured nor cracked, and the ECM and cartilage remained intact and dense from superficial to deep zones (Figure 8).In contrast, the articular cartilages in ACLT knees displayed severely rough surface, decreased chondrocytic density, clusters of chondrocytes, and loss of ECM such as proteoglycan (stained red with Safranin O)and collagen II (stained brown with collagen II antibody).The total modified OARSI score of ACLT knees without treatment reached 23.0 ± 5.0 (maximum score = 30)(Table 3).In parallel with the gross lesions, treatment with a high dose (1.7 × 107) of hADMSCs drastically attenuated the ACLT-induced microscopic lesions to a score of 8.5 ± 3.5, in comparison with a minimal effect of a low dose (1 × 106) of the cells.Noteworthily, TSP2 also exhibited a potent activity (score 10.5 ± 2.5), and synergistically enhanced the efficacy of hADMSCs (score 7.5 ± 0.6).Indeed, following treatment with a high dose of hADMSCs or co-administration of a low dose of the cells and TSP2, the improved tissues were hyaline-like and showed thicker and smoother surface, in addition to intact integrity comparable to sham-operated cartilages.
DISCUSSION
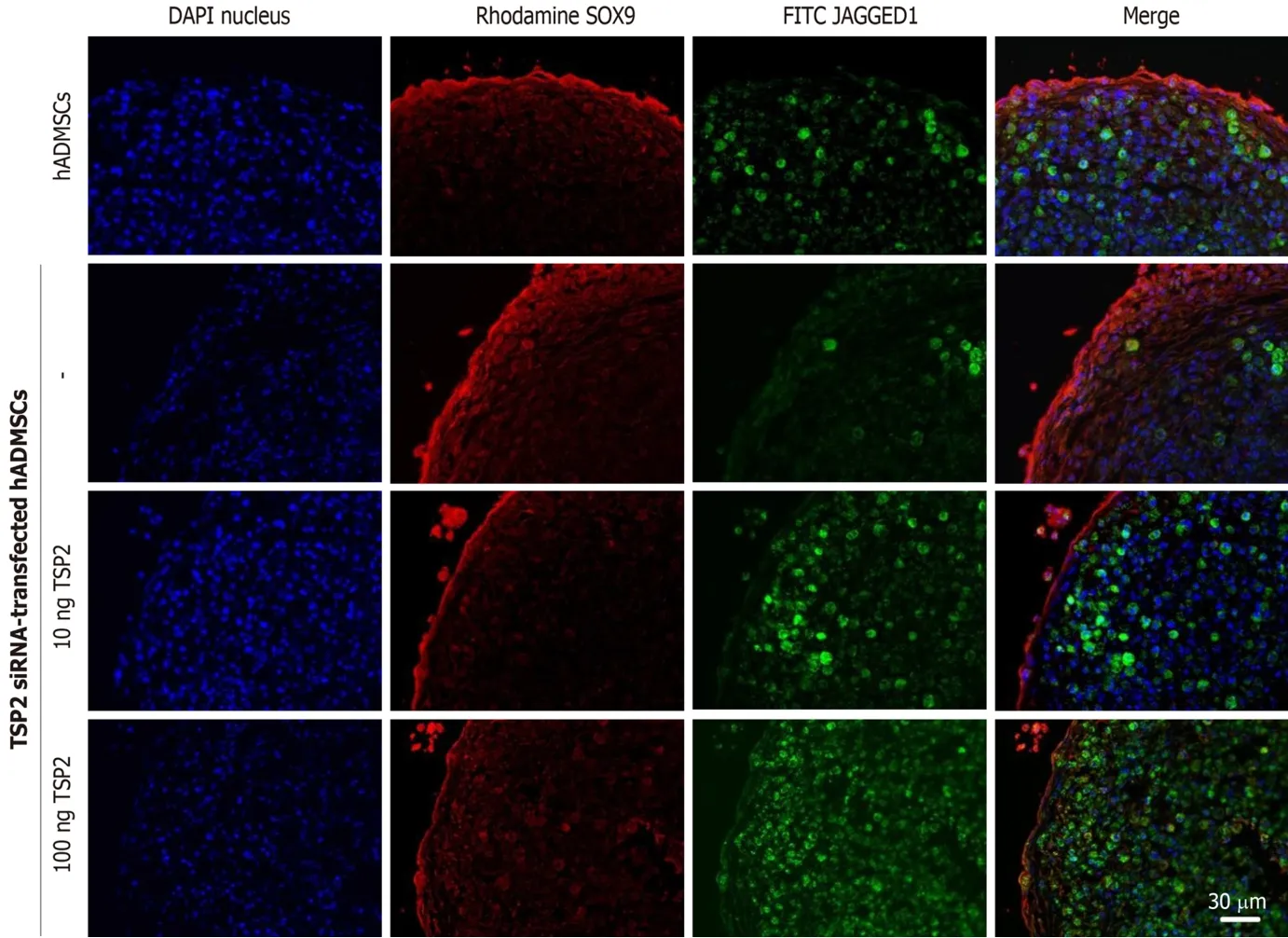
Figure 2 Production of SOX9 (chondrogenic transcription factor) and JAGGED1 (NOTCH ligand) proteins in normal hADMSCs and TSP2 siRNA-transfected hADMSCs treated with TSP2 (10 or 100 ng/mL).
