Roles of hepatic stellate cells in acute liver failure: From the perspective of inflammation and fibrosis
Juan Li, Ying-Ren Zhao, Zhen Tian
Juan Li, Ying-Ren Zhao, Zhen Tian, Department of Infectious Diseases, Institute of Hepatology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province,China
Abstract
Key words:Acute liver failure; Hepatic stellate cells; Inflammation; Fibrosis
INTRODUCTION
Liver failure, including acute, chronic and acute-on-chronic liver failure, is a rare but dramatic clinical syndrome characterized by massive hepatocyte death and overactivation of hepatic inflammation[1]. Acute liver failure (ALF), characterized by a rapid deterioration of liver function without pre-existing liver disease, usually results in hepatocellular dysfunction and coagulopathy and carries a high mortality rate. The main causes of ALF include viral hepatitis, ischemia and drug-induced toxicity[2].Currently, ALF continues to be a huge therapeutic challenge and apart from liver transplantation, few effective therapies are available.
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are resident mesenchymal cells that have features of resident fibroblasts and pericytes and account for 15% of total resident cells in the normal human liver. HSCs are one of the key nonparenchymal components in the sinusoid with multiple functions in the liver and are known for their roles in fibrosis[3].Under physiological conditions, HSCs exhibit a quiescent state and contain numerous vitamin A lipid droplets. Upon liver injury, HSCs lose lipid-rich granules and transdifferentiate into active myofibroblast-like cells characterized by the expression of α-SMA, production of extracellular matrix (ECM) and release of cytokines[4].Although the involvement of HSCs in liver fibrosis is well recognized, few studies have examined their roles in ALF. Some recent studies have indicated that the blockade of fibrosis by depleting activated HSCs in an acetaminophen (APAP)-induced mouse ALF model resulted in significantly more severe liver damage and a lower survival rate[5]. However, due to the dramatic clinical course of ALF, the role of HSC activation in the process of ALF is still unclear.
HSCs comprise approximately one-third of nonparenchymal cells and constitute the liver sinusoid together with sinusoidal endothelial cells and Kupffer cells (KCs).Upon stimulation by the gut microbiota and microbial byproducts in septic liver injury, KCs and sinusoidal endothelial cells produce inflammatory cytokines in the sinusoidal lumen and serve as the first gate against inflammatory stimuli in the portal circulation[6]. Although the role of HSC activation in liver fibrosis has been widely accepted and attracts much attention, whether and how HSCs participate in hepatic inflammation have not been examined. Anatomically, HSCs seem to respond to inflammatory stimuli from the sinusoids. Recent studies have revealed that activated HSCs may release inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18. HSCs from both humans and rodents produce inflammatory cytokines promoting hepatocellular carcinoma and immune-mediated hepatitis[7-9]. However, how HSCs participate in hepatic inflammation, and whether and how HSC inflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of ALF are still unknown (Figure 1).
PATHOGENESIS OF ALF
To date, ALF remains a life-threatening syndrome with a high mortality rate, and is characterized by massive hepatocyte death and overactivation of hepatic inflammation.
Cell death and regeneration in ALF
Hepatocyte injury and subsequent cell death are important during the pathogenesis of ALF[10]. Two different types of programmed cell death are thought to be involved in this process, including apoptosis and necrosis. Apoptosis is defined by chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation, cell shrinkage, blebbing of the plasma membrane, and the formation of apoptotic bodies that contain nuclear or cytoplasmic material; and necrosis, which is an alternative to apoptotic cell death and is considered to be a toxic process with the characteristics of cytoplasmic swelling,dilation of organelles, and mechanical rupture of the plasma membrane[11]. The relative contribution of apoptosis and necrosis during liver failure remains controversial. Studies have shown that a variety of injurious stimuli induce apoptosis at low dose while the same stimuli may result in necrosis at higher dose. The etiologymay also alter the type of cell death in ALF:necrosis is considered a prominent death pathway of hepatocytes in drug-induced ALF, and apoptosis is always found in viraland toxin-mediated liver failure[12,13].
