共生乳酸乳球菌加速黑腹果蠅發(fā)育
王曉陽,張樂宵,張 珂,李欣欣,蘇琬真,張笑添,劉 威,c*
(山西醫(yī)科大學汾陽學院a.臨床醫(yī)學系;b.醫(yī)學檢驗系;c.科技中心,中國山西汾陽032200)
All metazoan guts are populated with a vast microbial community that co-evolve with their hosts for millions of years in nature.Bacteria,ranging from beneficial mutualists to infectious pathogens,impact many aspects of host health and disease.Staubachet al[1]showed that the majority of intestinal bacteria contribute to host physiology,including metabolism,immunity,central nervous system and behavior.Most symbiotic bacteria currently in application are lactic acid bacteria(LAB)and Grampositive,acidophilic bacteria.They share a common metabolic property,that is,they consume hexoses to produce lactate as the major metabolic product from fermentation.LAB are widely spread in animals’gastrointestinal tract,on plant surfaces,and are used in food products,and they includeLactobacilli,Streptococci,BifidobacteriaandEnterococci.Gut LAB participate in food digestion and the synthesis of nutrients and metabolites that are crucial for host animal’s health.Many of these nutrients and metabolites derived from LAB are involved in the development,homeostasis and function of hosts[2,3].In addition,LAB provide a barrier against microbial pathogens,and generate antimicrobial substances that are found to be active to interfere with enteric bacterial pathogens in a series ofin vitroandin vivoassays[4].However,the underlying mechanisms of the beneficial impact on hosts still need to be elucidated,partially due to the diversity and complexity of consortia in mammalian guts[5].
Fruit fly,Drosophila melanogaster,is tightly linked to environmental and symbiotic microbes.Drosophilais saprophytic and mainly feeds on decaying fruits with an abundance of microbes(i.e.,bacteria,archaea,fungi,and viruses).Due to its amenability to genetic study,low complexity microbiota and the convenience of manipulating germfree(GF)flies,D.melanogasteremerges as an important model for host-microbe interactions,which can extend insights in animal-microbial symbiosis.Previous studies showed thatD.melanogastercommensals mainly containAcetobacter[6]andLactobacillus[7],but the composition of the natural bacterial microbiome is more diverse and complicated in wildcapturedD.melanogaster[5].The results of high throughput sequencing of bacteria showed that LAB are dominant commensals inDrosophila,and most of them belong to the genusLactobacillusand the family Enterococcaceae,and few to the generaLeuconostocandLactococcus[8].However,Lactococcuswas not isolated from the fly gut and its effects on host development remain largely unknown.
Using traditional bacterial culture and biomolecular technique,the diversity of intestinal symbiotic bacteria inD.melanogasterand the specific interactions of bacterial strains with their host were investigated.Here,Lactococcus lactis(L.lactis)isolated in wildD.melanogasterwith Hungate rolling tube technique was specially reported.The bacterial strain was found to colonize in the fly gut and accelerate the development ofDrosophilapupae formation by the growth rate.Moreover,the result de fined thatL.lactiswas required to activate the growth hormonal and insulin signaling pathways that are fundamental for fly development.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Fly stocks and maintaining
D.melanogasterOregon R(OR)was used as wild-type strain.Flies were cultured at 25℃,50%relative humidity and on a 12∶12-h(L∶D)cycle.The standard cornmeal-agar medium(1 L)for flies contained 1 350 mL ddH2O,13 g agar,0.83 g Ca-Cl2,31.6 g sucrose,63.2 g glucose,77.7 g cornmeal and 24 g yeast power[9].
1.2 Isolation and identification of bacteria
Bacterial strains were isolated from the guts of wild-captured flies using LAB-selective mediumMRS[2].Briefly,guts were dissected in PBS solution and washed in 70%(V/V)ethanol solution,and ground with pestles.The diluted mix was then plated in MRS medium and incubated overnight at 37℃.Single clones were selected for identification by sequencing 16S rRNA gene amplicons with PCR(PX2,Thermo,USA)upstream primer AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG and downstream primer GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT[10].The 16S rRNA gene sequences were submitted to GenBank and each obtained a bacterial accession number.The sequences of several related bacteria were downloaded from GenBank to generate a phylogenetic tree with MEGA 5.2 software.
