Evil-hunter: a novel web shell detection system based on scoring scheme
Truong Dinh Tu Cheng Guang Guo Xiaojun Pan Wubin
(1School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)(2Department of Information Technology, Tuyhoa Industrial College, Phuyen 620900, Vietnam)(3 Key Laboratory of Computer Network and Information Integration of Ministry of Education, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)
?
Evil-hunter: a novel web shell detection system based on scoring scheme
Truong Dinh Tu1,2,3Cheng Guang1,3Guo Xiaojun1,3Pan Wubin1,3
(1School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)(2Department of Information Technology, Tuyhoa Industrial College, Phuyen 620900, Vietnam)(3Key Laboratory of Computer Network and Information Integration of Ministry of Education, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)
In order to detect web shells that hackers inject into web servers by exploiting system vulnerabilities or web page open sources, a novel web shell detection system based on the scoring scheme is proposed, named Evil-hunter. First, a large set of malicious function samples normally used in web shells are collected from various sources on the Internet and security forums. Secondly, according to the danger level and the frequency of using these malicious functions in the web shells as well as in legal web applications, an assigning score strategy for each malicious sample is devised. Then, the appropriate score threshold value for each sample is obtained from the results of a statistical analysis. Finally, based on the threshold value, a simple algorithm is presented to identify files that contain web shells in web applications. The experimental results show that compared with other approaches, Evil-hunter can identify web shells more efficiently and accurately.
web shell detection; scoring scheme; malicious code identification
A malicious file that hackers plant on web servers through system vulnerabilities or web pages’ open source to create a backdoor for them to return next time is called a web shell. In other words, a web shell is a code written in languages such as PHP, active server page (ASP), Perl, Java server page (JSP) or Python, etc., which runs on the system and can remotely control a machine. Once the web shell is run, it provides a web Interface for remote operations on the server with attacker functionality, such as file transfers, command execution, network reconnaissance, database connectivity, SQL manager, etc.
The techniques used to build web applications are often developed in languages such as PHP, ASP, Java, Python, Ruby, Perl, etc. It not only supports full functions to access files, consoles, networks, and database, but also runs and manages the process in the system. This is quite convenient for building management applications in the web environment. However, this is also where the hackers will aim to create a backdoor. One of the usual ways to attack web servers is that the hackers use web shells to browse files, upload tools, and run commands; after that, they increase privileges and pivots to other targets. Thus, the role of web server managers is to ensure the privacy and security for customers’ web pages. A web page may contain thousands of code lines or more in each file; therefore, it is very difficult and sometimes impossible to review the source code manually to detect malicious files such as web shells. So, finding and detecting web shells inside web page applications are necessary for securing websites.
There are some known tools to find web shells, such as NeoPI[1], PHP shell detector (SD)[2], and Grep[3]. However, these tools have some disadvantages: 1) NeoPI can find and detect obfuscated and encrypted contents within text and script files. However, its disadvantage is that it cannot provide a threshold value for these indices to determine which files are web shells. Therefore, we have to analyze and decide from the experience of experts; 2) SD has a known web shell signature database saved in web servers. Its disadvantage is that if a new web shell has not been updated on a database, this tool will fail to detect it; 3) Grep is an UNIX command for searching files for lines matching a given regular expression. However, the disadvantage of this method is that it does not have a list of given dangerous functions. Thus, users must have experience and know which dangerous functions should be found to detect web shells. Therefore, this method has many false positives since some of these functions are also used by legal web applications. As a result, the Evil-hunter system is proposed in this paper to detect web shells and overcome the above-described existing disadvantages.
1 Background and Related Works
1.1 Overview of web shell
A web shell is a script/code written in various web scripting languages, such as PHP, ASP, Perl, JSP or Python, etc., which runs on the system and can remotely control a machine. In other words, a file containing malicious functionality that hackers have planted on web servers through system vulnerabilities or web pages’ open source to create a backdoor for them to return next time is called web shell.
There is no clear difference between web shells and normal administration websites since they both belong to remote control software. If it is used to sabotage the website, it is a web shell; but if it is used to manage all the web pages, it is normal management software. Only the administrator can judge whether a remote management webpage is behaving maliciously or not[4-5].
