Flexural-gravity wave resistances due to a moving point source on 2-D infinite floating beam *
Ji-suo Li (李繼鎖), Dong-qiang Lu (盧東強(qiáng)),2,3
1. Shanghai Institute of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China,E-mail: jsli_shu@yeah.net
2. State Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Engineering Simulation and Safety, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072,China
3. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Mechanics in Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China
Introduction
A very large floating structures (VLFS) is often used as an aircraft runway or a wind turbine power plant in the ocean engineering. VLFS has two basic hull types: the pontoon-type and the semi-submersible-type[1]. In the present work, we consider the pontoon-type VLFS only. In order to estimate operational safety, we need a theory to describe the wave resistance due to a moving load on the VLFS. A useful model is to idealize VLFS as a thin viscoelastic plate and the water as an inviscid incompressible fluid[2,3]. The vehicles and aircrafts on the VLFS can be modeled as a surface-moving source, which is associated with the Dirac delta function[2,4-6]. It has been demonstrated that this physical model provides possibility to get analytical solutions.
The wave resistance for a moving load has been a topic of interest. The generation of capillary-gravity waves due to a concentrated load was well studied in last decades. Applying the method of the Fourier integral transform and the stationary phase method,Raphael and De Gennes[7]derived the capillarygravity wave resistance equation for the source speed U larger than the minimal phase speedminc . Rather than assuming the fluid to be inviscid, Richard and Raphael[8]studied the effect of viscosity on the capillary-gravity wave resistance for the uniform velocity, and found that the wave resistance remains bounded as U approachesminc , unlike the prediction by the inviscid theory. A non-straight motion source was recently studied by Chepelianskii et al.[9]who investigated theoretically and experimentally the capillary-gravity wave resistance created by a small steel needle moving at the water-air interface along a circular trajectory, and demonstrated no critical velocity exists for a steady circular motion. The finite wave resistance exists even for U <cmin, and the similar phenomena was also found by Closa et al.[10]who investigated a load with accelerated and decelerated rectilinear motions.
All the above-mentioned work is concerned with capillary-gravity waves. As is well known, the flexural- and capillary-gravity waves have some similar characteristics in view of their dispersion relation.So the flexural-gravity wave resistance can be studied like the capillary-gravity one[11]. A well-known monograph by Squire et al.[12]was devoted to the rich topic of moving sources on the thin plate. Davys et al.[5]studied the wave patterns caused by a steadily moving point source, and found that the short-wavelength elastic waves propagate ahead while the long gravity waves appear behind. A further investigation was conducted by Schulkeset al.[13]who considered the effects of a lateral stress imposed on the plate, a uniform flow in the underlying water and the stratification of the underlying water. It showed that the internal wave remains a variety of wave patterns in a two-layer model and the laminar water increases the wave resistance. Yeung and Kim[14]studied the effects of a translating load on a plate, and found the transition of the drag near the critical speed. For a thin viscoelastic plate, Hosking et al.[2]investigated dynamic response of the plate to a steady moving source with a two-parameter memory function to express the viscoelastic behavior of the plate, and concluded that a small viscoelastic dissipation produces a lag behind the load. More complicated physical model was studied by Wang et al.[6]who derived the timedependent response of a viscoelastic plate to an impulsively started moving load. For the viscoelastic thin plate model, Kozin and Pogorelova[15]studied the linear Maxwell and Kelvin-Voigt models, and a generalized Maxwell-Kelvin model, concluding the calculate results agree with the experimental ones.Matiushinaet al.[16]analyzed the deflections of the ice cover during the landing of the airplane. Recently, Lu and Zhang[17]provided the analytical solutions of the flexural-gravity wave resistance due to a surfacemoving line source on a thin elastic plate.
There are many other researchers who investigated the flexural-gravity wave due to a surfacemoving source on a fluid covered by a thin plate. But most of their investigations were just concentrated on the wave profile. A major motivation for this study is that some features of the flexural-gravity wave has not been satisfactorily described by the elastic theory,such as the lag position of maximum depression behind the source[18]. The flexural-gravity wave resistance due to a moving load on an inviscid fluid covered by VLFS are studied in this paper. The moving load and VLFS are simulated by concentrated line source and a thin viscoelastic plate, respectively.The deflection of VLFS is described by the linear equation of thin viscoelastic plate, and the Kelvin-Voigt model is chosen to describe this viscoelastic plate. In order to make our calculation more precise,we consider two types of motion for the moving load,namely a uniform straight motion and an accelerated straight motion. By applying the method of the Fourier transform, the integral solutions for the surface deflections and the flexural-gravity wave resistances are obtained. In order to analyze the dynamic characteristics of the flexural-gravity waves,the asymptotic representation for the uniform straight motion is explicitly obtained by the residue theorem.With the method of stationary phase, the corresponding asymptotic solutions are derived for large time during the accelerated straight motion.
1. Mathematical formulation
The infinite homogenous viscoelastic plate floating on the fluid is investigated. The fluid is assumed to be incompressible, inviscid and the motion be irrotational. Let d andeρ denote the thickness and density of the plate, respectively. The -xaxis coincides with the plate-water interface while the -zaxis points upwards. The undisturbed fluid surface is at z = 0 and the impenetrable bed is at z = - H , as shown in Fig.1.
