Comparative Research on Facultative Anaerobic Cellulose Decomposing Bacteria Screened from Soil and Rumen Content and Diet of Dairy Cow
Li Yan-fang, Wang Lei, Liang Zi-chao, Zhang Mei-mei, Wang Jing-jing, and Liu Da-sen,
1 College of Animal Sciences and Technology, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
2 College of Science, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
Introduction
Cellulose as the most abundant, wasteless resource in the biosphere has caught the attention of researchers(Ulrich and Wirth, 1999).Cellulose is a polysaccharide constituted of D-glucose linked byβ-1, 4-glycosidic bonds and a helpful raw material for producing important chemicals (Ragauskaset al., 2006; Hahn-H?egerdalet al., 2006).Enzymatic hydrolysis is difficult because of insolubility and heterogeneity of cellulose.However, microorganisms could hydrolyse it with the help of a multi-enzyme system (Schwarz,2001).The cellulases consist of endoglucanases and cellobiohydrolases enzymes, which function together in degrading microbes (Dashtbanet al., 2009).Consequently, there is an urgent need for the studies about cellulolytic microorganisms as well as their degradation abilities in cellulose were carried out.Some celluloses are digested by protozoa, but it is indicated that degrading activity of protozoa is lower than that of bacteria (Cheng and Costerton, 1980),which are able to degrade cellulose by the action of extracellular cellulase.For years, cellulase-producing bacteria have been isolated from multitude of sources such as the feces of ruminants, soils and organic matter,agricultural residues and forestry (Lyndet al., 1991).
In the soil ecosystem, the cellulolytic bacteria play important roles in the decomposition and transformation of organic matter, and they also provide a significant carbon source to the microbial community in the soil.In the rumen, cellulolytic microorganisms are important to the rumen ecosystem for their role in providing volatile fatty acids (VFA) by fermenting plant polysaccharides, and VFA is the primary energy source for the ruminant animal (Mcdonaldet al.,2012).The reports of the cellulose decomposition bacteria isolated from the diary cow diets are rarely.
Majority of isolated cellulolytic bacteria belong to the aerobic bacteria (Lyndet al., 2002), because culturing the anaerobic bacteria needs specialized techniques and methods.Wenzelet al.(2002) isolated the facultative anaerobic cellulolytic bacteria from the gut of the termiteZootermopsis angusticollis.Cheng and Costerton (1980) indicated that extensive important populations of bacteria have been found not only in rumen fluid, but also in feed particles.Therefore, the fact that the cellulose-decomposing bacteria isolated from rumen contents might be associated with the cellulose-decomposing bacteria adhered on ration fed by animals was speculated in our laboratory.
The comparison researches about the facultative anaerobic cellulose-decomposing bacteria from different sources and their abilities of degrading cellulose are rare.Hence, the objective of this study was to isolate cellulose-decomposing bacteria from the rumen content of dairy cow, the soil around the barn and the ration of cow, respectively, and then evaluated what the relationship was among them by 16SrDNA gene sequences molecular biology methods,meanwhile, compared with their cellulase activities.The test would better qualify facultative anaerobic cellulolytic bacteria and provide basic data for using the bacteria in the future.
Materials and Methods
Animal care
The experimental procedure was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in Northeast Agricultural University.
Samples for separating bacteria
Three fistulaed dairy cows (three and a half years old)in dry period were provided a total mixed ration (TMR)with concentrate: forage at a 45 : 55 ratio to fulfill their nutrient requirement for maintenance.Compositions of the ration (kg · kg-1) were: 0.50 L.chinensis, 0.33 ground corn, 0.05 soybean cake, 0.05 rapeseed dregs,0.04 cottonseed meal, and 0.03 vitamins and minerals.The cows were fed twice daily at 6:00 a.m.and 6:00 p.m.,and accessed to fresh waterad libitum.Whole rumen contents withdrawn from each of the three cows prior to the first meal in the morning were mixed equally,and then were poured into a pre-warmed thermos which filled with carbon dioxide.Subsequently,1 mL rumen fluid and 1 g residue were put into two sterilized tubes, into which were added 9 mL sterile water and fully shaken for preparation of bacterial suspension.