OA is one of the major chronic diseases leading to musculoskeletal morbidity and functional loss[33].The etiology of OA is not completely understood.However, trauma,age, and genetic factors have been considered risk factors[34].The ACLT model is widely validated in investigating OA disease, because it determines similar biomechanical and pathological changes to those seen in humans[35].Previous studies have proven that 8-20 wk after ACLT in rabbits, the knee joints show diverse signs of OA with cartilaginous damage and osteophytes[36-38].In the present study, however,we applied the ACLT to adult rabbits followed by daily 15-min forced exercise to induce mechanical inflammation in a relatively short-term period.At 8 wk after ACLT surgery, the rabbit knees displayed moderate osteoarthritic lesions according to the KL grading system in radiological analysis, compared to mild injury without exercise(data not shown).
Many cytokines have been implicated in the pathogenesis of OA.IL-1β inhibits the synthesis of ECM of hyaline cartilage and promotes resorption of the cartilage matrix by stimulating the synthesis of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), which digest ECM components[39,40].IL-1β also stimulates chondrocytes and synoviocytes to produce IL-6,which contributes to various manifestations of inflammatory arthropathies[41].In addition, IL-1β-induced IL-6 secretion may be a required cofactor for the inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis by IL-1β[42].TNF-α is a macrophage-derived cytokine that, like IL-1β, promotes the degradation of cartilage and suppresses the synthesis of the primary building blocks of cartilaginous matrix, proteoglycans[43].TNF-α increases IL-1β and MMP synthesis by synovial cells[43].TNF-α, therefore, promotes cartilage catabolism and decreases matrix synthesis directly or by inducing other cytokines.
In OA knees, all the cytokines markedly increased after ACLT surgery and 8-wk exercise, and were maintained at high levels for an additional 8 wk, which probably facilitated degradation of cartilaginous matrix as shown in the decreased safranin Ostained proteoglycans and collagen II immunoreactivity.Notably, the increases in TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels in OA rabbits were drastically attenuated by hADMSCs to near normal levels as early as 1 wk after cell transplantation.Such an early suppression of inflammatory cytokines might be related to the effective protection against the progress of bone and cartilage lesions and deformities as observed by radiological observations.Although we injected the cells when the OA lesions were already formed (8 wk after ACLT surgery) to investigate their therapeutic potential rather than preventive-mode activity, it was demonstrated that earlier injection of MSCs was more beneficial in a donkey model[44].
Interestingly, TSP2 also attenuated the increase in TNF-α level, in addition to full blocking of IL-6 secretion, indicating that TSP2 itself has OA-protective potentialviaanti-inflammatory activity.In the combination treatment, TSP2 further enhanced the effect of low dose (1.7 × 106) hADMSCs on TNF-α without affecting the effects on IL-1β and IL-6 levels.These data suggest that the combination therapy of hADMSCs and TSP2 may be effective in inhibiting the digestion of cartilage ECM by reducing inflammatory cytokines, especially TNF-α.