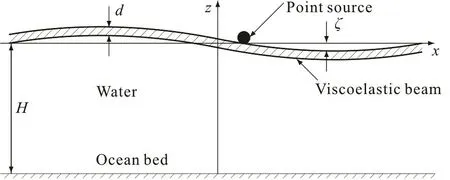
Fig.1 A single fluid of finite depth covered by an infinite viscoelastic beam
Let (,,)x z tφ represent the water velocity potential, then the governing equation satisfy the Laplace equation

For the ocean of finite depth, the boundary condition at the no-permeability bottom is given by


Let ζ(x, t) represent the vertical deflection of the thin plate subjected to a downward external load- Pext(x, t ). The period of the flexural-gravity wave is assumed to be much smaller than the relation time of plate. Thus the VLFSis modeled by athin viscoelasticplate. Following ,we usea linearretarded elastic Kelvin-Voigt medium to describe the thin viscoelastic plate. Then the linearized kinematical and dynamical conditions at z = 0 are written as
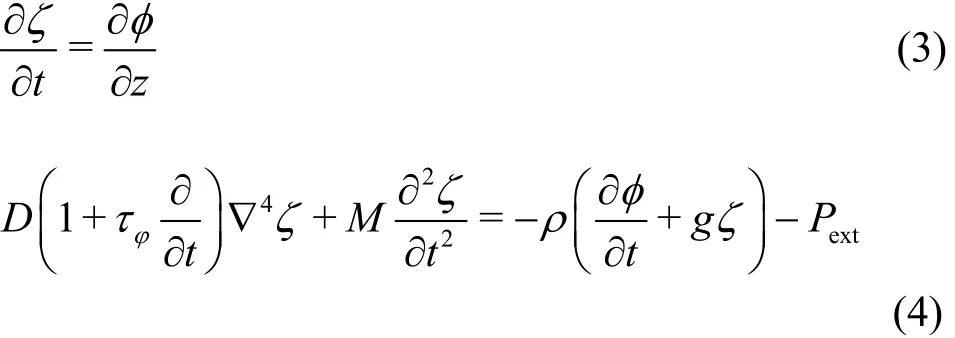
where D = Ed3/[1 2 (1-ν2)] is the flexural rigidity of the plate, E and ν are Young’s modulus and Possion’s ratio, respectively[19], ρ is the density of the fluid, τφ= η /E is the retardation time[3], η is the viscosity of the plate, M=ρed is the mass coefficient of plate. Obviously, Eq.(4) expresses the balance between the viscoelastic force and inertial force of the plate, the hydrodynamic force of the fluid and the downward external load.
In order to solve the forementioned equations, we introduce the Fourier transform
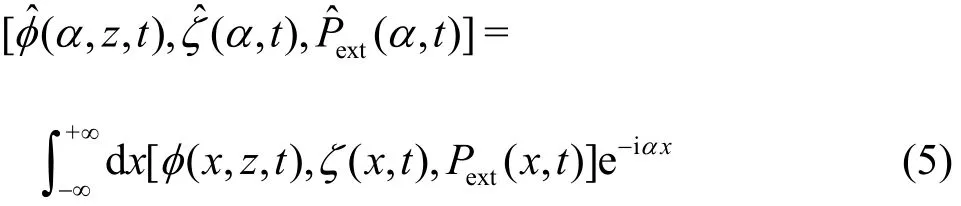
Applying the Fourier transforms to the combined equation of Eqs.(3) and (4), we can get
Obviously, Eq.(8) represents the dispersion relation between ω and k for the flexural-gravity wave motion on the elastic plate floating on an inviscid fluid.
2. Wave responses due to a steadily moving load
2.1 The ocean of finite depth
We consider a concentrated load steadily moving along a straight line with a constant speed U in the positive -xdirection[2,10,17,20]. Then the external load function reads

where δ(·) is the Dirac delta function and=. Substituting Eq.(10) into Eq.(6), we obtain the equation for the plate deflection, which can be solved by looking for the steady-state solutions with the form e-iαUt. Then the deflection function is
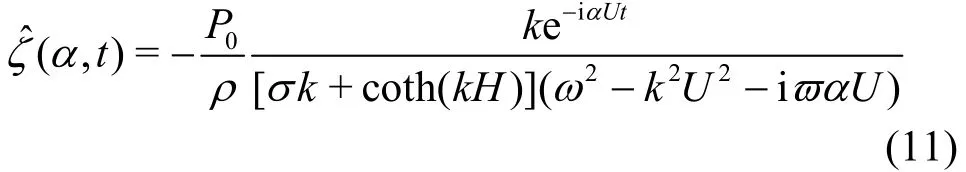
According to Kim and Webster[21], the wave resistance R on the moving load is calculated by the formula
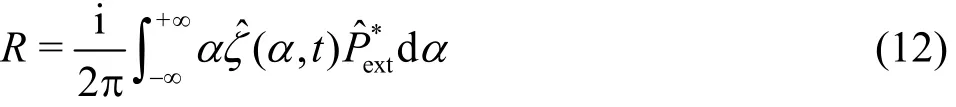
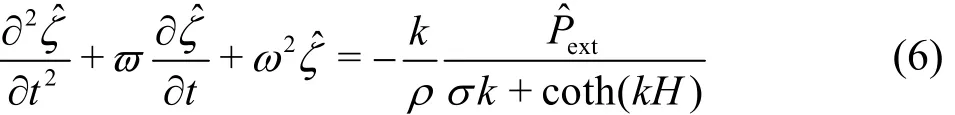
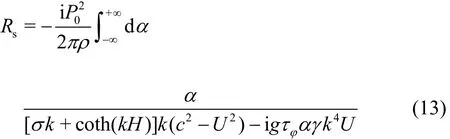
where
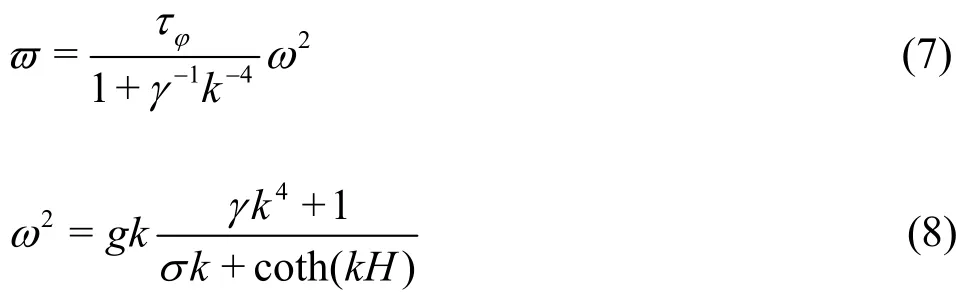
wheresR denotes the steady-state wave resistance,and =/ckω is the phase speed of the flexuralgravity wave motion on the elastic plate. For the travelling wave in the thin viscoelastic plate, the wave length is much larger than the thickness of the plate.
