Pancreatic islet regeneration and some liver biochemical parameters of leaf extracts of Vitex doniana in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic albino rats
Okpe Oche, Ibrahim Sani, Njoku Godwin Chilaka, Ndidi Uche Samuel, Atabo Samuel
Department of Biochemistry, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
Pancreatic islet regeneration and some liver biochemical parameters of leaf extracts of Vitex doniana in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic albino rats
Okpe Oche*, Ibrahim Sani, Njoku Godwin Chilaka, Ndidi Uche Samuel, Atabo Samuel
Department of Biochemistry, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
PEER REVIEW
Peer reviewer
Umar Ibrahim Alhaji, Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Kaduna, Nigeria.
Tel: +2347085490712
E-mail: smaumar@yahoo.com
Comments
This paper shows the plant not just has antidiabetic property but it most likely works by regeneration of the pancreatic islet which is very imperative in determining the type of plant extract a patient may require when compared to the level of damage due to diabetes.
Details on Page 129
Objective:To test two water soluble extracts (aqueous and ethanolic) obtained from the leaves of Vitex doniana in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats for their effects on pancreatic endocrine tissues and serum marker enzymes for a period of 21 d.
Vitex doniana, Pancreatic islet, Marker enzymes, Diabetes, Hepatoprotection
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a global health crisis, which has been affecting the humanity irrespective of the socioeconomic profile and geographic location of the population[1]. Though different types of oral hypoglycemic agents are available for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, there is increasing demand by patients to use antidiabetic natural products because of the undesirable side effects of the existing drugs[2]. After all, many of the currently available drugs have been derived directly or indirectly from plants[3]. In addition, herbal remedies continue to be more accessibleand affordable than conventional drugs and represent the first line of treatment available for many of the world’s population[4]. In many countries, much attention has been paid to find novel type of natural antidiabetic drugs from various medicinal plants[5-8]. Because of their effectiveness, limited side effects, and relatively low cost, herbal drugs are widely prescribed even when their biologically active compounds are unknown[9].
Data on ethnobotanicals suggest that about 800 plants may possess anti-diabetic potentials[3,10], however, very few of the ethnobotanicals for diabetes have received scientific or medical scrutiny, which invariably affect our knowledge of their mechanism of action[11]. Several mechanisms have been adduced for the hypoglycemic action of medicinal plants. They include inhibition of renal glucose reabsorption, enhanced secretion of insulin from β-cells of the pancreas, increased tissue uptake of glucose by enhancement of insulin sensitivity, regeneration/repair of the β-cells, stimulation of glycogenesis and hepatic glycolysis, increasing the size and number of cells in the islets of langerhans, protective effect on the destruction of the β-cells and/or prevention of oxidative stress that is possibly involved in pancreatic β-cells destruction[2,12,13]. The fiber of plants may also interfere with carbohydrate absorption, thereby affecting blood glucose[14].
Vitexis a perennial herb belonging to the dicotyledonous family of Verbenaceae. There are several reports on the medicinal applications ofVitex doniana(V. doniana). Research reported by Jameset al. showed that aqueous leave and stem bark extracts of the plant was effective against carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats[15]. The anti-microbial activities of acetone, ethanol, methanol, hot and cold water extracts of leaves ofV. donianahave been reported by Ejikeme and Henrietta[16]. The antihypertensive effect of extract of stem bark has also been reported by Ladejiet al[17]. In addition, the stem bark extracts demonstrated some level ofin vitrotrypanocidal activity againstTrypanosomabrucei brucei[18]. The effects of aqueous root-bark extracts on hematological parameters have also been reported[19]. The aqueous and methanolic extract of the plant have been reported to exhibit antidiarrhea activity[20], and they also have significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities mediated through sequential inhibition of the enzymes responsible for prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid[21].V. donianahas also been reported to possess a concentrationdependent inhibition of both acetylcholine and histamineinduced contractions[22]. The phytochemical studies ofV. donianashows that it has flavonoids, tannins, saponins, anthraquinones, balsam, carbohydrates and resin[23,24].However, to the best of our knowledge, no research has been carried out to investigate the effect of aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts ofV. donianaon pancreatic islet regeneration. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the pancreatic islet regeneration of the aqueous and ethanolic leaves extracts ofV. donianaand also find out its effects on some serum biochemical parameters.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plant samples collection and identification
Fresh leaves ofV. donianawere collected from Ankpa, Kogi State, Nigeria in the month of April 2011. The plant was identified and authenticated at the Herbarium Unit of the Department of Biological Sciences, Ahmadu Bello University Zaria, Nigeria, where a voucher specimen (900076) was deposited.