About 1 kg soil was randomly collected from five sites, which was near the dairy barn, but not polluted by the cow waste, and then sieved to remove vegetation waste.One g of mixed soil sample was dissolved in 100 mL sterile water, then cultured 2 h at 37℃ on an orbital shaker at 180 r · min-1(Ulrich and Wirth, 1999).One g of diet was also suspended in 100 mL distilled water and cultured shakily 2 h at 37℃ at 180 r · min-1.
Bacteria isolation and screening
The bacteria suspension of rumen fluid and residues,soil, and dairy diet were consecutively diluted into a serial solutions from 10-2to 10-6, then 100 μL of each of the dilutions was spread on the nutrient agar plate medium.Bacterial colonies capable of utilizing cellulose as sole carbon source were selected on sodium CMC agar media (composing of KH2PO40.5 g, MgSO40.25 g, gelatin 2 g, sodium car boxy methyl cellulose 20 g, and agar 12 g in 1 L of distilled water).
Morphological characteristic of bacterial colonies
Phenotypic characteristics of the isolated bacterial colonies were determined after cultured 48 h on the sodium CMC plate medium based on the microbial application laboratory manual in general microbiology 8th ed (Benson, 2005).Macroscopic and microscopic analyses were included, morphological feature about bacteria included color, surface, shape, border, eleva-tion, Gram's features and spore.
Cellulose degradation capability of bacteria
Bacteria were cultured for 48 h at 39℃ on Congo-Red agar medium.The diameter size of clear zones around strains indicated the capability of degrading cellulose of bacteria.In this paper, bacteria with more than 10 cm diameter of clear zone were described as stronger capability for degradation.
Determination of cellulase activity of bacteria
It is widely accepted that complete enzymatic degradation of cellulose need synergistic action of system of three major types of enzymes, which consist of endoglucanases (EG), exoglucanases (ExG) andβ-glucosidases (βG) (Dashtbanet al., 2010).The measurements of the individual enzymes and the total cellulase activities were described as the followings:
Filter paper assay (FPase activity): the total cellulase activities
Filter paper assay (FPAase) is the key method for analysis of the total cellulase activity based on Mandelset al(1976).Filter paper activity (FPase) was defined as the micromole of glucose from generated filter per minute.
Carboxymethyl cellulase assay (CMCase)
Endoglucanase (EG) activity was measured using CMC as substrate according to Ghose (1987).One unit(IU) of EG was defined as the amount of enzyme that liberated 1 μmol of glucose per minute under assay conditions (Mandelset al., 1976).
β-glucosidases assay
The activity ofβ-glucosidases was measured at pH 4.8 using 1 mmol · L-1p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside as substrate described previously by Kubicek (1982).One unit (IU) ofβ-glucosidase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that liberated 1 μmol of reducing sugar as glucose equivalents per minute (Chandraet al., 2009).
16SrDNA gene sequencing analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from the strains that showed stronger capability of cellulose decomposition following the methods of Johnson (1994).16SrDNA genes were amplified using universal primer of bacteria 27f (5-3'): AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG AACGAACGCT and 1 492f (5-3'): TACGGCTACC TTGTTACGACTTCACCCC (Weisburget al., 1991)by polymerase chain reaction (PCR).Amplification was conducted in a total reaction volume of 50 μL,containing 2 μL primers, 3 μL dNTPs, 25 μL PolymeraseTaqand 20 μL nuclease free water.
16SrDNA gene sequences were compared with database at GeneBank using Blast-N search program in the website of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).In light of similar results, the generic affiliation and homology of the bacterial were con firmed.The accession numbers of strains were also applied for by Bankit.
Data collection and analysis
All the data were analyzed by one way ANOVA using MIXED procedure of SAS 9.2.
