In vitro antibacterial activity of leaf extracts of Zehneria scabra and Ricinus communis against Escherichia coli and methicillin resistance Staphylococcus aureus
Bereket Abew, Samuel Sahile, Feleke Moges
1Department of Biology, Faculty of Natural and Computational Sciences, University of Gondar, Ethiopia
2Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Ethiopia
In vitro antibacterial activity of leaf extracts of Zehneria scabra and Ricinus communis against Escherichia coli and methicillin resistance Staphylococcus aureus
Bereket Abew1, Samuel Sahile1, Feleke Moges2*
1Department of Biology, Faculty of Natural and Computational Sciences, University of Gondar, Ethiopia
2Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Ethiopia
PEER REVIEW
Peer reviewer
Dr. Berhanu Andualem, Associate Professor, Department of Biotechnology College of Natural and Computational Sciences, Ethiopia.
Tel: +251918700027
E-mail: anberhanu2007@yahoo.com
Comments
This paper is very interesting and has wide application in biotechnology where many researchers can follow the screening and extraction of natural products for the discovery of noble compounds. Therefore, this study is helpful to initiate other researchers in the area of interest.
Details on Page 819
Objective:To evaluate the antibacterial activities of the crude leaves extracts of Zehneria scabra (Z. scabra) and Ricinus communis (R. communis) against Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and methicillin resistance S. aureus.
Antibacterial, Extracts, Inhibition zone, MBC, MIC
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative therapies and the therapeutic use of natural products, especially those derived from plants[1]. This interest in drugs of plant origin is limited due to several reasons, namely, conventional medicine can be inefficient (e.g. side effects and ineffective therapy), abusive and/or incorrect use of synthetic drugs results in side effects and other problems[2]. Large percentage of the world’s population does not have access to conventional pharmacological treatment, and folk medicine and ecological awareness suggests that natural products are harmless. However, the use of these substances is not always authorized by legal authorities dealing with efficacy and safety procedures, and many published papers explained the lack of qualityin the production, trade and prescription of phytomedicinal products. So, formulation of plants for standardization and regulation of phytomedicinal products is the most alternative way[3].
In Ethiopia, medicinal plants have been used as traditional medicine to treat number of human and animal ailments by the local people from time immemorial. About 80% of the population in Ethiopia uses traditional medicine, mainly herbal plants[4].Zehneria scabra(Z. scabra) andRicinus communis(R. communis) are some of the traditionally used medicinal plants.Z. scabra, vernacular name is called“Hareg Resa” in Amharic, is a climbing or trailing herb belongs to the Cucurbitaceae that can go up to 10 m. Old stems become woody with corky-ridged bark. It inhabits forest and on forest margins, riverine fringes and exotic plantations across 900-2 100 m above sea level with a widespread in tropical Africa, South Africa, Arabia, India, Java and the Philippines[5]. In Ethiopia,Z. scabrais one of the traditional medical plants commonly used for the treatment of alopecia, wound and eczema, burn remedy and skin rashes as part of a poly-herbal preparation, the ash and wash prepared from pounded leaves[6].R. communispopularly called castor bean in English andGuloin Amharic. It is widely spread as a wild plant through East and North Africa. In Ethiopia, castor plant is important to treat tooth ache, cold, dysentery and itachy, fetal membrane retention and rabies in different preparation[7-9].
Ethno-botanical studies revealed thatZ. scabraandR. communisare being used in the treatment of pathogenic organisms in the traditional health care system in Ethiopia. However, very little work has been done to evaluate their efficacy in scientific way[10]. Therefore, this study was aimed to evaluate thein vitroantibacterial activity of crude leaf extractions ofZ. scabraandR. communisagainst standard and clinical isolates ofEscherichia coli(E. coli),Staphylococcus aureus(S. aureus) including methicillin resistanceS. aureus(MRSA).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study area
The study was conducted at University of Gondar, Gondar town. It is located in the North West Ethiopia of Amhara region. The town has an elevation of 2 080 m above sea level with a mid-altitude climate and an average annual maximum temperature of 30 °C and minimum temperature of 16 °C[11].
2.2. Plant material
2.2.1. Sampling, sample collection and identification
Through random sampling, healthy and disease free of the leaves of a wild growingZ. scabraandR. communiswere collected from gardens in Gondar town by scissors and samples were kept in plastic bags. The plants were identified and confirmed using standard manuals by plant taxonomist.
