Modified particle swarm optimization-based antenna tiltangle adjusting scheme for LTE coverage optimization
Phan NhuQuan Jiang Huilin Bui ThiOanh Li Pei Pan Zhiwen Liu Nan
(1National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)(2Faculty of Mechatronics-Electronics, Lachong University, Bien Hoa City 810000, Vietnam)
?
Modified particle swarm optimization-based antenna tiltangle adjusting scheme for LTE coverage optimization
Phan NhuQuan1,2Jiang Huilin1Bui ThiOanh1Li Pei1Pan Zhiwen1Liu Nan1
(1National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)(2Faculty of Mechatronics-Electronics, Lachong University, Bien Hoa City 810000, Vietnam)
Abstract:In order to solve the challenging coverage problem that the long term evolution (LTE) networks are facing, a coverage optimization scheme by adjusting the antenna tilt angle (ATA) of evolved Node B (eNB) is proposed based on the modified particle swarm optimization (MPSO) algorithm. The number of mobile stations (MSs) served by eNBs, which is obtained based on the reference signal received power (RSRP) measured from the MS, is used as the metric for coverage optimization, and the coverage problem is optimized by maximizing the number of served MSs. In the MPSO algorithm, a swarm of particles known as the set of ATAs is available; the fitness function is defined as the total number of the served MSs; and the evolution velocity corresponds to the ATAs adjustment scale for each iteration cycle. Simulation results show that compared with the fixed ATA, the number of served MSs by eNBs is significantly increased by 7.2%, the quality of the received signal is considerably improved by 20 dBm, and, particularly, the system throughput is also effectively increased by 55 Mbit/s.
Key words:long term evolution (LTE) networks; antenna tilt angle; coverage optimization; modified particle swarm optimization algorithm
Received 2015-03-12.
Biographies:Phan NhuQuan (1980—), male, graduate; Pan Zhiwen (corresponding author), male, doctor, professor, pzw@seu.edu.cn.
Foundation items:The National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No.2014AA01A702), the National Science and Technology Major Project (No.2013ZX03001032-004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61221002, 61201170).
Citation:Phan NhuQuan, Jiang Huilin, Bui ThiOanh, et al. Modified particle swarm optimization-based antenna tilt angle adjusting scheme for LTE coverage optimization[J].Journal of Southeast University (English Edition),2015,31(4):443-449.[doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2015.04.003]
The optimization of capacity and coverage of the long term evolution (LTE) system is a fascinating area and it has attracted the interest of researchers all over the world[1-9]. With the constant population of mobile stations (MSs) such as mobile phones, laptops, tablets, etc., the networks must respond to the demands of the individual MS such as voice calls, games, movie, music, web surfing, etc. The network operators are facing great challenges on how to satisfy user services by increasing the system capacity and ensuring evolved Node B (eNBs) coverage, and to serve more and more MSs.
Recently, there has been little research on coverage optimization. In these works, coverage problems are mainly optimized through schemes, e.g., switching on/off the eNBs, adjusting the transmit power of eNBs, adjusting the antenna tilt angle (ATA) and optimizing the placement of antennas[10-15]. To overcome the blind coverage area, Gao et al.[10]proposed switching on/off the eNBs and adjusting the transmit power of the eNBs by multiple objects genetic algorithm based on the received signal code power parameter and the carrier to interference ratio. In Ref.[11], the call dropping ratio (CDR) is regarded as the evaluation criterion of the eNBs coverage. To decrease the CDR, they used a sparse sampling algorithm to adjust the ATAs. The coverage problems such as the coverage holes, loud neighbor overlap and cell overload of femtocell clusters is solved by using a modified particle swarm optimization (MPSO)-based heuristic power control scheme[12]. To maximize coverage, the branch and bound search algorithm is used to obtain the optimal placement of antennas within the coverage area[13]. Naseer ul Islam et al.[14]proposed a cooperative fuzzy Q-learning scheme by using the fuzzy rules to adjust the antenna tilt angle based on the antenna tilt angle and spectral efficiency state. In Ref.[15], the authors proposed to jointly change the mechanical antenna tilt and transmit power to aid maintaining coverage and reducing the system power consumption.
The tilt angle of the eNB antennas plays a key role in determining eNB coverage and management of interference, but it has not been paid much attention to by the research community. Traditionally, most of ATA adjustments are done by hand, whereas, the eNBs are increasingly more modern and are automatically adjusted. This makes eNBs more adaptive to dynamic ATA, and it is better for coordinating eNB coverage, such as minimizing coverage holes caused by the failure at the neighboring eNBs, and better in managing the interference of users’ deployment[16].
In this paper, an MPSO-based tilt angle adjusting algorithm for coverage optimization in the LTE network is proposed. We define the network coverage as the number of the served MSs of eNB, which is determined by eNBs’ ATA, and the coverage problem is solved by maximizing the number of MSs under the coverage of eNBs.
First, how to estimate the number of MSs served by eNBs is presented. The coverage of the eNBs is determined by the reference signal received power (RSRP) measured from the MSs. The MSs with the maximum RSRP from all eNBs larger than the RSRP threshold are recognized as under coverage. Then, the coverage optimization problem is figureted as the optimal number of MSs under the coverage of eNBs. Since the adjustment of each ATA can affect the maximum RSRP of each MS, how to cooperatively adjust all ATAs to maximize the total number of MSs under coverage becomes a critical problem. After that, an ATA adjusting scheme based on the MPSO is proposed to maximize the number of served MSs covered by eNBs.
1System Model and Problem figuretion
The simplified system is shown in Fig.1, in which the strong and weak signal strengths are shown by solid and dashed lines, respectively.