2.2. Experimental animals
Adult albino rats weighing between 140-220 g of both sexes were obtained from the laboratory animal house, Department of Pharmacology, ABU, Zaria. The animals were acclimatized for 2 weeks under ambient environmental conditions. They had access to grower’s mash (Vital feed, Grand Cereal Plc., Bukuru, Jos, Plateau State) and waterad libitum.
2.3. Preparation of plant sample
The plant leaves were rinsed in clean water and shadedried at ambient temperature for two weeks. The dry plant sample was ground into powder using pestle and mortar. The powder obtained was then used to prepare the extracts.
2.4. Aqueous extraction
To 100 g of powdered plant material, 500 mL portion of distilled water was added and the mixture was then boiled in a conical flask for 2 h. After the set time, the suspension was filtered using cloth with fine pore, and the filtrates were then concentrated in a crucible using a water bath set at 45 °C and the weight of the sample was taken. The concentrated extracts were then stored in an air-tight sample bottle in a refrigerator until required for analysis.
2.5. Ethanolic extraction
Five hundred grams of the powdered plant material were soaked in 2.5 L of 70% ethanol at room temperature in a conical flask for 72 h. After the set time, the suspension was filtered using cloth with fine pore and the filtrates were then concentrated in a crucible using a water bath set at 45 °C and the weight of the sample was taken. The concentrated extracts were then stored in an air-tight sample bottle in a refrigerator until required for analysis.
2.6. Acute toxicity test
The mean lethal dose (LD50) of the aqueous and ethanolic extracts were determined in albino rat (weighing 150 g-200 g) using the method described by Lorke[25].
2.7. Induction of diabetes
Diabetes was induced by single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ) (Sigma Chemicals Co., St. Louis USA) (60 mg/kg body weight in 0.1 mol/L citrate buffer, pH 4.5) into 16-18 h fasted rats[26]. The STZ-treated rats were kept for the next 24 h on 5% glucose solution bottles in their cages to prevent initial drug induced hypoglycemic mortality[27]. After 96 h of STZ injection, blood samples were collected by tail snip method and the sugar level of each animal was determined. All rats with fasting blood glucose concentration of greater than 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) were considered hyperglycemic and selected for the experiment[28].
2.8. Animal grouping and treatment
A total of 55 rats were used. The rats were divided into 11 groups of 5 rats. Group 1 was normal control rats that received vehicle of administration orally. Group 2 was diabetic control rats that received vehicle of administration orally. Group 3 was diabetic rats treated with 100 mg/kg bodyweight per day ethanolic extract orally. Group 4 was diabetic rats treated with 100 mg/kg bodyweight per day aqueous extract orally. Group 5 was diabetic rats treated with 200 mg/kg bodyweight per day ethanolic extract orally. Group 6 was diabetic rats treated with 200 mg/kg bodyweight per day aqueous extract orally. Group 7 was diabetic rats treated with metformin (250 mg/kg bodyweight per day) orally. Group 8 was normal rats treated with 100 mg/kg bodyweight per day ethanolic extract orally. Group 9 was normal rats treated with 100 mg/kg bodyweight per day aqueous extract orally. Group 10 was normal rats treated with 200 mg/kg bodyweight per day ethanolic extract orally. Group 11 was normal rats treated with 200 mg/kg bodyweight per day aqueous extract orally.
