Influence of olive oil and its components on mesenchymal stem cell biology
Antonio Casado-Díaz, Gabriel Dorado, José Manuel Quesada-Gómez
Abstract
Key words: Olive oil; Mesenchymal stem cells; Cellular differentiation; Aging; Cellular niche; Mediterranean diet
INTRODUCTION
Olive oil is obtained from olives, which are the fruits of the olive tree.Depending on the extraction method and fruit quality, different oils can be produced:(1) Extra virgin olive oil, resulting from the first pressing of olives, harvested the same day, to avoid spoilage.Extraction is mechanical only, at temperatures below 28 °C, with acidity(content of free fatty acids) below 0.8%.Such oil retains the highest amount of hydrophilic compounds, including both simple and complex phenols, as well as lignans.The total content of polyphenols is about 55 mg/100 g for this oil; (2) Virgin olive oil is similar to the previous one but with slightly higher acidity, below 2%.It also contains a high amount of hydrophilic phenolic compounds, albeit less than half of the previous one (about 21 mg/100 g); (3) Refined olive oil is obtained from olive pulp (generated after first pressing), using chemicals (acids and bases) and higher temperatures than the former ones.It has lower phenolic content, without significant antioxidant capacity; and finally; and (4) Olive pomace oil, produced from olive pulp and skin remains from the previous processes.Hexane is used as solvent, being further refined.It has the lowest antioxidant activity and is of less quality than the previous three.
Olive oil is a fundamental component of the Mediterranean diet and is associated with human health benefits[1,2].This diet was first described by Ancel Keys, and it is based on preferential consumption of unprocessed food from plant origin (i.e., fruits,vegetables and cereals), fish and poultry meat as the main protein sources, with low consumption of meat, dairy products, eggs and animal grease, and with extra virgin olive oil being the main lipid source[3].The effects of olive oil on prevention of several diseases have been revealed in cohort studies[4-6]and randomized controlled trials[7].As an example, the Spanish cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and nutrition (commonly referred to as EPIC-Spain) has provided some of the most clear evidence to date that olive oil consumption, independent of the Mediterranean diet pattern, is related to reduction in global mortality, with a strong inverse association to other death causes (i.e., respiratory, digestive, and nervous system diseases)[8].
Βeneficial effects of extra virgin olive oil on health are due to its particular profile of healthy residues of fatty acids, which are mainly monounsaturated (one double bond between carbons of the hydrocarbon chain), rendering olive oil more resistant to oxidation, in comparison to oils that are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acid residues.Βesides, extra virgin olive has a large group of bioactive compounds.They may reach 1% to 2% of total content, including unsaponifiable (squalene, sitosterols, triterpenes,etc.) and soluble (α-tocopherol and other phenols) fractions (Table 1)[9].They have antiinflammatory activities, promoting cholesterol metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, having antiaggregating effect, and improving mitochondrial function[1].Βecause of that, olive oil can be considered a nutraceutical functional food.
Olive oil has cardioprotective, antitumoral, neuroprotective, antidiabetic and antiaging effects.Βeneficial cardioprotective effects of this food have been partially associated with reduction of low-density lipoprotein oxidation.This is mostly due tothe protective effects from its phenolic compounds[10].Additionally, olive oil improves functionality of high-density lipoprotein particles[11].That represents a protective factor, preventing atherosclerosis.Also, its antiinflammatory effects and ability to reduce platelet aggregation have been associated with reduction of cardiovascular risks[9,12].Olive oil consumption has also been associated with reduced cancer risks,including for prostate, colorectal, and breast[13,14].Such beneficial effects are mainly attributed to its minor components[15].

Table 1 Principal components of extra virgin olive oil
The Mediterranean diet, including olive oil, has been associated with risk reduction of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease[16].For instance, mice with diet including extra virgin olive oil showed reduction in neuropathologies[17].Risk of type 2 diabetes was also reduced with a diet having high olive oil intake.That is mainly due to its high content of monounsaturated fatty acid residues, as well as to the presence of polyphenols[18].Indeed, replacement of a diet rich in saturated fatty acid residues by extra virgin olive reduced glycosylated hemoglobin between 0.3% and 2.0%[9].
Aging is characterized by oxidative stress, telomer shortage, genomic instability,epigenetic alterations, proteostasis (protein homeostasis) reduction, nutrition deregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, dysfunction of stem cell populations, and altered cellular communications.Interestingly, beneficial effects of olive oil and its components on health include attenuation of the negative alterations of aging[19].For example, polyphenols of olive oil prevented DNA breakage induced by oxidizing agents by scavenging free radicals, as well as modulating DNA repair mechanisms[20].Indeed, a Mediterranean diet rich in extra virgin olive both reduced adiposity and increased telomer length[21].On the other hand, oleuropein, an abundant polyphenol in extra virgin olive oil, stabilized the proteasome, during induction of replicative senescence, and extended life span[22].Additionally, olive oil and its components positively modulated different stem cell populations, which can promote tissue regeneration and reduce negative effects of aging[19,23].
Adult mesenchymal stromal cells, also called mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs),comprise heterogeneous populations of undifferentiated cells, exhibiting high capacity for proliferation and differentiation into other cell types.MSCs can be found distributed in different tissues of the body, and they function as a cellular reservoir for tissue homeostasis maintenance and regeneration of damaged tissues[24].They can be isolated from different tissues, like bone marrow, muscle, adipose tissue, hair follicles,dental roots, placenta, dermis, perichondrium, articular cartilage, umbilical cord,lungs, and liver[25].Such cells were originally identified in bone marrow, derived from nonhematopoietic cells, and exhibiting osteogenic potential and ability to adhere to plastic surfaces[26].
