Informed Design for Sustainable Growth
文/ Dr. Mirja K?lvi?inen, Noora Nylander, Antti Heinonen(Design Institute, Lahti University of Applied Sciences)
Informed Design for Sustainable Growth
文/ Dr. Mirja K?lvi?inen, Noora Nylander, Antti Heinonen(Design Institute, Lahti University of Applied Sciences)
Lahti Growth model in the Lahti University of Applied Sciences is joining together the regional hub for design competence and the committed development of circular economy solutions. On the strategic level the circular solutions try to prevent waste from occurring in any part of the production and consumption process. This demands also design for user consumer behavior change. New emphasis for design education is required with guiding students in solving this behavior change challenge instead of designing concrete products. The user research for green behavior change reveals practical everyday, social life and interest related hindrances explaining the typical attitude – behavior gap with green actions. From the the user perspective the need is for service thinking based solutions, where the information communication, findability and availability of the offering amongst the everyday activities and interests is essential. This paper presents three into the design education integrated cases that present possibilities of the circular economy design and fulfill some important aspets of the user needs. The information design case for renewable energy production in the countryside developed both static posters and storytelling based animations about the horse manure based energy possibilities. The renewable energy research results data wrangling was integrated with information design ideas and visualisation production. The information design project produced results for clear, positive, context related and systemic information delivery. It also produced communication messaging about the normality, savings and history related sensibility achieved through recycling and producing renewable energy in the countryside. The second design case was about preowned product recycling possibilities through applying user information and service design process. The cross-disciplinary students’ efforts produced finable, positive and without a car available service process, house cleaning and preowned product collecting services and activities for sharing, reuse, repair and redesign. These results provided easily usable activities for the consumer user with visible and meaningful results and possibilities for social sharing. Sustainable urban living example case dealt with bus travelling systems. Applying emphatic design thinking process to cross-disciplinary learning the work produced an application concept to support city visitors in bus travelling and a concept to incorporate intercative and challeging games to the bus company offerings. The user driven bus travelling design provided clear and easily obtainable information, easily fndable and usable bus travel possibilities for the visitors. The engaging and social side of solutions was also covered. The implemented and analysed project cases show that by appropriating user driven and emphatic design process, research knowledge integration, systemic thinking, and cross-disciplinary, collaborative aspects in design education offers means to tackle the circular economy behavior change challenges. Methods for information design, systems analysis, user driven design and co-design become the core of the behavior change enabling design instead of concrete product development methods.
circular economy, sustainable design, co-design, emphatic design, user expereince, information design, service design, systems design
1.Introduction
In the Lahti University of Applied Sciences and in the Lahti Institute of Design education is reformed through integrating societal project challenges from circular economy solutions inside the design based development courses. This pairing of design efforts with sustainability solutions is the basis for the University based regional growth model suggesting that design can be used as the means to tackle the pressing strategic level and systemic challenges. One of the routes to provide solutions for the less wasteful circular economy requires new emphasis for design education in guiding students to solve the challenges of promoting userconsumer behavior change. This demands using information design, service design and co-design type of approaches and solutions instead of material product development as the process and outcome of the design work. In the practical design projects run both inside the design courses and with interdisciplinary courses the methods of tackling the challenges have included integration of research knowledge into design work, user driven and emphatic approaches, and promoting interdisciplinary and creative co-designing with design thinking processes.
2.Growth model pairing design with circular economy

Figure 1. The Sustainable Growth Model for Lahti by Design in the Lahti University of Applied Sciences.
The Lahti University of Applied Sciences has ratifyed with the Ministry of Culture and Education a Lahti Growth model. This model is joining together the regionally significant hub for design competence and the committed development of circular economy solutions related to the regional agreement to be in the forefront of circular economy development as an answer to the major sustainability challenges societies have to solve. The pairing of design efforts with ecological sustainability solutions is the basis for the regional growth model suggesting that design can be used as the means to tackle even the strategic level challenges.
At the same time when this strategic plan for the pairing of design and circular economy has been launched Lahti Design Institute is running a national level creative industries project Design or die. This project investigates the appropriation of design thinking and design capabilities in business based and public sector innovation challenges and strategic planning. The project aims to renew design education and promote cross-disciplinary efforts and solutions in design with close relationship to the needs of businesses and work life organizations support the activities of paring the design efforts with circular economy since there aims are especially relevant in design for circular economy solutions.