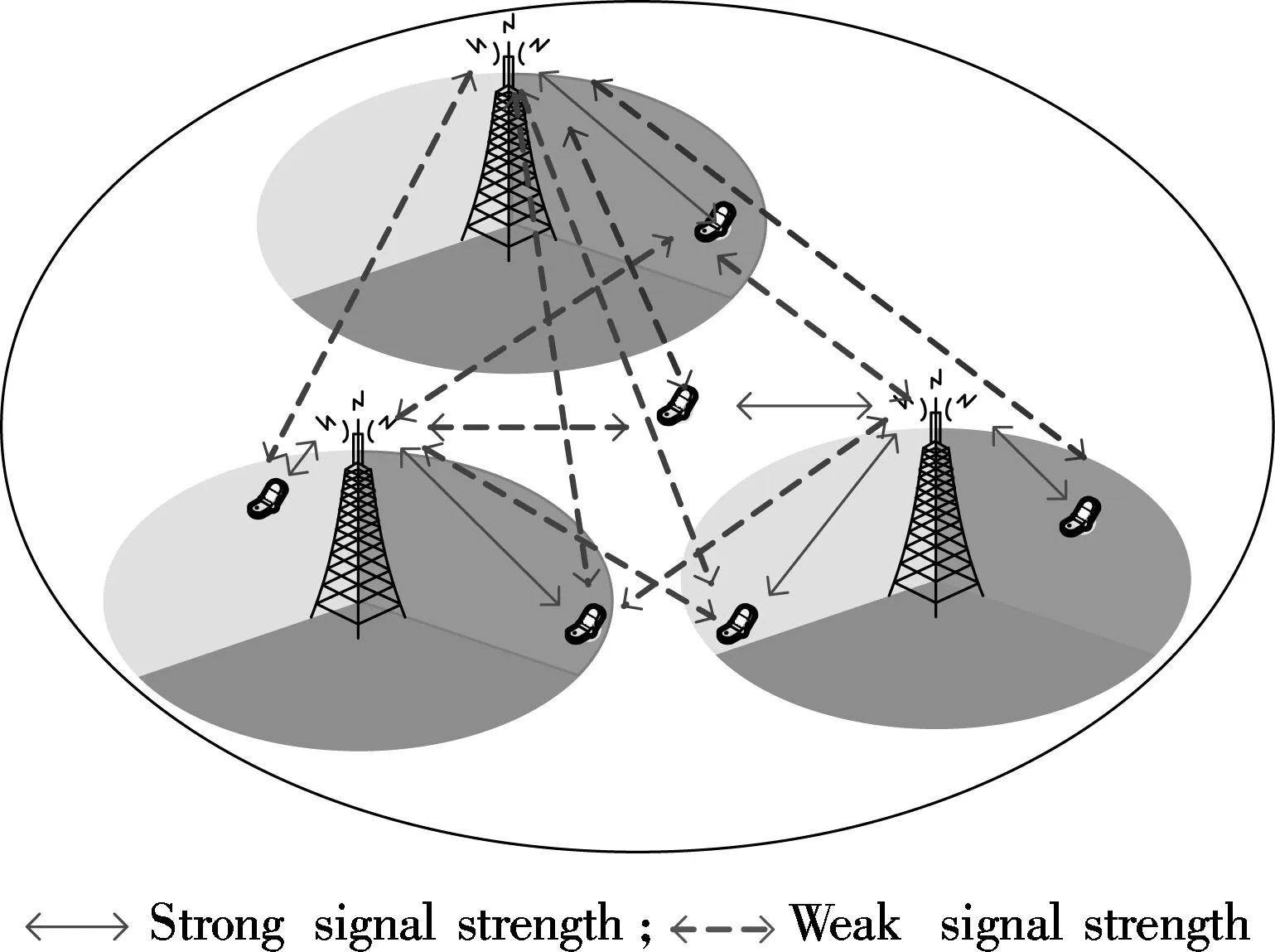
Fig.1 System model
1.1 Antenna down tilt angle
The ATA denoted as an elevation angle of the antennaθis described in Fig.2. When we change the ATA, the direction of the antenna’s main lobe will be changed. This is an important issue in determining the coverage area of eNB.
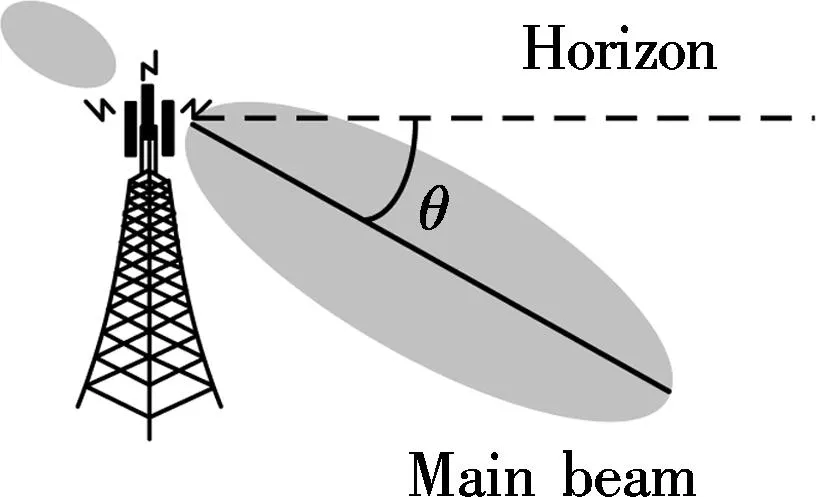
Fig.2 The relationship between antenna main lobe and tilt angle
1.2 Path-loss
To simplify, the path-loss is[17]
l=128.1+37.6log10d
(1)
wheredis the distance between MS and eNB antenna.
1.3 Shadow fading model
The effect of shadow fading is usually modelled on free space and shadow fading is logarithmically distributed[18-19]. Assume that the considered space has a map size ofx×yexpressed in square meters. The envelope of the autocorrelation shadow fading function is
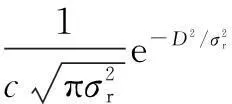
(2)
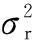
1.4 The number of MSs served by eNB
A 3GPP LTE multi-cell network as shown in Fig.1 withneNBeNBs,nantenantennas andnmsMSs is considered here. Since the system will be evaluated at each timet, for convenience, we omit the symboltin the following analysis. The reference signal received power (RSRP) on each subcarrier at timetfor MSjserved by eNBiand eNB antennakis
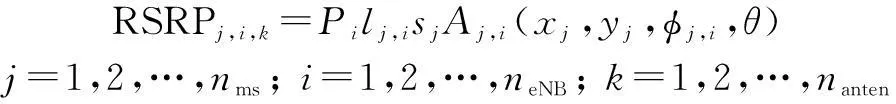
(3)
wherePiis the transmit power of eNBi;lj,iis the path loss at MSjfrom eNBi; (xj,yj) are the geographical position-coordinates of MSj;θis the eNB ATAkof eNBi; andφj,i=sin-1((yj-yeNBi)/r) is the azimuth angle between MSjand eNBi;sjis the position-related shadow fading of MSj;Aj,iis the antenna gain at MSjfrom eNBiin dBi. The MSs served by eNB antennas are determined as follows: If -60°≤φ<60°, the eNB antenna 1 is serving. If 60°≤φ<180°, the eNB antenna 2 is serving. If -180°≤φ<-60°, the eNB antenna 3 is serving.