1.3 In vitro fermentation assay
L.lactisstrains were inoculated in fermenting glass bottles containing 80 mL YCFA broth supplemented with glucose,starch,maltose and sucrose,and cultured at 37℃.TheODand pH values of bacterial suspension were assayed with spectrophotometer(UV-1800,Shimadzu,Japan)and acidometer(PB-10,Sartorius Stedim Biotech,Germany),respectively.
1.4 Generation of germ-free and gnotobiotic flies
Flies were collected within 4 days after eclosion and maintained on the grape juice plate with yeast paste overnight.Laid eggs within 8 h were collected and washed with tap water.
Eggs were disinfected 3 times with a 1∶30 dilution of Walch(Weilai,daily consumers’goods Ltd)for 1 min,followed by being disinfected once with HClO(Sigma,USA)of 1∶1 dilution for 1 min and twice with 70%ethyl alcohol for 1 min.The sterile eggs were mixed with PBS containing 0.01%(V/V)Triton X-100,and were transferred to autoclaved food vials sealed with plugs.The vials were placed in a clean incubator to cultivate GF flies.To verify the sterility of the eggs,they were ground and plated on the nutrition medium to observe bacterial clones after 48 h.OneODunit of bacteria were washed twice with PBS solution at the speed of 4 000 r/min and added to vials with GF eggs.Larvae ingested the fly food and acquired specific bacteria to generate gnotobiotic model.
1.5 Colonization of L.lactis in flies
Gnotobiotic flies withL.lactiswere generated and cultured with standard foods containing 4%(W/W)yeast powder.Ten individuals(larvae,pupae or adults)were collected and disinfected twice with 70%alcohol and homogenized in 0.2 mL of sterile PBS.The number of bacteria was quantified by plating the diluted homogenates from 10 individuals on MRS agar medium.The number of bacteria in fly medium was calculated by dissolving 100 mg food into 1 mL of sterile PBS buffer.
1.6 Growth and development of the flies
Conventional reared(CR),GF and gnotobiotic eggs were inoculated into fly food with 0.25%,0.5%and 1%yeast,respectively.The numbers of forming pupae and emerging adults were counted.Developmental timing was calculated with the formula:T=(T1×N1+T2×N2+…+Tm×Nm)/(N1+N2+…+Nm).In this formula,Tis the developmental timing,Tmmeans the days to form pupa and adults after egg laying andNmmeans the number of pupa and adults on themthday.
1.7 Growth rate assay
Eggs from CR,GF and gnotobiotic flies were inoculated into plates with both poor(0.5%yeast)and rich diets(2%yeast).Larvae(n>10)were collected from each group(CR,GF and gnotobiotic flies with 0.5%or 2%yeast)and frozen in liquid nitrogen each day until pupae formation.Larvae were imaged with microscope and the body area of each larva was calculated using ImageJ.
1.8 Immunofluorescent staining of fly guts
The proliferation of intestinal stem cells was assessed with immunofluorescent staining.The CR,GF andL.lactis-gnotobiotic flies were fed on concentration medium with 5.88%yeast.Adults within 4 days post-eclosion were starved for 10 h and followed with 1%(V/V)H2O2for 4 h.Ten guts were dissected in PBS buffer,and fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature.Guts were washed with 0.3%PBST(PBS with 0.3%Triton X-100)and blocked with blocking solution(0.3%PBST with 0.2%goat serum and 0.1%fetal calf serum)for 30 min at room temperature.After that,the guts were incubated in rabbit phosphohistone H3(PH3)antibody(the marker of mitosis,diluted to 1∶1 000 with 0.3%PBST)at 4℃ overnight.Samples were rinsed 3 times in 0.3%PBST for 15 min each,and then incubated with goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies(of a 1∶1 000 dilution with 0.3%PBST)and DAPI(of a 1∶1 000 dilution with 0.3%PBST)for 3 h at room temperature.Finally,the guts were washed and mounted for the observation with a fluorescence microscope(DM4000,Leica,Germany).
