Fusion protein of single-chain variable domain fragments for treatment of myasthenia gravis
Fangfang Li, Fanping Meng, Quanxin Jin, Changyuan Sun, Yingxin Li, Honghua Li, Songzhu Jin
Department of Immunology and Pathogenic Biology, College of Medicine, Yanbian University, Yanji, Jilin Province, China
Fusion protein of single-chain variable domain fragments for treatment of myasthenia gravis
Fangfang Li, Fanping Meng, Quanxin Jin, Changyuan Sun, Yingxin Li, Honghua Li, Songzhu Jin
Department of Immunology and Pathogenic Biology, College of Medicine, Yanbian University, Yanji, Jilin Province, China
Single-chain variable domain fragment (scFv) 637 is an antigen-specific scFv of myasthenia gravis. In this study, scFv and human serum albumin genes were conjugated and the fusion protein was expressed in Pichia pastoris. The af fi nity of scFv-human serum albumin fusion protein to bind to acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction of human intercostal muscles was detected by immuno fl uorescence staining. The ability of the fusion protein to block myasthenia gravis patient sera binding to acetylcholine receptors and its stability in healthy serum were measured by competitive ELISA. The results showed that the inhibition rate was 2.0-77.4%, and the stability of fusion protein in static healthy sera was about 3 days. This approach suggests the scFv-human serum albumin is a potential candidate for speci fi c immunosuppressive therapy of myasthenia gravis.
nerve regeneration; myasthenia gravis; acetylcholine receptor; anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody; single-chain variable domain fragment; human serum albumin; fusion protein; immunosuppressive therapy; autoimmune disease; NSFC grant; neural regeneration
Funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30360100, 30760234, 30860260, 81160373, 81360458.
Li FF, Meng FP, Jin QX, Sun CY, Li YX, Li HH, Jin SZ. Fusion protein of single-chain variable domain fragments for treatment of myasthenia gravis. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(8):851-856.
Introduction
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease associated with autoantibodies directed against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at neuromuscular junctions (De Baets and Stasson, 2002; Po?a-Guyon et al., 2005; Nikolic et al., 2012). These antibodies interfere with synaptic transmission by reducing the number of functional receptors or by impeding interactions between acetylcholine and its receptors. Acetylcholine is the sole transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. Anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody was detected in 85-90% of myasthenia gravis patients (Lagoumintzis et al., 2010; Higuchi et al., 2011; Cossins et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2012). Approximately 65% of anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies directed against the main immunogenic region (residues 67-76 of α-subunit of acetylcholine receptor) are highly pathogenic (Protopapadakis et al., 2005; Konstantakaki et al., 2007; Luo et al., 2009). Therefore, pathogenic antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the anti-acetylcholine receptor have a crucial role in the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis (Sun et al., 2010).
Single-chain variable domain fragment 637 (scFv637), a human scFv directed against the main immunogenic region of the human acetylcholine receptor, is constructed from its parental Fab637, which is isolated from thymus-derived phage display library of a myasthenia gravis patient (Graus et al., 1997). ScFv637 prevents antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the anti-acetylcholine receptor from the sera of myasthenia gravis patients binding to the human acetylcholine receptor, indicating it might be an alternative candidate for specific immunosuppressive therapy. Furthermore, it should have low immunogenicity in myasthenia gravis patients owing to its human origin (Meng et al., 2002). However, scFvs have disadvantages including a short half-life and instability. In addition, the characterization of scFv in animal models in vivo is difficult because of their rapid clearance from the bloodstream owing to their small size (Huston et al., 1996; Li et al., 1998; Kang et al., 1999; Kenanova et al., 2005).
It is well known that human serum albumin (HSA), the most abundant protein in plasma, is a potent carrier protein with a substantial circulatory half-life (up to 19 days in the human blood) and is widely distributed in vivo (Huang et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2012; Ding et al., 2013). The association of immunoglobulin fragments with serum albumin, whether by conjugation, fusion or noncovalent binding, results in extended persistence in plasma (Smith et al., 2001; de Bold et al., 2012; Zhao et al., 2012). In this study, we aimed to prepare a conjugate by linking scFv with HSA to increase its half-life and improve its stability in blood.
