Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulf de on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury
Department of Emergency Medicine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
Regulatory effects of hydrogen sulf de on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury
Zhi-wei Liu, Hai-ying Wang, Lan Guan, Bin Zhao
Department of Emergency Medicine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
BACKGROUND:The present study was undertaken to examine the regulatory effect of hydrogen sulf de (H2S) on endoplasmic reticulum stress in alveolar epithelial cells of rats with acute lung injury (ALI) induced by oleic acid (OA).
METHODS:Seventy-two male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were divided into control group, oleic acid-induced ALI group (OA group), oleic acid-induced ALI with sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) pretreatment group (OA+NaHS group), and sodium hydrosulfide treatment group (NaHS group). Rats of each group were further subdivided into 3 subgroups. Index of quantitative assessment of histological lung injury (IQA), wet/dry weight ratio (W/D) and H2S level of lung tissues were measured. The expressions of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers including glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and α-subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor-2 (elF2α) in lung tissues were measured by immunohistochemical staining and Western blotting.
RESULTS:The IQA score and W/D ratio of lung tissues at the three time points significantly increased in rats injected with OA, but significantly decreased in other rats injected with OA and NaHS. The level of H2S in lung tissue at the three time points signif cantly decreased in rats injected with OA, but signif cantly increased in other rats injected with both OA and NaHS. GRP78 and elF2α decreased in rats injected with OA, but increased in other rats injected with both OA and NaHS, especially at 4-hour and 6-hour time points.
CONCLUSION:The results suggested that H2S could promote alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with ALI.
Hydrogen sulf de; Acute lung injury; Endoplasmic reticulum stress
INTRODUCTION
Acute lung injury (ALI) can not only evoke acute lung diseases, but also evoke/exacerbate chronic lung diseases.[1]Many studies found the role of inf ammatory mediator,[2,3]reactive oxygen species,[4]nuclear factor-κB[5]and extracellular matrix[6]in the pathogenetic process of ALI, but the mechanisms underlying ALI have not been fully understood.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a protective measure at the cellular level in different cells and tissues plays an essential role in different diseases.[7]Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers include glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and α-subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor-2 (elF2α).[8]C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) inhibits anti-apoptotic effects when ER stress is activated and its expression is increased in the ALI model induced by lipopolysaccharide.[9]But the whole process it works in ALI is not clear.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), as the third gastransmitter after nitric oxide and carbon monoxide, has beenconfirmed to play a part in the development of a variety of cardiopulmonary diseases[10–14]by opening the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive K channel. And it could play an important role in the pathogenesis of ALI through regulating inflammatory response[15]and inhibiting oxidative stress response.[16]In rats with hyperhomocysteinemia-induced cardiomyocytic injury, H2S could relieve cardiomyocytic injury by inhibiting CHOP protein which induces apoptosis during ER stress.[17]But whether and how H2S regulates ER stress in ALI has not yet been fully understood.
Therefore, for the purpose of better understanding of the mechanisms underlying ALI, we attempted to examine the regulatory effects of hydrogen sulfide on alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with acute lung injury.
METHODS
Animals and materials
Seventy-two Sprague Dawley male rats (body weight 200–250 g) were provided by the Animal Center of Peking University First Hospital (China). Experimental protocols complied with the Animal Management Guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China, and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Peking University First Hospital (Beijing, People's Republic of China). Sodium hydrosulf de was supplied by Beijing Chemical Reagents Company (China). Other reagents and chemicals were of analytical grade supplied by Beijing Chemical Reagents Company (China). GRP78 antibody was bought from Bioworld Technology Inc. p-PERK antibody was bought from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. p-eIF2α antibody was bought from Cell Signaling Technology. Histostain TM-Plus Kits (IgG/Bio, S-A/ HRP, DAB) was bought from Beijing Zhongshan Goldenbridge Company, China.
