Trauma patterns in patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Emad Hokkam, Abdelaziz Gonna, Ossama Zakaria, Amany El-shemally
1Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Jazan University, Saudia Arabia
2Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Egypt
3Department of Surgery, Jazan General Hospital, Saudia Arabia
4Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Faisal University, Saudia Arabia
5Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Egypt
Trauma patterns in patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Emad Hokkam1,2, Abdelaziz Gonna3, Ossama Zakaria4, Amany El-shemally4
1Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Jazan University, Saudia Arabia
2Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Egypt
3Department of Surgery, Jazan General Hospital, Saudia Arabia
4Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Faisal University, Saudia Arabia
5Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University, Egypt
BACKGROUND:Modern civilization and the sharp rise in living standards have led to dramatic changes in trauma pattern in Saudi Arabia. This study aimed to describe the different patterns of injuries of patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan General Hospital (JGH) in the southwest corner of Saudi Arabia.
METHODS:A total number of 1 050 patients were enrolled in the study. A pre-organized data sheet was prepared for each patient attended the Emergency Department of JGH from February 2012 to January 2013. It contains data about socio-demographics, trauma data, clinical evaluation results, investigations as well as treatment strategies.
RESULTS:The mean age of the patients was 25.3±16.8 years. Most (45.1%) of the patients were at age of 18–30 years. Males (64.3%) were affected by trauma more common than females. More than half (60.6%) of the patients were from urban areas. The commonest kind of injury was minor injury (60%), followed by blunt trauma (30.9%) and then penetrating trauma (9.1%). The mean time from the incident to arrival at hospital was 41.3±79.8 minutes. The majority (48.2%) of the patients were discharged after management of trivial trauma, whereas 2.3% were admitted to ICU, 7.7% transferred to inpatient wards, and 17.7% observed and subsequently discharged. The mortality rate of the patients was 2.6%.
CONCLUSION:Trauma is a major health problem, especially in the young population in Saudi Arabia. Blunt trauma is more frequent than penetrating trauma, with road traff c accidents accounting for the majority.
Trauma; Injury; Emergency; Saudi Arabia
INTRODUCTION
Trauma is any physical injury caused by violence or other forces. Serious trauma puts the patient at risk of death or loss of function.[1]Trauma is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among all age groups.[2]
Trauma presents with a variety of injuries and problems that demand rapid evaluation, discussion and intervention to save the life and prevent permanent disability.[3]Injuries are classified as intentional or unintentional. Unintentional injury includes injuries related to traffic, occupational and work-related f rearms, drowning and falls. Intentional injury includes interpersonal violence and homicide.[4]
Throughout history, many medical institutions havemade efforts to reduce the mortality of trauma. Globally, about 16 000 people die from injury every day and about 5.8 million people die every year.[5]In Saudi Arabia, one person is killed and four are injured every hour due to traumatic causes.[6]Road traff c accidents (RTAs) account for 80%–85% of these traumas in this country.[7]
Trauma is the main leading cause of hospitalization in Saudi Arabia. About 20% of all admissions were the result of accident and adverse effects. Many of these patients require long-term rehabilitation care because of residual disabilities. It has been estimated that about 74% of all plegic patients in Saudi Arabia are due to RTAs.[6]
Injuries from road traff c accidents is the third most common cause of disability worldwide and the second most common cause in the developing world.[8]World widely, about 1.2 million people are killed in road crashes each year and almost 50 million are injured.[5,9]In 2005, data obtained from traff c sources of Saudi Arabia revealed that there were 283 684 RTAs, during which 5 883 people died.[10]
Domestic accidents are worldwide public health problems. In some European countries, accidents at home kill more people than road accidents, in spite of strict safety regulations and laws regarding buildings and living areas. Cuts are the most frequent accident type, followed by falls and burns.[11]
Occupational injuries show a signif cant decrease in the developed countries over the past 20 years, but the incidence of these injuries is still high in the developing world.[12]The incidence of such injuries in Saudi Arabian workers was comparable to that in other similar countries.[13]
Injuries caused by natural disaster appear to be rising disproportionally.[14]In Saudi Arabia, data related to human losses from disasters that occurred between 1980 and 2010 revealed that the number of killed people was 484, whereas the number of affected people was 29 203, most of them were due to f oods.[15]
Traumatic deaths caused by f rearm are not restricted to any region. Since 1945, 22 million people have been killed and three times as many injured during war or violent conflict.[16]Mortality due to trauma is only the tip of the iceberg, as compared with millions of people requiring hospital treatment for trauma. According to World Health Report 2002,[17]trauma accounts for 12.2% of total burden of disease. Trauma is thus a longoverlooked health problem. The present study was conducted to describe the different pattern of trauma in patients attending the emergency department of Jazan General Hospital, Saudi Arabia.