The received signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) of MSjserved by eNBiand eNB antennakat timetis
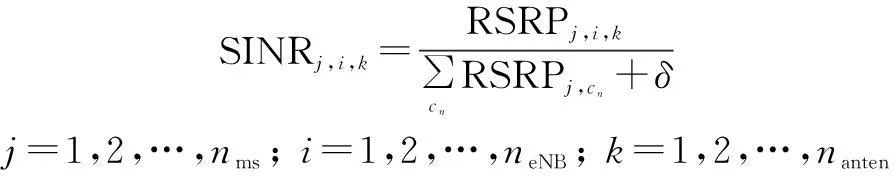
(4)
wherecnrepresents all the neighboring interfering cells andδis the noise power.
The system throughputTis
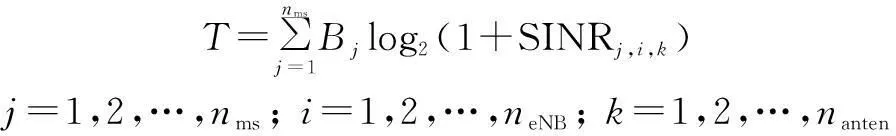
(5)
whereBjis the bandwidth allocated to MSj.
eNBiand eNB antennakwill serve MSjwith the maximum of RSRP which is greater than the RSRP threshold.
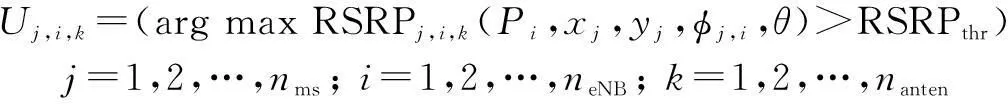
(6)
where RSRPthris the threshold used to judge which eNB and which eNB antenna are serving the MS.
The number of MSs being served by eNBiand eNB antennakis then determined by
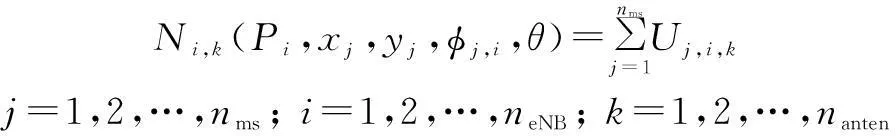
(7)
From Eq.(7), we can see that the number of MSs served by eNB is determined by the antenna tilt angles when the transmit power of eNBs and the horizontal angles are fixed and the position of MSs is changed. Therefore, the served MS number can be maximized by adjusting the antenna tilt angle.
The total number of MSs served by the eNBs is figureted as
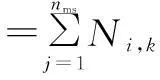
(8)
whereθ={θ1,θ2,…,θanten} is the ATAs set of the eNBs andθk(k∈[1,nanten]) is the ATAk.f(P,x,y,φ,θ) is used as the fitness function in the following proposed algorithm.
Then, the optimization problem can be figureted as
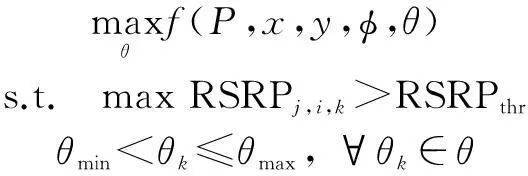
(9)
The objective is maximizing the total number of MSs served by the eNBs through finding the optimal ATAs setθ.
2MPSO-Based ATA Adjusting Algorithm
The optimal problem in Eq.(9) is a non-convex one, which is not easy to solve through computational efficient algorithms. It is fortunate that, taking the manifest non-linear and multimodal features of the solution into account, and taking into account that the search space can be constricted very quickly, the MPSO algorithm can be used to solve the ATA adjusting problem. As far as we know, there are not any efficient solutions to solve this problem, so we propose an ATA adjusting scheme based on the MPSO algorithm.
In the MPSO, there exists a swarm of particles, and each of them represents a potential solution to the optimization problem and corresponds to a fitness value determined by the fitness function of the optimization problem. All the particles update according to the evolution velocity calculated by the cooperation among the particles themselves[20].
For the proposed MPSO-based adjusting ATA algorithm aiming to solve the aforementioned coverage optimization problem, the solution is the ATAs set. A swarm of particles exists. Each particle represents a potential solution to the coverage optimization problem and corresponds to a fitness value. All the particles are updated according to the velocities calculated by their own experience and the global experience of the whole swarm.
ATAs are adjusted based on the total number of MSs served by the eNBs. First, many ATA sets are initialized randomly, each of which corresponds to a fitness value according to the fitness function (8). Secondly, all the sets of ATAs are updated in each iteration cycle according to the past experience of the best utility of each ATA set and the global best utility of all the ATA sets. The global best ATA can be obtained by iteratively updating these initial ATA sets when achieving a better fitness value. Finally, the global best solution can be obtained by the multiple restart processes.
For the optimization problem in (9), the fitness function is the total number of served MSs, and the evolution velocity corresponds to the ATAs adjustment scale for each iteration.
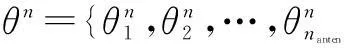
The algorithm consists of the following steps:
1) Given the number of the antennasnantenand the positions of the eNBs and MSs, set the number of particlesnp, the maximum number of the iteration timestmax, the maximum number of the restart timessmax, the inertia weightωand the acceleration coefficientsc1andc2.
2) Set the current restart times=0 for the restart processes.
3) Set the current iteration timet=0 for the iterations of the particle swarm.
