Hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor C to promote lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in breast cancer patients
Xiojin Ni, Yingchun Zho , Jingjing M, Tinsong Xi, Xion Liu, Qing Ding,Xioming Zh, Shui Wng,
aDepartment of Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210029, China;bDepartment of Breast Surgery, The Second People's Hospital Affiliated with Wannan Medical College,Wuhu, Anhui 241000, China;cState Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Department of Breast Surgery, Nanjing Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210029, China.Received 22 February 2013, Revised 15 April 2013, Accepted 05 June 2013, Epub 25 September 2013
INTRODUCTION
Breast carcinoma is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed among women. In breast cancer,metastasis primarily occurs through the lymphatic system, and the extent of lymph node involvement is a key prognostic factor for the disease. To facilitate the design and evaluation of new therapeutic strategies, a better understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying the systemic metastasis of breast cancer is needed. Lymphatic metastasis was previously reported to occur through pre-existing lymphatic vessels[1]. However, recent studies have suggested that lymphangiogenesis, the formation of new lymphatic vessels induced by tumors, is directly correlated with the extent of lymph node metastasis.
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C)is a major lymphangiogenic and angiogenic factor, which is commonly expressed in malignant cancers[2-4]. It promotes lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis,and lymph node metastasis in tumors by activating its specific receptor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3). Neutralizing VEGF-C or blocking VEGFR-3 signaling was reported to suppress the development of new lymphatic vessels, lymphatic hyperplasia and tumor metastasis in experimental cancer models[5].
Hypoxic conditions during tumorigenesis induce the expression of hypoxia-induced factor-1 (HIF-1),the master regulator of cellular oxygen homeostasis[6].HIF-1 is a heterodimeric transcription factor composed of HIF-1α and HIF-1β subunits; HIF-1α is an oxygen-regulated subunit and determines the level of HIF-1 activity. HIF-1α overexpression has been studied in several cancers, including bladder, breast,lung, esophageal, colorectal, ovarian, pancreatic, kidney, and prostate cancer[7-9]. It targets the transcription of over 60 genes involved in many aspects of tumor biology, including angiogenesis, cell invasion, cell apoptosis and proliferation, chemoradio-resistance and glucose metabolism. The transcriptional activity of a broad spectrum of genes, including the gene for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), is altered under hypoxic conditions by HIF-1α.
Only one previous study has evaluated HIF-1α in lymphangiogenesis of breast carcinoma performed on an Australian population in 2006. However, the role of HIF-1α in lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis and the relationship between the expressions of VEGF-C in breast carcinoma remain unclear and need further studies. In the present study, the expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF-C were found to be correlated with the levels of lymphatic vessel density (LVD)and microvessel density (MVD)by using immunohistochemistry. In addition, their correlations with clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes in Chinese patients with breast cancer were also analyzed.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patients and acquisition of tissue specimens
Seventy-five patients with histologically confirmed breast carcinoma who underwent radical operations at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University between January 2005 and October 2006 were included in the present study. Paracancerous normal tissue samples from 20 other patients were performed as controls. Patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy were excluded. Tumor, node,metastasis (TNM)staging was carried out according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)classification, and histological grading was performed according to the World Health Organization (WHO)criteria. Paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed surgical specimens were prepared and collected for immunohistochemical staining.
Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded tissues were evaluated by immunohistochemical analysis. A total of 38 samples of stage I/II patients and 37 samples of stage III patients were analyzed. Endogenous peroxidase activity was inhibited by immersing the slides in 0.3%hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 30 minutes. For pretreatment, microwave-based antigen retrieval was performed in 10 mmol/L citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The following primary antibodies were used, including a monoclonal antibody raised against HIF-1α (1:200;Abcam, Cambridge, UK), a polyclonal antibody raised against VEGF-C (1:400, R&D systems, Minneapolis,MN, USA), a monoclonal antibody raised against D2-40 (1:100, R&D System Europe, Lille, France), and a monoclonal antibody against CD31 (1:100, Zymed,Carlsbad, NM, USA). For HIF-1α immunostaining, a catalyzed signal amplification system (Dako, Glostrup,Denmark)was used. Immunoreactions were visualized with diaminobenzidine (DAB kit, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA), and the sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. To determine the specificity of immunostaining, the primary antibody was replaced with mouse normal IgG or Tris-buffered saline. Control slides were invariably negative for immunoreactions. HIF-1α was clearly expressed in the cell nucleus, and positive expressions of VEGF-C proteins showed a yellow or brownish-yellow stain in the cytoplasm of carcinoma cells.
