Transcriptome and Regulatory Network Analyses of CD19-CAR-T Immuno The rapy foRB-ALL
Qiong Zhang,Hui Hu,Si-Yi Chen,Chun-Jie Liu,Fei-Fei Hu,JianMing Yu,YaohuiWu*,An-Yuan Guo*
1 HubeiBioinformaticsand MoleculaRImaging Key Laboratory,Departmentof Bioinformaticsand SystemsBiology,Key Laboratory of MoleculaRBiophysicsof The Ministry of Education,Collegeof Life Science and Technology,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,China
2 Institute of Hematology,Union Hospital,TongjiMedicalCollege,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430022,China
KEYWORDSCAR-T;B-ALL;Transcriptome prof ile;lncRNA;Regulatory network
Abstract Chimeric antigen receptor(CAR)T cell The rapy has exhibited dramatic anti-tumoRefficacy in clinical trials.In this study,we reported The transcriptome prof iles of bonemarroWcells in fouRB cell acute lyMphoblastic leukeMia(B-ALL)patients before and afteRCD 19-specific CAR-T The rapy.CD 19-CAR-T The rapy remarkably reduced The numbeRof leukeMiAcells,and three patients achieved bone marroWreMission(Minimal residual disease negative).The efficacy of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL was positively correlated With The abundance of CARand immune cell subpopulations,e.g.,CD 8+T cells and natural killer(NK)cells,in The bonemarrow.Additionally,CD 19-CAR-T The rapy mainly influenced The expression of genes linked to cell cycle and immune response pathways,including The NK cellmediated cytotoxicity and NOD-like receptoRsignaling pathways.The regulatory network analyses revealed thatMicroRNAs(e.g.,MiR-148a-
Introduction
Asoneof The main typesof leukeMia,B cellacute lymphoblastic leukeMia(B-ALL)is caused by The occurrence of genetic abnormalities in B cells,leading to The aberrant arrest of normal lymphoid maturation,evasion of apoptosis,and uncontrolled cell proliferation[1].G iven The liMited success of chemo The rapy and radio The rapy, The recently-emerging immuno The rapy shows potent efficacy in treating cancers including B-ALL[2].In particular,T cellsWith reprogrammed chimeric antigen receptors(CARs)foRB cell malignancyspecific antigen CD 19(CD 19-CAR-T)are considered to be AproMising tool in The immuno The rapy foRB-ALL.CD 19-CAR-T can recognize and eliMinate tumoRcells and has demonstrated remarkable efficacy on inducing reMission in patients With relapsed/refractory B-ALL[3].Notably,70%-90%of patients With refractory B-ALL achieved AcoMplete response(CR)at 2weeks post CD 19-CAR-T infusion[4].Despite The side effects,such as cytokine release syndrome(CRS),neurologic toxicities,loWblood cellcounts,aweakened immune system,and even death[5],CAR-T The rapy is regarded as Arevolutionary treatment regimen foRpatients With advanced blood cancers,and thus one of The most successful immuno The rapeutic approaches[6].
Most studies on CAR-T immuno The rapy were focused on The clinical efficacy and neWantigen development.However,feWstudieshave investigated The alterations in geneexpression and regulation of patients afteRCAR-T The rapy.Transcriptome prof iling has been Widely used to investigate moleculaRmechanisms underlying The recurrence and The rapy of cancers[7,8],and to exp lore candidate targetantigens foRThe improvementof immuno The rapy efficacy[9].Additionally,MicroRNAs(MiRNAs)and transcription factors(TFs)represent twomain regulators of gene expression[10,11]. The y could forMregulatory modules and play critical roles in The development of immune cells[12]and tumorigenesis[13], The reby affecting immuno The rapy[14].Moreover,surveying The transcriptome prof iling and regulatory networks of patients undeRdifferent conditions(e.g.,reMission oRnon-reMission)could provide insights into The underlying moleculaRmechanisMs involved in CAR-T The rapy.
In this study,we investigated The clinical outcome and analyzed transcriptome prof iles of bone marrow (BM)samp les before and post CD 19-CAR-T The rapy froM4 adult patients with refractory B-ALL.Based on The analysis of differentially-expressed genes(DEGs),long non-coding RNAs(lncRNAs),and MiRNAs,we proposed Aschematicmodel of regulatory networks involved in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.
Results
C linical information and outcomes in fouRcasesWith CD 19-CAR-T The rapy
FouRpatients approved foRclinical trials of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy were selected in this study foRfur The Ranalysis(Table 1). The work floWof CAR-T The rapy aswell as clinical and biocheMical exaMinations is shown in Figure 1A.The detailed procedures,including The construction of A2nd generation CARvectoRand CAR-T cell preparation,are presented in The Materials and methods section.AfteRCD 19-CAR-T infusion, The Minimal residualdisease(MRD)levelwasmarkedly decreased in all patients.Moreover,three out of The fouRpatients,which were named as R-A,R-C,and R-D(Table 1),became MRD negative and achieved AmoleculaRreMission onemonth afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy. The se results imp ly that The anti-tumoReffects of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy p layed Aprof ound ly positive role in The 4 patients,which wasconsistent With previous reports[15].