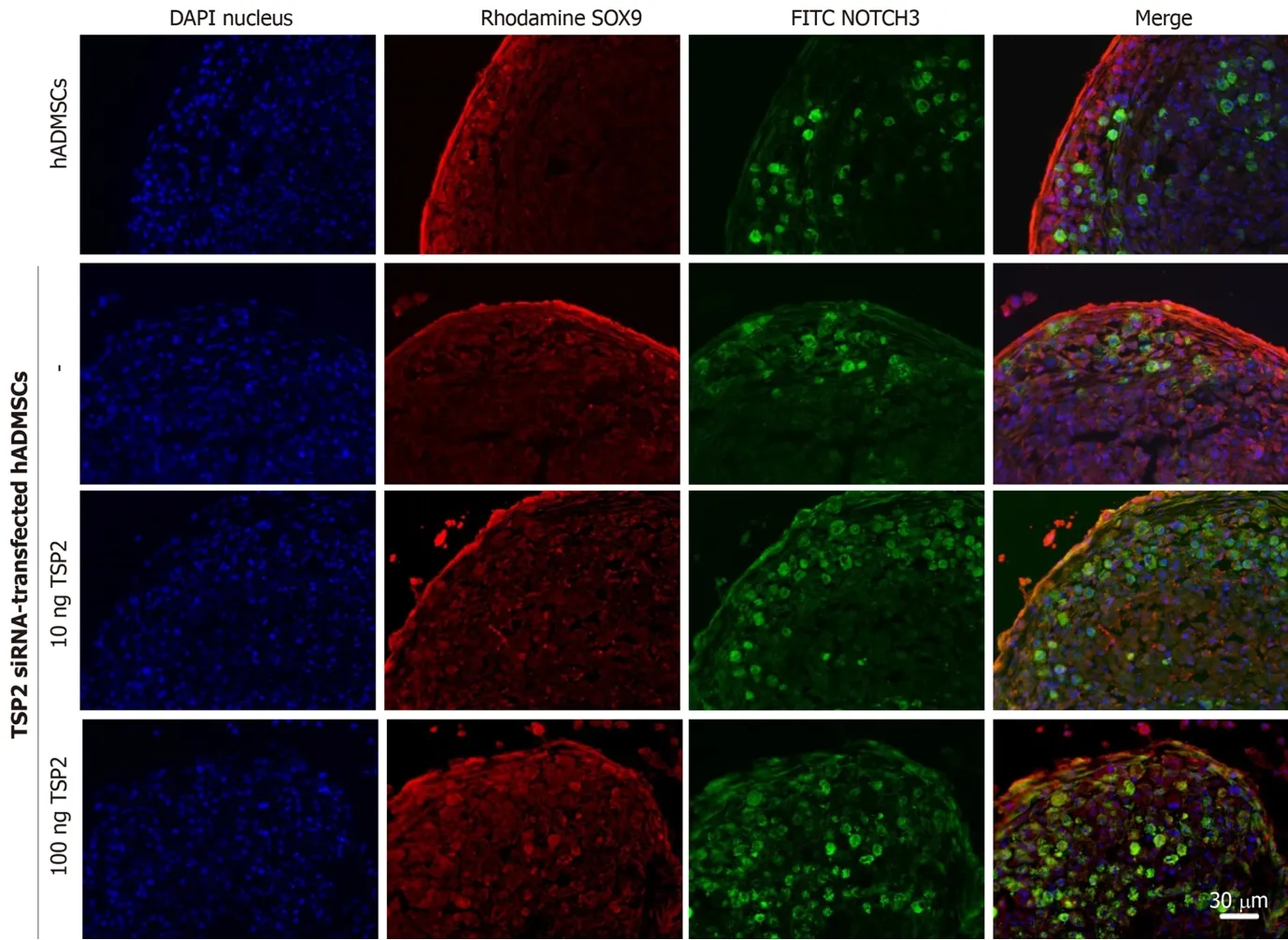
Figure 3 Production of SOX9 (chondrogenic transcription factor) and NOTCH3 (NOTCH receptor) proteins in normal hADMSCs and TSP2 siRNA-transfected hADMSCs treated with TSP2 (10 or 100 ng/mL).
ADMSCs can be isolated from various organs that have a limited amount of adipose tissue, and are easy to be culture-expanded.Therefore, obtaining autologous ADMSCs, compared to those derived from bone marrow or other tissues, is believed to be less aggressive and quantitatively advantageous[45,46].In the meantime, the number of ADMSC-based Investigational New Drug applications submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration as well as clinical trials registered worldwide significantly increased from 2011, indicating that adipose tissue is becoming an attractive cell source for MSC-based therapeutic application[47].