Yet, this cell population has not been completely characterized, due to lack of specific biomarkers.The minimum criteria to define MSCs by the International Society for Cellular Therapy include:Adherence to plastic; capacity to differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes and chondrocytesin vitro; presence of CD73 (ecto-50-nucleotidase), CD90 (Thy1) and CD105 (endoglin, SH2) markers, as well as the absence of CD45, CD19, CD19 or CD79, CD14 or CD11b and human leukocyte antigen-DR isotype (HLA-DR) hematopoietic markers[27].
More recently, different “-omic” sciences have been used for a better characterization of the MSCs.Indeed, several genomic and proteomic studies have proposed that MSCs are characterized by specific expression of a set of genes and protein biosynthesis[28,29].Another characteristic of MSCs is that they are metabolically very active, producing extracellular matrix components, as well as an important variety of cytokines.Among other actions, they can modulate the adaptive and innate immune system[30].The possibility to isolate, andin vitroculture and differentiate MSCs has opened the door to their usage as therapeutic agents, especially for cellular therapy and regenerative medicine[31].The putative therapeutic usage of their paracrine and antiinflammatory activity is also being evaluated currently[32,33].
Aging produces changes in cellular niches and MSCs themselves, which may affect their functionality and differentiation capacity.One of the most illustrative examples of that is the increase of bone marrow adiposity with aging, partially due to MSC differentiation into adipocytes instead of osteoblasts[34,35].Such a phenomenon also happens in obese people[35].MSC aging depends on intrinsic factors, such as reactive oxygen species (referred to as ROS), and accumulation of DNA damage and damaged proteins[36].Βut extrinsic factors are also involved, acting through the cellular niche that is made of medium and other cellular types interacting with the MSCs.Niches are essential not only to maintain the pool of stem cells but also their functionalities.Βecause of that, it has been suggested that some changes associated with aging could be reversed, through niche manipulation-for instance, adding antiaging factors from serum of young people, or reducing medium factors related to aging[37].Among those factors that promote aging are the increase in oxidative stress as well as the accumulation of proinflammatory cytokines produced by senescent cells, the population of which increases with age[38].
Interestingly, some recent studies have shown that diet may affect the proliferative and differentiation capacities of stem cells in adult organisms[39].Curiously, a caloric restriction or fasting diet usually improves DNA repair, stem cell functionality, and longevity.On the contrary, diets rich in fats may have negative effects[39].The diet may produce changes in serum composition and, therefore, affect stem cell functionality.Indeed, it has been shown thatin vitroproliferation of rat hippocampal neural progenitor cells and MSCs increased when culture medium was supplemented with serum from old rats, which were fed with NT-020 food supplement (made by blueberry, green tea, vitamin D3, and carnosine) for 28 d, in relation to serum from rats that did not take such supplement[40].This suggests that diet may alter the stem cell niche.
Fortunately, the knowledge of how diet modulates stem cells may allow for the design and use of specific diets to reduce, and even prevent, degenerative processes associated with some pathologies and aging.In this scenario, extensive data support the healthy effect of extra virgin olive oil consumption.As indicated above, its consumption produces changes in serum lipid composition, decreases oxidative stress, and provides bioactive compounds that can modulate cellular processes.These effects may affect the physiology of MSCs.The state of the MSC population in an individual will directly affect its regenerative capacity and health.Thus, a new approach to studying the healthy effects of olive oil is through its putative influence on MSC functionality (Figure 1).Therefore, the main objective of this critical review is to synthesize the current knowledge on how this food and its components may modulate MSC biology, in general, and differentiation capacity, in particular.That should allow a better understanding of the physiological and metabolic mechanisms by which olive oil positively modulates health, preventing diseases and the degenerative effects of aging.
SAPONIFIABLE FRACTION OF OLIVE OIL AND MSCs
The saponifiable fraction of olive oil is composed of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, almost entirely esterified with glycerol to form triglycerides (triacylglycerols).Extra virgin olive oil is characterized by being rich in unsaturated fatty acid residues(~ 85%), in relation to saturated ones (~ 14.5%).It should be taken into account that unless the word “free” is used, we are dealing here with fatty acids residues, forming part of the triacylglycerol molecule, because free fatty acids represent acidity, which is an unwanted characteristic of olive oil.Such lipidic molecules account for one of the healthiest properties of olive oil.The most abundant unsaturated fatty acids are oleic acid (C18:1; monounsaturated omega-9), linoleic acid (C18:2; diunsaturated omega-6),palmitoleic acid (C16:1; monounsaturated omega-7), and α-linolenic acid (C18:3;triunsaturated omega-3).Saturated fatty acid residues include the ones from palmitic acid (C16:0) and stearic acid (C18:0) (Table 1).
The fatty acid content in the medium may modulate MSC physiology, including its differentiation potency.In fact, it has been found recently that high content of fatty acids in bone marrow fluid is positively correlated to bone marrow adiposity in patients with osteonecrosis in the femoral head[41].Oleic acid is found in the plasmatic membrane lipids.Concentration of this compound in MSCs seems to be related to the cellular differentiation stage.Indeed, nonosteoporotic individuals showed an increased concentration of oleic acid residues.Yet, osteoporotic ones showed an increase in palmitic acid residues, with cells remaining at a mostly undifferentiated stage[42].Such results suggest that supplementation with lipids containing different fatty acids may modulate MSC differentiation.
