Hipbone Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis and Clinical Study after the Resection of Ischiopubic Tumors△
Ya-qi He *,Xue-lin Zhang ,Bing-hang Tang ,and Ang Yang
1CT Room,Zhongshan Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University (People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City),Zhongshan,Guangdong 528403,China
2Radiology Imaging Center,Southern Hospital,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China
PELVIS and its surrounding soft tissues are one of the predilection places of benign and malignant tumors.An early diagnosis of pelvic tumors is difficult because they grow insidiously.The tumor’s encroachment area is often comparatively large once it is detected,which leads to the increase of the operation’s difficulty.1The resection of pelvic tumors and pelvic reconstruction are still a big challenge that the orthopedist faces.Enneking and Dunham2divide the pelvic tumor surgery into four types according to its encroachment area.The pelvic stabilization will be affected in a certain degree regardless of the operation’s type;therefore,the repair and reconstruction of the pelvis are important after the operation.But many arguments often arise from whether the reconstruction is needed or what specific reconstruction methods are selected.After the pelvis type I and II resection,it is normally considered necessary to rebuild the pelvic structure and repair its anatomical continuity because the operation destroys its large area and mainly involves its weight-bearing arch.3Because only the excision of the superior and inferior ramus of the pubis and ischiadic ramus is needed but does not involve in the hip joint in the pelvis type III resection,it is normally considered unnecessary to make any special reconstruction.4,5But some scholars still advocate that the structural bone graft be used to rebuild the superior ramus of the pubis to prevent the destabilization of the homolateral sacroiliac joint in the convalescence.Long-term clinical follow-ups after the resection of ischiopubic tumors show that some convalescent patients are likely to develop such complications as sacrococcygeal region pain,lower lumbar part pain,lower extremity unequal length,pelvic band pain,sacroiliac joint functional disorder,sacroiliitis,pelvic obliquity,compensatory scoliosis,etc.,which enormously affect the patients’ life quality and brings them the distress.6-8The purposes of the study are to build the pre-and postoperative hipbone finite element model,analyze the biomechanical change of the identical part of the hipbone,explain the reason of the occurrence of complications,and guide the clinical pelvic reconstruction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Objects and methods
The experiment objects were two hipbone finite element models∶an intact hipbone model and a hipbone model without the ischiopubic ramus,which simulated Enneking’s type III operation.The detailed construction method of the three-dimensional hipbone finite element models was described elsewhere9and briefly presented here.The intact hipbone finite element model contained 80 958 elements and 124 369 nodes.With reference to Enneking’s type III,the excision regions of the postoperative hipbone finite element model contained the superior ramus of the pubis,inferior ramus of the pubis,ischiadic ramus,pubic symphysis,parts of the pubis,and ischium body nearby the retained acetabular rim.The initial DICOM data,construction flowsheet,parameters,and material properties of the postoperative model were the same as those of the intact model,but what was different in the construction of the postoperative hipbone finite element model was only deleting the pixels of the superior and inferior ramus of the pubis,ischiadic ramus,and pubic symphysis by using the mask and edition method when extracting these tissues.The postoperative hipbone finite element model contained 29 044 elements and 46 018 nodes.
The pre-and postoperative hipbone finite element models were input into AYSYS 10.0 software,respectively.The biomechanical state of unilateral hipbone in a natural bipedal standing position was simulated with the same constraint and loading mode and to pick up and calculate the same numbers of nodes and elements of the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac joints,greater sciatic notches,and acetabular roofs.The distribution and changed features of the displacement,stress,and strain of the corresponding nodes and elements were analyzed in a computer;meanwhile,the entire bearing condition of the hipbone was analyzed.