4) Initialize the set ofnpATA sets,
{θ1(t),θ2(t),…,θnp(t)}
{V1(t),V2(t),…,Vnp(t)}
5) Calculate the fitness valuefn(t) of each setθn(t) according to the fitness function (8).
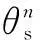
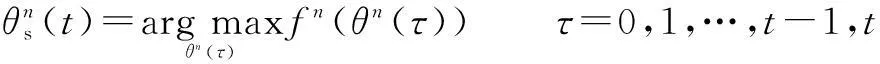
(10)
which is the best ATA set corresponding to the maximum number of the served MSs obtained so far by the setθn(t); the global best ATA set denoted byθg(t) is
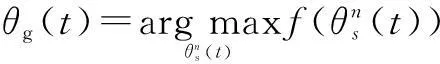
(11)
which is corresponding to the best ATA obtained so far for all sets of ATA.
7) Update the ATA adjustment scale for a typical setVnaccording to
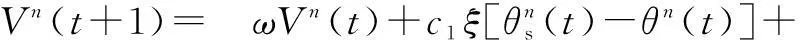
c2η[θg(t)-θn(t)]
(12)
whereω∈[ωmin,ωmax] withωmin=0.4 andωmax=1 is the inertia weight which keeps the update of the ATA adjustment scale and balances the local and global optimizing;c1andc2are two positive constants called the acceleration coefficients; andξ,η∈[0,1]. Since the parametersc1,c2,ξandηwill determine the sense of the variation of the velocity, according to the experimental studies,c1andc2are taken 1.49,ξandηare random numbers in [0,1][21-22]. The second part of Eq.(12) is the cognition part, and the third part is the social part.
8) Update the ATA setθnas
θn(t+1)=θn(t)+Vn(t+1)
(13)
9) If the maximum number of iterationstmaxis not satisfied, sett=t+1 and go to Step 5); otherwise, go to Step 10).
10) If the maximum number of the restart timessmaxis not satisfied, set the restart times=s+1 and go to Step 3) to restart the algorithm; otherwise, stop the algorithm and set the ATAs of the eNBs with the global bestθg(t).
3Simulation Results
The system with 19 eNBs under cell layout in three sectors is considered. The eNBs are in the center of the hexagonal and 1 000 MSs randomly move at a speed in the range of 0 to 120 km/h in eight directions (east, west, south, north, north-east, south-east, north-west and south-west). The shadow fading is considered. We assume that the azimuth angle is kept fixed, but the antenna tilt angle can be adjusted, and the height of eNBs and MSs are the same for all eNBs and MSs. The antenna pattern is in accordance with 3GPP standard[17]. The system parameters are listed in Tab.1.