The growth possibilities in circular economy according to Lacy and Rutqvist (2015, 30) point to eliminating waste in society with the elimination of wasted resources, capacity, lifecycles and embedded values. All of these eliminations demands changes of human behavior across the material lifecycles in production and consumption.
In integrating circular economy challenges into design courses the relevant content for Sustainability by Design Actions has been found via funded Research and Development projects form different fields of society. The typical ones connected to production side have been related to product development from biobased materials but even this design sector has been naturally involved into looking at how to design products from the new renwable materials that are desirable for the consumers. Many of the other projects concentrate on consumer user side of the production – consumption process and the bahaviour change required there. These kinds of proejcts have included
Information and Systems Design for renewable energy
Developing the recycling possibilities by design
Activating people to lower consumption
Developing solutions for Better Urban Living and Wellbeing
Public transportation Systems Design
This paper points out to one of the important phenomenon in the circular economy solutions. It is the emerging demand for the solutions that promote user consumer behavior change. This challenge requires new emphasis for design education in guiding students with solving this behavior change promotion instead of designing concrete products. The case examples presented with closer analysis in this paper are related to renewable energy information design, preowned product recycling possibilities and sustainable urban living withpublic transportation systems design.
3.Design for behaviour change
The circular economy solutions require designing tools for behavior change or for interactions and services instead of designing mere products. Design theory and studies have taken two paths to pursue user driven environmental sustainability. One path tries to enhance the performance of existing products and behavior related to them. The other path tackles sustainable lifestyle solutions that can be co-created with various stakeholders. The last approach especially embraces the possibilities of products as a service, service systems and other dematerialization type of solutions. (Doordan 2013, 60; Chick and Micklethwaite 2011, 118-137). Doordan (2013, 68) reminds how sectorial advances often fail to address systemic problems. The systems orientated design theory suggest that not only sectorial solutions are enough but systems require redesign.
The product based approaches often try to diminish the harmful impacts or too much resource use during the consumer use phase typically with the products that require the use of energy or water. The design aims at modifying the products so that the user would not behave wastefully (e.g. Cor and Zwolinskia 2014; Sohn and Nam 2015). Many Design for Sustainable Behaviour or Design for Behaviour Change studies have focused on this functional use phase usability type of approach with products. Such means as affordances, cues for acting in a certain way and adding information and feedback for the user can be found from these sources. In addition, the environmental psychology based approaches have considered the infra of the environment.
There has been also studies including testing with users of the impact with the proposed measures (Montazeri 2013). With these interventions the results from the user testing have not been exactly what the designers expected. (Cor and Zwolinski 2014; Sohn and Nam 2015) This proves more of the user research in the beginning of the processes would be beneficial. In the Lockton et al. (2013, 44) conducted user study of the interaction with in the office heating the result was that weather there was a sustainable heating behavior framing with usability changes in products or with supporting services it provided equal availability for changing user behavior into green direction. Many sustainable development related research centers have indeed advocated going beyond the products as the means for promoting sustainable consumption. They try to study and develop how an integrated mix of products and services together are able to satisfy customer demands.
The consumer research field has also been active in trying to study the consumer practices around ecological consumtion. The fndings typically reveal hindrances with time issues, knowledge, availability, price, family pressures, habits, social norms and concrete infra related restrictions explaining the typical attitude – behavior gap with green behavior (e.g. Gleim et al. 2013; Young et al. 2010). Values and attitudes are positive for ecological sustainability to more and more people but busy everyday activities are pressuring and guilt avoidance typical preventing the values and attitudes to come true in real life activities. The promotion of green behavior collides with more pressuring and selfish interests of building your own identity, health, food, family and social relationships. The user and consumer research about green behavior hindrances points out that from the the user perspective the need is for service thinking based solutions, where the findability and availability of the offering amongst the everyday activities and close interests is essential.
Product-service system (PSS) was defined in the United Nations Environment Programme 2009. The system design for eco-efficiency is about system of products and services that are together able to fulfil a particular customer demand based on the interactions of stakeholders. In the satisfaction-based economic model the need is fulfilled together with products, services and stakeholder interaction not by selling or using mere products. (Vezzoli 2013, 276-277) The possibilities for effcient operation of products, upgrading and availability as a shared resource can diminish the amount of material resources required. (Ryan 2013, 410-411) So Design for Sustainability is moving from the superior environmental performance seeking products to radical systems designs consisting of product service systems or even mere services.