2.2.2. Preparation of crude extract
The leaves ofZ. scabraandR. communiswere transported to Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Biology, Faculty of Natural and Computational Sciences, University of Gondar. The plant materials were washed using distilled water and air dried at room temperature under shade for 10 d and powdered using wooden-made pestle and mortar. The powdered materials were sieved and stored in air tight container until use.
A 100 g of air-dried plant powdered leaves were measured by electronic balance (CY510) and then placed in a 2 000 mL clean round bottomed flask at room temperature caped with aluminum foil. After that, 1 000 mL benzene was added to the flask which contained powdered leaves material [1 part test material and 10 parts of solvent (w/v)]. The mixture was kept on a rotary shaker at 200 r/min for 24 h. The macerate was first filtered through double layer muslin cloth then through Whatman No. 1 filter paper and it was assigned as extract 1. The residue was taken again and mixed with chloroform/ acetone with ratio 1:1 in a volume of 1 000 mL, and the filtrate was assigned as extract 2. The same procedure was followed using 70% alcohol and distilled water to obtain extract 3 and extract 4, respectively. These successive cold maceration methods were done with increasing order of their polarity[13]. The filtrates were allowed to concentrate under rotary vapor (RE 2000) at 40 °C, weighed and stored in sterilized air tight container at 4 °C for further analysis.
2.3. Test organisms
Standard strains ofE. coli(ATCC 25922) andS. aureus(ATCC 2923) were collected from Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences Research Center, University of Gondar while clinical isolates ofE. coli, MRSA andS. aureuswere collected from Ethiopian Health and Nutrition Research Institute, Addis Ababa. The microorganisms were transported to Microbiology Laboratory by using nutrient agar slant and preserved at 4 °C for further use.
2.4. Standard antibiotics
Ciprofloxacin (in the form of powder) having a broad spectrum property was used as a positive control (5 μg/mL).
2.5. Inocula preparation
The inocula preparation was carried out by growth methods[14,15]. The test organisms from nutrient agar slant were transferred into a nutrient agar medium to get a pure colony at 37 °C for 24 h. Three to five pure colonies were selected and transferred into a sterile test tube containing 5 mL of sterile nutrient broth and the solutions were mixed by a vortex mixer. The broth culture was incubated at 37 °C until it reached the turbidity of (105-106CFU/mL) which was equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standards (usually about 8 h) and turbidity was adjusted visually by comparing the test.
2.6. Agar well diffusion method
Susceptibility tests were performed by agar well diffusion method using Muller-Hinton agar[16,17]. A sterile cotton swabs were dipped into the adjusted suspension by pressing and rotating the swabs firmly against the inside of the tube above the fluid level. The swab was then evenly streaked over the entire surface of the Muller-Hinton agar plate repeatedly by rotating the plate approximately 600 each time and the rim of the agar was swabbed to obtain uniform inoculums. On each plate, six equidistant wells (one in the center and five wells at the corner) were made with a 6 mmdiameter sterilized cork borer, 2 mm from the edge of the plate[15].
Five of the holes were aseptically filled with 50 μL of different concentrations of each plant extracts (i.e. 100 mg/ mL, 200 mg/mL, 300 mg/mL, 400 mg/mL and 500 mg/mL) sequentially, and at the center, ciprofloxacin was added as a positive control. The amount of control was the same as the tested sample on the wells. Petri plates were placed at 4 °C for 2 h to allow diffusion of the extract into the agar and then incubated at (37±0.1) °C for 24 h. At the end the inhibition zones formed were measured to the nearest millimeters and the experiment was performed in duplicate. Experiments that gave contradicting results were done for the third time for an easy decision.
2.7. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
MIC of crude extracts of theZ. scabraandR. communiswere performed using two fold broth dilution methods[18]. The extract solution (500 mg/mL) was serially diluted with nutrient broth as 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64, 1:128 and 1:256 to bring 250 mg/mL, 125 mg/mL, 62.5 mg/mL, 31.25 mg/ mL, 15.63 mg/mL, 7.81 mg/mL, 3.95 mg/mL and 1.95 mg/ mL concentrations, respectively and 20 μL of a standard suspension of the test organism was added to each concentration of the extract. Two test tubes containing nutrient broth without antimicrobial agent were added in each test. One of these tubes was inoculated with the test organism; the other was left uninoculated and served as a control for media sterility. The broth plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The lowest concentration, at which there was no turbidity, was regarded as MIC value of the extract.