Tab.1 Setting of the system parameters
The simulation system is shown in Fig.3. The eNBs are shown by green triangles placed at the center of the hexagons, and the MSs (MS and user are interchangeable) are shown by red dots. Fig.4 shows the comparison of the served MSs number by the 1st, 2nd and 3rd antennas of eNBs with the fixed tilts of 0°, 6° and 16° and with the tilts adjusted by the MPSO algorithm. The sum of the served MSs number with the fixed tilt of 0° is 1 061 over the sum of the generated MSs number, with the fixed tilt of 6° is 805; with the fixed tilt of 16° is 424 and with the tilts adjusted by the MPSO algorithm is 877. Hence, we can see that, with the fixed tilt of 0°, the excessive coverage occurs; with the fixed tilt of 16°, the insufficient coverage occurs; with the fixed tilts of 6°, the coverage of eNBs can be acceptable; and the proposed algorithm achieves the best coverage compared with the fixed tilts. Obviously, compared with the fixed tilt of 6°, the proposed algorithm significantly improves the number of the served MSs by 7.2%. From the results of Fig.4, we select the fixed tilt of 6° to compare with the proposed scheme in the following simulation.
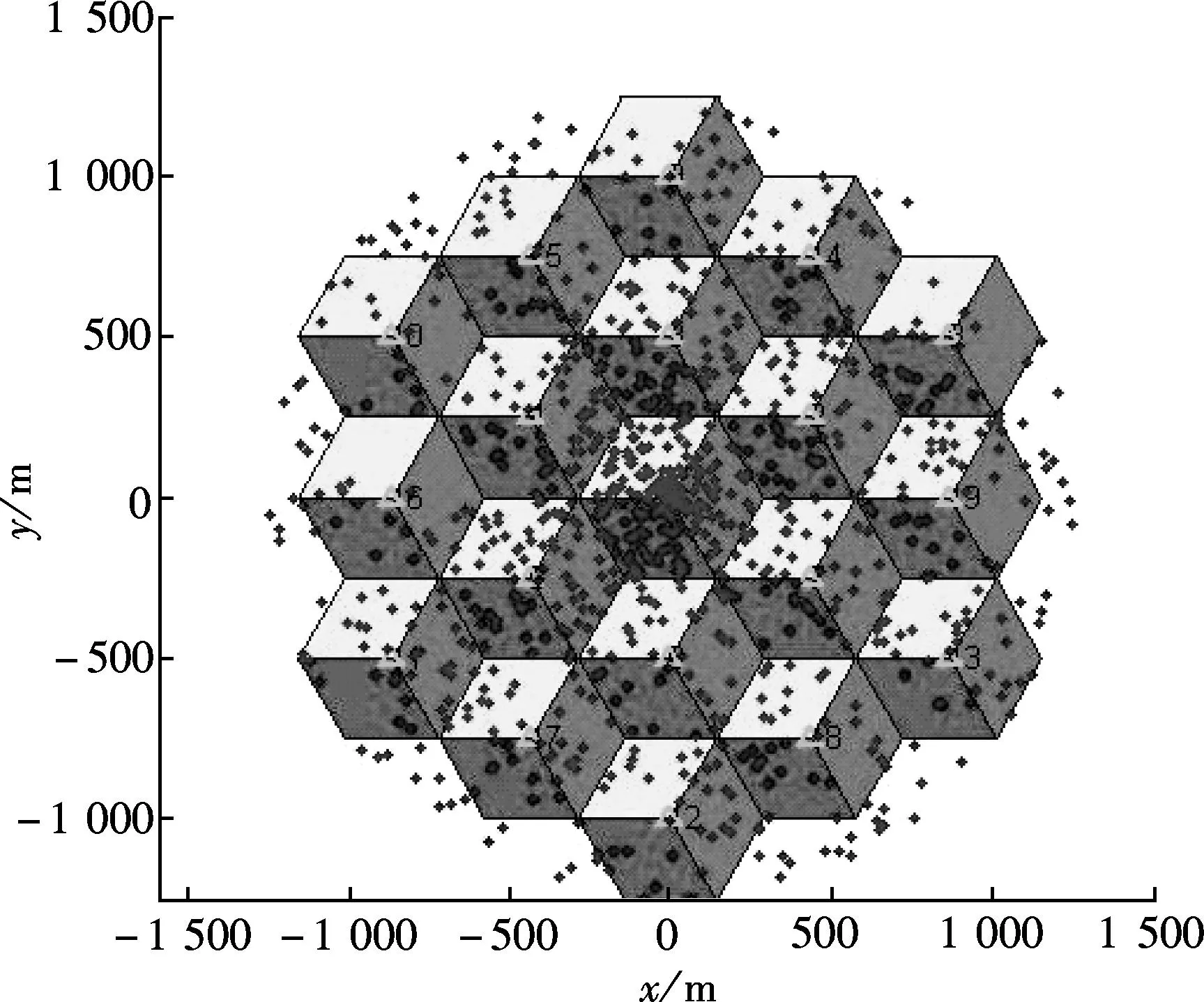
Fig.3 The simulation system
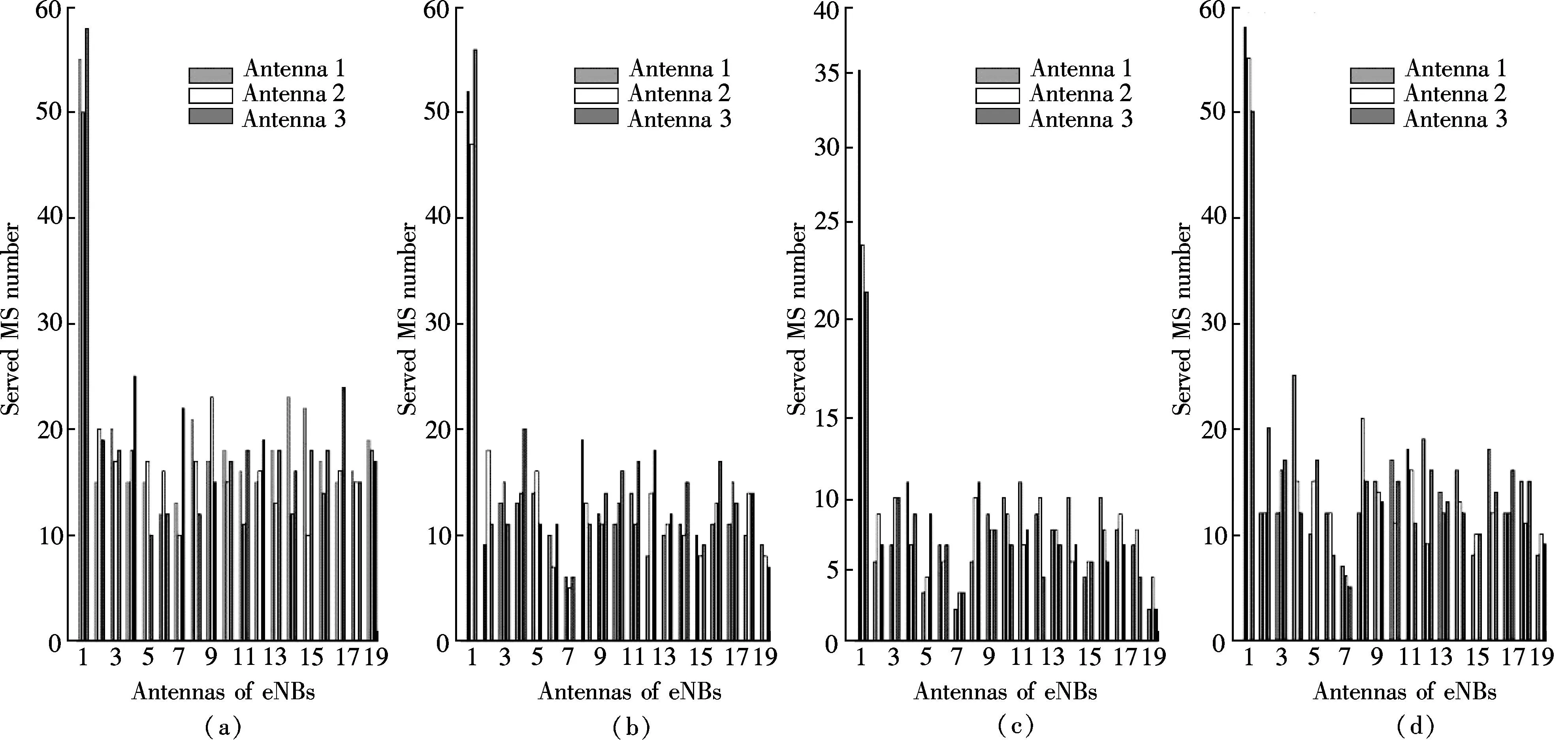
Fig.4 Comparison of served MSs number and antennas of eNBs. (a) 0°; (b) 6°; (c) 16°; (d) With tilts adjusted by MPSO
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the MSs’ RSRP comparison between the fixed tilt of 6° and the tilts adjusted by the MPSO algorithm is shown in Fig.5. We can observe that the proposed MPSO scheme improves the quality of received signal better than that of the fixed tilt of 6° by 20 dBm. Fig.6 illustrates that the MSs’ SINR of the proposed algorithm is significantly better than that of the fixed tilts of 6°. Users’ throughput and system throughput are illustrated in Fig.8. We can see that the system throughput is considerably improved by 55 Mbit/s compared with that of the fixed tilts of 6°.
