Polyethylene glycol as a promising synthetic material for repair of spinal cord injury
Xian-bin Kong, Qiu-yan Tang, Xu-yi Chen,, Yue Tu,, Shi-zhong Sun,, Zhong-lei Sun
1 Department of Brain, Af filiated Hospital of China Logistics College of People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin, China
2 Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Neurological Trauma Repair, Tianjin, China
4 Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
REVIEW
Polyethylene glycol as a promising synthetic material for repair of spinal cord injury
Xian-bin Kong1,2,#, Qiu-yan Tang3, Xu-yi Chen3,*, Yue Tu3,*, Shi-zhong Sun3,*, Zhong-lei Sun4,#
1 Department of Brain, Af filiated Hospital of China Logistics College of People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin, China
2 Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Neurological Trauma Repair, Tianjin, China
4 Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
Polyethylene glycol is a synthetic, biodegradable, and water-soluble polyether. Owing to its good biological and material properties, polyethylene glycol shows promise in spinal cord tissue engineering applications. Although studies have examined repairing spinal cord injury with polyethylene glycol, these compelling findings have not been recently reviewed or evaluated as a whole.us, we herein review and summarize the findings of studies conducted both within and beyond China that have examined the repair of spinal cord injury using polyethylene glycol.e following summarizes the results of studies using polyethylene glycol alone as well as coupled with polymers or hydrogels: (1) polyethylene glycol as an adjustable biomolecule carrier resists nerve fiber degeneration, reduces the inflammatory response, inhibits vacuole and scar formation, and protects nerve membranes in the acute stage of spinal cord injury. (2) Polyethylene glycol-coupled polymers not only promote angiogenesis but also carry drugs or bioactive molecules to the injury site. Because such polymers cross both the blood-spinal cord and blood-brain barriers, they have been widely used as drug carriers. (3) Polyethylene glycol hydrogels have been used as supporting substrates for the growth of stem cells aer injury, inducing cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Simultaneously, polyethylene glycol hydrogels isolate or reduce local glial scar invasion, promote and guide axonal regeneration, cross the transplanted area, and re-establish synaptic connections with target tissue, thereby promoting spinal cord repair. On the basis of the reviewed studies, we conclude that polyethylene glycol is a promising synthetic material for use in the repair of spinal cord injury.
nerve regeneration; spinal cord injury; polyethylene glycol; nerve tissue engineering; biomaterials; spinal nerve repair; biological drug; blood-spinal cord barrier; neural stem cells; carrier; cell culture; neural regeneration
Introduction
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a synthetic material with a wide range of clinical applications, as its functions can be modified by regulating the physical and chemical properties of it or its gra-related materials (Luo, 2004; Cui et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2015). For example, PEG has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use as a preservative additive prior to organ transplantation to limit cold ischemia/reperfusion injury (Pasut et al., 2016). PEG is also used to modify nanoparticles so that they cannot be recognized by the immune system. PEGylated copper oxide nanoparticles selectively reduce the activity of tumor cells and mitigate the inflammatory response (Giannousi et al., 2016). Another clinical use for PEG is to slow the removal of the nanoparticle pharmaceutical drug carrier. For example, the amount of time gold nanoparticles circulate throughout the blood and body is extended when they have been modified with PEG, promoting the accumulation of the nanoparticles at the tumor site (Huo et al., 2017).e application of PEG in SCI has been studied extensively. PEG has been shown to inhibit the inflammatory response, provide neuroprotection, suppress microenvironment changes in SCI, traverse the blood-brain barrier or blood-spinal cord barrier (Liu et al., 2008), and play important roles in cell therapy and tissue regeneration.