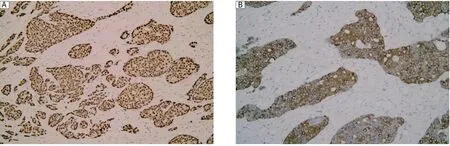
Fig. 1 HIF-1α and VEGF-C expression in breast carcinoma. A: High HIF-1α immunoreactivity in the nuclei of cancer cells (magnification×200). B: VEGF-C was expressed in the cytoplasm of breast carcinoma cells (magnification×200).
LVD was detected by immunostaining for D2-40 according to the criteria described by Masakau et al.[10].First, areas with highly D2-40-positive vessels (hot spots)in peritumoral and intratumoral areas were identified by scanning the sections at low magnification(×100). Then, the number of D2-40 positive vessels was counted in 5 high-magnification fields (×400)for each case. MVD was assessed at the site of the highest number of capillaries and small venules, and highly vascular areas were identified by scanning tumor sections at low power (×40). After the 5 areas with the highest degree of angiogenesis (hot spots)were identified, the microvessels were counted at ×200, and the mean values of the 5 fields were calculated[11].
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS 15.0 software (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). The correlations among the expressions of HIF-1, VEGF-C, the levels of LVD, and clinicopathologic characteristics were calculated by using the Student's t-test, the chisquare correlation test, and the Spearman's coefficient of correlation. The Kaplan-Meier method was performed to estimate survival time, and the log-rank test was performed to analyze survival differences.A multivariable test was performed to determine the factor correlated with survival length by Cox regression analysis. The statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05.
RESULTS
HIF-1α, VEGF-C, D2-40 and CD31 in breast carcinoma
Seventy five patients with breast carcinoma were included in the current study and 52 (69.3%)of them showed high HIF-1α expression, and 48 (64.0%)of them showed high VEGF-C expression (Fig. 1). However, normal tissue showed no immunoreactivity for HIF-1α or VEGF-C. Immunoreactive D2-40 proteins were found in the cytoplasm and cellular membranes of lymphatic endothelial cells. Generally, D2-40-positive cells were frequently distributed in peritumoral tissue. The lymphatic vessels were thin-walled and irregularly shaped and lacked erythrocytes. CD31 immunoreactivity in the blood vessel endothelial cells was observed in all the breast carcinoma tissue sections (Fig. 2).
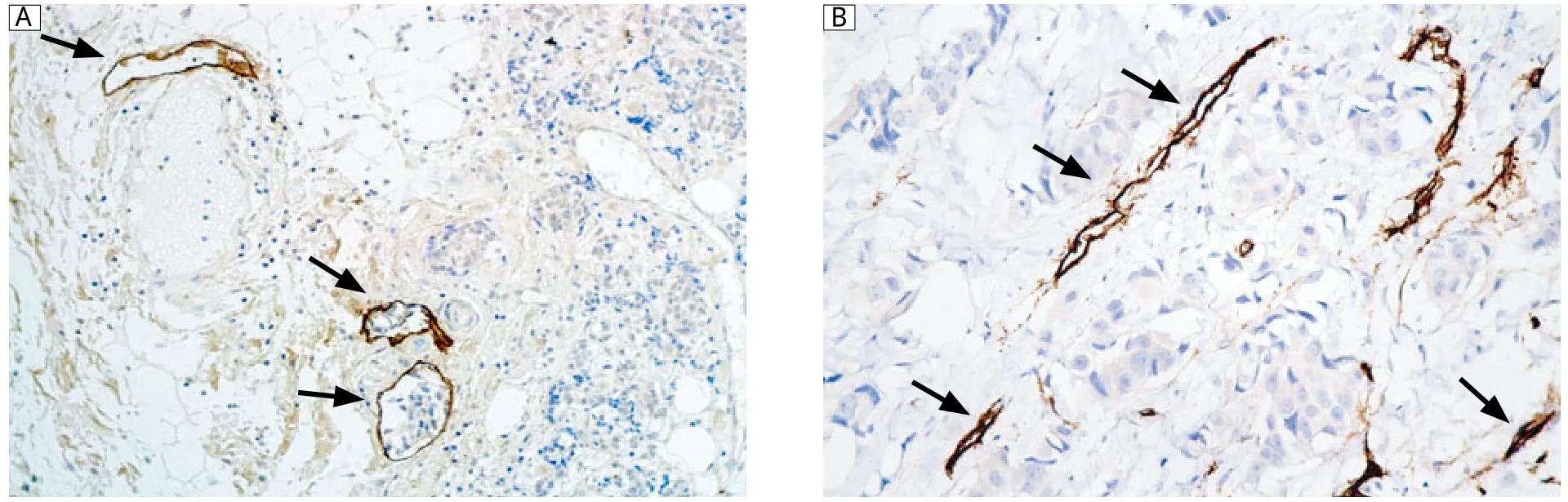
Fig. 2 Immunohistochemical staining of D2-40 and CD31. A: Immunoreactivity of D2-40 proteins was observed in the cytoplasm and cellular membrane of lymphatic endothelial cells (magnification×200). D2-40 expression was restricted to thin-walled lymphatic vessels containing no red blood cells (arrows). D2-40-positive cells were largely distributed in peritumoral tissue (hot spot). B: Representative sections showing CD31+staining in blood microvessels/endothelial cells (magnification×400).
