Susceptibility of Aedes albopictus from dengue outbreak areas to temephos and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis
Ahmad M ohiddin,Asmalia M d Lasim,Wan Fatma Zuharah,*School of Biological Science,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,MalaysiaCentre of Chemical Biology,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,MalaysiaVector Control Research Unit,School of Biological Science,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,Malaysia
?
Susceptibility of Aedes albopictus from dengue outbreak areas to temephos and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis
Ahmad M ohiddin1,Asmalia M d Lasim2,Wan Fatma Zuharah1,3*1School of Biological Science,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,Malaysia
2Centre of Chemical Biology,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,Malaysia
3Vector Control Research Unit,School of Biological Science,Universiti Sains Malaysia,Pulau Pinang,Malaysia
Original article http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.01.006
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received in revised form 23Aug 2015
Accepted 21 Sep 2015
Availableonline8 Jan 2016
Aedes albopictus Mosquito
Larvicide
Susceptibility
ABSTRACT
Ob jective:Tomonitor the current duration of the application rates in vector programme and the level of Aedes albopictus larvae susceptibility from three selected areas in northeast district of Penang on two selected larvicides,temephos and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis(Bti)which are commonly used by Penang Health Department for vector control.
M ethods:Themosquito larvaewere tested against two types of larvicides:(1)temephos (Abate?)w ith diagnostic dosage(0.012mg/L)and operational dosage(1mg/L)and(2) Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis(VectoBac?WG)w ith operational dosage ranging from 6000 international toxic units per L to 24000 international toxic unitper L. A total of 20 late third and early forth instar larvae were selected and transferred into paper cup sized 300 m L using w ide-mouthed pipette.The larvae were distributed into each 300 m L paper cup containing 50 m L of aged tap water.The experiment was replicated fi ve times foreach concentration tested.Each testwas repeated three times.The mortality was recorded after 24 h of exposure and recorded lethal timewasbased on 2 h for temephos and 6 h for Bti.The control consisted of ethanol for temephos and only seasoned water for Bti.
Resu lts:The result showed that Aedes albopictus from Flat Hamna,Kampung Sungai Gelugor and Kampung Tanjung Tokong were still susceptible to Bti and temephos. However,higher lethal time and resistance ratio were detected in strain from Flat Hamna which was a known dengue hot spot area in northeastof Penang.
Conclusions:The application of temephos and Bti in vector control activity in these selected localities is still relevant in the control of Aedes larvae populations.
1.Introduction
Insecticide is a toxic productand used to kill pest insects or elim inate diseases carrying pests.Natural insecticide can also be derived from naturalplants[1].An insecticidehas to beapplied in the living place or habitatof the target insect to ensure that the insecticide is touched or digested by the pest insects.Most of the insecticides are nerve poison and kill the insect by attacking the speci fi c part in themetabolism mechanism inside the insect's body[2].However,the excessive use of the insecticide brings several problems to the environment.The most problematic case is the environmental contam ination through basic food chain,which endangers the insect,wildlife, and human being.Many insects or animals are at risk as they rely upon the main source of food contam inated w ith insecticides.
Globally,temephos is themost w idely used as it is easy to handle,cheap in price,has good residual effect,has low toxicity to mammalian and safe to apply to drinking water[3–5].Temephos is one of a few organophosphates registered and produced commercially to control Aedes mosquito larvae as a larvicide used[6].Larvicidal activity is very important in vector control management because the effectiveness in polluted water,has a long residual activity and can be used on any stage of larva.Since 1970,it has been used againstmosquito larvae in stagnant water and in the vector management of dengue fever,malaria and fi lariasis especially in Thailand[7] and Malaysia since 1973[8].The larval control still primarily utilised the temephos,despite the known existence of temephos resistant populations inmany parts of theworld[9].
Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis(Bti)is a biological larvicide and widely used to controlmosquitoes and black fl ies [10,11].Bti showed a fast killing effect w ith a good toxicology pro fi le with the absence of cross-resistance w ith conventionally used pesticides[12].Productw ith Bti causes no harm and is safe to thebird,man,fi sh andmammals[13,14].Themodeof action of endotoxin to kill larvae is stillunclearbut the sequence of toxin activation iswell studied[15].Once the bacteriaare ingested,the crystalw illbe dissolved in the naturally alkaline pH in the larval m idgut and the endotoxin attached were activated.The larvae usually die w ithin 2 or 3 days[16].