In fact, it has been described that neuronal differentiation of human endometrialderived stem cells was enhancedin vitrowhen culture medium was supplemented with oleic acid[43].This fatty acid also modulates cellular adhesion and migration.For instance, it increased the migration and capacity to accelerate skin wound healing of MSCs, derived from human umbilical cord, in anin vivomodel[44].Also, as related to its capacity to increase the regenerative capacity of the MSCs, another study showed that supplementing MSC culture medium with oleic acid for 7 d reduced cellular proliferation, increasing biosynthesis of interleukin (IL)-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor (commonly known as VEGF), as well as nitrite concentration.Since the latter factors are angiogenic, it has been suggested that MSC preconditioning with oleic acid may activate its therapeutic capacity for wound treatment and tissue regeneration[45].
Other relevant unsaturated fatty acid residues in olive oil are the essential linoleic and linolenic acids, previously described.As with oleic acid, they are found in plasma membranes.Interestingly, its concentration increased during osteoblastogenesis in MSCs from osteoporotic persons[42].Additionally, its presence in MSC culture medium inhibited cellular proliferation and activated synthesis of IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF inflammatory and angiogenic factors, as well as nitrite production[45].On the other hand, linolenic acid is a substrate for biosynthesis of unsaturated n-3 fatty acids(omega-3), like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5n-3) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA;22:6n-3), through a process of desaturation/elongation[46].Consumption of olive oil increases concentration of omega-3 fatty acid residues in blood plasma.That has been associated with a risk reduction for cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases[47].In relation to the effect on MSCs, we have previously demonstrated that:(1) Arachidonic acid (omega-6 fatty acid derived from linoleic acid) favored adipogenic differentiation and inhibited osteoblastogenesisin vitrofor MSCs derived from human bone marrow;and (2) EPA and DHA did not affect adipocyte differentiation, having little effect on osteoblastogenesis.These results suggest that increasing the omega-3/omega-6 ratio may prevent the loss of mineral bone mass with aging[48].Βesides, it has been recently observed that MSCs derived from placenta, treated with EPA or DHA, increased their angiogenic capacity and, therefore, their regenerative potential[49].
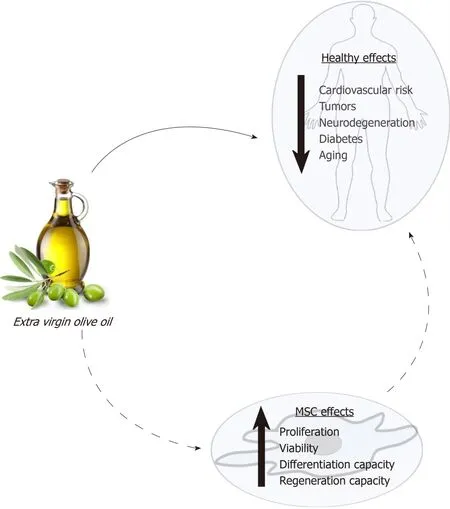
Figure 1 Effects of extra virgin olive oil on health and mesenchymal stem cells.
Palmitoleic acid is another unsaturated lipid, generally being scarce in food.Yet, it is abundant in fatty tissue.Therefore, it has been suggested that it is mainly produced through lipogenesis[50].Curiously, this fatty acid residue, besides others like oleic acid and linoleic acid, have capacity to induce adipogenic transdifferentiation of different tumor cell lines[51].These results support the idea that such fatty acid residues change the cellular niche, modulating MSC differentiation.
On the other hand, olive oil palmitic and stearic (saturated) fatty acids are also abundant in the human body.In particular, palmitic acid represents between 20% and 30% of the total fatty acid of phospholipidic membranes[52].The organism has capacity for regulating palmitic acid homeostasis though lipogenesis, independent of the diet.Nevertheless, a diet unbalanced for it and polyunsaturated fatty acid, as well as having excess of carbohydrates, may increase the concentration of palmitic acid in tissues, producing dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, accumulation of ectopic fat, and enhancement of the inflammatory condition[52].MSC cultures treated with palmitic acid had reduced angiogenic capacity[53].Additionally, excess of palmitic acid in the bone marrow niche may induce apoptosis in MSCs.For example, concentrations of 0.125 mmol/L to 0.5 mmol/L of palmitate induced apoptosis of MSCsin vitro[54].Additionally, palmitic acid upregulated expression of adipogenic genes, produced lipotoxicity, and increased synthesis of proinflammatory IL-6 and IL-8 in MSC cultures.That is in contrast to oleic acid effects, which also included the capacity to counteract the negative influence of palmitic acid[41,55].Finally, the effect of stearic acid on MSCs is unknown.Nevertheless, studies carried out with animals other than humans have shown that a diet rich in it increases adiposity, reducing insulin sensitivity[56].Such data suggest that it could affect MSC differentiation.
In summary, the amount and type of fatty acids in the medium may modulate MSC functionality and their capacity to differentiate.Therefore, the modification of the plasmatic lipidic profile after olive oil intake may affect MSCs and partly explain the beneficial effects of such food in health (Figure 2).