Preparation of the animal model
Rats were randomly divided into four groups: control group (n=18), OA group (n=18), OA+NaHS group (n=18), and NaHS group (n=18). Rats in the control group received normal saline (NS) at 0.1 mL/kg by intra-tail vein injection. Rats in the OA group received OA at 0.1 mL/kg by intra-tail vein injection. Rats in the OA+NaHS group received NaHS at 56 μmol/kg by intraperitoneal injection 30 minutes before OA injection. Rats in the NaHS group received NaHS at 56 μmol/kg by intraperitoneal injection 30 minutes before normal saline injection. Rats in all groups were randomly divided into 2-, 4- and 6-hour subgroups (n=6, each) according to the time after OA treatment. At the termination of the experiment, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection with 0.25% pentobarbital sodium at 40 mg/kg at each time point.[18]
Morphological analysis of lung tissues
Tissues of the right lung were taken and fixed in 10% (wt/vol) formalin, and then cut into paraffin sections (5 μm) routinely. The sections were colored by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. One slice was selected from each sample and 10 fields of each slice were observed under a microscope (original maganification×400). The severity of lung injury was evaluated by a semi-quantitative histological index of quantitative assessment (IQA). This assessment was divided into four grades from 0–3 means: minimal, mild, moderate, and severe, respectively. The items were alveolar edma, infiltration of neutrophils and hyaline membrane formation.[19]
Measurement of wet/dry weight (W/D) ratio in lung tissue
We isolated one lobe of the right lung, bolted blood and water on the lung surface, and evaluated the wet weight. The lobe was placed at 80 °C for 48 hours. Then we evaluated the dry weight and calculated the W/D ratio.
H2S concentration measurement of lung tissue
The tissues of the right lung for H2S content test was homogenized in 10 mmol/L phosphate buffer (PBS, pH 7.2) ice-cold by 0.1 g/mL. Detecting instrument was an ELIT Ion Analyzer (ELIT 9801) bought from Electro Analytic Instruments LTD, England as reported previously.[20]Prepared sulfide antioxidant buffer (SAOB) included sodium hydroxide (NaOH) 2.35 mol/L and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) 0.27 mol/L. Then 0.5 mL of SAOB was anti-graded with 0.5 mL of standard solution of H2S concentration including 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 and 100 μmol/L, respectively. And this solution was displayed as the woltage value by a sulf desensitive electrode and a reference electrode. Hence the standard curve was obtained from the voltage value and H2S concentration. In the same way, we got the voltage value of rat lung tissue, and plotted the concentration of lung tissue on this standard curve.
Evaluation of alveolar epithelial cell endoplasmic reticulum stress by immunohistochemical analysis
Lung tissue was collected on slides for the measurement of alveolar epithelial cell ER stress activation markers (GRP78 and p-eIF2α) and Fas protein by immunohistochemical staining. The lung tissues were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin with routine methods. The sections were de-paraffinized in xylene (3×20 minutes), and then hydrated in ethanol (3×10 minutes, concentrations 75%, 95% and 100%). Afterwards, these sections were rinsed in PBS (0.01 mol PBS, pH 7.2–7.4, 3×5 minutes), and then blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) at room temperature for endogenous peroxidase ablation. 3% H2O2was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). Antigen was repaired in pepsin for 20 minutes at 37 °C. The pepsin was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). The sections were dropped off the goat anti-mouse IgG, and incubated for 30 minutes at 37 °C. The goat serum was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). Again, the sections were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibody was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). The sections were reincubated with the secondary antibody for 1 hour at 37 °C, and then the secondary antibody was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). The sections were colored with 3,3-diaminobenzidin (DAB) without light for 3 minutes at room temperature. Coloration was done with the distilled water. At last, the sections were dehydrated, cleared and mounted with neutral gums. The aforementioned procedures were carried out in a moist chamber.
Microscopic image analysis and processing with the Automatic Image Analysis System (LeicaQ550CW, Germany) were used to measure lung tissue-positive color and calculate optical density of GRP78 and p-eIF2α.