METHODS
It is a prospective descriptive study. In one year (February 2012–January 2013) and after approval of our ethics committee, all patients with different kinds of trauma were enrolled into the study. Excluded from the study were patients with poisoning, burns or electrocution.
The clinical data were collected from a preorganized data sheet for each patient. The following were recorded: socio-demographic data, trauma data, clinical evaluation, investigations and treatment strategies. The socio-demographic data included data regarding age, sex, marital status, occupation, residence and educational level, but trauma data included the type and cause of trauma, time of hospital arrival, and any pre-hospital intervention. All of the included patients were subjected to clinical evaluation on arrival to the emergency department, focusing on measurement of vital signs, general examination, examination of the injured part, and whole body examination, so as to detect any unrecognized injuries.
All investigations performed to each patient whether they were laboratory or radiological were recorded. Also treatment strategies including first aid measures and def nitive management were recorded.
The fate of each patient was mentioned in the preorganized data sheet. The authors postulated 8 types of fate: the patient was discharged after treatment of trivial trauma, admitted to the emergency room for observation, admitted as an inpatient for further evaluation and management or discharged later, transferred to the operating room, admitted to the intensive care unit, discharged upon request or escaped, referred to the tertiary hospital, and died.
Data were collected including history and the results of clinical examination, laboratory investigation and management. All of them were coded, entered and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Scientists (SPSS) for Windows 15. The values were expressed as mean±SD. The mean values of the groups were compared by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and paired comparisons of the groups were made using Student's t test. P<0.05 was considered statistically signif cant.
RESULTS
The sociodemograhic characteristics of 1 050 patients with different kinds of trauma were analyzed. Their mean age was 25.3±16.8 years (range 1–80). Most(45.1%) of the patients were at age of 18–30 years. Males accounted for 64.3% of the patients. More than half (60.6%) of the patients were from urban areas (Table 1).
Most (60%) of the patients complained of minor injury. Of the patients, 30.9% had blunt trauma caused commonly by RTAs (19.7%), whereas stabbing was the common cause for penetrating trauma (5.9%). Most (52.2%) of the patients arrived at the hospital between 30 to 60 minutes after trauma (Table 2).
In 869 (82.8%) patients, no pre-hospital intervention was performed while intravenous fluids were given in 70 (6.6%) patients. First aid measures including cannula insertion and wound dressing were taken in 111 (10.6%) patients. In this series, 90.6% had no history of chronic illness, but 4.3% had hypertension, 3.1% diabetes, and 2% other chronic illnesses.
The mean heart rate of the patients was 88.4 beats/ minute (range 40–140). The majority (92.6%) of the patients were alert on AVPU scale and showed GCS 13–15. Forty-five (4.3%) patients showed unresponsivenesson AVPU scale and GCS 3–5 (Table 3). Hamoglobin level ranged from 4.5 to14 g/dL with a mean value of 8.4 g/dL. Brain CT was performed in 177 (16.9%) of the patients, with abnormal results in 66 (6.3%) patients. Abdominal ultrasound was carried out in 255 (24.3%) patients, and abnormal results were seen in 33 (3.1%) patients.