Materials and Methods
Construction of plasmid pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA
The VH and VL genes of scFv637 were amplified from pComb3H-Fab637 by PCR, and cloned into NcoI and NotI sites of vector pHEN2 to construct recombinant vector pHEN2-scFv637 (Meng et al., 2002). The HSA gene was ampli fi ed from pUC18-HSA using primers 1-7 amino acid residues of HSA (NCBI GenBank: AF190168) (5′-AAGAAT-TCGCGGCCGCAGGTGGAGGCGGTTCAGATGCACACAAGAGTGAGG-3′) and 581-585 amino acid residues of HSA (5′-ATGGATCCTGCGGCCGCTAAGCCTAAGGCAGC-3′), which append a NotI site (underlined) and a (Gly)4-Ser linker (italic) into the 5′ and 3′ ends of the PCR fragment, respectively. Tis PCR product was digested with NotI, and inserted into NotI-digested pHEN2-scFv637 to generate the final construct, pHEN2-scFv637-HSA. Purified pHEN2-scFv637-HSA from E. coli DH5α (preserved in our laboratory) was subsequently transformed into E. coli HB2151 for expression of scFv637-HSA. The fusion gene of scFv637-HSA was ampli fi ed from pHEN2-scFv637-HSA using primers “VH” (5′-GACTTACGTAGA-GGTGCAGCTGCTGGAG-3′) and “c-myc” (5′-CGGAATTCATTCAGATCCTCTTCTGAG ATG-3′), which append SnaBI and EcoRI sites (underlined) into the 5′ and 3′ ends of the PCR fragment, respectively. The PCR fragment was subcloned into pMD18-T Simple Vector after puri fi cation and addition of A-Tailing. The scFv637-HSA-T Vector fragment was cloned into pPIC9K vector after restriction digestion of the SnaBI and EcoRI sites. Competent cells of E. coli DH5α were prepared and transformed with pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA. The recombinant vector was sequenced to con fi rm the right sequence of scFv637-HSA and an open reading frame.
Expression of plasmid pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA in Pichia pastoris
Electroporation
Pichia pastoris strain GS115 (preserved in our laboratory) was transformed by electroporation. Plasmid pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA (10 μg) was linearized with SalI, phenol-chloroform extracted, ethanol precipitated, and dissolved in 10 μL of dH2O. Preparation of electrocompetent Pichia pastoris strain GS115 was performed using Pichia Expression Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Eighty microliters of competent cells were mixed with 10 μg of linearized pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA DNA in a 0.2 cm electroporation cuvette, incubated on ice for 5 minutes, and electroporated in an Electroporation Generator (BTX, A Division of Genetronics Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Electroporation conditions were C = 25 μF, PC = 200 Ω, V = 1.5 kV. After pulsing, 1 mL of ice-cold 1 mol/L sterilized sorbitol was added immediately to the cuvette, and the cells transferred to a sterile 1.5 mL centrifuge tube on ice again. Electroporated cells (400 μL) were spread onto MD plate and incubated for 2 days at 30°C. A number of colonies were then restreaked onto MD plates to isolate single colonies for PCR analysis and expression studies.
PCR analysis and selection of positive transformants
GS115 positive transformants were analyzed for the presence of pPIC9K-scFv637-HSA constructs using PCR with primers (5′ VH, GAC TTA CGT AGA GGT GCA GCT GCT GGA G, 3′ c-myc, CGG AAT TCA TTC AGA TCC TCT TCT GAG ATG). PCR components and conditions were as follows: 20 × MgCl2-Free buffer, 1 Unit Taq polymerase, 1 Unit Pfu polymerase and 15 pmol/L each primer 5′ VH and 3′ c-myc, at 94°C for 5 minutes, 1 cycle; at 94°C for 1 minute, at 55°C for 1 minute, at 72°C for 4 minutes, 30 cycles; and at 72°C for 5 minutes, 1 cycle. Positive transformants were selected and spread onto yeast extract peptone dextrose medium plates containing 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 mg/mL G418 respectively, and incubated for 2-3 days at 30°C.