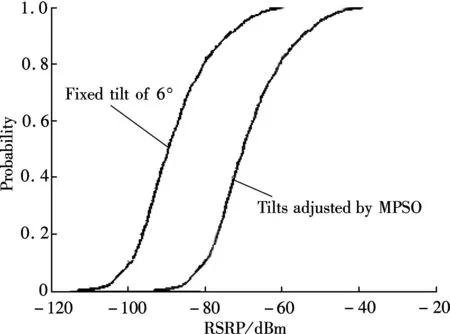
Fig.5 CDF of users’ RSRP
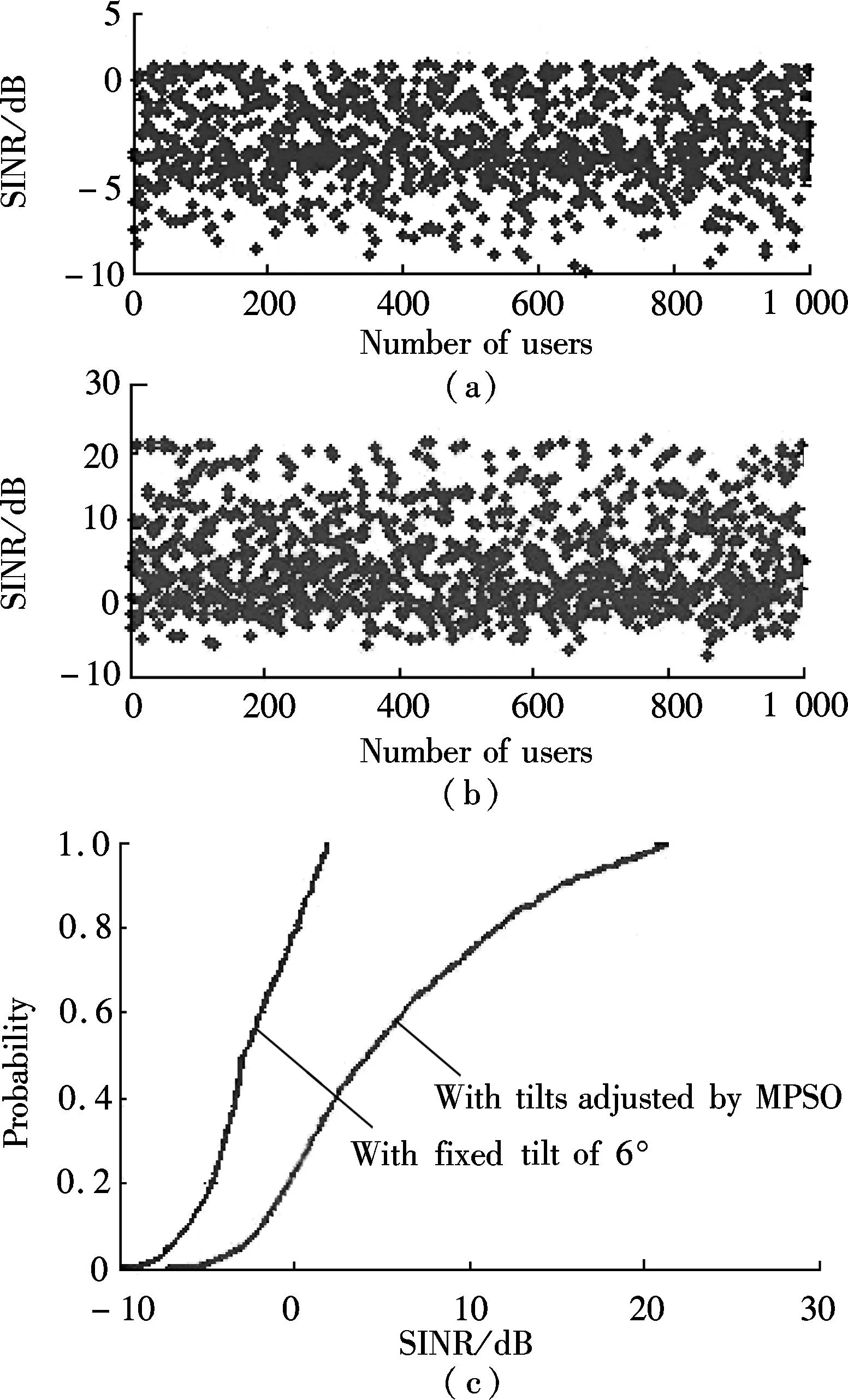
Fig.6 User’s SINR. (a) With fixed tilt of 6°; (b) With tilts adjusted by MPSO; (c) CDF
Fig.7 shows that the algorithm only needs a few iteration times to obtain the optimal value of the system throughput, and its convergence is fast. The computational complexity of the solution is polynomial time complexity.
