Intra-abdominal desmoid tumors mimicking gastrointestinal stromal tumors — 8 cases: A case report
Jwa Hoon Kim,Min-Hee Ryu,Young Soo Park,Hyun Jin Kim,Hyojung Park,Yoon-Koo Kang
Abstract
Key words: Desmoid tumor;Gastrointestinal stromal tumor;Radiology;Surgical resection;Imatinib mesylate;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract,originating from the interstitial cells of Cajal with KIT(85%) or PDGFRA (5%) mutations[1].The development of imatinib,a KIT- or PDGFRA-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI),has changed the paradigm of treatment and survival outcomes for both non-metastatic and metastatic GISTs[1].As the survival of patients with GIST is extended,additional primary malignancies in these patients have been reported in the literatures.
Although the association between GIST and other malignancies remains unclear,various solid tumors and hematologic malignancies were simultaneously or metachronously found with GIST[2].A previous case series proposed a potential link between the occurrence of desmoid tumors (DTs) and GISTs[3].The estimated risk of developing DT was significantly higher in patients with GIST than in the general population (standardized incidence ratio = 82,95% confidence interval 44-133)[3].The majority of DT cases (75%) developed after GIST[3],and were suggested to mimic the recurrence or progression of GIST.
DTs,also known as aggressive fibromatosis,are a rare mesenchymal neoplasm described as local infiltrative and non-metastatic disease.Severe local infiltrative growth and tissue invasion may cause deformity and functional impairment of adjacent organs,becoming life-threatening in cases with involvement of vital organs[4].DT is classified into extra-abdominal,abdominal wall,and intra-abdominal fibromatosis based on the anatomical location of the lesion[4].Intra-abdominal DT is extremely rare and its causes remain undetermined.It is thought that the occurrence of DT may be related to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP),Gardner syndrome,or trauma from previous neoplastic surgery[4].In cases of postoperative occurrence,intra-abdominal DT should be distinguished from the recurrence or progression of previous neoplasms.Cases of postoperative DT mimicking GIST have been reported[5-9].Meanwhile,secondary malignancy may be a differential diagnosis in patients with GIST following the development of a new single lesion.Currently,excisional biopsy is the only available method to distinguish a secondary malignancy from a GIST.Despite treatment with KIT or PDGFRA targeting TKIs is feasible suspecting recurrence or progression of GIST,performing an excisional biopsy is recommended following the clinical suspicion of secondary malignancy,to prevent unnecessary or inappropriate treatment with TKIs.In previous studies investigating DT mimicking GIST,the preoperative approach to the diagnosis of new lesions in patients with GIST suspected of DT was not described in detail.In addition,the preoperative radiological features of new lesions were not adequately investigated using computed tomography (CT) or18fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (18FDG-PET).
In this study,we report eight patients with intra-abdominal DT after GIST.We conducted an analysis of the clinical conditions and radiological and pathological findings of new lesions suggestive of intra-abdominal DT.
CASE PRESENTATION
A total of 2745 patients with histologically confirmed GIST were treated at the Asan Medical Center (AMC) in Seoul,Korea,from 2001 to 2017.We reviewed their medical records and tissue specimens in the prospectively collected GIST registry at the AMC.Among them,eight intra-abdominal DTs were identified in patients with GIST during treatment or regular follow-up.CT was used to evaluate tumor response according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.0 criteria.18FDG-PET was performed in cases of non-definitive evaluation of response or equivocal lesions with CT scan.The clinical conditions and radiological/pathological findings of the new lesions in eight patients are summarized below.Table 1 lists the characteristics of GIST and intra-abdominal DT.