One of themajor problems in vector control is development of resistance to existing insecticides in the vectors.Recently, resistance to temephos has been previously reported in Malaysia and other country[17–19].Thew idespread use of insecticide has led to insecticide resistance in mosquitoes and become another problem for the ability to control disease.Thus,Bti is an alternative candidate to manage the resistance to temephos[4]. It contains four different larvicidal proteins,each acting in different ways to make it dif fi cult to develop resistance[20]. Furthermore,there is no consistent resistance which has been detected after a long-term treatment w ith Bti[21],but only a moderate Bti resistance was reported locally[22].
Laboratory bioassay can only detect resistance when it presents in high frequencies in vector population.The early detection of the resistance can improve the vector ef fi cacy by improving the implementation of alternative control strategies. Diagnostic dosagewas used to determine insecticide resistance against Anopheles,Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti (Ae.aegypti)[23].It is a standard test for detecting and measuring resistance,which should be available to the researcher comm ittees to make a comparison between other countries in order to verify the standard dosage for all insecticides.The baseline of diagnostic dose is possible to be changed due to the current resistance status data.The mortality assay based on time is one of the convenient procedures which is easy,time-saving and feasible to determ ine insect susceptibility in the fi eld population[24].
Therefore,the purpose of this study is tomonitor the current duration of the application rates in vector programme and the level of Aedes albopictus(Ae.albopictus)larvae susceptibility from three selected areas in northeast districtof Penang on two selected larvicides,temephos and Btiwhich are commonly used by Penang Health Department for vector control.
2.M aterials and methods
2.1.Tested mosquitoes
The w ild strain of Ae.albopictus mosquitoes from the three selected areas w ith the highest reported dengue fever cases in northeast district of Penang were collected from the majority (>90%)of natural breeding sites such as tyres,discarded tins, cans and fl ower pots.Collections were carried out from three selected areas on Penang Island:Flat Hamna(FH)Sungai Dua, Kampung Sungai Gelugor(KSG)and Kampung Tanjung Tokong(KTT)based on themethodologiesdescribed previously [25].Collected samplesof Aedes larvaewere broughtback to the laboratory,identi fi ed and were used in the bioassay test.Ae. albopictus VCRU strain(susceptible strain),which served as control reference baseline was obtained from insectarium of Vector Control Research Unit,Universiti Sains Malaysia (5°21′N,100°18′E).This susceptible strain was colonised since 1980s formore than 800 generations.
2.2.Temephos bioassay
Larvicide testingwasprepared according to theWorld Health Organization(WHO)procedure w ith a modi fi cation on the applied dose of commercial Abate?1.1G[1.1%w/w,registered by BASF(Malaysia)Sdn.Bhd][8].Themosquito larvae were tested against two different dosages of temephos:(1) recommended dose at 0.012 mg/L and(2)operational dose that has been used by Department Health of Penang at 1mg/L and prepared w ith ethanol as solvent.A total of 20 late third and early fourth instar larvae were selected and transferred into paper cup sized 300 m L using w ide-mouthed pipette. Larvae were left for 1 h prior to the experiment to perm it acclimatization and no additional food was offered.A fter that period,any abnormal larvae were replaced w ith healthy ones. The larvae were distributed into each 300 m L paper cup containing 50m L of aged tap water.The experimentwas replicated fi ve times for each concentration tested.Each testwas repeated three times.
The testsolution was prepared by adding appropriate amount of temephos in solvent and stirred for 30 s w ith a glass rod. Fifteen m inutes after solution has been prepared(to allow the agent to m ix well in the solvent),the mosquito larvae were introduced into each cup and water was further added to make up the fi nal volumeof 200m L.The control(untreated)consisted of 1m L ofethanol for temephos.Larvalbioassay testswere run under laboratory condition at temperature of(26±2)°C and (60±20)%relative hum idity.Cumulative larvalmortality was recorded for2 h w ith intervalof 5m in foroperational dosage of temephos(1mg/L).Larvalmortality after 24 h was also recorded after the exposure to temephos.Themortality of Ae.albopictus was recorded after24 h of exposure and was presented as percentage,whereas,lethal time(LT)was based on 2 h.Lethal datawere log-transformed prior to statisticalanalysis to ful fi l the assumption of probitanalysis[26].The resistance ratio(RR)was calculated by dividing the LT of the fi eld strain by the LT of the susceptible strain.