The model used for cellulase activity was:Yij=μ+Ti+eij, where,Yijwas an observation of the dependent variableij;μwas the population mean for the variable;Tiwas effect of the bacterial strains ( fixed effect); andeijwas random error that associated with the observedij.
In all the cases, Duncan test was carried out to determine the significant difference within the variables with significance declaredp<0.05.The average mean of results of the three replicates was represented with standard deviations.
Results
Morphological characteristics of cellulose decomposing bacteria
For 29 strains of bacteria, both the gram-negative(GN) bacteria with coccus cell morphology and grampositive (GP) bacteria with bacilli cell morphology were found.By observation, many of GN bacteria were opaque yellowish-white colony with wet, convex and rounded characteristic.In addition, majority of GP bacteria were white colony with dry, convex and rounded profiles.Of the 29 strains, only four strains were GN bacteria with no spore, three of the four strains were isolated from rumen fluid, and the rest were from soil.Other 25 strains were GP bacteria with spore.The growth status of the strains in aerobic condition was not different compared with anaerobic condition, therefore, these strains were considered as facultative anaerobic bacteria.The diameters of clear zone of cellulose decomposing microorganisms were between 7-15 mm, and L5 was the largest, reaching to 15 mm.Table 1 showed the diameters of clear zone no less than 10 mm.
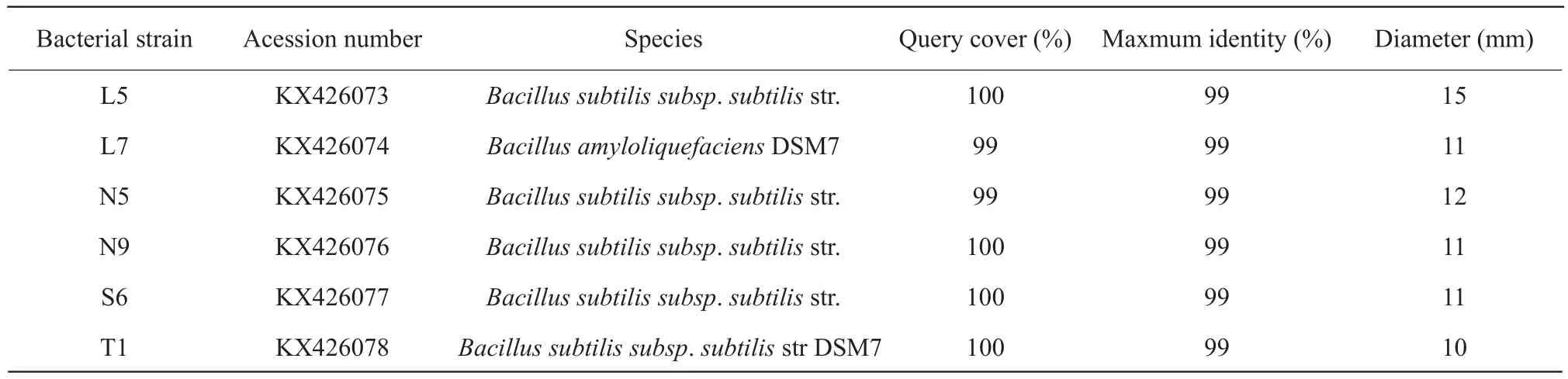
Table 1 BLAST-N results of 16SrDNA gene of isolates which diameter of clear circles ≥10 mm and their diameters of clear circles dyed by Congo red
Molecular identification of cellulolytic bacteria
Generally, bacteria with high level of 16SrDNA sequence similar to the genera at NCBI GenBank were thought to belong to the same species of genera.In the test, the sequences similar with databases sequences reached to more than 94% for most isolates.It was observed that only L1 strain pertained toAcinetobacter, all other isolates wereBacillusgenus(Table 2).For the isolates from rumen fluid, L3 belonged toBacillus sonorensis, L6 pertained toBacillus subtilis, while L8 belonged toBacillus amyloliquefaciens; for the isolates from rumen residue,many of them belonged toBacillus amyloliquefaciens,except N2, N5 and N7 belonged toBacillus subtilis;for the isolates from rations, all of them belonged toBacillus subtilisapart from S2 wasBacillus amyloliquefacien; for the isolates from soil, most of them pertained toBacillusn amyloliquefacien, besides T5 belonged toBacillus subtilis.