We assume 1kσ?, neglecting the accelerated term of the plate or 0σ→ in the following discussion[18].The wave resistance equation reduces to
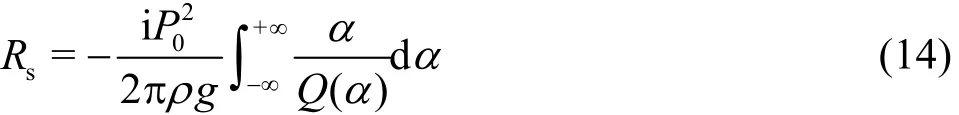
where
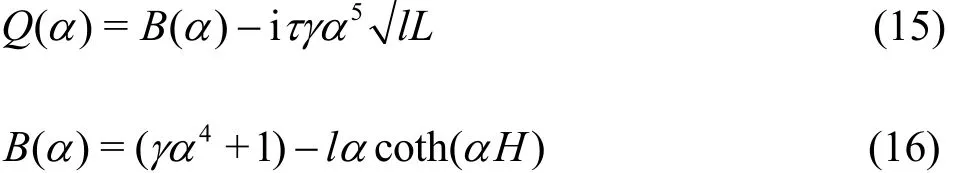
with τ = g/ Lτφ, l = U2/g and L =γ1/4
Equation (14) can be evaluated by the residue theorem. The non-dimension retardation time τ will be used as the perturbation parameter throughout the asymptotic analysis. For small τ, we assume the solution for Q (α)=0 takes the form of α=α0+iτα1, where α1is associated with the viscoelastic dissipation. Substituting α into Eq.(15), one obtains
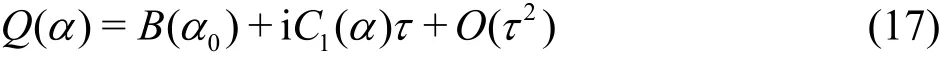
where
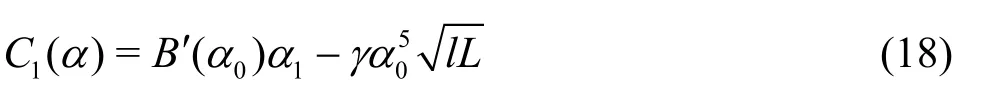
According to Lu and Zhang[17], no far-field wave exists for U <cmin. We only consider the case for U≥cmin. As>U>cmin, there are two zeros of Q(α), denoted by αp,j, which are given as
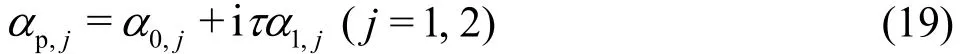
where
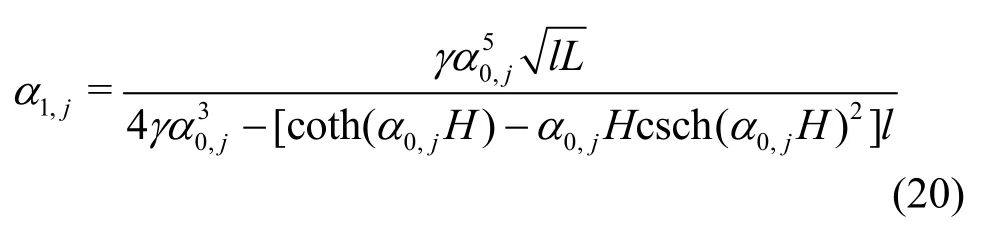

where
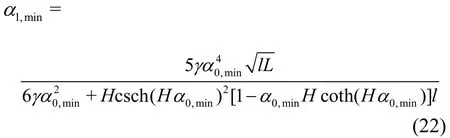
Once the zeros of ()Qαare worked out from Eq.(17), the residue theorem, according to Lighthill[22],can be used to calculate the wave resistance as follows

2.2 The ocean of infinite depth
For a finite value of H, we only have numerical solution for αp,jand αo,min. As H trends to ∞,we have exact analytical solution as follows.
When U >cmin, two real roots for B(α) = 0,denoted by α0,j, can be analytically expressed by[17]
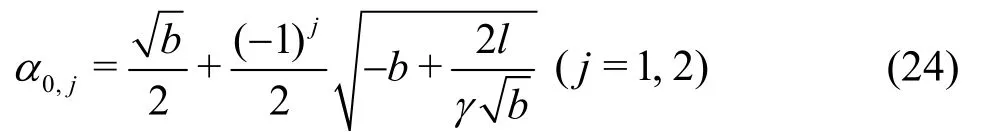
where
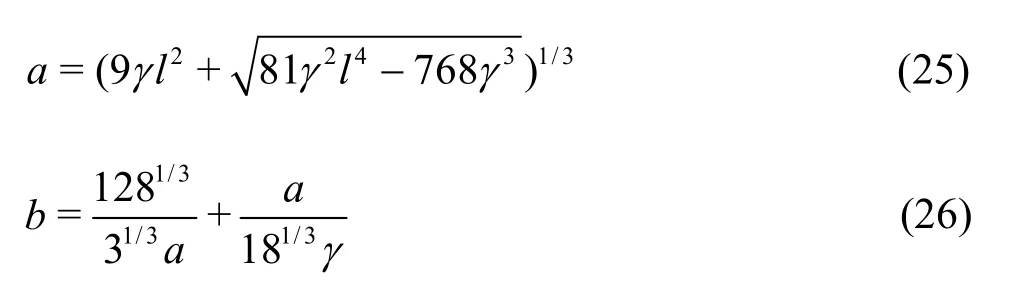
When U =cmin, there is only one real root, denoted by α =(3γ )-1/4. By substituting α into0,min0,minEq.(21), the zero point can be obtained.
A graphical representation of Eq.(23) is shown in Fig.2, for the case of infinite depth. The wave resistance due to a moving load on a fluid covered by a thin viscoelastic plate is discontinuous with U = cmin.The wave resistance is zero when U <cmin. The source speed is too small to produce the far-field wave motion[10]. As U >cmin, after the wave resistance reaches the peak of the curve and then decreases monotonously as U increases. This phenomenon is very similar to the characteristic of the capillarygravity wave resistance due to a slow moving object which was studied by Closa et al.[10]with the aid of asymptotic and numerical techniques. The dynamical similarity between the flexural- and capillary-gravity waves was studied by Lu and Dai[11]and is confirmed here for the wave resistance. Furthermore, a larger τ will produce a less wave resistance for the same speed.The effects of viscoelastic dissipation become heavy as U increases.