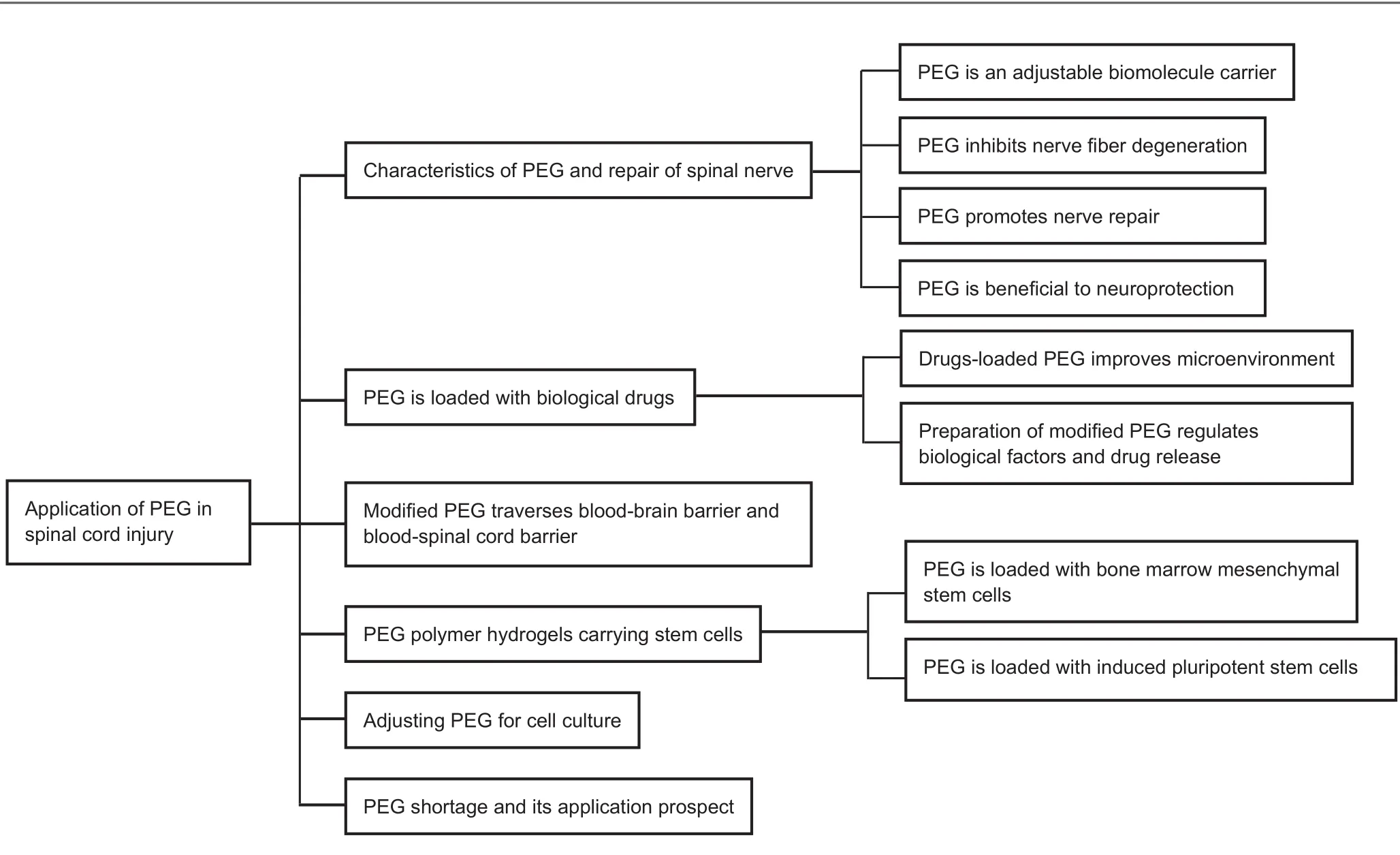
Figure 1 Overview of the topics discussed herein.
This review summarizes previous research findings examining the use of PEG in SCI (Figure 1) and provides new ideas and solutions for the particularly difficult problems associated with SCI repair. Although PEG is a potentially important material for the repair of SCI, we found some limitations in the use of PEG; thus, we also suggest future research directions for the development of improved PEG materials.