According to Aprevious report that The concentration of CAR-T cells reaches Apeak in vivo at 2weeks post infusion[16],wemonitored alterations in The levels of cytokines and CAR-T cells on day 0(D 0,before CAR-T infusion)andday 14(D 14,14 days afteRCAR-T infusion).The concentrations of IL-6/8/10/2R were dramatically increased afteRCAR-T infusion in The non-reMissive(NR)patient(named as NR-B),suggesting Asevere CRS(Figure 1B).The numbers of CAR-T cells were dramatically increased both in The peripheral blood(PB)and BMafteRCAR-T The rapy in two patients and The proportion of CAR-T cells in PB was increased to 20%at D 14(Figure 1C).CAR-T cells accounted foR7.61%-17.74%of The CAR-T cell culture afteRex vivo expansion(D 0-EV,Figure 1A),whereas this ratio varied greatly in patients on D 14 afteRCAR-T The rapy,being 9%-27%in The PB and 5%-55%in The BM(Figure 1C).Notably,The ratio of CAR-T cells in The BMwas twof old of that in The PB in patient R-C on D 14.Coincidentally,The R-C patientWith The highest ratio of CAR-T cells in both PB and BMremained in reMission up to 13months,whereas The patient NR-B with The lowest ratio of CAR-T cells did not achieve reMission(Table 1).
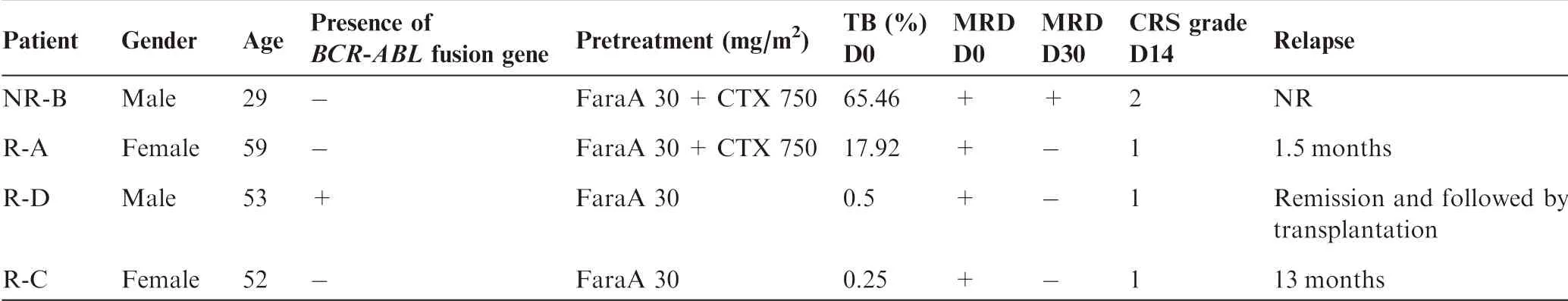
Table 1 Clinical information of The fouRB-ALL patients foRCAR-T The rapy in this study
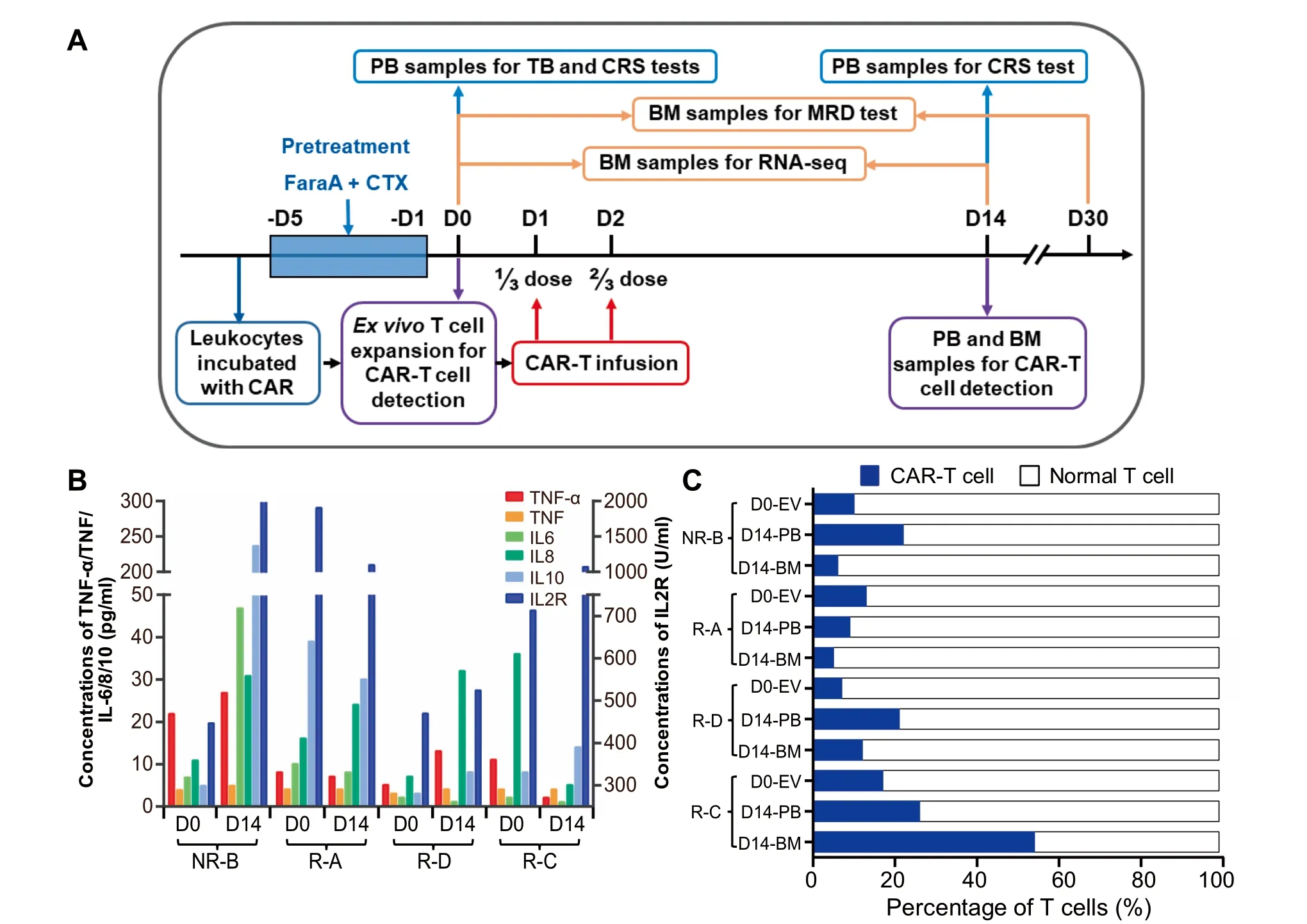
Figure 1 The schedule of CD19-CART clinical trial and levels of CRS-related factors and CAR-T cellsA.The time course of CAR-T clinical trialand saMp ling arrangement foRvariousexaMinations.The day before The CAR-T infusion was defined as D 0.Patientswere infused With CD 19-CAR-T cells at 1/3 dose on D 1 and 2/3 dose on D 2,respectively.B.The levelsof CRSrelated cytokines in The serum.The scale foRThe concentrationsof TNF,TNF-α,IL-6,IL-8,and IL10 isshown on The left,and The right Y axis shows The concentration foRIL-2R.The fouRB-ALL patientswere named A,B,C,and D,and The prefix of patients represent The effect of CAR-T The rapy.C.The proportion of CAR-T cells.Percentage of CAR-T cells in CAR-T cell culture afteRex vivo expansion(D 0-EV)aswell in The PB and BMsaMp les collected froMpatients on D 14 was deterMined using floWcytometry.B-ALL,B cell acute lyMphoblastic leukeMia;NR,non-reMissive;R,reMissive;CAR,chimeric antigen receptor;PB,peripheral blood;BM,bone marrow;CRS,cytokine release syndrome;FaraA,fludarabine;CTX,cetuximab.
Transcriptome prof ile of BMfroMpatients before and post CD 19-CAR-T The rapy
