Texture analysis on gadoxetic acid enhanced-MRI for predicting Ki-67 status in hepatocellular carcinoma:A prospective study
Zheng Ye ,Hanyu Jiang ,Jie Chen,Xijiao Liu,Yi Wei,Chunchao Xia,Ting Duan,Likun Cao,Zhen Zhang,Bin Song
1West China School of Medicine,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China;2Department of Radiology,West China Hospital,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China
Abstract Objective:To investigate the value of whole-lesion texture analysis on preoperative gadoxetic acid enhanced magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)for predicting tumor Ki-67 status after curative resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC).Methods:This study consisted of 89 consecutive patients with surgically confirmed HCC.Texture features were extracted from multiparametric MRI based on whole-lesion regions of interest.The Ki-67 status was immunohistochemical determined and classified into low Ki-67(labeling index≤15%)and high Ki-67(labeling index>15%)groups.Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator(LASSO)and multivariate logistic regression were applied for generating the texture signature,clinical nomogram and combined nomogram.The discrimination power,calibration and clinical usefulness of the three models were evaluated accordingly.Recurrence-free survival(RFS)rates after curative hepatectomy were also compared between groups.Results:A total of 13 texture features were selected to construct a texture signature for predicting Ki-67 status in HCC patients(C-index:0.878,95% confidence interval:0.791-0.937).After incorporating texture signature to the clinical nomogram which included significant clinical variates(AFP,BCLC-stage,capsule integrity,tumor margin,enhancing capsule),the combined nomogram showed higher discrimination ability(C-index:0.936 vs.0.795,P<0.001),good calibration(P>0.05 in Hosmer-Lemeshow test)and higher clinical usefulness by decision curve analysis.RFS rate was significantly lower in the high Ki-67 group compared with the low Ki-67 group after curative surgery(63.27% vs.85.00%,P<0.05).Conclusions:Texture analysis on gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI can serve as a noninvasive approach to preoperatively predict Ki-67 status of HCC after curative resection.The combination of texture signature and clinical factors demonstrated the potential to further improve the prediction performance.
Keywords:Hepatocellular carcinoma;Ki-67;MRI;texture analysis;radiomics
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)is one of the most lethal cancers with increasing mortality worldwide(1,2).Although hepatectomy is recommended as the mainstream curative therapy for HCC patients with well-preserved liver function,the high early recurrence rate and poor prognosis after hepatic resection remains a major concern in treatment(3,4).
Cell proliferation status is an important factor that reflects tumor biology and affects prognosis and treatment efficacy(5).Ki-67 protein,which is present in all phases of cell cycle(G1,S,G2and mitosis)except for resting cells(G0),is an established marker suggestive of active cell proliferation(6).Ki-67 status has been widely used as a prognostic indicator in many malignant tumors,including breast cancer,lung cancer and prostate cancer(7-9).In HCC patients,high levels of Ki-67 can be indicative of tumor aggressiveness,such as advanced tumor stages,portal vein invasion and intra-hepatic metastasis(10),which is associated with high early recurrence rate and poor prognosis(11-13).Thus,Ki-67 has been proposed as an independent prognostic factor for surgically resected HCC in recent studies(5,14).Typically,Ki-67 labeling index(Ki-67 LI)is assessed pathologically after surgery(6),therefore it is inapplicable to patients with surgical contraindications.Hence,a preoperative noninvasive way to predict Ki-67 status is needed to guide individualized HCC treatment and postoperative surveillance in clinical practices.
With high-throughput computing,texture analysis enables extraction and evaluation of innumerable quantitative features which are unavailable to human naked-eyes(15).It has been considered as a noninvasive method of assessing intra-tumor heterogeneity and predicting tumor biologic behaviors(16,17).By comparing differences in texture parameters or constructing comprehensive classifier models,texture analysis could assist in HCC tumor diagnosis(18),biologic aggressiveness evaluation(19)and therapeutic response assessment(20).Previous study has preliminarily explored feasibility of histogram-derived parameters based on whole-tumor magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)in Ki-67 prediction of HCC patients.In addition,MRI-based texture analysis has been reported to be the preoperative Ki-67 predictor and hence serves as a potential prognostic marker in malignant tumor,such as breast cancer(7,21).However,the value of texture analysis based on gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI in Ki-67 prediction of HCC is not yet discovered.
Therefore,the aim of this prospective study was to investigate the value of whole-lesion texture analysis on gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI in predicting Ki-67 status in HCC patients preoperatively.Early recurrences(<1 year)after curative resection were also explored and compared in patients with different Ki-67 statuses.
Materials and methods
Patients
This prospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of West China Hospital and written informed consents were obtained from all patients.The inclusion criteria were as followed:1)focal liver lesions suspected of HCC according to medical history;2)age≥18 years old;3)treatment naive[i.e.no hepatectomy,transcatheter arterial chemoembolization(TACE)or radiofrequency ablation(RFA)before gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI examination];and 4)surgical resection was recommended on the basis of clinical protocol in West China Hospital.Patients with 1)MRI contradictions or 2)breath-holding difficulties were considered ineligible.
From July 2015 to March 2018,122 consecutive patients were initially included in West China Hospital,among which,33 patients were excluded,due to non-HCC(n=16),poor imaging quality(n=14)and massive necrosis(n=3)(Figure 1).A total of 89 patients with histopathologically verified HCC(68 males and 21 females;age:50.72±11.40 years)were finally enrolled.And all patients underwent surgical resection after MRI examination with the median time interval of 2(range:0-8)d.