Characteristics of PEG and Repair of Spinal Nerves
PEG, as a biodegradable synthetic scaffold, shows good biocompatibility and low immunogenicity and it is nontoxic. PEG is soluble in both water and many organic solvents. PEG inhibits vacuole and scar formation and will not accumulate in the body (Potter et al., 2008; Krsko et al., 2009). PEG resists nerve fiber degeneration, reduces the inflammatory response, protects the nerve membrane, reduces cell death, protects mitochondria, accelerates improvement of electroneurographic signals, and can be used as a sealant for injured axon membranes (Luo et al., 2002, 2004; Laverty et al. 2004; Phillips et al., 2005; Burdick et al., 2006).
As soft polymers, PEG hydrogels can be used as drug carriers whose size, structure, and property can be controlled to differentially affect biological propertiesin vivo. Electron beam lithography and ultraviolet optical lithography have been used to tightly control the size and shape of hydrogels, successfully generating PEG hydrogels with controllable size and nanostructure (Bae et al., 2010). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy has been used to verify the formation of a cross-linking network between the polymer chains. A mesoporous silica templating method has also been used to adjust the molecular weight, particle size, and template of PEG hydrogel particles in biomolecular carriers (Cui et al., 2015), thereby reducing its phagocytosisin vivo.
PEG has been shown to lessen the inflammatory response and effectively inhibit nerve fiber degeneration in the early stage of SCI. Luo et al. (2004) suggested that PEG applied in the acute phase of SCI inhibits the formation of vacuoles and scars, effectively inhibits nerve fiber degeneration, and creates a good microenvironment for the regeneration of nerve fibers.e role of PEG in blocking nerve fiber degeneration may be related to its ability to protect cell integrity, reduce antigen release, and mitigate the inflammatory response.
PEG hydrogels can rapidly repair nerve conduction aer severe SCI, promote the myelination of axons, and improve sensory and motor functions.e implantation of PEG hydrogels into the cavity can provide an attachment or a new pathway for the continuous migration of astrocytes, which will migrate to the empty area, eliminate cell aggregation, and inhibit scar formation (Phillips et al., 2005; Burdick etal., 2006; Potter et al., 2008; Krsko et al., 2009). Estrada et al. (2014) implanted an immunologically inert PEG600 material into the scar area aer resection of a chronic SCI scar; their results showed that long-distance axonal regeneration at the scar area was conducive to the migration of beneficial cells (Schwann cells, endothelial cells, and astrocytes) and elongation (astrocytes), promoting neurological repair.
PEG reduces cell apoptosis by protecting cell membranes and mitochondria and inhibits free radicals and prevents lipid peroxidation. PEG implanted at the injury site markedly reverses the injury-induced changes in cell membrane permeability (Luo et al., 2002, 2004). Shi et al. (1999) showed that PEG implantation at the site of the completely transected spinal cord in pigs promotes reconstruction of the spinal cord and is conducive to the recovery of spinal cord function. Luo et al. (2007) reported that aer SCI, PEG significantly reduces caspase-3 activity by repairing damaged cell membranes and decreases programmed cell death.e interaction of PEG with mitochondria enhances mitochondrial function, decreases the release of cytochrome c, and then inhibits cell apoptosis. Laverty et al. (2004) showed that the application of an aqueous solution of PEG in the subarachnoid space reduces the cavity and promotes the recovery of function in dogs, and its local application protects nerve membranes and accelerates improvement of electroneurographic signals.
PEG Loaded with Biological Drugs
Modified PEG Traverses Blood-Brain and Blood-Spinal Cord Barriers
Transactivating-transduction protein (TAT) promotes absorption by human microvascular endothelial cells. TAT-modified PEG material can effectively traverse both the blood-brain barrier and the blood-spinal cord barrier (Liu et al., 2008). Liu et al. (2008) prepared the bioactive polymer TAT-PEG-b-cholesterol as a nanocarrier. Ciprofloxacin was successfully adsorbed on the nanocarrier. Scanning electron microscopy showed that the average diameter of the nanocarrier was less than 200 nm.ese TAT-modified nanoparticles are able to traverse the blood-brain barrier and enter the neuronal cytoplasm.