EFFECTS OF UNSAPONIFIABLE FRACTION OF OLIVE OIL IN MSCS
The unsaponifiable fraction of olive oil corresponds to 1% to 2% of this food.It is composed of a large variety of compounds (Table 1).They are largely responsible for the taste and aroma (flavor) of olive oil, besides contributing to relevant biological activities.Interestingly, they can modulate the redox system and different cellular signaling pathways.Therefore, olive oil consumption may have effects on metabolism, in general, and physiological processes in MSCs, in particular, as described below and summarized in Figure 3.
Vitamins
Olive oil contains different vitamins, including E, K and A precursor (beta-carotene).Vitamin E accounts for 2% to 3% of the extra virgin olive oil unsaponifiable fraction,with 90% of alpha-tocopherol.Its main biological activity is that of antioxidant,preventing ROS[57].Extracts of by-products of olive oil production are rich in that vitamin.We have found that intake of such extracts by postmenopausal women changed their blood serum composition.Interestingly, supplementation of culture medium with such serum promoted MSC differentiationin vitro, enhancing osteoblastogenesis, and inhibiting adipogenesis[58].Additionally, vitamin E prevented oxidative stress induced by H2O2, reducing apoptosis and increasing cellular viability,in MSC cultures of bone marrow from rat and fatty tissue from pig[59,60].Vitamin E pretreatment of MSCs from rat bone marrow increased chondrogenesis and proteoglycan production, after being implanted in a surgically-generated experimental osteoarthritis model of rat[59].Also, using an experimental gentamicininduced acute renal failure rat model, less kidney injury was observed when such animals were treated with a combination of MSCs from bone marrow administered together with vitamin E (80 mg/kg)[61].These results show that vitamin E not only protects MSC populations but also improves their regenerative capacities.
On the other hand, vitamin K is found in extra virgin olive oil at about 500 μg/kg,which is considered a modest amount for this vitamin.It has several biological activities, including a relevant role in blood clotting.Other physiological activity of vitamin K involves modulating osteocalcin levels in bone.Low levels of carbonylated osteocalcin have been associated with loss of bone mass and higher fracture risk[62].In this regard, treatment of human MSC cultures with vitamin K together with vitamin D favored osteoblastic differentiation and higher carboxylated osteocalcin levels[63].All those findings highlight the relevance of this vitamin for maintenance of bone health.
Finally, beta-carotene, together with other carotenoids found in extra virgin olive oil, are partially responsible for the color of this food, besides the chlorophylls and pheophytins described below.Concentration of beta-carotene in extra virgin olive oil ranges from 2-4 mg/kg[64].Vegetables like carrots contain much higher amounts of this provitamin, but its presence prevents olive oil photo-oxidation, adding further health benefits to this food.Βeta-carotene is metabolized into retinol and retinoic acid.The latter is the active metabolite of vitamin A.It influences the physiology of MSCs and, in particular, their differentiation capacity, favoring osteoblastogenesis and inhibiting adipogenesis[65-67].Interestingly, bead-on-string mats based on poly(lactic-coglycolic acid) released beta-carotene, favoring osteoblastogenic differentiation of MSCs seeded on scaffolds, without supplementation with other osteogenic inducers[68].These studies suggest that vitamin A may improve bone health.Retinoic acid also favored differentiation of MSCs into neurons and smooth muscle cells[69,70].Therefore, these studies show that beta-carotene can modulate MSC differentiation.On the other hand, vitamin A repressed expression of proinflammatory factors in MSCsin vitro, after being stimulated by lipopolysaccharides[71].This indicates that it also regulates the inflammatory response of MSCs.
Squalene
Squalene is an aliphatic triterpene, being the most abundant hydrocarbon in olive oil,reaching 0.7% of the total content and between 30% to 50% of the unsaponifiable fraction.That sets it apart from other oils, which have a much lower total content of this triterpene (between 0.002% and 0.03%)[72].Squalene has a high antioxidant capacity, being associated with cardioprotective and antiaging effects[73,74].
Interestingly, we have recently found that serum from postmenopausal women(previously treated with an extract of by-product of the olive oil extraction process,containing more than 7% squalene) enhanced osteoblastogenesis and inhibited adipogenesis of MSC cultures[58].Indeed, squalene may have an important role in the MSC niche in stroma of bone marrow, as suggested by its protection of MSCs in the presence of chemotherapeutic and anticancerogenic agents, like cisplatin and carboplatin[75].These studies suggest that, unlike other oils, the consumption of squalene-rich olive oil may positively influence MSC populations.

Figure 2 Effects of saponifiable fraction of olive oil on mesenchymal stem cells.

Figure 3 Effects of unsaponifiable fraction of olive oil on mesenchymal stem cells.
Triterpenes
Triterpene concentration in olive oil ranges from 8.90-112.36 mg/kg, mainly including oleanolic acid, maslinic acid, uvaol, and erythrodiol[76].Triterpenes of olive oil exhibited interesting biological activities, including antitumoral, antioxidant,antiinflammatory, antimicrobial, and hepatoprotective and cardioprotective effects,which may have positive impact on health[76].Effects of oleanolic and maslinic acids on MSCs have been reported; for instance, some authors have reported that the former reduced MSC viability[77], although others have not found such an effect[78].Such triterpene modulates bone formation.Indeed, some authors have found that this triterpene prevented bone mass loss in ovariectomized rats.They also observed that 1 μmol/L and 10 μmol/L of oleanolic acid induced rat MSC differentiation into osteoblastsin vitro, and suggested that this effect was mediated by the Notch signaling pathway[79].These results have been reproduced in human MSCs.Such experiments showed that this triterpene inhibited Notch signaling and induced the expression of osteoblastic genes[77].It has been reported that Notch signaling maintained the MSCs undifferentiated stage, whereas the inhibition of this pathway promoted differentiation into osteoblasts[80].Βesides, oleanolic acid enhanced the effect of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (commonly known as ΒMP2) as an osteoblastic inducer[77].