It is believed that proliferation of remaining host synovial chondrocytes as well as chondrocytic differentiation of transplanted stem cells are key factors for the restoration of OA cartilages.It is well known that among these GFs, transforming growth factor-β, insulin-like growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor are potent regulators of proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes[44,45].Notably, it was recently revealed that TSP2 contributes to the chondrogenic potential of hUCΒMSCs for the regeneration of cartilage defects[48].Moreover, TSP2 is released from hΒMMSCs and hUCΒMSCs themselves[16], and potentiates NOTCH signaling for selfchondrogenic differentiation[18,20,49,50].Therefore, it has been hypothesized that the chondrogenic potential of hADMSCs may be enhanced by TSP2viaNOTCH signaling.
Indeed, we showed that TSP2 regulated the chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs, which was mediated by the NOTCH signaling pathway.This hypothesis was elucidated in TSP2 siRNA-transfected cells, in which the expression of JAGGED1 and NOTCH3 was blocked, and eventually, the genes and proteins of SOX9 and collagen II were downregulated.However, the blocking of chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs by TSP2 siRNA was fully recovered by exogenous TSP2,confirming the involvement of TSP2 in MSC chondrogenic differentiation as previously reported[18,20,49,50].
According toin vitrostudies, it was expected that combination treatment with hADMSCs and TSP2 may lead to enhanced efficacy in the recovery of OA.hADMSCs alone improved the articular lesions in radiological, gross, and microscopic observations in a dose-dependent manner,i.e., 1.7 × 107cells were enough for full recovery in 8 wk, but 1.7 × 106cells displayed a partial effect.More specifically, the high-dose (1.7 × 107) hADMSCs greatly restored the cartilage structure as well as the integrity of ECM including proteoglycan and collagen II.It is of interest to note that co-administration of TSP2 and hADMSCs exhibited synergistic effects,i.e.repeated injections of TSP2 (100 ng/knee at 2-d intervals) increased the efficacy of low-dose(1.7 × 106) cells similar to or higher than that of 10-fold higher-dose (1.7 × 107) cells alone.In fact, however, TSP2 alone exerted beneficial effects to some extent, which may come from its paracrine action for the differentiation and proliferation of remaining host chondroprogenitor cells[16], in addition to anti-inflammatory potentialviacytokine regulation.