Analysis extracted from green action supporting solutions by Lockton et al. (2013, 46-47) demonstrated ‘social proof’ as people follow other peoples’actions and recommendations. Green activities supporting issues include selfimage, getting things done, seeing results, being normal, easing guilt, getting reward, and personal interests with health improvement. So research is suggesting using several incentives and barrier removals simultaneously when trying to design the positive solutions and supporting the long term consumer use with them.
Also emotional design with goals for desirability and attachment is important in green design. Ecological choices are not based mostly on rational arguments but even more on emotional feel issues (Tan and Johnstone 2011, 5). Design is about branding and providing immaterial, emotional-cultural value with the offerings. It seems that appealing to people’s innermost desires is a more effective means of behaviour change than the negative information campaigns. Desirability calls for social marketing based on positive appeals related to subjective well-being and selffulfilment, and not on tactics of scaringpeople and presenting dull educational campaigns. (Muratovski 2013, 178). Effective communication is vital to make sustainable offering appealing with “what’s in it for me” type of issues rather than with altruism or responsibility.
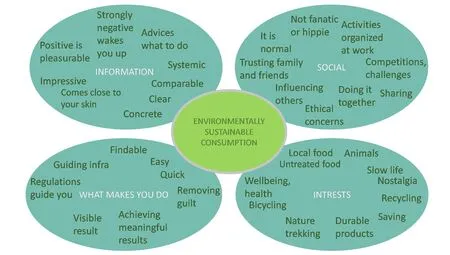
Figure 2. The map of issues promoting ecological behavior change.

Figure 3. Example poster made by Media content design –student Iiro Piipponen about Bio-gas production potential on horse farms.
Mackenzie (2013, 171-172) states that green marketing and eco-design have been unable to offer consumers benefits that consumer would find relevant, motivating or normal. Green offerings should be presented in a way that address powerful and universally important lower level of needs, such as security, health, family, friendship and peer comparison. Initializing change from the points of view that are interesting for the user are appropriating user willingness. Design projects can appropriate a wide spectrum of means to use for environmentally positive behavior change including the means to cross over the everyday barriers and habits and to provide emotional-social relationships with the design of suitable services and system solutions, not by designing mere products.
A Finnish user research 2013-2014 collected issues important for promoting ecologically sustainable behavior change to provide information for user driven ecological solution design. The research was sourcing this information from 76 visual stimulus based interviews. The research results map presents the felds of information, promoting doing, social interaction and interests to clarify how to prevent hindrances for green consumption change and how to support it and make it interesting. (K?lvi?inen 2015, 43)
4.Information Design based projects
The problem how to promote change in systems and behaviors to the sustainable direction lies often in not understanding the related information and processes in a concrete or systemic way. Information design can provide user tools for this.
In one of the projects providing information design solutions the aim has been to promote the communication of renewable energy production possibilities for the residents in the rural areas of Finland. The the year 2016 launched InforME project designs for crossing the gap from energy research information into practice so that the countryside residents would understand how they can produce renewable energy by using the side streams for renewable energy production.
The energy researchers have aimed to produce simple and comparable information for the designers to build it to different communication forms for ease of understanding and acting for the intended rural audience. The information design has been for the purpose of guiding the countryside residents how to consider and choose to apply in practice the different options in their own renewable energy production. The design work has been executed in the information design projects of the Lahti design Institute visualization courses.
The first material produced concerned the use of horse manure for biogas production and as a suitable fertilizer for crops. The material will be tested in the local rural area development meetings with countryside residents and SME:s. Also a wider, Internet based calculator with possibilities to count and compare the investments and saving with different energy solutions will be built with the design task to create the easily usable user interface and interactions.
Information concerning renewable energy is often complex and troublesome both for the designer to visualize and to the audience to understand and compare. Itusually includes convoluted information from production and consumption sequences affected by many variables. Furthermore in information design, knowledge of the needs of the audience group is relevant already in the beginning of the information concretization process (Lipton, 2007). In this project this understanding was provided by the Pro Agria national rural development company with the expertize on the needs and understanding of the rural residents.

Figure 4. An image collection from the horse manure based animation image library, that has been created for the effcient and collaborative production purposes.
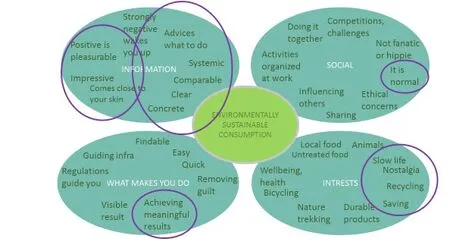
Figure 5. Renewable energy information design in relation to possibilities of behavior change.