Evaluation of GRP78 and p-eIF2α in alveolar epithelial cells by immunohistochemistry
Lung tissue was collected on slides for the measurement of ER stress activation markers (GRP78 and p-eIF2α) of alveolar epithelial cells by immunohistochemical staining. The lung tissues were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin with routine methods. The sections were deparaff nized in xylene (3×20 minutes) and then hydrated in ethanol (3×10 minutes at a concentration of 75%, 95% and 100% respectively). Afterwards, the sections were rinsed in PBS (0.01 mol PBS, pH 7.2–7.4, 3×5 minutes), and then blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) at room temperature for endogenous peroxidase ablation. 3% H2O2was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). Antigen was repaired in pepsin for 20 minutes at 37 °C, and the pepsin was discarded later by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). The sections were dropped off the goat anti-mouse IgG, and incubated for 30 minutes at 37 °C. The goat serum was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes), and the sections were incubated again with the primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibody was discarded by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). Then the sections were incubated with the secondary antibody for 1 hour at 37 °C, which was discarded subsequently by rinsing in PBS (3×5 minutes). The sections were colored with 3,3-diaminobenzidin (DAB) without light for 3 minutes at room temperature. The coloration was performed with distilled water. At last, the sections were dehydrated, cleared and mounted with neutral gums. The above procedures were performed in a moist chamber.
Microscopic image analysis and processing with the Automatic Image Analysis System (Leica Q550CW, Germany) were used to measure lung tissue-positive color and to calculate the mean optical density of GRP78 and p-eIF2α.
Evaluation of GRP78 and eIF2α in lung tissue by Western blot
The tissues were taken from the right lung for Western blot analysis. They were homogenized in lysis buffer ( pH 7.4) composed of 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl, 1 mmol/L EDTA, 0.25 mol/L sucrose, 20 mmol/L CHAPS, and 20 mmol/L PMSF. The homogenized lung tissue was centrifuged at 13 000×g for 20 minutes at 4 °C. The supernatant remained mixed with Coomassie brilliant blue for Western blot analysis. The concentration of proteins in the supernatant was measured by enzymelabeled instrument. 50 μg of proteins was added per lane and separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. β-actin conf rmed by HRP staining was loaded in each lane coincidently. The proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, blocked by milk, and incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibody was discarded by rinsing in PBS-T (4×10 minutes). The secondary antibody was incubated for 1 hour and then discarded by rinsing in PBS-T (4×10 minutes). The proteins were detected using substrate, and signal was quantif ed by AlphaImager.
Statistical analysis
Results were expressed as mean±SD. One-wayANOVA followed by a post hoc analysis (Bonferroni test) was used for comparison of the groups. Analysis was made using SPSS version 16.0 for Windows. IQA scores were tested by the rank-sum test. P<0.05 was considered statistically signif cant.
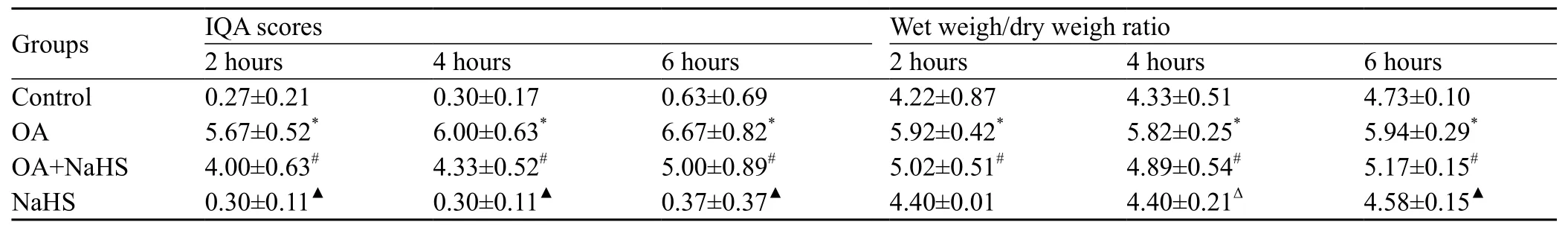
Table 1. Comparison of IQA score and wet/dry ratio in different groups
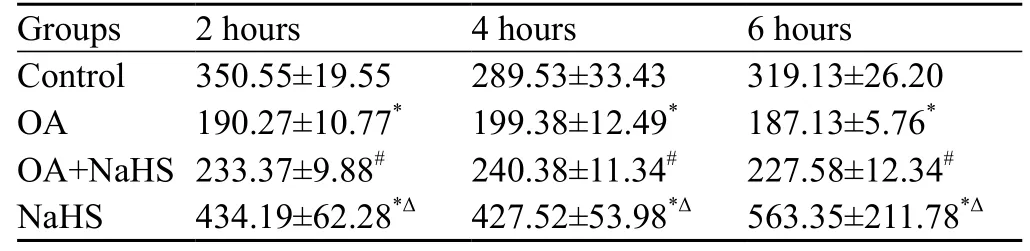
Table 2. The levels of H2S in homogenized lung tissues (μmol/L)
RESULTS
IQA of OA-induced lung injury in rats
At 2, 4 and 6 hours, the IQA of lung tissues was increased in the OA group compared with the control group (P<0.01). However, it was signif cantly decreased in the OA+NaHS group compared with the OA group (Figure 1, Table 1).
