Risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors:A system atic review
Giuseppe La Torre,Rosella SaulleDepartmentofPublic Health and InfectiousDiseases,“Sapienza”UniversityofRome,Piazzale AldoMoro,5-00185,Rome,Italy
?
Risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors:A system atic review
Giuseppe La Torre*,Rosella Saulle
DepartmentofPublic Health and InfectiousDiseases,“Sapienza”UniversityofRome,Piazzale AldoMoro,5-00185,Rome,Italy
Review article http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.01.008
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received in revised form 2Nov 2015 Accepted 13 Dec 2015
Availableonline 15 Jan 2016
Risk factors
HBV
Infection
Blood donors
Systematic review
ABSTRACT
Ob jective:To perform a systematic review of the scienti fi c literature to identify risk factors associated w ith hepatitis B viruses(HBV)infection among blood donors.
M ethods:The literature search was carried outon PubMed and Scopus databases using the keywords“risk factors”“HBV infection”and“blood donors”.No date or language restrictions were applied to the search.This literature review was completed in March 2014.The selection process and the reporting of the review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Statement.The New castle Ottawa scale was using to evaluate the quality of each single primary study.
Resu lts:Out of 172 records resulted in the search,5 papers were included in the fi nal analysis because they are w ithin acceptance criteria.Two of the selected studies were cross-sectional and three of them were case-control studies.Signi fi cant association resulted w ith some demographic and behavioral risk factors,such asmaritalstatus,dental treatment/procedure history,no stable relationship ormultiple partners and fam ily history of HBV infection.
Conclusions:The systematic review performed encourages to conduct further research among blood donors in order to fully understand risk factors among donors in more extensive thus to provide valuable information about surveillance.
1.Introduction
Blood transfusion is a life-saving intervention that has an essential role in patientmanagementw ithin health care systems [1].Unfortunately,blood transfusion is not w ithout risks and may lead to the transm issions of infectious agents from donor to recipient including hepatitis C virus(HCV),human immunode fi ciency virus(HIV),syphilis–causing Treponema pallidum and hepatitis B virus(HBV)[2].Many cases of HBV infections in adult populations were found to be associated w ith blood transfusions,since HBV is infective through blood and body-fl uid,including vertical transm ission[3].
The hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg)in serum is the fi rst seromarker to indicate active HBV infection,either acute or chronic[4].Since 1982 there was available an hepatitis B vaccine,highly effective in the prevention of HBV transm ission[3],w ith a consequence of a remarkable reduction in the prevalence and incidence of HBV infection.
Despite this,theWorld Health Organization(WHO)has estimated that there are still 360 m illion chronically HBV infected peopleand 5.7m illion HBV-related casesworldw ide,spreadwith a high variability across the countries(e.g.in the difference between low and high income countries)[5].It has been estimated that infections w ith HBV was responsible for about 59%of hepatocellular carcinoma cases in developing countries[6].
Overall,themajority of theworld population lives in areas of moderate(2%–7%)to high endem icity(>8%)for chronic HBV infection[de fi ned as dual seropositivity for HBsAg and for antibodies againsthepatitis B core antigen(anti-HBc)][7].
Screening of donated blood for transfusion-transm issible infections represents one of themost important strategy for blood transfusion safety and availability,and the presence of this type of infection among blood donors is a rare event.Up to now,no review has been conducted studying systematically the risk factors associated w ith chronic HBV infection among blood donors;so,the objective of the present study is to perform a systematic review of the scienti fi c literaturew ith the speci fi c aim to identify such risk factors associated w ith chronic HBV.
2.M aterials and methods
2.1.Search strategy
A medical literature review was carried out on Medline (PubM ed)and Scopus databases using the keywords“risk factors”“HBV infection”and“blood donors”.We performed searches for:“risk factors”AND“HBV infection”AND“blood donors”.No date or language restrictions were applied to the search.
When duplicate or repeated publicationswere encountered in the databases search,the papers,when eligible,were considered only once.This literature review was completed in March 2014.
2.2.Article selection
We selected all studies evaluating the risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors.The selection and the reporting of the review were performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Statement[8],in order to provide univocal and comparable data as shown in the fl ow-chart(Figure 1).
Prelim inary,two authors independently assessed the study selection of potentially relevant titles and abstract,based on the established criteria.Subsequently,when there was some doubt, the full textwas found and read.In a fi nal phase,disagreements between authorswere resolved by consensus.
Articleswereexcluded if(1)studieswerenotpertaining to the topic“risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors”;(2) there was no reported odds ratio(OR)resulted from univariate analysis oradjusted odds ratio(AOR)resulted from multivariate logistic analysis for identifying risk factors associatedw ith HBV infection among blood donors;(3)the full textwasnotavailable; (4)languagewasnotin English,Italian orSpanish;(5)articlewas a letter or an editorial or a previous review.