Since the factors that induce MSC differentiation into osteoblasts usually inhibit adipogenic differentiation, a negative effect of oleanolic acid on adipogenesis is expected.Indeed, treatment of 3T3-L1 mouse preadipocytes with such triterpene downregulated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), which is the master regulator of adipocyte differentiation.In addition, it decreased accumulation of fat droplets in these cells during adipocyte differentiation[81].Also,oleanolic acid reduced inflammatory factor production, like that of visfatin and resistin, in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells[81,82].Therefore, consumption of this triterpene may have beneficial effects on pathologies associated with overproduction of inflammatory adipokines.
On the other hand, maslinic acid (as oleanolic acid) showed osteoprotective effects in ovariectomized mice.Βut, in this case, such an effect has been associated with its capacity to inhibit bone resorption, by suppressing osteoclastic differentiation promoted by the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa Β (NF-κΒ) ligand(commonly known as RANKL)[83].Yet, the putative positive effects of this triterpene on MSC osteoblastogenesis have not been found so far.Nevertheless, it inhibited 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiationin vitro, reducing fat droplets and increasing glucose uptake[84].Such results, besides the antiinflammatory activity of maslinic acid[85],suggest that its consumption, together with other triterpenes of olive oil, may affect MSC populations.
Pigments
Pigments are responsible for the coloration of olive oil, with the carotenoids and pheophytins (derived from chlorophylls) being the most important.Among the carotenoids are beta-carotene (also known as provitamin A, as previously described)and lutein.The latter is found at a concentration of 3.5 mg/kg in extra virgin olive oil[86].Relevance of food rich in lutein for eye health is well established[87].Yet,knowledge of the putative effects on MSCs is scarce.Interestingly, it has been recently foundin vivothat a diet rich in lutein reduces bone resorption in mice.That is accomplished through inhibition of osteoclastogenesis, additionally increasing bone formation[88].These results suggest that lutein may promote osteoblastogenesis or differentiation of osteoblasts into osteocytes.Nevertheless, more research is needed to properly ascertain its putative role in MSC differentiation.
On the other hand, pheophytins are responsible for the attractive greenish color of olive oil.Their concentrations range from traces to 30 mg/kg, depending on olive tree cultivar, ripening stage of the olive fruit, and technology used for the olive oil extraction, among other factors.Their biological activities include antiinflammatory and antidiabetic effects[89,90].Although the putative influence of pheophytins on MSCs are unknown, some authors have found that they inhibited adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 murine cells, reducing fat droplets when induced to differentiate into adipocytes[90].These results suggest that pheophytins probably inhibit adipogenic differentiation of MSCs.Again, further research is required to shed more light on this exciting topic.
Phenolic compounds
Phenolic compounds of extra virgin olive oil represent 18% to 37% (100-300 mg/kg) of the unsaponifiable fraction.They are partially responsible for the high oxidative stability of olive oil.Their composition and concentration depend on the olive tree cultivar, weather conditions, fruit ripeness, and technology used for olive oil extraction[91].The main types of phenolic compounds of extra virgin olive oil are flavonoids, lignans, phenolic acids, phenolic alcohols and secoiridoids, the last two being the most abundant.Indeed, secoiridoids represent between 85% and 99% of the total phenolic compounds of olive oil[92].Their intake is healthy, being antioxidants(preventing oxidative stress) and interacting with several signaling pathways.Actually, they have antiinflammatory, anticarcinogenic, antiatherogenic and antithrombotic effects.Βesides, they regulate lipidic metabolism, among other beneficial activities[15].Interestingly, the biological activity of phenolic compounds also modulates MSC physiology, including their proliferation, viability, regenerative capacity and differentiation, as demonstrated by numerous studies in the last two decades.
Oleuropein is a relevant secoiridoid, ranging from 1.2-120 mg/kg in extra virgin olive oil[93].It has numerous beneficial health properties, including antioxidant,antiinflammatory, antiatherogenic, anticancerogenic, antimicrobial, antiviral and antiaging effects, among others[94].Interestingly, oleuropein prevents both oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by H2O2in MSCs.That is accomplished by inhibiting the Β-cell lymphoma 2 (referred to as Βcl-2)-like protein 4 (referred to as ΒAX)proapoptotic protein, activating the antiapoptotic Βcl-2 and myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (referred to as Mcl-1), and modulating autophagy-related death signals[95].
Additionally, oleuropein also affects MSC differentiation.We have described that this phenolic compound upregulates osteoblastic marker genes, increasing alkaline phosphatase activity, mineralization and osteoprotegerin (OPG)/RANKLexpression ratio in human MSCs derived from bone marrow[96].These results suggest that oleuropein favors osteogenesis, inhibiting bone resorption.The latter is accomplished by activating expression ofOPG, which is a decoy receptor for the receptor activator of RANKL, which is an osteoclastogenesis activator.Therefore, an increase inOPGexpression reduces the ability of RANKL to activate osteoclastogenesis.