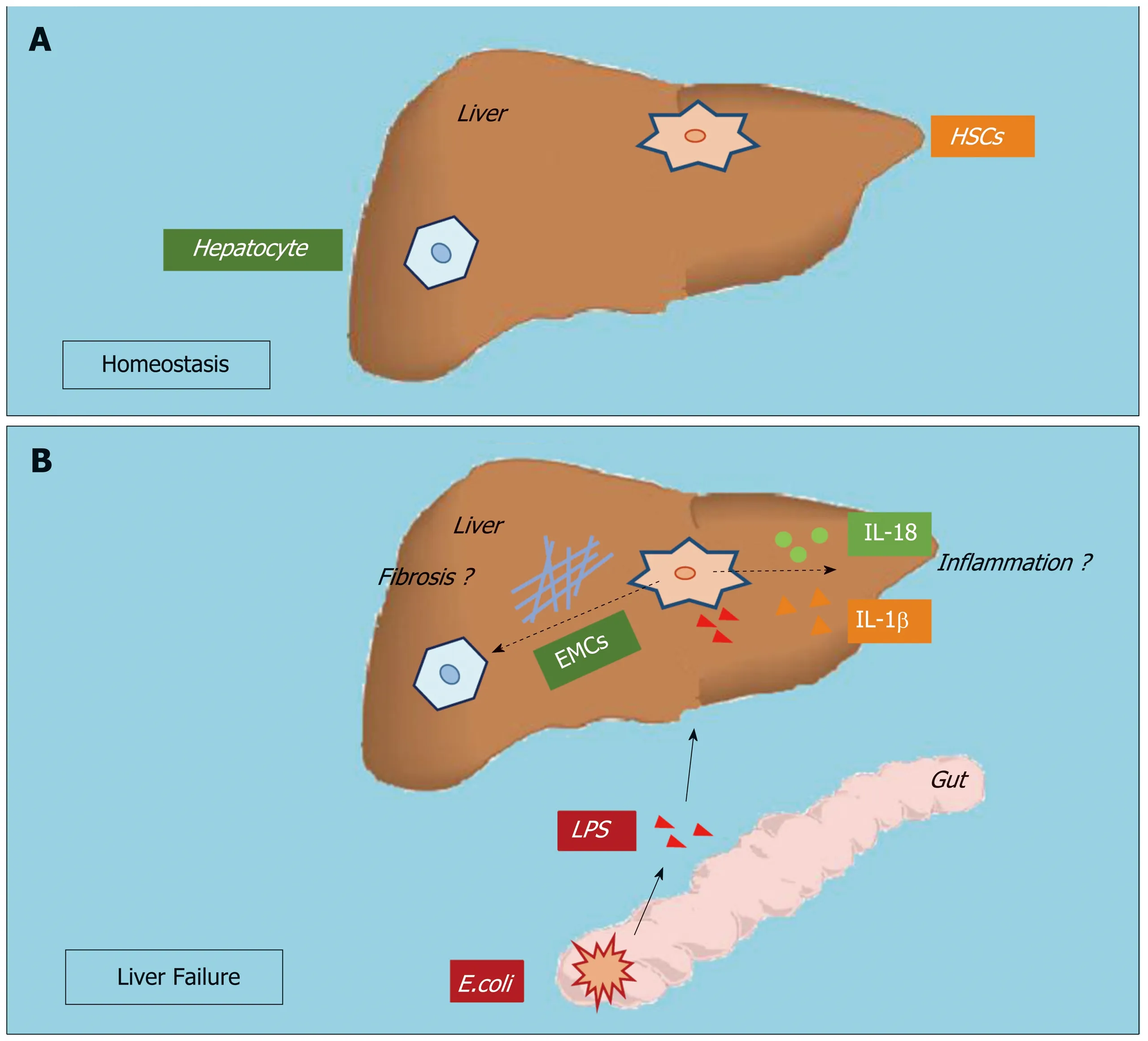
Figure 1 Hepatic stellate cell activation and inflammation participate in acute liver failure.
Clinicians have observed that some ALF patients may recover spontaneously and the clinical outcomes largely depend on the balance between hepatocyte loss and regeneration[14]. Under mild conditions, lost cells can quickly be replaced by neighboring healthy hepatocytesviareplication in an attempt to restore hepatic architecture and function. However, the regenerative capacity of the remaining hepatocytes may not be sufficient upon extensive injury and massive hepatocyte death, and the resident liver progenitor cells (LPCs) are then activated to take over the role of hepatocytes in hepatic regeneration[15]. However, for many liver failure patients, even the regenerative process by LPCs is inadequate to match the rapid process of hepatocyte death and dramatic deterioration in liver function, which means that apart from liver transplantation, few effective therapies exist[16]. To date, the mechanisms promoting hepatic cell death and the processes mediating liver regeneration are not fully understood.