Expression and screening of scFv637-HSA
G418-resistant transformants were grown overnight in buffered methanol-complex medium at 30°C and shaking at 280 r/min in 50 mL centrifuge tubes until the absorbance at 600 nm was 2-6. The cells were recovered by centrifugation and resuspended in buffered methanol-complex medium to 1.0 of an absorbance for induction, and grown again at 30°C, 280 r/min in 250 mL glass culture tubes. Fresh methanol was added to a total of 1% to maintain induction every 24 hours. Fusion proteins were measured at 24, 48, 72, 96, and 132 hours post-induction in 1 mL media by centrifugation. After 132 hours, the supernatants were concentrated 25 times by lyophilization. Samples of the supernatants were analyzed by electrophoresis on NEXT GEL? 10% (Amresco, Solon, OH, USA) followed by Coomassie brilliant blue (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) staining and western blot analysis. Western blot analysis was achieved using a wet blotting method with the MINI-TRANS-BLOT electrophoretic transfer system (Bio-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA), with NEXT GEL? electrophoretic buffer (Amresco) at 90 V for 2 hours. The protein samples were detected using a mouse anti-c-myc monoclonal antibody (1 μg/mL; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) and goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (0.08 μg/mL; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA). The horseradish peroxidase activity was visualized with DAB.
Immuno fl uorescence staining of scFv637-HSA expression in human intercostal muscle
Binding of scFv637-HSA to acetylcholine receptor in situ at the neuromuscular junction was verified by immunohistochemical staining on human intercostal muscle frozen sections (Yanbian University, Yanji, Jilin Province, China). Slides were incubated with supernatants of media above for 60 minutes at 37°C, and then washed three times with 0.01 mol/L PBS (pH 7.4) for 5 minutes each time. Subsequently, sections were incubated with 1:100 diluted mouse anti-c-myc mAb together with rhodamine-labeled α-bungarotoxin (Sigma), and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (1:1,000; Sino-American Biotechnology, Beijing, China) for 30 minutes at 37°C after washing with PBS. As a negative control, sections were incubated with PBS instead of primary antibody. This study was in accordance with the guideline established by the Ethical Review Committee at Yanbian University, China.
Inhibition of scFv637-HSA on the binding of myasthenia gravis patient sera to human acetylcholine receptor
The capacity of scFv-HSA to inhibit the binding of serum anti-human acetylcholine receptor antibodies from myasthenia gravis patients in vitro was measured using a competitiveELISA kit (Institute of Neurology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China). Twelve cases of myasthenia gravis patient sera with positive anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies (Yanbian Wenhuan Ma Institute of Myasthenia Gravis, Yanji, Jilin Province, China) were tested. One hundred microliters of concentrated samples were added to wells of a human acetylcholine receptor-coated ELISA plate and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C. After rinsing, 100 μL myasthenia gravis patient sera was added and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C. After rinsing, the inhibition of scFv-HSA was measured by incubation with goat anti-human IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (1:1,000; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA). o-Phenylenediamine and H2O2in buffer were then added and the absorbance values at 492 nm were recorded (Microplate reader, Thermo Electron Corporation, Vantaa, Finland). The result was expressed as a percentage of inhibition of myasthenia gravis patient sera binding. This study was performed in accordance with the guidelines established by the Local Ethical Review Committee at Yanbian University, China.
Stability of scFv637-HSA in static healthy sera
Concentrated supernatants containing fusion protein scFv637-HSA were mixed and preserved in sterilized healthy sera for 7 days at 37°C water-bath. Mixed sample (100 μL) was stored at 4°C everyday to detect its inhibition by competitive ELISA as above.
Statistical analysis
All data presented were expressed as mean ± SEM. Graphpad Prism 5.0 statistical software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for statistical analysis of experimental data.