2.9. Treatment of samples/pancreatic tissues examination
At the end of 21 d, all the animals were anaesthetized using chloroform and bled by cardiac puncture 24 h after the last treatment. The blood sample was collected in specimen bottles, allowed to clot and the serum separated by centrifugation at 3 000×g for 10 min and then subjected to some biochemical parameters analysis. The pancreatic tissues were dissected out of all the experimental animals and washed on ice cold saline immediately. A portion of the pancreatic tissue was fixed in 10% formalin fixative solution for histological studies. After fixation, tissues were embedded in paraffin, solid sections were cut at 5 μm and the sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin. The stained section on the slide was covered with a thin glass to protect the tissue from being scratched in order to provide better optical quality for viewing under microscope at a magnification of ×250[29].
2.10. Biochemical analysis
Serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was determined by methods described by Haussament (1977). Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were both determined by methods described by Reitman and Frankel[30]. Total bilirubin and direct bilirubin were both quantified by acid diazo methods of Doumaset al., while unconjugated bilirubin was calculated by subtracting the values of direct bilirubin from total bilirubin[31].
2.11. Statistical analysis
The analysis was carried out in triplicates for all determinations and the results of the triplicate were expressed as mean±SEM. The SPSS program (version 17.0 SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the analysis of variance followed by the new Duncan’s multiple range test for multiple comparisons of the means[32].P<0.05 between mean values were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of leaf extract of V. doniana on liver function parameters
Table 1 shows the ALP, ALT and AST concentration in serum after administration of the extract for 21 d. There was a marked significant increase (P<0.05) in the concentration of these marker enzymes in the diabetic groups when compared to the normal control. The levels of ALP, ALT and AST in the diabetic treated groups and metformin group were, however, significantly reduced (P<0.05) in the diabetic treated groups relative to the untreated diabetic control.
Table 1 also shows the serum bilirubin of diabetic rats treated with the plant extracts and metformin for 21 d. There was a significant increase (P<0.05) in the levels of total and unconjugated bilirubin with a concomitant reduction in the levels of direct bilirubin in untreated diabetic control when compared to the diabetic treated groups and the normal control rats. However, there was no significant change (P>0.05) in the levels of these parameters in the non-diabetic treated groups (Table 2) when compared with the normal control rats.
On the other hand, the effect of the extracts on the marker enzymes in non-diabetic treated rats is presented in Table 2. There were no significant increase (P>0.05) in the level of ALT for all groups. Furthermore, the AST level showed similartrend as the ALT, with the exception of the group treated with 200 mg/kg ethanolic extract which shows a decrease in the level of AST. However, no significant change (P>0.05) in the level of ALP was observed between all the extracts treated groups and the normal control.

Table 1 The effects of daily doses of aqueous and ethanolic leaves extracts of V. doniana on liver function parameters of STZ-induced diabetic albino rats.

Figure 1.Photomicrographs of the endocrine region of the pancreas of diabetic rats treated with aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of V. doniana and metformin for 21 d.A: Normal architecture of islet cells of pancreas; B: There was complete depletion of islet cells; C: Prominent sinusoids and sinusoidal spaces were seen, along with areas of necrosis; D: Slight regeneration of diffused proliferated islet cells was seen; E: Distorted pancreatic cells with mononuclear cellular infiltration and areas of necrosis; F: Slight restoration of diffused proliferation of islet cells; G: Diffused cellular infiltration, with better preservation of islet cells. Eth.: Ethanolic extracts; Aq.: Aqueous extracts; Met.: Metformin.
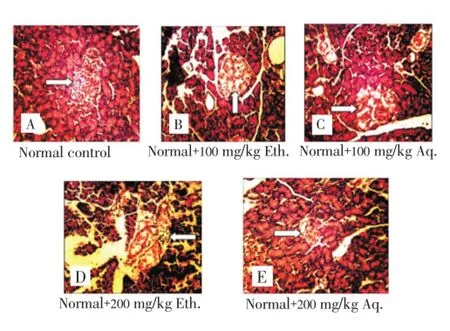
Figure 2.Photomicrographs of the endocrine region of the pancreas of non-diabetic rats treated with aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of V. doniana for 21 d.A: Normal architecture of pancreatic cells; B: Slight areas of necrosis, but good preservation of islet cells; C: The islet cells and sinusoidal spaces were well defined and tend closer to control; D: There is observed sinusoidal spaces with few scattered areas of necrotic islet cells; E: Most islet cells were seen to be intact. The pancreas tends towards the control. Eth.: Ethanolic extracts; Aq.: Aqueous extracts.