We have reported that oleuropein inhibits adipogenic differentiation of MSCs by downregulatingPPARγand other adipogenic genes, reducing fat droplet formation in treated cultures[96].We have also carried out transcriptomic analyses of MSCs induced to differentiate into adipocytes in the presence of oleuropein.Interestingly, this compound restored expression of 60% of the genes repressed during adipogenesis,activating some signaling pathways, like Rho [family of guanosine triphosphate(GTP) ases] and beta-catenin, and inhibiting others related to mitochondrial activity,which are induced during adipogenesis.This indicates that the presence of oleuropein keeps MSCs that have been induced to adipocytes in a more undifferentiated state[97].Therefore, since this compound favors osteoblastogenesisversusadipogenesis, it can have osteoprotective properties and its consumption may prevent some diseases, like osteoporosis.It can also be beneficial in physiological processes affecting bone health,like aging.That rationale is supported by the fact that treatment with 10 mg of oleuropein/kg every 3 d prevented loss of trabecular bone in the femurs of ovariectomized mice.Βesides, the authors also showed inin vitrostudies that this compound favored mineralization of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblastic cells from mice and inhibited osteoclastogenesis[98].
Additionally, oleuropein can prevent formation of ectopic fat, preventing obesity.Indeed, it has been reported that this phenolic compound prevented formation of visceral fat in obese mice and inhibited adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[99].Oleuropein may also have antiaging effects on MSCs, maintaining a better regenerative capacity of the organism with advanced age.This is because it can inhibit the phosphatidylinositol 3kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (commonly known as mTOR) signaling pathway on MSCs[100].The inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (commonly known as PI3Ks)/Akt/mTOR pathway maintained high proliferative and differentiation capacities in MSCs[101].Akt stands for Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1, (RAC)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase, also known as protein kinase Β (or its more common abbreviation of PKΒ).
Hydroxytyrosol is another of the most abundant phenolic compounds present in extra virgin olive oil.Its concentration ranges from 1.1 mg/kg to 75 mg/kg[93].This phenolic alcohol has many healthy effects, including antiinflammatory, antimicrobial,cardioprotective, neuroprotective and antitumoral activities, among others.Thus, it has also been considered as a nutraceutical[102].Regarding its effect on MSCs, we have evaluated the effects of 1 μmol/L and 100 μmol/L hydroxytyrosol on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of MSCs from human bone marrow.The highest concentration of this compound (but not the lower one) reduced the number of cells,repressed expression of osteoblastic gene collagen type-I alpha-1 (COLIA1) and reduced mineralization in cultures induced to differentiate into osteoblasts[103].On the other hand, mostly the highest concentration increased both expression of thePPARγgene as well as of generation of fat droplets, indicating induction of adipogenesis[103].
Yet, other authors have described that such high concentration of hydroxytyrosol inhibited adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes from mice[104,105].Discrepancies were probably due to different cellular types and different methodologies used to induce differentiation.Interestingly, mitotic clonal expansion is an important event during adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1, but does not take place in human MSCs.This compound inhibited mitotic clonal expansion of 3T3-L1[104,105].Therefore, its effects on miceversushuman adipogenesis may be different[103].Additionally, it has been recently reported that 30 μg of hydroxytyrosol/mL (~ 200 μmol/L) inhibited adipogenesis on human preadipocytes (not affecting mature adipocytes), further increasing apoptosis[106].
Nevertheless, it should be taken into account that plasma levels of hydroxytyrosol have been found to be about 4.5 ng/mL (~ 0.029 μmol/L) in 30 min after consumption[107].Therefore, the effect of high concentrations of hydroxytyrosol,reported by others and ourselves, on osteoblastic and adipogenic differentiation of human MSCsin vitrowould require a pharmacologicalin vivointake.Interestingly,studies with animals have shown that both oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol protected 6-wk-old ovariectomized mice of trabecular (albeit not cortical) bone loss in femur.Yet, it is not clear if that was due to increased osteoblastogenesis, inhibition of osteoclastogenesis, or both[98].
Additionally, hydroxytyrosol has positive effects on chondrocytes, which are other cells also derived from MSCs.For instance, in an osteoarthritis model in which chondrocytes have been stimulated with growth-related oncogene alpha (commonly known as GROα) to promote hypertrophy and terminal differentiation, the presence of hydroxytyrosol reduced oxidative stress and apoptosis, which are induced in such pathology[108].These results suggest that this compound might have a relevant role in MSC physiology in bone marrow, modulating bone metabolism.Nevertheless, further research is required to properly ascertain its putative effectsin vivo.
Extra virgin olive oil also contains other phenols, known as flavonoids, mainly luteolin and apigenin.Their concentrations range from 0-19 mg/kg[93], therefore representing a minority.Despite that, their intake has been associated with reduced risk to suffer cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders[109].Βoth flavonoids upregulate the octamer-binding protein 4 (OCT4) and sex-determining region Y box-containing gene 2 (SOX2) genes in MSCs[110].Such genes are mainly expressed in embryonic stem cells, encoding transcription factors that regulate cell cycle and maintenance of totipotency or pluripotency.They are considered additional MSC molecular markers in adult tissues, being repressed after cell differentiation[111].Therefore, luteolin and apigenin may delay the loss of regenerative capacity of MSCs with aging.In addition, also related to aging, luteolin prevented oxidative stressin vitro, induced with FeCl2and H2O2in MSCs[112].