BLAST_N results of 16SrDNA gene of isolates are presented in Tables 1 and 2.The sequences of all the isolates had been reserved in GeneBank under the consecutive accession numbers of the bacterial strains which the clear zone diameter more than 10 mm were KX426073 to KX426078.And others were KX588160 to KX588172 except for the isolates which had lower Query cover compared with the database.
Cellulase activity of bacteria
The cellulase production of different strains about the total cellulase, endoglucanases andβ-glucosidases were presented in Table 3.Filter paper activity (FPase)and CMCase activity which represented the total cellulase and endoglucanases activity, respectively,were the highest in L5, moreover, FPase activity had no significantly different in L7, N5 and L5 and they produced 57% more glucose than T1, which implied that CMCase and FPase activities were the highest in the strains isolated from rumen fluid and the lowest isolated from soil.The differences ofβ-glucosidases activity among various strains were significant(p<0.05), with the highest activity in T1 and the lowest in N5.Additional,β-glucosidases activity was the highest in strains isolated from soil, and the lowest isolated from rumen residues.CMCase activities were similar among L7, N5 and N9, but higher than those of S6 and T1.The data is shown in Table 3.
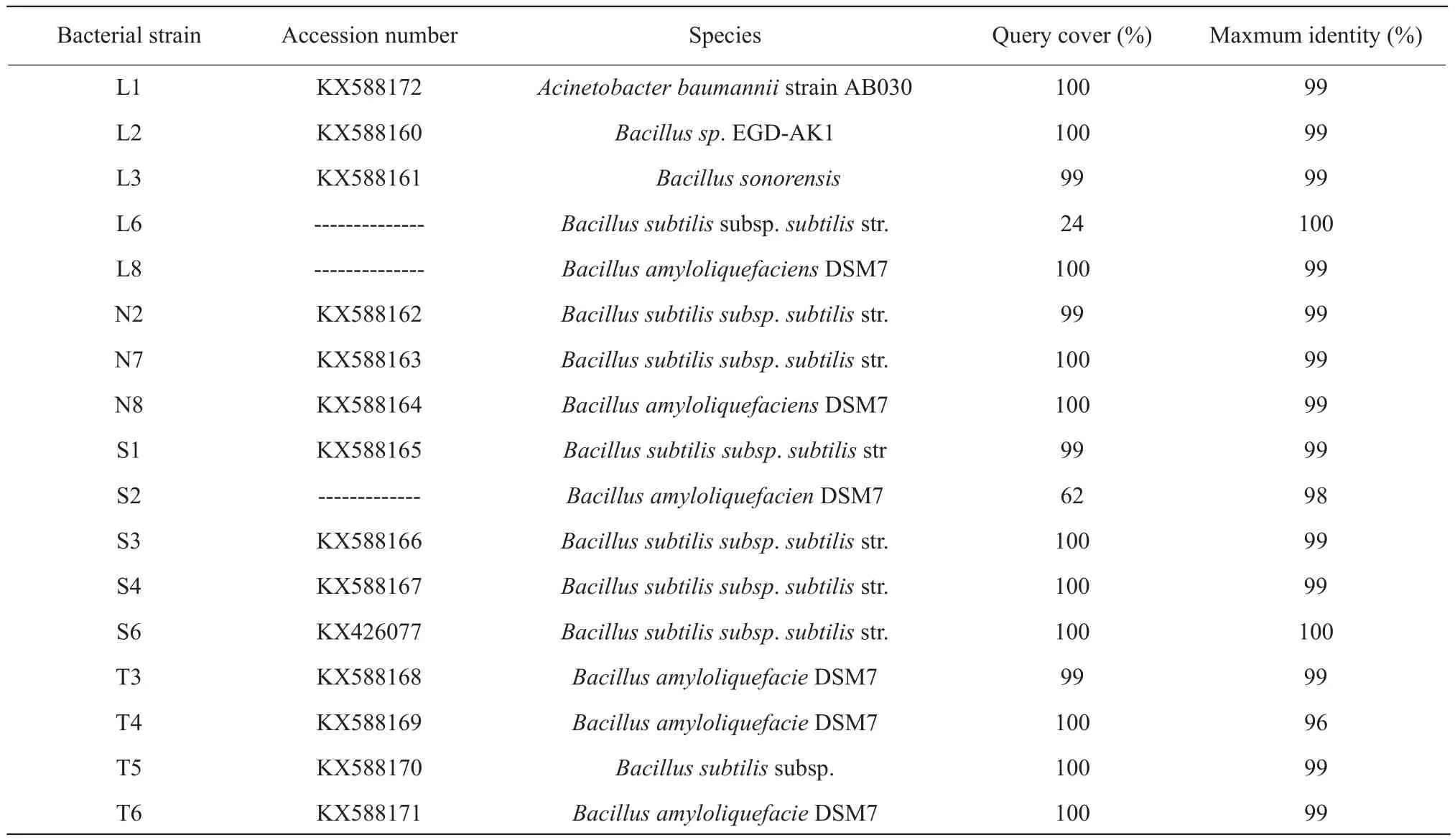
Table 2 BLAST-N results of 16SrDNA gene isolate
Nearest relatives on GenBank and percentage similarities are listed.L, Bacterial strains isolated from rumen fluid; N, Bacterial strains isolated from rumen residue; S, Bacterial strains isolated from rations; T, Bacterial strains isolated from soil.
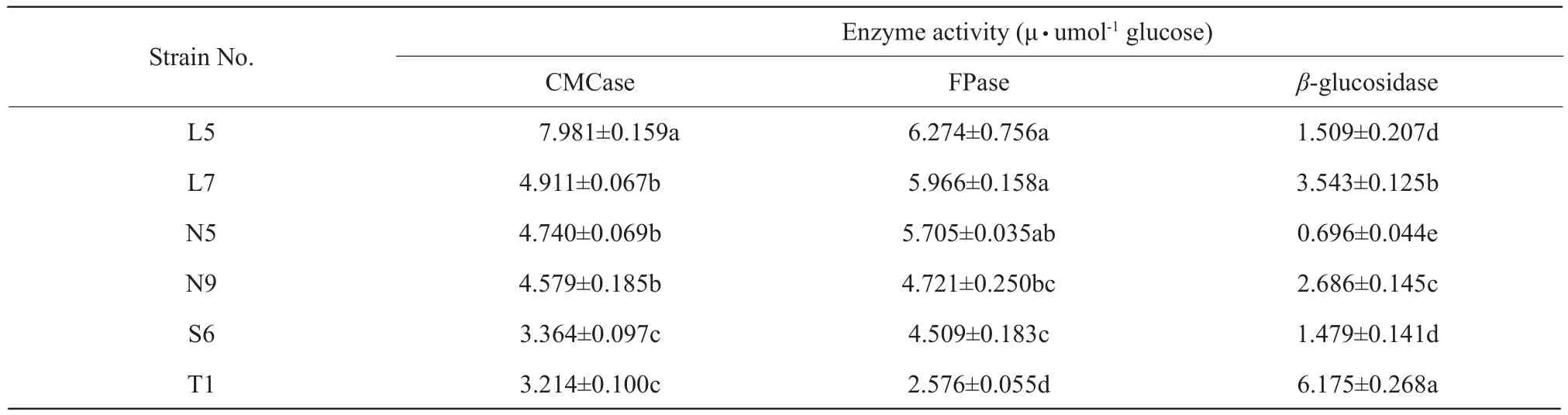
Table 3 Comparison of cellulase production among different strains on the total cellulase, endoglucanases and β-glucosidase
Different letters in the same column differ significantly (p<0.05) (means±SD) (n=3).L, Bacterial strains isolated from rumen fluid; N, Bacterial strains isolated from rumen residue; S, Bacterial strains isolated from rations; T, Bacterial strains isolated from soil.