Occurrence of a new single lesion after primary resection of low-risk GIST (patient 1)
A 59-year-old female patient presented with an asymptomatic lesion newly observed on regular follow-up.She was diagnosed as having low-risk gastric GIST and advanced gastric cancer (AGC) (pathological T2bN0M0 according to American Joint Committee on Cancer 6thedition).She had no personal or family history of disease,including FAP or Gardner syndrome.She underwent total gastrectomy and was followed up without adjuvant therapy.However,a new 3.7-cm mass occurred in the right diaphragmatic crus approximately 2 years after the primary resection of GIST.The new lesion was not palpable and there were no specific findings on physical and laboratory examinations.This mass was well-defined ovoid shaped with delayed or mild enhancement and had homogeneous enhancement patterns on CT.The maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) on18FDG-PET was 3.5 (mild).Based on previous pathological findings,the risk of recurrence of both GIST and AGC was low,and biopsy was necessary for the diagnosis of the new lesion.
Occurrence of a new single lesion while receiving adjuvant therapy with imatinib after the primary resection of GIST (patients 2-6)
Five patients (men,4;woman,1;median:58,range 50-67 years) presented with abdominal pains or no symptoms,and new lesions were observed during adjuvant therapy with imatinib (400 mg/d) due to high or intermediate risk of recurrence,following the primary resection of localized GIST.They had no personal or family history of disease,including FAP or Gardner syndrome.There were no specific findings on physical and laboratory examinations except for a palpable mass with mild tenderness in patient 4.These masses were well-defined ovoid shaped with delayed or mild enhancement and had homogeneous enhancement patterns on CT.The SUVmaxon18FDG-PET was 2.2 (mild) in patient 2,no hypermetabolic activity in patient 3 and 5,and 3.2 (mild) in patient 6.On the contrary,initial GIST showed lobulated masses with heterogeneous enhancement patterns on CT and hypermetabolic activity on18FDG-PET.Initial GIST in two patients (patient 2 and 5)showed SUVmaxof 4.3 and 6.3.
Occurrence of a new single lesion while receiving palliative treatment with imatinib for metastatic GIST (patient 7)
A 40-year-old female patient presented with an asymptomatic lesion newly observed during palliative treatment with imatinib (400 mg/d) for metastatic GIST at small bowel,peritoneum,ovary,and liver after initial debulking surgery.She had no personal or family history of disease,including FAP or Gardner syndrome.The palliative treatment decreased the size of the lesions,including the liver metastasis.However,approximately two years after the initial debulking surgery,a new lesion developed in the pelvic mesentery.The new lesion was not palpable and there were no specific findings on physical and laboratory examinations.This mass was welldefined ovoid shaped with delayed or mild enhancement and had homogeneous enhancement patterns on CT.The SUVmaxon18FDG-PET was 2.7 (mild).The findings of the CT and18FDG-PET examinations in a typical patient (patient 7) are shown in(Figure 1).
Occurrence of an incidental desmoid tumor in a patient with advanced GIST receiving palliative treatment with imatinib (patient 8)
A 72-year-old male patient who underwent wedge resection of the stomach for primary gastric GIST 6 years ago was found to have newly developed masses in thesmall bowel and peritoneum.He had abdominal discomfort and had no personal or family history of disease,including FAP or Gardner syndrome.There were no specific findings on physical and laboratory examinations and he received palliative treatment with imatinib (400 mg/d) for recurrent GIST.The lesion in the peritoneum of the left adrenal fossa was well-defined ovoid shaped with delayed or mild enhancement and had homogeneous enhancement patterns on CT.On the contrary,other GIST lesions showed lobulated masses with heterogeneous enhancement patterns on CT and hypermetabolic activity with SUVmaxof 4.9 on18FDG-PET.During treatment for GIST,the disease remained stable without the occurrence of new lesions.