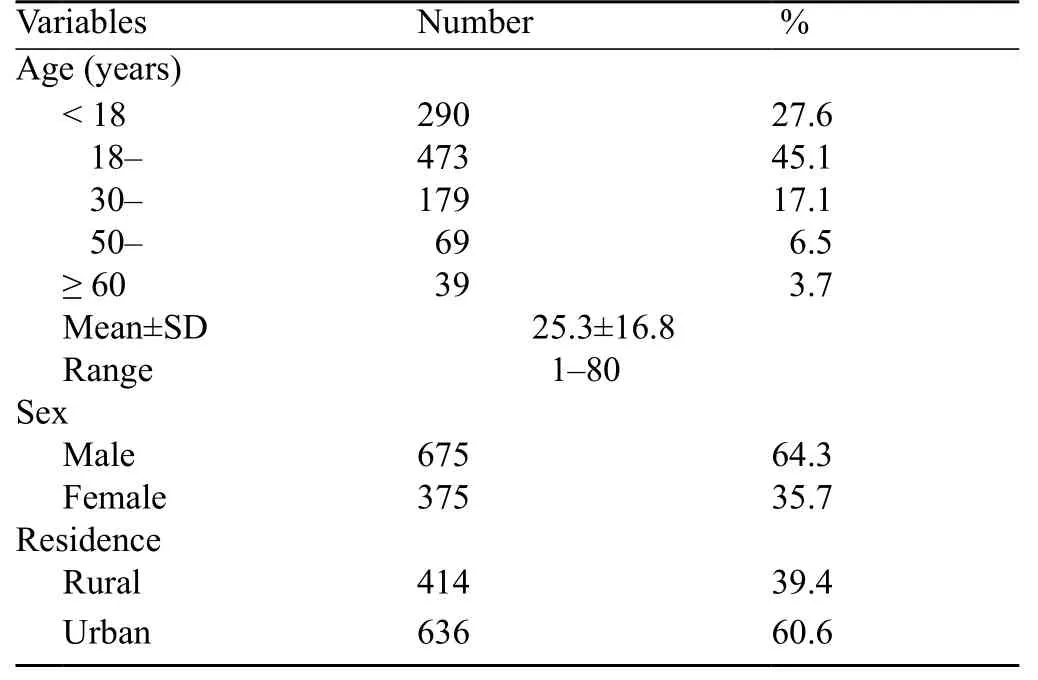
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of the patients (n=1 050)
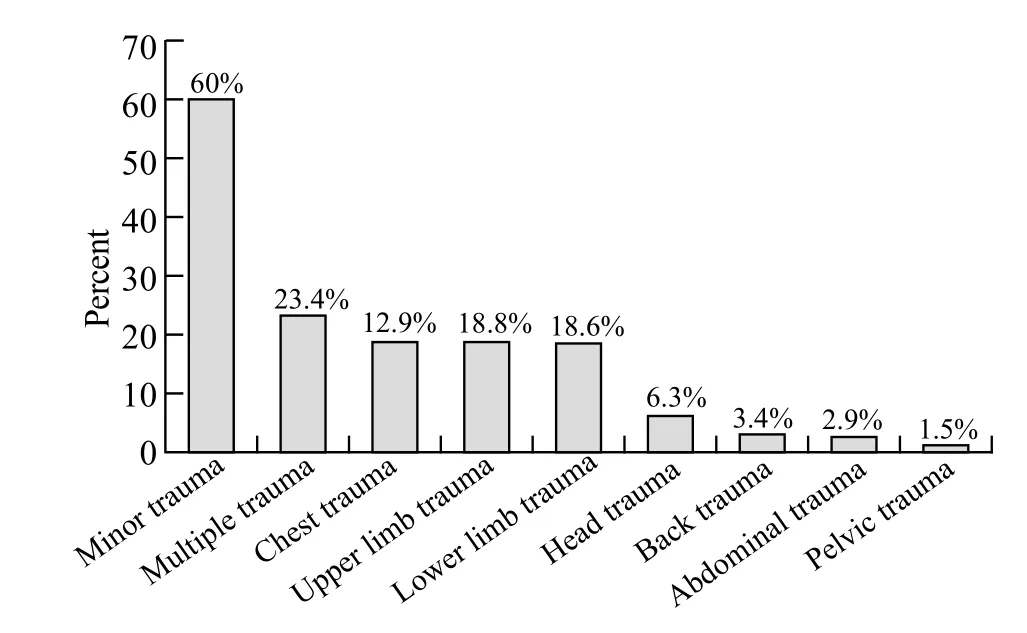
Figure 1. The f nal diagnosis of the patients (n=1 050).
Minor injuries were seen in 60% of the patients, multiple traumas in 246 (23.4%), and head traumas in 66 (6.3%) (Figure 1). The mortality rate in this series was approximately 2.6%. Twenty-four (2.3%) patients were admitted to ICU, 81 (7.7%) admitted to inpatient wards, and 17.7% observed and discharged later. The majority (48.2%) of the patients were discharged from the hospital after treatment of trivial trauma (Figure 2).