1.9 Sugar measurement
To assess glucose concentration,ten 3rdinstar stage larvae were collected and then 1 μL hemolymph from them was mixed with 150 μL of Glucose(HK)Assay Reagent(Sigma,USA).After incubation at 37℃for 16 h,the amount of total hemolymph glucose was measured at 340 nm according to the manufacturer’s instructions(EON,BioTek,USA).For each experiment,standard curves of standard glucose concentrations were generated.
1.10 Real-time quantitative PCR analysis
CR,GF andL.lactis-gnotobiotic flies were fed with the standard medium with 0.5%yeast,and the larvae and pupae were selected from the 3th day after egg deposition to the 3th day after pupal formation.The fly samples were homogenized,and total RNA was extracted with Trizol reagent(Invitrogen,USA).Up to 2 mg total RNAs were used as templates of reverse transcription with the oligo-dT primer for the real-time quantitative PCR(ABI 7500,BioRad,USA).The primer sets forPTTH,InRandrp49 were showed in Table 1.The ΔCt method was employed to analyze data withrp49 as the reference gene.The relative expression value was calculated with formula:△Ct=Ct(target gene)-Ct(reference gene),the relative=2-△△Ct.
1.11 Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean±SEM().Significance was determined by analysis of variance(ANOVA)or standardttests with GraphPad Prism software program.
2 Results
2.1 Isolation and identification of D.melanogaster-associated Lactococcus
One LAB strain was isolated from the intestine ofD.melanogasteradults using MRS medium.This strain was a Gram-positive,spherical bacterium.To investigate its phylogeny and taxonomy,the genomic DNA was extracted and the nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene was specifically amplified with universal primer sets targeting this gene.The obtained 16S rRNA sequence of the strain was 1 463 bp.Its sequence was submitted to GenBank and obtained a bacterial accession number(MF281053).This sequence displayed>99%similarity with a published sequence ofLactococcus lactisin GenBank,so this strain was nominated asLactococcus lactisFY.As shown in Fig.1,the closest relatives were selected to construct a phylogenetic tree with MEGA 5.2[9].The strain was phylogenetically placed within the clade ofL.lactis.According to the gene sequence alignments,the closest relationship isLactococcus lactisstrain NBRC 100933(NR 113960.1)with 99.4%homology(1 442/1 450 bp).Moreover,L.lactiswas relatively close to other LAB,such asLactobacillus brevisandLeuconostoc,but far fromAcetobacteriaandEnterobacter.This is indicative of the diversity and complexity of fly commensals.
2.2 In vitro metabolic traits of L.lactis
To explore the metabolic traits ofL.lactis,we firstly assessed anin vitrofermentation ofL.lactisin YCFA medium replenished with different carbohydrate sources.As shown in Fig.2A,the growth of strain FY increased in media with glucose,maltose and sucrose,but the cells were rare in starch medium.The results indicated thatL.lactismetabolized simple sugars rather than polymerized carbohydrate.Most LAB reduced the pH value by converting simple sugars to lactate during fermentation.The pH value approximately declined to 4.5 in the medium with maltose,glucose or sucrose at the end of fermentation,but changed little in the medium with starch(Fig.2B).Since most pathogens ofD.melanogasterare sensitive to low pH,this result implied thatL.lactismight be one of the probiotics and commensals inD.melanogaster.

Table 1 Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR analysis
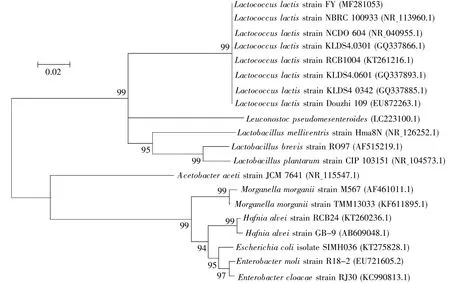
Fig.1 The phylogenetic tree of L.lactis and its homologues
2.3 Colonization of L.lactis
Next,we assayed the commensalism ofL.lactisandD.melanogasterwith colonization tests.The number ofL.lactisthat colonized in flies was more than 104CFU during larval and pupal stages,and increased to 106CFU in the newly emerged adults(Fig.2C),indicating thatL.lactiswas efficient to colonizeD.melanogaster.To further demonstrate thatL.lactisis a commensal bacterium ofD.melanogaster,we tested the quantity of the bacteria in fly food.It was observed that strain FY was maintained in fly medium(Fig.2D).L.lactisload increased during larval development,and ultimately reached a relatively stable density of 109CFU/g at the late larval stage.Altogether,these results suggested thatL.lactiswas tightly linked withD.melanogasterand acted as one of the symbiotic bacteria ofD.melanogaster.