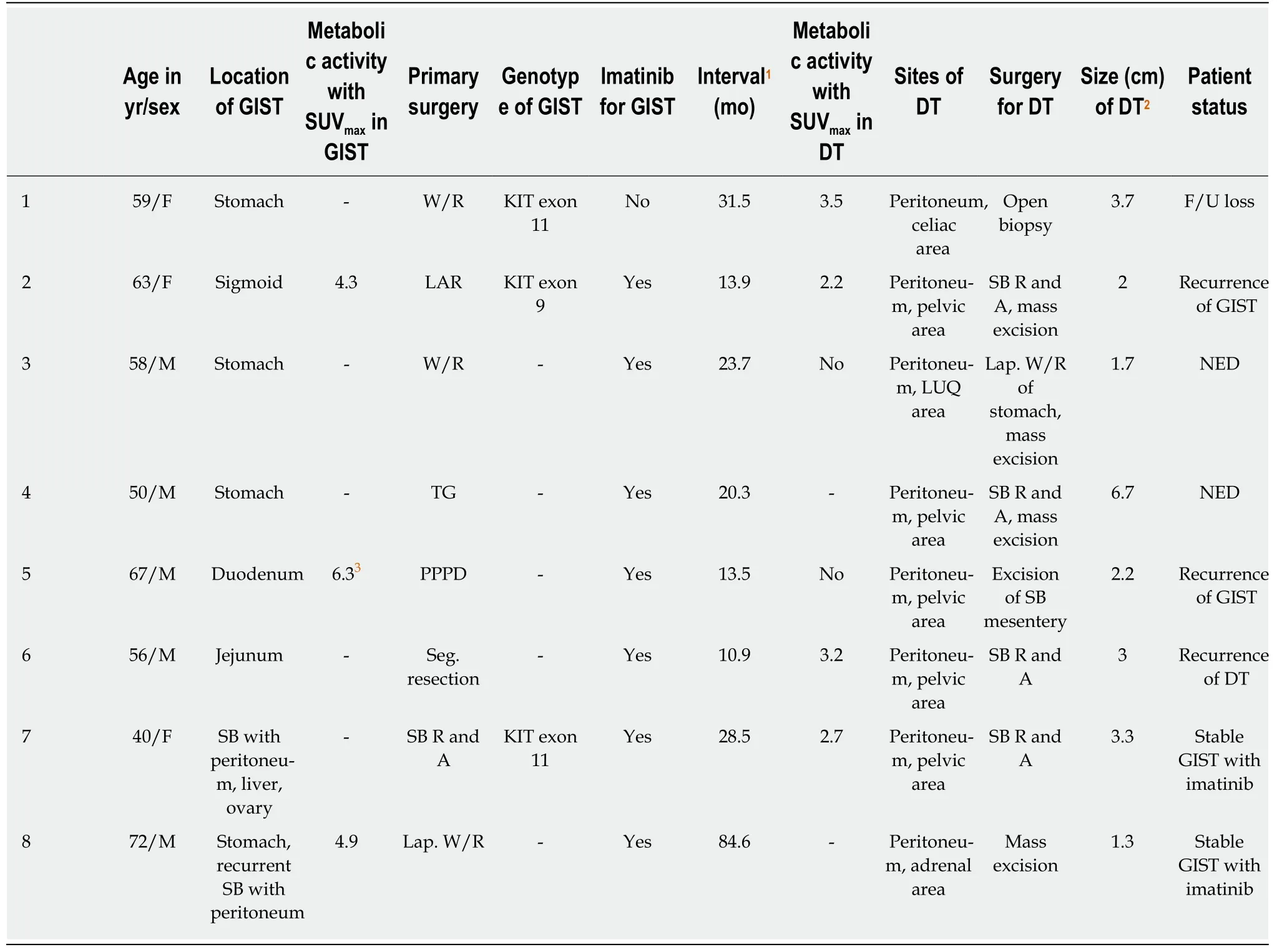
Table1 Summary of the clinical features of eight patients with intra-abdominal desmoid tumor after gastrointestinal stromal tumor
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The suspicious lesions were surgically removed for both diagnostic and treatment purpose except for one unresectable lesion in the right diaphragmatic crus,which was located near the aorta in patient 1.Patient 1 underwent open biopsy.The tumor specimens were examined by an experienced pathologist.Representative tumor sections were made into formalin-fixed,paraffin-embedded blocks and hematoxylin and eosin stained slides were reviewed.Immunohistochemical staining such as CD117,CD34,DOG-1,smooth muscle actin (SMA),S-100,and β-catenin were also performed for differential diagnosis.The size of most tumors ranged from 1cm to 4cm and tumors were firm and grossly circumscribed without necrosis,cystic change,or hemorrhage.Microscopic examination showed spindle cell proliferation in fibrotic background with infiltrative growth patterns.The spindle cells lacked cytologic atypia,atypical mitosis,or epithelioid component.On immunohistochemical staining,tumor cells were negative for CD117 and CD34 but,positive for β-catenin.SMA and S-100 were negative.All these features were consistent with DT and a representative case (patient 7) is shown in (Figure 2).