2.3.Btibioassays
VectoBac?WG was a commercial biolarvicidal formulation of Bti w ith a potency of formulation 3000 international toxic unit(ITU)/mg against Ae.aegypti.The larvalbioassay testswere conducted w ith slightmodi fi cations as previously described[27–30].The recommended dose by the manufacturer was 2–8 g/ 1000 L(equivalent to 6000 ITU/L–24000 ITU/L).The operational dose used for Bti application for control program in Penang was based on the recommended dose by the manufacturer as mentioned on the label.Three concentrations were used in this study,which were 6000,15000 and 24000 ITU/L w ith water as the solvent.The test of Bti was assessed for 10 m in–6 h after Bti applications and 24 h after exposure to all of the concentrations tested.For each bioassay, 20 larvae per cup were exposed to different concentrations of Bti.The appropriate dilution from stock solution was added to the water in the cups to obtain the desired target doses.Five cups per concentration(100 larvae)were performed for each concentration tested.Each bioassay was repeated three times and a control group was tested using water.Themean LT and the RR were obtained for each sample,as described above.
3.Results
3.1.Toxicity of insecticide in 24 h
The study was performed based on three strains of Ae. albopictus colonies collected from different localities and VCRU susceptible strain was used as a reference strain.The susceptibility testsof temephoswerebased on the numberof Ae. albopictus mortality for FH,KSG and KTT strain.A ll of the strainsshowed 100%mortality on 0.012mg/L(WHO diagnostic dose)and 1 mg/L(operational dose for Health Department of Penang)dosages(Table 1).Recommended dose for temephos proposed by WHO(0.012 mg/L)and Health Department of Penang(1mg/L)whichwas83.3%higher thanWHO dose,gave the same resultof 100%mortality after24 h post-treatment.Test on Bti also showed 100%mortality against 6000,15000 and 24000 ITU/L after 24 h post-exposure for all strains tested (Table 2).This indicated that the Bti dosage recommended by manufacturerwas stilleffectiveagainst Ae.albopictus larvae for all strains.
3.2.Temephos
The result showed the VCRU susceptible strain had the lowest LT values compared to other fi eld strains(FH,KSG and KTT).The LT50values against Ae.albopictus from VCRU,FH, KSG and KTT ranged from 36.44 m in to 68.31 m in.W ild strains required longer time to be killed compared to the laboratory strain(36.44 m in).The LT50of the operational dose against Ae.albopictus from VCRU,FH,KSG and KTT were 36.44,68.31,64.86 and 50.61m in respectively.A llof the LT50valueswere higher for the fi eld strains(Table 1).
The results obtained from bioassay test revealed that FH strains had signi fi cantly longer LT when tested w ith operational dosage(1 mg/L)compared to VCRU and KTT strain(nonoverlapping of 50%and 95%CLs,P<0.01;Table1).However, the values of LT50for FH strain showed no statistical difference compared to KSG strain(overlapping of 50%and 95%CLs, P<0.01;Table 1).Our result indicated that low mortality was recorded w ithin the fi rst 2 h after treatment w ith 0.012 mg/L temephos dose in all of fi eld strains due to the lower concentration compared to operational dose for Health Department of Penang(1mg/L).

Table1 Larval susceptibility of Ae.albopictus strainsafter 24 h of continuous exposure to temephos.
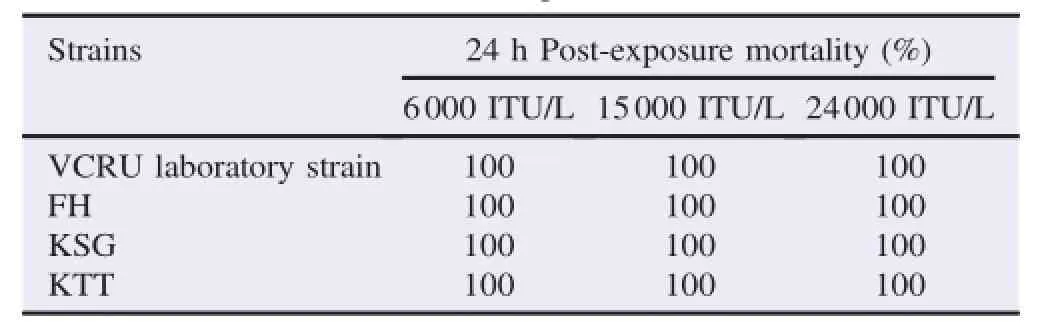
Table 2 Larvalmortality of Ae.albopictus strains to differentdosesof VectoBac?WG(Bti)after24 h of continuousexposure.