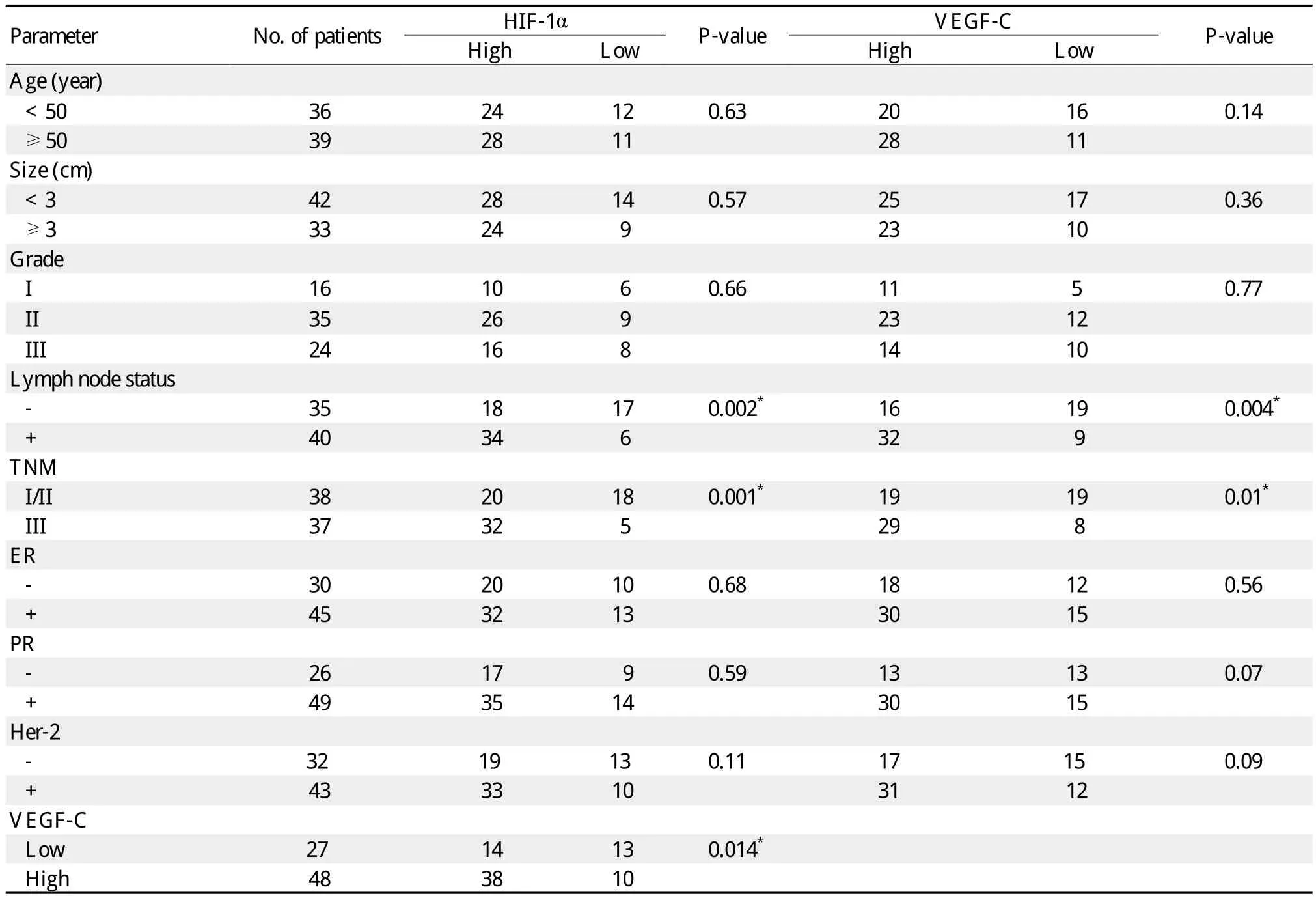
Table 1 Relationship between HIF-1α and VEGF-C expression and clinicopathological characteristics of patients with breast cancer
Relationship among HIF-1α, VEGF-C and clinicopathologic characteristics
The correlations between HIF-1α and clinicopathologic factors, VEGF-C and clinicopathologic factors in breast carcinoma are shown in Table 1. There was no significant correlation between HIF-1α expression and age, grade, size, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR)or Her-2 (P > 0.05, chi-square test).Similarly, VEGF-C expression was not correlated with the above-mentioned clinicopathological characteristics (P > 0.05, chi-square test). However, high level expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF-C were correlated with the presence of lymph node metastasis (P = 0.002 and P = 0.004, respectively)and TNM stage (P = 0.001 and P = 0.01, respectively). A significant association between high level expressions of HIF-1α and VEGFC was observed (r = 0.273, P = 0.014).