Classic web shell attacks: The attacker finds vulnerabilities in a hosted web application and uploads a malicious dynamic web page to a vulnerable web server; then he uses the web shell to browse files, upload tools, and run commands[6-8]. After that, he acquires privileges and pivots to other targets as allowed (see Fig.1).
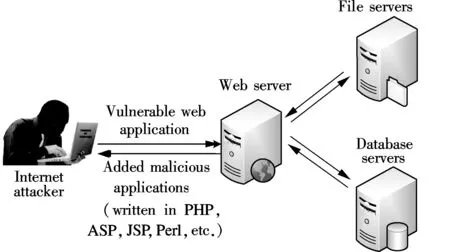
Fig.1 The classic model of web shell attacks
Web shells can be classified into two main categories.
? Non-encrypted web shell: The source code of this web shell is stored in apparently normal text. From the source code files, we can see the functions used in it.
? Encrypted web shell: The source code of this kind of web shells usually contains characters that are obfuscated and not meaningful, but it still executes its features properly. The encryption functions such as base64_encode(), base64_decode(), etc.[9]are popular and most attackers often use these in their web shells.
1.2 Related works
Web servers attacks are one of the most frustrating problems for administrators. Some researchers have become concerned about this threat and their strategies have been useful for detecting malicious files on webpage applications. Behrens and Hagen[1]built a project called NeoPI, using a variety of statistical methods to detect obfuscated and encrypted contents within text and script files. However, the NeoPI offered only file statistics with the index of coincidence, entropy, longest word values, respectively, in order to help administrators find suspicious files. It cannot decide whether the file, which has obfuscated or encrypted contents, is a web shell or not. Thus, the administrators need manual analyses to decide. Luczko et al.[2]also built a PHP script called the PHP shell detector (SD) to help with finding and identifying web shells. Basically, the SD has a known web shell database saved at web servers, and previously calculated the MD5 value in each file. This method has the disadvantage that if a new web shell has not been updated in the database, this approach will fail to detect it. Mingkun et al.[10]conducted a study on the principles and characteristics of ASP web shells to find a method to identify ASP shells. Hu et al.[11]presented a study on the characteristics and mechanisms of web shells, and proposed a detection model based on the decision tree algorithm to detect them. Rahul[12]proposed some analyses to prove that the Anti-Virus software packages have a very poor web shell detection rate. Hou et al.[13]used the machine-learning approach to detect malicious web pages. In general, they analyzed malicious dynamic web pages to find important features which are input for training the classifier or obtaining the predicted class of pages.
2 Proposed Approach: Evil-Hunter
In this section, we describe a brief overview of Evil-hunter overall and describe the components of Evil-hunter in detail.
2.1 Overview of Evil-hunter
As mentioned previously, the web shell is viewed as a malignant tumor for web applications on the Internet, finding and detecting web shells are very important for website security. The goal of the proposed approach is to identify suspicious files containing web shells inside web applications. To achieve this goal, we propose a system, called Evil-hunter. The framework of Evil-hunter consists of three main components as shown Fig.2. They are:
1) The collection of malicious signature/function samples. In this section, we collect a large set of malicious signature/function samples that are often used in known web shells and assign them their danger levels.
2) Scoring scheme. In this section, we describe an appropriate scoring scheme for malicious signature/function samples collected in the above section. The score range to be used is a range of numbers depending on their danger levels. On the other hand, in this section we also propose one calculation method to determine the threshold value to distinguish web shell files from benign files.
3) An algorithm for detecting web shells. In this section, we propose an algorithm based on the above-mentioned scoring scheme to identify web shells. In this technique, there are two main modules: scanning and matching signature/function samples and scanning to find obfuscated or encrypted contents. Moreover, in order to improve the detection effectiveness of the Evil-hunter system, we also propose another supporting module, namely scanning and matching keywords in the blacklist.

Fig.2 Framework of Evil-hunter
Evil-hunter starts from a set of known malicious signatures/functions that are involved in malicious activities of the web shell. Each signature/function has different danger levels, in which some signatures/functions are also used in legal web pages. Thus, in order to assign these danger levels, we propose a scoring method for each signature/function, as well as proposing a method to calculate the threshold value to detect web shells. In the next step, we propose one technique to detect web shell files based on the scoring scheme proposed above.