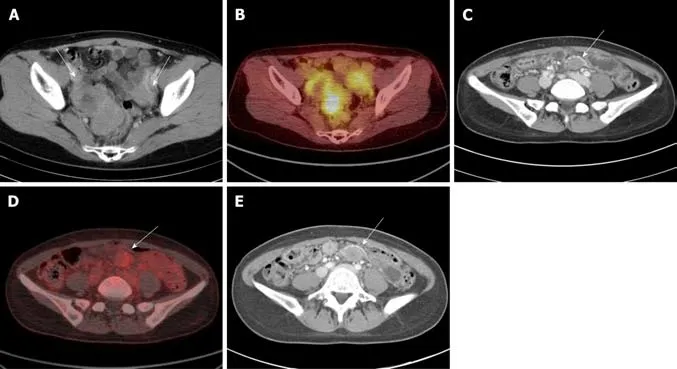
Figure1 Abdominal computed tomography and 18fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography revealed intra-abdominal desmoid tumors in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors,showing well-defined ovoid shaped masses with delayed or mild enhancement on computed tomography and mild or absence of hypermetabolic activity on 18fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography.
TREATMENT
Patient 1 initiated imatinib (400 mg/d) for unresectable DT.In patient 2-6,all patients had new lesions in the peritoneum approximately 1-2 years after primary resection of GIST and the initial suspicion was postoperative reactive change or recurrence of GIST.Among them,four patients maintained the dose of the adjuvant imatinib (400 mg/d) because peritoneal changes were not regarded as recurrence of GIST.However,in one patient with initial suspicion of recurrence of GIST,the dose was escalated to 800 mg/d.In four patients maintaining 400 mg/d imatinib,the size of the tumors increased.In contrast,such an increase in tumor size was not observed in the patient treated with 800 mg/d imatinib,with the tumor remaining stable for approximately 1 year.Subsequently,a change of enhancement within a new lesion was considered as focal progression (FP) of GIST.All patients eventually underwent surgical resection of tumors and DT was newly diagnosed and removed.In patient 7,because the new lesion was initially suspected as disease progression,the dose of imatinib was escalated to 800 mg/d.The tumor showed stable disease for 1.3 years and surgical resection of residual lesions after disease control with imatinib was performed.DT was newly diagnosed and removed.In patient 8,surgical resection of the residual lesions was performed after disease control with imatinib,and DT was incidentally diagnosed in the peritoneum of the left adrenal fossa and removed.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
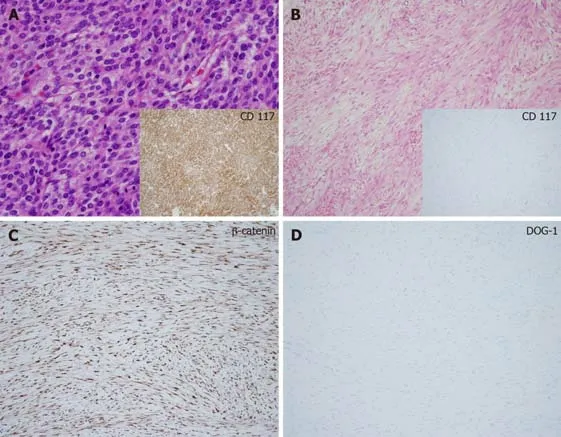
Figure2 Histological examination of intra-abdominal desmoid tumors in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors showed low or moderate cellularity with proliferative spindle cells in a fibrotic background and infiltrative growth patterns (hematoxylin and eosin,original magnification × 400).