MRI acquisition protocol
Preoperative MRI examination was performed on a 3.0 T scanner(MAGNETOM Skyra,Siemens,Healthcare,Erlangen,Germany)with an 18-channel phased-array body coil and spine coil.All patients were asked to fast for 6-8 h before examination.In all patients,the following breathhold transversal sequences were conducted:(1)T2-weighted(T2W)fat-suppressed turbo spin echo:time of repetition(TR)=2,160 ms,time of echo(TE)=100 ms,field of view(FOV)=43 cm×43 cm,slice thickness=6 mm.(2)T1-weighted pre-contrast(PRE)and enhanced sequences[arterial phase(AP),portal venous phase(PVP),transitional phase(TP)and hepatobiliary phase(HBP)]:TR=3.95 ms,TE=1.92 ms,FOV=40 cm×40 cm,slice thickness=2 mm.A standard dose(0.025 mmol/kg)of gadoxetic acid disodium(Primovist?;Bayer Schering Pharma AG,Berlin,Germany)was intravenously injected at a rate of 2.0 mL/s via a dual power injector,followed by a 30 mL saline flush at the same rate.The test-bolus technique with 2 mL gadoxetic acid and 30 mL saline was firstly applied to determine the imaging delay time of AP,and then AP was acquired accordingly.Thereafter,PVP,TP and HBP images were obtained in 60 s,180 s and 20 min after contrast material administration,respectively.All images were sent to our picture archiving and communications system(PACS)to be interpreted at workstations.
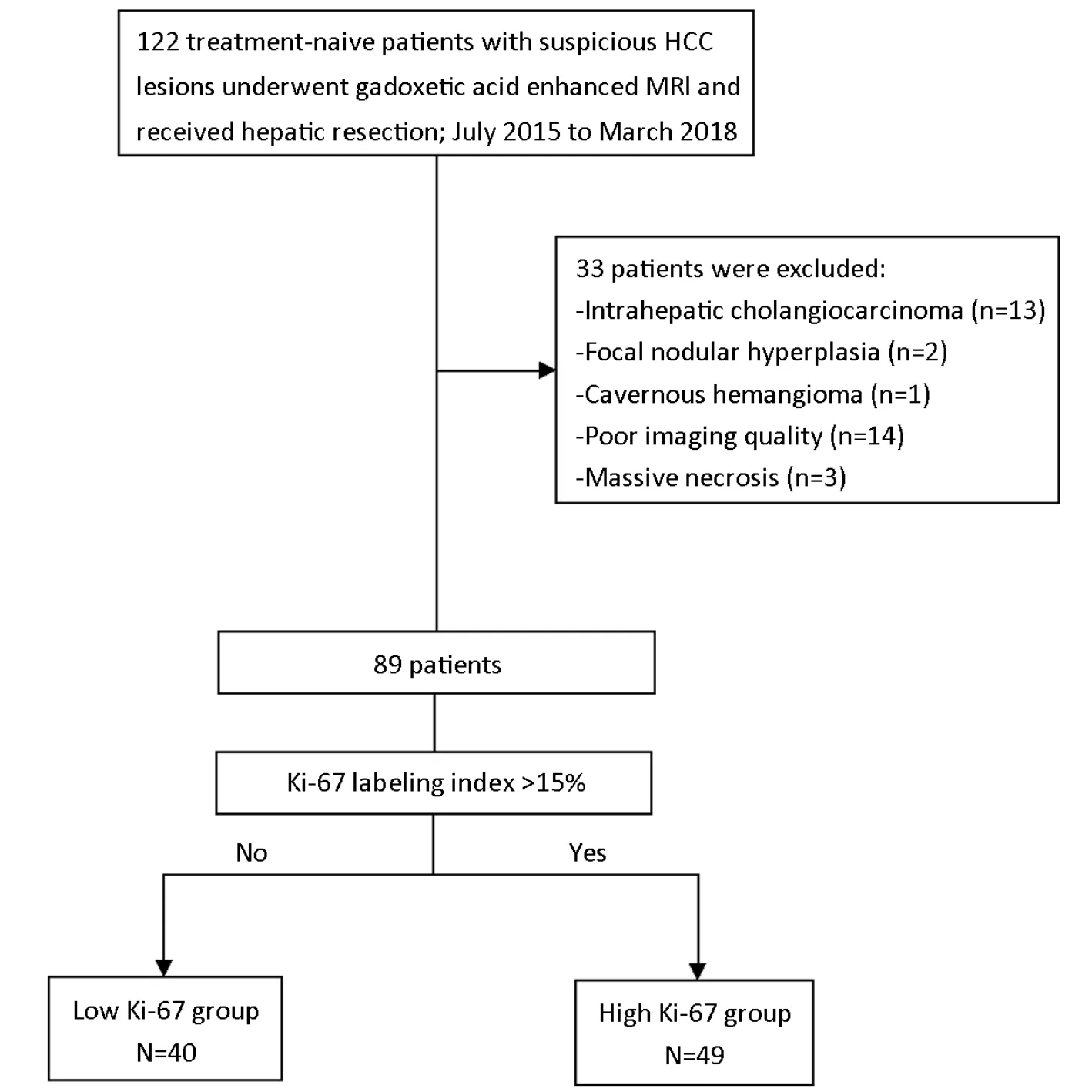
Figure 1 Flowchart of study inclusion.HCC,hepatocellular carcinoma;MRI,magnetic resonance imaging.
Texture signature
Feature extraction
ITK-SNAP software(22)(Version 3.6.0;http://www.itksnap.org/pmwiki/pmwiki.php?n=Main.HomePage)was used for three-dimensional manual imaging segmentation.The whole-lesion region of interest(ROI)was delineated on each slice of the T2W,PRE,AP,PVP and HBP images along the entire tumor border.The ROIs were independently drawn by two radiologists(H.J.and X.L.)in 30 randomly chosen patients to assess the interobserver reproducibility,and by the first radiologist(H.J.)in the remaining patients.