2.8. Determination of minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
MBC is the lowest concentration of an antibiotic required to kill a microorganism[18]. The MBC were determined by sub-culturing 20 μL of the test dilutions from MIC tubes on to fresh nutrient agar plates incubating at 37 °C for 24 h. The lowest concentration that killed the entire bacterial colony on the plates was recorded as MBC.
2.9. Statistical analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for determination of the antimicrobial susceptibility test of phyto-chemical extracted by different solvents in the specific concentration. Values were expressed as mean ±SEM by using SPSS version 16 software and presented as tables.Pvalues less than 0.05 were taken as statistically significant[19].
3. Results
3.1. Agar well diffusion assay of the crude leaf extracts of Z. scabra and R. communis
Among the standard test strains,S. aureus(ATCC 2923) was the most susceptible bacteria [(14.00±2.00) mm], followed byE. coli(ATCC 25922) [(6.85±0.91) mm] to the extracts ofZ. scabra. Among clinical isolates most susceptible strains for extracts ofZ. scabrawasS. aureus[(9.95±1.79) mm] followed by MRSA [(7.80±1.24) mm] andE. coli[(3.50±0.97) mm]. Similarly, the most susceptible standard strains for extracts ofR. communiswasS. aureus(ATCC 2923) [(15.90±2.13) mm], followed byE. coli(ATCC 25922) [(15.20±1.53) mm] and clinical isolates ofS. aureus[(9.90±1.98) mm], MRSA [(9.50±2.12) mm] andE. coli[(7.75±0.91) mm] (Table 1).
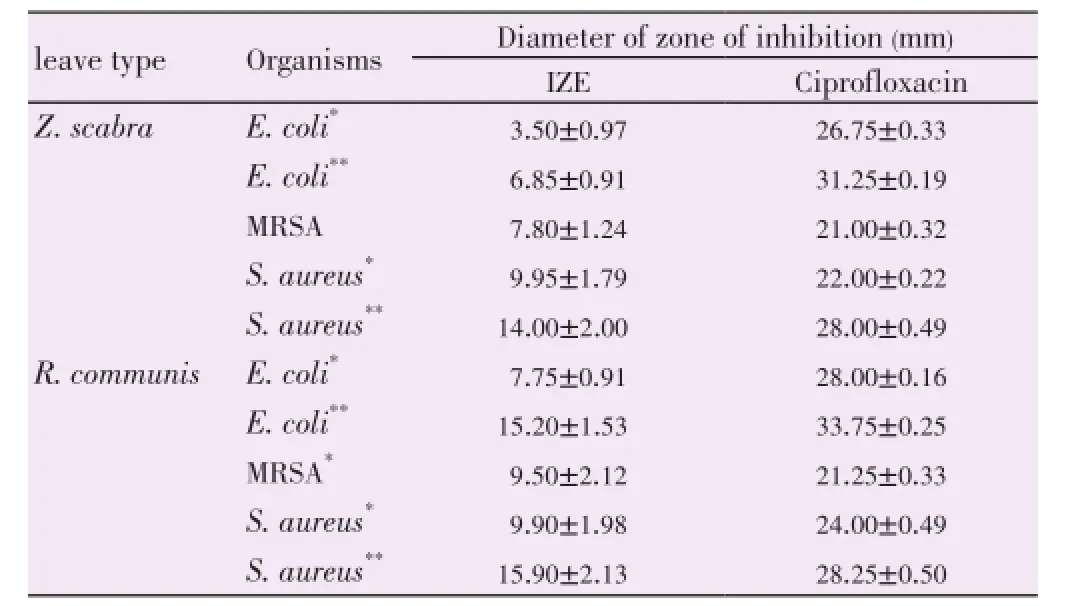
Table 1 Zone of inhibition against test organisms of leaf extract fractions of Z. scabra and R. communis.
3.2. TheMICvalues of Z. scabra and R. communis extracts against test organisms
The MIC value of plant extracts ofZ. scabraagainst the test bacteria ranged from 1.95 mg/mL (extract 3 for both clinical and standard stains ofS. aureus) to 250.00 mg/mL (extract 1 and extract 4 for both clinical and standard strains ofE. coli), respectively, (Table 2). The MIC values of extract 3 ranged from 1.95 mg/mL to 62.5 mg/mL with the least MIC values compared to other crude leaf extract fraction. Extract 4 had MIC values ranged from 15.62 mg/mL (on standard strains ofS. aureus) to 250.00 mg/mL (on standard strains ofE. coli) where as MIC values were negligible to other strains (particularly on clinical isolates). The overall trend showed that the MIC values of Gram-positive bacteria were lower than Gram-negative bacteria (Table 2).