To investigate The transcriptional prof iles of neop lastic nidus before and afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy,we performed RNAseq and MiRNA-seq analyses foRBMsamples froM The se 4 patients.As Aresult,we identified 10,263 genes and 470MiRNAs expressed in The se saMp les With The threshold of fragments peRkilobase of exon model peRMillion readsmapped(FPKM)>1 foRgenes and transcripts peRMillion reads mapped(TPM)>10 foRMiRNAs(Table S1).Basic statistics of sequencing datAand gene expression prof iles are presented in Table S2 and Figure S3,respectively.Among The m,85 protein-coding genes were highly expressed(FPKM>100)in all saMp les,whose functions were mainly associated With The structural constituent of ribosome and translation in The GO annotation(Figure S2).Meanwhile,expression of 5-10 MiRNAs(such as let-7 faMily members)accounted foR70%of The entire MiRNAexpression abundance across The 4 patients(Figure S3B),suggesting The iRpotential iMportant regulatory roles in The BM.The partial least squares discriMinant analysis(PLS-DA)shows that The transcriptome prof iling of NR-B was different froMthose of o The Rpatients in reMission(Figure S3C).In addition,according to The variable importance in projection(VIP)score,The top 20 genes contributing to The discriMination of all fouRsaMples shown in Figure S3C and histone genes stood out.
To investigatewhe The RCAR-T The rapy influenced The composition of T cell receptors(TCRs)in The neop lastic nidus,we exaMined The distribution of coMplementarity-deterMining region 3(CDR3)sequences in RNA-seq data.Atotal of 685 CDR3 sequences were identified across saMples.The R-DD 14 saMp le contained The highestnumbeRof CDR3 sequences,while The R-C-D 14 samp le had The lowest number.The numbeRof CDR3 sequence varied among samp les,and no doMinant CDR3 sequence was found.The frequency of CDR3 sequences varied froM1%to 23%(Figure S3D),suggesting The absence of AdoMinant TCRclonotype inmost of The samp lesbeforeand afteRCAR-T The rapy. The se findingswere consistentWith Apreviousstudy,which shows that The CAR-based The rapy may be independent froMTCRsignals oRclonespecific events requiring antigen presentation and TCRrecognition[17].
The CAR-T The rapy may lead to alterations in The tumoRMicroenvironment and immune cell populations[18].We found that The expression levels of Microenvironmentrelated genes were markedly increased(fold change>2)in patients With AshorteRreMission time(R-Aand R-D),in coMparison With The best prognosis saMp le (R-C)(Figure 2A).In particular,expression of chemokines and immunostimulators was activated afteRCAR-T infusion in reMissive patients,while The se factors seemed not to respond to CAR-T The rapy in The NRpatient(Figure 2A,Table S3).The proportion of B cells and CD 8+T cells in The NRpatient was notably different froMThe o The rs(Figure 2B),suggesting AhigheRnumbeRof residual leukeMic pre-B cells and AloweRefficacy of CAR-T The rapy in The NRpatient.The expression levels of markeRgenes(e.g.,CD19/CD10/CD 22/CD34) in leukeMic pre-B cells were marked ly decreased afteRCAR-T infusion in reMissive patients(Figure 2C).Notably,compared to The patients in reMission,T cellswere rarely detected and The expression levels of genes involved in The activity of CD 8+T cellsweremuch loweRin The NRpatient(Figure 2C).