3.2. Effects of leaf extracts of V. doniana on endocrine region of the pancreas
Histological section of the endocrine region of the pancreas of STZ-induced diabetic rats (Figure 1) revealed a significant reduction in the size of islet cells, distorted pancreatic architecture, mononuclear cellular infiltration and sinusoidal spaces when compared to that of normal groups. Furthermore, the study revealed the presence of damaged β-cell population was due to STZ-induction. The administration of the plant extract ofV. donianatothe diabetic rats revealed restoration of size of the islets along with β-cells repair (Figures 1D, E, F and G). This recovery of the β-cell was more evident at lower dose level (100 mg/kg body weight) of the fed animal groups. However, administration of the extracts to non-diabetic rats (Figure 2) shows sinusoidal spaces with few scattered areas of necrotic Islet cells (Figure 2B, C, D and E).
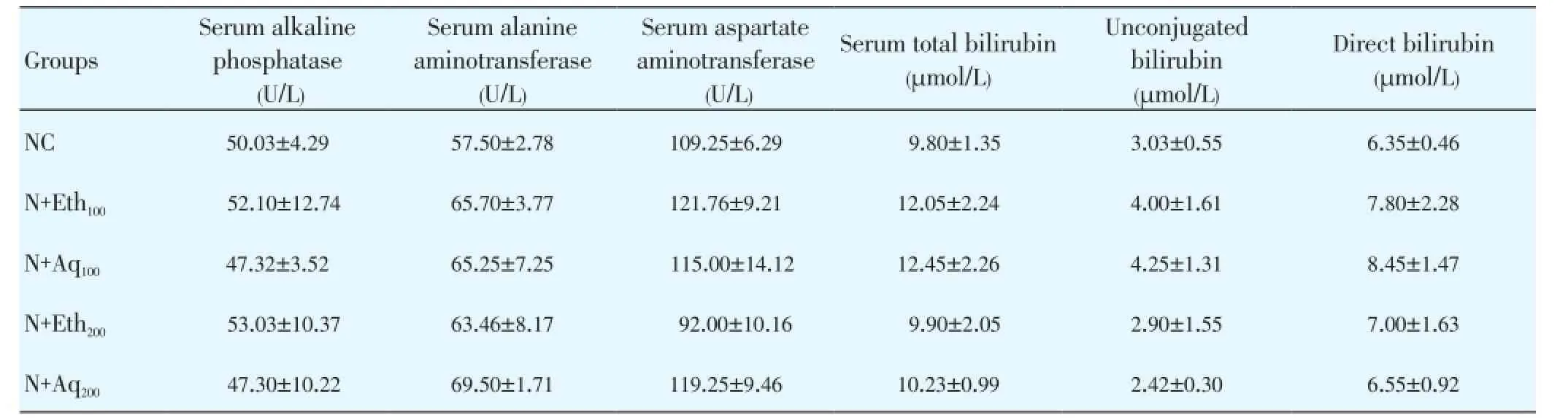
Table 2The effects of daily doses of aqueous and ethanolic leaves extracts of V. doniana on liver function parameters of normoglycemic albino rats.
4. Discussion
STZ has been widely used intravenously or intraperitoneally to induce type I diabetes in animal models, especially rats and mice[33]. In the present study, the injection of STZ induces hepatocellular damage, which is one of the characteristic changes in diabetes as evidenced by high serum levels of AST, ALT and ALP in untreated diabetic control group. The release of these enzymes into the serum is as a result of tissue injury or changes in the permeability of liver membranes, hence the concentration may increase with acute damage to liver cells[34].