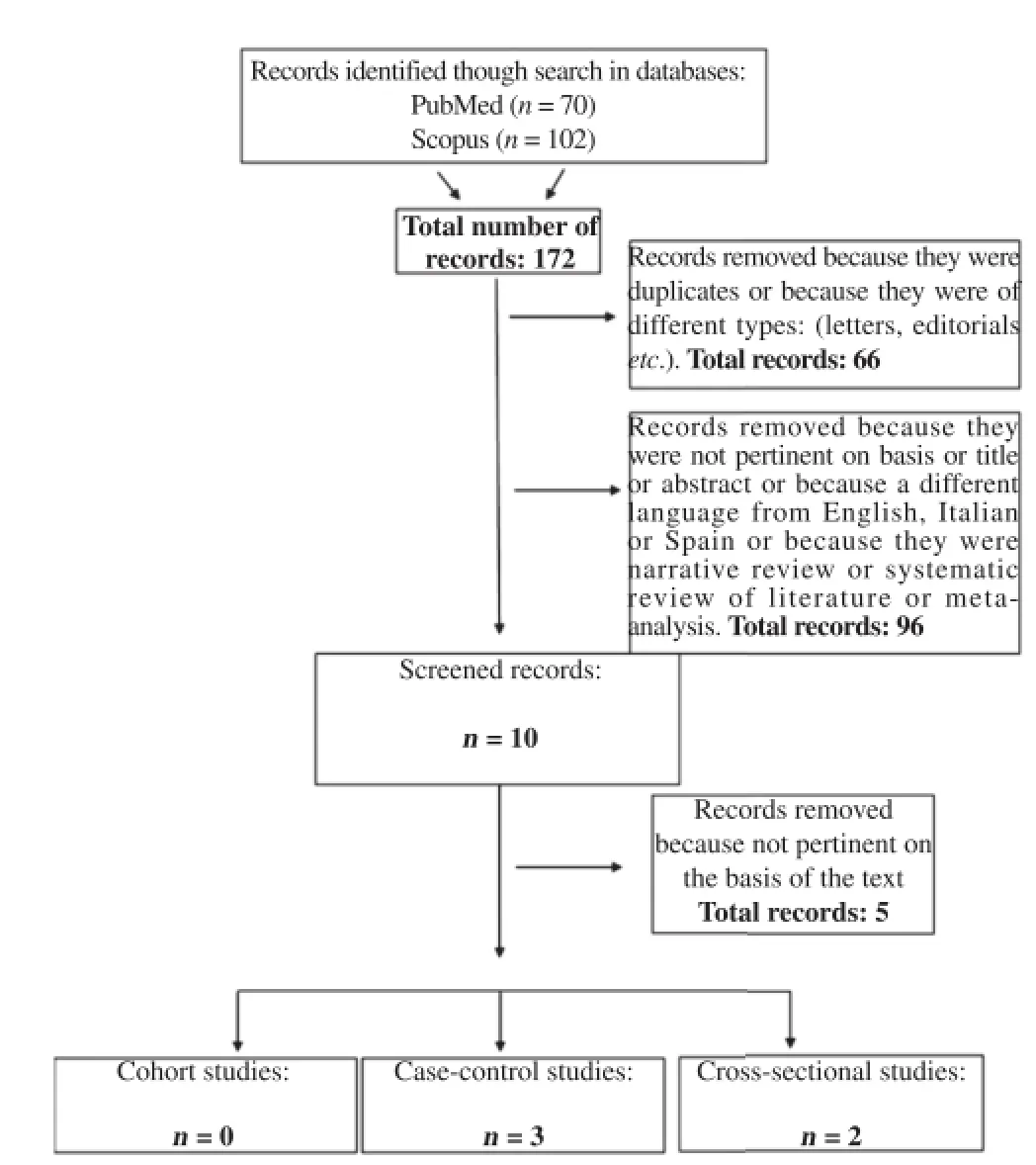
Figure 1.Flow chartof the selection studies of the systematic review.
2.3.Data extraction and quality assessment
A ll publications were analyzed by both investigators,who independently reviewed the papers to identify relevant information and to extract data.Disagreements were resolved by consensus.
The Newcastle Ottawa scale for case-control studies was performed[9],and the adapted form of the New castle Ottawa cohort scale for cross-sectional studies were used to evaluate the quality of the studies[10].Disagreements were resolved by consensus.
3.Resu lts
Outof the 172 references identi fi ed in the initial search,162 were removed because they were duplicates or because they were of different types:(letters,editorials,etc.)or because they aligned w ith the study objectives or because they were in language different from English,Italian and Spanish.A fter the abstractselection,10 full-textwereevaluated.Of these,5 studies were included in the review because they met the inclusion criteria.A fl ow chart illustrating allselection process isshown in Figure 1.References of the included studies w ith the relative results are shown in Table 1 and the quality assessment score is shown in Table 2.