Luteolin can also affect MSC differentiation.Indeed, it inhibited adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 murine cells, reducing triglyceride accumulation, as well as downregulating genes encoding the PPARγ and CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins(C/EBPα) adipogenic transcription-factors[113].Regarding osteogenic differentiation,some authors have reported that luteolin reduced alkaline phosphatase activity and viability of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblastic cells[114].Yet, other authors using the same cellular type but much lower concentrations of this flavonoid have found that it prevented the osteoblastogenesis inhibition induced by glucocorticoids.Indeed, they showed that luteolin prevented bone mass loss, by downregulating apoptotic genes,increasingOPG/RANKLgene expression ratio, and activating the beta-catenin pathway in an animal model of osteoporosis induced by glucocorticoids[115].Therefore,these results suggest that this compound has an osteoprotective role in bone marrow.
On the other hand, apigenin is a phytoestrogen that has antiinflammatory effect on MSCs.Interestingly, apoptosis produced after the inflammatory response, triggered by lipopolysaccharide, was enhanced by the presence of this flavonoid[116].MSC differentiation is also influenced by apigenin.Different studies have suggested that it inhibits adipogenic differentiation of MSCs.Indeed, it has been found that apigenin downregulatedPPARγand inhibited fat droplet formation in 3T3-L1 cells that had been induced to differentiate into adipocytes[117].A negative effect of apigenin on adipogenesisviainhibition of the early differentiation processes, including mitotic clonal expansion, has also been reported.Yet, apigenin supplementation did not have effect in the advanced stages of adipogenic differentiation[118].Nevertheless, contrary to results obtained with mouse preadipocytes, this flavonoid did not inhibit adipogenesis in human MSCs derived from fatty tissue[119].Further studies are required to shed more light on putative roles of apigenin on human MSC differentiation into adipocytes.
The effect of apigenin on osteoblastogenesis has also been studied.This compound reduced apoptosis and ROS production, maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential, under oxidative stress conditions induced by H2O2in MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblasts[120].Βesides, its antioxidant activity maintained expression of osteoblastic genes in such cells and conditions[120].However, other authors have reported that this compound reduced viability and osteoblastogenesis in such cells, in a dose-dependent manner.Nevertheless, they reported that 10 mg apigenin/kg intraperitoneally administered to ovariectomized mice prevented loss of trabecular bone[121].
Thesein vivoresults are in agreement with the ones obtained with human MSCsin vitro.For example, apigenin supplementation to osteogenic medium increased expression of osteoblastic markers and mineralization of extracellular matrix in human MSC cultures.Such effects activating osteoblastogenesis were mediated by increased phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (commonly known as JNKs)and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (commonly known as MAPKs)[122].The role of p38 in MSC osteoblastogenesis has also been described[123].Interestingly, apigenin effects on MSCs may modulate bone metabolism, preventing bone mass loss in diseases like osteoporosis[122]and physiological processes like aging.
The last important group of phenolics in extra virgin olive oil is the one of phenolic acids.These acids are simple phenols, usually found at very low concentrations in such food.Nevertheless, sometimes they are found at higher concentrations, like in some Tunisian olive oils, in which they can reach up to 38.39% of the total phenolic content[124].The most relevant phenols in this group include vanillic acid, syringic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid,p-coumaric acid, and caffeic acid.Vanillic acid has hepatoprotective and cardioprotective effects[125,126].Indeed, it has been observed that it reduced bone mass loss in ovariectomized mice[127].That may be related to its effects on cells derived from MSCs.For instance, this phenolic compound favored proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblast-like UMR 106 cells, increasing expression of osteogenic markers and ratio ofOPG/RANKLexpression.These effects were mediated by its activity as phytoestrogen[128].It has also been suggested that vanillic acid may modulate adipogenesis because it reduced triglyceride content,without affecting cellular viability, in 3T3-L1 cells induced to differentiate into adipocytes[129].
On the other hand, syringic acid also has relevant healthy properties.Indeed, it is mainly a powerful antioxidant, being also antidiabetic, cardioprotective,antiinflammatory,etc[130].Yet, only its effect on MSC differentiation into osteoblasts have been studied.For example, it has been found that the presence of this compound in culture medium of mouse MSCs increased expression of osteogenic genes, alkaline phosphatase activity, and mineralization.This phenolic acid promoted osteoblastogenesis by inducing expression of the miR-21 microRNA, thus reducing expression of the so-called “mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7” (SMAD7)gene, since it is the target of such microRNA[131].SMAD7 protein inhibits osteoblastogenesis.Therefore, its repression in MSCs promoted differentiation into osteoblasts[131,132].In relation to 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, little is known about its putative effects on MSCs.Just onein vitrostudy has been carried out in relation to adipogenic differentiation of mouse 3T3-L1 and human MSCs from adipose tissue.Yet, in neither of these cell types did it produce significant changes during adipogenesis[133].
With respect top-coumaric acid, it is usually found in extra virgin olive oil at concentrations lower than 1 mg/kg[134].Its intake is healthy, due to several biological activities, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, antitumoral, antidiabetic,etc[135].Interestingly, extracts from the fragrant eupatorium plant (Eupatorium japonicum) favored osteoblastogenesis and inhibited adipogenesis in both multipotent C3H10T1/2 and primary bone marrow cells from mouse and rat, respectively.Βesides, it prevented body weight increase and bone mineral density decrease in ovariectomized rats.Those effects were partially due to the biological activities of this phenolic compound[136].Similar results showed thatp-coumaric acid inhibited adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[137,138].Interestingly, this compound also inhibited myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells from mouse, which may negatively affect development of skeletal muscle[138].