Data visualization can be produced by static images or using linear storytelling and interactive solutions with digital media. The information design process should, of course, concentrate on utilizing facilities of the selected media and format. For example, storytelling type of data handing is important in an animation type of audio visual products and sorting or presentation methods in an interactive application.
Information design with research data requires data wrangling as a process where raw data is sorted and cleaned into a usable form. It is a transformation process that enables data for analysis and findings and in the design case for concretizations and visualizations. In-depth sorting and evaluating usability of the data should be accomplished before starting the analysis (Kandel et al. 2011). There might be a need to iterate and look or collect raw data again during the wrangling process for specific visualization types. The specifications for a presenting media should be considered already during the data analysis. The process of information design requires that the researchers and the designers collaborate during the data wrangling. Designing of the visualizations is possible to begin before data analysis is fully done but constant checking of the content is required until the data analysis is complete. (Lipton, 2007)
The research results of energy production possibilities on Finnish horse farms were produced to different forms of visualizations from the given data. The interplay between energy specialists and design students produced an interesting learning environment. The observations from this process revealed that both information design experts and energy specialists led process is essential for the informative visualization outcome. It was important that the students were able to check facts, ideas and completed visualizations quickly with the energy experts. Using a full range of skills and abilities from both research and design directions during the visualization process is the prerequisite for producing reliable, useful and informative visualizations.
Both static posters and 2d- and 3d-animations with a storyline were produced form the material.
The different forms of visualizations allowed the comparison of the different media types as a tool for information carries in the case for renewable energy information. With the static presentations the complexity of the data and stakeholders cause challenges. With animations the processes of the energy sources and production are easily described but this demands not only data but creating scripts for the storylines. Linear working pipeline is inflexible and animation processes are resource consuming. For the last challenge a separately stored cleaned files for reusable characters and style were created as an asset for further productions and for marketing materials for the project. The made productions have been based on creating better tools and pre-sets for improving the production economy. This enables the idea that other designers, or in this case especially design students, can continue to work with the fles in the future. As a design learning idea this promotes the designer role not as an individual creator butas a team player in the bigger information visualisations projects. The project will also continue with audience user feedback so that the messages can be designed better after collecting and analysing experiences and feedback. The economical animation project model enables, for example, analysis between different animation versions after testing.
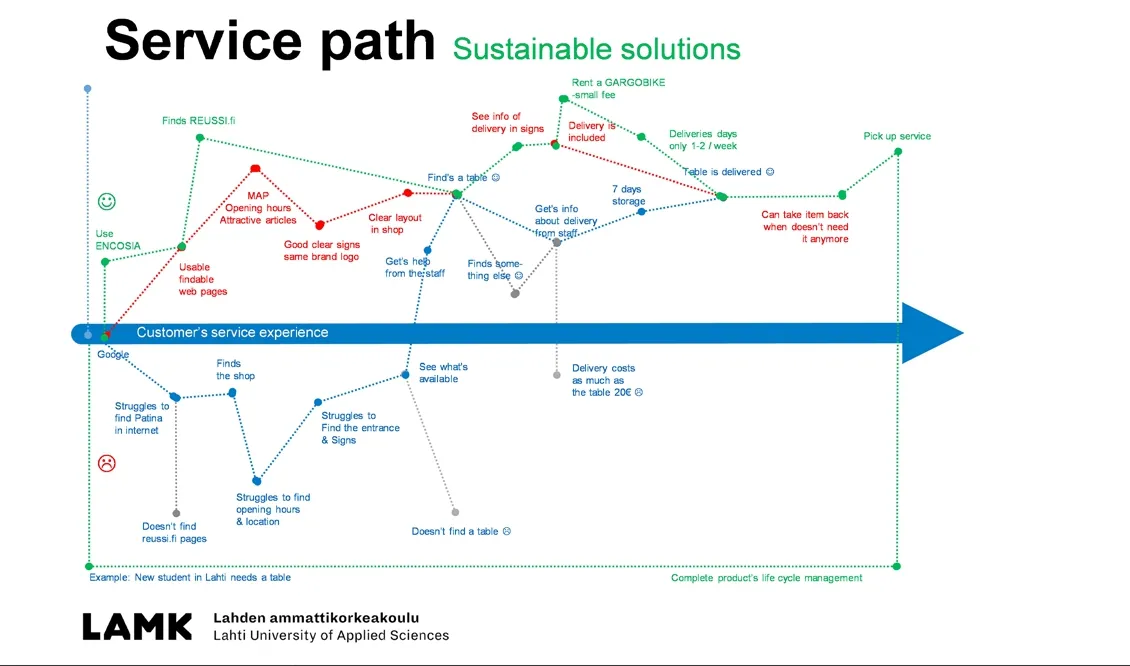
Figure 6. Student work example from the sustainable design course: User trip reveiling negative service moments and user driven service path making the moments positive. Service design for the city recycle centre, Flea market shopping experience made easy without a private car ownership.