Quantitative texture features extraction was performed with in-housed algorithms using Analysis Kit software(Version v3.0.1;A,GE Healthcare,Shanghai,China).In total,396 texture features from the category of histogram,texture,form factor,gray level co-occurrence matrix(GLCM),and grey level run-length matrix(GLRLM)were finally extracted from each MRI sequence(SupplementaryTable S1).
Feature selection and signature construction
To avoid overfitting in this high-dimension data analysis,the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator(LASSO)regression(23)model with ten-fold crossvalidation was applied.By optimizing the tuning parameter(λ)in LASSO regression,most of the coefficients of features were reduced to zero and the remaining features with non-zero coefficients were selected(24).Therefore,we were able to identify the texture features with the strongest discriminating powers and then construct a linear combination of these extracted features for each sequence.The multivariate logistic regression was used to construct the texture signature with a combination of the sequence weighted by their respective coefficients.
Ki-67 assessment
Surgical resected specimens were fixed with 10%paraformaldehyde solution,embedded in paraffin and cut into 4 μm-thick sections for immunohistochemistry(IHC)of proliferation status(Ki-67 antigen).With monoclonal antibody(Rabbit monoclonal,SP6,Abcam,Cambridge,UK)(1:100 dilution),Ki-67 staining was performed by standard avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex method,and 3,3’-diaminobenzidine(DAB)solution was used for color development.The Ki-67 LI was assessed by noting the percentage of positively stained cells.With the threshold value of 15%,we classified HCC lesions into low Ki-67 group(Ki-67 LI≤15%)and high Ki-67 group(Ki-67 LI>15%).The histopathological evaluation was performed by a senior pathologist with more than 10 years of experience,who was blinded to all radiological and clinical results.
Clinical model and combined model
Clinical factors
Laboratory indexes and imaging features which potentially related to tumor proliferation status were investigated and recorded.The serum level of alpha-fetoprotein(AFP),hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg),hepatitis C antibody(A-HCV)and Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer(BCLC)classification(0,A,B,or C)were included,as well as 1)cirrhosis;2)multifocality;3)arterial phase hyperenhancement(APHE);4)washout;5)capsule integrity,defined as complete capsule when observe the uniform border around most or all of the tumor,unequivocally thicker or more conspicuous than fibrotic tissue around background nodules,otherwise as incomplete integrity or not applicable;6)internal arteries,which is the persistence of discrete arterial enhancement within the tumor in the arterial phase;7)tumor margin,defined as non-smooth margin with budding portion protruding into the liver parenchyma or infiltrative appearance at the tumor periphery,otherwise as smooth margin;8)enhancing capsule,which is a distinct high-signal-intensity ring along most or all of the tumor border in PVP or TP;and 9)HBP peritumoral hypointense halo,which is a hypointense rim partially or completely circumscribing the tumor on HBP images.
The imaging features were evaluated independently by two experienced radiologists(H.Y.and X.J.,with 5 and 15 years of experience in abdominal MRI interpretation,respectively)who were blinded to the laboratory,histopathologic,and follow-up results.After the first independent image analysis,interobserver agreement was assessed for MR imaging features.Afterwards,they reached a consensus by discussion for the discordant cases.
Models construction
Binary clinical risk factors in different Ki-67 groups were firstly compared.Significant factors in the univariate analysis were then selected into a multivariate logistic regression.Interobserver agreement of imaging features was analyzed by Cohen’s kappa test.A κ statistic of 0.80-1.00 was considered as almost perfect agreement;0.60-0.79 as substantial agreement;0.40-0.59 as moderate agreement;0.20-0.39 as fair agreement;and 0-0.19 as poor agreement(25).Two prediction models were derived based on multivariate logistic regression analysis:1)the clinical model,comprising of only significant clinical factors and 2)the combined model,which incorporated the texture signature into clinical factors.The Akaike information criterion(AIC)(26)was calculated to assess the risk of data overfitting.
Performance of texture signature,clinical nomogram and combined nomogram
The clinical and combined models were converted into easy-to-use nomograms with individualized assessment of Ki-67 status in HCC patients.In this study,discrimination is the ability to distinguish between the HCC patients who belonged to the high Ki-67 group and those who belonged to the low Ki-67 group.The Harrell concordance indexes(C-index)(27),ranging from 0.5(no better concordance than chance)to 1.0(perfect concordance),were measured in the texture signature,clinical and combined nomograms to identify the discrimination performance of the models.
The nomogram calibration curves were generated to assess the agreement between pathologically confirmed Ki-67 status and the predictions of the models.The Hosmer-Lemeshow(H-L)test was conducted to evaluate the goodness of fit for logistic regression models,where a significant test statistic(P<0.05)implies a poor calibration(28).Finally,clinical usefulness and net benefit were estimated on the basis of the threshold probability by decision curve analysis(DCA)(29).
Follow-up
Patients were postoperatively followed up with their AFP level and abdominal contrast enhanced computed tomography(CT)or MRI examination in the first month after surgery,and every 3 months afterward during the first year and every six months thereafter,according to the follow-up protocol at our institution.The endpoint of this study was recurrence-free survival(RFS),which was defined as the time from the surgery date until either the date of relapse(i.e.,new lesions with tumor stain during postoperative TACE,intrahepatic recurrence or extrahepatic metastases in the CT/MR)or until the date that the patient was last known to be free of relapse(censored).Median follow-up period was 10(range,1-34)months.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were compared with Student’st-test if normally distributed or Mann-Whitney U-test if not normally distributed.Categorical variables were compared using Pearson’s Chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test,where appropriate.RFS rates in two Ki-67 groups were evaluated by Kaplan-Meier method and compared by logrank test.