When the integrity of the hepatocellular membrane is compromised, there is extrusion of the marker enzymes into the plasma[35]. Therefore, the significant elevation (P<0.05) in the levels of the marker enzyme in the serum as observed in the diabetic untreated control when compared to the normal control suggests possible damage to the liver or muscle. However, the extracts treated groups and the metformin treated groups showed a significant reduction in the levels of these enzymes when compared to the diabetic untreated control, thus an indication of the protective effects of the extracts over STZ-induced liver damage accords with the report of other investigators[36]. The levels of the marker enzymes particularly in the ethanolic extracts treated group were lower than the aqueous extracts treated group, suggesting a strong hepatoprotective ability of the ethanolic extracts. Bilirubin is excreted by the liver, therefore, interference with the normal liver functions affects its rate of conjugation and excretion. Thus a high level of bilirubin is used as indices for liver function and bile excretion status[37]. The present study showed a significant increase (P<0.05) in total and unconjugated bilirubin in diabetic untreated control. These levels are, however, markedly reduced in the extract-treated groups, suggesting the enhancement of liver functions by the extracts. This accords with similar findings on these biochemical parameters by Atawodiet al., Jameset al, Ladeji and Okoye and Ushaet al[15,37-39]. There was no significant increase (P>0.05) in the serum activities of the marker enzymes (ALT, AST and ALP) in the non-diabetic treated rats, thus suggesting little or low level of toxicity of the extracts.
Reports have shown that the reduction in pancreatic β-cells can be as high as 50% during diabetes[2,40,41]. The present study revealed the presence of damaged β-cell population due to STZ induction. The histopathological study of diabetes-treated groups indicates increase in the volume density of islets, percent of β cells and size of islet in the groups that received the plant extracts, which may be a sign of regeneration along with β-cells repairs. The restoration of the β-cells was more evident at lower dosage (100 mg/kg body weight of the fed animal groups). Administration of the extract to non-diabetic rats show distorted pancreatic architecture and mononuclear cellular infiltration and sinusoidal spaces, suggesting that the extracts at the concentration used is relatively toxic to the pancreas of non-diabetic rats. Sign of regeneration of β-cells has been reported following consumption of some other plants in STZ-induced diabetic animals[42-44].Vinca roseaextract as reported by Ghosh and Suryawanshi act by β-cell regeneration[45]. These reports are consistent with the present study, thus, islet cell replacement or regeneration therapy may offer therapeutic benefit to people with diabetes[46,47].
Photomicro graphical data in our studies suggests that the healing of pancreas byV. donianaleaves extracts may be a plausible mechanism of their anti-diabetic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Comments
Background
Damage caused by diabetes has become a major issue worldwide. Therefore, in the management of the disease, it is imperative to consider the ability of the drug (or in this case, plant extract) to protect or cause a regeneration of the islet of langerhans. The literature reports various works that have been carried out with other medicinal plants including this one. However, no work has been done on the area considered in this paper, to the best of the authors’ knowledge. In addition, most of the plant extract do not regenerate islet of langerhans.
Research frontiers
The paper shows that the extract exhibited antidiabetic potential by regeneration of the islet of langerhans. Indeed, there are many plants that have exhibited antidiabetic properties. However, their mechanism of actions are still largely unknown.
Related reports
The data obtained shows the ability of the plant extract to stabilize the liver marker enzymes for diabetesi.e. reduces the elevated level of these marker enzymes which were caused by the diabetes. This action is in agreement with other medicinal plant extracts that are known antidiabetic agents (Sharmaet al., 2010). There was a sign of regeneration of the islet, which accords with other publications (Xiuet al., 2001).
Innovations and breakthroughs
This paper clearly shows that this plant is not just an antidiabetic agent but has the ability to regenerate damaged pancreatic cells, which several reports has not delved into. It adds further credence to the use of the plant as an antidiabetic agent and to the ability of medicinal plants to regenerate islet of langerhans.
Applications
This paper shows that the plant can be used for the management of diabetes as well as regenerate damaged pancreatic islets.
Peer review
This paper shows the plant not just has antidiabetic property but it most likely works by regeneration of the pancreatic islet which is very imperative in determining the type of plant extract a patient may require when compared to the level of damage due to diabetes.
[1] Khan V, Najmi AK, Akhtar M, Agil M, Mujeeb M, Pillai KK. A pharmacological appraisal of medicinal plants with antidiabetic potential. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2012; 4(1): 27-42.
[2] Zhou JY, Zhou SW, Zeng SY, Zhou JY, Jiang MJ, He Y. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of ethanolic extracts of Mirabilis jalapa L. root on normal and diabetic mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012; doi:10.1155/2012/257374.