Discussion
Isolate and screening of cellulose decomposition microbes
Sodium CMC medium is the traditional culture medium used for screening cellulose degradation bacteria, bacterial colonies capable of utilizing cellulose as sole source of carbon are isolated on cellulose agar media (Guptaet al., 2012).Based on morphological and molecular identification of 16SrDNA gene, the cellulose bacteria screened in this experiment mainly belonged to GPBacillus, this result was in accordance with the reports that lots of producing cellulose bacteria are GPBacillus(Dekaet al., 2011; Mohammedet al., 2003).However,three strains that isolated from rumen fluid were GN bacteria, this might be related to the foraging situation of cows.When cows were fed a concentrate diet, the bacteria were predominantly of the gramnegative cell wall type, if cows were fed normal diets, the bacteria were gram-positive bacteria in rumen fluid (Cheng and Costerton, 1980).The phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial strains using its 16SrDNA sequence data showed that strains had the highest homology withBacillusgenus.Due to lacking overall genome relatedness, chemotaxonomic data, the specific epithet of the strains could not be assigned and identified asBacillussp., this still need lots of relevant researches to be proved.
Congo-Red is an indicator for cellulose degradation in an agar medium, which provides the basis for a rapid and sensitive screening for cellulolytic bacteria(Guptaet al., 2012).In this experiment, the range of clearing zone diameter was between 7-15 mm,which was smaller than that of previous reports, the clearing zone diameter reached to more than 28 mm,whereas the strains were isolated from four different invertebrates in previous study.This could be due to various sources of cellulase micro-organisms, but could also be the result of the problems associated with enzyme activity determinations.
Cellulolytic activity of bacterial isolates
Cellulase activity ranged from 2.578 to 6.274 IU · mL-1for FPCase, and 3.214 to 7.981 IU · mL-1for endoglucanase in our trial.However, Guptaet al.(2012)reported that the bacterial cellulase activities ranged from 0.012 to 0.196 IU · mL-1for FPase and 0.162 to 0.400 IU · mL-1for endoglucanase assay, which were much lower than ours, this could be related to the methods of enzyme activity determinations, kinds of strains, culture time, determination conditions and other factors.For CMCase and FPase activities, the strains isolated from rumen fluid were dominant,which was in accordance with the reports that domestic and international studies have confirmed,the reason might be that there existed fungi that could secrete cellulase in rumen fluid, the cellulolytic enzyme activity of rumen fungi was higher than that of rumen bacteria (Kamra, 2005).It was shown that CMCase and FPase activities were the lowest in soil cellulose-decomposing bacteria, of which the reasons needed to be researched.
Conclusions
All of the 29 strains cellulose-decomposing bacteria screened from rumen residues, rumen fluid, soil and ration of dairy cow were facultative anaerobic,and most of them wereBacillusgenus, although the bacterial strains of four sources could not be completely separated by the genus.The activities of FPase and CMCase were significantly higher for L5 bacterial strains isolated from rumen fluid than other strains.However,β-glucosidase activity was the highest for T1 bacterial strain.
Benson H J.2005.Microbiological applications : laboratory manual in general microbiology.McGraw-Hill, 85(4): 173-174
Chandra M, Kalra A, Sharma P K,et al.2009.Cellulase production by sixTrichodermaspp.fermented on medicinal plant processings.Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 36(4): 605-614.
Cheng K J, Costerton J W.1980.Adherent rumen bacteria—their role in the digestion of plant material,urea and epithelial cells.Digestive Physiology and Metabolism in Ruminants.Springer Netherlands.