Results
Construction and expression of ScFv637-HSA
scFv637-HSA was cloned and purified from E. coli, DH5α by PCR. The size of scFv637-HSA-His-c-myc was 2,607 bp including scFv637, Linker1, HSA, Linker2, His, Linker3 and c-myc, as checked by gene sequencing. A band of about 2,600 bp appeared after digestion of recombinant T Simple Vector by SnaBI, EcoRI and PvuI (Figure 1). Since the sizes of T Vector and insert (scFv637-HSA-His-c-myc) are similar, it is dif fi cult to distinguish them by electrophoresis. However, only T Simple Vector has a PvuI site, but no insert. The scFv construct was successfully inserted into the SnaBI and EcoRI sites of pPIC9K as shown by PCR (Figure 2).
Pichia pastoris was chosen to express the fusion protein to increase the expression quantity and improve its functions. The eukaryotic kanamycin resistance gene confers resistance to the related antibiotic G418. The level of G418 resistance can be roughly correlated to vector copy number (Scorer et al., 1994). Pichia pastoris must be fi rst transformed to His+prototrophy; then multicopy transformants are screened by replica-plating to plates containing G418. There were 10, 8 and 2 positive transformants on the yeast extract peptone dextrose medium plates containing 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 mg/mL G418, respectively. The molecular weight of the fusion protein was 89 kDa as shown by western blot analysis (Figure 3).
Binding of ScFv637-HSA to acetylcholine receptor in human intercostal muscle
ScFv637-HSA could bind to acetylcholine receptor in situ at the neuromuscular junction of human intercostal muscles, indicated by immunohistochemical staining (Figure 4).
Inhibition of scFv637-HSA in myasthenia gravis patient seraIn the sera from 12 myasthenia gravis patients, the inhibition rate of binding to acetylcholine receptor was 2.0-77.4% (Figure 5). The mean inhibition rate was 31.4%.
Stability of scFv637-HSA in static healthy sera
The stability of scFv637-HSA in static healthy sera was maintained for about 3 days. The inhibition rate was 65.1%, 32.8% and 31.3% per day, respectively (Figure 6). From the fourth day, the inhibition rate decreased to zero and the fusion protein had no activity.
Discussion
Small recombinant antibody molecules such as scFv are rapidly cleared from the circulation. Usually, the chemical conjugation of small recombinant proteins to polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an established strategy to extend their typically short circulation times to a therapeutically useful range (Schlapschy et al., 2007; Noberini et al., 2011; Danial et al., 2012; Kumagai et al., 2012). Biologically active peptides or low molecular weight protein can be fused genetically to HSA, which has a longer plasma half-life so the short peptide half-life can be extended (Kenanova et al., 2010; Furukawa et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2011; Lei et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012). For example, extended plasma half-life of bispecific single-chain diabodies (scDb) possessing a molecular mass of approximately 55 kDa have been achieved by various strategies including PEGylation, N-glycosylation and fusion to an albumin-binding domain (ABD) from streptococcal protein G (Stork et al., 2009).
In this study, we describe a strategy to successfully yield recombinant scFv637-HSA against the main immunogenic region of acetylcholine receptor using Pichia pastoris expression technology. The aim of this study was to produce an anti-acetylcholine receptor scFv637-HSA. The binding of anti-acetylcholine receptor scFv to acetylcholine receptor could block pathogenic antibodies from binding to acetylcholine receptors. Accordingly, acetylcholine receptors were protected. An approximately 89 kDa protein band was con fi rmed via western blot analysis using anti-c-myc monoclonal antibodies, suggesting the secreted fusion protein was intact. By immuno fl uorescence analysis, green staining was observed around human intercostal muscles, revealing that the character of the fusion protein binding to human acetylcholine receptor was retained. Furthermore, the ability of scFv to bind to acetylcholine receptors was not affected by conjunction with the HSA gene. Inhibition of the binding of pathogenic antibodies from myasthenia gravis patient serato human acetylcholine receptors was 77.4% (maximum) by ELISA. The fusion protein from scFv637-HSA was effective in protecting acetylcholine receptors. However, the inhibition was only 2.0% in the fifth case, probably owing to the very high af fi nity of pathogenic antibodies to human acetylcholine receptors. The inhibition rate of the scFv637-HSA was still 31.3% in static healthy sera at day 3. However, from the fourth day, the inhibition rate decreased to zero. Thus, activity of the fusion protein was maintained for about 3 days. This result was similar with the observation by Stork (Stork et al., 2009) where PEGylated scDb and scDb-ABD were present in high concentrations in the blood, which resulted in increased levels in other organs. Tumorto-blood ratios of scDb-A′-PEG40kand scDb-ABD in CEA+tumors were weaker and gradually increased to a value of 1.5 and 3, respectively, at day 4. Its stability is lower than the half-life of HSA (19 days). This short half-life observed was different from the result by Smith (Smith et al., 2001), but it was higher than the half-life of scFv.