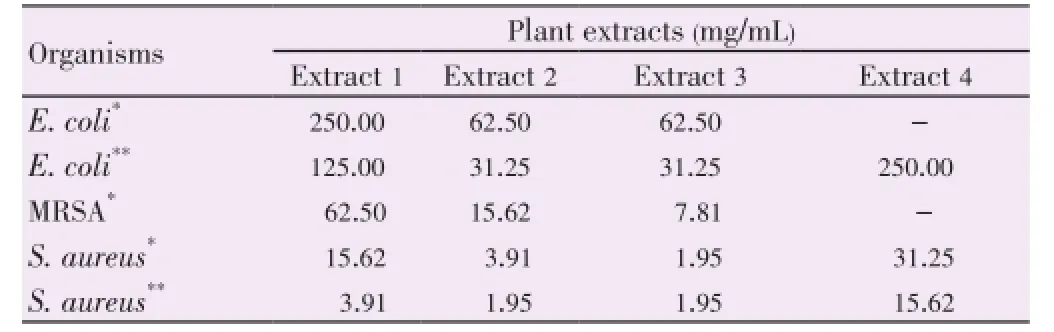
Table 2 The MIC values of Z. scabra leaf extract fractions against test organisms using two fold broth dilution methods.
As indicted from Table 3,R. communisleaf extract showed MIC value ranging from 1.95 mg/mL to 250.00 mg/mL. The most effective extract that inhibited the growth of bacteria was extract 3 with value ranged from 1.95 mg/mL to 62.5 mg/ mL. Extract 4 inhibited all standard strains in low MIC values ranged from 3.91 mg/mL (S. aureus(ATCC 2923) to 7.81 mg/ mL (E. coli(ATCC 25922). Standard strain ofS. aureus(ATCC 2923) was the most sensitive with MIC value of 1.95 mg/mL toextracts 2 and 3 followed by standard strain ofE. coli(ATCC 25922) and clinical isolate ofS. aureus(1.95 mg/mL) to extract 3. The most resistant bacteria were clinical isolate ofE. coli(62.5 mg/mL) at extract 2 and 3 followed by clinical isolate ofE. coli(250.00 mg/mL) at extract 1 (Table 3).

Table 3 The MIC values of R. communis leaf extract fractions against test organisms using two fold dilution methods.
3.3. TheMBCvalues of Z. scabra and R. communis extracts against test organisms
MBC value of fraction 3 from leaf extract ofZ. scabrawas ranged from 1.95 mg/mL against clinical and standard strains ofS. aureusto 62.5 mg/mL against clinical isolate ofE. coli. The second important extract inZ. scabraleaf was extract 2 ranged from 3.91 mg/mL against standard strainS. aureusto 62.5 mg/mL against clinical isolate ofE. colifollowed by extract 1 that ranged from 7.81 mg/mL against standard strainS. aureusto 500.00 mg/mL against clinical isolate ofE. coli(Table 4).
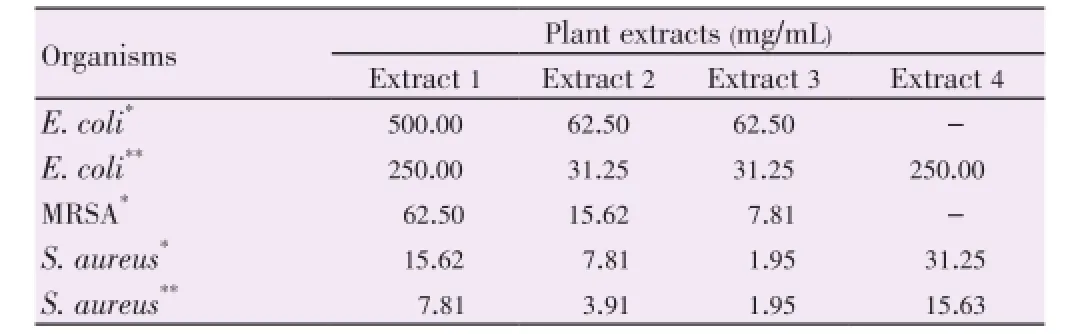
Table 4 The MBC of Z. scabra leaf extract fractions against test organisms.