Relationship among HIF-1α, VEGF-C, LVD and MVD
High levels of HIF-1α and VEGF-C expression were found to be significantly associated with higher LVD, especially in the peritumoral region (P = 0.003 and P = 0.017, respectively)(Fig. 3A, 3C). The MVD assessed by using CD31-positive endothelial cells was significantly higher in the high VEGF-C/HIF-1α group than in the low VEGF-C/HIF-1α group (P =0.033 and P = 0.037, respectively)(Fig. 3B, 3D).
Survival analysis
By the end of the 60-month follow-up period, 36 of the 75 patients had died. The overall 5-year survival (OS)for all patients was 52.0%. Analysis of the impact of HIF-1α status is shown in Fig. 4A. Patients with high levels of HIF-1α expression had poorer prognoses than patients with low levels of HIF-1α expression (P = 0.045, log-rank test). Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival stratified by VEGF-C status are shown in Fig. 4B. The survival time of patients with higher level of VEGF-C expression was shorter(P = 0.043, log-rank test). In Cox regression for OS including lymph node metastasis, histological differentiation, TNM staging, HIF-1α expression, VEGF-C expression, LVD and MVD, only TNM stage (P =0.018, RR = 1.891, 95% confidence interval, 1.358-4.781), HIF-1α expression (P = 0.037, RR = 2.249,95% confidence interval, 1.382-6.452)and peritumoral LVD (P = 0.023, RR = 3.292, 95% confidence interval, 1.889-11.546)remained independent prognostic factors.
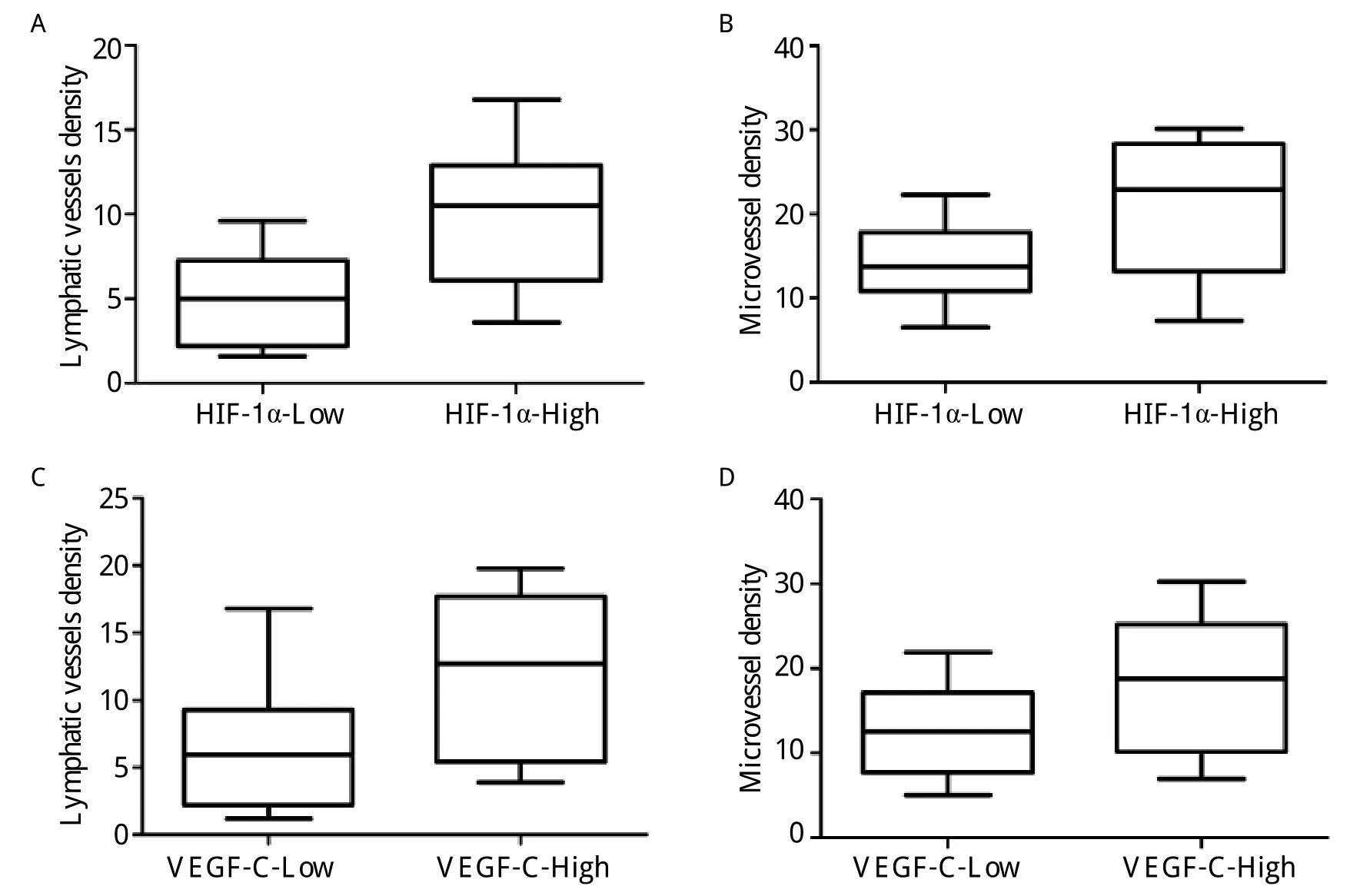
Fig. 3 Box-blot showing statistically significant association between lymphatic vessel density (LVD), microvessel density(MVD), and HIF-1α-expression. A, B, C, and D: P = 0.003, P = 0.033, P = 0.017, P = 0.037, respectively, Mann-Whitney test.
DISCUSSION
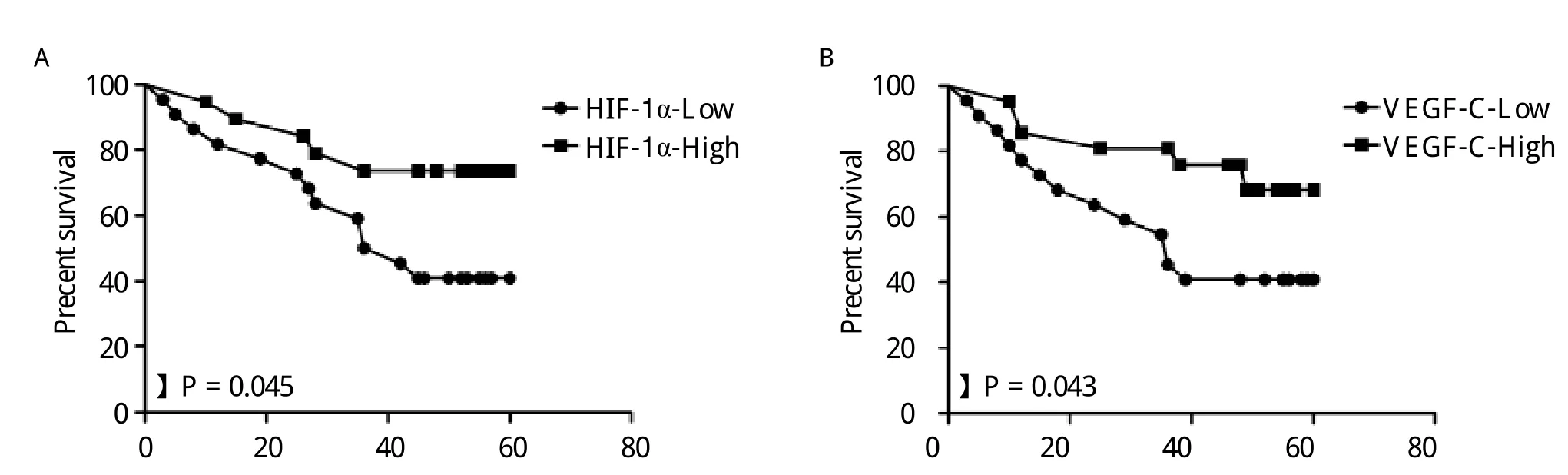
Fig. 4 Kaplan-Meier overall survival curves for 75 patients with breast carcinoma. A: Patients with high HIF-1α expression had a significantly worse overall survival (OS)than patients with low HIF-1α expression (P = 0.045). B: Patients with high levels of VEGF-C expression had a significantly worse OS than those with low levels of VEGF-C expression (P = 0.043).