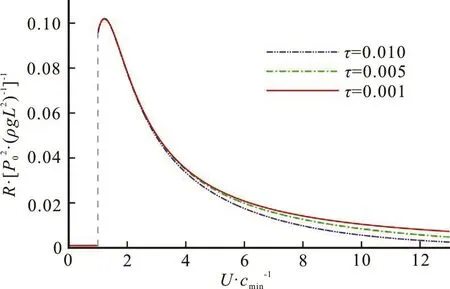
Fig.2 (Color online) Non-dimensional wave resistance R/( /ρ gL2)vs. U/ c min
3. Wave responses due to an unsteadily moving load
3.1 The ocean of finite depth
Now, we consider the case that the load moving on the viscoelastic plate is suddenly accelerated to a constant velocity U at =0t[6,10]. Accordingly the external load function reads

where H (·) is the Heaviside unit step function. We have P ?ext= P0H( t)e-iαUt.
It is assumed that there are no initial elevation or speed at the plate-fluid interface. Equation (6) is solved with the initial conditions

With the initial conditions Eq.(28), the deflection function becomes
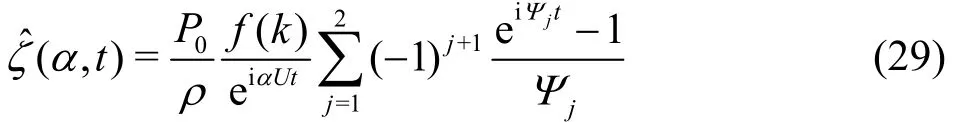
where
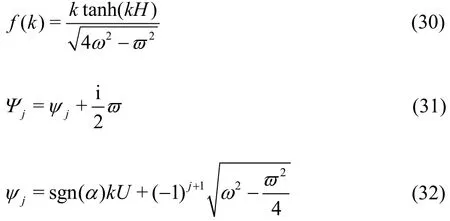
and sgn()α is the sign function of α.
By inserting Eq.(29) into Eq.(12), the wave resistance ()R t becomes

where
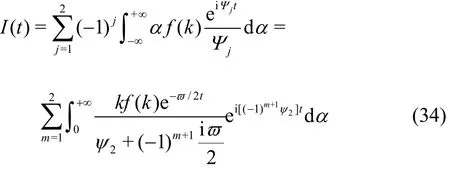
It is difficult to calculate Eq.(33) directly. We evaluate I( t) and Rsseparately. It is noted Rshas been given by Eq.(14). By applying the method of stationary phase, Eq.(34) is evaluated from the main contribution at the points of stationary phase.
For simplicity the subscript “2” in ψ2(k)is hereinafter neglected. With thephysical parameters typical givenby Squire et al.[12], E =5 GPa,ν = 0.3, d =2.5 m, H = 350 m , ρ=1024 kg/m3and ρ=917 kg/m3, a graphical representation for
ethe phase speed cand the group speed cgis shown in Fig.3, where cg= ? ω/?k. From Fig.3, we can see ψ( k ) has no stationary points when U <cgmin. ψ(k)is a monotonic decreasing function of k. It means that I( t) decays exponentially and approaches to the steady state relatively rapidly.
As U =cgmin, ψ(k) has an inflexion point at k=ks, and ψ(k) is expanded at k=ksby the Taylor series expansion[11]. For U ≈cgmin, one obtains
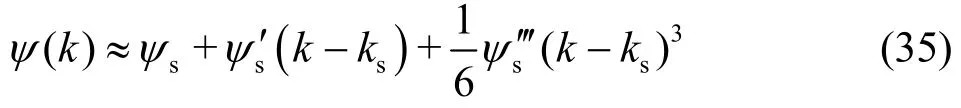
where ψs= ψ ( ks), ψs′ = ψ ′(ks) and ψs′= ψ ′(ks).By substituting Eq.(35) into Eq.(34), I( t)can be analytically expressed as
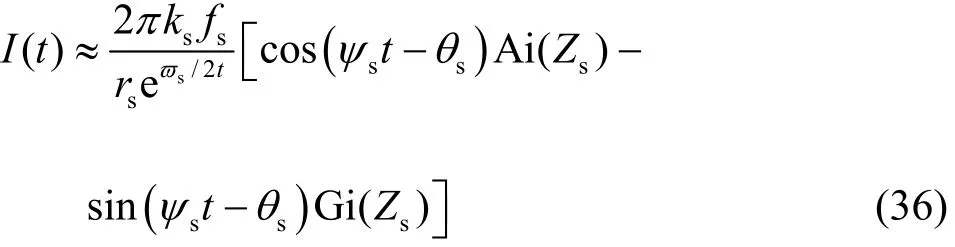
where
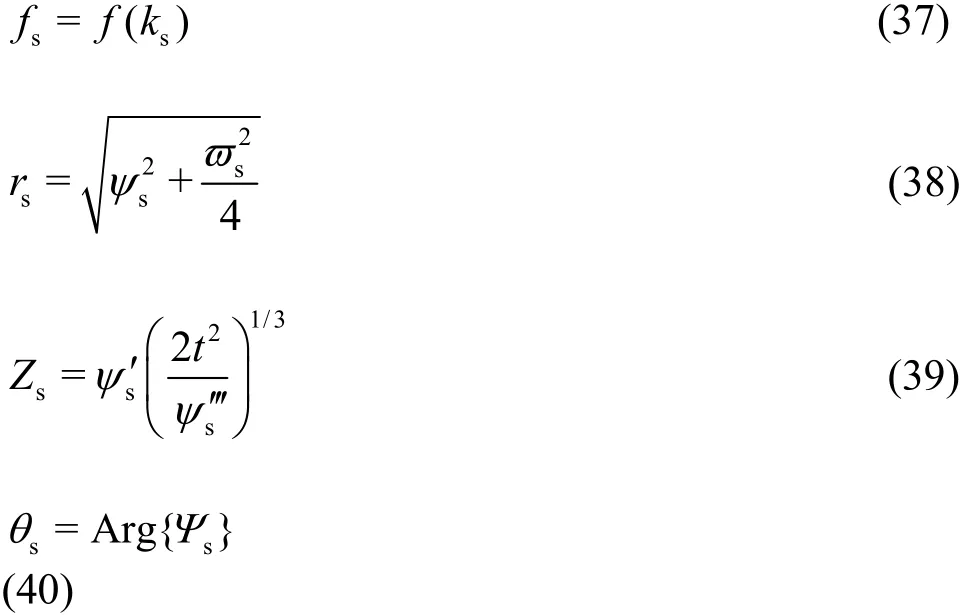
Arg{·} is the argument function, Ai(·) the Airy func- tion, and Gi(·) the Scorer function[23].