3.3.VectoBacWG?susceptibility
The results obtained from Bti bioassay revealed that FH strains had signi fi cantly longer LT in all three dosages tested compared to other strains(non-overlapping of 50%and 95% CLs,P<0.01;Table3),which indicated that FH strain was less tolerant to Bti.The result showed the VCRU susceptible strain had the lowest LT values compared to other three fi eld strains (FH,KSG and KTT).The LT50of the 6000 ITU/L against Ae. albopictus for VCRU,FH,KSG and KTT were 52.70,107.06, 88.56 and 59.81 m in respectively followed by 15000 ITU/L (26.09,63.92,46.10,32.94 m in)and 24000 ITU/L(20.65, 40.90,34.87,27.96 m in).A ll the LT50valueswere higher for the fi eld strainsand the LT reduced w ith the increasing dose of Bti.However,the LT values between each strain showed signi fi cant differences between tested doses(F=1692.59,df=2, P=0.00).Generally,the susceptibility decreased in order of VCRU strain>KTT>KSG>FH.
3.4.Resistance ofmosquito to temephos and Bti
A llmosquitoes found to be still susceptibleagainst temephos at operational dosage(1 mg/L)(Table 1).Ae.albopictus from FH showed the highest value of RR50w ith 1.87 folds followed by KSG and KTT w ith 1.77 and 1.39 respectively.The level of susceptibility of Ae.albopictus larvae strains from FH,KSG and KTT was generally considered susceptible to Bti(Table 3).At 6000 ITU/L Bti(VectoBac?WG),FH strain had the highest valueof RR at2.03 followedw ith KSG and KTT atRR 1.68 and1.13 respectively.For 15000 ITU/L,FH,KSG and KTT showed RR of 2.45,1.77 and 1.26 respectively,while RR against 24000 ITU/L at LT50for all three localitieswas 1.98,1.69 and 1.35 respectively(Table 3).
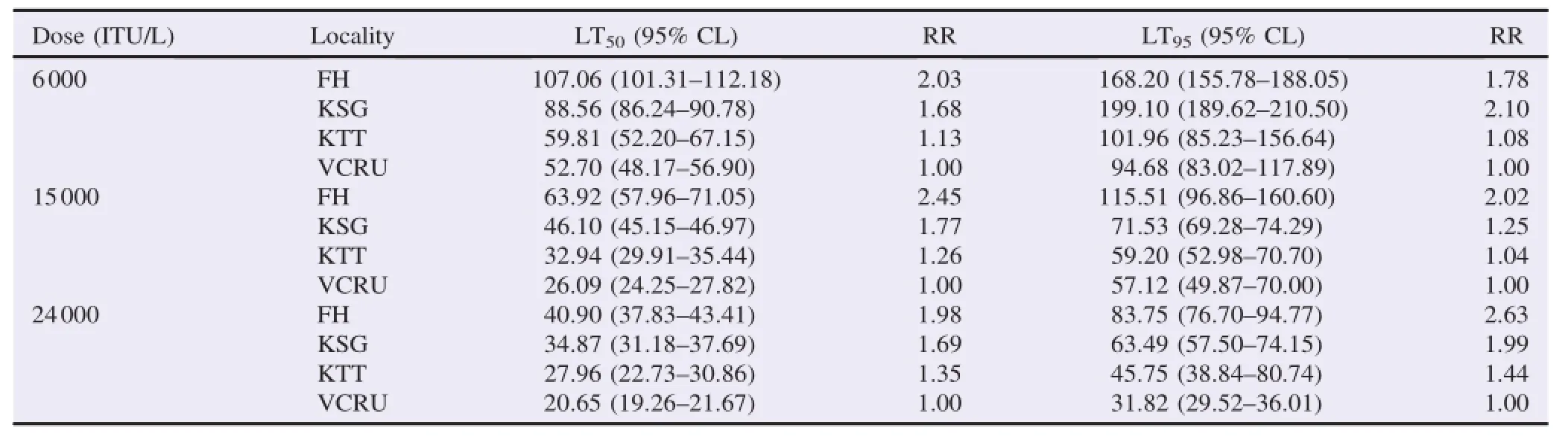
Table3 LT and RR of Ae.albopictus from different localities to VectoBac?WG(Bti).
