High-quality draft genome sequence of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 with strong anti-MRSA ability, isolated from the frozen soil of Tibet in China
XiMing Chen , Ling Zhang , HaiLi Sun , ShuYan Li , SiJing Chang ,QingFeng Zhang , BingLin Zhang , Tuo Chen , GuangXiu Liu *, Paul Dyson
1. Key Laboratory of Desert and Desertification, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Extreme Environmental Microbial Resources and Engineering of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
3. Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Science, Urumqi, Xinjiang 830011, China
4. School of Chemistry and Environment Science, Lanzhou City University; Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
5. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
6. School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
7. Institute of Life Science, College of Medicine, Swansea University, Singleton Park, Swansea SA2 8PP, UK
High-quality draft genome sequence of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 with strong anti-MRSA ability, isolated from the frozen soil of Tibet in China
XiMing Chen1,2, Ling Zhang3, HaiLi Sun4, ShuYan Li5, SiJing Chang1,2,QingFeng Zhang6, BingLin Zhang1,2, Tuo Chen1,2, GuangXiu Liu1,2*, Paul Dyson7
1. Key Laboratory of Desert and Desertification, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Extreme Environmental Microbial Resources and Engineering of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
3. Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Science, Urumqi, Xinjiang 830011, China
4. School of Chemistry and Environment Science, Lanzhou City University; Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
5. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
6. School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, China
7. Institute of Life Science, College of Medicine, Swansea University, Singleton Park, Swansea SA2 8PP, UK
Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 with strong anti methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ability, isolated from the frozen soil of Tibet in China, has a strong ability to kill the multi-drugs-resistant MRSA. To identify the second-ary metabolism ability of this strain, we describe here the phenotypic characteristics of this strain, along with its high-quality draft genome sequence, its annotation, and analysis. The 7.1M draft genome encodes 6,284 putative open reading frames(ORFs), of which 4,416 ORFs were assigned with clusters of orthologous genes (COG) categories. Also, 65 tRNA genes and 24 rRNA operons were identified. The genome contains 12 gene clusters involved in antibiotics production and 1 gene cluster involved in anticancer-compounds production; 4 gene clusters belong to polyketides and nonribosomal peptides, 1 gene cluster belong to the butyrolactone, 4 gene clusters belong to the bacteriocin or lantipeptide, and 3 gene clusters belong to the others. This genome-sequence data will facilitate efforts to probe the potential of new antibiotics to kill multidrugs-resistant MRSA.
Streptomyces; antibiotic; multi-drugs-resistant MRSA; genome; gene cluster
1 Introduction
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) has occurred in many countries since its discovery in 1961 (Rosenbach, 1884; Hiramatsu, 2001).However, in recent years, clinicians have been con-cerned by the increased frequency of MRSA infections (Hiramatsu et al., 1997; Chambers, 2001). This resurging MRSA problem seems to be based on the lack of potent therapeutic agents having an unequivocal cell-killing effect, and thus capable of eliminating MRSA from the patient's body. MRSA is now a problem in hospitals worldwide and is increasingly recovered from nursing homes and the community(Hussain et al., 2000; Enright et al., 2002). The methicillin-resistance gene (mecA) encodes a methicillin-resistant, penicillin-binding protein that is not present in susceptible strains and is believed to be acquired from a distantly related species (Hiramatsu et al., 2001). MecA is carried on a mobile genetic element, the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec,of which four forms have been described that differ in size and genetic composition (Stefani et al., 2009).Many MRSA isolates are multiply resistant and a cause of great public health concern.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in East Asia is a unique and important permafrost environment.However, its microbiology remains largely unexplored to date. Members of the genus Streptomyces,gram-positive filamentous actinomycetes, are an attractive source for bioactive secondary metabolites(Yabuuchi, 2001; Procopio et al., 2012). These species have also been exploited for heterologous expression of a variety of secondary metabolites (Baltz,2010). Various new species of Streptomyces have been isolated from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (Zhang et al., 2016). Analysis the Streptomyces, which lived in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, will facilitate efforts to probe the potential of new antibiotics to kill multidrugs-resistant MRSA.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Preparation of high-molecular-weight DNA
The Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 was cultured in the 2X YT medium at 30 °C for 3 days. The culture was divided into 5-mL aliquots, and the mycelium harvested by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature; the supernatant was discarded, and the mycelium washed with 5 mL of 20%glycerol; aliquots not to be immediately processed were stored in 20% glycerol at 20 °C. Washed mycelium was harvested by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature, providing about 0.5 mL of wet mycelial pellet that was used as starting material for the salting-out protocol (Gomez-Escribano et al., 2015), using the same volume of solutions despite the lower amount of starting mycelium;incubation times with lysozyme and proteinase K were increased as required until a clear lysate was obtained.
2.2 DNA sequencing and assembly with Illumina and Pacific Biosciences
A shotgun paired-end library (average size of 550 bp) was prepared using the Illumina Nextera kit;no PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification was performed. Sequencing was performed in an Illumina HiSeq device. 1.14 Gb from 8.2 million reads were assembled. The PacBio library was constructed with a 20-kb, size-selected protocol using DNA Template Prep Kit 2.0, purified, and further selected for long insert size with a 0.35X AMPure bead-size selection. The library was sequenced on a PacBio RSII device using the reagents DNA/Polymerase Binding Kit P4, DNA Sequencing Reagent 2.0 PN, SMRT Cell V3, and Magbead, loading at 200 pM on the plate.Data were collected with Stage Start with 180-minute movies. During the single 180-min run time,1,018,308,244 read bases were generated, with 136,287 reads.
2.3 General visualisation, analysis, and manipulation of DNA sequence data
Visualisation and manipulation of text files was performed with advanced text editors Notepad++ (http://notepad-plus-plus.org/) or TextWrangler(http://www.barebones.com/products/textwrangler/)under MacOSX 10.6.8. DNA sequence analysis and annotation were predicted by Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline, version 2.8. Pfam searches were performed at the Pfam web server (http://pfam.xfam.org/) (Finn et al., 2014). Automated searches for natural product biosynthetic gene clusters were performed at the antiSMASH server (Weber et al., 2015).COG (clusters of orthologous genes) func-tional categories were calculated with BASys (Tatusov et al., 1997, Van Domselaar, et al., 2005).