All statistical analyses were performed by R software(Version 3.3.2;R Foundation for Statistical Computing,Vienna,Austria)and MedCalc statistical software(Version 15.8;MedCalc Software,Seoul,Republic of Korea).All statistical tests were two-sided,and P values of<0.05 were considered significant.The detailed R packages were listed inSupplementary Table S2.
Results
Patients’baseline characteristics
The baseline characteristics of patients in the low and high Ki-67 groups were summarized inTable 1.Patients with high Ki-67 status represented 49(55.06%)of all patients.There were no significant differences in age(P=0.099),sex ratio(P=0.826)and tumor size(P=0.550)between the low and high Ki-67 groups.
Texture signature construction
The interobserver reproducibility in feature extraction was assessed and described inSupplementary materials.A total of 13 features with non-zero coefficients were selected out of 1,980 candidate features(396 features per sequence)by LASSO,among which 3,3,3 and 4 features were from T2W,PRE and AP and PVP images,respectively.The texture signature was constructed based on these features and corresponding coefficients by multivariate logistic regression.The particular features and formulas were presented inSupplementary Table S3.
Clinical model and combined model construction
Univariate analyses of preoperative clinical factors associated with proliferation status were shown inTable 1.Interobserver agreement for imaging features which were significantly different between the low Ki-67 and high Ki-67 groups was substantial to almost perfect with κ=0.970 for capsule integrity;κ=0.766 for tumor margin and κ=0.751 for enhancing capsule(Figure 2).The clinical model was comprised of only significant clinical factors(AFP,BCLC-stage,capsule integrity,tumor margin and enhancing capsule),while the combined model was consisted of significant clinical factors and the texture signature.The detailed model formulas were inSupplementary materials.The AIC of texture signature and two models was demonstrated inTable 2.
Performance of texture signature,clinical nomogram and combined nomogram