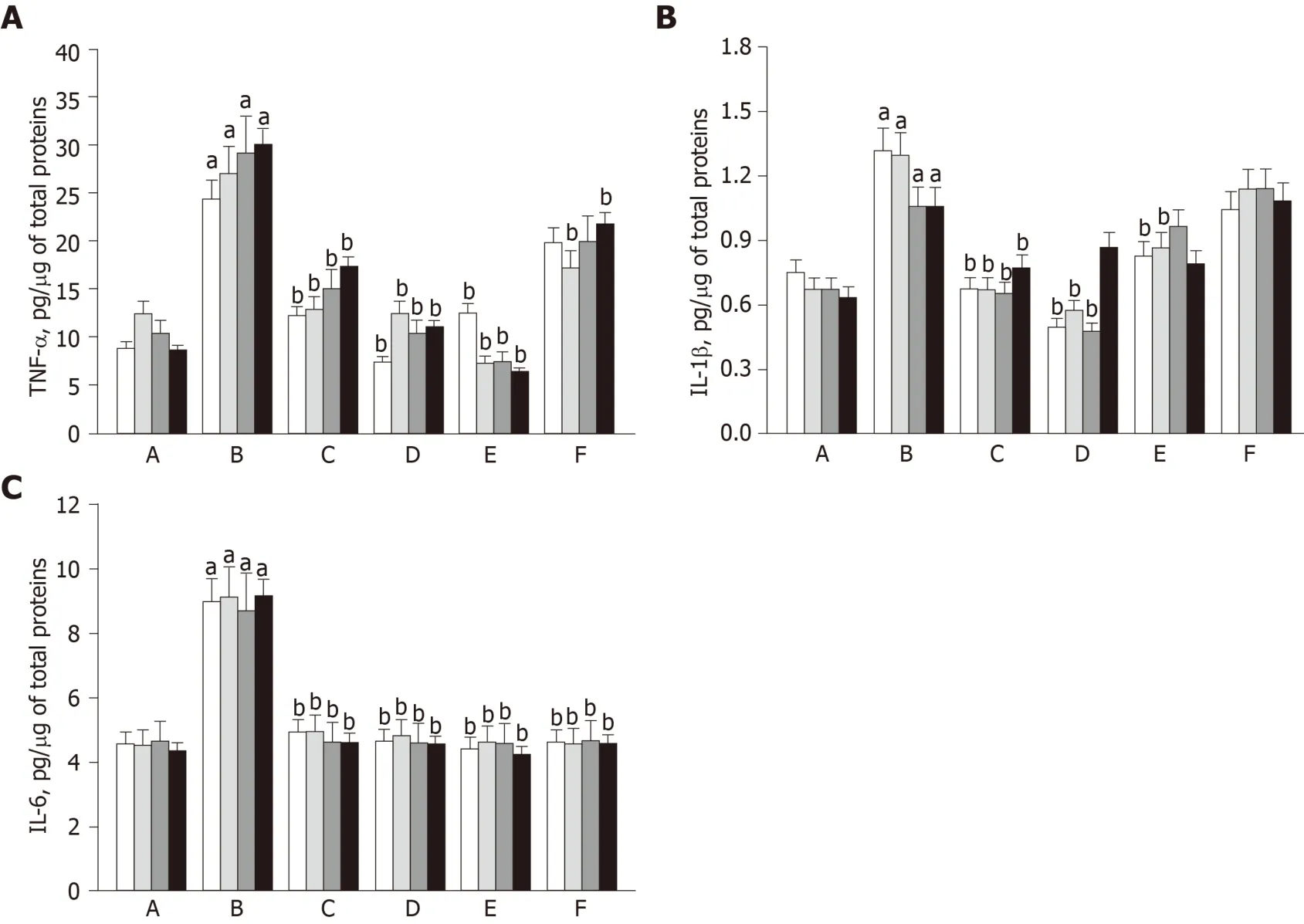
Figure 4 Concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the synovial fluid 1 wk (white), 2 wk (light grey), 4 wk (dark gray), and 8 wk (black) after cell transplantation.
Actually, there are controversies on the long-term survival, attachment to the injured articular surface, and differentiation into chondrocytes of transplanted autologous or allogeneic human stem cells due to limited clinical studies on those issues.However, it has been demonstrated that autologous equine ΒMMSCs survive longer than 6 mo and integrates within the existing articular cartilage[44].Therefore, it is anticipated that similar long-term survival and participation of human stem cells in the reparative process of human OA joints would be practical.In our recent study,heterologous human ADMSCs transplanted to rabbits’ synovial cavity were also found to attach on the injured articular surface, survive some periods, and recover OA cartilages by secreting GFs, as inferred from the fact that direct injection of conditioned medium of hADMSCs exerted OA-improving activity to some extent(unpublished results).Despite the high activities of hADMSCs shown in this study,the potential, especially in proliferation and chondrogenic efficiency, of MSCs from individuals are somewhat different according to the age and health conditions.Thus,we selected healthy stem cells from a single individual to obtain consistent results.
Taken together, in this study, ACLT plus exercise were carried out to induce moderate to severe OA conditions to explore the efficacy of hADMSCs and TSP2.Our investigations demonstrated enhanced beneficial effects of the combination treatment of hADMSCs plus TSP2, showing well-organized tissues with low cytokine contents,smooth articular surfaces, and abundant ECM contents in diverse radiological, gross,and microscopic evaluations.As an underlying mechanism on the role of TSP2, we propose its potential to stimulate the chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs as well as anti-inflammatory activity.
In conclusion, TSP2 enhanced chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCsviaJAGGED1/NOTCH3 signaling, and the combination therapy with hADMSCs and TSP2 exerted synergistic efficacy in the cartilage regeneration of OA joints of rabbits.It is suggested that the beneficial effects of human ADMSCs plus TSP2 combination treatment could be obtained in human patients.