When cgmin<U<cmin, ψ(k) has two stationary points, denoted by ks1and ks2. We have
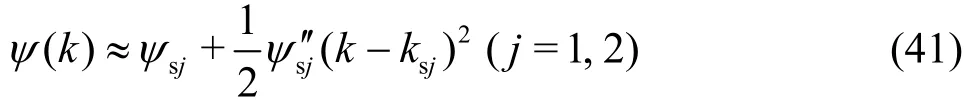
By applying the method of stationary phase[22],()I t can be obtained as follows
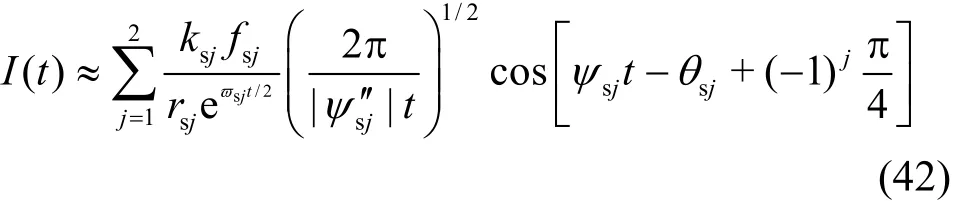
where

When the source speed U is equal to the critical velocityminc , it is a complex case from the mathematical viewpoint. ()kψ has two positive stationary points and one of them coincides with one zero point of ()kψ ats2k(see Fig.3). The contour of integral ()I t should be deformed to avoid this singularity points2k . ()I tcan be evaluated by the method of steepest descent ats1=k k[22]. Then the asymptotic expression for ()I t froms1=k kcan be given by
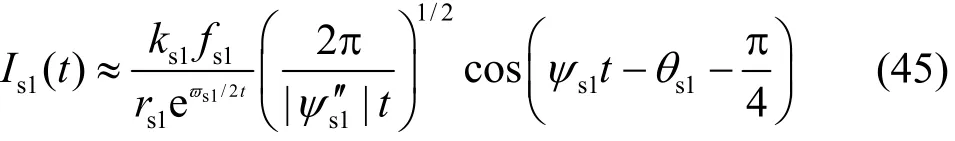
To find the asymptotic expansion for I( t)nearby k = ks2, we use the method which was derived by Schulkeset al.[4]. For the positive pole ks2, z=i(k - ks2) and the Taylor series expansion ofψ(k)at k = ks2is inserted into I( t) to obtain
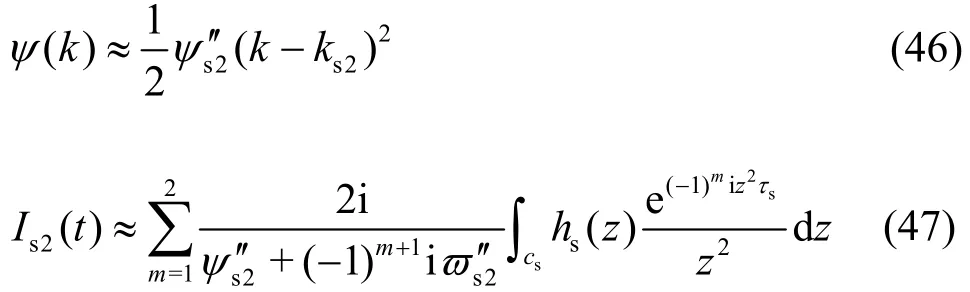
where
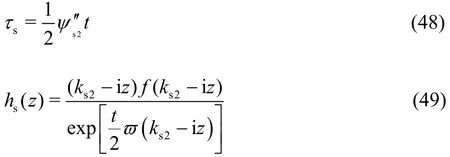
the subscript “s2 ” denotes the values of I( t) at k =ks2, and csis an contour apart from k =ks2.Then the asymptotic expansion for Is2(t) takes the form
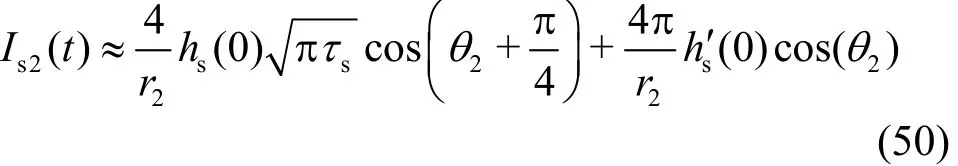
where

Now, we have

As cmin< U <, Eq.(34) has two positive poles, denoted by k =kz1and k = kz2at which ψ≈0, and two stationary points ks1and ks2for ψ. In order to give the asymptotic expansion of I( t) nearby the stationary points, the method of steepest descent is used. The contour of I( t) is deformed near the real axis and together with four steepest-descent links across the points of stationary phase, such that ψ (k)will have no zeros in the new contour. Now I( t)is given by