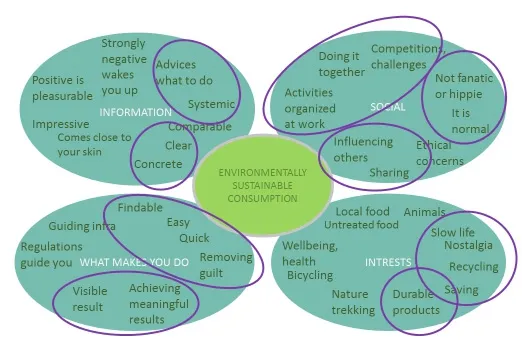
Figure 7. Recycling process development results refected on the map of issues important in designing for ecologicalbehavior change.
When considering the effects of this information design for renewable energy production the effects of the combined research and design work can be mirrored on the map of issues important in designing for ecological behavior change. Naturally the most impact with information design is on the various issues of the information sector. The information can also carry out communication about the social normality, personal interests for savings and feelings of meaningfulness achieved through the actions made in producing renewable energy. When discussing about the nature of the renewable energy production in the countryside the image of the activities also reminds of the kind of nostalgic, historical situation where everything in the production and from waste was used and recycled as much as possible.
5.Recycling based services development
The cross-disciplinary sustainable design MA course studies during the years 2015-2016 have focused on the circular economy recycle, reuse and repurposing feld considering the activities of the Lahti city based and owned Work’s place organisation (http://www.lahdenpaikka.fi/), that owns consumer products related recycling operation and does rehabilitation work for people in unfortunate circumstances. The K?lvi?inen (2015) user research findings and related advice materials have been appropriated as the starting point for this work with cross-disciplinary student groups including design, media, engineering and business students. The sustainable design workshops for recycling services have been conducted by using the user research fndings and from that produced guidelines together with service design tools since the user research results indicate that service based thinking is important for the consumer users.
Circular economy models promoting the multiplication of use circles also in the use phase cherishes reusing, repairing, reselling, reallocating, redesigning and repurposing services. Supporting platforms such as Ebay advertise themselves as advocates of this kind of sustainability with phrases such as: “The most ecological product is the one never made.” Ebay types of platforms support and enable the reselling of the already existing products to further use even multible times.
In the recycle case one solution applying the user driven spirit was the redesign of the Work’s place city centre fea market service from the user customer point of view. The service was redesigned via user trip activity that was looking at the service path and the touchpoints in it trying to figure out how the negative touchpoints can be transformed into positive ones. The new service path was also created in a waythat it allows the customer to use it without your own car. The before the physical core service stage activity was secured with a possibility of checking the available pre-used products from the Internet based e-library. The solution also provided the post service possibility of returning the utensil back with a small reward after the customer’s need for it ended. This emphasized the efficient product capacity use and further sharing of product capacity.
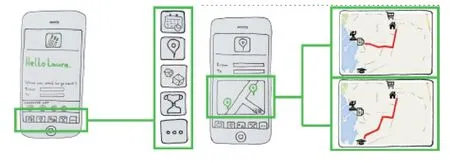
Figure 8. Crude visualizations for the application by Pilssari & Severi 2016 as examples of the concrete making part of the solution creation process.
The further work for the Work’s place solutions reached a wide scope of activities and geographical reach in collecting, repairing and using the preowned products. Also for these solutions the user driven information was used as a starting point and emphatic user analyses provided understandable innovation platform for the cross-disciplinary development. An example of an emphatic solution included a renting station for private people, small businesses, schools and kindergartens to accommodate these kind of customers and actors extra and occasional needs for utensils without buying their own ones. This solution was once again adding the product capacity appropriation and sharing perspective to the real user needs.