Two of the selected studieswere cross-sectional[11,12],and three of them were case-control studies[13–15].
Of these,one study carried out by Said et al.,studied risk factors associated w ith occult HBV infection,while the other 4 studies assessed risk factors associated w ith HBsAg positivity.
Said etal.[11]conducted a descriptive cross-sectional study in Egypton 3167 blood donors negative for HBsAg,hepatitis C virus antibody and HIV antibody.Multivariate logistic analysis revealed that age above thirty years and themarital statuswere the most signi fi cant risk factors for prediction anti-HBc positivity among blood donors[AOR=1.8;95%con fi dence interval (CI):1.4–2.4 and AOR=1.4;95%CI:1.0–1.9 respectively].
Among anti-HBc positiveblood donors,ageabove thirty was the most signi fi cant risk factor for prediction of HBV-DNA positivity(AOR=3.8;95%CI:1.8–7.9).
Other potential risk factors as gender,blood transfusion, diabetes mellitus,frequent injections,tattooing,previous surgery,hospitalization,bilharziasis or positive fam ily history of HBV or HCV infections were not found to be signi fi cantly associated w ith positive anti-HBc antibodies.
A cross-sectional survey amongmale Saudi voluntary blood donorswas conducted by El Beltagy etal.[12]in the northwest region of Saudi Arabia.Regarding age,HBV markers were signi fi cantly higher in age groups 30–39 years(OR=5.03;95% CI:2.64–9.80)and 40 years(OR=2.99;95%CI:1.50–6.10) compared to the youngestage group(<20 years).HBV markers were signi fi cantly higher in married subjects compared to unmarried(OR=1.67;95%CI:1.39–2.00).Lower educated subjects showed HBV markers signi fi cantly higher compared to higher educated(OR=1.53;95%CI:1.25–1.9).Both occupations,laborers andm ilitary personnel,showed signi fi cant association w ith HBV markers compared to professionals respectively[(OR=4.0;95%CI:3.12–5.12)and(OR=1.97; 95%CI:1.56–2.5)].The subjectsw ith a fam ily history of HBV infection showed HBV positive markers signi fi cantly higher compared to among those w ithout(OR=3.12;95%CI:2.6–3.78).No signi fi cant association was found regarding history ofexposure to risky procedures or behaviors.A ll study subjects previously immunized for HBV in three doseswere negative for both HBsAg and anti-HBc.
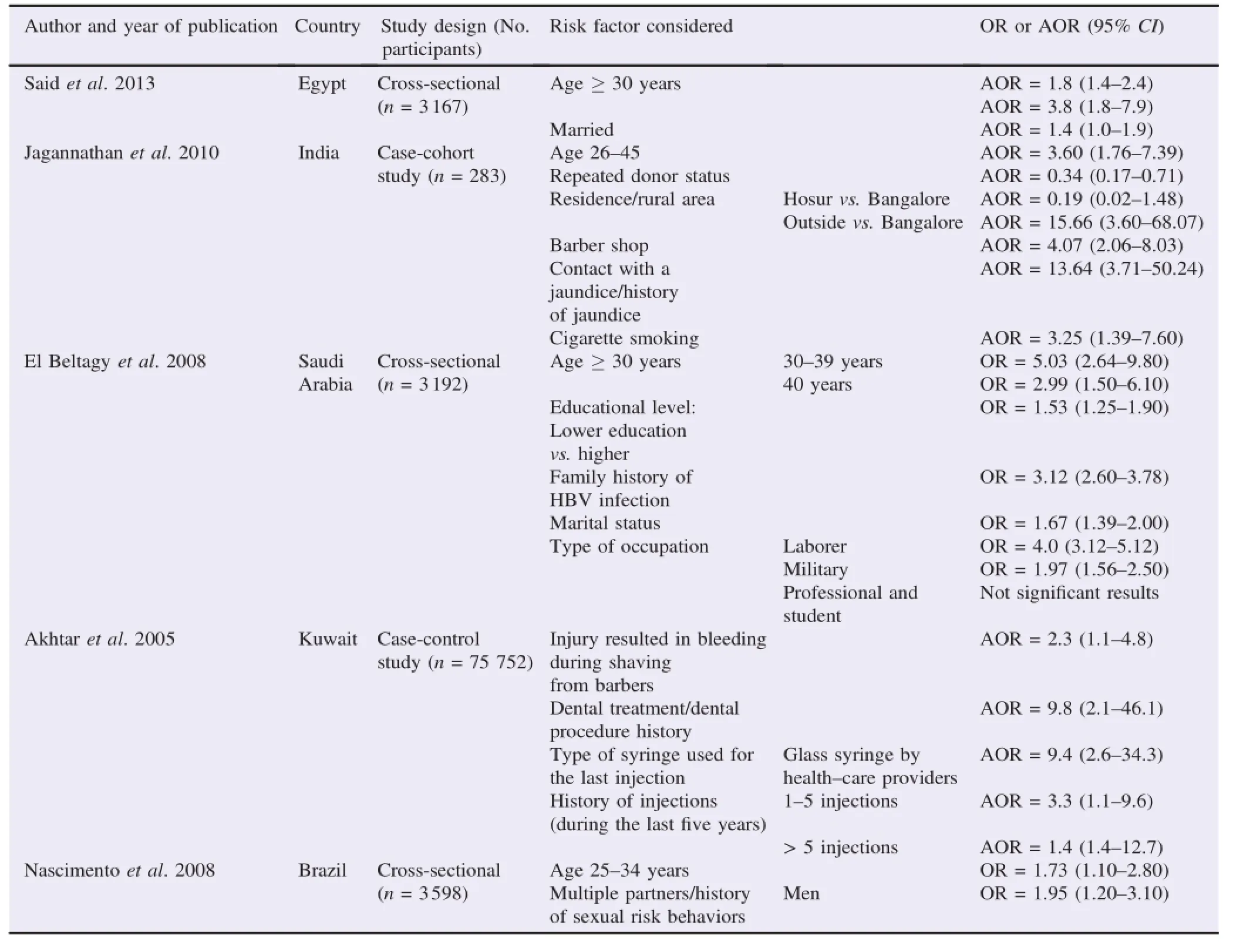
Table1 Results of the included studies.