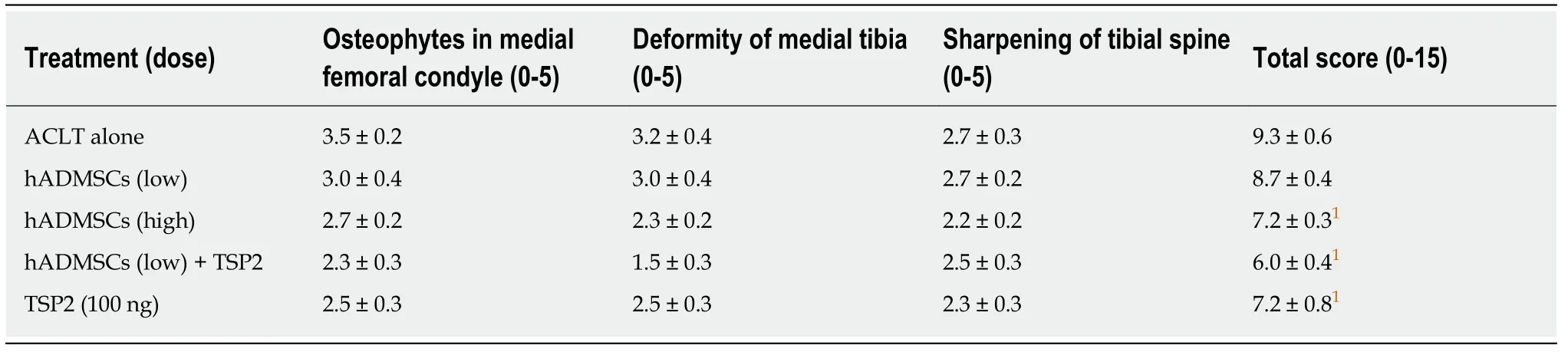
Table 1 Radiological evaluation scores 8 wk after cell transplantation
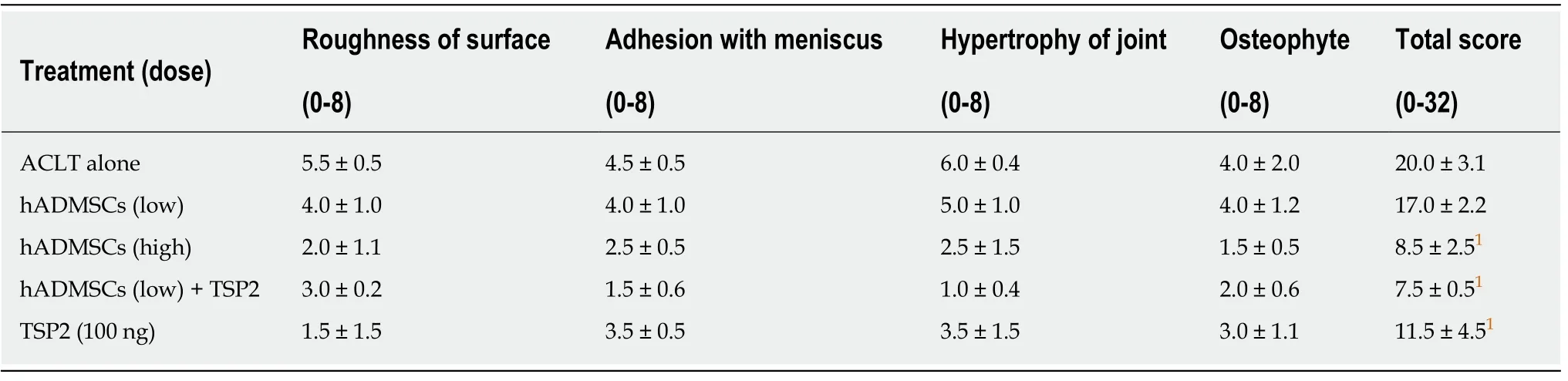
Table 2 Gross evaluation scores
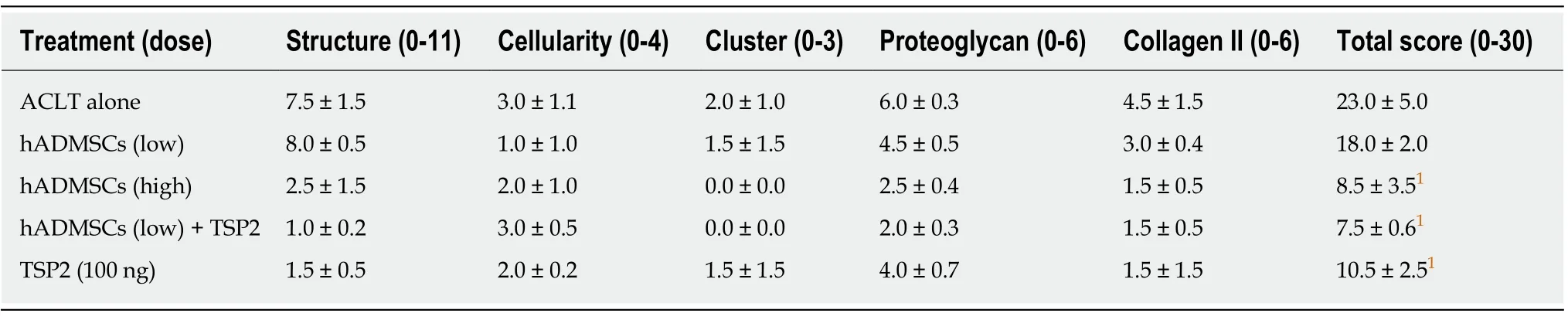
Table 3 Microscopic evaluation scores