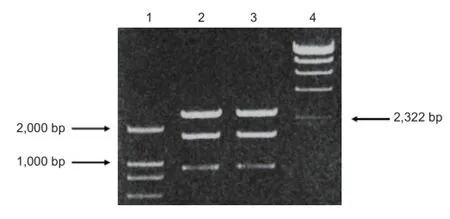
Figure 1 PCR results of recombinant plasmid pMD18-T Simple Vector-single-chain variable domain fragmeng 637-human serum albumin digested with SnaBI/EcoRI/PvuI.

Figure 2 PCR detection of recombinant vector after electroporation into GS115.

Figure 3 Western blot analysis of fusion protein scFv637-HSA.
The scFv637-HSA fusion protein was successfully expressed in Pichia pastoris, indicating it might be a potential candidate for speci fi c immunosuppressive therapy of myasthenia gravis.
Author contributions:Meng FP designed and revised the manuscript. Li FF performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Jin QX, Sun CY, Li YX, Li HH and Jin SZ provided technological support. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Con fl icts of interest:None declared.
Cossins J, Belaya K, Zoltowska K, Koneczny I, Maxwell S, Jacobson L, Leite MI, Waters P, Vincent A, Beeson D (2012) Te search for new antigenic targets in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1275:123-128.
Danial M, van Dulmen TH, Aleksandrowicz J, P?tgens AJ, Klok HA (2012) Site-speci fi c PEGylation of HR2 peptides: e ff ects of PEG conjugation position and chain length on HIV-1 membrane fusion inhibition and proteolytic degradation. Bioconjug Chem 23:1648-1660.
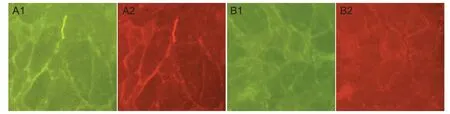
Figure 4 Binding of single-chain single-chain variable domain fragment 637-human serum albumin (scFv637-HSA) to acetylcholine receptor (AChR) in situ at neuromuscular junctions of human intercostal (immunohistochemical staining, × 200).

Figure 5 Competitive inhibition of binding to acetylcholine receptor (AChR) in myasthenia gravis (MG) patient sera by single-chain single-chain variable domain fragment 637-human serum albumin (scFv637-HSA).

Figure 6 The stability of single-chain variable domain fragment 637-human serum albumin (scFv637-HSA) in static healthy sera.
De Baets M, Stassen MH (2002) Te role of antibodies in myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Sci 202:5-11.
de Bold MK, She ffield WP, Martinuk A, Bhakta V, Eltringham-Smith L, de Bold AJ (2012) Characterization of a long-acting recombinant human serum albumin-atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) expressed in Pichia pastoris. Regul Pept 175:7-10.
Ding Y, Fan J, Li W, Yang R, Peng Y, Deng L, Wu Y, Fu Q (2013) Te effect of albumin fusion patterns on the production and bioactivity of the somatostatin-14 fusion protein in Pichia pastoris. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:1637-1648.
Furukawa M, Tanaka R, Chuang VT, Ishima Y, Taguchi K, Watanabe H, Maruyama T, Otagiri M (2011) Human serum albumin-thioredoxin fusion protein with long blood retention property is e ff ective in suppressing lung injury. J Control Release 154:189-195.
Graus YF, de Baets MH, Parren PW, Berrih-Aknin S, Wokke J, van Breda Vriesman PJ, Burton DR (1997) Human anti-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor recombinant Fab fragments isolated from thymus-derived phage display libraries from myasthenia gravis patients reflect predominant specificities in serum and block the action of pathogenic serum antibodies. J Immunol 158:1919-1929.