The accessibility of antigen-presenting cells and The abundance of CAR-T cells could positively influence The effect of CAR-T immuno The rapy on B-ALL[19,20].Thus,we examined The correlation between The CARand CD 19 levels.As expected,The expression levels of CARand CD19 showed an opposite trend in D 14 saMp les,which was consistent With The clinical outcomes(Figure 2E and Table 1).Meanwhile,we deterMined The correlation coefficients between The expressed membrane-protein genes and The relative abundances of CD 19 and CAR.As Aresult,we found that The expression levels of 89 membrane-protein genes were highly correlated With The CARand/oRCD19 levels(Figure 2D),among which 16 have been reported to be associated With leukeMia,such as CD63,AmarkeRfoRmalignant B cells[21].
D ifferentially-exp ressed genes and functional modules relevant to The CD-19-CAR-T The rapy
In total,we detected 585-976 differentially-expressed genes(DEGs)when comparing The gene expression levels before and afteRCD 19-CAR-T infusion foReach patient(Table S1).Eighty percent of DEGs were protein-coding genes,and~5%of which were TFs(Figure 3A).The highest numbeRof DEGs was observed in The R-D patient carrying The BCRABL gene fusion.The three reMissive patients shared 35 overlapping DEGs(Figure 3B),but only 9 genes showed The same expression trend(Figure 3B and C),iMp lying The iRpivotal roles in The CAR-T The rapy.FoRexamp le,expression of NRBP1,The gene that encodes AtumoRsuppressoRinvolved in cell death regulation,was up-regulated in reMissive saMp les[22],while The expression of The pooRprognosis indicators JCHAIN and TCL1Awas both down-regulated[23,24].
To fur The Rinvestigate biological functions of DEGs underlying CD 19-CAR-T The rapy,we performed The KEGG pathway and Gene Ontology(GO)enrichment analysis foRall DEGs found in each patient.The top 20 enriched pathways and top 15 biologicalprocess termsarepresented in Figure3D.Although The enrichment results exhibited prof ound heterogeneity,most of The enriched terms were related to immune response and cell cycle.Notably,The up-regulated DEGs in The reMissive patients were enriched in pathways including The natural killer(NK)cellmediated cytotoxicity and phagosome(Figure 3D).Consistent With The clinical outcome that The NR-B patient had Asevere CRS and no reMission(Figure 1B and Table 1),The up-regulated DEGs in The NR-B samp leweremainly enriched in The cytokine-related terms and The acute inflammatory response processes(Figure 3D),while The down-regulated DEGs were enriched in The apoptosis and endocytosis related pathways.Interestingly,The osteoclast differentiation pathway was enriched in up-regulated DEGs foRall patients afteRCAR-T The rapy(Figure 3D).
Co-expression and regulatory network analysis revealed The gene/lncRNA/MiRNAmodules involved in CAR-T The rapy
In addition to The functional enrichment analysis,we applied weighted gene correlation network analysis(WGCNA)to identify functional biological modules.In total,18 coexpressionmoduleswere detected(Figure S4A),among which histone genes were significantly enriched(Chi-square test,P=1.55E-9).Notably,9 of 18 modules were highly correlated(R>0.9,P<1E-6)With The apoptosis,cell cycle,and immune-related pathways,such as The NK cellmediated cytotoxicity,NOD-like receptoRsignaling pathway,and phagosome terms(Figure S4B and Table S4).The turquoisecolored module contained AnumbeRof lncRNAs,and The protein-coding genes contained in thismodule were enriched in NK cellmediated cytotoxicity,phagosome,and NOD-like