Only malignant breast carcinomas showed HIF-1α expression in the nuclei, suggesting that nuclear expression of HIF-1α takes place in mammary carcinogenesis. As a result of the adaptation of tumor cells to hypoxia, HIF-1α is overexpressed in a variety of human malignancies, including cancers involving the lung, prostate, breast, stomach, pancreas and skin[12].Hypoxia is a common phenomenon in various types of malignant tumors, and contributes to the progression of cancer to a more aggressive phenotype[13]. HIF-1α overexpression has been reported to be closely cor-related with highly aggressive disease, resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and poor prognosis in some types of cancer, such as oligodendroglioma,ovarian and oropharyngeal cancer[7-9]. In the present study, HIF-1α expression was correlated with LVD,MVD, the presence of lymph node metastases and advanced TNM stages in breast cancer patients. As reported by Schoppmann et al., there was significant association between HIF-1α expression and the amount of peritumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel invasion in lymph node-positive invasive breast cancer[14]. In this way, HIF-1α may be a key regulator of angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.
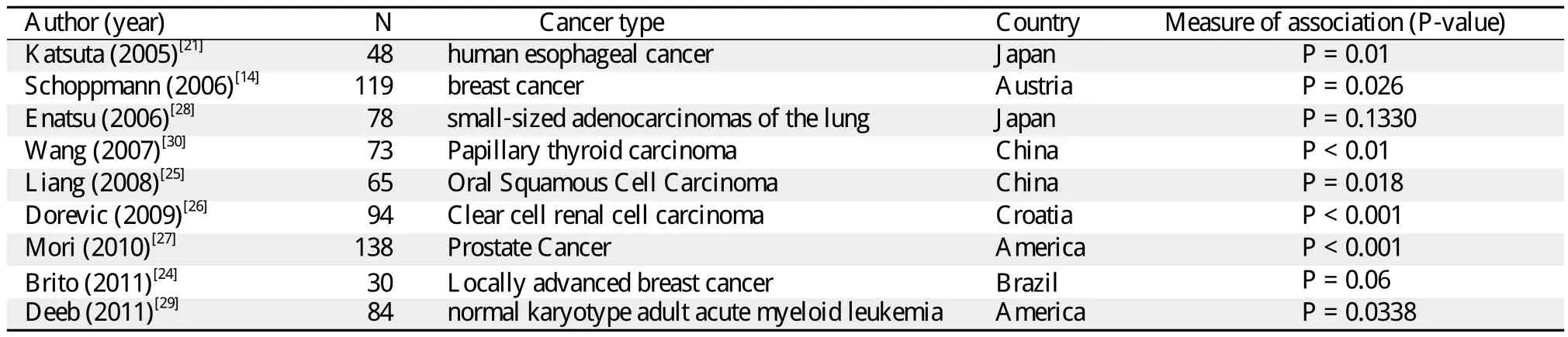
Table 2 Studies of relationship between HIF-1α and VEGF-C expression
VEGF-C, a member of the VEGF family of angiogenic factors, activates VEGF receptor-3 (VEGFR-3),which is expressed on the lymphatic endothelium.Studies have recently shown that VEGF-C can promote tumor-associated lymphatic vessel growth in xenotransplantation and transgenic mouse models of cancer, resulting in metastasis of tumors to sentinel lymph nodes[15]. It has also been expressed at high levels in certain cancers, including gastric carcinoma,and to have a negative influence on prognosis and a positive correlation with lymph node metastasis[16].VEGF-C, a member of the VEGF family, also induces angiogenesis by activating VEGFR-2[17]. Sedivy et al.observed that VEGF-C overexpression seemed to induce the formation of new lymphatics and blood vessels around the primary cancer[18]. The results of the present study showed that primary breast carcinoma tissue elevated the expression of VEGF-C. Significant association was observed between the expression of VEGF-C and the presence of lymph node metastases and advanced TNM stage. There was also a positive correlation between the expression of VEGF-C and peritumoral LVD. VEGF-C derived from the carcinoma may play an important role in lymphangiogenesis,increased aggression, and poor prognosis.