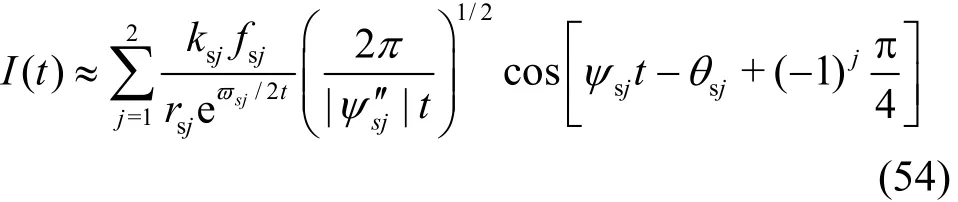
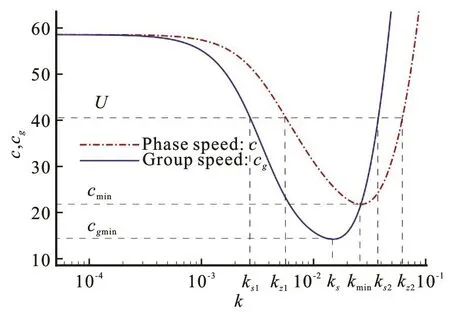
Fig.3 (Color online) c and gc vs. k. Note that the wave number scale is logarithmic
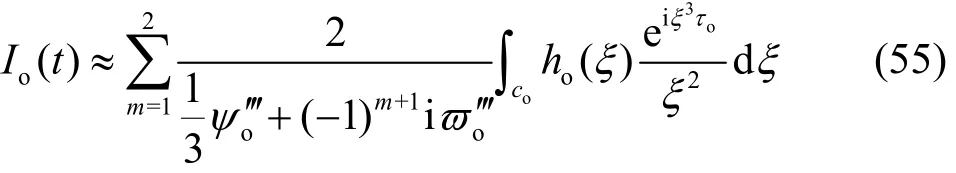
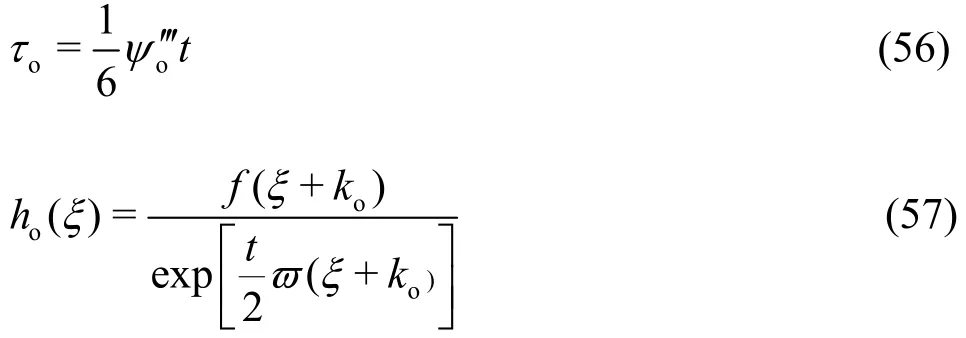
cois contour apart from k =ko. Then the asymptotic expansion is obtained
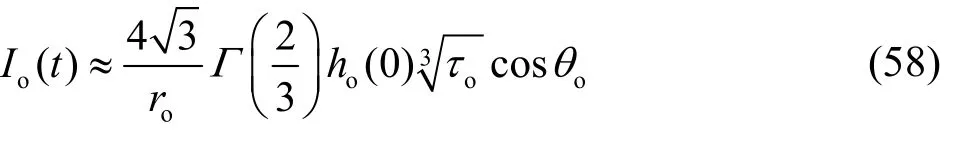
where

By combining the above equation, the asymptotic expansion of I( t) is found as I ( t) = Is2( t) + Io(t).
When cmin<U <, ψ2(k) has one point of stationary phase at k =ks2and one zero point at k=kz2. The method for the case with cmin<U<can be applied to evaluate the wave resistance nearby k =ks2and k =kz2.
3.2 The ocean of infinite depth
In this section, we consider the cases for the ocean of finite depth. When U =cgmin, ψ(k) has an inflexion point ks. Now the analytical formula for ksis given by

In combination with Eq.(36), a graphical representation of the wave resistance is shown in Fig.4(a).We can see that when the moving source is suddenly accelerated, the wave resistances appear and decay rapidly with time. Eventually the wave resistances approach to zero.
When cgmin<U<cmin, ψ(k) has two stationary points, ks1and ks2, which can be given by
where
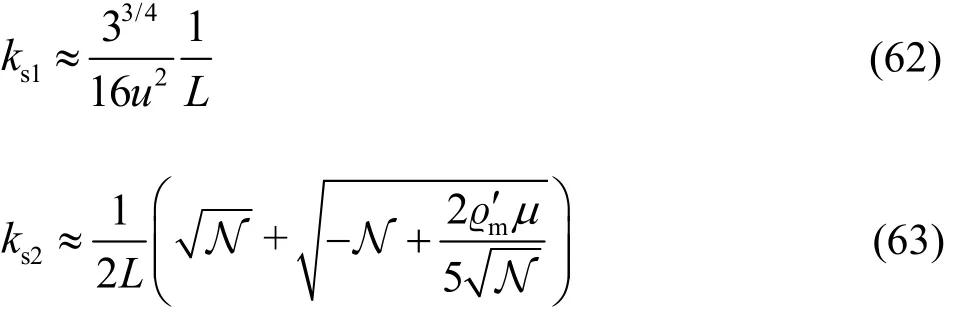
where
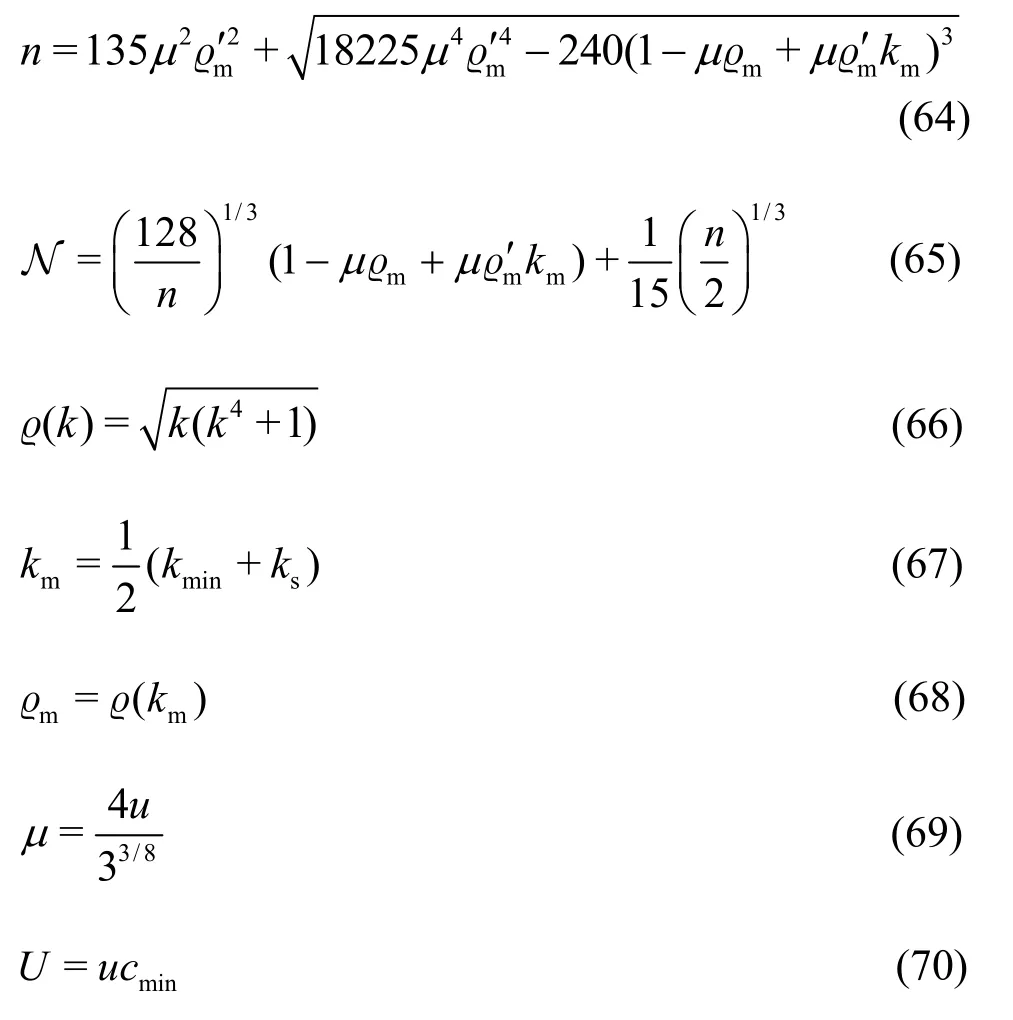