2.2 Components of Evil-hunter
In the following sections, we provide details for the components of the proposed system.
2.2.1 Collecting malicious signatures/function samples
The malicious signatures/function samples are those that attackers often use for their web shells, and are rarely used in benign web source code[9]. These malicious functions can be classified into the encoded/decoded support functions, command execution functions, file system functions, compressed functions, etc.[6-7,9]. Therefore, collecting the malicious functions is necessary to aid detecting web shells.
We collect a large set of malicious signatures/functions based on common tasks that are often used in the web shell, such as file management functions, database server access functions, file system functions, etc.[7,9,14-16]. The list of these malicious signatures/function samples are stored in a XML database file, which can be easily updated for further development.
2.2.2 Scoring scheme
In this section, we discuss how to assign a score for malicious signatures/function samples and how to determine a suitable threshold value for each sample to identify suspicious web shell files.
1) Assigning scores for malicious signatures/functions
The web application source code often uses many functions, in which each function has different danger levels. For example, system_exec() or system() are dangerous functions that are rarely used in benign web source code[9]. In order to indicate the danger level for each function, we use the scoring scheme. The scoring scheme is proposed based on a numerical scale, such as 1-10, where a score corresponds to low, medium, and high danger level, (low <5, medium=5-9, and high ≥10). Thus, a high score of 10 or more may indicate almost no false positives; a medium score of 6-9 may imply a possibility of some false positives and higher sensitivity while a low score of 5 or less can imply audit level sensitivity.
For example, if the functions have a high danger level, they almost do not appear in benign web application source codes; then the score for these functions may be assigned to 10 points or more. However, if the functions have a medium danger level and they are sometimes used in normal websites, then the scores for these functions may be assigned with 6-9; and the functions that have a low danger level may be assigned with 1-5.
The list of all the malicious signatures/functions and corresponding scores are stored in a XML database file (XMLDB). Thus, they can be easily altered, removed from or added to systems for further development.
2) Determining threshold value
A threshold value is the minimum value that the system can use to classify whether a file is a web shell or not. To determine a threshold value for malicious signatures and function samples, we collect a set of signatures and functions based on common tasks that are often used in the web shell, such as file management functions, database server access functions, file system functions, etc.[7,9,15-16]. After obtaining a set of necessary signatures and functions, we complete the task of scanning for a large amount of benign source code, and calculate the total score of the frequency of using these functions. Therefore, we can give a suitable threshold value for each sample.
For example, in order to choose a suitable threshold value for malicious function samples, we scan each file of the legal web pages, count the appearance frequency of the dangerous functions (which are stored in XMLDB) in benign files, and calculate the total score of those files (e.g., {ts1, ts2, …, tsn}={6, 8, …, 18}. In which tsiis the total score of thei-th benign file, andnis the number of subfiles (e.g. js, css, PHP) that a webpage may include. Moreover, we also scan and count the appearance frequency of those malicious functions in the sample files containing web shells, and calculate the total score for each sample file (e.g, {wts1, wts2, …,wtsm}={30, 77, …, 80} in which wtsiis the total score of thei-th sample file contained web shells, andmis the number of web shell files). From there, we choose a suitable threshold value for malicious function samples, such as Threshold_MF=20. Similarly, we can also determine a suitable threshold value for dangerous signature sample (Threshold_S).
To determine a threshold value for the longest word (Threshold_LW), we conduct a scan to look for the longest word from a set of samples encrypted web shells given and a set of legal web sources. From the list of values obtained, we decide an appropriate threshold value for the longest word.
For example, in order to choose a suitable threshold value for the longest word, we scan each file of the legal web pages, meanwhile, calculate the value of the longest word for each file (e.g., {lw1, lw2, …, lwn}={63, 52, …, 82}, in which lwiis the value of the longest word of thei-th legal file). Similarly, we also scan and calculate the value of the longest word in a set of samples of encrypted web shell (e.g., {ws1, ws2, …, wsm}={118, 5 847, …, 208 496}, in which wsithe value of the longest word of thei-th web shell file, andmis the number of web shell files). Then, we choose a suitable threshold value for the longest word, such as Threshold_LW=100.