In the current study, HIF-1α expression was positively correlated with VEGF-C expression, and there was a positive correlation between the overexpression of both genes with LVD and MVD. In contrast to the effect of HIF-1α on angiogenesis, the effect on lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis remains poorly understood. HIF-1α acts as a transcription factor. A recent study showed that the transcriptional activity of a broad spectrum of genes, including the gene for VEGF, is altered by HIF-1 under hypoxic conditions[19]. Stabilized HIF-1α protein is transported into the nucleus, wherein it heterodimerizes with HIF-1 and binds to DNA at the hypoxia response elements(HREs), thereby activating the VEGF gene[20]. The VEGF family consists of VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGFC, VEGF-D and VEGF-F. Katsuta et al. examined the expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF-C in 5 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)cell lines[21].The findings suggested that HIF-1α may play a role in lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis through the induction of VEGF-C. Okada et al. suggested that VEGF-C was also up-regulated by HIF-1α in human breast IDC cells[22]. These studies suggested the probable existence of a novel lymphangiogenic pathway. In this pathway, the overexpression of HIF-1α stimulates VEGF-C up-regulation and induces lymphangiogenesis, by which the tumor cells spread into the lymphatic system. In this way, HIF-1α may act as a lymphangiogenic factor through its interactions with VEGF-C. The results of the present study also indicated that HIF-1α may upregulate the expression of VEGF-C to stimulate angiogenesis in breast cancer. However, VEGF-C is 4 to 5 times less potent than VEGF, as determined by the vascular permeability assay[23]. For this reason, the activity of tumor angiogenesis stimulated by HIF-1α in the VEGF-C/VEGFR-2 pathway may be weaker than that stimulated in the VEGF-3 pathway in breast cancer.
These results are a small but developing part of literature on the association between HIF-1α and VEGFC expressions. Nine other studies have examined this association[14,21,24-30](Table 2). Only the study of Enatsu et al. reported that the strong expression of HIF-1α was associated with VEGF-A expression but not with VEGF-C (P = 0.133)in small-sized adeno-carcinomas of the lung[24]. Mori et al.[28]showed that HIF-1α may play a role in the regulation of VEGF-C and tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in prostate cancer (P < 0.001). Dorevic et al. reported that cytoplasmic HIF-1α expression (cHIF-1α)was positively correlated with diffuse staining of VEGF-C (P <0.001)in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[27]. Liang et al.showed that HIF-1α overexpression was significantly correlated with VEGF-C overexpression (P = 0.018)in oral squamous cell carcinoma[26]. In the study of Brito et al., HIF-1α expression and VEGF-C expression were marginally associated with each other (P = 0.06)in breast cancer[29]. Similar results were also found in the studies on lung cancer, leukemia and esophageal cancers. All these findings have suggested that HIF-1α may play a role in lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis through the induction of VEGF-C, which strongly supports our results.
In summary, significant correlations were observed between the expression of HIF-1α and lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis, the expression of VEGF-C and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. The results suggest that HIF-1α may act as a regulator of VEGFC in tumor-associated angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer. However, the present study has some limitations, such as the small number of cases. Further studies on larger populations should be undertaken to confirm the results and to provide evidence for the potential role of HIF-1α in lymphangiogenesis. It may be useful as a prognostic marker and as a novel target of anti-tumor drugs in the treatment of human breast carcinomas.
[1]Padera TP, Kadambi A, di Tomaso E, Carreira CM,Brown EB, Boucher Y, et al. Lymphatic metastasis in the absence of functional intratumor lymphatics. Science 2002; 296: 1883-6.
[2]Scavelli C, Weber E, Agliano M, Cirulli T, Nico B, Vacca A, et al. Lymphatics at the crossroads of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. J Anat 2004; 204: 433-49.
[3]Takahashi M, Yoshimoto T, Kubo H. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis. Int J Hematol 2004; 80:29-34.
[4]Ran S, Volk L, Hall K, Flister MJ. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer. Pathophysiology 2010; 17: 229-51.
[5]Lin J, Lalani AS, Harding TC, Gonzalez M, Wu WW,Luan B, et al. Inhibition of lymphogenous metastasis using adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer of a soluble VEGFR-3 decoy receptor. Cancer Res 2005; 65:6901-9.
[6]Semenza GL. HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 2000; 88: 1474-80.
[7]Bos R, Zhong H, Hanrahan CF, Mommers EC, Semenza GL, Pinedo HM, et al. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha during breast carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93: 309-14.