Glutathione PEGylated liposomes were developed to safely enhance drug delivery to the brain.e results of Rip et al. (2014) support the versatility of glutathione-PEG liposomes for enhanced drug delivery to the brain. Wang et al. (2010) suggested that TAT-conjugated PEGylated magnetic polymeric liposomes (TAT-PEG-MPLs) could traverse the blood-spinal cord barrier in rats. They observed low magnetic resonance imaging signals in T2-weighted images and found that TAT-PEG-MPL nanoparticles had significantly accumulated around the injury site as well as inside neurons as determined by their histological analysis as well as by cryo-electron microscopy and flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry (Wang et al., 2010).
Although fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) has excellent potential for treatment of SCI because of its angiogenic and trophic effects, it is unable to penetrate spinal cord tissue when delivered locally (Reuss et al., 2003). However, conjugation to PEG is known to improve penetration of proteins into tissue by reducing clearance and providing immunogenic shielding. Kang et al. (2010) conjugated PEG to FGF2 to nearly double the concentration of FGF2 in the injured spinal cord, indicating that PEGylation of FGF2 enhances tissue penetration.
PEG Polymer Hydrogels as Carriers for Stem Cells
Hardy et al. (2015) showed that oxime cross-linked hydrogels formed by PEG and hyaluronic acid derivatives are conducive to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell adhesion. Bhutani et al. (2010) chemically fused mouse embryonic stem cells with human fibroblasts under the induction of PEG, and successfully induced human fibroblasts into pluripotent stem cells. Mulyasasmita et al. (2014) developed protein-PEG hybrid hydrogels, called MITCH-PEG, which slowly release encapsulated vascular endothelial growth factor, and provide significant protection from cell damage. MITCH-PEG co-delivery of induced pluripotent stem cells and vascular endothelial growth factor was found to reduce inflammation and promote angiogenesis.
Adjusting PEG for Cell Culture
Gelatin- and PEG-based hydrogels provide a powerful cell culture platform for tissue engineering applications (Li et al., 2016; Truong et al., 2016). Truong et al. (2016) used a rapid cross-linking process to form hydrogels within minutes of mixing the polymer solutions under physiological conditions, showing that hydrogels can be used as injectable materials. Murine embryonic fibroblastic cells cultured in sogels demonstrate high cell viability.
The addition of silica nanoparticles has been shown not only to improve the mechanical strength and cell adhesion properties of PEG hydrogels but also to control the degree of cell adhesion for use in biomedicine. Gaharwar et al. (2013) found that the addition of silica nanospheres noticeably inhibited the degree of hydration of the PEG hydrogels, which indicated surface interactions between the polymer chains and the silica nanospheres. No obvious change in hydrogel microstructure or average pore size was detected after the addition of the silica nanospheres. Nevertheless, addition of silica nanospheres markedly increased both the mechanical strength and toughness of the hydrogel networks.e biological properties of these nanocomposite hydrogels were assessed by seeding fibroblasts on the hydrogel surface.e addition of silica nanospheres enhanced cell adhesion, promoted cell spreading, and increased the metabolic activity of the cells (Gaharwar et al., 2013).
Kim et al. (2016) believed that the concentration and molecular weight of the PEG cross-linkers could be varied to control the swelling/shrinking behavior and drug release properties as well as lower the critical solution temperature of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-PEG hydrogels.is strategy could be applied to various hydrogel systems to control their physical properties for biomedical applications. Akimoto et al. (2016) prepared a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel cross-linked by PEG for three-dimensional cell culture. By altering the temperature, the volume and the storage elastic modulus of the gel were changed. C2C12 cell adhesion was confirmed using RGDS pendants. Such PEG-cross-linked hydrogels are expected to be useful as new material for three-dimensional cell culture to control cell fate and to improve the biocompatibility of cells.
PEG Limitations and Proposed Applications
Rao et al. (2011) suggested that the ef ficacy of PEG alone is not ideal but that polylysine-modified PEG hydrogel promotes nerve cell adhesion, elevates biocompatibility and stability of neural tissue integration, and contributes to axon regeneration and remyelination.e use of PEG alone cannot completely mimic the three-dimensional porous structure of the spinal cord, and the biocompatibility is relatively insuf ficient. In addition, its position aer transplantationin vivois randomly relative to the structure of the spinal cord, allowing the upper and lower fiber bundles to grow in mismatched or even misplaced channels or pores.