Patient 1 achieved stable disease with imatinib (400 mg/d) for 6 mo,after which she was lost to follow-up.In patient 2-6,DT was treated with surgical resection and,in one patient treated with the escalated dose of imatinib (800 mg/d),the dose was subsequently reduced to 400 mg and all patients completed the planned adjuvant therapy with imatinib for GIST.Additional peritoneal changes occurred in three patients.One patient immediately underwent excisional biopsy since DT was strongly suggested because of similar radiological findings of the peritoneal mass to those of the first DT.However,two patients with multiple peritoneal seeding nodules were administered imatinib (400 mg/d) suspecting for recurrent GIST.In one of those patients,the treatment was maintained with equivocal change in the seeding nodules for 8 mo.However,the size of the tumor increased in one patient during one year of treatment with imatinib (400/800 mg/d) and surgical resection of focal progressive disease was performed.Recurrence of GIST was pathologically confirmed and the patient was treated with sunitinib (37.5 mg/d) and resumed imatinib for approximately one year each.The patient was lost to follow-up and expired one year later.In patient 7 and 8,there was no recurrence of DT after surgical resection for subsequent 4 and 1.3 years of follow-up.They continued palliative treatment with imatinib (800 mg/d and 400 mg/d,respectively) for minimal residual GIST without disease progression.
DISCUSSION
The possibility of secondary malignancy should always be considered in patients with GIST when a new single lesion develops.This is relevant regardless of the patients’clinical settings;whether their diseases are localized,or whether they are receiving imatinib for palliative or adjuvant treatment.Intra-abdominal DT has been considerably related to GIST[3]and should be included as a differential diagnosis in cases of occurrence of new single lesion in patients with GIST.The present case series provide clinical information on the preoperative approach in suspecting intraabdominal DT in patients with GIST,since excisional biopsy is necessary for the diagnosis of intra-abdominal DT.Moreover,the present case series described in detail the characteristic findings of DT on CT or18FDG-PET.The following clinical conditions and radiological findings contributed to the suspicion of intra-abdominal DTs:(1) Occurrence of a new single lesion in the peritoneum around the surgical sites of GIST resection;(2) uncontrolled lesion with imatinib while other lesions being controlled with imatinib;(3) well-defined ovoid shaped lesion with delayed or mild enhancement and absence of necrosis,hemorrhage,and cystic change on CT;and (4) a lesion showing mild or no hypermetabolic activity (low values of SUVmax) on18FDGPET,contrary to initially hyperactive lesion of GIST.
Table2 summarizes 27 previously reported cases of DT after GIST[3,5-9].The study population was predominantly male (one case showed no gender data),and the median age of the included patients was 58 years (range:34-74 years).Primary locations of GIST were the stomach (n= 20),small bowel (n= 11),and peritoneum (n= 2).All patients underwent surgical resection of GIST,and 19 patients were treated with imatinib following the occurrence of new lesions.The median time to diagnosis of DT was 2.5 years (range:0.5-15.9 years) after the surgical resection of GIST.The most common site of DT was the peritoneum around surgical sites,and the median size of DT was 6.5 cm (range:1.6-17 cm).None of the patients were diagnosed preoperatively.In the present case series,the patients were predominantly male(male-to-female ratio = 5:3),and their median age was 58.5 years (range:40-72 years).Consistent with previous cases,all patients had a history of surgical resection of GIST and the median time to diagnosis of DT was 1.8 years (range:0.9-7.1 years) after the surgical resection.The locations of primary GIST were the stomach (n= 4),small bowel (n= 3),and sigmoid (n= 1).All sites of DT were in the peritoneum around the surgical sites of GIST.