2.4 L.lactis accelerated the developmental timing of D.melanogaster
In the case ofL.lactisfunctioning as a commensal,we tested whether the bacterium could sustain the development ofD.melanogasteron cornmeal-sucrose food with dosage-dependent yeast.To understand the potential contributions of the microbe to its host systemic growth,we generated germ-free(GF)and gnotobiotic flies by removing microbes on the surface of eggs with chemicals as described[9].As shown in Fig.3A,the developmental timing of pupal formation decreased in a yeast dosage-dependent manner,suggesting that yeast provided nutrition to sustain the development of fly.In CR flies,the developmental times of CR eggs into a pupa un der poor-nutrition(0.25%yeast)and rich-nutrition(1%yeast)conditions were 6 d and 5 d,respectively(Fig.3A).However,the developmental times of GF eggs into pupa under the corresponding conditionswere 19 d and 11 d,respectively.Compared to CR,the developmental timing of GF pupa was significantly prolonged by 6 d(P<0.001)in rich-medium and 13 d in poor-medium(P<0.001).The discrepancy of developmental timing was less in yeast dosagedependent manner(Fig.3A).Compared to CR fly,the timing ofL.lactis-associated flies was delayed by 4 d in poor-medium and 3 d in rich-medium.Our data suggested thatD.melanogaster-associated commensals were integral to accelerate the development of hosts,particularly under poor nutrition condition.The addition ofL.lactissignificantly ameliorated the developmental timing of GF fly under poor and rich nutrition conditions(Fig.3A and 3B,bothP<0.001),indicating thatL.lactisaccelerated the development