Dashtban M, Maki M, Kamtin L,et al.2010.Cellulase activities in biomass conversion: measurement methods and comparison.Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 30(4): 302-321.
Dashtban M, Schraft H, Qin W S.2009.Fungal bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues; opportunities & perspectives.International Journal of Biological Sciences, 5(5): 578-595.
Deka D, Bhargavi P, Sharma A,et al.2011.Enhancement of cellulase activity from a new strain of bacillus subtilis by medium optimization and analysis with various cellulosic substrates.Enzyme Research, 2011(2011): 151656.
Ghose T K.1987.Measurement of cellulase activities.Pure & Applied Chemistry, 59(2): 257-268.
Gupta P, Samant K, Sahu A.2012.Isolation of cellulose-degrading bacteria and determination of their cellulolytic potential.International Journal of Microbiology, 2012(6): 578925.
Hahn-H?gerdal B, Galbe M, Gorwa-Grauslund M F,et al.2006.Bioethanol–the fuel of tomorrow from the residues of today.Trends in Biotechnology, 24(12): 549-556.
Johnson J L.1994.Similarity analysis of DNAs.In: Gerhardt P,Murray R G E, Wood W A.Methods for general and molecular bacteriology.American Society for Micro-biology, Washington, DC.pp.656-682.
Kamra D N.2005.Rumen microbial ecosystem.Current Science,89(1): 124-135.
Kubicek C P.1982.β-glucosidase excretion byTrichoderma pseudokoningii: correlation with cell wall boundβ-1.3-glucanase activities.Archives of Microbiology, 132(4): 349-354.
Lynd L R, Weimer P J, van Zyl W H,et al.2002.Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology.Microbiology &Molecular Biology Reviews, 66(3): 506-577.
Lynd L R, Cushman J H, Nichols R J,et al.1991.Fuel ethanol from cellulosic biomass.Science, 251(4999): 1318-1323.
Mandels M, Andreotti R, Roche C.1976.Measurement of saccharifying cellulose.Biotechnology & Bioengineering Symposium, 16(6):21-33.
Mcdonald J E, Rooks D J, Mccarthy A J.2012.Methods for the isolation of cellulose-degrading microorganisms.Methods in Enzymology,510: 349-374.
Mohammed N, Onodera R, Or-Rashid M M.2003.Degradation of tryptophan and related indolic compounds by ruminal bacteria,protozoa and their mixturein vitro.Amino Acids, 24(1): 73-80.
Ragauskas A J, Williams C K, Davison B H,et al.2006.The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials.Science, 311(5760): 484-490.
Schwarz W.2001.The cellulosome and cellulose degradation by anaerobic bacteria.Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56(5):634-649.
Strobel H J.2010.Basic laboratory culture methods for anaerobic bacteria.Humana Press, Biofuels.pp.247-261.
Ulrich A, Wirth S.1999.Phylogenetic diversity and population densities of culturable cellulolytic soil bacteria across an agricultural encatchment.Microbial Ecology, 37(4): 238-247.
Wenzel M, Sch?nig I, Berchtold M,et al.2002.Aerobic and facultatively anaerobic cellulolytic bacteria from the gut of the termiteZootermopsis angusticollis.Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92(1):32-40.
Weisburg W G, Barns S M, Pelletier D A,et al.1991.16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study.Journal of Bacteriology,173(2): 697-703.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2018年1期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2018年1期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Operational Performance Evaluation of Corn Processing Industry Technological Innovation Alliance Based on Survey Data in Heilongjiang Province
- Spatial and Temporal Variation in Water Productivity and Grain Water Utilization Assessment of Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China
- Analysis of Process of Microwave Puffing Blueberry Snacks
- Stability Analysis of a Lignocellulose Degrading Microbial Consortium
- Pharmacokinetics of Milbemycin Oxime in Dogs Following Its Intravenous and Oral Administration
- Effect of Mineral and Vitamin Supplementation on Performance and Haemotological Values in Broilers