[3] Patel DK, Prasad SK, Kumar R, Hemalatha S. An overview on antidiabetic medicinal plants having insulin mimetic property. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2012; 2(4): 320-330.
[4] Okpara JO, Okpala EJ, Mamman M, Ayo JO, Cole TA. Antidiarrhoeal activity of the ethanolic extract of Adansonia digitata leaves. Vom J Vet Sci 2007; 1(4): 8-13.
[5] Shimada T, Kosugi M, Tokuhara D, Tsubata M, Kamiya T, Sameshima M, et al. Preventive effect of pine bark extract (Flavangenol) on metabolic disease in western diet-loaded tsumura suzuki obese diabetes mice. Evid Based Complment Alternat Med 2011; doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep231.
[6] Ghosh S, Ahire M, Patil S, Jabgunde A, Bhat Dusane M, Joshi BN, et al. Antidiabetic activity of Gnidia glauca and Dioscorea bulbifera: potent amylase and glucosidase inhibitors. Evid Based Complment Alternat Med 2012; doi: 10.1155/2012/929051.
[7] Benhaddou-Andaloussi A, Martineau L, Vuong T, Meddah B, Madiraju P, Settaf A, et al. The in vivo antidiabetic activity of Nigella sativa is mediated through activation of the AMPK pathway and increased muscle Glut4 content. Evid Based Complment Alternat Med 2011; doi: 10.1155/2011/538671.
[8] Leite ACR, Araújo TG, Carvalho BDM, Maia MBS, Lima VLDM. Characterization of the antidiabetic role of Parkinsonia aculeata (Caesalpineaceae). Evid Based Complment Alternat Med 2011; doi: 10.1155/2011/692378.
[9] Al-Aboudi A, Afifi FU. Plants used for the treatment of diabetes in Jordan: a review of scientific evidence. Pharm Biol 2011; 49(3): 221-239.
[10] Ponnusamy S, Ravindran R, Zinjarde S, Bhargava S, Ravi Kumar A. Evaluation of traditional Indian antidiabetic medicinal plants for human pancreatic amylase inhibitory effect in vitro. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; doi: 10.1155/2011/515647.
[11] Fr?de TS, Medeiros YS. Animal model to test drugs with potential antidiabetic activity. J Ethnopharmacol 2008; 115: 173-183.
[12] Rajalaksmi M, Eliza J, Cecilia EP, Nirmala A, Daisy P. Antidiabetic property of Tinospora cordifolia stem extracts on STZ-induced diabetic rats. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2009; 3(5): 171-180.
[13] Ayodhya S, Kusum S, Anjali S. Hypoglycemic activity of different extracts of various herbal plants. Int J Ayurveda Res Pharm 2010; 1(1): 212-224.
[14] Nelson RW, Ihle SL, Lewis LD, Salisbury SK, Bergdall V, Bottoms GD. Effects of dietary fiber supplementation on glycemic control in dogs with alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus. Am J Vet Res 1991; 52(6): 2060-2066.
[15] James DB, Owolabi OA, Bisalla M, Jassium H. Effect of aqueous leaves and stem extracts of Vitex doniana on carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats. Br J Pharmacol Toxicol 2010; 1(1):1-5.
[16] Nwachukwu E, Uzoeto HO. Antimicrobial activities of leaf of Vitex doniana and Cajanus cajan on some bacteria. Researcher 2010; 2(3): 37-47.
[17] Olusola L, Okoye ZSC, Uddoh F. Effects of Vitex doniana stem bark on blood pressure. Phytother Res 1996; 10(3): 245-247.
[18] Atawodi SE. Comparative in vivo trypanocidal activities of petroleum ether, chloroform, methanol, and aqueous extracts of some Nigerian savannah plants. Afr J Biotechnol 2005; 4(2): 177-182.
[19] Abdulrahman FI, Akan JC, Sodipo OA, Onyeyili PA. Effect of aqueous root-bark extract of Vitex doniana Sweet on haematological parameters in rats. J Am Sci 2010; 6(12): 8-12.