Among three models,the combined nomogram demonstrated the best discrimination capability(C-index:0.936,95% CI:0.863-0.977)than the texture signature(Cindex:0.878,95% CI:0.791-0.937)or the clinical nomogram(C-index:0.795,95% CI:0.696-0.873)(P<0.05)(Table 2).The nomograms and calibration curves were presented inFigure 3,which depicted good agreement between the predicted and the pathologically confirmed HCC Ki-67 status(P>0.05 in H-L test).
Furthermore,the decision curve analysis graphically showed that the combined nomogram had a higher overall net benefit than the clinical nomogram or the texture signature alone across different threshold probabilities(Figure 4).
Early recurrence after curative resection
A total of 24 patients(6 from low Ki-67 group while 18 from high Ki-67 group)relapsed during follow-up,among which 13 patients were confirmed early recurrence by postoperative TACE,8 patients with contrast enhanced CT and 3 patients with contrast enhanced MRI.Intrahepatic recurrence was found in all relapsed patients,and 7 of them also had extrahepatic metastases(lymph node in two patients,bone in one patient,lung in one patient,simultaneously bone and lung in one patient,simultaneously lung and brain in one patient,andsimultaneously lung,adrenal and lymph node in one patient).The high Ki-67 group showed significantly lower RFS rates compared with low Ki-67 group(63.27%vs.85.00%,P=0.009 in log-rank test)(Figure 5).
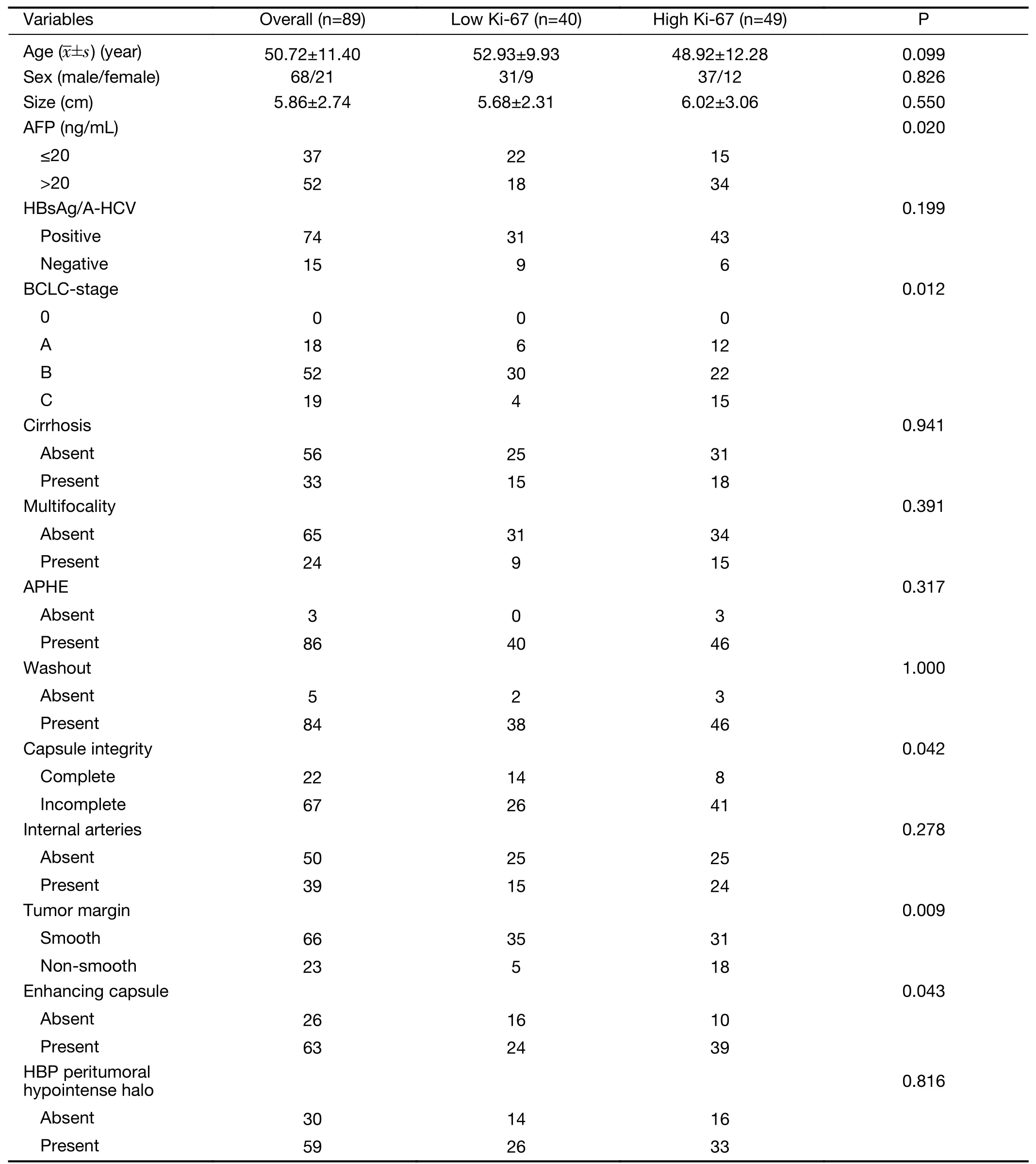
Table 1 Baseline characteristics and clinical factors of HCC patients in this study
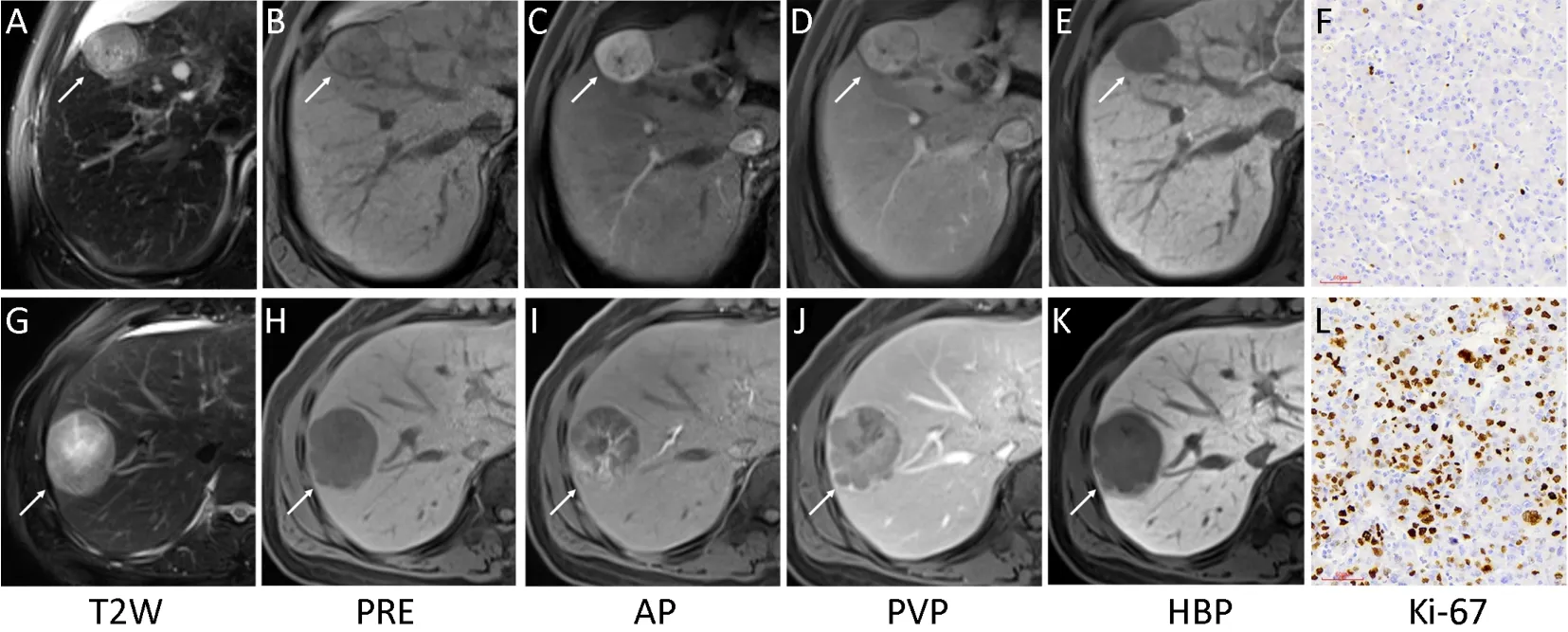
Figure 2 Representative images of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)and Ki-67(magnification,×200).A low Ki-67 hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)lesion(white arrow)showed complete capsule,smooth tumor margin and non-enhancing capsule in MRI(A-E)with Ki-67 labeling index of 3.56%(F).And a high Ki-67 HCC lesion(white arrow)showed incomplete capsule,non-smooth tumor margin and enhancing capsule in MRI(G-K)with Ki-67 labeling index of 49.37%(L).T2W,T2-weighted;PRE,pre-contrast;AP,arterial phase;PVP,portal venous phase;HBP,hepatobiliary phase.