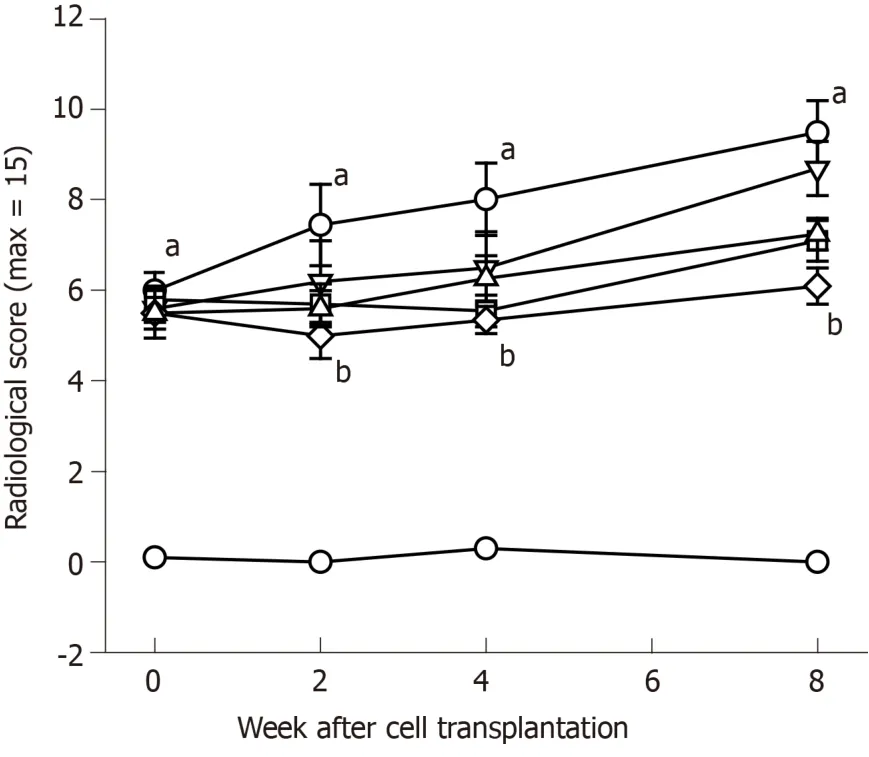
Figure 5 Time-course radiological evaluation on knee joints.
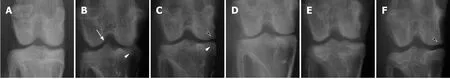
Figure 6 Representative radiological images 8 wk after cell transplantation.
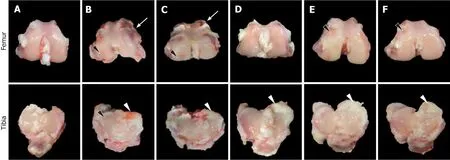
Figure 7 Representative gross findings.