The confirmative diagnosis of DT should be based on histological examination with positive immunohistochemical staining for β-catenin[4].Mutation in the β-catenin gene is found in approximately 85% of sporadic DT cases,and its analysis is encouraged for the diagnosis of sporadic DT[4].However,considering that intra-abdominal DT mimics the recurrence or progression of GIST,it is difficult to perform excisional biopsy in every patient with GIST.Preoperative CT or18FDG-PET may be useful in suspecting intra-abdominal DT in patients with GIST.The following eight characteristics on CT suggest the diagnosis of DT:Extra-gastrointestinal location,ovoid or irregular contour,homogeneous enhancement,absence of intralesional necrosis,mild degree of enhancement,and low lesion/aorta CT attenuation ratio[10].Despite the limited data available for patients examined through18FDG-PET,those with intra-abdominal DT demonstrated relatively low SUV,below a SUVmaxof 4.7[11].In contrast,examinationviaCT showed that GISTs were hypervascular lesions in the arterial phase and washout lesions in the portal phase,showing heterogeneous enhancement with a low attenuation center due to necrosis,hemorrhage,and cystic change[10].The mean basal SUVmaxon18FDG-PET was relatively higher in GISTs (5.8) than in DTs[12].In the present case series,all intra-abdominal DTs had a well-defined ovoid shape,with delayed or mild enhancement on CT,and mild hypermetabolic activity with an SUVmaxof 2.0-3.5 on18FDG-PET.Although the initial impression was recurrence or progression of GIST,the radiological findings of the new single lesion strongly suggested to perform excisional biopsy for the diagnosis of intra-abdominal DT.Consequently,unnecessary treatment was avoided in these patients.The diagnosis of recurred DT in one patient was also facilitated because of the immediate excisional biopsy performed based on radiological findings.Furthermore,on18FDG-PET for the diagnosis of initial or recurrent GIST in three patients,all GISTs showed relatively higher hypermetabolic activity compared to one’s own intra-abdominal DTs.This finding suggests that changes in metabolic activity may assist in distinguishing intraabdominal DT from GIST.
With a new single lesion,recurrence or FP[13]may be initially considered in patients with localized or metastatic GIST.The guidelines[1,14,15]and recent studies[16-18]suggest the beneficial role of surgical resection of FP in metastatic GISTs,compared with either dose escalation of imatinib or switching to a second-line TKI.In addition,secondary malignancy,especially the intra-abdominal DT,should be distinguished from GIST when a new single lesion occurs.Excisional biopsy is also a curative treatment for resectable DT.Taken together,surgical resection for a new single lesion as FP disease in patients with GIST could be recommended for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Notably however,two patients in our case series had intra-abdominal DTs that remained stable for over one year with imatinib.In specific,the intra-abdominal DT progressed while on 400 mg/d of imatinib but stayed stable when dose was escalated to 800 mg/d.Previous phase II studies evaluating the efficacy of imatinib for unresectable or advanced DT reported objective response rate (ORR) ranging 6%-25%[19-21].The highest ORR of 25% among the cited studies was achieved in a study which every patient initiated 800 mg/d of imatinib[21].Although heterogeneity of tumor locations exists and the small number of patients does not permit to draw conclusions,the higher dose of imatinib (800 mg/d) was shown to be necessary for antitumor activity in patients with intra-abdominal DT.Nevertheless,both patients inour case series eventually underwent surgical resection for the intra-abdominal DTs as recommended by current standards.