Constraint and loading mode
Intact hipbone finite element modelTotally,167 nodes on the iliac areas of the sacroiliac joint were picked up uniformly,and a vertical load of 250 N was imposed onto the marked nodes by imitating the load of a weight of 60 kg person standing at his single leg.And 125 nodes on the acetabular roof were picked up uniformly,and the degree of freedom(DOF) of nodes was constrained.In addition,85 nodes on the symphysial surface were picked up uniformly.Because the displacement of the pubic symphysis under the physiological state was tiny and it only played a stabilization part,a little horizontal (-x direction) load,the force of which was requested almost not to cause any displacements of the pubic symphysis,was imposed onto the marked nodes.The force was measured to be 5 N with the cut and try method.
Postoperative hipbone finite element modelMeanwhile,141 nodes on the iliac areas of the sacroiliac joint and 107 nodes on the acetabular roof were respectively picked up.Their constraints and loading modes,directions,and values were the same as those of the intact hipbone finite element model.The difference was that the loss of the pubic symphysis resulted in no load on the symphysial surface after the ischiopubis resection.
Solution and output of the results
The fundamental solutions of all the nodes (nodes’ displacement) and their derivative solutions (stress,strain,and element values) were obtained by setting the analysis type as the static and automatically choosing the solution tool.The output forms of the results included specific values of solutions displayed by listing,distribution regions displayed by color isograms,displacement and deformation displayed by the vector and animation images,etc.
Statistical analysis
The same numbers of nodes of different parts of the pre-and postoperative hipbone finite element models were selected.The population mean of the nodes’ solutions of the same area was compared (SPSS 13.0,ttest of independent sample,P≤0.05),to analyze if there were any significant differences in the displacement,stress,and strain of the same area of the pre-and postoperative hipbone.The statistical data included∶(1) the nodes’ displacement value of the sacroiliac articular facet before and after the operation;(2) the nodes’ stress value of the sacroiliac articular facet before and after it;(3) the nodes’ stress value of the greater sciatic notch before and after it;(4) the nodes’stress value of the acetabular roof before and after it;(5)the nodes’ strain value of the sacroiliac articular facet before and after it;(6) the nodes’ strain value of the greater sciatic notch before and after it;(7) the nodes’strain value of the acetabular roof before and after it.
RESULTS
Displacement results of nodes on the sacroiliac articular facet
The displacement values of nodes on the sacroiliac articular facet before and after the operation refer to Table 1.
The nodes with the maximum displacement value of the preoperative model were located in the iliac crest,being 11.682×10-3mm,while those with the minimum value,located in the acetabular roof,being 1.298×10-3mm.The displacement distribution of the preoperative hipbone model was described by the color isograms (Fig.1A).The maximum area of the displacement covered the anterior superior iliac spine,iliac crest,and medial surface of the posterior superior iliac spine.The feature of displacement distribution of the iliac wing,iliac fossa,and iliac body was that their displacement became increasingly large over the posterior and upper area.The minimum area of the displacement was evenly distributed over the acetabulum,ischial body,pubic body,superior ramus of pubis,pubic symphysis,and part of the inferior ramus of pubis.This area’s displacement was well-distributed.
The maximum and minimum displacement areas of the postoperative model were the same as those of the preoperative one and the feature of the displacement distribution and its value of the postoperative model were similar to those of the preoperative one (Fig.1B).The total displacement values of the nodes of the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac joint were recorded ast=-2.072,P=0.040,which had their statistically significant differrence.

Table 1.Displacement values of the sacroiliac articular facet nodes before and after the operation (n=80,×10-3 mm)
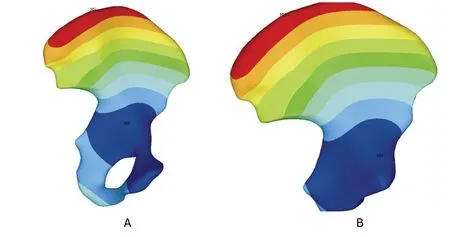
Figure 1.Interior display of displacement vector sum of preoperative (A) and postoperative hipbone nodes (B).