of hosts,but that it did not meet all the needs of nutrition in theD.melanogaster.The similar role ofL.lactisin stimulating adult eclosion was observed(Fig.3B).Taken together,our results demonstrated thatL.lactiswas important to accelerate the development inD.melanogaster.
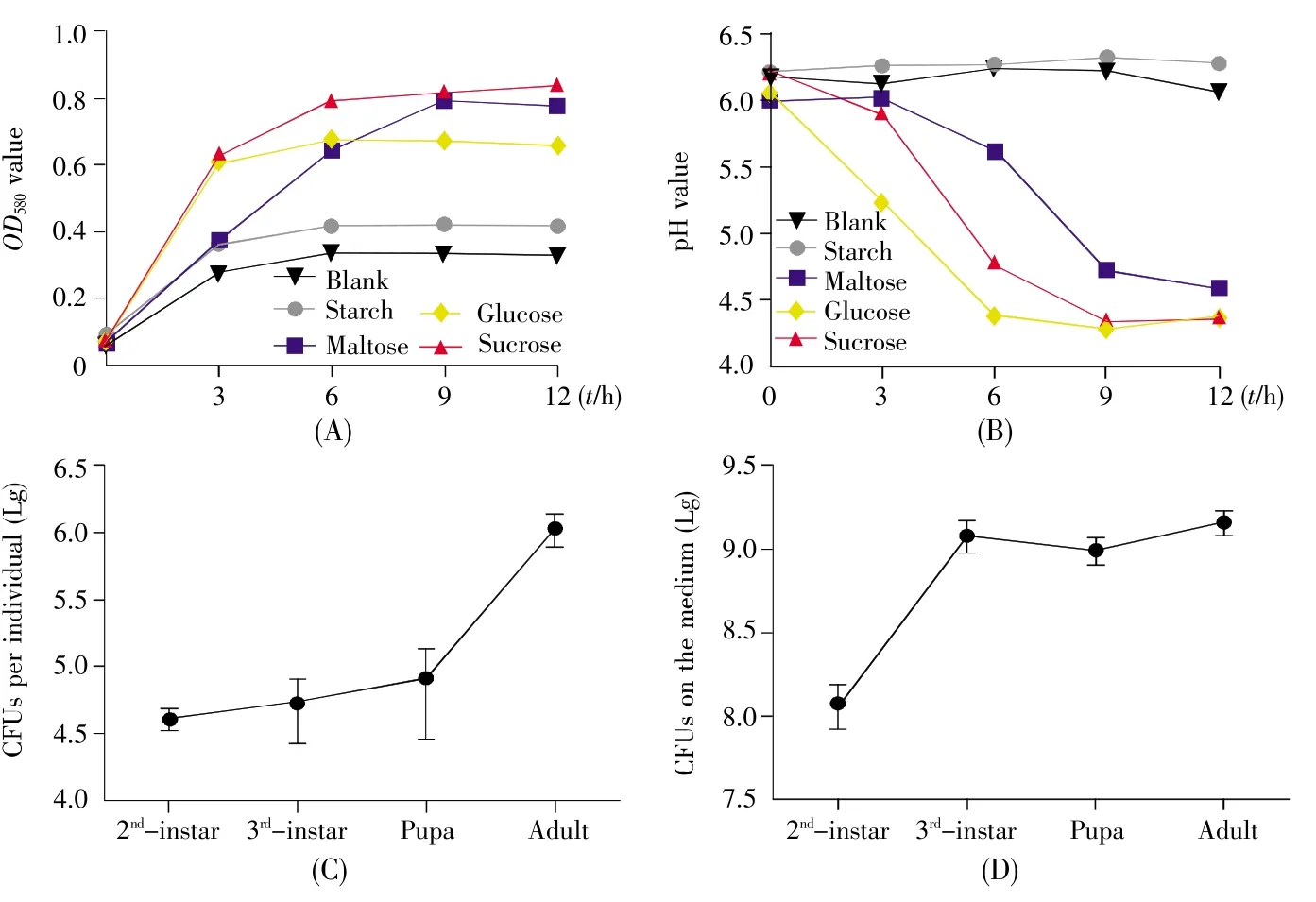
Fig.2 In vitro fermentation assay and colonization of L.lactis in the gut of D.melanogaster and the media
2.5 L.lactis promoted the growth rate
InD.melanogaster,the weight of GF adults didn’t significantly differ from CR individuals[11].However,L.lactisremarkably shortened the developmental timing ofD.melanogaster(Fig.3),indicating thatL.lactiscould accelerate the growth rate ofD.melanogaster.To quantify growth rate,we compared the change of the body surface area ofD.melanogasterfrom 1stinstar larva to pupa in poor and rich cornmeal-yeast diets.According to the analysis of linear regression,the slope of regression line showed 1.5-fold increase in CR flies compared with GF ones in rich diet(2%yeast,Fig.4A),and a 2.0-fold increase in poor diet(0.5%yeast,Fig.4B),indicating that the intestinal symbiotic bacterium was sufficient to accelerate the growth rate.Moreover,the slope of regression line was a 1.5-fold increase inL.lactis-associatedD.melanogastercompared with GF larvae raised on the poor diet,but was comparable on the rich diet.This result suggested thatL.lactisincreased the growth rate under the poor nutrition condition.Combined with the result of the developmental timing,our data showed thatL.lactispromoted the developmental timing of hosts by accelerating the growth rate during larvae.