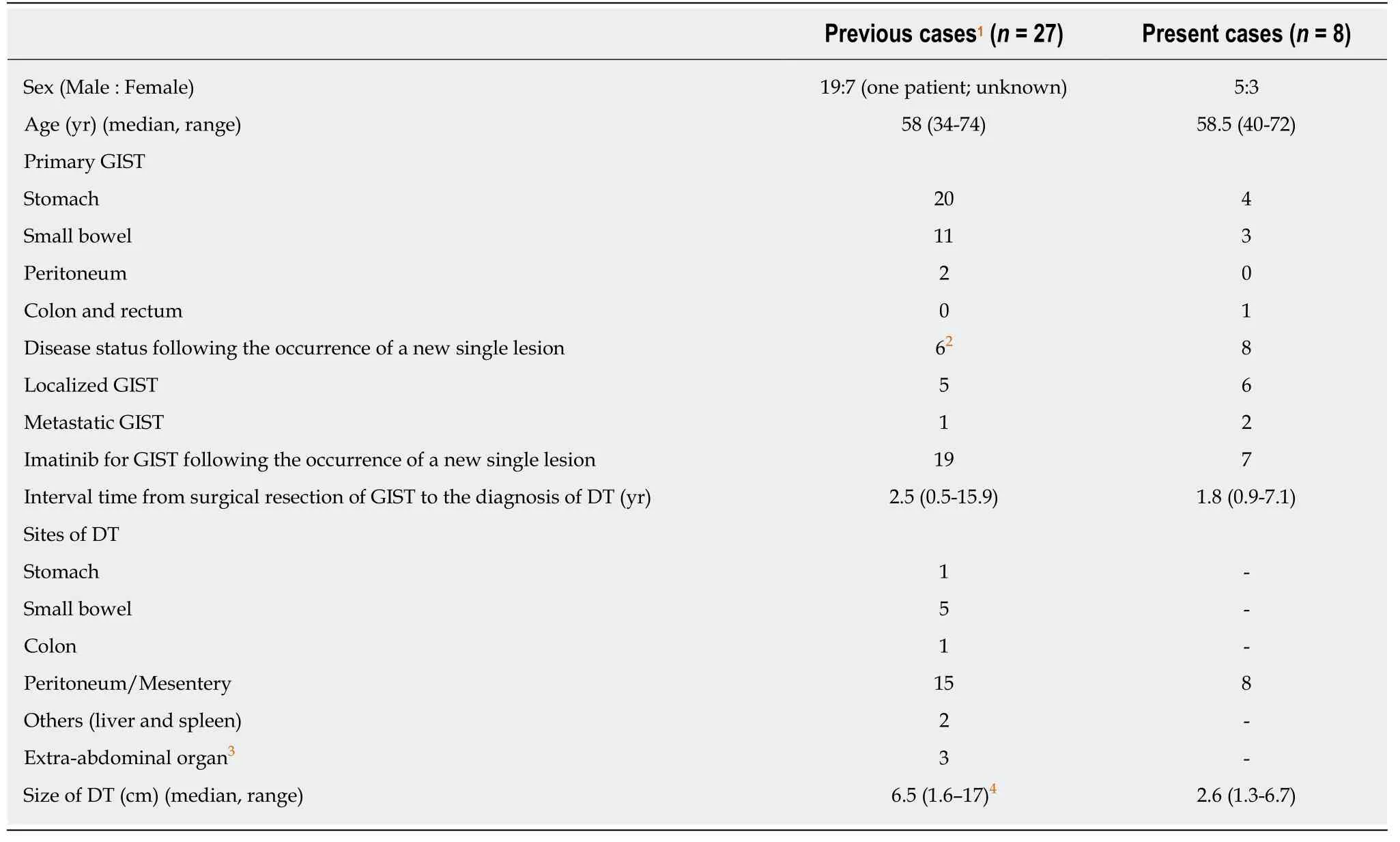
Table2 Comparison between previous cases in the literatures and patients included in the present case series
CONCLUSION
Secondary malignancy should be suspected in cases of occurrence of a new single lesion in patients with GIST.Considering the close relationship between intraabdominal DT and GIST,DT should be considered as an important differential diagnosis.Surgical resection is necessary for both the diagnosis and treatment of intra-abdominal DT to avoid unnecessary or inappropriate treatment.Clinical experiences and radiological findings using CT or18FDG-PET may assist in performing surgical resection.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2019年16期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2019年16期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Assessment of chronic radiation proctopathy and radiofrequency ablation treatment follow-up with optical coherence tomography angiography: A pilot study
- Dual energy computed tomography for detection of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- Comparison of decompression tubes with metallic stents for the management of right-sided malignant colonic obstruction
- Role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Immune response pattern varies with the natural history of chronic hepatitis B
- Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes the Warburg effect possibly by inducing pyruvate kinase M2 phosphorylation in liver precancerous lesions