By inserting Eq.(62) into Eq.(42), an analytical form of the wave resistance is obtained. Figure 4(b)shows the wave resistance versus time. Obviously, the wave resistances attenuate rapidly after the first peak and approach to zero exponentially with alternating signs. Comparing with Fig.4(a), we can see that the amplitude of the wave resistance becomes larger when the source speed approaches to cmin. Mathematically, when U is nearby cminwith the wave number approaching to the pole of the integrand, the integral value becomes large. Physically, when U→cmin, the wave energy will accumulate instead of radiation. The flexural-gravity wave resistance becomes large. Moreover, a larger τ has larger energy dissipation, as shown in Fig.4(b).
As U =cmin, ψ(k) has two stationary points ks1and ks2and ks2coincides with one zero point of ψ at kmin, where
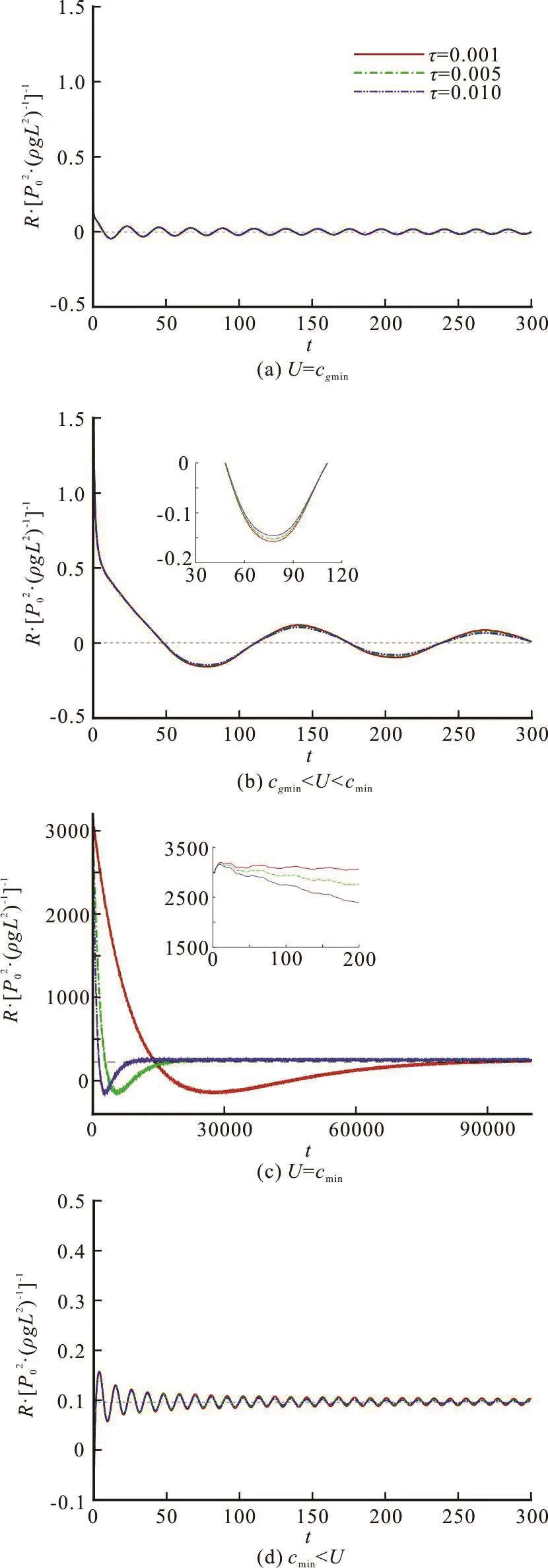
Fig.4 (Color online) Non-dimensional wave resistance R/( /ρ gL2)vs. t for various source speeds

Substituting Eq.(71) into Eqs.(45) and (50), we get the flexural-gravity wave resistance. A graphical representation for the wave resistance is shown in Fig.4(c). The initial wave resistance is extremely large.The physical reason is that the energy continuously accumulate instead of radiate at this critical speed,U = cmin=cg, and the similar physical explanation for wave profile has been given by Davys et al.[5]. In addition, the inset highlights that the wave resistance decaying is an extraordinarily slow process. However,the viscoelastic dissipation eventually makes the wave resistance return to the steady state.