The wet/dry weight ratio in lung tissue
At 2, 4 and 6 hours, the wet/dry weight ratio of lung tissues in the OA group was increased compared with the control group (P<0.01). However, it was decreased significantly at each time point in the OA+NaHS group compared with the OA group (P<0.01). There was no difference between the control group and the NaHS group (Table 1).
Level of H2S in homogenized lung tissues
At 2, 4 and 6 hours, the levels of H2S in lung tissues were significantly decreased by 46%, 32% and 42% in the OA group compared with those in the control group (P all< 0.01). However, the levels of H2S in lung tissues were significantly increased by 22%, 21% and 22% at different time points in the OA+NaHS group compared with those in the OA group (Table 2).
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in lung tissues and alveolar epithelial cells
Western blot showed that at 6 hours, GRP78 expression in lung tissues in the OA group was significantly decreased compared with the control group (P<0.01), which was in accordance with the changes in alveolar epithelial cells demonstrated by immunohistochemical analysis (Figure 2). In rats with ALI pretreated with NaHS, the expression significantly increased compared with that of the OA group (P<0.01). However, it did not change signif cantly at 2 hours and 4 hours compared with the control group (Figure 3A).
At 4 hours and 6 hours, the ratio of p-eIF2α/eIF2α in lung tissues significantly decreased in the OA group compared with that of the control group (P all< 0.01), but immunohistochemical analysis showed that the p-eIF2α expression exhibited a similar trend in alveolar epithelial cells to the ratio of p-eIF2α/eIF2α in lung tissues (Figure 2). In rats with ALI pretreated with NaHS, it signif cantly increased compared with that of the OA group (P all<0.01). However, they did not change significantly at 2 hours compared with controls (Figure 3B).
DISCUSSION
ALI results from serious infections, trauma, shock, acidosis and harmful gas inhalation. Its clinical manifestations include severe hypoxaemia and stiff lungs.[21]However, the mechanism underlying ALI/acute respiratory distress syndrome has not yet been fully understood.
OA-induced rat ALI model is a classic one. In the model of ALI, OA-treated rats showed diffused edema and severe inflammatory cell infiltration in alveoli and the interstitium of the lung. Hemorrhage and thickened interlobular septa were also demonstrated. These changes are consistent with the clinical characteristics of ALI.[22]
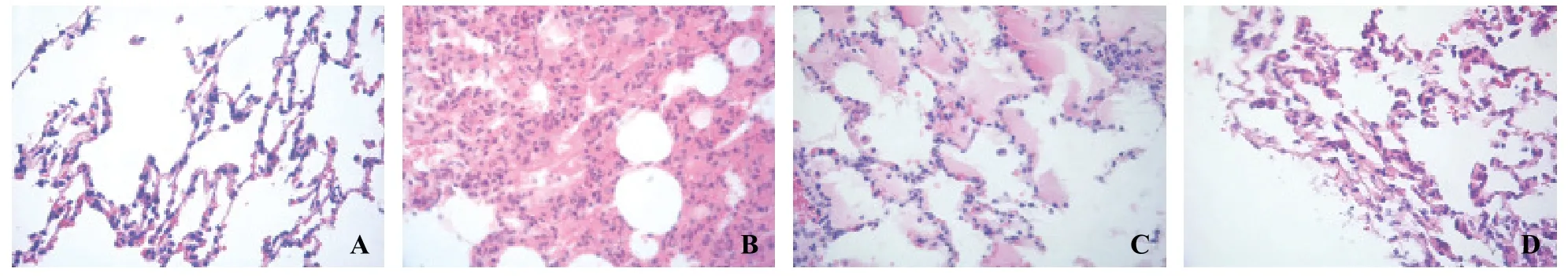
Figure 1. Microphotographs of morphological changes of lung tissues (HE staining, original magnif cation ×400). A: control group at 6 hours; B: OA group at 6 hours; C: OA+NaHS group at 6 hours; D: NaHS group at 6 hours.