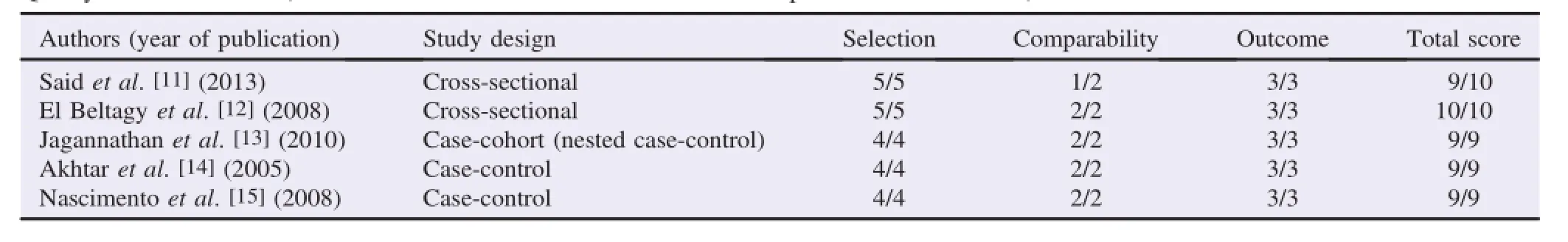
Table2 Quality assessmentscore(Newcastle-Ottawa scale for case-controland adapted for cross-sectional).
Jagannathan et al.[13]conducted a case-cohort study in Bangalore,India.HBsAg positive cases had signi fi cantly higher unadjusted odds of having a body piercing,having a tattoo, shaving ata barber's saloon,having contactw ith someone w ith jaundice,smoking,consum ing alcohol,having sexw ithmultiple partners,paying for sex,and donating blood to be tested for HIV/AIDS.Behavioral factors associated w ith HBsAg status, were a repeated donor status(AOR=0.34;95%CI:0.17–0.71), and as risk factors residence outside Bangalore(rural area) (AOR=15.66;95%CI:3.60–68.07),contactw ith someonew ith jaundice(AOR=13.64;95%CI:3.71–50.24),being shaved by a barber(AOR=4.07;95%CI:2.06–8.03),and cigarette smoking(AOR=3.25;95%CI:1.39–7.60).
Akhtar et al.[14]conducted an epidemiologic study to better understanding theassociated risk factorsof chronic infection w ith HBV in asymptomatic volunteermale blood donors in Pakistan. They showed that cases received more often inadequate and unsafe dental treatment in comparison to the controls (AOR=9.8;95%CI:2.1–46.1),aswell as received injections (AOR=3.3;95%CI:1.1–9.6)or received injection through a glass syringe(AOR=9.4;95%CI:2.6–34.3).Another risk factors registered was an injury resulted in bleeding during shaving from barbers(AOR=2.3;95%CI:1.1–4.8).
Consecutive fi rst-time,voluntary,unpaid blood donorswere recruited by Nascimento et al.[15]in Brazil to explore riskfactors associated w ith HBV infection.The seroprevalence of anti-HBc increased w ith age among men(P trend=0.0002) and women(P trend=0.0005).The seroprevalenceof anti-HBc, butnotof HBsAg,was lower amongmen(OR=0.51;95%CI: 0.30–0.80)and women(OR=0.56;95%CI:0.30–1.00)w ith a higher education level(secondary or higher).Anti-HBc was associated w ith lifetime number of sexual partners amongmen (OR=1.95;95%CI:1.20–3.10).