Hepatic inflammation in ALF
Overactivation of hepatic inflammation is another important characteristic of ALF.Clinically, ALF shares many features with severe sepsis, including a systemic inflammatory response and progression to multi-organ failure[17]. Patients with ALF often present with endotoxemia and increased serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels due to increased gut permeability[18]. LPS can cause the release of a wide variety of inflammatory mediators and contribute to the pathogenesis of various diseases,including ALF. Studies have also found elevated plasma inflammatory cytokines,such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, in ALF patients[19].Moreover, approximately 60% of ALF patients fulfill the criteria for systemic inflammatory syndrome irrespective of the presence or absence of infection[20].Inflammasome activation serves as a double-edged sword, which contributes to both the protective antimicrobial response and cell death when excessively active during the pathogenesis of various diseases[21]. Inflammation is a common element in thepathogenesis of most liver diseases. ALF is now known as an inflammation-mediated hepatocellular injury process. During the disease process of ALF, inflammation first participates in the initiation and amplification steps leading to cell injury and hepatocyte death; these injured/dead hepatocytes then release damage-associated molecular patterns that can drive inflammasome activation, directly perpetuate further cell death, and mediate additional organ failure forming a vicious circle.Studies have shown that inhibition of hepatic inflammation can successfully delay/prevent the progression of ALF[22,23]. However, the mechanisms promoting hepatic inflammation during ALF are still not fully understood.
LIVER FAILURE AND HSC ACTIVATION
Hepatic fibrosis and HSCs in ALF
Liver fibrosis is a highly conserved and coordinated wound-healing process aimed at maintaining organ integrity, which results from acute or chronic liver injury and is always associated with excess hepatocellular death[24]. Chronic liver injury always accompanies progressive hepatocyte apoptosis and subsequent liver fibrogenesis. In chronic liver injury, fibrosis is widely acknowledged as a damaging process, which results in cirrhosis, portal hypertension and liver cancer[25]. ALF is associated with massive short-term hepatocyte death by provoking excessive apoptosis and necrosis,and consequently, deterioration of liver function[26]. When the disease is not fatal, the liver has a unique capacity to recoverviaproliferation and regeneration, and HSC activation has also been found to participate in the pathogenesis of ALF[27]. However,data on the roles of fibrosis during the pathogenesis of ALF are still scarce.
HSC activation is the central step during liver fibrogenesis, and HSCs are known for their role in the initiation, progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis. A recent study has shown that fibrogenic cells, including HSCs and myofibroblasts, are activated early after acute/chronic liver injury to produce ECM components[24]. The engulfment of hepatocyte-derived apoptotic bodies formed during liver failure was shown to promote the expression of fibrogenic genes in HSCs[28]. Moreover, Dechêneet al[29]found that ALF was accompanied by active hepatic fibrogenesis and revealed a positive correlation between liver stiffness, hepatocyte death and HSC activation,which suggests that fibrosis is an attempt to repair liver damage responding to ALF.Besides, a decrease of liver stiffness in the remission stage of the disease was also found in these ALF patients. Our previous data indicated that this short-term occurrence of fibrosis during the progression stage of ALF is a potentially beneficial response by the liver and serves as a scaffold to support the parenchyma and maintain hepatic integrity[30]. Thus, liver fibrosis may play a protective role during ALF.