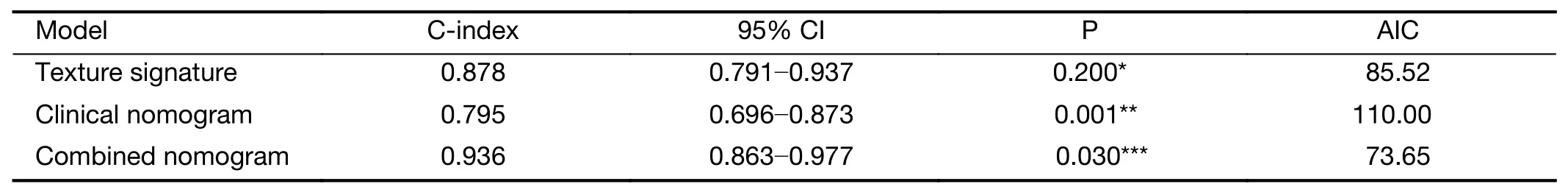
Table 2 Performance of three models
Discussion
In this study,we identified multiparametric MRI-based texture analysis as a noninvasive approach for prediction of Ki-67 status preoperatively in HCC.In addition,we found that the combined nomogram incorporating texture signature and significant clinical factors demonstrated incremental value to the clinical nomogram or texture signature alone for individualized Ki-67 estimation.Furthermore,patients with high Ki-67 HCCs showed higher early tumor recurrence rates(<1 years)than patients with low Ki-67 HCCs after curative hepatectomy.
Texture analysis provides an effective method to depict the spatial relationships and arrangement of the imaging pixels quantitatively with first-,second-,or higher order statistical outputs,which are generally unavailable to human naked-eyes(15,30).First-order statistics,commonly known as the histogram features,describes the distribution of grey-level values of individual voxels without reflecting spatial relationships or correlations between voxels.The value of first-order texture features in the Ki-67 prediction of HCC has been preliminarily evaluated,revealing the potential of histogram-derived parameters of apparent diffusion coefficient(ADC)map and AP for predicting Ki-67 LI in HCC patients(31).Second-order statistics,which is widely known as“texture analysis”,describes spatial relationships between voxels with similar gray levels within a lesion(32),in whichGLCMandGLRLMare often used to highlight local heterogeneity and depict imaging roughness(30).Recently,a study of Meyeret al.reported MRI texture analysis on conventional unenhanced sequences as a noninvasive approach in Ki-67 prediction in thyroid cancer(33).However,no other studies have investigated the possible value of texture analysis,integrating clinical factors,in predicting Ki-67 status and early recurrence in HCC before,to our knowledge.
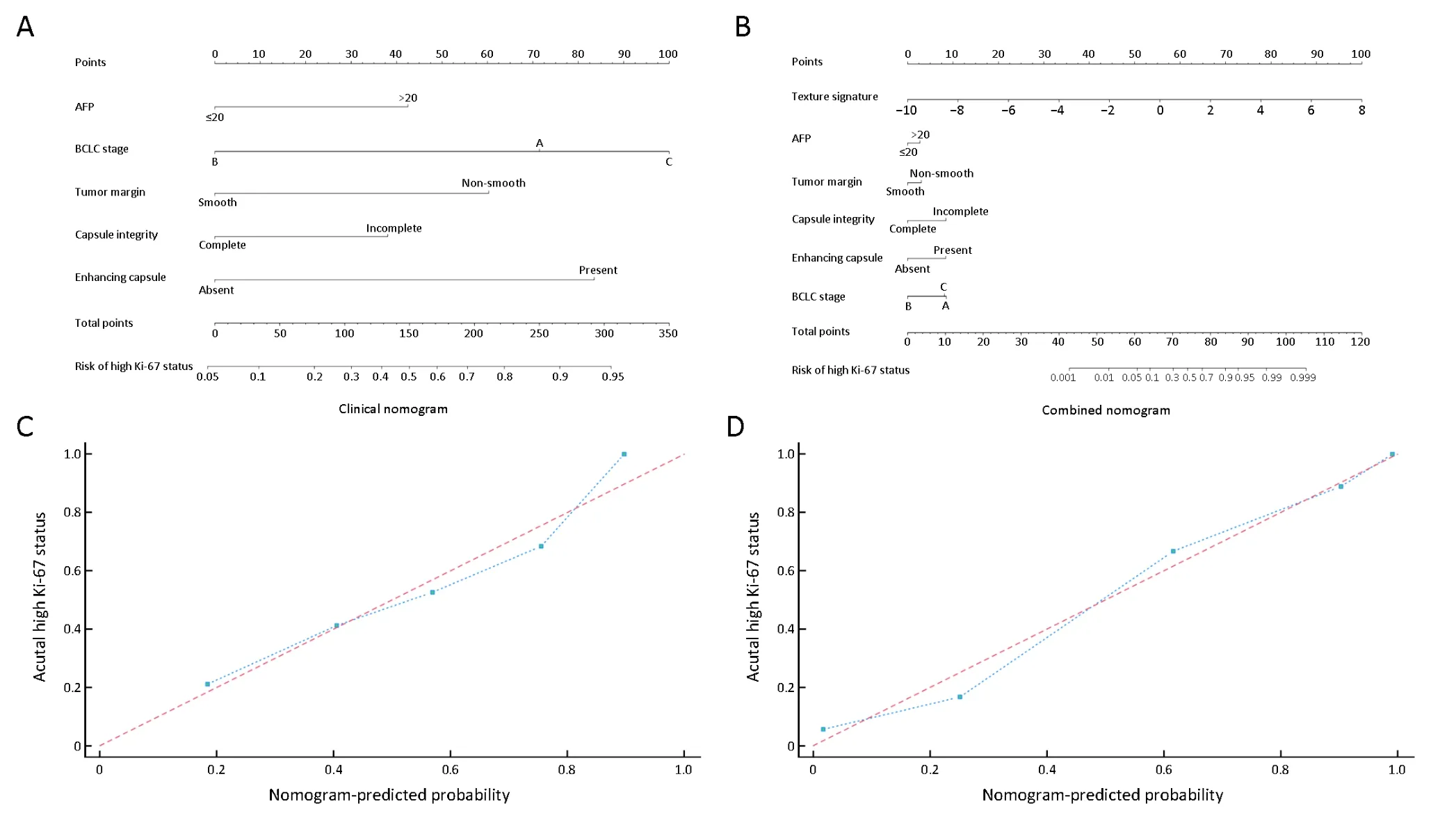
Figure 3 Clinical and combined nomograms with calibration curves.(A)Clinical nomogram included only the significant clinical parameters(AFP,BCLC-stage,capsule integrity,tumor margin and enhancing capsule);(B)Combined nomogram included all significant clinical factors and texture signature.Locate each variate on the corresponding axis,draw an upward vertical line to the Points axis for the number of points,add all of single point as a total point,and draw a line straight down from the total points axis to the risk axis to determine the high Ki-67 status probability.Calibration curves of both clinical nomogram(C)and combined nomogram(D)depicted good agreement between the predicted and pathologically confirmed Ki-67 status in HCC patients with dotted line(actual calibration)closed to dashed line(perfect calibration)and P>0.05 in Hosmer-Lemeshow test.AFP,alpha-fetoprotein;BCLC,Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer.