Based on the above-mentioned approach, in the following section, we present an algorithm to identify web shells.
2.2.3 Algorithms for web shell detection
To work with the above-mentioned scoring scheme, we build an algorithm as shown in Algorithm 1 for identifying web shells. There are three steps in the algorithm: 1) Scanning and matching signature/function samples with database XMLDB; 2) Scanning to find obfuscated or encrypted contents; 3) Scanning and matching keywords in blacklist.
Algorithm 1 Identifying web shell
For each file in web application do
STS=0; MFTS=0;
Scanning and matching signatures/function samples
if sample.Type=1 then
nCount=Count the number of occurrences of this sample in the file.
STS+=nCount*sample.Score
else if sample.Type=2 then
nCount=Count the number of occurrences of this sample in the file.
MFTS+=nCount*sample.Score
LW=Count the number of characters in the longest word in the file.
if (STS>=Threshold_S) or (MFTS>=Threshold_MF)
Or (LW>=Threshold_LW) then add the file to suspicious list.
Scanning and matching keywords from the blacklist
if the keyword is in the blacklist then add the file to the suspicious list
The detail of these steps is explained as follows:
1) Scanning and matching signatures/function samples
In this module, we scan each file in the web application to filter malicious functions in these files and determine their dangerous levels according to malicious signatures/function samples in the XMLDB database. As shown in Algorithm 1, sample.Type=1 implies that it is a dangerous signature sample; sample.Type=2 implies that it is a malicious function sample. In the next step, we count the appearance frequency of those signatures/functions and calculate the signature total score (STS) and the malicious function total score (MFTS) of the files. If the STS exceeds a threshold value of signature (Threshold_S), that file is marked as suspicious. If MFTS exceeds a threshold value of malicious functions (Threshold_MF), that file is also marked as suspicious.
2) Scanning to find obfuscated or encrypted contents
Obfuscated or encrypted contents are often stored as an uninterrupted long string within a file. These strings can be decoded into malicious codes to execute them. Finding the longest uninterrupted string existing in the files is very useful to identify obfuscated or encrypted contents.
Typically, the source code is written in a relatively short length of words. So, identifying files with unusual long strings can help us to recognize files with obfuscated or encrypted codes.
Behrens and Hagen[1]used this method in their NeoPI project to find obfuscated and encrypted contents within text or script files. However, if it is scanned on a set of source codes that contain many images, videos, rich-text-format, js, css, the false alert rate will be very high. Thus, we try to test NeoPI on a set of benign source codes, and the result shows a relatively high false alert rate, which implies that NeoPI does not work well when identifying web shells accurately.
This stage checks only the longest string that starts and ends with header tags, such as “ for PHP language, “<\%@ Page Language>” for ASPX language, similarly for other languages because the source code is only executed when it is enclosed in header tags.

Algorithm2 FindingthelongestwordIf(data.Count(“longest: longest=length longest_word=word
Algorithm 2 will search and identify the longest word (LW) in the file that starts and ends with header tags. As discussed previously, if the LW exceeds a threshold value of the longest word (Threshold_LW), that file is also marked as suspicious.
3) Scanning for and matching dangerous/blacklist keywords
The web shell files are often written and developed by many hackers, in which there are comment lines with suspicious keywords on the source codes. Therefore, searching for these suspicious keywords, such as a web shell by *, Hack by *, developed by *, r57, c99, n3shell, TrYaG Team, http://cctea-m.ru/update/c999shell, http://ccteam.ru/files/c999sh_sourc-es, etc.,[17]is useful for finding web shells. The above keywords are rarely used in a benign website the source, so their appearance inside the source code has the possibility of being highly malicious and may be marked as a suspicious file.
3 Experiment and Evaluation
3.1 Data set
For our test, we collected a total of 13 151 files from the test dataset which included 12 982 files of benign web pages (with high confidence) that did not contain malicious codes and 169 malicious web shell files.
For legal web pages, we downloaded directly from open sources websites which are prestigious and of high rank based on Alexa[18]; for malicious web shell files, we downloaded and collected them from several security forums that were published and discussed on the Internet[17, 19]. We named this testing file T1.