R. communisleaf extract fraction showed greater effects in inhibiting bacterial growth in this study, with MBC values ranged from 1.91 mg/mL of extract 3 against standard and clinical isolates ofS. aureusto 250 mg/mL of extract 1 against clinical isolate strains ofE. coli. Standard strain ofE. coliwas the most sensitive strains next toS. aureus(3.91 mg/mL from extract 3) (Table 5).
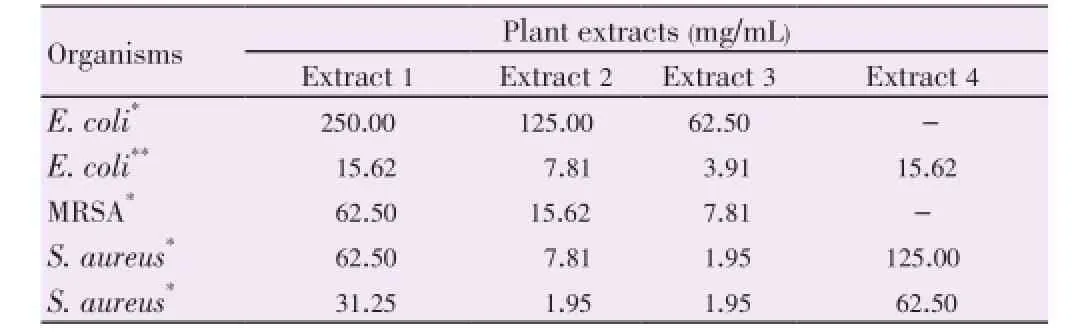
Table 5 The MBC of R. communis leaf extract fraction against test organisms.
4. Discussion
In this study, leaf extracts ofZ. scabrashowed maximum zone of inhibition (14.00±2.00) mm against standard strain ofS. aureus(ATCC 2923) followed by (9.95±1.79) mm against clinical isolate ofS. aureus. The least diameter of zone of inhibition recorded was (3.50±0.97) mm against clinical isolate ofE. coli. Similarly, other study conducted by Anandet al.indicated that ethanol, methanol, ethyl acetate and aqueous extracts of the shoot ofZ. scabrafrom the standard bacterial pathogen ofS. aureusshowed maximum zone of inhibition (50.00±0.11) mm[20], while in a study conducted by Bruck[21], methanol leaves extracts ofZ. scabrahad no effect on the tested microbes except at higher concentration low activity against standard strain ofS. aureus(6 mm). These variations in zone of inhibitions may be due to the difference in concentration of active pricnciple; type of solvent used for extraction and type of bacterial strains tested[20].
Crude leaves extracts ofR. communisdemonstrated maximum zone of inhibition against standard strains ofS. aureus(ATCC 2923) was (15.90±2.13) mm, followed byE. coli(ATCC 25922) [(15.20±1.53) mm], clinical isolates ofS. aureus[(9.90±1.98) mm] and MRSA [(9.50±2.12) mm]. The least inhibition zone was recorded from clinical isolate ofE. coli(7.75±0.91) mm. A similar study conducted by Kensa and Yasmin showed that the most sensitive strain wasE. coli(11.3 mm)[22]. While other reports by Chukwukaet al. showed thatR. communisleaf extract did not inhibitE. coli[23]. The difference might be related to many factors such as age of the plant, plant part used, solvent concentration, tested strains used and extraction procedures followed[21].
The results of the present study showed that standard bacterial strain ofS. aureuswas the most susceptible bacterium, which may be attributed to the absence of outer membrane of the organism that makes it more accessible to permeation by active principles of the leaves extracts ofZ. scabraandR. communis[18]. Promising inhibition zone was also obtained against MRSA which shows that herbal preparations are important alternatives for drug resistant bacteria pathogens. Crude leaves extracts ofZ. scabraandR. communishave shown an interesting profile of antibacterial activity against standard bacterial strains more than clinical isolates and Gram-positive strains are more sensitive to the extracts. Therefore, further study is needed to isolate the pure compounds from these crude extracts.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially funded by University of Gondar, Faculty of Natural and Computational Science, School of Graduate Studies, and Department of Biology. The financial assistance received from University of Gondar under teaching and learning program (UoG/Budget code: 6417) was greatly acknowledged.