3 Results
3.1 Organism information
To screen new antibiotics, Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 was isolated from the frozen soil of Tibet in China. This strain grew well on IPS (International Streptomyces project) 4, ISP5, and MS agar. The color of aerial mycelia was white, and that of the reverse side was yellow on IPS4 agar. Diffusible pigments were not formed on any agar media that we examined.A scanning electron micrograph of this strain is shown in Figure 1. Growth occurred at 10~37 °C (optimum 28 °C) and pH 5~9 (optimum pH 7). Strain 5-1-8 exhibited growth with 0%~7% (w/v) NaCl (optimum 0.5% NaCl). Strain 5-1-8 utilized D-glucose,sucrose, inositol, L-rhamnose, D-mannitol, D-raffinose, D-fructose, L-arabinose, and D-xylose for growth(Table 1). The genes encoding 16S rRNA were amplified by PCR using two universal primers, 8 F and 1492R. Homology search of the sequence indicated the highest similarity (1481/1481, 100%) to Streptomyces agglomeratus NBRC 13663 as the closest type strain. A phylogenetic tree was reconstructed on the basis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence (Perriere and Gouy, 1996; Thompson et al., 1997; Chen et al.,2015) (Figure 2). The phylogenetic analysis confirmed that the strain 5-1-8 belongs to the genus Streptomyces.
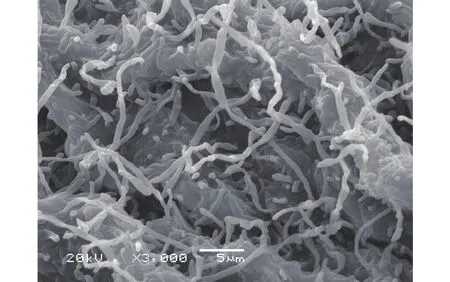
Figure 1 Scanning electron micrograph of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 grown on ten-fold diluted ISP 4 medium agar for 10 days at 28 °C. Bar, 5 μm
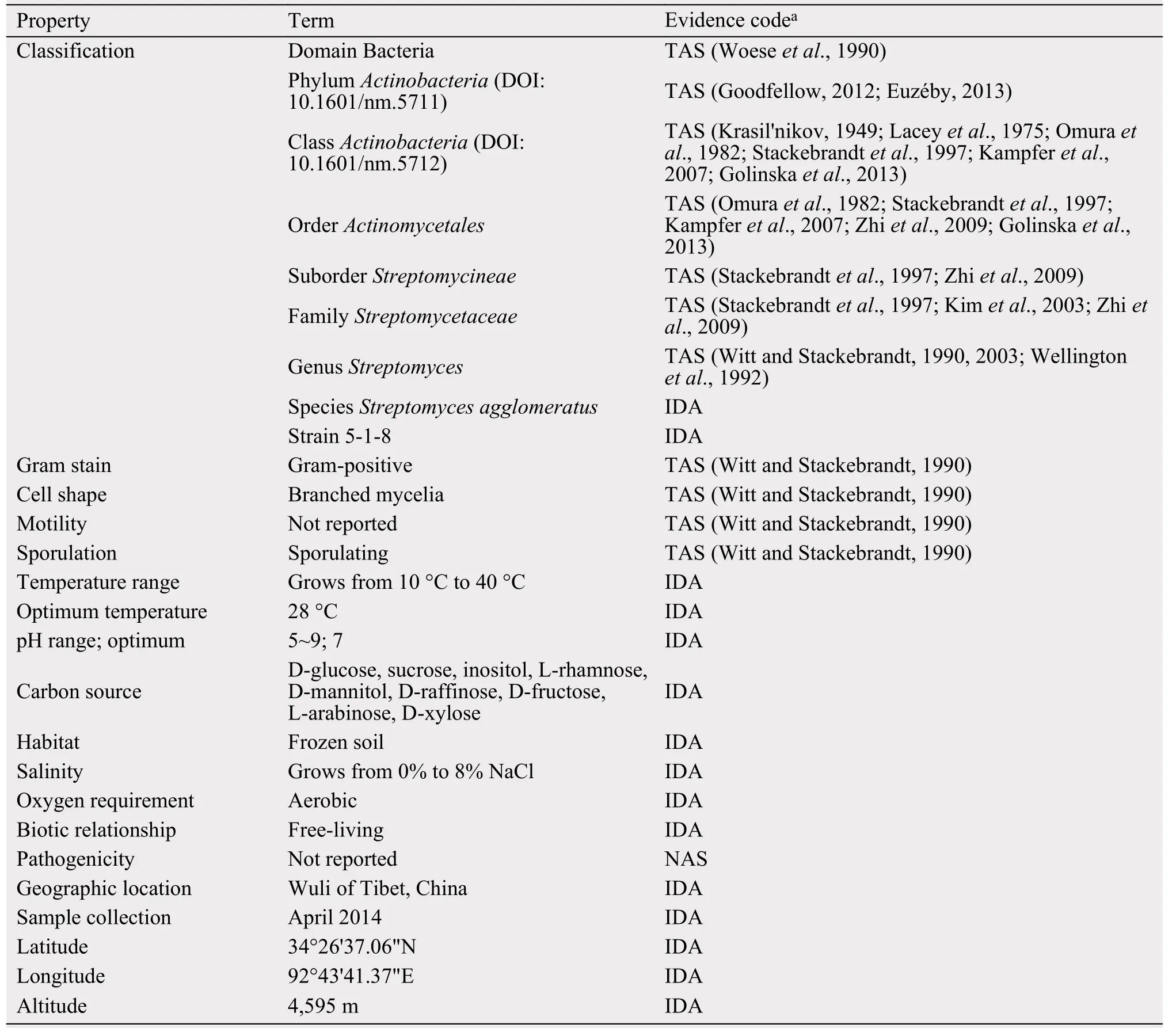
Table 1 Classification and general features of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8
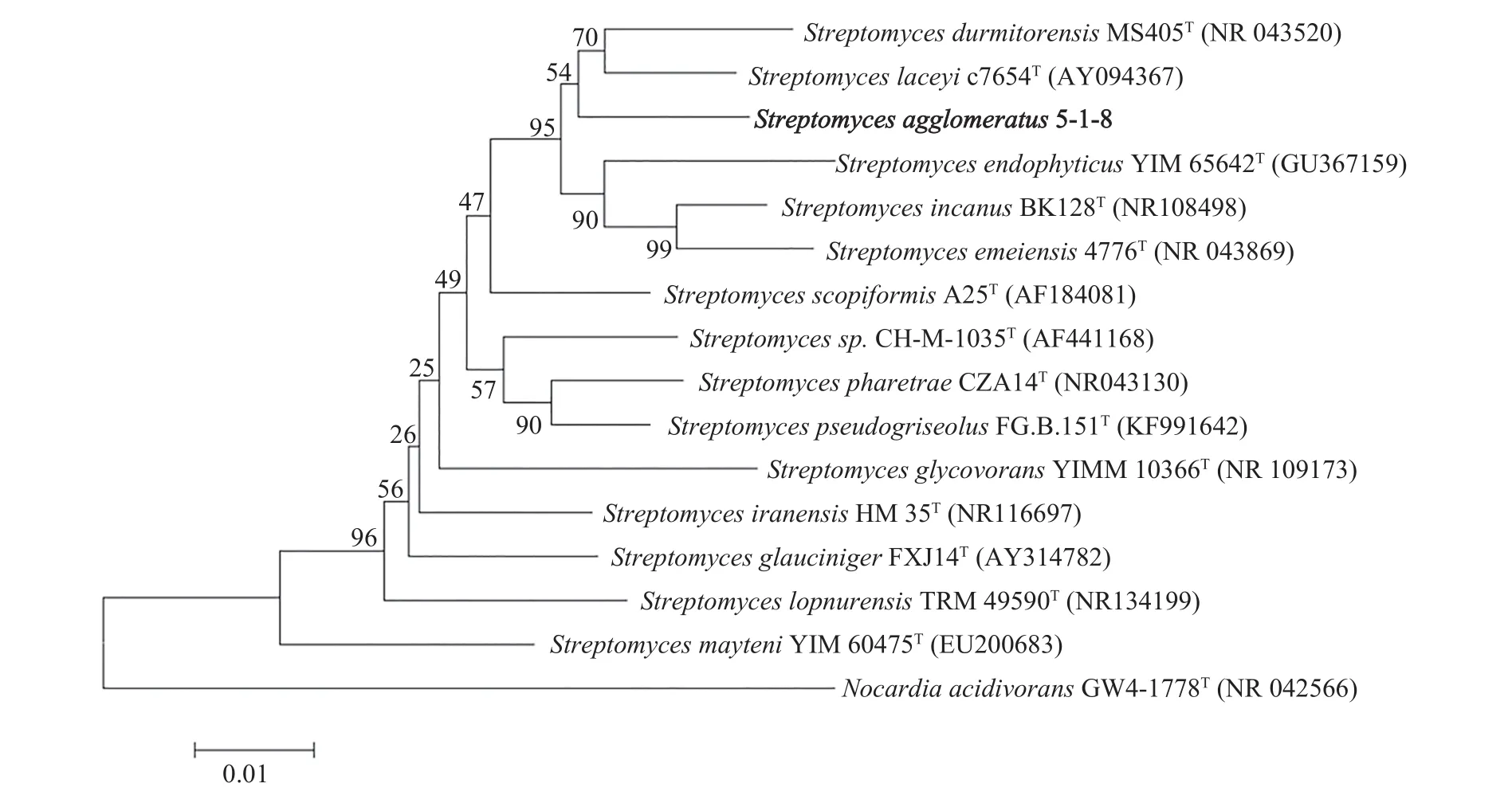