A significant difference in age, sex and interval between trauma and hospitalization and a duration of stay in emergency room were observed between patientswith blunt trauma and those with penetrating trauma. Patients with penetrating trauma arrived at the hospital faster than those with blunt trauma (P=0.001). No difference was seen in residency, mortality rate and ICU stay (Table 4). The relationship between the time from trauma to hospitalization and the fate of the patients with same type of trauma is shown in Table 5.
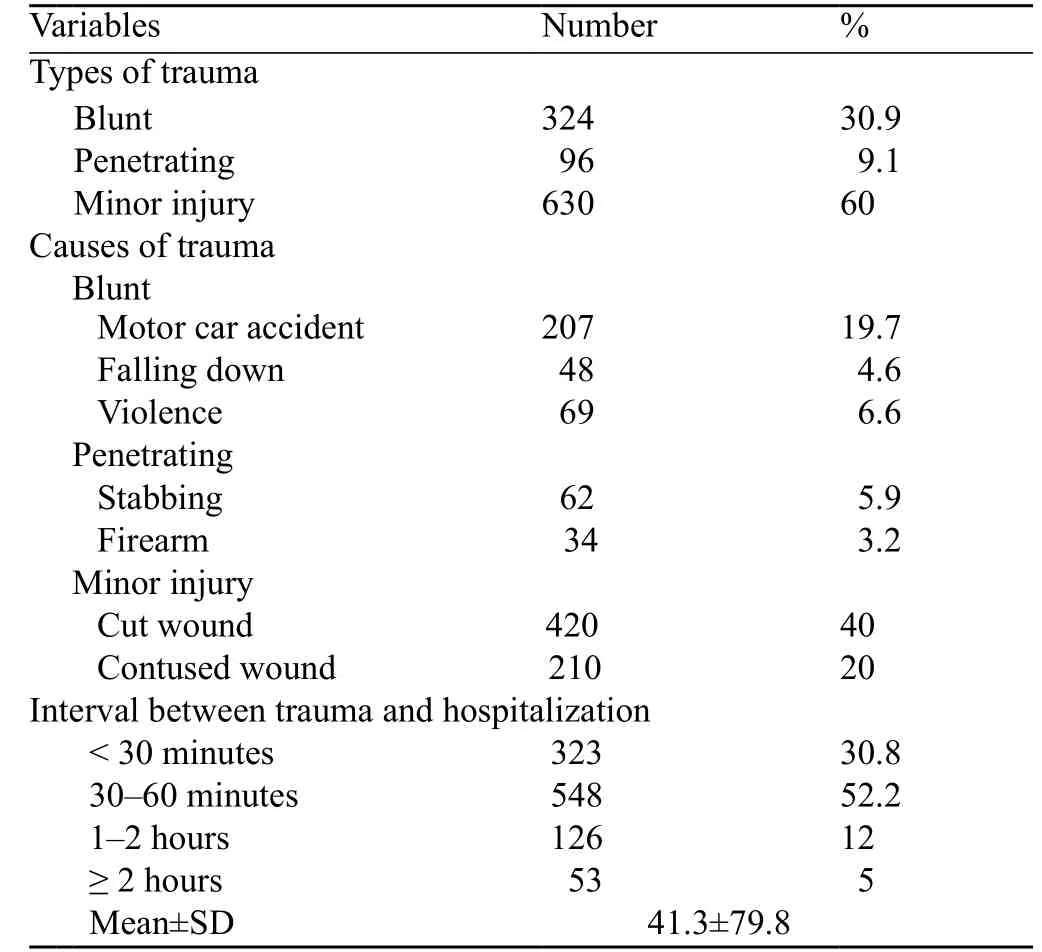
Table 2. Trauma characteristics of the patients (n=1 050)
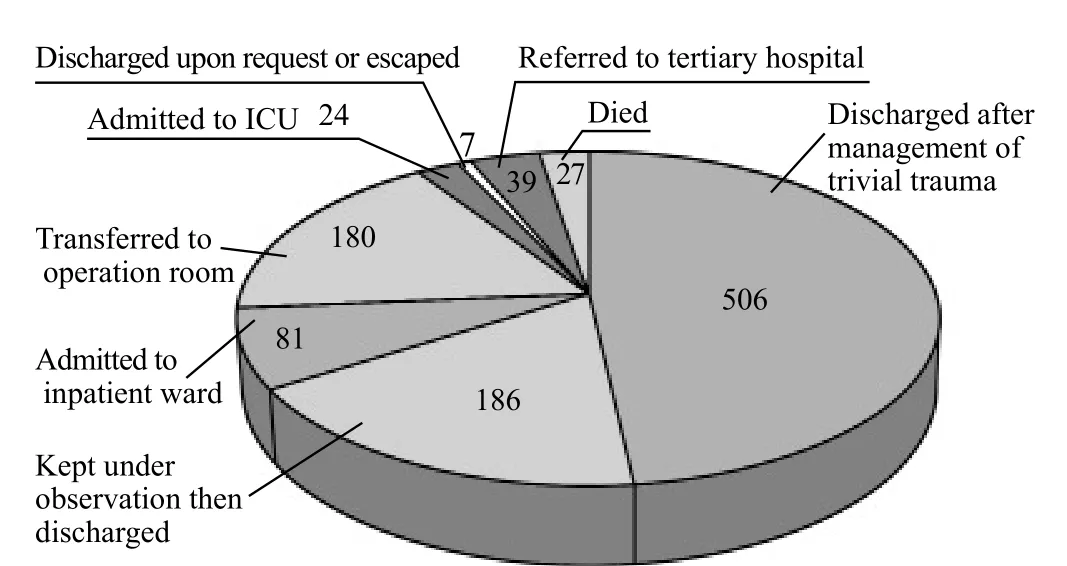
Figure 2. Fate of the patients.
DISCUSSION
Trauma is a leading cause of disability and preventable death.It occurs frequently in the people at age of 15–40 years, with a global mortality rate of 10%. For every trauma death, several patients are leftpermanently disabled and represent a major economic burden for society. Injuries accounted for 17% of the total disease burden in adults aged 15–59 years in 2001, thus f guring among the ten leading causes of burden of disease worldwide.[18]
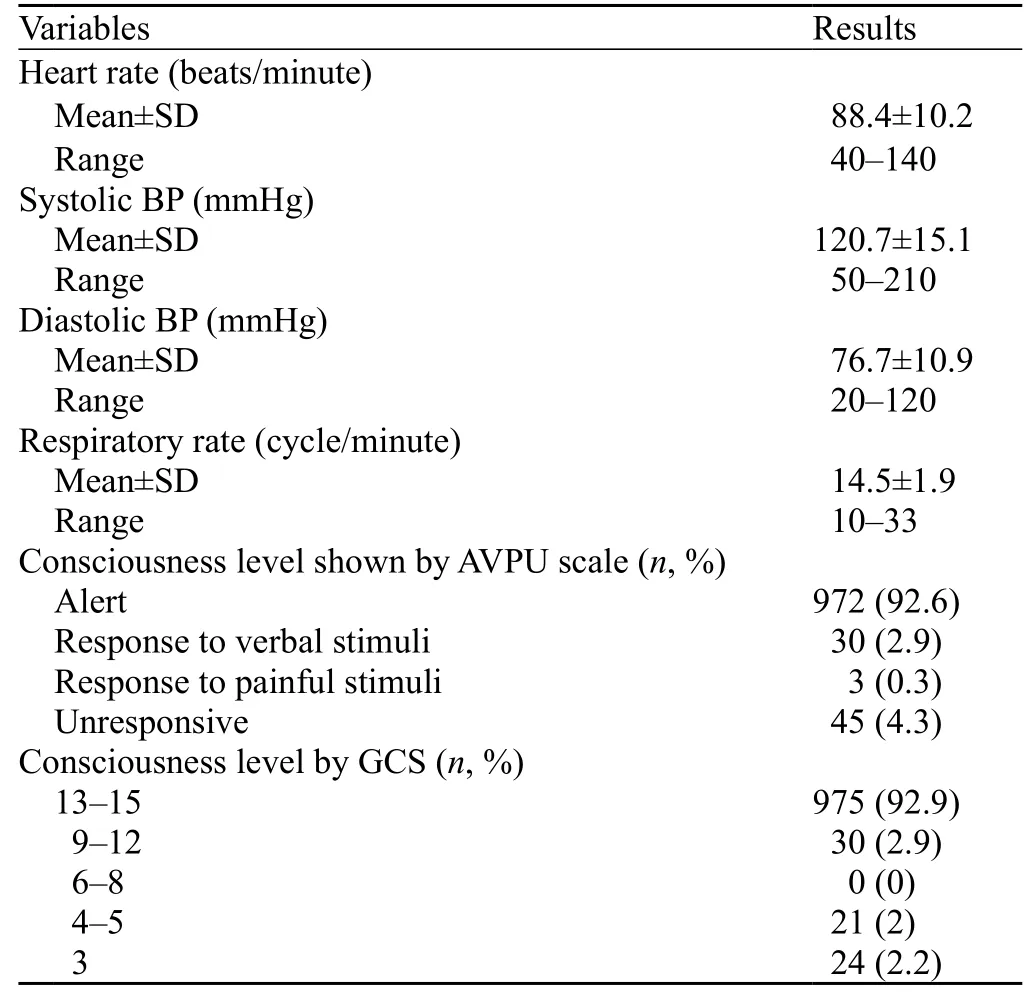
Table 3. Results of clinical evaluation of the patients (n=1 050)
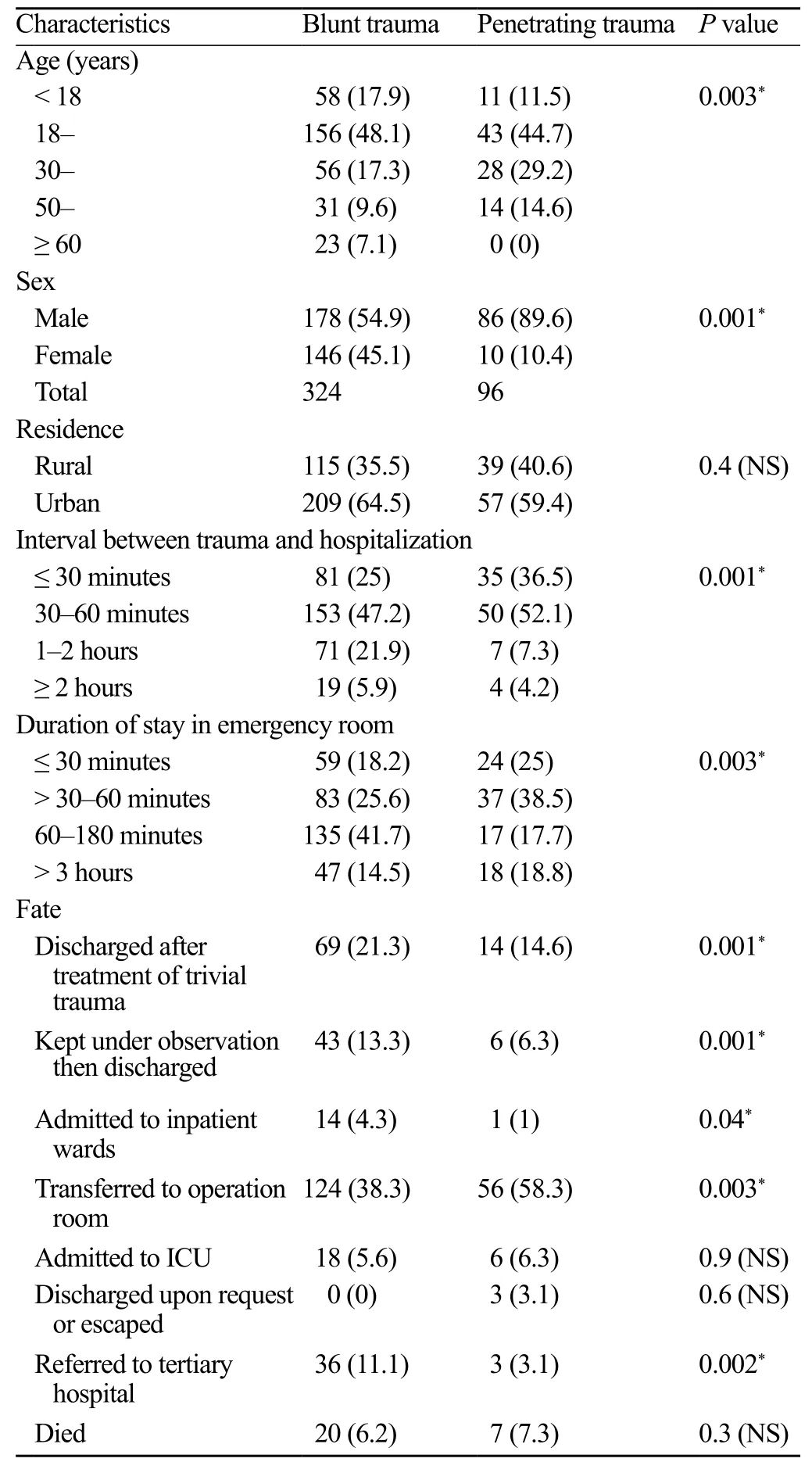
Table 4. Comparison between patients with blunt trauma and those with penetrating trauma (n, %)

Table 5. The relationship between the time from trauma to hospitalization and the fate of the patients with same type of trauma (n)