On the other hand, we also collected 32 895 files of open sources web pages, such as Oscommerce, VBB, Joomla, WordPress, PhpNuke, Phpbb, etc., which were shared on the Internet (these web pages may or may not contain malicious files). We named this testing file T2.
3.2 Experimental results
The experiments are run on a machine with an Intel?Pentium?CPU G640 2.80 GHz processor with 4 GB memory. We use python language to build a software for Evil-hunter.
We run Evil-hunter to scan for T1 with different threshold values. The threshold value is configurable to adjust the detection rate. The results in Fig.3 show that when we set thresholds (LW, S, MF ) higher, i.e., (354, 10, 30) which is marked as S1, Evil-hunter had a true positive (TP) rate of 62.72% with a false positive (FP) rate of 0.57%. It means that, Evil-hunter indentified 106 of the total 169 malicious web shell files correctly, and 74 of total 12 982 files of legal web pages were mistaken for web shell files. On the other hand, when we set low thresholds (354, 10, 2) marked as S2, Evil-hunter obtained a true positive rate of 82.25% with a false positive rate of 5.03%. It means that the Evil-hunter identified 139 of total 169 malicious web shell files correctly, and 653 of total 12 982 files of legal web pages were mistaken for web shell files.

Fig.3 True positive rates and false positive rates at different threshold values (LW, S, MF)
Compare test results of Evil-hunter with some other de-tection tools and Anti-Virus (AV) software packages, such as Norton Anti-Virus (NA), Bit Defender (BD), Microsoft Safety Scanner (MSS), AVG Anti-Virus (AVG), Kaspersky Anti-Virus (KS), 360 Shadu (360 SD), Avast Antivirus (AVAST), and PHP shell detector (PHP SD)[2]. As shown in Fig.4, the comparison results show that Evil-hunter has a relatively high detection rate and identifies web shells better than other Anti-Virus software such as Kaspersky Anti-Virus(76%), 360 Shadu (0%), AVG Anti-Virus (37%), Norton Anti-Virus (20%), and Microsoft Safety Scanner (14%).

Fig.4 True positive rates and false positive rates for different detection tools on T1
We also scanned to check the detection ability of unknown web shells on T2 from the above software packages. Results in Tab.1 show that the software packages of NA, BD, MSS, AVG, KS, 360SD, AVAST did not detect any suspected web shell files in T2. Meanwhile, the PHP SD tool at the time of writing this paper, had 499 well-known shells in its database[2]and gave warning of 763 suspicious files, in which 4 files were precisely web shells because they matched MD5 with the database of PHP SD on servers. On the other hand, Evil-hunter gave warning of 187 suspicious files. Through another manual analysis and submitting suspicious files to the virus total[20]for checking and analyzing, we determined exactly 11 web shell files that were possibly inserted into the web application’s source code by hackers or web developers for malicious purposes before sharing them on the Internet. However, there are also 176 files that were false alerts, because programmers used a few dangerous function samples for the purpose of installing or encrypting sensitive information such as passwords or personal information[21].
Tab.1 Comparison of other tools and software packages on T2 dataset

ApproachNumberofsuspiciousfilesTruewebshellfilesFalsewebshellfilesBDAVASTKSAVGNAMSS360SDPHPSDEvil-hunter120000076318712000004110000000759176
3.3 Discussion and evaluation
For AV software packages, as shown in Fig.4 and Tab.1, on the T1 and T2 datasets, we find that the AV software packages have a relatively poor web shell detection rate. Rahul[12]also provided some analyses to prove that the efficiency of current AV software in detecting web shells is inadequate. Therefore, web server administrators should combine other detection tools with it to effectively detect web shells.
Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of some other web shell detection tools, we have:
1) Grep[3]is a Unix command for searching files for lines matching a given regular expression. The advantage of this method is that it can easily find files containing the keywords. However, the disadvantage of this method is that it does not provide a list of dangerous functions. To detect web shells, users must know which dangerous functions should be found beforehand. Therefore, this method has many false positives since some of these functions are also used by benign web applications. Evil-hunter can find the dangerous functions automatically based on the XMLDB database that was collected previously.