Comments
Background
In developing countries, about 80% of the population uses medicinal plants as traditional medicine to treat infectiousdiseases.Z. scabraandR. communisare being used for treatment of pathogenic organisms in the traditional health care system. This study aimed to evaluate antibacterial activity of crude extract fromZ. scabraandR. communisagainst clinical and standard strains.
Research frontiers
In this study, leaf extracts ofZ. scabraandR. communisshowed maximum zone of inhibition against standard strain ofS. aureus. Promising inhibition zone were also obtained against MRSA which shows that medicinal plant extracts are important alternatives for drug resistant bacterial pathogens. Crude leaves extracts ofZ. scabraandR. communishave shown an interesting profile of antibacterial activity against standard bacterial strains more than clinical isolates. Grampositive were more sensitive than Gram-negative strains.
Related reports
The antimicrobial effect of plant extracts against test organisms were depend on different solvents used. Similar study reported by Anandet al., 2012 indicated that ethanol, methanol, ethyl acetate and aqueous extracts of the shoot ofZ. scabrashowed maximum zone of inhibition for standard strains ofS. aureus.
Innovations and breakthroughs
Promising inhibition zone were obtained againstS. aureusand MRSA which shows that medicinal plant extracts fromZ. scabraandR. communisare important alternatives for drug resistant bacterial pathogens.
Applications
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative therapies and the therapeutic use of natural products, especially those derived from plants.Z. scabraandR. communishave antimicrobial components, therefore looking for its formulation and components of the extract may lead to the production of important antibiotic alternative for the treatment of infectious diseases.
Peer review
This paper is very interesting and has wide application in biotechnology where many researchers can follow the screening and extraction of natural products for the discovery of noble compounds. Therefore, this study is helpful to initiate other researchers in the area of interest.
[1] Ghosh L, Gayen JR, Sinha S, Pal S, Pal M, Saha BP. Antibacterial efficacy of Rumex nepalensis Spreng. roots. Phytother Res 2003; 17(5): 558-559.
[2] Vaghasiya Y, Chanda S. Screening of some traditionally used Indian plants for antibacterial activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Herb Med Toxicol 2009; 3(2): 161-164.
[3] Amit L, Vikas G, Vaibhav T, Vikash K, Siddhartha G. Phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Bersama englerina Guerke - an overview. Int Res J Pharm 2010; 1: 89-94.
[4] Kassaye KD, Amberbir A, Getachew B, Mussem Y. A historical overview of traditional medicine practices and policy in Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev 2006; 20: 127-134.
[5] Aschwanden C. Herbs for health, but how safe are they? Bull World Health Organ 2001; 79: 691-692.
[6] Edwards S, Tadesse M, Hedberg I. Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Addis Ababa: The National Herbarium; 1995, p. 27.
[7] Teklehaymanot T, Giday M. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by people in Zegie Peninsula, Northwestern Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 2007; 3: 12-15.
[8] Yirga G, Teferi T, Gidey M, Zerabruk S. An ethno veterinary survey of medicinal plants used to treat livestock diseases in Seharti-Samre district, Northern Ethiopia. Afr J Plant Sci 2012; 6(3): 113-119.
[9] Yineger H, Yewhalaw D, Teketay D. Ethnomedicinal plant knowledge and practice of the Oromo ethnic group in Southwestern Ethiopia. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 2008; 4: 11.
[10] Giday M, Asfaw Z, Woldu, Z. Ethnomedicinal study of plants used by Sheko ethnic group of Ethiopia. J Ethnopharmacol 2010; 132: 75-85.
[11] Ethiopian Mapping Authority. National Atlas of Ethiopia. 1st ed. Addis Abeba: Ethiopian Mapping Authority; 1988.
[12] Jeet K, Tomar S, Thakur N. Antipyretic activity of whole aerial part from Argyreia nervosa. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2012; 4: 1-2.
[13] Lalitha MK. Manual on antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 2004. [Online] Available from: http://www.google.com.hk/ url?sa=t&rct=j&q=Manual%20on%20Antimicrobial%20 Susceptibility%20Testing&source=web&cd=1&ved=0CCoQFjA A&url=http%3a%2f%2fwww%2eijmm%2eorg%2fdocuments%2fA ntimicrobial%2edoc&ei=V3wZU8mXJIKOkwWzrIHADw&usg= AFQjCNEzTSnwiSIbkuc6SWnCiiupflK0hw&bvm=bv.62578216,d. aGc&cad=rjt [Accessed on 20th January, 2014]
[14] Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc 2008; 3(2): 163-175.