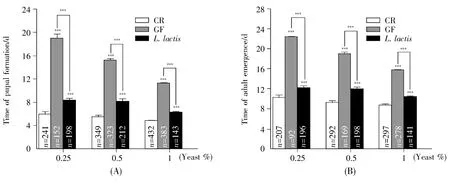
Fig.3 L.lactis promoted the timing of fly development
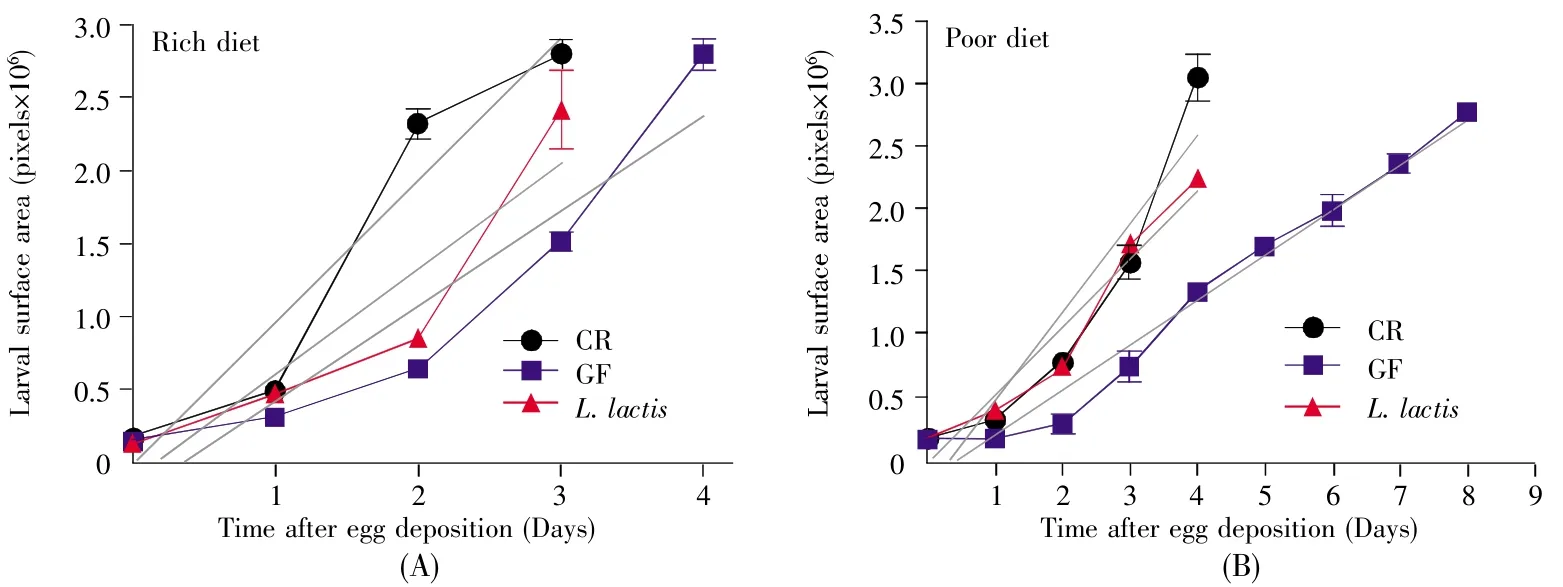
Fig.4 L.lactis association promoted the larval growth rate
2.6 L.lactis impacted the intestinal cell proliferation
A previous study showed that oral infection withEcc15 stimulated epithelium turnover in the intestine and strongly activated the transcription of genes known to respond to oxidative stress[12].We monitored epithelium renewal inD.melanogasterwith 1%H2O2,and the dividing cells were labeled using an anti-phosphohistone H3(anti-PH3)antibody.The number of metaphase cells in the midgut of GF flies was less than that of CR siblings(Fig.5A,5B and 5D,CR:2.1,GF:0.3,P<0.05),suggesting thatD.melanogaster-associated commensals accelerated intestinal cell proliferation during oxidative stress.Similarly,the mitotic cells inL.lactis-associated fly guts were more than those of GF ones(Fig.5B,5C and 5D,L.lactis:1.8,P<0.05),indicating thatL.lactisplayed a role in stimulating intestinal cell proliferation in case of damage.
2.7 L.lactis influenced the expression of PTTH
Prothoracicotropic hormone(PTTH)has been found to have an essential role in regulating the production and release of ecdysone,a steroid hormone that accelerates molting and metamorphosis[13].In fruit flies,PTTH expression was regulated by developmental time,whose peak occurred between terminal 3rdinstar and early pupal stage.Thus,PTTH has become a molecular target to evaluateD.melanogasterdevelopmental status.As shown in Fig.6A,the peak expression of PTTH appeared at 7 d in CR flies,whereas it was delayed at 10 d in GF flies,indicating that bacterial consortia triggered the properemergence of hormone.This result was consistent with the earlier timing of development in CR flies other than GR siblings.Remarkably,the level of PTTH expression in the CR flies was significantly high,indicating thatD.melanogaster-associated bacteria accelerated the larval-to-pupal transition by cumulating the amount of PTTH.Moreover,the peak expression of PTTH appeared at 8 d inL.lactis-associatedD.melanogaster,and its level was higher than that in the GF fly but comparable with that in the CR one,suggesting commensalL.lactiswas sufficient to trigger the expression of PTTH.