2) NeoPI[1]has the advantage that it can find and detect obfuscated and encrypted contents within text and script files by calculating and listing some indices such as coincidence, entropy, longest word, signature; after that it will give a rank for all the files and the top ten files with the highest ranking. However, its disadvantage is that it cannot provide a threshold value for these indices to determine which files is a web shell. Therefore, we have to analyze and judge from experts. Evil-hunter calculates the score and determines the appropriate threshold value to detect web shells.
3) PHP shell detector (SD). Basically, SD has a known web shell signature database saved in web servers. The advantage of this method is that its true positive rate can be up to 99% for known web shells in the database[2]. However, it has the disadvantage that if a new web shell have not been updated in the database, this approach will fail to detect it. Evil-hunter can detect unknown web shells based on the threshold value and a large set of malicious signatures/functions collected previously. As shown in Tab.1, the detection ability of Evil-hunter on T2 is better than that of PHP SD.
4 Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a novel web shell detection system based on the scoring scheme. From a large set of malicious signatures/functions involved in malicious activities of the web shell, we propose a scoring method to indicate their danger levels, as well as a technique to determine the threshold value for detecting web shells. We implemented this approach in a tool, called Evil-hunter, and validated it on large datasets that we collected previously. The results show that Evil-hunter can identify web shells more efficiently compared to some other approaches. Generally, Evil-hunter can minimize time and cost for administrators by reviewing a source code automatically and give warnings for any file suspected of being malicious.
[1]Behrens S, Hagen B. Web shell detection using NeoPI [EB/OL]. (2012-04-13)[2013-10-10]. http://resources.infosecinstitute.com/web-shell-detection/.
[2]Luczko P, Thornton J. PHP shell detector [EB/OL]. (2012-06-12)[2013-10-10]. https://github.com/emposha/PHP-Shell-Detector.
[3]Unix operating system. A manual for grep [EB/OL]. (2008-05-20)[2013-09-10].http://www.gnu.org/savannah-checkouts/gnu/grep/manual/grep.html.
[4]Jakobsson M, Ramzan Z.Crimeware:understandingnewattacksanddefenses[M]. New York: Addison Wesley, 2008: 608.
[5]Canali D, Balzarotti D, Francillon A. The role of web hosting providers in detecting compromised websites [C]//Proceedingsofthe22ndInternationalConferenceonWorldWideWeb. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013: 177-187.
[6]Garg A, Singh S. A review on web application security vulnerabilities [J].InternationalJournalofAdvancedResearchinComputerScienceandSoftwareEngineering, 2013, 3(1): 222-226.
[7]Mirdula S, Manivannan D. Security vulnerabilities in web application an attack perspective [J].InternationalJournalofEngineeringandTechnology, 2013, 5(2): 1806-1811.
[8]Cova M, Kruegel C, Vigna G. Detection and analysis of drive-by-download attacks and malicious javascript code [C]//Proceedingsofthe19thInternationalConferenceonWorldWideWeb. Raleigh, NC, USA, 2010: 281-290.
[9]Exploitable PHP functions [EB/OL]. (2012-03-22)[2013-09-10].http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3115559/exploitable-php-functions.
[10]Mingkun X, Xi C, Yan H. Design of software to search ASP web shell [J].JournalofProcediaEngineering, 2012, 29(1): 123-127.
[11]Hu J K, Xu Z, Ma D H, et al. Research of webshell detection based on decision tree [J].JournalofNetworkNewMedia, 2012, 1(6): 15-19.(in Chinese)
[12]Rahul S. Effectiveness of antivirus in detecting web application backdoors [EB/OL]. (2012-07-30)[2013-10-10]. http://www.chmag.in/article/feb2011/effectivenessantivirus-detecting-web-appli-cation-backdoors.
[13]Hou Y T, Chang Y, Chen T, et al. Malicious web content detection by machine learning [J].ExpertSystemswithApplications, 2010, 37(1): 55-60.
[14]Koo T M, Chang H C, Hsu Y T, et al. Malicious website detection based on honeypot systems [C]//The2ndInternationalConferenceonAdvancesinComputerScienceandEngineering. Paris:Atlantis Press, 2013:76-81.