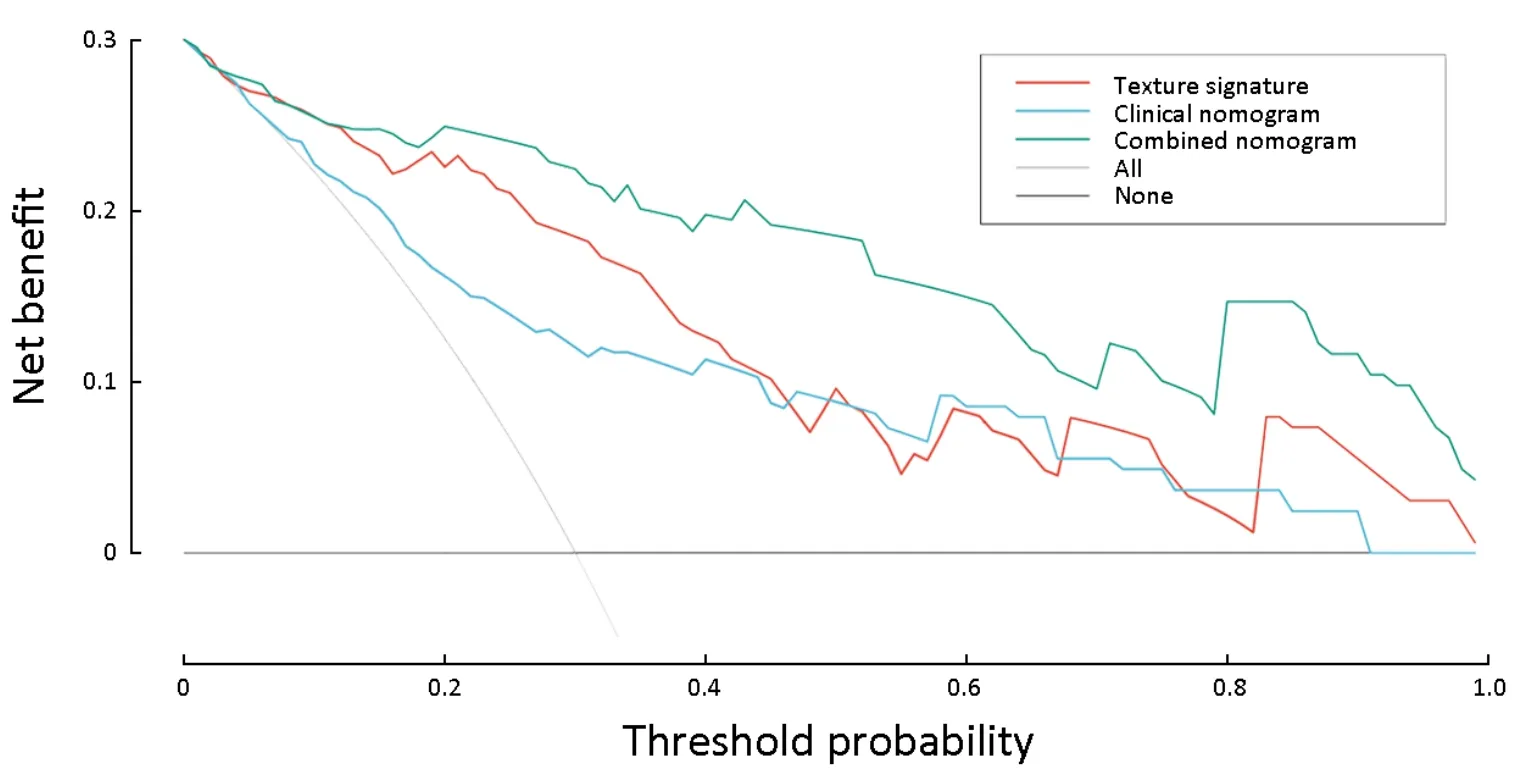
Figure 4 Decision curve analysis for three models.Y-axis measures net benefit.Among three models,combined nomogram showed the highest net benefit and clinical usefulness.
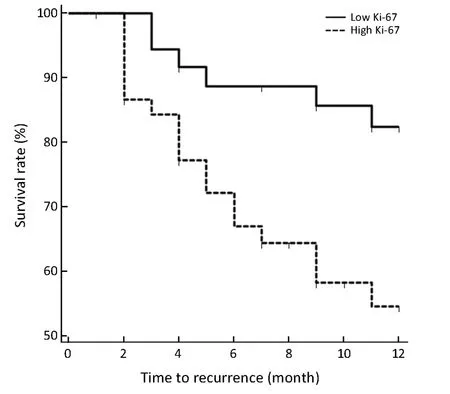
Figure 5 Recurrence-free survival(RFS)curves in high and low Ki-67 groups.RFS rates at 1 years in patients with high Ki-67 hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)were significantly lower than that in patients with low Ki-67 HCC(63.27% vs.85.00%,P=0.009 in log-rank test).