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 relative to phylogenetically close type strains within the genus Streptomyces. The strains and their corresponding GenBank accession numbers for 16S rRNA genes are shown in parentheses. The tree uses sequences aligned by ClustalX2 (Thompson et al., 1997), and constructed by the neighbor-joining method (Perriere and Gouy, 1996; Chen et al., 2015). All positions containing gaps were eliminated.The building of the tree also involved a bootstrapping process repeated 1,000 times to generate a majority-consensus tree; and only bootstrap values above 50% are shown at branching points (Cole et al., 2007).Nocardia acidivorans GW4-1778 (Golinska et al., 2013) was used as an outgroup
3.2 Genome-sequencing information
3.2.1 Genome project historyThis organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its strong ability to kill MRSA. The genome sequencing was performed in September 2015, and the Whole Genome Shotgun project was deposited in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under the accession number MEHL00000000. The version described in this study is the first version, labeled MEHL00000000.1. The sequencing-project information and its association with the Minimum Information about a Genome Sequence version 2.0 compliance are described in Table 2.
3.2.2 Growth conditions and genomic DNA preparation
The strain was cultured aerobically in a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of 2XYT medium, on a rotary shaker at 200 rpm. and 30 °C. Genomic DNA was isolated from 50 mL of culture using the Omega Bacterial DNA Kit, following the standard protocol recommended by the manufacturer. The quantity and purity of the extracted genomic DNA were assessed with a Picodrop Microliter UV/Vis Spectrophotometer, respectively. Finally, a DNA concentration of 560.0 ng/μL and OD 260/OD 280 of 1.82 was determined.