[8]Kuwai T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Onogawa S, Matsutani N, Kaio E, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is associated with tumor vascularization in human colorectal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2003; 105: 176-81.
[9]Theodoropoulos VE, Lazaris A, Sofras F, Gerzelis I,Tsoukala V, Ghikonti I, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression correlates with angiogenesis and unfavorable prognosis in bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2004; 46:200-8.
[10]Ohno M, Nakamura T, Kunimoto Y, Nishimura K,Chung-Kang C, Kuroda Y. Lymphagenesis correlates with expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 2003; 10: 939-43.
[11]Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1-8.
[12]Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton D A, Zagzag D, et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5830-5.
[13]Semenza GL. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 2010;29: 625-34.
[14]Schoppmann SF, Fenzl A, Schindl M, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Nagy K, Gnant M, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006; 99: 135-41.
[15]Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Janes L,Velasco P, et al. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 2001; 7: 192-8.
[16]Shida A, Fujioka S, Kobayashi K, Ishibashi Y, Nimura H,Mitsumori N, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and -D in gastric carcinoma.Int J Clin Oncol 2006; 11: 38-43.
[17]Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E, et al. A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3)and KDR (VEGFR-2)receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 1996; 15: 290-8.
[18]Sedivy R, Beck-Mannagetta J, Haverkampf C, Battistutti W, Honigschnabl S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C correlates with the lymphatic microvessel density and the nodal status in oral squamous cell cancer. J Oral Pathol Med 2003; 32: 455-60.
[19]Semenza GL. Hypoxia, clonal selection, and the role of HIF-1 in tumor progression. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2000; 35: 71-103.
[20]Sivridis E, Giatromanolaki A, Gatter K C, Harris AL and Koukourakis MI. Association of hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha with activated angiogenic pathways and prognosis in patients with endometrial carcinoma. Cancer 2002; 95: 1055-63.
[21]Katsuta M, Miyashita M, Makino H, Nomura T, Shinji S, Yamashita K, et al. Correlation of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha with lymphatic metastasis via vascular endothelial growth factor-C in human esophageal cancer.Exp Mol Pathol 2005; 78: 123-30.
[22]Okada K, Osaki M, Araki K, Ishiguro K, Ito H, Ohgi S.Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1alpha),VEGF-C and VEGF-D in non-invasive and invasive breast ductal carcinomas. Anticancer Res 2005; 25:3003-9.
[23]Ogawa S, Oku A, Sawano A, Yamaguchi S, Yazaki Y,Shibuya M. A novel type of vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-E (NZ-7 VEGF), preferentially utilizes KDR/Flk-1 receptor and carries a potent mitotic activity without heparin-binding domain. J Biol Chem 1998;273: 31273-82.
[24]Enatsu S, Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Hamasaki M, Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and its prognostic significance in smallsized adenocarcinomas of the lung. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2006; 29: 891-5.
[25]Wang Y, Hua Q. Clinical significance of HIF-1 alpha,VEGF and VEGF-C expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi (in Chinese)2007; 21: 204-6, 8.
[26]Liang X, Yang D, Hu J, Hao X, Gao J, Mao Z. Hypoxia inducible factor-alpha expression correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression and lymphangiogenesis/angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2008; 28: 1659-66.
[27]Dorevic G, Matusan-Ilijas K, Babarovic E, Hadzisejdic I,Grahovac M, Grahovac B, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor A and C indicating worse prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2009; 28: 40.
[28]Mori R, Dorff TB, Xiong S, Tarabolous CJ, Ye W, Groshen S, et al. The relationship between proangiogenic gene expression levels in prostate cancer and their prognostic value for clinical outcomes. Prostate 2010; 70:1692-700.
[29]Brito LG, Schiavon VF, Andrade JM, Tiezzi DG, Peria FM and Marana HR. Expression of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor-C in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Clinics (Sao Paulo)2011; 66: 1313-20.
[30]Deeb G, Vaughan MM, McInnis I, Ford L A, Sait S N,Starostik P, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein expression is associated with poor survival in normal karyotype adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 2011; 35: 579-84.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2013年6期
THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2013年6期
- THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH的其它文章
- Multimodality image fusion for diagnosing coronary artery disease
- The miR-183~96~182 cluster promotes tumorigenesis in a mouse model of medulloblastoma
- Human blood plasma-based electronic integrated circuit amplifier configuration
- Pulmonary cystic disease associated with integumentary and renal manifestations
- Volume conduction energy transfer for implantable devices
- Individual differences in transcranial electrical stimulation current density