[20] Agunu A, Yusuf S, Andrew GO, Zezi AU, Abdurahman EM. Evaluation of five medicinal plants used in diarrhea in Nigeria. J Ethnopharmacol 2005; 101(1-3): 27-30.
[21] Iwueke AV, Nwodo OFC, Okoli CO. Evaluation of the antiinflammatory and analgesic activities of Vitex doniana leaves. Afr J Biotechnol 2006; 5(20): 1929-1935.
[22] Kumar R, Sharma RJ, Bairwa K, Roy RK, Kumar A. Pharmacological review on natural antidiarrhoel agents. Der Pharma Chemica 2010; 2(2): 66-93.
[23] Omoregie EH, Emmmanuel OO, Grace U, SaboAM, Ibrahim I, Samuel OE, et al. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial studies of methanol, ethylacetate and hexane extracts of Vitex doniana (stem bark and leaf). Nat Sci 2010; 8(8): 177-185.
[24] Suleiman MM, Yusuf S. Antidiarrheal activity of the fruits of Vitex doniana in laboratory animals. Pharmacol Biol 2008; 46(6): 387-392.
[25] Lorke D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Arch Toxicol 1983; 54(4): 275-287.
[26] Katsumata K, Katsumata K Jr, Katsumata Y. Protective effect of diltiazem hydrochloride on the occurrence of alloxan-or streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Horm Metab Res 1992; 24(11): 508-510.
[27] Dhandapani S, Subramanian VR, Rajagopal S, Namasivayam N. Hypolipidemic effect of Cuminum cyminum L. on alloxaninduced diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res 2002; 46(3): 251-255.
[28] Burcelin R, Eddouks M, Maury J, Kande J, Assan R, Girard J. Excessive glucose production, rather than insulin resistance, account for hyperglycemia in recent onset streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 1995; 38(3): 283-290.
[29] Strate T, Mann O, Kleighans H, Rusani S, Schneider C, Yekebas E, et al. Micro circulatory function and tissue damage is improved after the therapeutic injection of bovine hemoglobin in severe acute rodent pancreatitis. Pancreas 2005; 30(3): 254-259.
[30] Reitman S, Frankel S. A colourimetric method for the determination of serum glutamine oxaloacetic acid and glutamic pyruvic acid transaminase. Am J Clin Pathol 1957; 28(1): 56-63.
[31] Doumas BT, Perry BW, Sasse EA, Straumfjord JV. Standardization in bilirubin assays: evaluation of selected methods and stability of bilirubin solutions. Clin Chem 1973; 19: 984-993.
[32] Duncan DB. Multiple range and multiple F-test. Biometrics 1955; 11: 1-42.
[33] Yin P, Zhao S, Chen S, Liu J, Shi L, Wang X, et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of polyphenols from burs of Castanea mollissima blume. Molecules 2011; 16(11): 9764-9774.
[34] Hsueh CJ, Wang JH, Dai L, Liu CC. Determination of alanine aminotransferase with an electrochemical nano Ir-C biosensor for the screening of liver diseases. Biosens 2011; 1(3): 107-117.
[35] Moss DW, Henderson AR. Enzymes. In: Tietz NW, editor. Tietz fundermental of clinical chemistry. 4th ed. Philadalphia: Sounders Elsevier; 1996, p. 283-335.
[36] Sharma B, Salunke R, Balomajumder C, Daniel S, Roy P. Antidiabetic potential of alkaloid rich fraction from Capparis decidua on diabetic mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2010; 127(2): 457-462.
[37] Usha K, Mary KG, Hemalatha P. Hepatoprotective effect of Hygrophila spinosa and Cassia occidentalis on carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in experimental rats. Indian J Clin Biochem 2008; 22(2): 132-135.
[38] Atawodi SE, Atawodi JC, Idakwo GA, Pfundstein B, Hambner R, Wutela G, et al. Evaluation of the polyphenols content and antioxidants properties of methanol extracts of leaves, stem and root barks of Moringa oleifera lam. J Med Foods 2010; 13(3): 710-716.
[39] Ladeji O, Okoye ZSC. Anti-hepatotoxic properties of bark extract. Pharm Biol 1996; 34(5): 355-358.