3.2.3 Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome of strain 5-1-8 was sequenced using the single-molecule, real-time DNA sequencing platform on the Pacific Biosciences RS II sequencer with P5 polymerase-C3 sequencing chemistry and Illumina Hiseq 4000 platform. A 20-kb insert SMRT-cell library was prepared from the sheared genomic DNA and loaded onto two SMRT cells. During the single 180-min run time, 1,018,308,244 read bases were generated with 136,287 reads. The reads of less than 100 bp or with low accuracy (below 0.8) were removed. A 300-bp insert library was prepared from the sheared genomic DNA. 1,146 M bp read bases were generated, with 8,187,498 reads by the Illumina Hiseq 4000 platform.
All post-filtered reads were assembled de novo using the RS hierarchical genome assembly process,version 3.3, in SMRT analysis software, version 2.3.0(Pacific Bio-sciences), and resulted in 3 contigs, with 305-fold coverage. The maximal contig length and N50 contig length had the same size of 7,047,685 bp. The whole genome was found to be 7,087,990 bp long.
3.2.4 Genome annotation
The protein-coding sequences were predicted by Prok-aryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline, version 2.8, on the NCBI website (Tatusova et al., 2016). Additional gene prediction and functional annotation were performed on the Rapid Annotation using Subsystems Technology (RAST) server and antibiotics & Secondary Metabolite Analysis shell (antiSMASH), respectively.
3.2.5 Genome properties
The genome size of strain 5-1-8 was found to be 7,087,990 bp, with the average G+C content of 70.81%. The genome was predicted to contain a total of 6,284 genes, which include 5,969 protein-coding genes with 89 RNA genes (24 rRNAs and 65 tRNAs).Of these, 4,301 genes were assigned to putative functions; and 4,416 genes (approximately 70.27%) were assigned to the COG functional categories. The genome statistics are presented in Table 3. The gene distribution within the COG functional categories is presented in Table 4.