[15]Canali D, Balzarotti D. Behind the scenes of online attacks: an analysis of exploitation behaviors on the web [C]//Proceedingsofthe20thAnnualNetwork&DistributedSystemSecuritySymposium. San Diego, CA, USA, 2013:1-18.
[16]Verma A, Insan D S. Signature based detection of web application attacks [J].InternationalJournalofAdvancedResearchinComputerScienceandSoftwareEngineering, 2013, 3(8): 117-121.
[17]Certified ethical hacker [EB/OL]. (2012-02-200[2013-09-10]. http://ceh.vn/@4rum/forumdisplay.php?fid=10.
[18]Alexa—The web information company[EB/OL]. (2012-03-30)[2013-09-10].http://www.alexa.com.
[19]Project hosting on google code provides a free collaborative development environment for open source projects [EB/OL]. (2012-05-16)[2013-09-10].http://code.google.com/.
[20]VirusTotal—Free online virus, malware and url scanner [EB/OL].(2007-02-01)[2013-09-10].https://www.virustotal.com.
[21]Agbefu R E, Hori Y, Sakurai K. Domain information based blacklisting method for the detection of malicious webpages [J].InternationalJournalofCyber-SecurityandDigitalForensics, 2013, 2(2): 36-47.
Evil-hunter:基于評(píng)分機(jī)制的web shell檢測(cè)系統(tǒng)
張庭秀1,2,3程 光1,3郭曉軍1,3潘吳斌1,3
(1東南大學(xué)計(jì)算機(jī)科學(xué)與工程學(xué)院,南京210096)(2綏和工業(yè)學(xué)院信息技術(shù)部門, 富安 620900, 越南)(3東南大學(xué)計(jì)算機(jī)網(wǎng)絡(luò)和信息集成教育部重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室,南京210096)
針對(duì)及時(shí)檢測(cè)攻擊者利用系統(tǒng)漏洞或篡改網(wǎng)頁(yè)開(kāi)源代碼秘密地在web服務(wù)器上嵌入的惡意代碼web shell問(wèn)題,提出了一種基于評(píng)分機(jī)制的web shell檢測(cè)系統(tǒng)Evil-hunter.首先,從互聯(lián)網(wǎng)和各種安全論壇上收集了大量的web shell經(jīng)常使用的惡意函數(shù)樣本數(shù)據(jù).其次,根據(jù)惡意函數(shù)在web shell 和正常web應(yīng)用中的不同危險(xiǎn)級(jí)別和使用頻度,利用所提出的評(píng)分策略對(duì)所收集的樣本數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行評(píng)分,并分析統(tǒng)計(jì)結(jié)果以得出適當(dāng)?shù)姆謹(jǐn)?shù)閾值.最后,根據(jù)所得出的分?jǐn)?shù)閾值,借用簡(jiǎn)單的檢測(cè)算法來(lái)對(duì)web 應(yīng)用中所包含的惡意代碼web shell進(jìn)行識(shí)別.實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明,與其他方法相比Evil-hunter具有更高的識(shí)別率和準(zhǔn)確度.
web shell 檢測(cè);評(píng)分策略;惡意代碼檢測(cè)
TP393.08
s:The Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangsu Province (No.BE2011173), the Future Network Proactive Program of Jiangsu Province (No.BY2013095-5-03), the Program for Special Talent in Six Fields of Jiangsu Province (No.2011-DZ024).
:Truong Dinh Tu, Cheng Guang, Guo Xiaojun, et al. Evil-hunter: a novel web shell detection system based on scoring scheme[J].Journal of Southeast University (English Edition),2014,30(3):278-284.
10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2014.03.004
10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2014.03.004
Received 2014-01-17.
Biographies:Truong Dinh Tu (1979—), male, graduate; Cheng Guang (corresponding author), male, doctor, professor, gcheng@njnet.edu.cn.
 Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)2014年3期
Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)2014年3期
- Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Observation and characterization of asphalt microstructure by atomic force microscopy
- Research on asphalt concrete pavement deicing technology
- Influence of different curing regimes on the microstructure and macro performance of UHPFRCC
- Intelligibility evaluation of enhanced whisper in joint time-frequency domain
- Islamic traditional architecture environment overlapping the modern architecture design
- Hom-dimodules and FRT theorem of Hom type