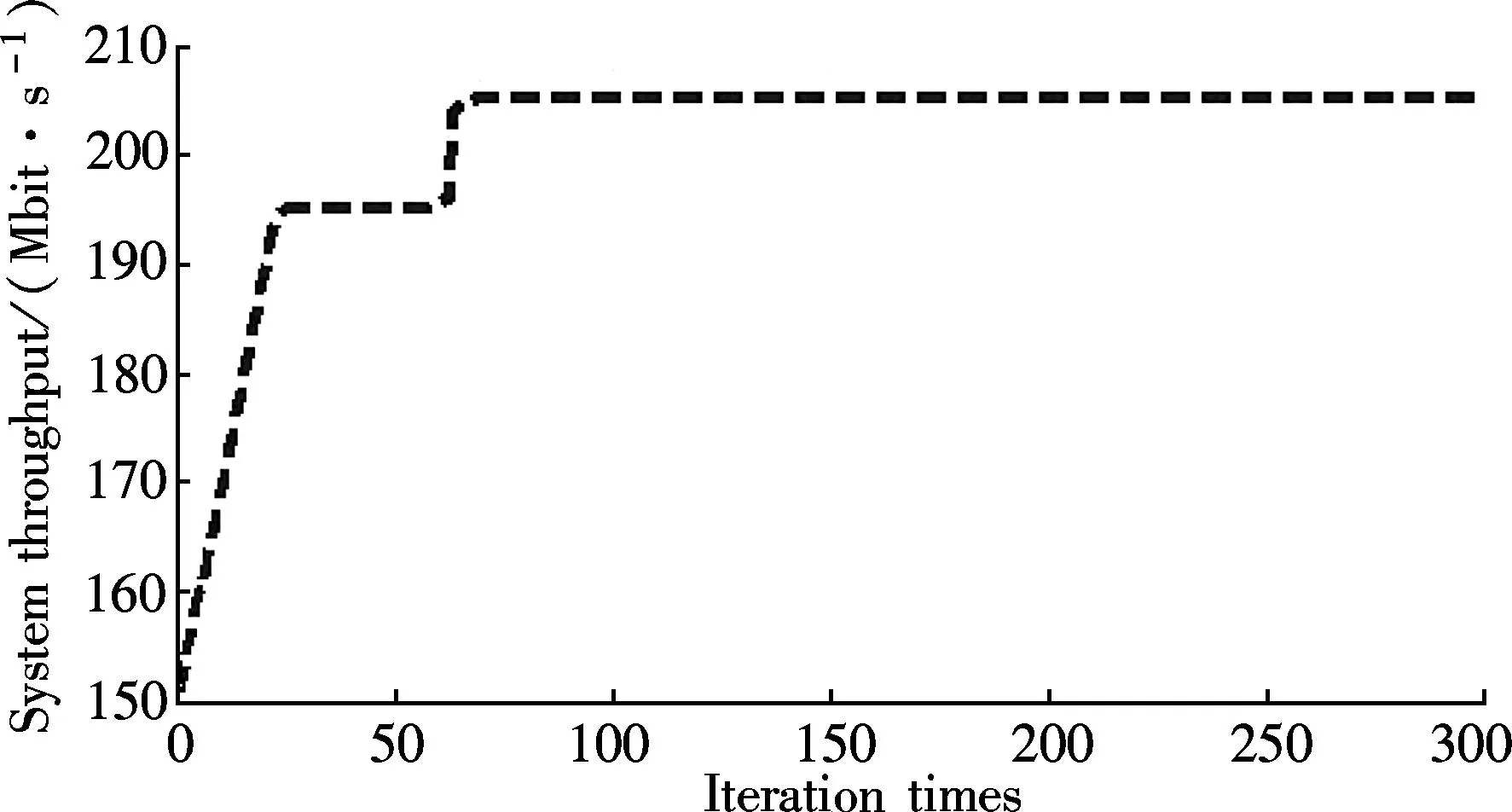
Fig.7 The convergence of solution
From Figs.4 to 8, we can see that the proposed MPSO-based ATA adjusting algorithm can significantly increase the number of MSs served by eNBs and also improve both the MSs’ SINR and system throughput. It demonstrates that, the proposed algorithm is a promising solution for the optimization of both the eNB coverage area and the system capacity in LTE networks.
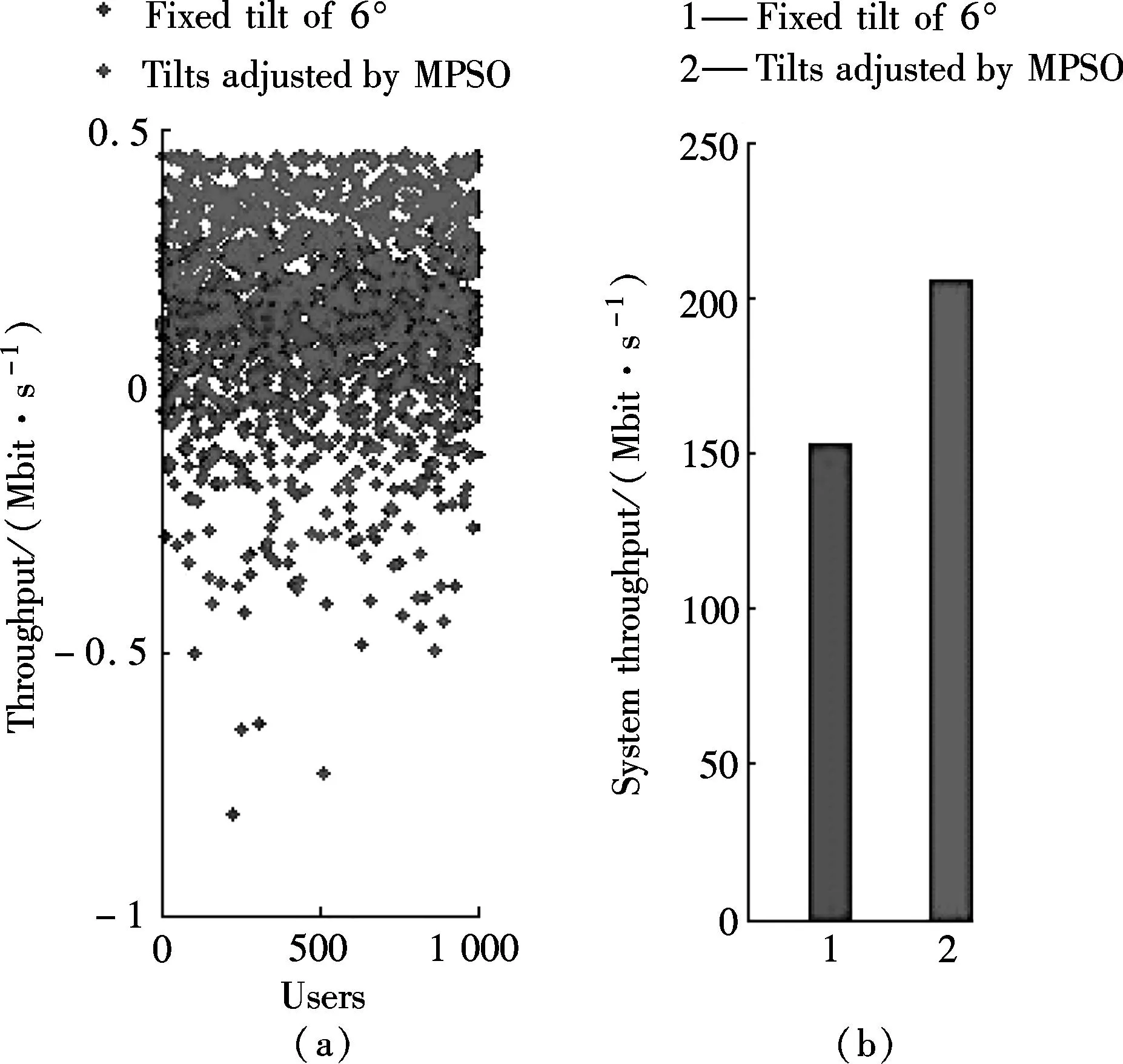
Fig.8 Throughput. (a) The users’ throughput; (b) System throughput
4Conclusion
In this paper, an MPSO-based coverage optimization scheme is proposed for adjusting the tilt angle of the antennas of eNBs to solve the coverage problem in LTE networks. We define the network coverage as the number of served MSs of eNB. A swarm of particles known as the set of ATAs is available; the fitness function is defined as the total number of the served MSs, and the evolution velocity corresponds to the ATAs adjustment scale for each iteration. Simulation results show that compared with the fixed ATA, the number of served MSs by eNBs is significantly increased by 7.2%, the quality of received signal is considerably improved by 20 dBm, and, particularly, the system throughput is also effectively increased by 55 Mbit/s benefiting from the proposed algorithm. However, without considering the load of eNBs, some eNBs are heavy load and some are light load. We will take the load of eNBs into account in future work.