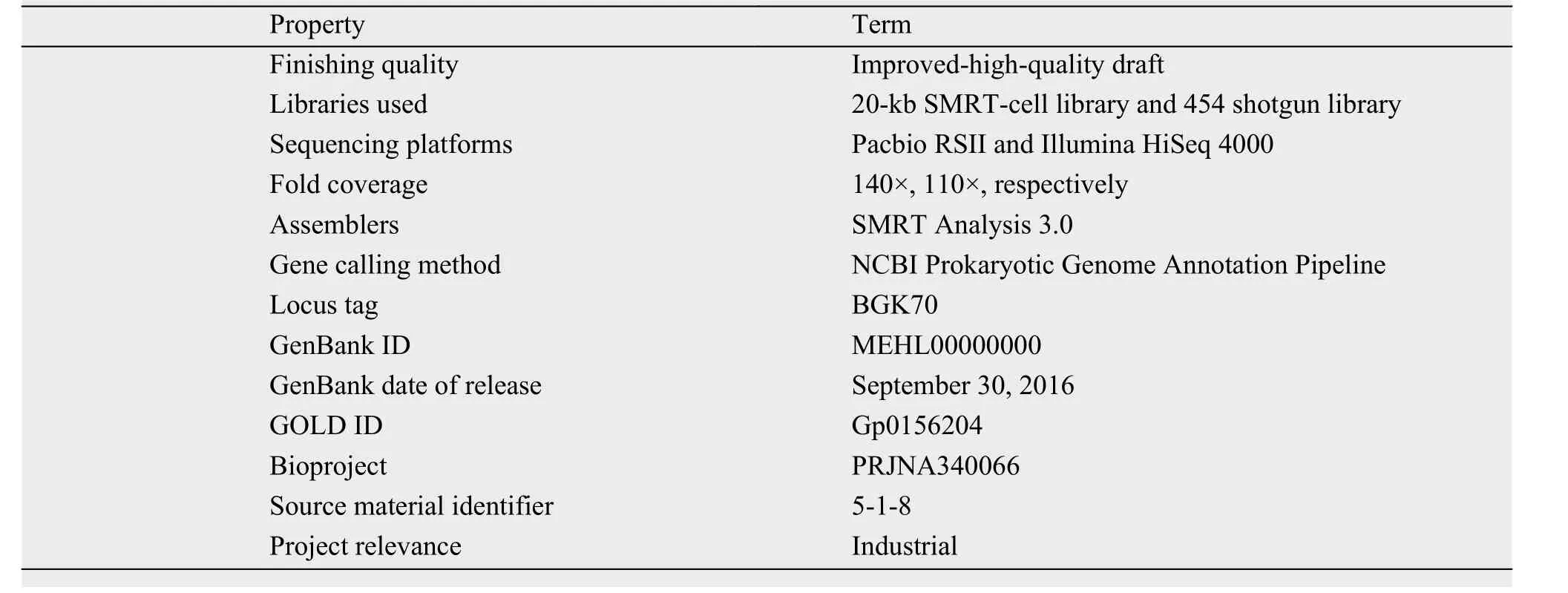
Table 2 Project information
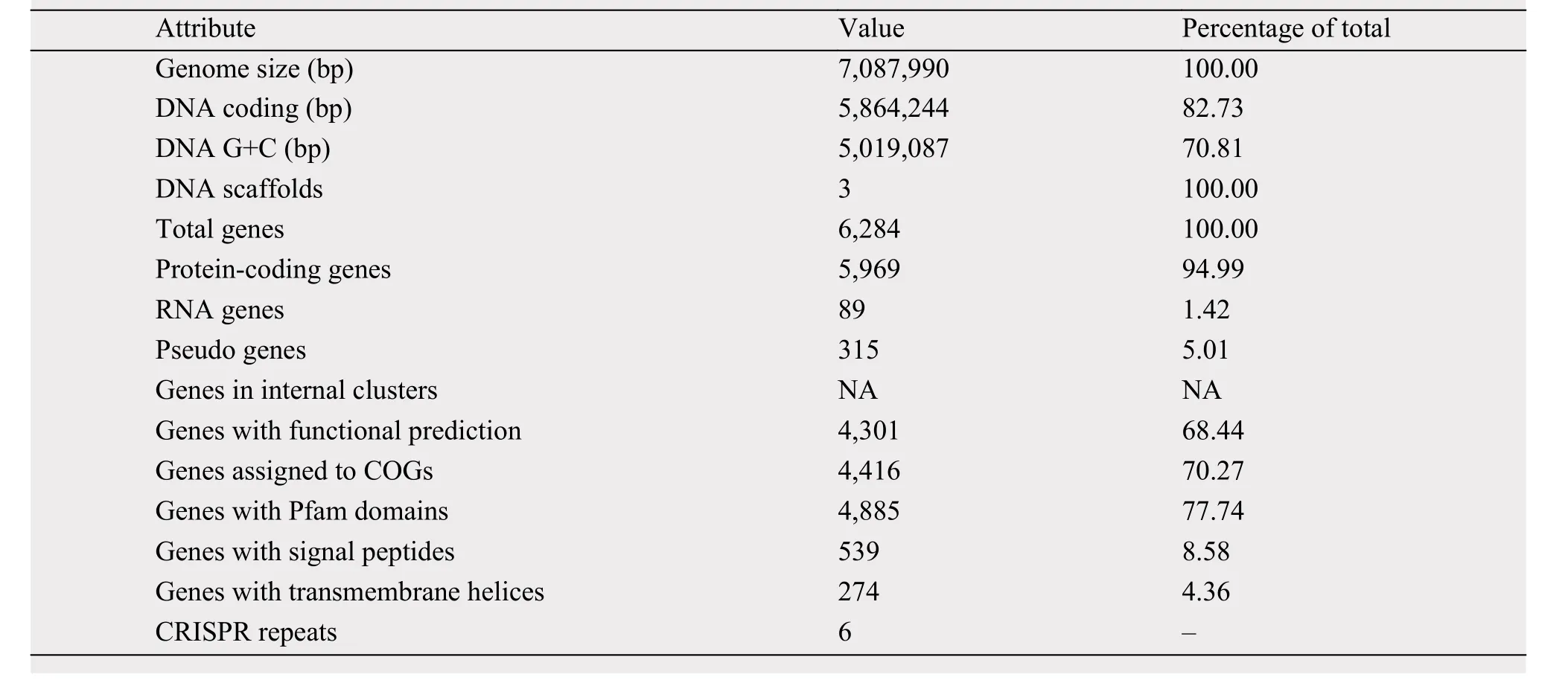
Table 3 Genome statistics
3.2.6 Insights from the genome sequence
When the strain 5-1-8 was cultured on the ISP4 medium over 1 week, the medium had a strong ability to kill the MRSA strain 337 (Foxr, Fusr, Eryr, Rifr,Dapr, Vanr, Tecr) and MRSA strain 414 (Foxr, Genr,Rifr, Lzdr, Cipr, Dapr), with the diameter of the inhibition zone being 25 mm and 25 mm, respectively. Using antiSMASH to analyze the antibiotics and secondary metabolite gene clusters in the strain of 5-1-8, it was found that the genome contains 12 gene clusters involved in antibiotics production and 1 gene cluster involved in anticancer-compounds production; 4 gene clusters belong to polyketides and nonribosomal peptides, 1 gene cluster belongs to the butyrolactone, 4 gene clusters belong to the bacteriocin or lantipeptide,and 3 gene clusters belong to the others (Table 5).These findings suggest the strain of 5-1-8 is a good candidate for discovery of a new antibiotic to kill MRSA or cancer.
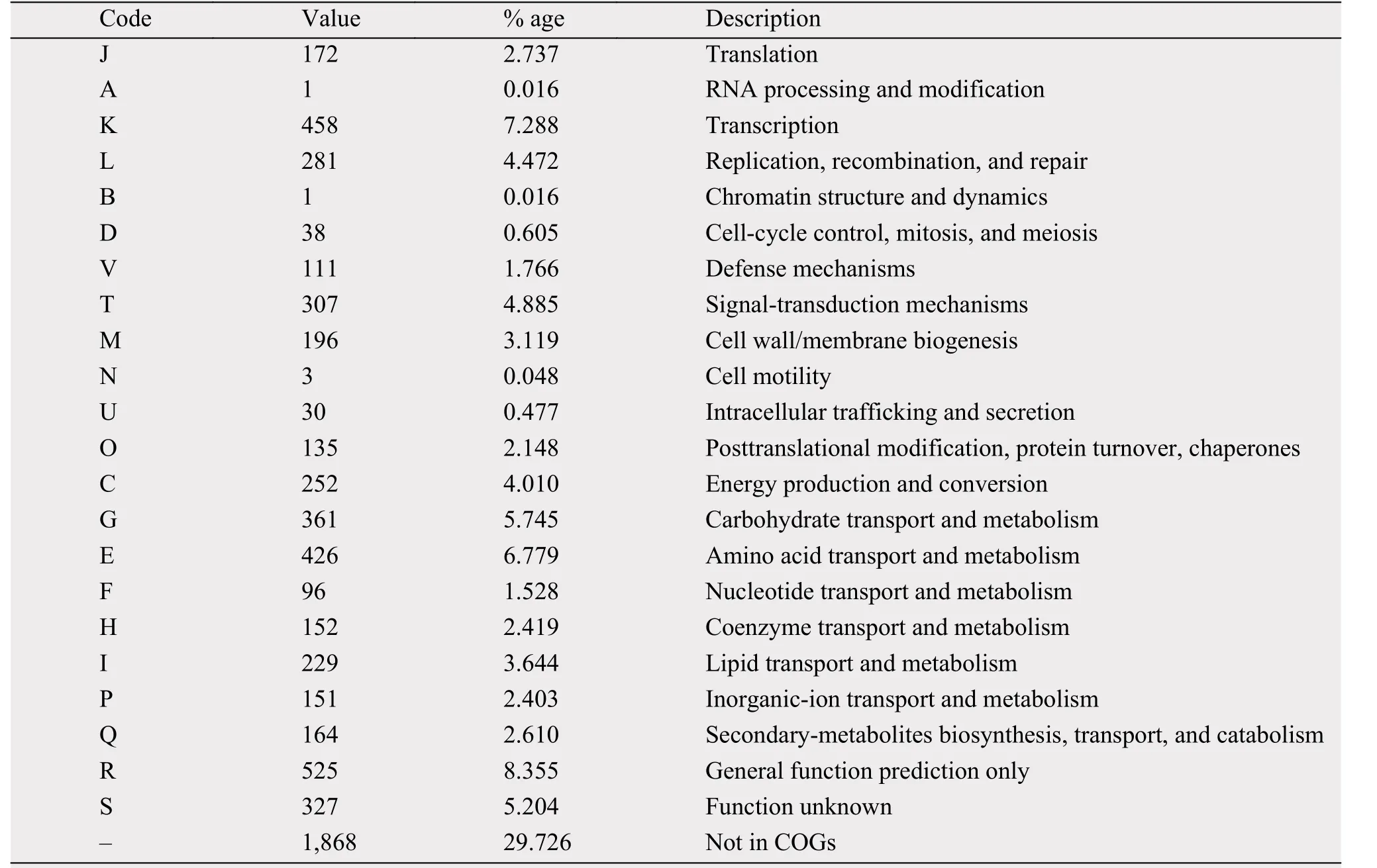
Table 4 Number of genes associated with general COG functional categories
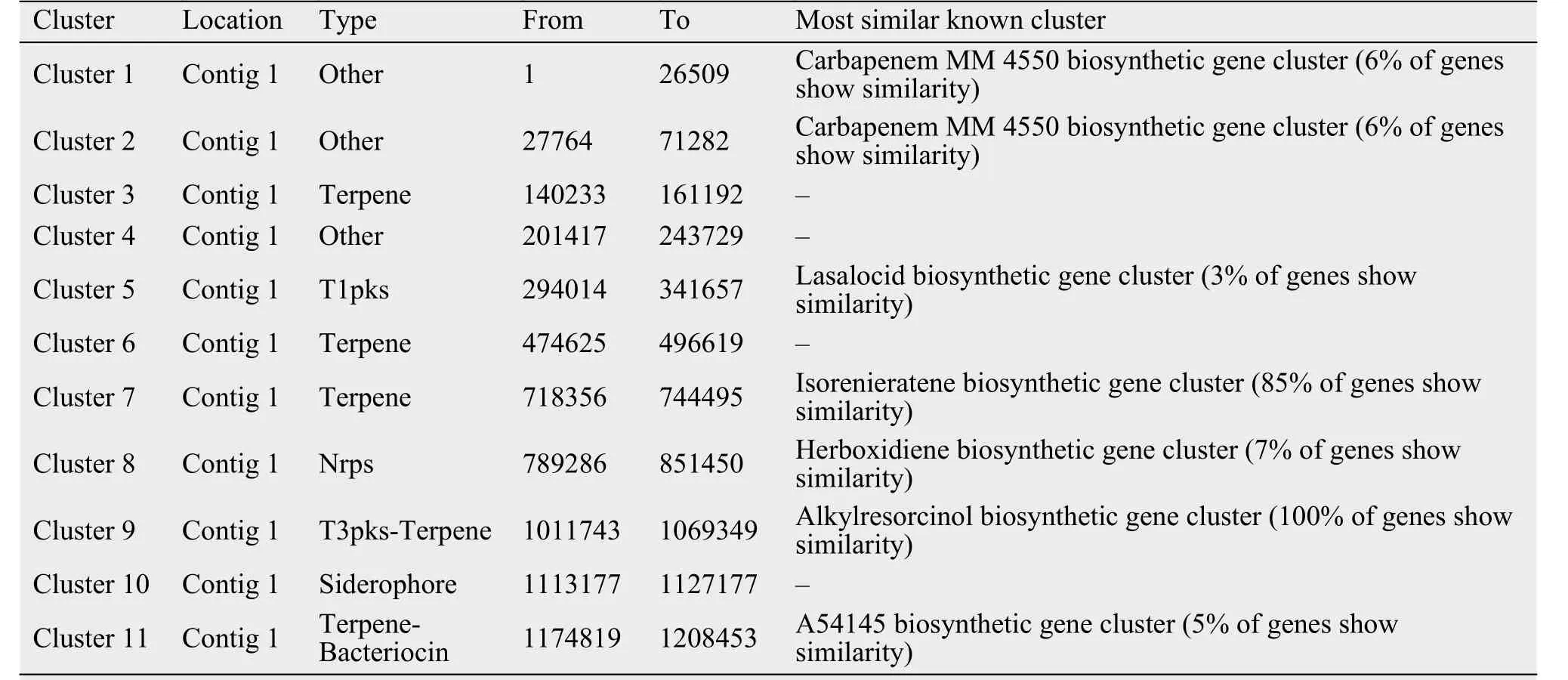
Table 5 The predicted secondary metabolite clusters in the strain of 5-1-8
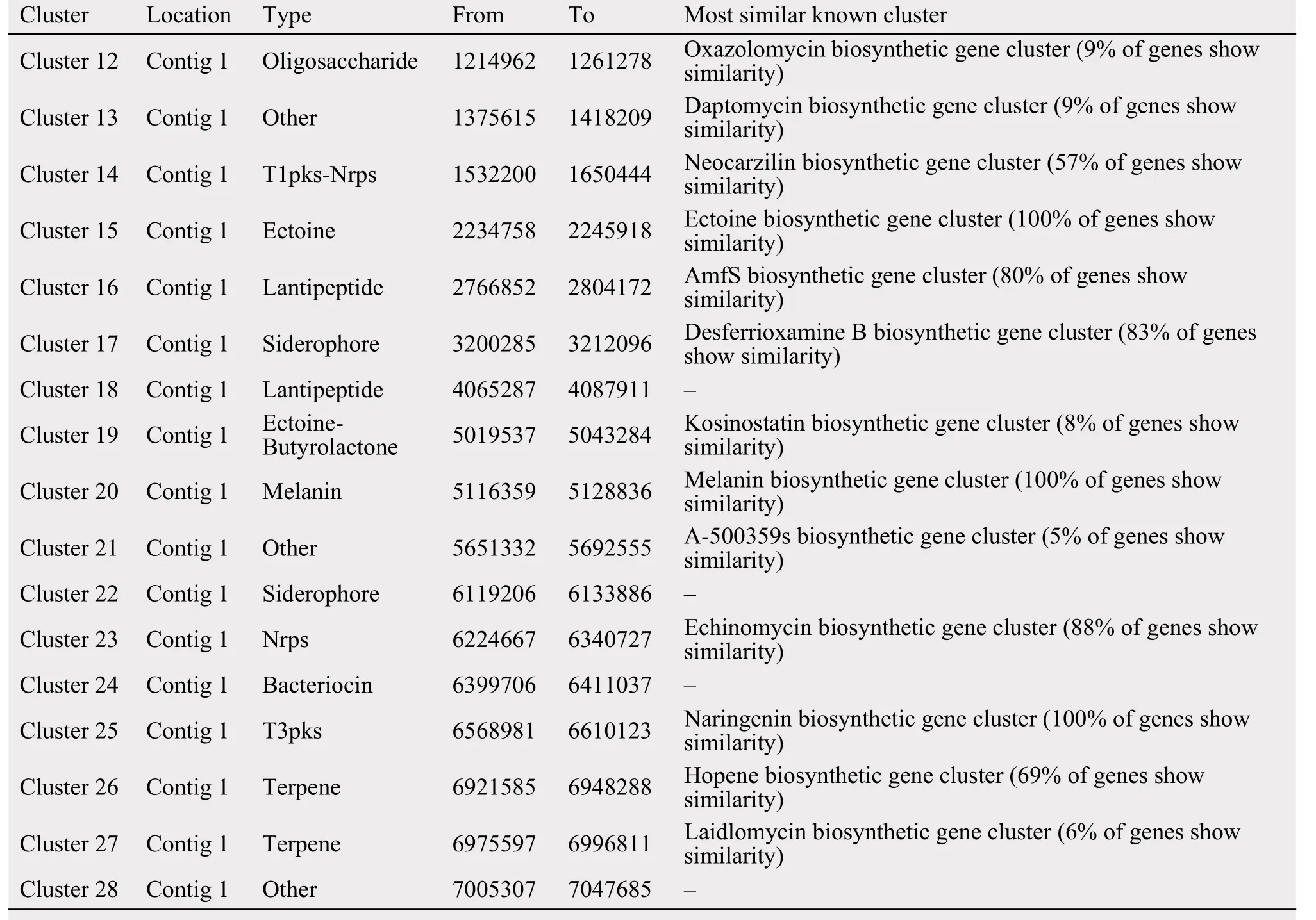
Table 5 The predicted secondary metabolite clusters in the strain of 5-1-8
4 Conclusions