PEG-poly (-L-lactic acid) (PLLA) hydrogels provide biodegradable, porous structures with pore sizes that do not change during degradation. Chiu et al. (2013) found that the pore size was controlled by the particulate size, and they adjusted the polymer concentration, optimized the degradation time, and provided additional guidance for the optimization of material properties to generate three-dimensional, degradable, porous PEG hydrogels. Such coupled hydrogels mitigate the disadvantages of PEG alone.e optimized design of the three-dimensional, porous PEG polymer scaffold along with the biomimetic spinal cord scaffold created by three-dimensional printing technology provided a structural basis for the extension of nerve cell growth across the diseased spinal cord (Namba et al., 2009; Soman et al., 2012). However, because of the limitations imposed by mechanical properties and changes in the microenvironment aer SCI, three-dimensional bioprinting of biomimetic porous PEG scaffolds remains a tough challenge and a hot topic in tissue engineering.
PEG has shown good safety and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a preservative additive and in modified nanoparticles for use before organ transplantation to reduce the inflammatory response and slow thein vivoclearance rate of nanoparticle drug carriers (Giannousi et al., 2016; Pasut et al., 2016; Huo et al., 2017). However, Romano et al. (2014) found that pegylated liposomal doxorubicin used for treating multiple myeloma wasassociated with some adverse events, including thrombocytopenia (9%), peripheral neuropathy (8%), and infections (8%). In addition, low-molecular-weight PEG accelerated the accumulation of platelet derived growth factor and reduced its activity, thereby reducing the differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells into oligodendrocytes (Elliott Donaghue et al., 2015). Because of the wide use of PEG, the safety of PEG and PEG polymersin vivoneeds to be further improved.
Although PEG has several shortcomings, it has been used as a component of new materials. Many of its properties may be transferred to these conjugates, giving the material new properties, such as hydrophilicity and flexibility. The end groups of PEG play decisive roles, as the various end groups offer different advantages. Functional groups, such as toluenesulfonate, amino, carboxyl and aldehyde, can be introduced into both ends of the PEG chain to further expand the useful applications of PEG.us, PEG has broad application prospects in organic synthesis, peptide synthesis, the slow or controlled release of drugs, targeted drug delivery, and stem cell transplantation.
Conclusions
Multiple disciplines are involved in the repair of SCI. Engineered materials, such as PEG, are important components of research in spinal cord tissue engineering. Research has shown that in addition to being stable, nontoxic, and biocompatible, PEG does not accumulate in the body, can be used as a sealant for injured axon membranes, inhibits the formation of vacuoles and scars, protects against nerve fiber degeneration, reduces inflammation, protects nerve membranes, decreases cell death, protects mitochondria, suppresses cell apoptosis, and improves electroneurographic signals. Such advantages of PEG offer promise for its use coupled with bioactive molecules and drugs as tissue-engineered scaffolds in the repair of the injured spinal cord.
Author contributions:XBK conceived and prepared the paper. XBK and ZLS collected the data. XYC, YT and SZS provided critical revision of the paper. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Conflicts of interest:None declared.
Open access statement:
Contributor agreement:A statement of “Publishing Agreement” has been signed by an authorized author on behalf of all authors prior to publication.
Plagiarism check:This paper has been checked twice with duplication-checking soware ienticate.
Peer review:A double-blind and stringent peer review process has been performed to ensure the integrity, quality and significance of this paper.
Open peer reviewer:Idiris Altun, KSü University Medical faculty of Turkey, Turkey.
Adams M, Carlstedt T, Cavanagh J, Lemon RN, McKernan R, Priestley JV, Raisman G, Verhaagen J (2007) International spinal research trust research strategy. III: a discussion document. Spinal Cord 45:2-14.
Akimoto AM, Hasuike E, Tada H, Nagase K, Okano T, Kanazawa H, Yoshida R (2016) Design of Tetra-arm PEG-crosslinked thermoresponsive hydrogel for 3d cell culture. Anal Sci 32:1203-1205.