In the current study,we analyzed 396 texture features,consisting of histogram,texture,form factor,GLCM and GLRLM in each sequence.A total of 13 features with the strongest discriminating powers were selected from T2W,PRE,AP and PVP images after LASSO.However,the direct correlation between an individual texture feature and a particular biologic process remains inconclusive and elusive.Thus,we could hardly rely on any individual texture feature to predict Ki-67 status in HCC patients,and the multi-factor panel can be a more reliable approach in this setting(34,35).Our study found that the identified multiparametric texture signature was able to depict the intra-tumor heterogenous characteristics which may reflect the cell proliferation status and aggressiveness of HCCs in a noninvasive way.Therefore,the texture signature demonstrated great potential in preoperative prediction of Ki-67 level(C-index:0.878,95% CI:0.791-0.937),and was also indicative of postoperative recurrence.However,further investigation is required to explore the potential correlation between texture features and the pathophysiologic basis.
Our study revealed that serum AFP level and BCLC stage were significantly different in high and low Ki-67 groups.High AFP expression and advanced BCLC stage are correlated with more biologically aggressive properties and more unfavorable tumor behaviors of HCCs(36-38).Therefore,high AFP level and advanced BCLC stages(stage B or C)were more likely to be observed in the highly proliferated HCCs.In addition,we also found that HCCs with high Ki-67 levels have the propensity to demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern.This finding was in accordance with previous studies(39-43),which reported that non-smooth tumor margin,incomplete capsule and enhancing capsule were generally more frequently observed in progressed HCCs and were related to more aggressive biologic behaviors,hence were predictive of early recurrence after curative hepatectomy.
Although individual texture features and clinical markers can be indicative of HCC Ki-67 status,estimations based on combined parameters were more reliable and comprehensive,as doctors naturally rely on several patient characteristics to make estimations(35,44).Thus,we established the easy-to-use multiparametric clinical and combined nomograms to predict Ki-67 status before treatment.The combined nomogram achieved superior predictive performance than either the clinical nomogram or texture signature alone,with the lowest AIC(73.65),the highest discrimination ability(C-index:0.936,95% CI:0.863-0.977)and good calibration(P>0.05 in H-L test).The combined nomogram also demonstrated the best clinical usefulness than either the clinical nomogram or texture signature by decision curve analysis,which indicated the incremental value of texture signature to the traditional laboratory and imaging risk factors for individualized Ki-67 estimation.Our results were consistent with previous studies which showed superior performance of the combined models than the clinical models(35,45,46).The combined nomogram in our study might serve as a predictive tool for preoperative assessment of Ki-67 status in HCC patients,hence enabling more precise risk stratification for personalized treatment.
The recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy is usually classified as early or late with a cut-off of one year(47).Our study showed that RFS rate within 1 year was significantly lower in high Ki-67 HCCs than in low Ki-67 HCCs(63.27%vs.85.00%,P=0.009).Several previous studies have reported Ki-67 as a significant biologic marker for early recurrence and poor prognosis in HCC patients after curative resection,and the patients with high Ki-67 levels usually demonstrated shorter recurrence-free,disease-free and overall survival time compared with those with low Ki-67 levels(5,11,48,49).One possible reason for the higher recurrence rate in high Ki-67 HCCs was that these HCCs were generally more actively proliferated with aggressive histologic behaviors,and also were more likely to be categorized as advanced stage tumors with portal venous invasions(10).Therefore,the Ki-67 status,which can be preoperatively predicted by MRI-based texture analysis according to our study,should be taken into consideration for personalized treatment strategy making.Patients with high Ki-67 HCCs may need intensive surveillance and adjuvant therapy.Our study has several limitations.First,external validation was not conducted because of the relatively small sample size in our study,which may lead to data overfit to some extent(15).Although a larger independent cohort is needed to validate the generalizability of the results,the DCA used in this study requires only the dataset on which the models are tested(50)(i.e.DCA can be applied directly to a dataset and does not require the collection of additional information,which suggested that the identified combined nomogram hold great potential for clinical application in preoperative Ki-67 estimation).Second,we define“Ki-67 LI>15%”as high Ki-67 in this study according to previous studies(51,52).However,the optimal cut-off value of high Ki-67 is not yet standardized in HCC(e.g.5%,10% and so on)(31,53).Thus,it might be controversial for us to set this threshold.Future researches are warranted to explore and validate the optimal cut-off value before Ki-67 could be established as a reproducible and robust prognostic factor for HCC.
Conclusions
Whole-lesion texture analysis on gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI was a helpful tool in predicting HCC Ki-67 status preoperatively.The combined nomogram incorporating the texture signature and significant clinical factors can further improve the prediction power for individualized Ki-67 estimation,and thus could potentially guide personalized treatment.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Science and Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province(No.2017SZ0003)and Research Grant of National Nature Science Foundation of China(No.81471658).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest:The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2019年5期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2019年5期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- A study on service capacity of primary medical and health institutions for cervical cancer screening in urban and rural areas in China
- Medical expenditures for colorectal cancer diagnosis and treatment:A 10-year high-level-hospital-based multicenter retrospective survey in China,2002-2011
- Surgical outcomes of hand-assisted laparoscopic liver resection vs.open liver resection:A retrospective propensity scorematched cohort study
- Machine-learning-assisted prediction of surgical outcomes in patients undergoing gastrectomy
- Prognostic significance of lymphovascular infiltration in overall survival of gastric cancer patients after surgery with curative intent
- Phosphoglucose isomerase gene expression as a prognostic biomarker of gastric cancer