The 7.1-Mb draft genome of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8, which has a strong ability to kill multi-drugs-resistant MRSA, has been deposited at GenBank/ENA/DDBJ under accession number MEHL00000000. We successfully identified 12 gene clusters involved in antibiotics production and 1 gene cluster involved in anticancer-compounds production;4 gene clusters belong to polyketides and nonribosomal peptides, 1 gene cluster belongs to the butyrolactone, 4 gene clusters belong to the bacteriocin or lantipeptide, and 3 gene clusters belong to the others.The genome-sequence information disclosed in this study will be utilized for the investigation of additional new bioactive compounds from this strain and will also serve as a valuable reference for evaluation of the metabolic potential of frozen-soil-derived Streptomyces.
Acknowledgments:
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31400437),the international cooperation program of Gansu(1504WKCA097), the application transformation foundation of CAS (HHS-CGZH-16-02), and UK BBSRC China Partnering Grant (BB/J020419/1).
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, et al., 2000. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nature Genetics, 25(1): 25–29. DOI: 10.1038/75556.
Baltz RH, 2010. Streptomyces and Saccharopolyspora hosts for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 37(8): 759–772. DOI:10.1007/s10295-010-0730-9.
Chambers HF, 2001. The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus? Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal, 7(2): 178–182.DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03903.x.
Chen X, Zhang B, Xiao J, et al., 2015. RfiA, a novel PAP2 domaincontaining polytopic membrane protein that confers resistance to the FtsZ inhibitor PC190723. Future Microbiology, 10(3):325–335. DOI: 10.2217/fmb.14.131.