The present study aimed to describe the pattern of different injuries in trauma patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan Gereral Hospital. Analysis of the socio-demographic characteristics of our patients showed that most of them were young people (45.1% of the patients were between 18 to 30 years). Unlike many chronic diseases that occur later in one's life, trauma has a disproportionate impact on young and middle-aged people.[19]Male gender predominated in trauma patients (64.3%) in the present study, which is consistent with other studies such as Ako?lu et al[20]who reported a rate of 67% for males. It is possible to suggest that males are more liable to trauma and hence they constitute the majority of that kind of studies.[21]
In our study, most patients (60.6%) were from urban areas. The urban development and modern civilization in Saudi Arabia resulting from the oil boom, and the sharp rise in living standards has contributed to increased number RTAs.[10]Most (90.6%) of the patients have no history of chronic diseases, which is consistent with the finding of Morris et al in 2009[19]that victims of severe trauma are often previously healthy.
In the present study, minor injuries (60%) were the most common type of trauma, and blunt trauma was more common than penetrating trauma (30.9% vs. 9.1% respectively). The commonest cause of injury in patients with blunt trauma was RTAs, but stabbing was the commonest cause of injury in patients with penetrating trauma.
In 2006, Ali et al[2]studied the pattern of injuries in patients with different kinds of trauma who were brought to the Accident and Emergency Department of Jinnah Hospital, Lahore. In 111 413 patients treated at the department, 30% had blunt trauma, 2.86% had penetrating f rearms injury, and 51.99% had penetrating sharp injury. These percentages for the different causes of injury in blunt trauma patients are similar to ours. However, the rates of penetrating injuries were higher in their trauma patients. This may be due to the presence of terrorism and social differences between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia.
Most (82.8%) of the patients were not subjected to pre-hospital intervention as they were not transported by ambulance. Despite excellent epidemiological data, there is debate over the benefit of pre-hospital interventions, transportation methods, and training of first responders dealing with trauma patients.[22]Current thinking prioritizes methods for the decrease of pre-hospital time by addressing only life-threatening injuries through control of bleeding, cervical-spine stabilization, and similar interventions.[23]
Rapid transport to the hospital is critically important.[24]In the current study, the interval between the accident and hospitalization was 41.3±79.8 minutes and most patients arrived at the hospital 30–60 minutes after trauma. The duration of transport varied markedly among studies from 20–30 minutes[2]up to 50.6 minutes.[24]
In 2004, Kazmi et al[25]found that the majority of injured patients (69%) were brought home after immediate treatment, but 14% were shifted to the wards of their hospital or other hospitals. The overall mortality of these patients was 5%. These f ndings were consistent with those of the current study. The difference between the studies may be due to the variability of equipments and facilities among hospitals.
The present study shows that the arrival of ambulance at the locality of the accident followed by quick transportation by trained personnel may improve the outcome of the victim. Nevertheless in hospitals with limited resources including equipments, ICU beds and drugs, a rapid resuscitation and convenient assessment with early referral of the patient to a tertiary hospital would be of paramount importance.
We conclude that trauma is a common cause of death and that most of trauma patients with minor injuries can be treated at a primary health care center. This can decrease the load upon tertiary hospitals and thus more attention can be given to critically injured patients. RTAs account for the majority of blunt trauma patients in Saudi Arabia.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:Not needed.
Conflicts of interest:The authors declare that there are no conf icts of interest relevant to the content of the article.
Contributors:Hokkam E proposed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the f rst draft. All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts.
1 Baker SP. Where have you been and where are you going with injury control? In: Mohan D, Tiwari G. eds. Injury prevention and control. New York: Taylor and Francis Publishers; 2000: 22.