References
[1]Jiang Y, Yu P, Li W, et al. Automated coverage optimization scheme based on downtilt adjustment in wireless access networks[C]//InternationalWirelessCommunicationsandMobileComputing(IWCMC). Limassol, Cyprus, 2012: 945-948.
[2]Naseer ul Islam M, Mitschele-Thiel A. Reinforcement learning strategies for self-organized coverage and capacity optimization [C]//IEEEWirelessCommunicationsandNetworkingConference(WCNC). Shanghai, China, 2012: 2818-2823.
[3]Engels A, Reyer M, Xu X, et al. Autonomous self-optimization of coverage and capacity in LTE cellular networks [J].IEEETransactionsonVehicularTechnology, 2013, 62(5): 1989-2004.
[4]Berger S, Fehske A, Zanier P, et al. Online antenna tilt-based capacity and coverage optimization [J].IEEEWirelessCommunicationsLetters, 2014, 3(4): 437-440.
[5]Rouzbeh R, Siegfried K, Holger C. A fuzzy reinforcement learning approach for self-optimization of coverage in LTE networks [J].BellLabsTechnicalJournal, 2010, 15(3): 153-175.
[6]Luketic I, Simunic D, Blajic T. Optimization of coverage and capacity of self-organizing network in LTE [C]//Proceedingsofthe34thInternationalConvention. Opatija, the Republic of Croatia, 2011: 612-617.
[7]Razavi R, Klein S, Claussen H. Self-optimization of capacity and coverage in LTE networks using a fuzzy reinforcement learning approach[C]//IEEEInternationalSymposiumonPersonalIndoorandMobileRadioCommunications(PIMRC). Istanbul, Turkey, 2010: 1865-1870.
[8]Karvounas D, Vlacheas P, Georgakopoulos A, et al. An opportunistic approach for coverage and capacity optimization in self-organizing networks [C]//FutureNetworkandMobileSummit. Lisboa, Portugal, 2013: 1-10.
[9]Combes R, Altman Z, Altman E. Self-organization in wireless networks: a flow-level perspective [C]//ProceedingsofIEEEINFOCOM. Orlando, FL,USA, 2012: 2946-2950.
[10]Gao M, Huang L, Cai H. Intelligent coverage optimization with multi objective genetic algorithm in cellular system [C]//InternationalConferenceonComputerScience&Education(ICCSE). Colombo, Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, 2013: 859-863.
[11]Thampi A, Kaleshi D, Randall P, et al. A sparse sampling algorithm for self-optimization of coverage in LTE networks [C]//InternationalSymposiumonWirelessCommunicationSystems(ISWCS). Paris, France, 2012: 909-913.
[12]Huang L, Zhou Y, Hu J, et al. Coverage optimization for femtocell clusters using modified particle swarm optimization [C]//IEEEInternationalConferenceonCommunication(ICC). Ottawa, ON, USA, 2012: 611-615.
[13]Hafiz H, Aulakh H, Raahemifar K. Antenna placement optimization for cellular networks [C]//26thAnnualIEEECanadianConferenceonElectricalandComputerEngineering(CCECE). Regina, SK, USA, 2013: 1-6.
[14]Naseer ul Islam M, Mitschele-Thiel A. Cooperative fuzzy q-learning for self-organized coverage and capacity optimization [C]//IEEEInternationalSymposiumonPersonalIndoorandMobileRadioCommunications(PIMRC). Sydney, Australia, 2012: 1406-1411.
[15]Gao Y, Li Y, Zhou S, et al. System level performance of energy efficient dynamic mechanical antenna tilt angle switching in LTE-advanced systems [C]//IEEEInternationalWirelessSymposium(IWS). Beijing, China, 2013: 1-4.
[16]Partov B, Leith D J, Razavi R. Utility fair optimization of antenna tilt angles in LTE networks [J].IEEE/ACMTransactionsonNetworking, 2014, 23(1): 175-185.
[17]3GPP. TR36.814 Evolved universal terrestrial radio access (E-UTRA); Further advancements for E-UTRA physical layer aspects [S]. San Antonio, USA: 3GPP, 2010.
[18]Gudmundson M. Correlation model for shadow fading in mobile radio systems [J].ElectronicsLetters, 1991, 27(23): 2145-2146.
[19]Giancristoraro D. Correlation model for shadow fading in mobile radio channels [J].ElectronicsLetters, 1996, 32(11): 958-959.
[20]Shi Y, Eberthart R. A modified particle swarm optimizer[C]//IEEEInternationalConferenceonEvolutionaryComputationProceedings. Anchorage, AK, USA, 1998: 69-73.
[21]Liu Y T, Fu M Y, Gao H B. Multi-threshold infrared image segmentation based on the modified particle swarm optimization algorithm[C]//2007InternationalConferenceonMachineLearningandCybernetics. Hong Kong, China, 2007: 383-388.
[22]Lalwani S, Kumar R, Gupta N. A study on inertia weight schemes with modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for multiple sequence alignment[C]//2013SixthInternationalConferenceonContemporaryComputing(IC3). Noida, India, 2013: 283-288.
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2015.04.003