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, et al., 2007. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Research, 35(Database issue):D169–172.
Enright MC, Robinson DA, Randle G, et al., 2002. The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(11): 7687–7692. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122108599.
Euzéby J, 2013. Validation List No. 152. List of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,63: 2365–2367. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.024562-0.
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, et al., 2014. Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(Database issue):D222–230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1065.
Golinska P, Wang D, Goodfellow M, 2013. Nocardia aciditolerans sp.nov. isolated from a spruce forest soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek,103(5): 1079–1088. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-013-9887-3.
Gomez-Escribano JP, Castro JF, Razmilic V, et al., 2015. The Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii genome: de novo sequencing and assembly in single contigs of the chromo-some, circular plasmid pSLE1 and linear plasmid pSLE2. BMC Genomics, 16: 485. DOI:10.1186/s12864-015-1652-8.
Goodfellow M, 2012. Phylum XXVI. Actinobacteria phyl. Nov. 2 Edition. New York: Springer.
Hiramatsu K, 2001. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a new model of antibiotic resistance. Lancet Infectious Diseases,1(3): 147–155. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(01)00091-3.
Hiramatsu K, Cui L, Kuroda M, et al., 2001. The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staph-ylococcus aureus. Trends in Microbiology, 9(10): 486–493. DOI: 10.1016/S0966-842X(01)02175-8.