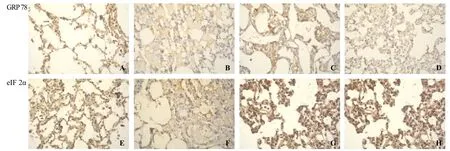
Figure 2. Immunohistochemical staining of endoplasmic reticulum stress marker proteins including GRP78 and p-eIF2α in alveolar epithelial cells (original magnif cation×400). A: GRP78 in the control group at 6 hours; B: GRP78 in the OA group at 6 hours; C: GRP78 in the OA+NaHS group at 6 hours; D: GRP78 in the NaHS group at 6 hours; E: p-eIF2α in the control group at 6 hours; F: p-eIF2α in the OA group at 6 hours; G: p-eIF2α in the OA+NaHS group at 6 hours; H: p-eIF2α in the NaHS group at 6 hours.
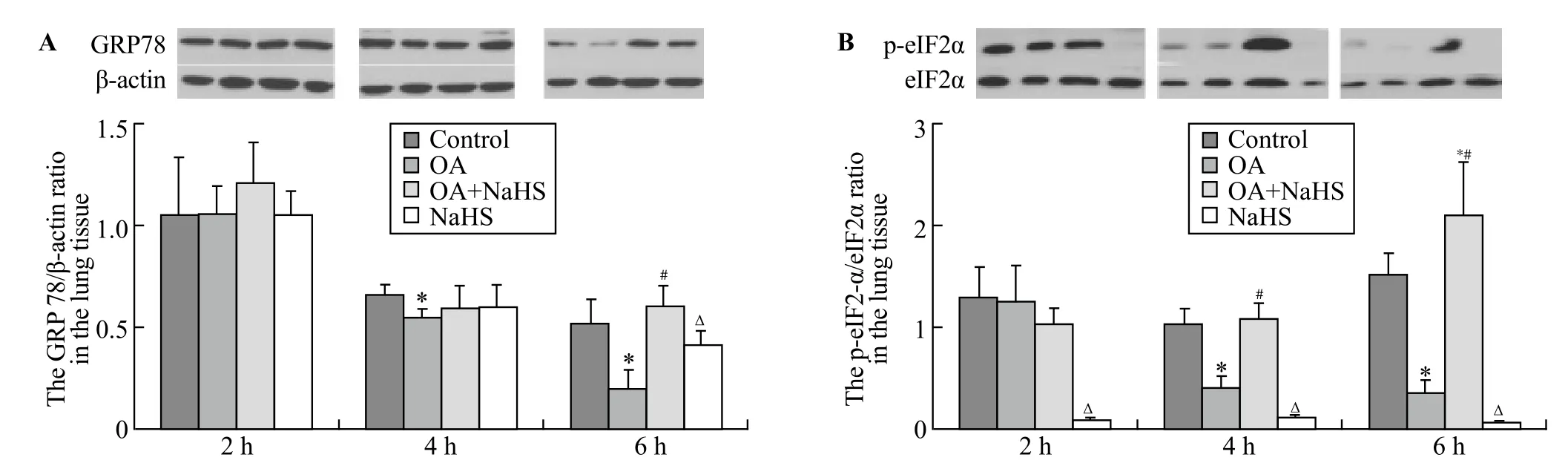
Figure 3. Western blotting of endoplasmic reticulum stress marker proteins. A: Western blot of GRP78 in lung tissues; B: the ratio of p-eIF2α/ eIF2α in lung tissues. Compared with the control group,*P<0.01; compared with the OA group,#P<0.05; compared with the OA+NaHS group,Δ<0.01.