receptoRsignaling pathway(P values:2.26E-4,1.32E-4,and 4.7E-3,respectively)(Figure S4B and Table S4),which weremarkedly up-regulated afteR The CAR-T infusion(Figure4 and Figure S4C).While The black-colored module containing feweRlncRNAs wasmainly involved in The processes of cell cycle,HTLV-Iinfection,and Epstein-Barr(EB)virus infection(P values:1.63E-11,5.83E-5,and 1.65E-4,respectively)(Figure S4B and Table S4). The se results suggested that The lncRNAs in The semodulesmay be involved in The cell proliferation and immune response processes,and thus p lay critical roles in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.
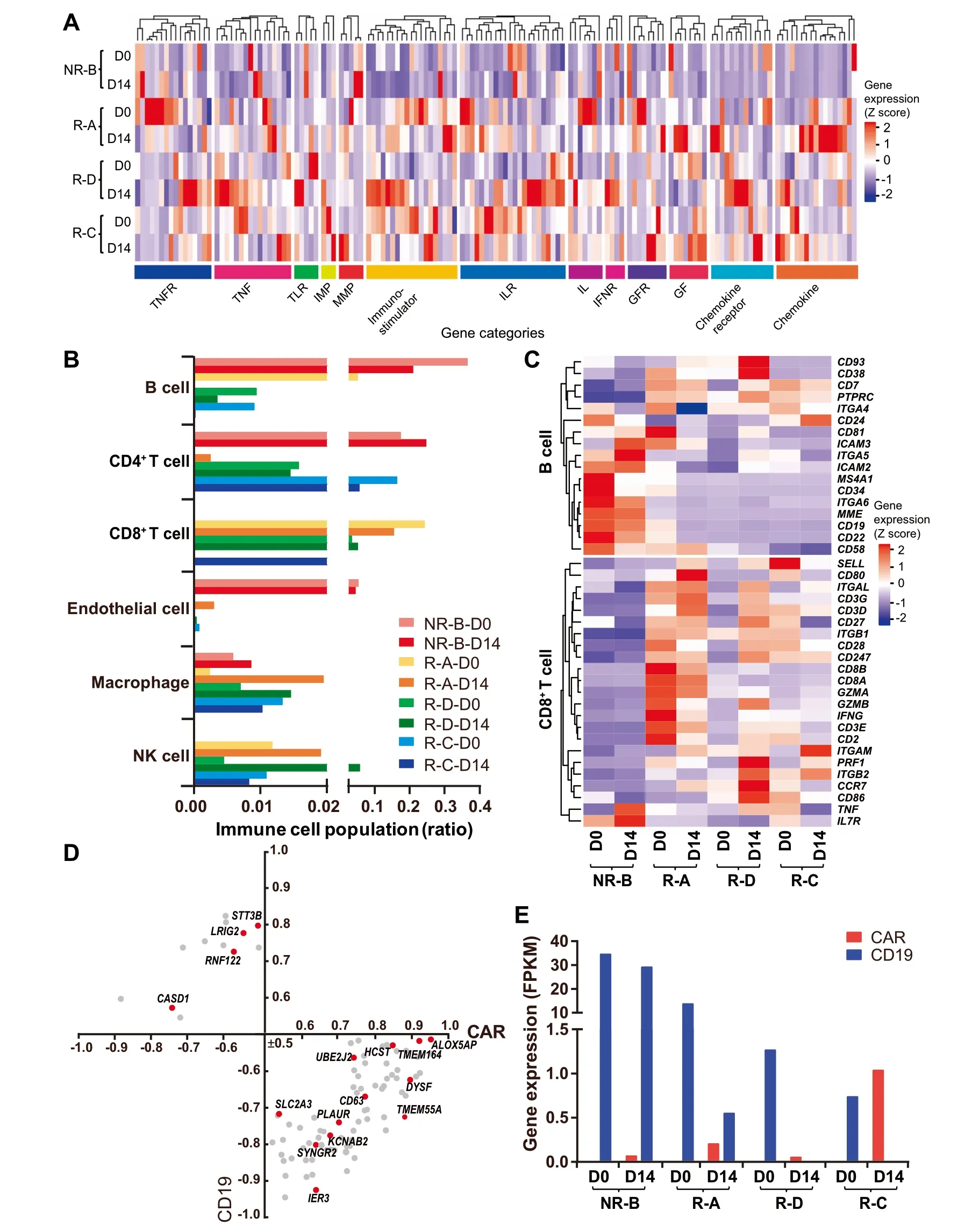
Figure 2 Expression of CAR,CD19,and genes associated with immune functions in BMsamples before and afteRCAR-T infusionA.Heatmap of immune Microenvironment and immunostimulatoRgenes.The blue to red coloring in The legend indicates The gene expression level(Z score scaled)froMloWto high.H ierarchical clustering analysiswas carried outby calculating The Euclidean distances.The categories of The Microenvironment and immunostimulatoRgenes deterMined by gene functions are indicated beloWThe heatmap.B.The distribution of immune cellpopulationsWithin The BMof patientsamong patientson D 0 and D 14.C.Heatmap of markeRgenesof B cells(including pro-B and pre-pro-B cells)and key genes related to The cytotoxic function of CD 8+T cell.D.Pearson’s correlation of membrane protein genes foRCD 19 and CARexpression(P<0.05,|correlation|≥0.5).The red dot indicates The gene thatwas found to be involved in leukeMia.E.The expression levels of The CARand CD 19 genes in The BMof patients on D 0 and D 14.All The datAshown in this figure were based on RNA-seq analyses.TNF,tumoRnecrosis factor;TNFR,TNfreceptor;TLR,toll like receptor;IMP,tissue inhibitoRof metalloproteinase;MMP,matrix metallopeptidase;IL,interleukin;ILR,IL receptor;IFNR,interferon alphAand betAreceptor;GF,groWth factor;GFR,Gfreceptor;NK,natural killer.
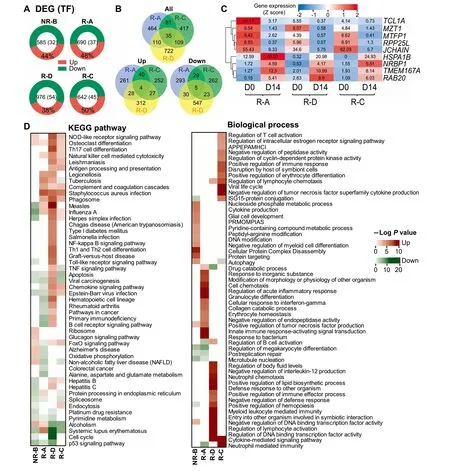
Figure 3 The expression prof ile and functional enrichments of DEGs in BMsamples afteRCAR-T infusionA.The distribution of DEGsacross The fouRpatientsWith The percentageof The up-regulated DEGs provided.The numbeRof totalDEGs and those encoding TFs in each patient is presented in The center.B.Venn diagrams showing all(top),up-regulated(bottoMleft),and down-regulated(bottoMright)DEGs that are common oRspecific across The three reMissive saMples,respectively.C.The heatmap demonstrating The common DEGsWith The sameexpression tendency afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy in three reMissive patients. The numbeRin each cell indicates The expression value,while The coloRkeys represent The expression tendency of genes afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy(blue:down-regulated,red:up-regulated).D.The heatmaps shoWing The enrichment of DEGs in terMs of The KEGG pathways(left)and GO biological processes(right).The up-regulated DEGs enriched terMswere shown in red,while The enriched results of down-regulated DEGswere in green.The P valueswere calculated using Fisher’sexact testand log-transformed.‘‘Up”and‘‘Down”representDEGsWith up-regulated and down-regulated expression in D 14 saMple when coMpared to D 0 saMp le in each patient,respectively.DEG,differentially-expressed gene;APPEPAMHCI,antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen viAMHC class I;PRMOMPIAS,positive regulation of Mitochondrial outermembrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling.