Different types of repair possibilities and social activism were also considered. Repair yourself with help services included a Repair (Family) Café idea with a free meeting place for repairing things together. The Café would provide tools, materials and elderly expert volunteers to support the repair work. For the volunteers it would provide a social meeting place to enjoy a cup of tea or coffee and help others. This was an idea created through the user analysis since the retired elderly people often have more craft skills than the younger ones and they might have extra time and need for social meeting points. These design ideas follow Manzini and Tassinari (2013, 224) suggestions of enabling systems for supporting activism such as sets of products, services and communication to improve accessibility, effectiveness, and reliability of a collaborative organization. They also mention the importance of support from the flexible spaces that can be used by communities for mixed public-private functions and logistic services to support new producer-consumer networks. In this case the student work further considered also repair and reuse possibilities with traditional Repair Service and Design Services for redesign and repurposing against fees.
Further social ideas with promoting the reuse of products included a spectrum of happenings such as recycle evens for schools, kindergartens, seniors and other groups to activate people for recycling and repairing more stuff. Also specifc company recycle and repair events by order and for a fee were suggested. For the rehabilitation clients in the Work’s Place there was a plan to construct their special skill profles to the web pages so that it would be easy to order one of them as a home help for small repair tasks and at the same time offer possibilities for them to fnd working opportunities.
Also a Pop up container and route plan for this was created for collecting the proper and usable products that consumers did not need any more. The Work’s Place had a container in a remote Garbage station but the moving Pop up solution was created to follow the idea that sustainable solutions should be taken to the easy reach for people: to suburbs, marketplaces and town squares so that they are accessible even without a car. The Pop up container would be a demonstration to make Work’ place recycle activities more visible to citizens and bring the recycle activity close to living areas and everyday life. It would also provide an ordering service against fee when somebody needed it for special occasions: happenings, fairs or company events. The idea was further that the mobile pop up container would be a marketing tool for advertising the possibilities of purchasing the preowned products.
Another way of gathering the unused products from homes or offces was an idea about a house cleaning service. This could mean a total house or fat clear-out against a fee with stuff separation to reusable, reparable and waste materials. The intended clients were analysed as people selling their house or moving to another, elderly people and they relatives when the elderly needed to move to a senior house or relatives facing the house cleaning task in the case of death.
When considering the effects of recycling solutions on the map of issues important in designing for ecological behavior change there are several sectors that are tackled. With information issues such as clear and advising what to do information was considered. In use sense easily findable and usable solutions have been suggested. The solutions with recycling provide visible and meaningful result with capabilities of removing guilt. Also socially active, normal, sharing and ethical solutions have been considered. Promoting recycling provides naturally important notions of the importance of product durability, savings and nostalgic lifestyle where the disposal of products is slowed down with sharing, reselling, reuse and repair activities.
6.Interdisciplinary co-designing for Urban Living and Transportation
The Summer School 2016 appropriated cross-disciplinary learning activities with design thinking process for circular economy solutions. This Lahti University of Applied Sciences Summer School consisted of different challenges about Better Urban Living and Wellbeing. The case for public transportation and vistors bus travel experience provides possibilities to look at the learning structure of design thinking as co-design and especially creativity enabling activity (Nylander, Gong and Kretschme 2016).
In the summer school type of studies guiding non-design students to think and act as designers in a short project was challenging with such demands as holistic and creative thinking and rough prototyping. A major challenge was to promote the team members’ creativity to come up with innovative solutions to complex real-life problems especially as they were typically used to logical solution building. To overcome these challenges the projects were managed so that a common framework design thinking methodology for each project was built to enable creative team work and collaboration and to define project briefs. (Nylander, Gong and Kretschme 2016)
Especially the project around public transportation design and new possibilities of remaking the bus travel experience offered a platform to look at the learning process for this creative co-design with illdefined problems. The client was Lahti Region Transport (LSL) who runs public transport services within the region of Lahti with eight other stakeholders. The aim in this producer network was to search for user driven service ideas and improvements. A challenge with a network of production stakeholders is always in creating a joint new user driven vision and how to communicate this new vision to all the stakeholders.
In the beginning of the summer school the students gained understanding of design thinking as a holistic process that includes human, business and technological factors in the forming and solving of problems. This approach enabled to integrate the social sciences, engineering and business expertise. (Plattner, Meinel & Leifer 2011.) Furthermore the Manzini & Vezzoli (2003, 851) based notion was brought out, that the design of a context related systems of products and services that are able to satisfy customer needs, rather than the design of products, is strategically the most effcient.