Clinical data have revealed that patients with chronic liver disease are not sensitive to the deleterious effects of toxic compounds due to elevated levels of fibrosis:patients with long-term elevated liver enzyme levels are less sensitive to the hepatotoxicity of statins[31], and patients with chronic liver disease have shown increased tolerance to APAP compared to healthy individuals[32]. Moreover, in experimental mouse models, Osawaet al[33]showed that mice with bile duct-ligatedinduced fibrosis were more resistant to the lethal effect of Fas. Acute and chronic injury can both induce HSC activation and subsequent ECM accumulation. In the pathogenesis of ALF, ECM has been shown to protect hepatocytes from death through the maintenance of cell attachment and the architecture of liver tissue[30].However, the mechanism by which ECM participates in protecting hepatocytes from death remains complex. In a recent study, collagen 1, the most abundant form of collagen in both normal and pathologic livers, has been shown to increase resistance to various injurious stimuli and protect hepatocytes from apoptotic or necrotic deathviaactivation of the ERK1/2-MAPK signaling pathway[27]. In addition, some adaptor molecules such as the integrins, focal adhesion kinase, integrin-like kinase, PINCH and others are also likely to contribute to hepatocyte survival[34]. Matrix metalloproteinases are a family of proteinases that are capable of degrading all ECM proteins. A recent study revealed that IL-1β induced the production of matrix metalloproteinases during liver failure, which provoked the collapse of sinusoidsviaECM degradation and led to parenchymal cell death and loss of liver function in response to hepatic toxins[35]. Taken together, HSC activation leads to hepatic fibrosis,which participates in the maintenance of cell attachment and the architecture of liver tissue and protects hepatocytes from injurious stimuliviaECM production.
Hepatic regeneration and HSCs in ALF
The liver is the main site of drug detoxification. It is exposed to numerous chemicalsin the body that may induce cell injury or even death, and the ability for regeneration is of importance to maintain liver homeostasis[36]. It is known that the key strategy for the treatment of ALF is to reduce hepatocyte death and stimulate hepatocyte regeneration. Liver regeneration is the process by which the liver is able to replace lost liver tissueviagrowth from the remaining tissue. Liver regeneration driven by epithelial cell (including hepatocytes and LPCs) proliferation is a highly controlled process regulated by a complex signaling network and has important implications for stimulating hepatic recovery and improving survival during liver failure[12,37]. The induction of liver regeneration depends on cross-talk between epithelial cells and nonparenchymal cells, especially HSCs.
HSCs are liver-specific mesenchymal cells that play vital roles in promoting liver fibrosis and maintaining hepatic homeostasis. There is growing evidence to show that HSCs have a profound impact on the proliferation, differentiation and morphogenesis of other hepatic cell types during liver development and regeneration[38]. HSCs are in direct contact with hepatocytes and LPCs, and their close anatomic relationship in the space of Disse suggests that HSCs are part of the local “stem cell niche” for hepatocytes and LPCs. Activated HSCs have been shown to assist liver regeneration by producing growth factors, which can modulate the proliferation of both hepatocytes and LPCs around them. Conditioned medium collected from HSCs at an early stage of liver regeneration in a 2-acetylaminofluorene/partial hepatectomy injury model was found to contain high levels of hepatic growth factor and epidermal growth factor, which target and act primarily on epithelial cells[39]. These factors may directly enhance the proliferation of hepatocytes and LPCs. It has also been shown that early-activated HSC-derived paracrine factors can evoke an enhanced liver protective response in APAP-induced ALF in mice by promoting LPCs proliferation[40]. In addition, depletion of activated HSCs has been shown to correlate with severe liver damage and abnormal liver regeneration in APAP-induced acute liver injury in mice[5]. We hypothesize that HSCs may assist liver regeneration during liver failure by producing growth factors.
LIVER FAILURE AND HSC INFLAMMATION
Hepatic inflammation and HSCs
Inflammation is one of the most characteristic features of chronic liver disease of viral,alcoholic, fatty and autoimmune origin[41]. Inflammation has been shown to typically present in different disease stages and is associated with the pathogenesis of cirrhosis,hepatocellular carcinoma and ALF[42]. Fibrosis is a highly conserved response to hepatic injury occurring in diseases with hepatocellular death. A number of studies have focused on explaining the links between inflammation and fibrosis.
Hepatocyte injury followed by inflammation and activation of the innate immune system leads to liver fibrosis mediated by HSC activation[43]. HSCs are quiescent in the normal liver and upon activation by liver injury become activated. HSCs have been characterized as the main effector cells in liver fibrogenesis and receive a wide range of signals from injured/dead hepatocytes and liver immune cells, predominantly KCs. KC-derived transforming growth factor-β1 activates HSCs and is the most potent fibrogenic agonist. KCs also enhance liver fibrosis by promoting activated HSC survival in a NF-κB dependent manner. The cross-talk between KCs and HSCs have been shown to be mediated by inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β and TNF-α[44].In addition, inhibition of IL-1β significantly led to increased apoptosis of HSCs and decreased liver fibrosis[45].