Bae M, Divan R, Suthar KJ, Mancini DC, Gemeinhart RA (2010) Fabrication of poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel structures for pharmaceutical applications using electron beam and optical lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanometer Struct Process Meas Phenom 28:C6P24-6P29.
Bakshi A, Fisher O, Dagci T, Himes BT, Fischer I, Lowman A (2004) Mechanically engineered hydrogel scaffolds for axonal growth and angiogenesis aer transplantation in spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine 1:322-329.
Bhutani N, Brady JJ, Damian M, Sacco A, Corbel SY, Blau HM (2010) Reprogramming towards pluripotency requires AID—dependent DNA demethylation. Nature 463:1042-1047.
Burdick JA, Ward M, Liang E, Young MJ, Langer R (2006) Stimulation of neurite outgrowth by neurotrophins delivered from degradable hydrogels. Biomaterials 27:452-459.
Chiu YC, Kocag?z S, Larson JC, Brey EM (2013) Evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of porous poly (ethylene glycol)-co-(L-lactic acid) hydrogels during degradation. PLoS One 8:e60728.
Cui J, De Rose R, Alt K, Alcantara S, Paterson BM, Liang K, Hu M, Richardson JJ, Yan Y, Jeffery CM, Price RI, Peter K, Hagemeyer CE, Donnelly PS, Kent SJ, Carusof(2015) Engineering poly (ethylene glycol) particles for improved biodistribution. ACS Nano 9:1571-1580.
Elliott Donaghue I, Shoichet MS (2015) Controlled release of bioactive PDGF-AA from a hydrogel/nanoparticle composite. Acta Biomater 25:35-42.
Estrada V, Brazda N, Schmitz C, Heller S, Blazyca H, Martini R, Müller HW (2014) Long-lasting significant functional improvement in chronic severe spinal cord injury following scar resection and polyethylene glycol implantation. Neurobiol Dis 67:165-179.
Flynnj R, Graham BA, Galea MP, Callister RJ (2011)e role of propriospinal interneurons in recovery from spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 60:809-822.
Gaharwar AK, Rivera C, Wu CJ, Chan BK, Schmidt G (2013) Photocrosslinked nanocomposite hydrogels from PEG and silica nanospheres: structural, mechanical and cell adhesion characteristics. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 33:1800-1807.
Giannousi K, Hatzivassiliou E, Mourdikoudis S (2016) Synthesis and biological evaluation of PEGylated CuO nanoparticles. J Inorg Biochem 164:82-90.
Hardy JG, Lin P, Schmidt CE (2015) Biodegradable hydrogels composed of oxime crosslinkedpoly(ethylene glycol), hyaluronic acid and collagen: a tunable platform for sotissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 26:143-161.
Huo S, Chen S, Gong N (2017) Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles behavior in vivo modulated by surface polyethylene glycol (PEG) grafting. Bioconjug Chem doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00488.
Huo S, Chen S, Gong N, Liu J, Li X, Zhao Y, Liang XJ (2016) Synthesis, characterization, and application of reversible PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA copolymer thermogels in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 6:19077.
Jiang G, Sun J, Dingf(2014) PEG-g-chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel for implant drug delivery: cytotoxicity, in vivo degradation and drug release. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 25:241-256.
Kang CE, Tator CH, Shoichet MS (2010) Poly (ethylene glycol) modif ication enhances penetration of fibroblast growth factor 2 to injured spinal cord tissue from an intrathecal delivery system. J Control Release 144:25-31.
Kim S, Lee K, Cha C (2016) Refined control of thermoresponsive swelling/deswellin and drug release properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels using hydrophilic polymer crosslinkers. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 27:1698-1711.
Krsko P, McCann TE, Thach TT, Laabs TL, Geller HM, Libera MR (2009) Length-scale mediated adhesion and directed growth of neural cells by surface-patterned poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels. Biomaterials 30:721-729.
Kumar M, Coburn J, Kaplan DL, Mandal BB (2016) Immuno-informed 3d silk biomaterials for tailoring biological responses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 43:29310-29322.