Even with the complex and uncertain fuzzy front end a clearly structured process with different stages, gates, and refection helps the cross-disciplinary team. Allocating the stages of a Design-Thinking process to the project was beneficial. Stages such as Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test gave necessary structure especially to the inexperienced team members. (Nylander, Gong and Kretschme 2016) In the specific Experience-Travel-Project, the Test-stage was left out in the Summer School course due to the short time-frame.
The working process of creating a better service experience for public transportation began with the public transportation societal context where students gathered understanding of the economic, energy and environmental benefits of public transportation, common fare cards, passenger routes, timetables and related information systems. Interviews with client organization revealed the producer observations about the service challenges. Empathize stage concerning the bus travel users followed so that the project team of university students from diverse countries and fields of study did some firsthand brainstorming about the possible customer needs. Then practical user studies were conducted with the non-Lahti resident travellers to obtain firsthand information from the users about the real reasons that were the obstacles on having a great travel experience. The methods used were mystery shopping observation to create empathy towards users of the service and experiencing the travel situation oneself. Bus trips were taken and information shown on the bus stops and in the bus was documented by photographing it for user experience discussion. These methods helped to provide rich and emphatic understanding about existing problems and possibilities within the LSL services.
The research information and visualizations were printed and the information classified to get some pattern and inspiration. By visualizing and organizing the answers it become concrete what the possible visiting users think about the public transportation, and what they care about. Emphatic, feeling based and visual research led into diversity of solutions, richer than the mere functional and rational analysis would have led to. Also an ideation about the further possibilities to create an emotional link to the service was inspired by the emphatic design thinking process.
The main results of the project were an application software suggestion and some service scenarios for LSL for providingsatisfying services and an emotional service connection with visiting students as customers. The Application concept supported both people who come to visit Lahti for the first time and local people to orientate and plan their trip, and to make their trip easier by providing all the necessary information before and during the trip. Another concept was to incorporate games within the LSL services in order to advertise LSL buses to the students, get them motivated to take buses and also to make the bus journey enjoyable. The idea was also to provide engaging interactions, collaboration and feedback with the help of the games combining prizes to be won from the gaming activities such as getting discounts on bus tickets, food stores or clothing stores or even winning a free bus ticket. With collaborative student events and contests the idea was to provide positive experience based information and advertising possibilities for LSL services. Also memorable visualizations were suggested for the LSL bus stops and environments to make sure that the cusotmers will remember and be pleased about the Lahti’s public transportation.
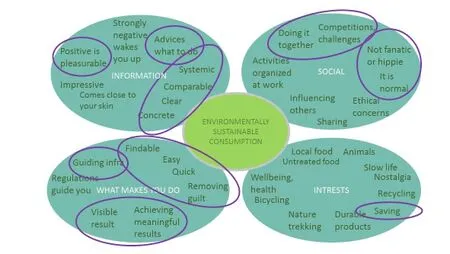
Figure 9. Transportation service design solutions mirrored to the map for issues inecological behavior change.
The last stage of the design thinking process in the public transportation case emphasized how concretizing also the concepts with crude visual prototypes is important. Even if the use context and user experience are researched, the information is never totally covering. The creation of concepts and imperfect or unfinished prototypes is one means to encourage creation in an uncertain situation. The solutions build the understanding about the felds of possibilities and problems and help learning about the optimal and production ft solutions.
Also this user driven transportation system design provides important solutions for ecological behavior change. Communication issues such as clear and easily obtainable information and advise information of what to do were considered with the solutions. In use sense easily findable and usable solutions have been suggested. The engaging and social side of solutions was also covered well in the concepts created with the help of emphatic and cross-disciplinary design thinking process.
7.Conclusions
In all of the presented design project cases even more issues of green behavior change can be added to the list to be achieved through user driven design process and through various ways of interacting with research and collaborative cross-disciplinary work. This requires and is made possible by appropriating user driven and emphatic design process, research knowledge integration, systemic thinking, and collaborative aspects in design education. For tackling the societal challenges information such as user behavior, emotional user experience, sustainable energy, sustainable material techniques, recycling business and transportation logistics needs to be integrated into the design process and combined in synthetic and systems producing way. The outcomes of design and the meaning of design in these projects require rethinking as they are often something else than the concrete products. Methods for information design, systems analysis, user driven design and co-design become the core of the process instead of concrete product development methods when sustainability has to be defeated by designing services and systems for enabling behavior change.