Fig.5 L.lactis sustained the proliferation of guts upon oxidative damage
2.8 L.lactis activated insulin signaling pathway
Earlier studies showed that commensal bacteria promoted the development ofD.melanogasterby activating insulin signal pathway[14,15].To testify the role ofL.lactisin insulin signal pathway,we mea sured the transcriptional rate ofInR,a negative regulator of insulin signaling,with real-time quantitative PCR.The level ofInRexpression was apparently low in CR flies during larval and early pupal stages(Fig.6B),reflecting high activity of insulin signaling pathway.In contrast,the level ofInRexpression was high at early larval stage of GF fly,and substantially decreased after late third larval stage(at 11 d AED),indicating that the activity of insulin signaling pathway was delayed.These results suggested that symbiotic bacteria activated the insulin pathway at early stage.Similarly,the expression ofInRinL.lactis-associatedD.melanogasterwas lower than that in the corresponding GF one,but a little higher than that in CR one,indicating thatL.lactiscould increase the activity of insulin signaling pathway.InD.melanogaster,the insulin signaling is well-known to decrease the circulating glucose in hemolymph.To verify this,the hemolymph glucose was assayed.Consistently,the serum glucose of the CR fly was lower than that in the GF fly(Fig.6C,CR:3.8 mg/mL,GF:5.9 mg/mL,P<0.001),suggesting thatD.melanogaster-associated commensals were integral to regulate the circulating glucose.Similarly,the concentration of glucose ofL.lactis-associated fly was lower compared to that in GF(L.lactis:4.3 mg/mL,P<0.05),but did not differ from that in CR.Taken together,the results suggested thatL.lactisactivated the insulin signaling pathway inD.melanogaster.
3 Discussion
All metazoans,including human,are intricately linked to symbiotic microbes that influence host health and disease.The present results showed thatL.lactiswas isolated and identified from the fly gut(Fig.1).Commensal bacteria usually develop specific mechanisms to tolerate and evade the host immune response and,consequently,can colonize the gut of hosts[16].Our data showed thatL.lactisefficiently colonized fly guts,suggesting thatL.lactisacted as one commensal ofD.melanogasterbacterial community(Fig.2).The composition and quantity of the intesti-nal bacterial community dynamically fluctuate in response to diet,environmental habitats,and host physical activities[17].L.lactiswas first isolated from plants and has been applied in dairy product fermentation[18].Hence,it is conceivable thatL.lactisconsumes and ferments nutrition in ripening fruits for their proliferation and could synthesize and release more nutrients available forD.melanogaster,thereby creating a new niche for survival and reproduction of hosts in ecology.Fruit flies are a kind of metatrophic insect,and rely mainly on rotten fruits in a great variety of habitats.During ingestion,D.melanogasteracquires polymicrobial mixtures of bacteria as well as plant food,which frequently replenish the intestinal bacterial community[17].Moreover,L.lactiswould become more active and multiply after being ingested into host guts.In turn,D.melanogasterserves as a vector and promotes dispersal of the microbial cells into environment[1].Therefore,L.lactisandD.melanogasterform a beneficial relationship with each other.