In rats with OA-related lung injury, GRP78 and eIF2α decreased markedly at 4 and 6 hours, indicating that endoplasmic reticulum stress is likely involved in the development of acute lung injury.
Lung injury IQA was significantly aggravated at 2, 4 and 6 hours; whereas the expressions of GRP78 and eIF2α decreased at 4 and 6 hours, not at 2 hours. The reasons for these changes are not clear. A previous study[23]found that when the injury was mild, GRP78, PERK, eIF2α, ATF4 and ATF6 were up-regulated to protect mildly injured cells, but when the injury was severe, apoptosis was active to eliminate severely injured cells.
Endogenous H2S is produced from the metabolism of homocysteine and cysteine in mammals.[24]Fu et al[16]reported that endogenous H2S could protect the lung from ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by reducing theproduction of malondialdehyde (MDA) and the activities of potentiated superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). Li et al[15]found that NaHS, an H2S donor, could lower the levels of inf ammatory cytokines and increase anti-inf ammatory cytokines. Liu et al[25]also found that NaHS could inhibit apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells. But Aslami et al[26]found that H2S played a protective role in ventilator-induced lung injury. These findings suggested that H2S might play an important role in the acute inflammatory response. Interestingly, we found that the level of endogenous H2S in lung tissue was significantly decreased in the OA group compared with the control group, suggesting that endogenous H2S is likely involved in the pathogenesis of ALI.
In the present study, H2S donor treatment signif cantly decreased the level of endogenous H2S in the lung as well as the IQA scores. These f ndings suggest that H2S might play a role in ALI. At the same time, H2S donor treatment in OA-treated rats significantly elevated the levels of GRP78 and p-eIF2α in the lung, suggesting that H2S promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress during the early stage of ALI.
In conclusion, there is an association between H2S-induced protection from ALI and up-regulated protein of endoplasmic reticulum stress. This f nding would help us to understand the pathophsiological significance of H2S in the prevention of ALI. Further experiments are needed to investigate the mechanisms underlying the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress by H2S.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:The present study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing, China.
Conf icts of interest:The authors declare that there is no conf ict of interest relevant to the content of the article.
Contributors:Liu ZW proposed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the f rst draft. All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts.
1 Luhr OR, Antonsen K, Karlsson M, Aardal S, Thorsteinsson A, Frostell CG, et al. Incidence and mortality after acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome in Sweden, Denmark, and Iceland. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159: 1849–1861.
2 Kang P, Kim KY, Lee HS, Min SS, Seol GH. Anti-inf ammatory effects of anethole in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Life Sci 2013; 93: 955–961.
3 Han HJ, Li M, Son JK, Seo CS, Song SW, Kwak SH, et al. Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, attenuates neutrophil pro-inflammatory activity andacute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2013;17: 471–477.
4 Semple JW, Kim M, Hou J, McVey M, Lee YJ, Tabuchi A, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin prevents murine antibody mediated acute lung injury at the level of neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. PLoS One 2012; 7: e31357.
5 Wang G, Huang X, Li Y, Guo K, Ning P, Zhang Y. PARP-1 inhibitor, DPQ, attenuates lps-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting NF-κB mediated inflammatory response. PLoS One 2013; 8: e79757.
6 Eckle T, Koeppen M, Eltzschig HK. Role of extracellular adenosine in acute lung injury. Physiology (Bethesda) 2009; 24: 298–306.
7 Lai E, Teodoro T, Volchuk A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: signaling the unfolded protein response. Physiology (Bethesda) 2007; 22: 193–201.