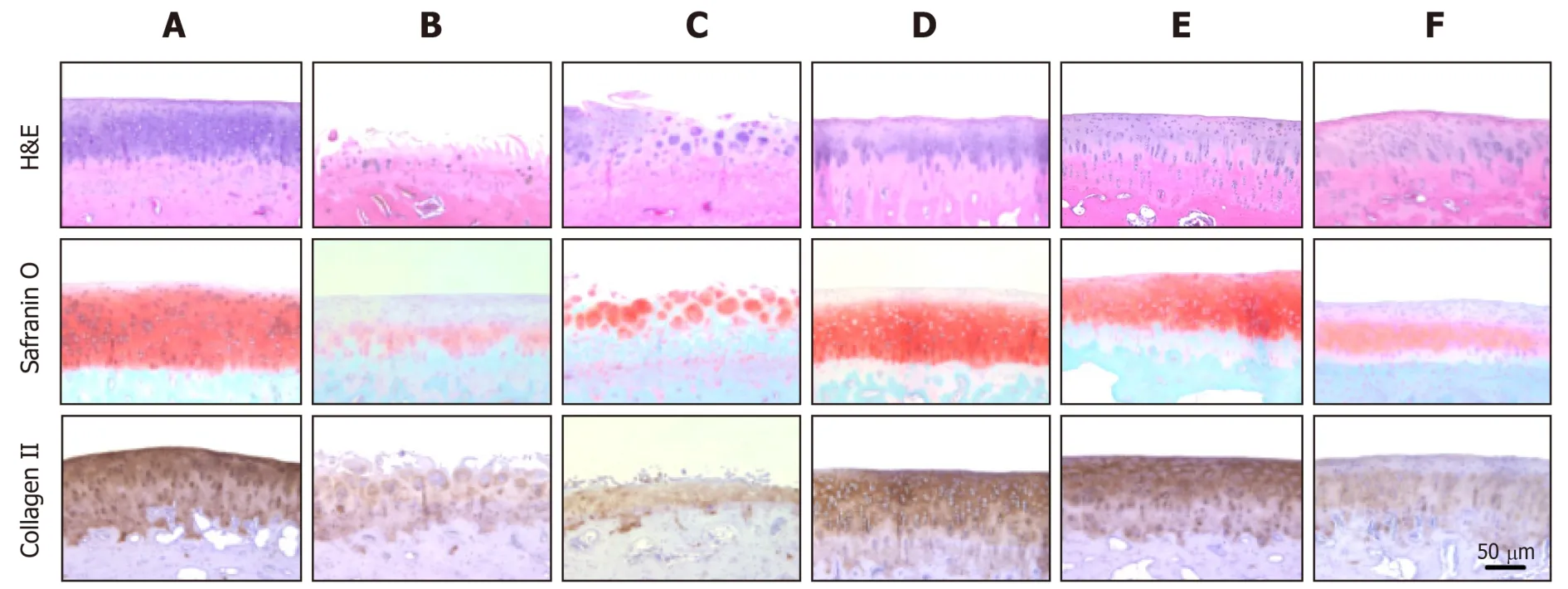
Figure 8 Representative microscopic images stained with H&E (for structure, chondrocyte density, and cluster formation), safranin O (for proteoglycan contents) or collagen II antibody (for extracellular matrix).
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reportedly differentiate into chondrocytes and have a potential for articular cartilage regeneration.Therefore, they may be a novel strategy for osteoarthritis(OA) treatment.
Research motivation
Since MSCs can be differentiated into osteocytes, adipocytes, and other cells, in addition to chondrocytes, the efficiency for OA treatment is limited.We tried to increase the ratio of chondrocytic differentiation of human adipose-derived MSCs (hADMSCs) with thrombospondin 2 (TSP2), thereby enhancing OA therapeutic efficacy.
Research objectives
The present study investigated whether TSP2 induces the chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs and potentiates the therapeutic effects of hADMSCs in OA rabbits.
Research methods
In vitro, the chondrogenic potential of TSP2 in hADMSCs was investigated by analyzing the expression of chondrogenic markers as well as NOTCH signaling genes in normal and TSP2 siRNA-treated stem cells.In vivo, hADMSCs were injected into the injured knees of OA rabbits alone or in combination with TSP2, and OA progression was monitoredviagross, radiological,and histological examinations.
Research results
In hADMSC culture, TSP2 increased the expression of chondrogenic markers as well as NOTCH signaling genes, which were inhibited by TSP2 siRNA treatment.In vivo, combination treatment with hADMSCs and TSP2 not only attenuated cartilage degeneration, osteophyte formation, and extracellular matrix loss, but also decreased synovial inflammatory cytokines.
Research conclusions
TSP2 enhances chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCsviaJAGGED1/NOTCH3 signaling,and combination therapy with hADMSCs and TSP2 exerts synergistic effects in the cartilage regeneration of OA joints.
Research perspectives
We demonstrated the positive roles of TSP2 in the chondrogenic differentiation of hADMSCs and in OA therapy.TSP2 could be an adjunct therapeutic for enhancing the cartilage-restoring efficacy of hADMSCs.
 World Journal of Stem Cells2019年12期
World Journal of Stem Cells2019年12期
- World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- MiR-301a promotes embryonic stem cell differentiation to cardiomyocytes
- Mechanoresponse of stem cells for vascular repair
- Small molecules for mesenchymal stem cell fate determination
- Three-dimensional cell culture systems as an in vitro platform for cancer and stem cell modeling
- Influence of olive oil and its components on mesenchymal stem cell biology
- Induced pluripotent stem cells for therapy personalization in pediatric patients: Focus on drug-induced adverse events