2 Ali K, Arain GM, Masood AS, Aslam M. Pattern of injuries in trauma patients presenting in Accident and EmergencyDepartment of Jinnah Hospital, Lahore. Ann King Edward Med Coll 2006; 12: 26.
3 Tabish SA, Shah S, Bhat AS, Bhat FA, Shoukat H, Mir My. Clinical profile and mortality pattern in patients of ballistic trauma. JIMSA 2004; 13: 247–250.
4 World Health Organization. World report on violence and health: Summary. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2002; 1–34.
5 Soroush AR, Ghahri-Saremi SH, Rambod M, Malek-Hosseini SA, Nick-Eghbal S, Khaji A. Pattern of injuries in Shiraz. Chinese J Trauma 2008; 11: 2–8.
6 Ansari S, Akhdar F, Mandoorah M, Moutaery K. Causes and effects of road traff c accidents in Saudi Arabia. Public Health 2000; 114: 37–39.
7 Al-Turki S. Trauma and ATLS training in Saudi Arabia. Middle East J Emerg Med 2001; 1: 50–55
8 Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997; 349: 1498–1504.
9 Celso B, Tepas J, Langland-Orban B, Pracht E, Papa L, Lottenberg L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing outcome of severely injured patients treated in trauma centers following the establishment of trauma systems. J Trauma 2006; 60: 371–378.
10 Al-Naami MY, Arafah MA, Al-Ibrahim FS. Trauma care systems in Saudi Arabia: an agenda for action. Ann Saudi Med 2010; 30: 50–58.
11 Bhanderi DJ, Choudhary S. A study of occurrence of domestic accidents in semi-urban community. Indian J Community Med 2008; 33: 104–106.
12 Drever F. Occupational Health Decennial Supplement. 1st edition, London: HMSO, 1995.
13 Al-Dawood K. Non-fatal occupational injuries requiring admission to hospitals in Al-Khobar City, Saudi Arabia: prospective cohort study. Croat Med J 2000; 41: 323–326.
14 Smith K. Enviromental Hazards. 2nd edition, London, New York: Routledge, 1996.
15 UNISDR: preventionweb Saudi Arabia - Disaster Statistics. Available at: http://www.preventionweb.net/english/countries/ statistics/?cid=150.
16 Summerf eld D. The social, cultural and political dimensions of contemporary war. Med Conf Surviv 1997; 13: 3–25.
17 World Report on Road Traffic Injury Prevention–Summary. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
18 Mizelle HL, Rothrock SG, Silvestri S, Pagane J. Preventable morbidity and mortality from peripheral paralytic assisted intubation. Prehospital Emerg Care 2002; 6: 472.
19 Morris SC. The Team Approach to Management of the Polytrauma Patient. Virtual Mentor 2009; 11: 516–520.
20 Ako?lu H, Denizba?? A, ünlüer E, Güneysel O, Onur O. Demographic characteristics of trauma patients of the emergency department of Marmara University Hospital. Marmara Med J 2005; 18: 113–122.
21 Norris FH. Epidemiology of trauma: frequency and impact of different potentially traumatic events on different demographic groups. J Consult Clin Psychol 1992; 60: 409–418.
22 Liberman M, Mulder D, Lavoie A, Denis R, Sampalis JS. Multicenter Canadian study of prehospital trauma care. Ann Surg 2003; 237: 153–160.
23 Shaf S, Gentilello L. Pre-hospital endotracheal intubation and positive pressure ventilation is associated with hypotension and decreased survival in hypovolemic trauma patients: an analysis of the National Trauma Data Bank. J Trauma 2005; 59: 1140–1145.
24 Vajda P. Prehospital care of the adult trauma patient. Bratisl Lek Listy 2007; 108: 371–374.
25 Kazmi TH, Omair A, Inam SB, Shaikh I, Jamali S. Spectrum of injuries at the Emergency Department of a Tertiary Care Hospital. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2004; 14: 61.
Received May 7, 2014
Accepted after revision January 6, 2015
Emad Hokkam, Email: ehokkam@gmail.com
World J Emerg Med 2015;6(1):48–53
10.5847/wjem.j.1920–8642.2015.01.009
 World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis
- Instructions for Authors
- Lingual angioedema after alteplase treatment in a patient with acute ischemic stroke
- Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulf de on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury
- Relationship between intubation rate and continuous positive airway pressure therapy in the prehospital setting
- Acute intoxication cases admitted to the emergency department of a university hospital