8 Schroder M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008; 65: 862–894.
9 Nakagomi T, Kitada O, Kuribayashi K, Yoshikawa H, Ozawa K, Ogawa S, et al. The 150-kilodalton oxygen-regulated protein ameliorates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice. Am J Pathol 2004; 165: 1279–1288.
10 Pan TT, Feng ZN, Lee SW, Moore PK, Bian JS. Endogenous hydrogen sulf de contributes to the cardioprotection by metabolic inhibition preconditioning in the rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2006; 40: 119–130.
11 Qiao W, Chaoshu T, Hongfang J, Junbao D. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide is involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 396: 182–186.
12 Luo L, Liu D, Tang C, Du J, Liu AD, Holmberg L, et al. Sulfur dioxide upregulates the inhibited endogenous hydrogen sulfide pathway in rats with pulmonary hypertension induced by high pulmonary blood flow. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 433: 519–525.
13 Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, Feng ZN, Ali MY, Zhou S, et al. Role of hydrogen sulfide in the cardioprotection caused by ischemic preconditioning in the rat heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006; 316: 670–678.
14 Du JT, Li W, Yang JY, Tang CS, Li Q, Jin HF. Hydrogen sulf de is endogenously generated in rat skeletal muscle and exerts a protective effect against oxidative stress. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013; 126: 930–936.
15 Li TS, Wang C, Wang HY, Liu ZW, Zhao B, Jin HF, et al. Regulation of hydrogen sulf de on interleukins in rats acute lung injury. Chin J Emerg Med 2008; 4: 345–350.
16 Fu ZF, Liu XM, Geng B, Fang LP, Tang CS. Hydrogen sulfide protects rat lung from ischemia–reperfusion injury. Life Sci 2008; 82: 1196–1202.
17 Wei HL, Zhang RY, Jin HF, Liu D, Tang XY, Tang CS, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates hyperhomocysteinemia induced cardiomyocytic endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. Antioxid Redox Signal 2010; 12: 1079–1091.
18 Davidson KG, Bersten AD, Barr HA, Dowling KD, Nicholas TE, Doyle IR. Lung function, permeability, and surfactant composition in oleic acid induced acute lung injury in rats. Am J Physiol 2000; 279: 1091–1102.
19 McGuigan RM, Mullenix P, Norlund LL, Ward D, Walts M,Azarow K. Acute lung injury using oleic acid in the laboratory rat: Establishment of a working model and evidence against free radicals in the acute phase. Curr Surg 2003; 60: 412–417.
20 Geng B, Cui Y, Zhao J, Ward D, Walts M, Azarow K, et al. Hydrogen sulfide down regulates the aortic L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007; 293: R1608–1618.
21 Jain S, Bellingan G. Basic science of acute lung injury. Surgery (Oxford) 2007; 25: 112–116.
22 Schuster DP. ARDS: clinical lessons from the oleic acid model of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 149: 245–260.
23 Xu C, Bailly MB, Reed JC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2656–2564.
24 Wang R. The gas transmitter role of hydrogen sulf de. Antioxid Redox Signal 2003; 5: 493–501.
25 Liu WL, Liu ZW, Li TS, Wang C, Zhao B. Hydrogen sulfide donor regulates alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis in rats with acute lung injury. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013; 126: 494–499.
26 Aslami H, Heinen A, Roelofs J, Coert JZ, Marcus JS, Nicole PJ. Suspended animation inducer hydrogen sulf de is protective in an in vivo model of ventilator-induced lung injury. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36: 1946–1952.
Received June 6, 2014
Accepted after revision January 12, 2015
Bin Zhao, Email: lzhw84@163.com
World J Emerg Med 2015;6(1):67–73
10.5847/wjem.j.1920–8642.2015.01.012
 World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
World journal of emergency medicine2015年1期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- The role of regulatory T cells in immune dysfunction during sepsis
- Instructions for Authors
- Lingual angioedema after alteplase treatment in a patient with acute ischemic stroke
- Relationship between intubation rate and continuous positive airway pressure therapy in the prehospital setting
- Acute intoxication cases admitted to the emergency department of a university hospital
- Trauma patterns in patients attending the Emergency Department of Jazan General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