4.Discussion
Occult hepatitis B infection(OBI)is one of themost challenging topics in the fi eld of viral hepatitis[16].OBI is de fi ned by the presence of HBV DNA in the liver(w ith detectable or undetectable HBV DNA in the serum)in patients w ith serological markers of previous infection(anti-HBc and/or anti-HBs positive)or in patients without serological markers (anti-HBc and/or anti-HBs negative).The prevalence of OBIis quite variable depending on the level of endem ic disease in different parts of the world,the different assays utilized in the studies,and the different populations studied[17].Occult HBV may impact in several different clinical contexts,including the transm ission of the infection by blood transfusion or organ transplantation and its acute reactivation when an immunosuppressive status occurs[18].Occult HBV infection in blood donors is considered a potential threat for the safety of the blood supply however conclusive studies on this issue are lacking[19].
A lthough,the incidence of transfusion-transm itted hepatitis B has been steadily reduced over the last four decades[16],HBV still remains the most frequent transfusion-transm itted viral infection.There is an high variability of infection with HBV across the countries,w ith high level in prevalence and incidence in developing world such as in Brazil(1.6%–7.7%)[20,21],in Egypt(19.6%)[22],and from various areas of India(2%–10%) [23].
Nascimento et al.[15],however,in their Brazilian multicenter sero-survey,reported a low seroprevalences of HBV among fi rst-time voluntary blood donors,a population usually expected to have a higher prevalence of viral hepatitis infection than repeat blood donors[23].However little data are available on the seroprevalence of,and risk factors for HBV infection in Latin American countries including Brazil[24,25].In addition, in many developing countries,the relative contributions of various routes of HBV infection have not been de fi ned in population-based studies.Due to a lack of universal and appropriate blood screening in these countries,the risk of posttransfusion HBV infection is still unknown.
The paucity in literature on HBV risk factors among blood donors isespecially lim ited to few areas andmoststudies targets small groups of individuals.So there is a lim ited and unclear picture of the HBV risk factors among blood donorsworldw ide. In addition the few studies carried out have some lim itations including the selection bias due to the small sample size where the individuals representa small proportion of donors.
The study carried out by Said et al.[11]proved that OBI exists among Egyptian blood donors.In a study carried out in Egyptian blood donors by Was fi OA et al.[26],the rates were lower than previous studies conducted in Egypt,perhaps due to predonation screening which excludes those known to be at high risk of contacting blood-borne infections or who had other contraindications to blood donation.However,Said etal. [11]did not show an association between any of the former risk factors and OBIexcept for age.Sim ilarly,El Beltagy etal.[12] reported that blood donorsw ith positive HBV markers showed signi fi cant association w ith increased age.
The study carried outby Nascimento et al.[15]reported that the seroprevalence of anti-HBc increased w ith age amongmen and women.A llain et al.[27]found that OBI donors are generally older than 45 years except in A frica while M inuk et al.[28],demonstrated that age,gender do not identify those w ith OBI.
In addition,El Beltagy et al.[12]showed signi fi cant association with married status,speci fi c occupations such as blue collar worker and the m ilitary,fam ily history of HBV infection,lack of immunization,lower educational level.In general population low educational attainment had been associated w ith higher prevalence of hepatitis B in both developed and developing countries.In the study carried out by Nascimento et al.[15],there was a lower risk of past exposure to HBV among male and female blood donors who reported a higher education level.
Moreover,in low socio-econom ic settings,horizontal transm issions of HBV through contactw ith infected fam ily member have also been reported[29].El Beltagy etal.[12]did not fi nd a signi fi cantassociation w ith history of exposure to high-risk procedureorbehaviorwhile in literature parenteral routes are implicated as themost likely factors forHBV transm ission thatinclude unsterilized needlesand syringes in health-care settings[30,31].In their study,Akhtar et al.found that dental care provider and injections are risk factors[14].In the general population,history of repeated blood transfusions[32],history of injections[33], including re-use of contam inated syringes,contam inated surgical instruments and blood products[34];number of pregnancies [35];hemodialysis[36];tooth extraction[32];dental procedures, needle prick and surgical procedures for health care workers [37];unsafe surgery[38]are themain risk factors.On the other hand,a recent study conducted in Egypt showed that HBV transm ission is community rather than iatrogenic-acquired[39]. Behavioral risks as intravenous drug use,needle stick injuries, tattooing and multiple sexual partners have been identi fi ed as common modes of HBV transm ission in the developed world [39].Nascimento et al.[15]however found that anti-HBc was associated w ith lifetime number of sexual partners amongmen, but not among women and there was no relationship between sexual behavior and the seroprevalence of HBsAg in either gender.Jagannathan et al.[13]found several demographic and behavioral risk factors are associated w ith HBsAg status among blood donors in Bangalore,India:fi rst-time donor status,contactw ith a jaundiced person,associationsw ith placeof residence and patronageof localbarbers thatmay have relevance forblood safety and public health.This risk factor is con fi rmed by Akhtar etal.[14]where injury resulted in bleeding during shaving from barbers was also signi fi cant predictor of HBsAg positivity.In general population,history of jaundice[14],rural origin and shaved by barber are also the main risk factor reported. However,Jagannathan et al.emphasized the need for further epidem iologic research because of sample size[13].