Laverty PH, Leskovar A, Breur GJ, Coates JR, Bergman RL, Widmer WR, Toombs JP, Shapiro S, Borgens RB (2004) A preliminary study of intravenous surfactants in paraplegic dogs: polymer therapy in canine clinical SCI. J Neurotrauma 21:1767-1777.
Lee S, Tong XM, Yangf(2016) Effects of the poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogelcrosslinking mechanism on protein release. Biomater Sci 4:405-411.
Liu L, Guo K, Lu J, Venkatraman SS, Luo D, Ng KC, Ling EA, Moochhala S, Yang YY (2008) Biologically active core/shell nanoparticles self-assembled from cholesterol-terminated PEG-TAT for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. Biomaterials 29:1509-1517.
Liu L, Venkatraman SS, Yang YY, Guo K, Lu J, He B, Moochhala S, Kanl(2008) Polymeric micelles anchored with TAT for delivery of antibiotics across the blood-brain barrier. Biopolymers 90:617-623.
Luo J, Borgens R, Shi R (2002) Polyethylene glycol immediately repairs neuronal membranes and inhibits free radical production aer acute spinal cord injury. J Neuroehem 83:471-480.
Luo J, BorgensR, Shi R (2004) Polyethylene glycol improves function and reduces oxidative stress in synaptosomal preparations following spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 21:994-1007.
Luo J, Shi R (2004) Diffusire oxidative stress following acute spinal cord injury in guinea pigs and its inhibition by polyethylene glycol. Neurosci Lett 359:167-170.
Luo J, Shi R (2007) Polyethylene glycol inhibits apoptotic cell death following traumatic spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1155:10-16.
Li Y, Meng H, Liu Y, Narkar A, Lee BP (2016) Gelatin microgel incorporated poly (ethylene glycol)-based bioadhesive with enhanced adhesive property and bioactivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:11980-11989.
Lawrence PB, Price JL (2016) How PEGylation influences protein conformational stability. Curr Opin Chem Biol 34:88-94.
Mehrotra S, Lynam D, Maloney R, Pawelec KM, Tuszynski MH, Lee I, Chan C, Sakamoto J (2010) Time controlled protein release from layer-by-layer assembled multilayer functionalized agarose hydrogels. Adv Funct Mater 20:247-258.
Mulyasasmita W, Cai L, Dewi RE, Jha A, Ullmann SD, Luong RH, Huang NF, Heilshorn SC (2014) Avidity-controlled hydrogels for injectable co-delivery of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells and growth factors. J Control Release 191:71-81.
Namba RM, Cole AA, Bjugstad KB, Mahoney MJ (2009) Development of porous PEG hydrogels that enable ef ficient, uniform cell-seeding and permit early neural process extension. Acta Biomater 5:1884-1897.
Pasut G, Panisello A, Folch-Puy E, Lopez A, Castro-Benítez C, Calvo M, Carbonell T, García-Gil A, Adam R, Roselló-Catafau J (2016) Polyethylene glycols: an effective strategy for limiting liver ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 22:6501-6508.
Phillips JB, Bunting SC, Hall SM, Brown RA (2005) Neural tissue engineering: a self-organizing collagen guidance conduit. Tissue Eng 11:1611-1617.
Potter W, Kalil RE, Kao WJ (2008) Biomimetic material systems for neural progenitor cell-based therapy. Front Biosci 13:806-821.
Rao SS, Han N, Winter JO (2011) Polylysine-modified PEG-based hydrogels to enhance the neuro-electrode interface. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 22:611-625.
Rip J, Chen L, Hartman R, van den Heuvel A, Reijerkerk A, van Kregten J, van der Boom B, Appeldoorn C, de Boer M, Maussang D, de Lange EC, Gaillard PJ (2014) Glutathione PEGylated liposomes: pharmacokinetics and delivery of cargo across the blood-brain barrier in rats. J Drug Target 22:460-467.