[15] British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Birmingham: BSAC; 2010. [Online] Available from: http://bsac.org.uk/wp-content/ uploads/2012/02/Version_9.1_March_2010_final-v2.pdf [Accessed on 15th January, 2014]
[16] Sheeba E. Antibacterial activity of Solanum surattense Burm. F. J Sci Eng Tech 2010; 6(1): 1-4.
[17] Uddin N, Rahman A, Ahmed NU, Rana S, Akter R, Masudul AM, Chowdhury A. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and antimicrobial properties of Eclipta alba ethanol extract. Int J Biol Med Res 2010; 1(4): 341-346.
[18] Paulson DS. Biostatistics and microbiology: a survival manual Bozeman: Bioscience Laboratories Inc.; 2008, p. 222.
[19] Anand SP, Doss A, Jeyachandran R. Antagonistic microbial screening of shoot extracts of Zehneria scabra (L.F.) Sonder. Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm 2012; 3(1): 109-111.
[20] Bruck M. Studies on extracts of some medicinal plants traditionally used for dermatological disorders in Ethiopia [dissertation]. Addis Ababa: Addis Ababa University; 2004.
[21] Kensa VM, Yasmin SS. Phytochemical screening and antibacterial activity on Ricinus communis L. Plant Sci Feed 2011; 1(9): 167-173.
[22] Chukwuka KS, Ikheloa JO, Okonko IO, Moody JO, Mankinde TA. The antimicrobial activities of some medicinal plants on Escherichia coli as an agent of diarrhea in livestock. Adv Appl Sci Res 2011; 2(4): 37-48.
10.12980/APJTB.4.201414B16
*Corresponding author: Feleke Moges, Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Post Box 196, University of Gondar, Ethiopia.
Tel: +251918778160
E-mail: Mogesfeleke@gmail.com
Foundation Project: Supported by University of Gondar under teaching and learning program (UoG/Budget code: 6417).
Article history:
Received 9 Jan 2014
Received in revised form 12 Feb, 2nd revised form 19 Feb, 3rd revised form 28 Feb 2014
Accepted 5 Jun 2014
Available online 16 Jul 2014
Methods:The crude powdered leaves of Z. scabra and R. communis were extracted successively by organic solvents in increasing polarity [benzene, chloroform:acetone (1:1), 70% alcohol and distilled water]. The antibacterial susceptibility of the crude leaves extracts of were tested against standard strains of E. coli (ATCC 25922) and S. aureus (ATCC 2923) and clinical isolates of E. coli, S. aureus and methicillin resistance S. aureus using agar well diffusion method.
Results:In Z. scabra and R. communis leaf extracts, the most sensitive standard strain was S. aureus with an inhibition zone of (14.00±1.20) mm and (15.90±2.13) mm, respectively. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of Z. scabra extracts against test organisms ranged from 1.95 mg/mL for extract 3 in clinical and standard strains of S. aureus to 250 mg/mL for extract 1 and 4 in clinical and standard strains of E. coli. The MIC values of R. communis extracts against test organisms ranged from 1.95 mg/mL for extract 2 and 3 standard strains of S. aureus to 250 mg/mL for extract 1 in clinical isolate of E. coli. Most of the minimum bactericidal concentration and MIC values of plant extracts were almost similar particularly in R. communis, or minimum bactericidal concentration equal to one dilution factor less than MIC value of the extracts mainly in Z. scabra.Conclusions:The potency of plant extracts against test organisms were depend on different organic solvents used. Clinical isolate of bacterial pathogens showed less zones of diameter compared to the standard strains. Gram-positive had wide inhibition zones than Gram-negative bacteria. Further studies should be carried out to isolate the pure compounds and standardization of the methods of plant extracts for an in vitro testing.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年10期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年10期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Disseminated toxocariasis in an immunocompetent host
- Human ophthalmomyiasis externa caused by the sheep botfly Oestrus ovis: a case report from Karachi, Pakistan
- Calcinosis circumscripta in a captive African cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus)
- Production and purification of a bioactive substance against multi-drug resistant human pathogens from the marine-sponge-derived Salinispora sp.
- In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Korean blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) extracts
- Efficacy of seed extracts of Annona squamosa and Annona muricata (Annonaceae) for the control of Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus (Culicidae)