4.Discussion
Penang Island has experienced increased breeding of Ae. albopictus which supposedly leads to an increase in the number of dengue fever cases.Therewere 878 cases during fi rst half of 2014,an increase of 175%compared to 2013[31].The present study indicated that both the larvicide are still effective against Ae.albopictus larvae as reported previously[17,32].In comparison,the standard larvicides used in mosquito control are still effective against the United States,Thailand and India population but themonitoring and the need of development of new tools is still in the fi rst priority[33].Detection of resistance in larvae often forestall resistance in adultmosquito. It can also show that the resistance in the larvae can be expressed and determ ined in the adultmosquito population.
In Malaysia,temephos has been introduced since the fi rst nationw ide dengue feveroutbreak in 1973[34].The fi rststudy on temephos resistance in Ae.aegypti was conducted in Kuala Lumpur in 1984 and resistance was not detected[35].A reevaluation was carried out in Jinjang,Kuala Lumpur in 1989 and it was found that Ae.aegypti started to develop low resistance towards temephos[36].However,other study has found that the larvae of Ae.albopictus were less susceptible to temephos than in Ae.aegypti[37].Aedes mosquitoes have a potential to develop resistance towards temephos under selection pressure,which is found to be correlated w ith the time and fi tness costs[38–40].
Temephos is used extensively and intensively in dengue outbreak areas.This seems to enhance the development of resistance in the fi eld strains.The FH and KSG areas have been treated repeatedly w ith operational dose of temephos.Despite this,Ae.albopictus larvae are still considered susceptible to temephosw ith completemortality in 24 h asshown in ourstudy. In this study,FH strain,has shown the possibility to develop faster resistance towards temephos in the future as the RR50was the highestamong the strains.Sim ilar fi ndingswere reported by Chen et al.[17].There is no failure in control activity(100% mortality in 24 h)in Argentina,but the lethal concentration and RR values show incipient resistance.It is therefore crucial to continuously monitor the nationw ide temephos resistance status of Ae.albopictus prior to emergence of high level of resistance[41].
In the current study,Ae.albopictus was susceptible to VectoBac?WG in all concentrations tested.In Penang,Btihasbeen used to control dengue vectors since 2003 and such use was intensi fi ed in 2010.Itwas used as an alternative larvicide other than temephos.In M alaysia,as in other parts,there is no report of resistance among Aedes mosquitoes againstBti.Btiis applied in the fi eld to supplement temephos in order to optim ize the ef fi ciency of the larviciding program.This is sim ilar w ith the fi nding in Lahore,Pakistan,which reported theexposure against Bti causing RR of 1.97 and 2.22[25].No cross-resistance between Bti and temephos has been reported so far[4]. However,low resistance to Bti has been reported from other countries[42].
Resistance against Btiwas reported due to reduction of the toxin binding to epithelial lining in the insect gut or the enhancementof the digestion process of Btiby the gut protease [25,43].The frequency of gene resistancemay be changed if they are occasionally exposed or routinely exposed to the insecticide which brings an advantage to the resistance gene.Other study also suggested that resistance also occurred from the standing genetic variation in the affected areas[44].The fl ow of the low genetic variation from treated areas can cause Bti resistance in other population[45].The resistance against Bti has also been found in the laboratory[43,44].Development of resistance to Bti is related to the mosquito habitat types which is an important factor in determ ining the effectiveness of Bti.