Studies have shown that inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-6, are produced in activated HSCs. HSCs of murine or human origin are highly responsive to LPS and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, resulting in the activation of proinflammatory signaling pathways and the subsequent production of inflammatory chemokines/cytokines. This positive inflammatory feedback loop then maintains a sustained inflammatory process and ensures the survival and activation of HSCs[46,47].
Hepatic inflammation and HSCs in ALF
ALF is characterized by elevated inflammation. ALF shares many features with severe sepsis, including a systemic inflammatory response and progression to multi-organ failure.
Two main mouse models are now used to study ALF, including the LPS/D-galactosamine and Concanavalin A (Con A) models. Intraperitoneal injection of LPS may activate immune cells located in the circulation and the sinusoids, and these activated cells produce large amounts of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines resulting in massive hemorrhagic liver injury or even hepatocyte death[46]. D-galactosamine is a hepatotoxic agent, which inhibits protein synthesis and is usually used together with LPS to create ALF mouse models[48]. A recent study showed that compared to wild-type mice, HSC-depleted mice presented with decreased cytokine and chemokine expression and attenuated liver injury after LPS/D-galactosamine administration[49]. Con A is a lectin, carbohydrate-binding protein, extracted from the jack-bean (Canavalia ensiformis). An intravenous injection of Con A constitutively activates intrahepatic and systemic immune cells resulting in excessive inflammatory cytokines and chemokines production[50]. In a Con A-induced liver injury mouse model, inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and interferon-β, caused massive hepatocyte necrosis with dense infiltration of leukocytes. A recent study on a Con A-induced liver injury model showed that HSCs received inflammatory signals generated in the sinusoids and relayed them to the liver parenchyma[8]. Thus, we hypothesize that HSCs have important roles in hepatic inflammation during the pathogenesis of ALF.
Our recent work showed that during the pathogenesis of ALF, reactive oxygen species activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote inflammation in HSCs. We also revealed that LPS treatment induced reactive oxygen species generation in HSCsviamitophagy inhibition[51]. Studies have suggested that in hepatocytes, reactive oxygen species play important roles in the pathophysiology of diseases, including ALF. Injured/dead hepatocytes greatly increase oxidative stress during liver failure,which in turn contributes to inflammation, further hepatocyte loss and impedes regeneration[52]. Taken together, these data suggest that HSC inflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of ALF by producing inflammatory cytokines upon stimulation and relaying inflammation signaling from the sinusoids to parenchyma (Figure 2).
CONCLUSION
ALF is a life-threatening disease, which has a high mortality rate. Hepatocyte death and overactivation of hepatic inflammation are two main characteristics of ALF. HSCs play both protective and promotive roles during the pathogenesis of ALF:first, HSC activation participates in the maintenance of cell attachment and the architecture of liver tissueviaECM production; second, HSC activation assists liver regeneration by producing growth factors; and third, HSC inflammation plays a role in relaying inflammation signaling from the sinusoids to parenchymaviathe secretion of inflammatory cytokines. A better understanding of the roles of HSCs in the pathogenesis of ALF will lead to improvements and novel strategies for the treatment of patients with ALF.
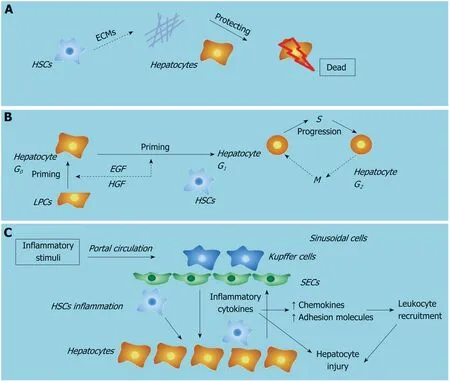
Figure 2 Roles of hepatic stellate cells in liver failure.
 World Journal of Hepatology2019年5期
World Journal of Hepatology2019年5期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Successful treatment of noncirrhotic portal hypertension with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A case report
- Neonatal cholestasis and hepatosplenomegaly caused by congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type 1: A case report
- Carvedilol vsendoscopic variceal ligation for primary and secondary prevention of variceal bleeding: Systematic review and metaanalysis
- Expanding etiology of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
- Hepatitis C virus antigens enzyme immunoassay for one-step diagnosis of hepatitis C virus coinfection in human immunodeficiency virus infected individuals
- Hepatitis C virus cure with direct acting antivirals: Clinical,economic, societal and patient value for China