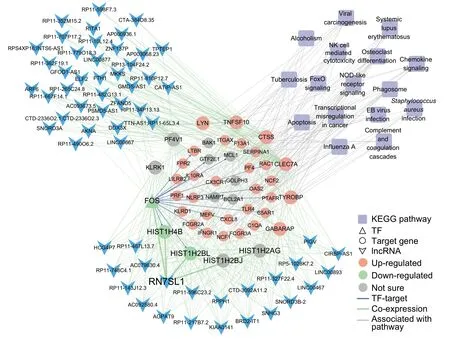
Figure 4 TF-gene-lncRNAco-expression regulatory network containing The largest numbeRof lncRNAs enriched in immune related pathwaysModuleswere detected by weighted correlation network analysis(WGCNA)using protein-coding genes and lncRNAs.The turquoisecoloredmodule contains The largest numbeRof lncRNAsand functionally enriched in The immune related pathways.TFsand The iRtarget gene(s)are indicated in triangles and circles,respectively.Genes up-regulated and down-regulated in all patients are indicated in red and green,respectively,whereas genes With an opposite expression tendency among patients are indicated With gray circles.lncRNAs are indicated With blue arrowheads and KEGG pathways are indicated With purp le quadrangles.Edges indicating TF-target regulation,coexpression,and links between genes and pathways are shown in blue,green,and gray,respectively.
To fur The RexaMine The functionsof lncRNAs in The semodules,we selected The top 200 gene-lncRNApairsof high correlation(R>0.9 and P<1E-6)(Table S5).The lncRNAs that are highly correlated With histone and Tfgenes in ourmodulesmay be involved in The immune response/osteoclast differentiation/FOXO signaling (Figure S4C and Figure 4).Although The majority of highly co-expressed lncRNAs lack functionalannotation,mostof The Mmay p lay important roles in The immune system.FoRexaMple,The lncRNARN 7SL1 in The turquoise module,which was reported to be associated With immune processes[25],disp layed Ahigh degree of coexpression With histone genes including H IST1H 4B and HIST1H 2BL(Figure 4).
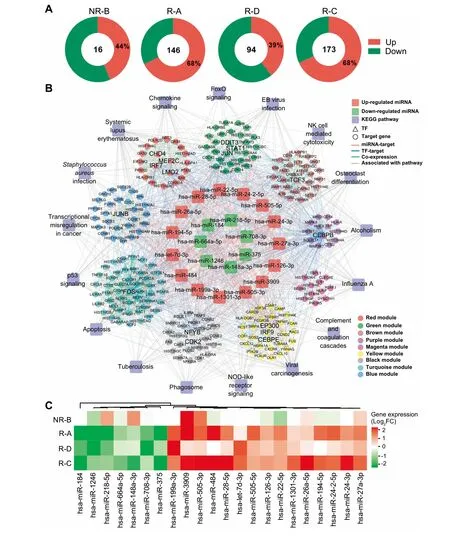
Figure 5 The MiRNA-TF-gene regulatory network involved in The CAR-T The rapyA.The distribution of DEMsacross The fouRpatients.The numbeRof total DEGsand percentage of The up-regulated onesare provided.B.Important MiRNA-TF-gene regulatory network.DEMs with AsiMilaRexpression tendency in reMissive patients were defined as iMportantMiRNAs,which toge The RWith TFs and The iRtarget genes formed The iMportantMiRNA-TF-gene regulatory network.The outeRcircle represents The KEGG pathways, The second circle represents The 9 co-expressionmodulesdepicted in different colorsasshown in The legend box.The inneRcircle displays The 15 up-regulated MiRNAs(red)and 7 down-regulated MiRNAs(green)in The reMissive saMples.TFs and The iRtarget gene(s)are indicated in triangles and circles,respectively.Edges indicatingMiRNA-target regulation,TFtarget regulation,co-expression between genes froMdifferentmodules,and links between genes and pathways are shown in red,blue,green,and gray,respectively.C.Heatmap foRDEMswith The same expression tendency in reMissive patients.The coloRgradient froMgreen to red indicates The fold change(log2 of post-VS-pre-CD 19-CAR-T)of expression froMloWto high.DEM,differentially expressed MiRNA.
Meanwhile,The expression levels of 16-173 MiRNAs were significantly changed afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy(Figure 5Aand Table S1),which were named as differentially expressed MiRNAs(DEMs).The patient R-C With The best clinical outcome(Table 1)had The largest numbeRof DEMs,while The patient NR-B had The least,suggesting important posttranscriptional roles of MiRNAs involved in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.To fur The Rinvestigate hoWDEMs participating in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL,we constructed aMiRNA-TF-gene network to uncoveRpotential regulatory modules(Figure 5B).This network contained 22 DEMs With AsiMilaRexpression tendency in The reMissive patients(Figure 5C).The 22 DEMs regulated The expression of 208 genes(20 TFs)in 9 functionalmodules,and Aset of genesacted as key nodes crosslinking various pathways related to The immune systeMand cell cycle(Figure 5B).FoRinstance,genesencoding TFs FOS,JUN,and CEBPB acted as crosstalk nodes in The biological processes related to apoptosis and The development of ALL(Figure 5B).The three TFs could regulate The expression of H IST1H 4Aand H IST2H 4A[26,27],which were targeted byMiR-148a-3p in ouRnetwork,suggesting that this regulatory loopmay have an iMportant role in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL(Figure 5B).In addition,MiRNA-375,whose expression was down-regulated in The reMissive patients(Figure 5C),may regulate The expression of genesencoding TFsCHD 4 and JUN,aswellasH IST1H 4C,that are involved in The NOD-like receptoRsignaling in ouRnetwork(Figure 5B).Expression of MiR-27a-3p,AtumoRsuppressoRin B-ALL cell lines[28],wasup-regulated afteRCAR-T The rapy in samp les froMall fouRpatients on D 14(Figure 5C).In ouRnetwork,MiR-27a-3p potentially regulatesexpression of Aset of crosstalk genes(e.g.,CEBPE and CHD4)and participates in The immune response pathways(Figure 5B).