Higuchi O, Hamuro J, Motomura M, Yamanashi Y (2011) Autoantibodies to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 in myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol 69:418-422.
Huang YJ, Lundy PM, Lazaris A, Huang Y, Baldassarre H, Wang B, Turcotte C, C?té M, Bellemare A, Bilodeau AS, Brouillard S, Touati M, Herskovits P, Bégin I, Neveu N, Brochu E, Pierson J, Hockley DK, Cerasoli DM, Lenz DE, et al. (2008) Substantially improved pharmacokinetics of recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase by fusion to human serum albumin. BMC Biotechnol 8:50.
Huston JS, George AJ, Adams GP, Sta ff ord WF, Jamar F, Tai MS, Mc-Cartney JE, Oppermann H, Heelan BT, Peters AM, Houston LL, Bookman MA, Wolf EJ, Weiner LM (1996) Single-chain Fv radioimmunotargeting. Q J Nucl Med 40:320-333.
Kang NV, Hamilton S, Sanders R, Wilson GD, Kupsch JM (1999) Effi cient in vivo targeting of malignant melanoma by single-chain Fv antibody fragments. Melanoma Res 9:545-556.
Kenanova V, Olafsen T, Crow DM, Sundaresan G, Subbarayan M, Carter NH, Ikle DN, Yazaki PJ, Chatziioannou AF, Gambhir SS, Williams LE, Shively JE, Colcher D, Raubitschek AA, Wu AM (2005) Tailoring the pharmacokinetics and positron emission tomography imaging properties of anti-carcinoembryonic antigen single-chain Fv-Fc antibody fragments. Cancer Res 65:622-631.
Kenanova VE, Olafsen T, Salazar FB, Williams LE, Knowles S, Wu AM (2010) Tuning the serum persistence of human serum albumin domain III:diabody fusion proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 23:789-798.
Konstantakaki M, Tzartos SJ, Poulas K, Eliopoulos E (2007) Molecular modeling of the complex between Torpedo acetylcholine receptor and anti-MIR Fab198. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:569-575. Kumagai M, Shimoda S, Wakabayashi R, Kunisawa Y, Ishii T, Osada K, Itaka K, Nishiyama N, Kataoka K, Nakano K (2012) E ff ective transgene expression without toxicity by intraperitoneal administration of PEG-detachable polyplex micelles in mice with peritoneal dissemination. J Control Release 160:542-551.
Lagoumintzis G, Zisimopoulou P, Kordas G, Lazaridis K, Poulas K, Tzartos SJ (2010) Recent approaches to the development of antigen-speci fi c immunotherapies for myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity 43:436-445.
Lee MS, Kim YH, Kim YJ, Kwon SH, Bang JK, Lee SM, Song YS, Hahm DH, Shim I, Han D, Her S (2011) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of human serum albumin-TIMP-2 fusion protein using near-infrared optical imaging. J Pharm Pharm Sci 14:368-377.
Lei J, Guan B, Li B, Duan Z, Chen Y, Li H, Jin J (2012) Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant human interleukin-2-serum albumin (rhIL-2-HSA) fusion protein in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 84:154-160.
Li Q, Hudson W, Wang D, Berven E, Uckun FM, Kersey JH (1998) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of radioimmunoconjugates of anti-CD19 antibody and single-chain Fv for treatment of human B-cell malignancy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 47:121-130.
Liu M, Huang Y, Hu L, Liu G, Hu X, Liu D, Yang X (2012) Selective delivery of interleukine-1 receptor antagonist to inflamed joint by albumin fusion. BMC Biotechnol 12:68.
Luo J, Taylor P, Losen M, de Baets MH, Shelton GD, Lindstrom J (2009) Main immunogenic region structure promotes binding of conformation-dependent myasthenia gravis autoantibodies, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor conformation maturation, and agonist sensitivity. J Neurosci 29:13898-13908.
Meng F, Stassen MH, Schillberg S, Fischer R, De Baets MH (2002) Construction and characterization of a single-chain antibody fragment derived from thymus of a patient with myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity 35:125-133.