(責(zé)任編輯 童永生)
Chick, A. – Micklethwaite, P. 2011. Design for Sustainable Change. How design and designers can drive thesustainability agenda. AVA Publishing SA.
Cor, E. – Zwolinski, P. 2014. A procedure to define the best design intervention strategy on a product for a sustainable behavior of the user. 21st Conference on Life Cycle Engineering. Procedia CIRP 15 (2014) pp. 425-430.
Doordan, D. P. 2013. Developing Theories for Sustainable Design. In The Handbook of Design for Sustainability. Eds. Stuart Walker and Jacques Giard. Bloomsbury Publishing Pld. London, New York, pp. 57-72.
Gleim, M. R., Smith, J.S., Andrews, D. & Cronin, J. J. Jr. 2013. Against the Green: A Multi-method Examination of the Barriers to Green Consumption. Journal of Retailing 89 (1, 2013), pp. 44–61.
Kandel, S. – Heer, J. - Plaisant, C. - Kennedy, J. - van Ham, F. - Riche, N. H. - Weaver, C.- Lee, B. - Brodbeck, D.– Buono, P. 2011. Research Directions in Data Wrangling: Visualizations and Transformations for Usable and Credible Data, Information Visualization Journal, 10(4), pp. 271–288.
K?lvi?inen, M. 2015. K?ytt?j?tietoa ymp?rist?my?t?isen muotoilun l?ht?kohdaksi. In Ymp?rist?my?t?ist? arkik?ytt??n. Editor Kristiina Soini-Salomaa. Lahti University of Applied Sciences Publications 13. pp. 27-47.
Lacy, P. - Rutqvist, J. 2015. Waste to Wealth. The Circular Economy Advantage. Palgrave Macmillan.
Lipton, R. (2007). The Practical Guide to Information Design. John Wiley & Sons.
Lockton, D. – Harrison, D.J. – Cain, R. – Stanton, N.A. – Jennings, P. 2013. Exploring Problem-framing through Behavioural Heuristics. International Journal of Design Vol. 7 No. 1 2013. 37-53.
Manzini, E. – Tassinari, V. 2013. Sustainable qualities. Powerful drivers of social change. In Motivating Change. Sustainable Design and Behaviour in the Built Environment. Robert Crocker and Steffen Lehmann Eds. Earthscan/ Routledge (Oxon UK, New York US.) pp.217-232
Manzini, E., and C. Vezzoli. 2003. A Strategic Design Approach to Develop Sustainable Product Service Systems: Examples Taken from the ‘environmentally Friendly Innovation’ Italian Prize. Journal of Cleaner Production 11/8, pp. 851-57.
Montazeri, S. 2013. Design for Behavior Change: The Role of Product Visual Aesthetics in Promoting Sustainable Behavior. A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Design Science) in the University of Michigan 2013.
Nylander, N., Gong, M. and Kretschme, M. 2016. Creativity Enabling for a Mixture Team by Design Thinking. Summer School 2016: Co-designing Better Urban Living and Wellbeing. Editor Sari Horn. The publication series of Lahti University of Applied Sciences 28. Lahti, pp. 69 -73.
Plattner, H., Meinel, C. and Leifer, L. 2011. Design Thinking: Understand - Improve - Apply (Understanding Innovation). Berlin. Springer.
Ryan, C. 2013. Critical Agendas: Designing for Sustainability from Products to Systems. In the Handbook of Design for Sustainability. Eds. Stuart Walker and Jacques Giard. Bloomsbury Publishing Pld. London, New York, pp. 408-427.
Sohn, M. – Nam, T-J. 2015. Understanding the attributes of product intervention for the promotion of proenvironmental behavior. A framework and its effect on immediate user reactions. international Journal of Design, 9(2), pp. 55-77.
Vezzoli, C. 2013. System design for sustainability. The challenge of behavior change. In Motivating Change. Sustainable Design and Behaviour in the Built Environment. Robert Crocker and Steffen Lehmann Eds. Earthscan/Routledge (Oxon UK, New York US.)pp. 276-290.
Young, W., Hwang, K., McDonald, S. & Oates, C. J. 2010. Sustainable consumption: green consumer behavior when purchasing products. Sustainable Development, Volume 18, Issue 1, January/ February 2010, pp. 20–31.
10.3969/J.ISSN.1674-4187.22017.03.012