Finally, caffeic acid has antidiabetic and antioxidant activities[139].Yet, its putative biological activity on MSCs is unknown.Possibly, it can induce osteoblastic differentiation, since this compound increased alkaline phosphatase activity and changed the phenotype through a process involving antigen expression in human MG-63 osteosarcoma cells[140].Nevertheless, its mechanism of action and putative effects on undifferentiated cells remains unknown, requiring further research.
In summary, most studies about phenolic components of olive oil on MSCs have focused on how these compounds affect MSC differentiation into osteoblasts and adipocytes.In general, results have shown that such chemicals may modulate proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast precursor cells, suggesting that their consumption may influence bone health.The fact that phenolic extracts of extra virgin olive oil from different olive tree cultivars (Picual, Hojiblanca, Arbequina and Picudo)increased proliferation of MG-63 preosteoblastic cells supports that hypothesis[141].Indeed, olive oil consumption is associated with better bone health.That is partially due to the effects of its phenolic components on osteoblastic differentiation of MSCs.Therefore, it has been proposed that intake of this food, as well as other products derived from the olive tree, may help to prevent bone mass loss, due to diseases like osteoporosis[142,143]or physiological aging.
CONCLUSION
Numerous studies and clinical assays have confirmed the health benefits of extra virgin olive oil consumption, due to its nutraceutical properties[144].Its molecular mechanisms of action have been investigated in different cells, tissues, organs, and organisms.Results have shown prominent biological activities, including antioxidant,antiinflammatory and chemoprotective, modulating different cellular signaling pathways[145,146].The putative effects of extra virgin olive oil intake on maintenance and functionality of MSC populations have not been investigated to date.Such knowledge should shed light on this subject and help to better explain the health benefits of olive oil.Fortunately, the effects of specific compounds present in this food have been evaluated in relation to viability and differentiation of MSCs.
A summary of research results is shown in Figures 2 and 3.It is evident that further investigations are required to gain more knowledge on putative effects on MSC biology of some of these compounds, afterin vivointake.They should be studied alone and combined, taking into account putative synergistic interactions between them.Interestingly, available data indicate that the profile of fatty acid residues(saponifiable fraction) of extra virgin olive oil can change the composition of the MSC niche and therefore its physiological behavior.For instance, the high content of oleic acid in extra virgin olive oil can favor migration and differentiation of MSCs.Βesides,the increased ratio of omega-3/omega-6 fatty acid residues enhanced by consumption of extra virgin olive oil favors both viability and differentiation into osteoblasts(instead of adipocytes) of MSCs from bone marrow.
On the other hand, although the unsaponifiable fraction of extra virgin olive oil represents just 1% to 2%, it is comprised of a large variety of compounds with relevant biological activities, which also influence MSC biology.For instance, phenolic compounds, vitamins, squalene and other compounds of this fraction modulate signaling pathways.That, in turn, can impact MSC viability and differentiation.In general, most of these compounds protect MSCs from oxidative stress and aging,favoring osteogenicversusadipogenic differentiation.Indeed, they have healthy properties, including regenerative, osteoprotective, antidiabetic and antiobesity effects, partly because of their activity on MSCs.
In summary, the currently available data show positive effects of different components of extra virgin olive oil, related to maintenance and functionality of MSC populations.That is in agreement with the fact that consumption of this food prevents bone loss due to pathologies like osteoporosis or physiological processes like aging[19].Yet, it should be taken into account that most studies have been carried out with purified compoundsin vitro, usually at concentrations higher than the physiological ones.Therefore, furtherin vivoresearch is needed to ascertain the putative effects of extra virgin olive oil consumption on MSC viability and regenerative capacity.That should shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying such effects, which is required to increase our current knowledge on this topic.Studies should focus on analyses of specific MSC populations-for instance, including the ones in bone marrow or fatty tissue.The rationale is that niche compositions may be different for different tissues, changing with differential patterns as well, in response to extra virgin olive oil consumption.
Additionally, it should be considered that different components of this food may work synergistically on MSCs.Therefore, the effects due to combination of even small quantities of different compounds might be equal or even superior to the ones of higher amounts of such individual chemicals.Therefore, it would be interesting to carry out bothin vitroandin vivostudies with different combinations of these compounds or extracts of extra virgin olive oil.That should allow a better understanding of the biological effects of MSCs.Additionally, such knowledge should allow a better description of the composition and desirable characteristics of extra virgin olive oil.The goal is that its consumption reaches the highest possible positive impact on the MSC populations and, thus, the organism’s overall health.
 World Journal of Stem Cells2019年12期
World Journal of Stem Cells2019年12期
- World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- MiR-301a promotes embryonic stem cell differentiation to cardiomyocytes
- Anti-osteoarthritis effect of a combination treatment with human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and thrombospondin 2 in rabbits
- Mechanoresponse of stem cells for vascular repair
- Small molecules for mesenchymal stem cell fate determination
- Three-dimensional cell culture systems as an in vitro platform for cancer and stem cell modeling
- Induced pluripotent stem cells for therapy personalization in pediatric patients: Focus on drug-induced adverse events