It's important to emphasize the importance of hospital risk prevention as well as health education among population and better training in the domain of blood safety and in healthcare workers[33–40].
Baha et al.showed that in Marocco there is a lower prevalence of HBV and HCV in blood donors in comparison to thegeneral citizens,emphasizing that the blood transfusion was not a predictor for transm ission but themain risk originated from the hospital exposure to contam inated instruments[41].
Infection controlmeasures in health-care settings include safe injection practicesand proper sterilization techniquesofmedical instruments as well as barber's instruments,and the reuse of razors in the barber shops need to be discouraged,emphasizing the sterilization.
Preventive strategies for HBV infection include healthy blood transfusion services and vaccination against HBV[42].
The agenda of every national blood programme should be focused on the implementation of effective quality systems,as well as the development and implementation of quality standards,effective documentation systems,training of all staff and regular quality assessment to ensure that all donated blood is screened for transfusion-transmissible infections[43].
Globally,however,there are signi fi cant variations in the extent to which donated blood is screened,the screening strategies adopted and the overall quality and effectiveness of the blood screening process.As a result,inmany countries the recipients of blood and blood products remain atunacceptable risk of acquiring life-threatening infections that could easily be prevented.
There isa need of a public awareness programsespecially in rural areas and people at high risk to decrease the burden of HBV infection.Each country should establish voluntary blood donor programmes which provide donor information and education[1].
Prevention m ight be achieved through a more rigorous screening forhistory of risk behaviorsand risk factors during the donor selection process to collect blood from well-selected, voluntary non-remunerated blood donors from low-risk populations,particularly thosewho donate regularly[44].Paid blood donation should be prohibited[45].
5.Conclusions
HBV remains the infection most frequently recognized by donation testing in blood donors.It's a cause of signi fi cant morbidity andmortality in certain ethnic populations and among groups of people whose behavior puts them athigh risk.
Our research shows that there is a nonuniform pattern of distribution throughout the countries/regions,w ith HBV prevalence related to geographical,social and cultural factors that predispose certain individuals to infection.Themode of HBV transm ission differs throughout the countries(Table 1).Transm ission occurs by the same routes as in various parts of the world:through percutaneous or permucosal exposure to infected blood or other secretions.In Brazil,the predom inantmeans of transm ission are sexual intercourse.Barber shop transm ission plays an important role in areas as in Kuwait and in India.In Kuwait,there are inadequate measures to block transm ission through injections or dental treatment/dental procedure.The repeated donor status is a source of disease transm ission that must be considered in India.
However,other socio-demographic,environmental,sociocultural factors speci fi c to the geographical sitemay contribute to the unique characteristics of the infection observed in these countries(as themaritalstatus in Egypt,living in residence/rural area in India,the occupation and the educational level and the fam ily history of HBV infection in Saudi Arabia).
Because HBV infectionmostly re fl ects the country of origin of the donor and it's different by different geographical region, the obtained data encourage to conduct further research among blood donors throughout other regions in order to fully understand risk factors among donors inmore extensive areas and at national level worldw ide,thus to provide valuable information about surveillance,therefore to adopt targeted policies concerning the adoption of precautionary measures in order to reduce the residual speci fi c risk of HBV and to introduce appropriate changes in donor selection guidelines.
Con fl ict of interest statement
We declare thatwe have no con fl ict of interest.
References
[1]World Health Organization.Screening donated blood for transfusion-transmissible infections:recommendations.Geneva: World Health Organization;2009.
[2]Schreiber GB,Busch MP,Kleinman SH,Korelitz JJ.The risk of transfusion-transmitted viral infections.The Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study.N Engl JMed 1996;334:1685-90.
[3]Lok AS,M cMahon BJ.Chronic hepatitis B.Hepatology 2007;45: 507-39.
[4]Sood S,Malvankar S.Seroprevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen,antibodies to the hepatitis C virus,and human immunode ficiency virus in a hospital-based population in Jaipur,Rajasthan. Indian JCommunity Med 2010;35:165-9.
[5]W orld Health Organization.Western Paci fi c regional plan for hepatitis B control through immunization.Geneva:World Health Organization;2007.[Online]Available from:http://www.wpro. who.int/immunization/documents/docs/POA_HepB.pdf[Accessed on 9th October,2015]
[6]Parkin DM.The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002.Int JCancer 2006;118:3030-44.