For U >cmin, ψ(k) has two stationary points at k =ks1, ks2and two zero points at k =kz1, kz2.Thus analytical solutions for the stationary points become
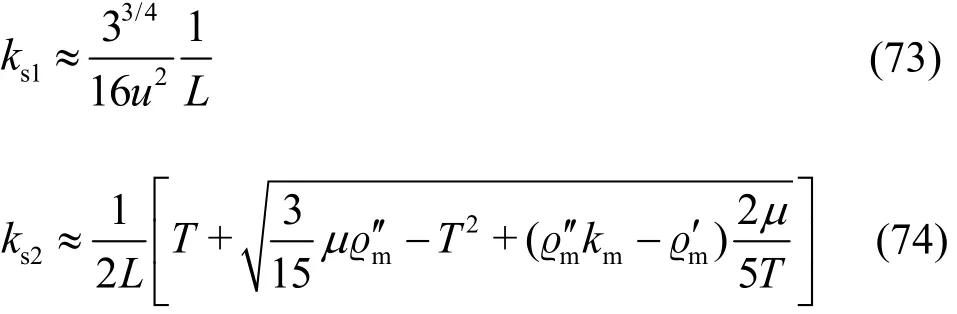
where
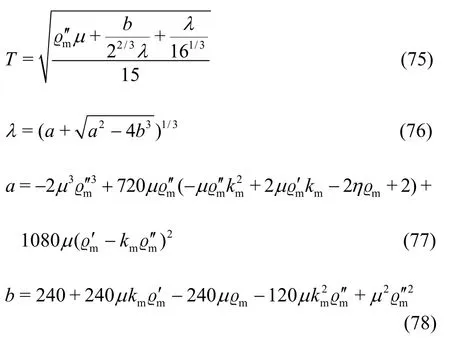
Andm=1/k L. Then ()I t is obtained from Eq.(54).The wave resistance is shown inFig.4(d).
4. Conclusion
In this article, the flexural-gravity wave resistance responses to a surface-moving line source undergoing a rectilinear uniform or accelerated motion is analytically studied within the framework of linear potential theory. Asymptotic solutions are derived by means of the residue theorem and the method of stationary phase. It is found that the velocity threshold exists for the uniform straight motion in this thin viscoelastic plate model, while the wave resistance is zero for the subcritical speed. The flexural-gravity waves consist of the steady-state and transient component during the accelerated straight motion. When the source speed is less than the minimal group velocity,only the transient-state wave resistance exists and the wave resistance decays to zero at last. When the source speed is equal to the minimal phase speed, the transient wave resistance is extremely large and decays very slowly with time due to the viscoelastic dissipation. When the source speed is close to the minimal phase speed, the amplitude of the wave resistance becomes large. It also shows that larger retardation time will dissipate more energy and the wave resistance will decay to the steady-state wave resistance much faster.
[1] Suzuki H., Bhattacharya B. Very large floating structures[M]. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2007, 397-398.
[2] Hosking R. J., Sneyd A. D., Waugh D. W. Viscoelastic response of a floating ice plate to a steadily moving load[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 196: 409-430.
[3] Pogorelova A. V. Plane problem of the impact of several shock pulses on a viscoelastic plate floating on a fluid surface [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics, 2010, 51(2): 155-163.
[4] Schulkes R. M. S. M., Sneyd A. D. Time-dependent response of floating ice to a steadily moving load [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 186: 25-46.
[5] Davys J. W., Hosking R. J., Sneyd A. D. Waves due to a steadily moving source on a floating ice plate [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1985, 158: 269-287.
[6] Wang K., Hosking R. J., Milinazzo F. Time-dependent response of a floating viscoelastic plate to an impulsively started moving load [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2004,521: 295-317.
[7] Raphael E., De Gennes P. G. Capillary-gravity waves caused by a moving disturbance: Wave resistance [J].Physical Review E, 1996, 53(4): 3448-3455.
[8] Richard D., Raphael E. Capillary-gravity waves: The effect of viscosity on the wave resistance [J]. Europhysics Letters, 1999, 48(1): 49-52.
[9] Chepelianskii A. D., Chevy F., Raphael E. Capillarygravity waves generated by a slow moving object [J].Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(7): 074504.
[10] Closa F., Chepelianskii A. D., Raphael E. Capillarygravity waves generated by a sudden object motion [J].Physics of Fluids, 2010, 22(5): 052107.
[11] Lu D. Q., Dai S. Q. Flexural-and capillary-gravity waves due to fundamental singularities in an inviscid fluid of finite depth [J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2008, 46(11): 1183-1193.
[12] Squire V., Hosking R. J., Kerr A. D. et al. Moving loads on ice plates [M]. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1996, 105-106.
[13] Schulkes R. M. S. M., Hosking R. J., Sneyd A. D. Waves due to a steadily moving source on a floating ice plate.Part 2 [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1987, 180: 297-318.
[14] Yeung R. W., Kim J. W. Effects of a translating load on a floating plate-structural drag and plate deformation [J].Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2000, 14(7): 993-1011.
[15] Kozin V. M., Pogorelova A. V. Effect of the viscosity properties of ice on the deflection of an ice sheet subjected to a moving load [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics, 2009, 50(3): 484-492.
[16] Matiushina A. A., Pogorelova A. V., Kozin V. M. Effect of impact load on the ice cover during the landing of an airplane [J]. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering, 2016, 26(1): 6-12.
[17] Lu D. Q., Zhang H. Flexural-gravity wave resistances due to a surface-moving line source on a fluid covered by a thin elastic plate [J]. Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters, 2013, 3(2): 022002.
[18] Nugroho W. S., Wang K., Hosking R. J. et al. Timedependent response of a floating flexible plate to an impulsively started steadily moving load [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 381: 337-355.
[19] Kozin V. M., Pogorelova A. V. Wave resistance of amphibian aircushion vehicles during motion on ice fields [J].Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics,2003, 44(2): 193-197.
[20] Lu D. Q., Chwang A. T. Unsteady free-surface waves due to a submerged body moving in a viscous fluid [J].Physical Review E, 2005, 71(6): 066303.
[21] Kim J. W., Webster W. C. The drag on an airplane taking off from a floating runway [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 1998, 3(2): 76-81.
[22] Lighthill J. Waves in fluids [M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2001.
[23] Vallee O., Soares M. Airy functions and applications to physics [M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2004, 27-30.
- 水動力學(xué)研究與進(jìn)展 B輯的其它文章
- Editorial Message
- ICHD’ 2018 The 13th International Conference on Hydrodynamics First Announcement September 2-6, 2018 Sheraton Grand Inchecon Hotel Songdo, Incheon Korea
- Compressible effect on the cavitating flow: A numeric study *
- Design and experiment of the centrifugal pump impellers with twisted inlet vice blades *
- Two timescales for longitudinal dispersion in a laminar open-channel flow *
- Numerical simulation of a two-dimensional flapping wing in advanced mode *