An attempt has been made to evaluate the effectiveness of temephos and Bti againstmosquito larvae.Themonitoring of resistance status must be initiated and fully documented.The vector control programme w ill not succeed w ithout any extra resistance status information,which becomes one of the lim itation in vector controlactivities.This study provided abaseline reference for the futuremonitoring on the resistance status of Ae.albopictus in FH,KSG and KTT.It is very important to monitor the development of resistance in dengue outbreak areas.The occurrence of resistance should be mapped out carefully.However,we preferred source reduction asone of the most effective strategies.Besides,this method is more direct and simple to reduce themosquito population for a long-term activity.The application of temephos and VectoBac?WG in vector controlmanagement in FH,KSG and KTT is still relevant and serves as an effective tool to control Aedes populations.
Con fl ict of interest statement
We declare thatwe have no con fl ict of interest.
Acknow ledgments
The authors would like to thank the Director General of Health M alaysia for the perm ission to publish this paper,Director of Penang Health Department and Vector-Borne Disease Control Program,Penang for all support and technical assistance.We also would like to thank the staffs of Vector Control Research Unit,University Science M alaysia for all assistance during thisproject.Wearegrateful to the volunteersand resident from all three localities for theiractive participation.Thisproject was funded by FGRS Grant by M inistry of Education and Universiti Sains M alaysia(203/PBIOLOGI/6711359).This is partof M.Sc thesis,Universiti Sains M alaysia,Penang.
References
[1]M iresmailli S,Isman MB.Botanical insecticides inspired by plantherbivore chem ical interactions.Trends Plant Sci2014;19(1):29-35.
[2]Casida JE,Durkin KA.Neuroactive insecticide:targets,selectivity, resistance,and secondary effects.Annu Rev Entomol 2013;58:99-117.
[3]Chang KS,Shin EH,Yoo DH,Ahn YJ.Enhance toxicity of binary mixtures of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis and three essentialoilmajor constituents to w ild Anopheles sinensis(Diptera: Culicidae)and Aedes albopictus(Diptera:Culicidae).J Med Entomol 2014;51(4):804-10.
[4]Ara′ujo AP,Diniz DFA,Helvecio E,de Barros RA,de Oliveira CMF,AyresCFJ,etal.The susceptibility of Aedes aegypti populations displaying temephos resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis:a basis for management.Parasit Vectors 2013;6:297.
[5]World Health Organization.Temephos in drinking water:use for the vector control in drinking-water sources and containers. Geneva:World Health Organization;2009.[Online]Available from:http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/ temephos.pdf[Accessed on 4th August,2015]
[6]Reyes-Solis Gdel C,Saavedra-Rodriguez K,Suarez AF, Black WC 4th.QTL mapping of genome regions controlling temephos resistance in larvae of themosquito Aedes aegypti.PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014;8(10):e3177.
[7]Jurjevskis I,Stiles AR.Summary review of larvicides tested at stage IV/V fi eld trials 1964–1977.Geneva:World Health Organization;1980.
[8]Chen CD,NazniWA,Lee HL,So fi an-Azirun M.Susceptibility of Aedesaegypti and Aedesalbopictus to temephos in four study sites in Kuala Lumpur City Center and Selangor State,Malaysia.Trop Biomed 2005;22(2):207-16.
[9]de Souza Leal Diniz MMC,da Silva Henriques AD,da Silva Leandro R,Aguiar DL,Beserra EB.Resistance of Aedesaegypti to temephos an adaptive disadvantage.Rev Saude Publica 2014; 48(5):775-82.
[10]W illiams GM,Faraji A,Unlu I,Healy SP,Farooq M,Gaugler R, et al.Areaw ide ground applications of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis for the control of Aedes albopictus residential neighbourhoods:from optimization to operation.PLoSOne 2014;9(10): e110035.
[11]Monnerat R,Pereira E,Teles B,Martins E,Pra?a L,Queiroz P, et al.Synergistic activity of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins against Simulium spp.larvae.J Invertebr Pathol 2014;121:70-3.
[12]Marcombe S,Darriet F,Agnew P,Etienne M,Yp-Tcha MM, Y′ebakima A,et al.Field ef fi cacy of new larvicide products for control ofmulti-resistant Aedes aegypti populations in M artinique (French W est Indies).Am JTrop Med Hyg 2011;84(1):118-26.