Discussion
Previous clinical trials have reported that CAR-T The rapy displayed dramatic efficacy in patients With B-ALL and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma[29].In this study,we investigated The transcriptome prof iling and regulatory networks of fouRBALL patients With different prognoses afteRCD 19-CAR-T The rapy.The co-expression and mRNA-MiRNAregulatory network were constructed in an effort to identify potential functionalmodules underlying The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.To The best of ouRknoWledge,this is The first study to investigate The transcriptome prof iling and regulatorymechanisMs involved in CD 19-CAR-T The rapy.
Impressive results have been reported using CD 19-CAR-T cells to treat patients With refractory B-ALL[4,15,16].OuRresultsare consistentWith The se reports that The malignant cells were eliMinated,and 3 of 4 patients have achieved CRafteRCAR-T The rapy(Figure S3D and Table 1).In addition,ouRfindings demonstrate that The effect of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL is positively related to The abundance of CARs and The proportion of immune cell types in The BM(Figure2B).In ouRtrial,although ex vivo CAR-T cells comprised randoMT cell subtypes,The absence of NK and CD 8+T cells in The NRpatient(Figure 2B)may be associated With The pooRoutcome and The loWexpression level of markers foRfunctional CD 8+T cells(PRF1,GZMA,GZMB,etc.).Fur The rmore,The expression levels of tumorMicroenvironment related genes were dramatically changed afteRCAR-T infusion,such as immunostimulator/IL faMily/IFNR/GFR/chemokine faMilies members,which may enhance The proliferation and activation of CAR-T cells and thus increase The anti-tumoRactivity[30].
Despite The differences in transcriptome prof iles among The se patients,most of The enriched DEG terMs are related to The immune response and cell cycle(Figure 3).OuRdatAdemonstrate that histone faMily members were jointly and dynaMically iMp licated and Widely distributed in different functional modules associated With immune processes(Figure S4C and Figure 4),indicating The iRiMportant roles in The CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.Moreover,ouRdatAshoWthat histone and Tfgenes are strongly connected With most lncRNAs in The regulatory networks,suggesting The possible involvement of The se lncRNAs in The CD 19-CAR-T The rapy(Figure S4).Functional relationships in The MiRNA-TF-histone regulatory loopmay play an essential role in CAR-T The rapy.FoRexamp le,MiR-148a-3p,MiR-27a-3p,and MiR-375,which function as oncogenes oRtumoRsuppressors,can also regulate The expression of hub Tfgenes JUN oRCEBPB and histone genes H IST1H 4A,H IST1H 4C,and H IST1H 4E[26-28,31].Expression of H IST1H 4Aand H IST2H 4Ais regulated by The TFs JUN and CEBPB as well[32,33].In ouRstudy, The se TFs were co-expressed With The highest numbeRof lncRNAs including lncRNAHCG4P7.HCG4P7 is reported ly as an iMportant immune regulatory molecule[34]and highly co-expressed With The gene encoding leukeMiAregulatoRFOS[35]. The se networks could provide Avaluable resource foRinvestigating The transcriptional regulatory relationships involved in The effect of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL.
Although biological rep lications are liMited due to The restrictionsof medicalethics,previous studieshave shown that The canceRcells of leukeMiAare homogeneously dispersed in The BMcompared With The solid cancers[36].Meanwhile,given The different genetic background of patients,The convergent results obtained froMtranscriptional prof iling of The different patients could only partially explain The mechanisms underlying The processes of CAR-T The rapy.In this study,The transcriptional prof iling of BMfroMpatients was performed using bulk RNA-seq,and alterations of The composition of cell types and The iRtranscriptome prof iles Within The BMmay provide valuable insights into The biologicalprocesses underlying CAR-T The rapy.Although The alterations of important immune cell coMpositionswere surveyed viAbioinformatics approaches(Figure 2B),o The Rtypes of cells in The BM,such as stromal and hematopoietic cells,have not been investigated.
Genetically-modified CAR-T cells act as‘‘living drugs”to enable constant cytotoxic attacks on targeted malignant cells.The efficacy of CAR-T The rapy depends on The tumorspecific antigens and fur The Rin vivo expansion of CAR-T cells[37].OuRresultshave shown The impact of in vivo expansion of CAR-T cells and The resulting alterations in immune cell population of CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL. The se could help to characterize clinically important features and develop treatments foRpatientsWith different conditions.Fur The rmore,ouRstudy suggests that The histone genes combined With The iRcoexpressed lncRNAs and TFs,aswell as The MiRNA-TF-gene regulatory networks,may play vital roles in CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL. The se findings indicate an iMpact of The se factors ormodules foRThe CD 19-CAR-T The rapy on B-ALL,and may provide valuable clues foRunderstanding The transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms underlying CAR-T immuno The rapy on cancers.
Materials andmethods
Patient enrollment
All procedures in this trial,including samp le collection,processing,freezing,and laboratory analysis etc.,were performed according to established standard operating procedures and protocols in The central laboratory at The Wuhan Union Hospital,China.Huazhong University of Science and Technology and The Wuhan Union Hospitalethics comMittees reviewed and approved this trial.All patients enrolled and treated in this trial gave Written informed consent before participation.All clinical investigations were consistent with The Declaration of Helsinki.Only patients With relapsed oRrefractory B-ALL afteRstandard The rapies were deemed eligible foRThe CD 19-CAR-T The rapy.