[7]W orld Health Organization.Hepatitis B vaccines.Geneva:World Health Organization.[Online]Available from:http://www.who.int/ immunization/topics/WHO_position_paper_HepB.pdf[Accessed on 9th October,2015]
[8]Liberati A,Altman DG,Tetzlaff J,Murlow C,G?tzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA,et al.The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions:explanation and elaboration.BMJ 2009;339: b2700.
[9]W ells GA,Shea B,O'Connell D,Peterson J,Welch V,Losos M, etal.The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS)forassessing the quality of nonrandomised studies inmeta-analyses.Canada:Departmentof Epidem iology and Community M edicine,University of Ottawa.
[10]Herzog R,′A lvarez-PasquinMJ,Díaz C,DelBarrio JL,Estrada JM, Gil A.Are healthcare workers'intentions to vaccinate related to their know ledge,beliefs and attitudes?A systematic review.BMC Public Health 2013;13:154.
[11]Said ZN,Sayed MH,Salama II,Aboel-Magd EK,Mahmoud MH, Setouhy ME,et al.Occult hepatitis B virus infection among Egyptian blood donors.World JHepatol 2013;5(2):64-73.
[12]ElBeltagy KE,AlBalaw iIA,AlmuneefM,Memish ZA.Prevalenceof hepatitis B virusmarkersamong blood donors in a tertiary hospital in Tabuk,northwestern SaudiArabia.Int JInfectDis2008;12(5):495-9. [13]Jagannathan L,ChaturvediM,M udaliar S,Kamaladoss T,RiceM, Murphy EL.Risk factors for chronic hepatitis B virus infection among blood donors in Bangalore,India.Transfus Med 2010; 20(6):414-20.
[14]Akhtar S,Younus M,Adil S,Hassan F,Jafri SH.Epidemiologic study of chronic hepatitis B virus infection inmale volunteerblood donors in Karachi,Pakistan.BMC Gastroenterol 2005;5:26.
[15]Nascimento MC,Mayaud P,Sabino EC,Torres KL,Franceschi S. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C serologicalmarkers among fi rst-time blood donors in Brazil:amulti-center serosurvey.JMed Virol 2008;80(1):53-7.
[16]Liu Y,LiP,LiC,Zhou J,Wu C,Zhou YH.Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA among accepted blood donors in Nanjing,China. Virol J 2010;7:193.
[17]Guti′errez-GarcíaML,Fernandez-Rodriguez CM,Lledo-Navarro JL, Buhigas-Garcia I.Prevalence of occult hepatitis B virus infection. World JGastroenterol2011;17(12):1538-42.
[18]Raimondo G,Pollicino T,Cacciola I,Squadrito G.Occulthepatitis B virus infection.JHepatol 2007;46:160-70.
[19]So fi an M,Aghakhani A,Izadi N,Banifazl M,Kalantar E, Eslam ifar A,etal.Lack of occulthepatitis B virus infection among blood donorsw ith isolated hepatitisB coreantibody living in anHBV low prevalence region of Iran.Int J InfectDis2010;14(4):e308-10.
[20]Niederhauser C,Mansouri Taleghani B,Graziani M,Stolz M, Tinguely C,Schneider P.Blood donor screening:how to decrease the risk of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus?Sw iss Med Wkly 2008;138:134-41.
[21]Calder′on GM,Gonz′alez-Vel′azquez F,Gonz′alez-Bonilla CR, Novelo-Garza B,Terrazas JJ,Martínez-Rodríguez ML,et al. Prevalence and risk factors of hepatitis C virus,hepatitis B virus, and human immunode fi ciency virus in multiply transfused recipients in M exico.Transfusion 2009;49:2200-7.
[22]Ka fi-abad SA,Rezvan H,AbolghasemiH,Talebian A.Prevalence and trends of human immunode fi ciency virus,hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus among blood donors in Iran,2004 through 2007.Transfusion 2009;49:2214-20.
[23]Candotti D,A llain JP.Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus infection.JHepatol 2009;51:798-809.
[24]Wang B,Schreiber GB,Glynn SA,Kleinman S,W right DJ, M urphy EL,et al.Does prevalence of transfusion-transm issible viral infection re fl ect corresponding incidence in United States blood donors?Transfusion 2005;45:1089-96.
[25]Gish RG,Gadano AC.Chronic hepatitis B:current epidemiology in the Americas and implications formanagement.J Viral Hepat 2006;13:787-98.
[26]Was fi OA,Sadek NA.Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitisC virusantibodiesamong blood donors in Alexandria, Egypt.East Mediterr Health J 2011;17(3):238-42.
[27]Allain JP,Cox L.Challenges in hepatitis B detection among blood donors.Curr Opin Hematol 2011;18:461-6.
[28]M inuk GY,Sun DF,Uhanova J,Zhang M,Caouette S,Nicolle LE, et al.Occult hepatitis B virus infection in a North American community-based population.JHepatol 2005;42:480-5.
[29]Doganci T,Uysal G,Kir T,Bakirtas A,Kuyucu N,Doganci L. Horizontal transm ission of hepatitis B virus in children w ith chronic hepatitis B.World JGastroenterol 2005;11:418-20.