[13]Land M,M ijland M.Biological control ofmosquitoes using Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis:a pilot study effects on target organisms,non-target organism s and humans.M istra EviEM Pilot Study 2014[Online]Available from:http://www.eviem.se/ Documents/F%C3%B6rstudier/PS4%20Biological%20control% 20of%20mosquitoes%20using%20Bacillus%20thuringiensis% 20israelensis_a%20pilot%20study%20of%20effects%20on% 20target%20organisms%20non-target%20organisms%20and% 20humans.pdf[Accessed on 4th August,2015]
[14]Wu C,Wu L,Zhang L,Gelbic I,Xu L,Guan X.Characterization of eight Bacillus thuringiensis isolates originated from fecal samplesof Fuzhou Zoo and Fuzhou Panda Centre.JAsia Pac Entomol 2014;17:395-7.
[15]Lee SB.Toxin binding receptorsand themode ofaction of Bacillus thuringiensissubsp.israelensis cry toxins[dissertation].Riverside: University of California;2013.
[16]Jayapriyra G,Shoba FG.Evaluation of Gambusia af fi nis and Bacillus thuringiensis var.israelensis as Culex quienquefasciatus control agents.JEntomol Zool Stud 2014;2(3):121-5.
[17]Chen CD,NazniWA,Lee HL,Norma-Rashid Y,Lardizabal ML, So fi an-Azirun M.Temephos resistance in fi eld Aedes(Stegomyia) albopictus(Skuse)from Selangor,Malaysia.Trop Biomed 2013; 30(2):220-30.
[18]Marcombe S,Mathieu RB,Pocquet N,Riaz MA,Poupardin R, S′elior S,et al.Insecticide resistance in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti from M artinique:distribution,mechanism and relations w ith environmental factors.PLoSOne 2012;7(2):e30989.
[19]Bisset JA,Rodriguez MM,Ricardo Y,Ranson H,Perez O, Moya M,et al.Temephos resistance and esterase activity in the mosquito Aedes aegypti in Havana,Cuba increased dramatically between 2006-2008.Med Vet Entomol 2011;25(3):233-9.
[20]W irth MC.M osquito resistance to bacterial larvicidal toxins.Open Toxicol J 2010;3:126-40.
[21]Ben-Dov E.Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis and its dipteran-speci fi c toxins.Toxin(Basel)2014;6:1222-43.
[22]Tetreau G,StalinskiR,David JP,Despres L.Monitoring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.israelensis in the fi eld by performing bioassays w ith each Cry toxin separately.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2013;108(7):894-900.
[23]W orld Health O rganization.Instruction for determ ining the susceptibility or resistance ofmosquito larvae to insecticide.Geneva: World Health Organization;1981.
[24]Tikar SN,Kumar A,Prasad GBKS,Prakash S.Temephos-induced resistance in Aedes aegypti and its cross-resistance studies to certain insecticides from India.Parasitol Res 2009;105:57-63.
[25]Jahan N,Shahid A.Evaluation of resistance against Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis WDG in dengue vector from Lahore, Pakistan.Pak J Zool 2012;44(4):945-9.
[26]Litch fi eld JT Jr,W ilcoxon F.A simpli fi ed method of evaluating dose-effectexperiments.JPharmacol Exp Ther 1949;96:99-113. [27]Dylo P,Martin C,Mhango C.Ef fi cacy of Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis(Bti)on Culex and Anopheline mosquito larvae in Zomba.Malawi JSci Technol 2014;10(1):40-52.
[28]GorashiNE,Elsha fi e HAF,Hamid HA,Dirar DH.Characterization of Sudan strains of Bacillus thuringiensis pathogenic to the larvae of the housemosquito Culex quinquefasciatus.Agric Biol JN Am 2012;3(7):271-9.
[29]Achille GN,Christophe HS,Yilian L.Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis var.israelensis(H-14)on Culex,Aedes and Anopheles larvae(Cotonou;Benin).Stem Cell 2010;1(1):60-8.
[30]Lee YW,Zairi J.Laboratory evaluation of Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 against Aedes aegypti.Trop Biomed 2005;22(1):5-10.
[31]M inistry of Health Malaysia.The currentsituation ofdengue fever in Malaysia for week 25 of 2014(15 to 21 June 2014).Putrajaya: M inistry of Health Malaysia;2014.[Online]Available from:http:// www.moh.gov.my/english.php[Accessed on 4th August,2015]
[32]Kamgang B,Marcombe S,Chandre F,Nchoutpouen E,Nwane P, Etang J,etal.Insecticide susceptibility of Aedesaegypti and Aedes albopictus in Central Africa.Parasit Vectors 2011;4:79.