[40] Wang L, Zhang XT, Zhang HY, Yao HY, Zhang H. Effect of Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaves extract on blood glucose and plasma lipid levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2010; 130(3): 465-469.
[41] Lee SH, Park MH, Heo SJ, Kang SM, Ko SC, Han JS, et al. Dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava inhibits alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase in vitro and alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2010; 48(10): 2633-2637.
[42] Xiu LM, Miura AB, Yamamoto K, Kobayashi T, Song QH, Cyong JC. Pancreatic islet regeneration by ephedrine in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Am J Clin Med 2001; 29: 493-500.
[43] Sivaraj A, Devi K, Palani S, Vinoth KP, Senthil KB, David E. Anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hypolipidemic effect of combined plant extract of Cassia auriculata and Aegle marmelos in streptozotocin induced diabetic albino rats. Int J Pharm Technol Res 2009; 1(4): 1010-1016.
[44] Muji? A, Grdovi? N, Muji? I, Mihailovi? M, ?ivkovi? J, Poznanovi? G, et al. Antioxidative effects of phenolic extracts from chestnut leaves, catkins and spiny burs in streptozotocin-treated rat pancreatic β-cells. Food Chem 2011; 125: 841-849.
[45] Ghosh S, Suryawanshi SA. Effect of Vinca rosea extracts in treatment of alloxan diabetes in male albino rats. Indian J Exp Biol 2001; 30: 748-759.
[46] Moss JB, Koustubhan P, Grenman M, Parsons MJ, Walter I, Moss LG. Regeneration of the pancreas in adult zebrafish. Diabetes 2009; 58(8): 1844-1851.
[47] Halban PA, German MS, Kahn SE, Weir GC. Current status of islet cell replacement and regeneration therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(3): 1034-1043.
10.1016/S2221-1691(14)60220-3
*Corresponding author: Okpe Oche, Department of Biochemistry, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
Tel: +2348066804929
E-mail: ocheking10@gmail.com, chatwitocheking@yahoo.com
Foundation Project: Supported by the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria (Grant No. ABUBCH-0102-0005).
Article history:
Received 15 Oct 2013
Received in revised form 27 Oct , 2nd revised form 10 Nov, 3rd revised form 1 Dec 2013
Accepted 18 Jan 2014
Available online 28 Feb 2014
Methods:A total of 55 rats divided into 11 groups of 5 rats each were assigned into diabetic and non-diabetic groups and followed by a daily administration of ethanolic and aqueous extracts for 21 d. Group 1 was the normal control while group 7 was treated with standard drug.
Results:The histopathological studies of the diabetic rats indicated increase in the volume density of islets, percent of β-cells and size of islet in the groups that received the plant extracts, which suggested regeneration of β-cells along with β-cells repairs, as compared with the non-treated diabetic control which showed complete degeneration of the islet cells. There was significant reduction (P<0.05) in the serum activities of marker enzymes, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase in diabetes treated rats, whereas an insignificant increase (P>0.01) in the serum activities of marker enzymes was observed for non-diabetic treated rats. Results of total bilirubin, direct bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin showed that diabetic control group was significantly higher (P<0.05) in total bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin compared with treated groups while non-diabetic treated groups showed no significant increase (P>0.01) in total bilirubin and direct bilirubin compared with the normal control.
Conclusion:This herbal therapy appears to bring about repair/regeneration of the endocrine pancreas and hepatic cells protection in the diabetic rat.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年2期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年2期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacterial isolates from urinary tract infections at Dessie Health Research Laboratory, Ethiopia
- Inhalation of Shin-I essential oil enhances lactate clearance in treadmill exercise
- Anti-inflammatory activity and qualitative analysis of different extracts of Maytenus obscura (A. Rich.) Cuf. by high performance thin layer chromatography method
- Ameliorative effect of alkaloid extract of Cyclea peltata (Poir.) Hook. f. & Thoms. roots (ACP) on APAP/CCl4induced liver toxicity in Wistar rats and in vitro free radical scavenging property
- Investigation of in vivo neuropharmacological effect of Alpinia nigra leaf extract
- A pharmacobotanical study of two medicinal species of Fabaceae