Nikolic A, Djukic P, Basta I, Hajdukovic Lj, Stojanovic VR, Stevic Z, Nikolic D, Bozic V, Lavrnic S, Lavrnic D (2013) Te predictive value of the presence of di ff erent antibodies and thymus pathology to the clinical outcome in patients with generalized myasthenia gravis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:432-437.
Noberini R, Mitra S, Salvucci O, Valencia F, Duggineni S, Prigozhina N, Wei K, Tosato G, Huang Z, Pasquale EB (2011) PEGylation potentiates the e ff ectiveness of an antagonistic peptide that targets the EphB4 receptor with nanomolar a ffi nity. PLoS One 6:e28611.
Po?a-Guyon S, Christadoss P, Le Panse R, Guyon T, De Baets M, Wakkach A, Bidault J, Tzartos S, Berrih-Aknin S (2005) E ff ects of cytokines on acetylcholine receptor expression: implications for myasthenia gravis. J Immunol 174:5941-5949.
Protopapadakis E, Kokla A, Tzartos SJ, Mamalaki A (2005) Isolation and characterization of human anti-acetylcholine receptor monoclonal antibodies from transgenic mice expressing human immunoglobulin loci. Eur J Immunol 35:1960-1968.
Schlapschy M, Teobald I, Mack H, Schottelius M, Wester HJ, Skerra A (2007) Fusion of a recombinant antibody fragment with a homo-amino-acid polymer: e ff ects on biophysical properties and prolonged plasma half-life. Protein Eng Des Sel 20:273-284.
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene expression. Biotechnology (N Y) 12:181-184.
Smith BJ, Popplewell A, Athwal D, Chapman AP, Heywood S, West SM, Carrington B, Nesbitt A, Lawson AD, Antoniw P, Eddelston A, Suitters A (2001) Prolonged in vivo residence times of antibody fragments associated with albumin. Bioconjug Chem 12:750-756.
Stork R, Campigna E, Robert B, Müller D, Kontermann RE (2009) Biodistribution of a bispeci fi c single-chain diabody and its half-life extended derivatives. J Biol Chem 284:25612-25619.
Sun C, Meng F, Li Y, Jin Q, Li H, Li F (2010) Antigen-speci fi c immunoadsorption of anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies from sera of patients with myastenia gravis. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 38:99-102.
Yang M, Hoppmann S, Chen L, Cheng Z (2012) Human serum albumin conjugated biomolecules for cancer molecular imaging. Curr Pharm Des 18:1023-1031.
Zhang B, Tzartos JS, Belimezi M, Ragheb S, Bealmear B, Lewis RA, Xiong WC, Lisak RP, Tzartos SJ, Mei L (2012) Autoantibodies to lipoprotein-related protein 4 in patients with double-seronegative myasthenia gravis. Arch Neurol 69:445-451.
Zhao T, Cheng YN, Tan HN, Liu JF, Xu HL, Pang GL, Wang FS (2012) Site-specific chemical modification of human serum albumin with polyethylene glycol prolongs half-life and improves intravascular retention in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 35:280-288.
Zhu RY, Xin X, Dai HY, Li Q, Lei JY, Chen Y, Jin J (2012) Expression and puri fi cation of recombinant human serum albumin fusion protein with VEGF165b in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 85:32-37.
Copyedited by Croxford L, Norman C, Yu J, Yang Y, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
10.4103/1673-5374.131611
Fanping Meng, Ph.D., Department of Immunology and Pathogenic Biology, College of Medicine, Yanbian
University, 977# Gongyuan Road,
Yanji 133002, Jilin Province, China, fpmeng@ybu.edu.cn.
http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2014-03-01
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Virtual reality interface devices in the reorganization of neural networks in the brain of patients with neurological diseases
- Regulatory effects of anandamide on intracellular Ca2+concentration increase in trigeminal ganglion neurons
- Nasal mucosal inhalation of amyloid-beta peptide 3-10 defective adenovirus attenuates cytotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid (1-42)
- The synthetic thyroid hormone, levothyroxine, protects cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus of naturally aged mice
- Similar effects of substance P on learning and memory function between hippocampus and striatal marginal division
- Citalopram increases the differentiation ef fi cacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neuronal-like cells