[33]Marcombe S,Farajollahi A,Healy SP,Clark GG,Fonseca DM. Insecticide resistance status of United States populations of Aedes albopictus and mechanisms involved.PLoS One 2014;9(7): e101992.
[34]Cheong WH.The present status of dengue fever/dengue haemorrhagic fever and its control in West Malaysia.Asian J Infect Dis 1978;2:136-8.
[35]Lee HL,Lee TW,Law FM,Cheong WH.Preliminary studies on the susceptibility of fi eld collected Aedes(Stegomyia)aegypti (Linneaus)to Abate?(temephos)in Kuala Lumpur.Trop Biomed 1984;1:37-40.
[36]Lee HL,Lime W.A re-evaluation of the susceptibility of fi eldcollected Aedes(Stegomyia)aegypti(Linnaeus)larvae to temephos in Malaysia.Mosquito Borne Dis Bull 1989;6:91-5.
[37]Chen CD,NazniWA,Lee HL,So fi an-Azirun M.Weekly variation on susceptibility status of Aedes mosquitoes against temephos in Selangor,Malaysia.Trop Biomed 2005;22(2):195-206.
[38]Martins AJ,Ribeiro CD,Bellinato DF,Peixoto AA,Valle D, Lima JB.Effects of insecticide resistance on development, longevity and reproduction of fi eld or laboratory selected Aedes aegypti populations.PLoSOne 2012;7(3):e31889.
[39]Strode C,de Melo-Santos M,M agalhaes T,Araujo A,Ayres C. Expression pro fi le of genes during resistance reversal in a temephos selected strain of dengue vector,Aedes aegypti.PLoSOne 2012;7(8):e39439.
[40]Belinato TA,Martins AJ,Valle D.Fitness evaluation of two Brazilian Aedes aegypti fi eld populations w ith distinct levels of resistance to the organophosphate temephos.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2012;107(7):916-22.
[41]Llinas GA,Seccacini E,Gardenal CN,Licastro S.Current resistance status to temephos in Aedesaegypti from different regionsof Argentina.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2010;105(1):113-6.
[42]StalinskiR,Tetreau G,Gaude T,Despres L.Pre-selecting resistance against individual Bticry toxins facilitates thedevelopmentof resistance to the Bti toxinscocktail.J Invertebr Pathol2014;119:50-3.
[43]Tetreau G,Bayyareddy K,Jones CM,Stalinski R,Riaz MA, Paris M,et al.Larval midgutmodi fi cations associated w ith Bti resistance in the yellow fevermosquito using proteomic and transcriptom ic approaches.BMC Genomics 2012;13:248.
[44]Paris M,Marcombe S,Coissac E,Corbel V,David JP,Despres L. Investigating the genetics of Bti resistance using m RNA tag sequencing:application on laboratory strains and natural populations of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti.Evol Appl 2013;6: 1012-27.
[45]Paris M,David JP,Despres L.Fitness costs of resistance to Bti toxins in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti.Ecotoxicology 2011; 20:1184-94.
14 Aug 2015
*Corresponding author:Wan Fatma Zuharah,Vector Control Research Unit, School of Bio logical Science,Universiti Sains M alaysia,Pulau Pinang,M alaysia.
Tel:+60 4 6536130
Fax:+60 4 5251525
E-mails:w fatma@usm.m y,wan fatma@gmail.com
Foundation Project:Funded by FGRS Grant by M inistry of Education and Universiti Sains M alaysia(203/PBIOLOGI/6711359).
Peer review under responsibility of Hainan M edical University.The journal implements double-blind peer review practiced by specially invited international editorial boardmembers.
2221-1691/Copyright?2016 Hainan Medical University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open accessarticle under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年4期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年4期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Pediculosis capitis among p rimary and m idd le school children in Asadabad,Iran:An epidem iological study
- Know ledge,attitude and recommenda tions for p ractice regarding dengue among the resident population of Queensland,Australia
- Sudden death in a captive mee rkat(Suricata surica tta)w ith arterial m edial and m yocardial calcification
- The African Moringa is to change the lives ofm illions in Ethiopia and far beyond
- Com putational in telligence in tropicalm edicine
- Risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors:A system atic review