Reuss B, Dono R, Unsicker K (2003) Functions of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and FGF-5 in astroglial differentiation and bloodbrain barrier permeability: evidence from mouse mutants. J Neurosci 23:6404-6412.
Romano A, Chiarenza A, Conticello C, Cavalli M, Vetro C, Di Raimondo C, Cunsolo R,Palumbo GA, Di Raimondof(2014) Salvage therapy with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory myeloma patients. Eur J Haematol 93:207-213.
Shi R, Borgens RB, Blight AR (1999) Functional reconnection of severed mammalian spinalcord axons with polyethylene glycol. J Neurotrauma 16:727-738.
Soman P, Tobe BT, Lee JW, Winquist AA, Singec I, Vecchio KS, Snyder EY, Chen S (2012)ree-dimensional scaffolding to investigate neuronal derivatives of human embryonic stem cells. Biomed Microdevices 14:829-838.
Truong VX, Hun ML, Li F, Chidgey AP, Forsythe JS (2016) In situ-forming click-crosslinked gelatin based hydrogels for 3D culture of thymic epithelial cells. Biomater Sci 4:1123-1131.
Walmsley AR,Mir AK (2007) Targeting the Nogo-A euritis pathway to promote recovery following acute CNS injury. Curr Pharm Des 13:2470-2484.
Wang H, Zhang S, Liao Z, Wang C, Liu Y, Feng S, Jiang X, Chang J (2010) PEGlated magnetic polymeric liposome anchored with TAT for delivery of drugs across the blood-spinal cord barrier. Biomaterials 31:6589-6596.
Xiao RZ, Zeng ZW, Zhou GL, Wang JJ, Li FZ, Wang AM (2010) Recent advances in PEG-PLA block copolymer nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 5:1057-1065.
Xu P, Gong WM, Li Y, Zhang T, Zhang K, Yin DZ, Jia TH (2008) Destructive pathological changes in the rat spinal cord due to chronic mechanical compression. Neurosurg Spine 8:279-285.
Yang ZQ, He Y, Shi JD (2015) Polyethylene glycol effects on the performance of rifampicin-polylactic acid-glycolic acid polymer microspheres. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu 19:421-426.
Zhang K, Tang X, Zhang J, Lu W, Lin X, Zhang Y, Tian B, Yang H, He H (2014) PEG-PLGA copolymers: their structure and structure-influenced drug delivery applications. J Control Release 183:77-86.
Zhou XH, Wei DX, Ye HM, Zhang X, Meng X, Zhou Q (2016) Development of poly(vinyl alcohol) porous scaffold with high strength and well ciprofloxacin release ef ficiency. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 67:326-335.
Copyedited by Smith T, Raye W, Wang J, Li CH, Qiu Y, Song LP, Zhao M
How to cite this article: Kong XB, Tang QY, Chen XY, Tu Y, Sun SZ, Sun ZL (2017) Polyethylene glycol as a promising synthetic material for repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res 12(6):1003-1008.
Funding: This study was supported by a grant from National Key Science and Technology Research & Development Plan in China, No. 2016YFC1101500; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11672332.
*Correspondence to:
Xu-yi Chen, M.D. or Yue Tu, M.D. or Shi-zhong Sun, Chenxuyi1979@126.com or ytumail@vip.126.com or loveicu@126.com.
orcid:
0000-0002-6293-1340
(Xu-yi Chen)
0000-0003-2645-0168
(Yue Tu)
0000-0002-0430-8980
(Shi-zhong Sun)
10.4103/1673-5374.208597
Accepted: 2017-04-05
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 may be an intervention target for improving sensory and locomotor functions after spinal cord contusion
- Novel aspects of extracellular adenosine dynamics revealed by adenosine sensor cells
- Electroacupuncture regulates the stress-injury-repair chain of events after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
- Immunomodulators and microRNAs as neurorestorative therapy for ischemic stroke
- High-frequency and brief-pulse stimulation pulses terminate cortical electrical stimulation-induced afterdischarges
- Mild closed head traumatic brain injury-induced changes in monoamine neurotransmitters in the trigeminal subnuclei of a rat model: mechanisms underlying orofacial allodynias and headache