Hiramatsu K, Hanaki H, Ino T, et al., 1997. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 40(1):135–136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/40.1.135.
Hussain FM, Boyle-Vavra S, Bethel CD, et al., 2000. Current trends in community-acquired methicil-lin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a tertiary care pediatric facility. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 19(12): 1163–1166. DOI: 10.1097/00006454-200012000-00009.
Kampfer P, Huber B, Buczolits S, et al., 2007. Nocardia acidivorans sp. nov. isolated from soil of the island of Stromboli. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57(Pt 6):1183–1187. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.64813-0.
Kim SB, Lonsdale J, Seong C, et al., 2003. Streptacidiphilus gen. nov.,acidophilic actinomycetes with wall chemotype I and emendation of the family Streptomycetaceae (Waksman and Henrici (1943)AL) emend.
Kim SB, Lonsdale J, Seong CN, et al., 2003. Streptacidiphilus gen.nov., acidophilic actinomycetes with wall chemotype I and emendation of the family Streptomycetaceae (Waksman and Henrici(1943)AL) emend.
Krasil'nikov NA, 1949. Guide to the Bacteria and Actinomycetes[Opredelitelv Bakterii i Actinomicetov]. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow.
Lacey J, Goodfellow M, Lacy J, et al., 1975. A novel actinomycete from sugar-cane bagasse: Sac-charopolyspora hirsuta gen. et. sp.nov. Journal of General Microbiology, 88(1): 75–85. DOI:10.1099/00221287-88-1-75.
Omura S, Takahashi Y, Iwai Y, et al., 1982. Kitasatosporia, a new genus of the order Actinomycetales. The Journal of Antibiotics,35(8): 1013–1019. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1013.
Perriere G, Gouy M, 1996. WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Bio-chimie, 78(5): 364–369. DOI:10.1016/0300-9084(96)84768-7.
Rainey et al., 1997. Streptacidiphilus gen. nov., acidophilic actinomycetes with wall chemotype I and emendation of the family Streptomycetaceae (Waksman and Henrici (1943)AL) emend. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 83(2): 107–116. DOI: 10.1023/A:1023397724023.
Procopio RE, Silva IR, Martins MK, et al., 2012. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases, 16(5):466–471. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.08.014.
Rosenbach FJ, 1884. The microorganisms in the sore-infections diseases. J.F. Berg-mann, Wiesbaden.
Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Wardrainey NL, 1997. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, actinobacteria classis nov. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 47(2): 479–491. DOI:10.1099/00207713-47-2-479.
Stefani S, Bongiorno D, Cafiso V, et al., 2009. Pathotype and susceptibility profile of a community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain responsible for a case of severe pneumonia. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease, 63(1):100–104. DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.09.012.
Tatusov RL, Koonin EV, Lipman DJ, 1997. A genomic perspective on protein families. Science, 278(5338): 631–637. DOI: 10.1126/science.278.5338.631.
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, et al., 2016. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(14):6614–6624. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569.
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, et al., 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows in-terface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research,25(24): 4876–4882. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876.
Validation List No. 11, 1983. Validation of the publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSB. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 33:672–674.
Validation of publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSEM, 2003. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53(1): 1–2.
Van Domselaar GH, Stothard P, Shrivastava S, et al., 2005. BASys: a web server for automated bacterial genome annotation. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(Web Server Issue): W455–459. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki593.
Weber T, Blin K, Duddela S, et al., 2015. AntiSMASH 3.0-a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Researchearch, 43(W1): W237–243. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv437.
Wellington EM, Stackebrandt E, Sanders D, et al., 1992. Taxonomic status of Kita-satosporia, and proposed unification with Streptomyces on the basis of phenotypic and 16S rRNA analysis and emendation of Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943, 339AL. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 42(1): 156–160. DOI:10.1099/00207713-42-1-156.
Witt D, Stackebrandt E, 1990. Unification of the Genera Streptoverticillum and Streptomyces, and Amendation of Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943, 339AL. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 13(4): 361–371. DOI: 10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80234-1.
Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML, 1990. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 87(12): 4576–4579. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576.
Yabuuchi E, 2001. Current topics on classification and nomenclature of bacteria. 7. Taxonomic outline of Archeae and bacteria in the Second Edition of Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology.Kansenshogaku Zasshi, 75(8): 653–655.
Zhang B, Tang S, Chen X, et al., 2016. Streptomyces lacrimifluminis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium that produces antibacterial compounds isolated from soil from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,66(12): 4981–4986. DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001456
Zhi XY, Li WJ, Stackebrandt E, 2009. An update of the structure and 16S rRNA gene sequence-based definition of higher ranks of the class Actinobacteria, with the proposal of two new suborders and four new families and emended descriptions of the existing higher taxa. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59(3): 589–608. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.65780-0.
: Chen XM, Zhang L, Sun HL, et al., 2017. High-quality draft genome sequence of Streptomyces agglomeratus 5-1-8 with strong anti-MRSA ability, isolated from the frozen soil of Tibet in China. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 9(5): 0503–0510.
10.3724/SP.J.1226.2017.00503.
*Correspondence to: GuangXiu Liu, Key Laboratory of Desert and Desertification, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences. No. 320, West Donggang Road, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000,China. E-mail: liugx@lzb.ac.cn
October 19, 2016 Accepted: January 13, 2017
 Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions2017年5期
Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions2017年5期
- Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions的其它文章
- Intrastorm stemflow variability of a xerophytic shrub within a water-limited arid desert ecosystem of northern China
- Palynological assemblage in the late Early Cretaceous from Sikouzi Section, Liupanshan Group, Central China and its implication to paleoenvironment change
- Complex network analysis of climate change in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China
- Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils of Baghrash County, Xinjiang,Northwest China
- Chemistry and environmental significance of aerosols collected in the eastern Tianshan
- Characteristics of thawed interlayer and its effect on settlement beneath embankment in permafrost regions-A case study for the Qinghai-Tibet Highway