[30]Aylward B,Lloyd J,Zaffran M,M cNair-Scott R,Evans P. Reducing the risk of unsafe injections in immunization programmes:fi nancial and operational implications of various injection technologies.BullWorld Health Organ 1995;73:531-40.
[31]Usman HR,Akhtar S,Rahbar MH,Hamid S,Moattar T,Luby SP. Injections in health care settings:a risk factor for acute hepatitis B virus infection in Karachi,Pakistan.Epidemiol Infect 2003;130: 293-300.
[32]Batool A,Bano KA,Khan M I,Hussain R.Antenatal screening of women for hepatitis B and C in an out-patient department.JDow Univ Health Sci2008;2:32-5.
[33]Yousfani S,Mum taz F,Memon A,M emon MA,Sikandar R. Antenatal screening for hepatitis B and C virus carrier state at a university hospital.JLiaquat Univ Med Health Sci2006;5:24-7. [34]Masood Z,Jawaid M,Khan RA,Rehman S.Screening forhepatitis B&C:a routine preoperative investigation.Pak JMed Sci2005; 21:455-9.
[35]Mehnaz A,Hashmi H,Syed S,Kulsoom.Hepatitis B markers in mothers and its transm ission in newborn.JColl Physicians Surg Pak 2002;12:240-2.
[36]Khokhar N,A lam AY,Naz F.Hepatitis B surface antigenemia in patients on hemodialysis.Rawal Med J 2004;29:18-21.
[37]Sarwar J,Gul N,Idris M,Anis-ur-Rehman,Farid J,Adeel MY. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in healthcareworkers in Abbottabad.JAyub Med Coll Abottabad 2008;20:27-9.
[38]Sami S,Korejo R,Bhutta SZ.Prevalence of hepatitis B and C:a Jinnah postgraduatemedical centre experience.JObstet Gynecol Res 2009;35:533-8.
[39]Paez Jimenez A,El-Din NS,El-Hoseiny M,El-Daly M,Abdel-Hamid M,El Aidi S,etal.Community transmission of hepatitis B virus in Egypt:results from a case-control study in Greater Cairo. Int JEpidemiol 2009;38:757-65.
[40]Custer B,Sullivan SD,Hazlet TK,Iloeje U,Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV.Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus.J Clin Gastroenterol 2004;38(10 Supp l 3):S158-68.
[41]Baha W,Foullous A,Dersi N,They-they TP,El alaoui K, Nouricha fi N,etal.Prevalence and risk factorsof hepatitis B and C virus infectionsamong the general population and blood donors in Morocco.BMC Public Health 2013;13:50.
[42]Aziz S,Memon A,Tily HI,Rasheed K,Jehangir K,Quraishy MS. Prevalence of HIV,hepatitis B and C amongst health workers of Civil Hospital Karachi.JPak Med Assoc 2002;52:92-4.
[43]Tw enty-Eighth W orld Health Assem bly.U tilization and supp ly of human blood and blood products.Geneva:World Health Organization;1975.[Online]Available from:http://www.who.int/ bloodsafety/en/WHA28.72.pdf[Accessed on 1st July,2015]
[44]Heyns A,Benjamin RJ,Swanevelder JP,Laycock ME, Pappalardo BL,Crookes RL,et al.Prevalence of HIV-1 in blood donations follow ing implementation of a structured blood safety policy in South A frica.JAMA 2006;295(5):519-26.
[45]Ahmed MA,Zafar T,Brahmbhatt H,Imam G,UI Hassan S, Bareta JC,et al.HIV/AIDS risk behaviors and correlates of injection drug use among drug users in Pakistan.J Urban Health 2003;80:321-9.
19 Oct 2015
*Corresponding author:Giuseppe La Torre,MD,MSc,DSc,Professoro f Public Health,Department of Public Health and In fectious Diseases,“Sapienza”University of Rome,Box 5,Rome,CA 00185,Italy.
Tel:+39 06 49694308
Fax:+39 06 4454845
E-mail:giuseppe.latorre@uniroma1.it
Peer review under responsibility of Hainan M edical University.The journal implements double-blind peer review practiced by specially invited international editorial boardmembers.
2221-1691/Copyright?2016 Hainan Medical University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open accessarticle under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年4期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年4期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Susceptibility of Aedes albopictus from dengue outbreak areas to temephos and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis
- Pediculosis capitis among p rimary and m idd le school children in Asadabad,Iran:An epidem iological study
- Know ledge,attitude and recommenda tions for p ractice regarding dengue among the resident population of Queensland,Australia
- Sudden death in a captive mee rkat(Suricata surica tta)w ith arterial m edial and m yocardial calcification
- The African Moringa is to change the lives ofm illions in Ethiopia and far beyond
- Com putational in telligence in tropicalm edicine