Stress results of nodes of the hipbone model
The distribution of the nodes’ von Mises stress (SEQV) of the preoperative hipbone model refers to Fig.2A.The maximum SEQV area of the preoperative hipbone model concentrated on the greater sciatic notch and acetabular roof.A small local area with comparatively high stress could be seen at the center of the sacroiliac articular facet,while the stress of the other parts of the hipbone model was well-distributed without any unusual stress concentrations.The distribution of the nodes’ SEQV of the postoperative hipbone model refers to Fig.2B.The distribution feature of the postoperative model was similar to that of the preoperative one.
The difference in the SEQV values on the region close to the greater sciatic notch and acetabular roof was increased.Compared with the preoperative one,the region extended to the pubic body and iliac body.The stress at the center and the medial part of the sacroiliac articular facet became higher than that of the preoperative one.The mean stress intensity (SINT) values of the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac articular facet were recorded as (111.418±45.004)×10-3and (96.399±37.884)× 10-3N/mm2,which did not have any statistically significant difference (nodes=50,t=1.805,P=0.074).The mean SEQV values of the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac articular facet were recorded as(100.925±40.678)×10-3and (87.433±34.356)×10-3N/mm2,which did not have any statistically significant difference(nodes=50,t=1.792,P=0.076),either.
The mean SINT [(293.870±175.434)×10-3vs.(303.429±171.586)×10-3N/mm2,nodes=30;t=-0.213,P=0.832]and SEQV values [(282.827±169.570)×10-3vs.(292.388±164.157)×10-3N/mm2,nodes=30;t=-0.222,P=0.825]of the pre-and postoperative greater sciatic notch did not have any statistically significant difference.
The mean SINT [(191.472±107.787)×10-3vs.(341.171±213.033)×10-3N/mm2,nodes=40;t=3.925,P=0.000]and SEQV values [(170.080±95.321)×10-3vs.(305.197±187.608)×10-3N/mm2,nodes=40;t=4.061,P=0.000]of the pre-and postoperative acetabular roof had their statistically significant difference.
Strain results of nodes of the hipbone model
The maximum von Mises total strain (EPTOEQV) area of the preoperative hipbone model concentrated on the greater sciatic notch and acetabular roof.The strain of other parts of the hipbone model was well-distributed.The distribution feature of the EPTOEQV of the postoperative model was similar to that of the preoperative one.The EPTOEQV values of the region close to the greater sciatic notch increased.The central part of the sacroiliac articular facet displayed some enlarging areas scattered by some small EPTOEQV.The strain of the other parts of the hipbone model was well-distributed.The EPTOEQV values of the nodes of the hipbone model before and after the operation refer to Table 2.The mean EPTOEQV values of the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac articular facet (t=-3.763,P=0.000)and acetabular roof (t=-2.864,P=0.005) had their statistically significant difference.

Figure 2.Lateral display of von Mises stress of intact (A) and postoperative hipbone nodes (B).

Table 2.von Mises total strain values of hipbone nodes before and after the operation (×10-5)
SEQV distribution of elements of the hipbone model
The distribution of the SEQV of the preoperative hipbone model elements was similar to that of their nodes.The maximum positive stress area concentrated on the greater sciatic notch and acetabular roof,and the stress of the other parts of the hipbone model was well-distributed.The stress concentration area of the postoperative hipbone model did not display any change,but its range became larger than that of the preoperative one,the feature of which was the same as that of its nodes.
EPTOEQV distribution of elements of the hipbone model
The distribution of the EPTOEQV of the preoperative hipbone model elements was similar to that of their nodes(Fig.3A).The maximum EPTOEQV area concentrated on the greater sciatic notch and acetabular roof,and the strain of the other parts of the hipbone model was well-distributed.The maximum strain area of the postoperative hipbone model did not display any change,but its range became larger than that of the preoperative one,the feature of which was the same as that of its nodes (Fig.3B).