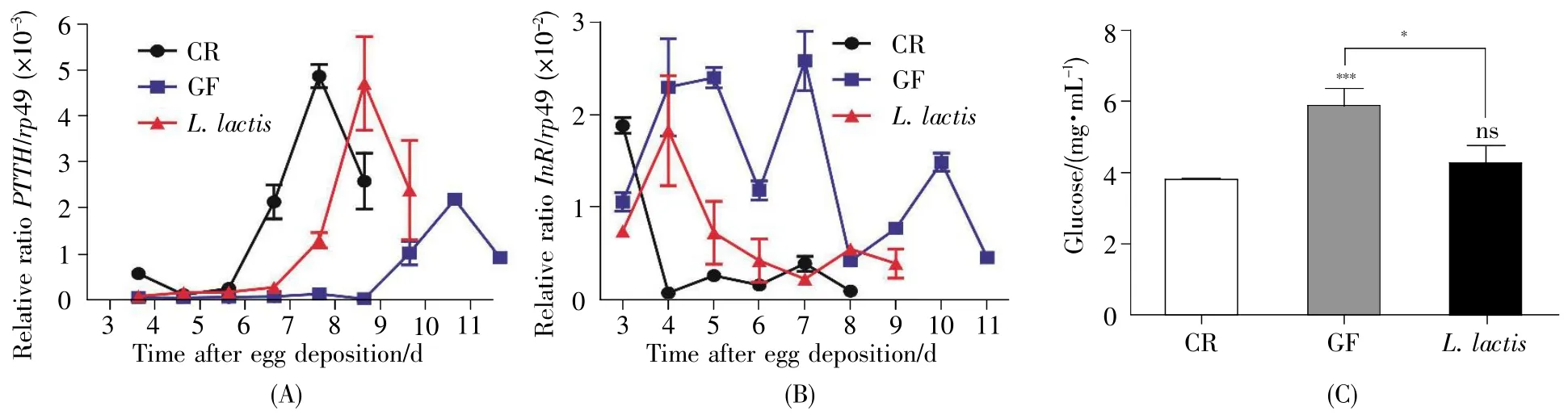
Fig.6 L.lactis promoted the expression of hormonal and insulin signals
Our study specifically highlighted thatL.lactisfacilitated the development timing ofD.melanogasterthrough the growth rate.A previous study has showed thatLactobacillis plantarum(L.plantarum)enhanced systemic growth upon nutrient scarcity by promoting larval growth rate and reducing the dura tion of the growth period[2].L.lactisdisplayed the similar effect onD.melanogastersystemic growth(Fig.3 and Fig.4),and this further supported the fact thatL.lactisfunctioned as one commensal ofD.melano-gasterbacterial community.It has been shown that microbes are necessary for the growth and development ofD.melanogaster[19].Resident bacteria collaborate to digest complex substrates,synthesize nutrition,and even stimulate the excretion of digestive enzymes of hosts.Thus,diet containing commensal bacteria could be more beneficial for developingD.melanogasterlarvae than sterile one.The replenishment ofL.lactisevidently ameliorated the developmental timing(Fig.3)and the growth rate of GF flies(Fig.4).However,it is notable that the role ofL.lactisin stimulatingD.melanogasterdevelopment did not recapitulate commensal microbiota,because the timing ofL.lactis-associated flies was still delayed compared to that of CR flies.This result suggested thatL.lactisshould need to cooperate with other commensals to promote the development ofD.melanogaster.
At the molecular level,L.lactistriggered the expression of PTTH during metamorphosis.PTTH is required to regulate the production and release of ecdysone,a steroid hormone that stimulates molting,and activates insulin signaling pathway,accounting for the stimulation ofD.melanogasterdevelopment and systemic growth.The commensal bacterium,Acetobacter pomorum,has been demonstrated to accelerate the host development by modulating insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling(IIS)inD.melanogaster[7].Our study showed thatL.lactisdecreased the expression level ofInRgene and reduced the concentration of glucose(Fig.6B and 6C),suggesting thatL.lactisactivated insulin signal pathway inD.melanogaster.It is established that insulin signaling pathway takes an important position in nutrient uptake,gene transcription and expression and cell proliferation,thus supporting the development and systemic growth.Hence,the results suggested thatL.lactisactivated the insulin signaling that promoted the development inD.melanogaster.
As an independent strain and a different species fromL.plantarum,L.lactiscould better colonize inD.melanogasterbut had a poorer effect on the growth rate and development.Moreover,L.plantarumandL.lactishad distant phylogenetic relationships in the phylogenetic tree,which implied thatL.lactishad an independent phylogenetic status.
Microbiota could accelerate the development of host through nutrition,including protein enrichment or vitamin biosynthesis.Alternatively,microbiota could promote the expression of peptidase in host guts and enhance protein digestion[20].The underlying mechanism thatL.lactiscan stimulate the development inD.melanogasterneeds to be explored in future.
In conclusion,L.lactisacted as one commensal of the bacterial community inD.melanogasterand promoted the growth of flies.D.melanogasterprovides an excellent model to decipher the intricate relationship between the microbes and hosts,and this will lead to a better understanding of their ecological relationships.