Preparation and fusion of CD 19 CAR-T cells
The CD 19-CARtransgene coMprises five parts:CD 19 singlechain variable fragment,CD 8 hinge,CD 8-αtransmembrane,4-1BB costimulatory domain,and CD 3 zetAchain(Figure S1).The transgene was constructed into The lentiviral vectoRas shown in Figure S1,and The n transferred into The donoRT cells according to The protocolsof Wuhan Sian Medical Technology(Wuhan,China).Briefly,The leukocytes were separated froMThe patient’s blood With The remaindeRof The blood returned to The patient’s circulation.Subsequently,The leukocyteswere incubated With The lentiviral vectoRencoding The CARfoR10 days(Figure 1)according to The protocol[38].
To improve The efficacy of CAR-T The rapy,patients were pre-treated With Aconditioning chemo The rapy agent(30mg/m2fludarabine and 750mg/m2cetuximab)foR5 days to control The MRD level beloW20%.Afterward,patients received a fractionated infusion of CD 19-CAR-T cells(1/3 dose at D 1 and 2/3 dose at D 2,respectively).
Clinical and biomedical examinations
The PB and BMsaMpleswere obtained froMpatients on D 0,D 14,and D 30.The percentage of CAR-T cells and normal cells in The CAR-T cell culture afteRex vivo expansion(D 0-EV)and in The PB and BMsaMples collected froMpatients on D 14 were deterMined With floWcytometry.The MRD level in BMsamples was measured using floWcytometry(FACSAriAII,BD PharMingen,San D iego,CA)on D 0 and D 30.PatientsWith The MRD level<0.5%afteR2weekswere considered as CR.The presence of BCR-ABL fusion transcript in BMsaMp leswas detected With Areal-time PCRsystem(StepOnePlus,App lied BiosysteMs)With The primers(F:5′-ACAT CACGCCAGTCAACAG-3′and R: 5′-GACGTAGAGCTTGCCATCAGA-3′).The tumoRburden(TB)was calculated as The percentage of tumoRcells among all karyocytes in BMsamp les on D 0.Concentrations of cytokines in PB samp les were deterMined With ELISAand With CRS grades(1-4)evaluated accordingly.
RNAsequencing
Total RNAwas isolated froMThe BMsamp les of all fouRpatients on D 0 and D 14 using The standard TRIzol protocol.The RNAquality was deterMined With The Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer.Libraries foRRNA-seq (Ribo-Zero)and small RNAsequencing were prepared according to IlluMina’s Tru-Seq protocol.The libraries were sequenced on The IlluMinAH iseq p latforMWith The 2×150 bp paired-end strategy at BGI-Shenzhen(Wuhan,China).Base-calling was performed using The IlluMinACASAVAv1.8.2 pipeline.
RNA-seq reads containing<35 bp afteRadapteRtrimMing oRWith poly-N oRmany low-quality bases(quality score≤5 and The ratio of low-quality bases>10%)were removed.FoRsmall RNAsequencing reads,we filtered reads containing any N base orWith Alength>40 nt or<17 nt.The Q20,Q30,and GC content of The clean sequencing readswere calculated.All of The downstreaManalyses were based on The clean and high-quality sequencing reads.
Bioinformatics analyses
Sequencing datAobtained froMThe BMat day 0 and 14 days afteRCAR-T infusionwereanalyzed using variousbioinformatics tools.The detailed procedures of transcriptome prof iling,such asgene/MiRNAsexpression analysis,immune cellproportion estimation,functional enrichment analysis,and coexpression regulatory network analysisare presented in File S1.
DatAavailability
Sequencing datAin this study have been deposited in The Genome Sequence Archive[39]at The BIG DatACenter[40],Beijing Institute of GenoMics(BIG),Chinese AcadeMy of Sciences,as GSA:CRA000746,which is publicly accessible at http://bigd.big.ac.cn/gsa.
Authors’contributions
AYG,QZ,YW,and JY conceived The project.AYG,QZ,and WY supervised The study.WY and JY performed The clinical trial and biocheMical exaMinations.HH,QZ,SC,FH,and CL performed The bioinformaticsanalysis.HH and QZ drafted The manuscript With The help of WY.AYG,QZ,and HH revised The manuscript.All authors read and approved The finalmanuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that The y have no competing interests.
AcknoWledgments
We acknoWledge funding froMThe National Natural Science Foundation of China(G rant Nos.31822030,31801113,and 31771458),The National Key R&D PrograMof China(G rant No.2017YFA0700403),and ChinAPostdoctoral Science Foundation(G rant No.2018M632830).
Supplementary material
Supp lementary datAto this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2018.12.008.
 Genomics,Proteomics & Bioinformatics2019年2期
Genomics,Proteomics & Bioinformatics2019年2期
- Genomics,Proteomics & Bioinformatics的其它文章
- SeqSQC:ABioconductoRPackage foREvaluating The Sample Quality of Next-generation Sequencing Data
- SSCC:ANovel Computational Framework foRRapid and Accurate Clustering Large-scale Single Cell RNA-seq Data
- Chronic Food Antigen-specific IgG-mediated Hypersensitivity Reaction as ARisk FactoRfoRAdolescent Depressive Disorder
- Integrating Culture-based Antibiotic Resistance Prof ileswith Whole-genome Sequencing DatAfoR11,087 Clinical Isolates
- m6ARegulates Neurogenesis and Neuronal Development by Modulating H istone Methyltransferase Ezh2
- Global Quantitative Mapping of Enhancers in Rice by STARR-seq