DISCUSSION
Biomechanical change of the sacroiliac joint and its clinical significance
The anterior pelvic ring consists of the pubic symphsis,and the posterior pelvic ring consists of two sacroiliac joints.The acetabula divide the pelvic ring into two arches∶anterior arch and posterior arch.The posterior arch,being the main weight-bearing structure in a bipedal standing position,consists of the upper sacrum,sacroiliac joint,and part of the ilium.The anterior arch consists of the ischium and pubis,the functions of which are to connect two sides of the posterior arches,make the pelvis become a containing ring,strengthen and stabilize the posterior structure.The anterior structure has 40% of the function of stabilizing the pelvic ring and the posterior structure has 60%.10The connection function of the pubic symphsis is removed by the ischiopubic resection,and the biomechanical state of the sacroiliac joint produces a remarkable effect on the posterior pelvic ring structure.This study showed that the total displacement change between the pre-and postoperative sacroiliac joint had its statistically significant difference,which prompted the tendencies of the enlarging motion extent,unsteadiness,and dislocation of the sacroiliac joint after the resection of the pubic symphysis and superior ramus of the pubis.The strain value mainly displays some relative changes of the length,shape,and volume.The strain value of the pre-and postoperative model had its significant difference,and the color isograms also showed the tendency of the enlargement of the strain region,which prompted the obvious change in the overall geometric shape of the sacroiliac joint after the operation.Under the same boundary conditions of the pre-and postoperation,the statistical results can reveal that pubic symphysis has the function of maintaining the stability of the sacroiliac joint.
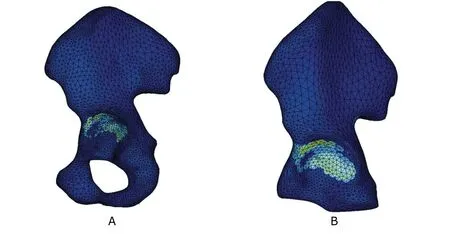
Figure 3.Lateral display of von Mises total strain of the intact (A) and postoperative (B) hipbone elements.
The sacroiliac joint is an amphiarthrosis,11whose osseous stability is mainly determined by the rough and uneven surface and the mutually biting and interlocking shape of the sacroiliac joint.Shadmehret al12discovered that an angular motion existed in young persons’ sacroiliac joints with its oblique sagittal plane being 9 degrees and its oblique cross section being 3 degrees,and the hip joint movement had the obvious relationship with the sacroiliac joint.Kotsenas13described that the angular motion extent of the sacroiliac joint was 1-2 degrees from its supine position to its standing or sitting position,and 2-3 degrees from its standing position to its thighs hyperextension position.If the situation of insufficient or excessive activity occurred to the sacroiliac joint and its inter-motion disturbed the interlocking shape on the articular facet,it could lead to the low back pain and the function disorder in the sacroiliac joint,which was the common cause of the low back pain.14,15When violence or other causes destroyed the stability of the sacroiliac joint and resulted in the unsteadiness or dislocation of the sacroiliac joint,some severe pain could also occur to the low back and pelvis in clinic.Ebraheimet al16discovered that when the iliac bone relative to the sacrum was moving to the posterior and superior direction,the contact area of the sacrum articular facet and the iliac articular facet was minimal,and it was easiest for the dislocation to occur to the sacroiliac joint.Liet al17did the similar research and found that when the iliac bone moved 15 mm towards the posterior and superior direction,the sacroiliac joint lost 71.6% of its contact area and only 28.4% remained to provide its fixation.The loss percentage of the articular contact area was the biggest as moving towards the posterior and superior direction.The pubic symphysis and superior ramus of the pubis played a very important role in the structures of maintaining the sacroiliac joint’s stability.Garciaet al18used three dimensional finite element analysis to evaluate the efficiency of several internal and external fixation methods for pelvic fracture,and found that the most effective fixation method for the vertical and rotatory instability of pelvic fracture was the internal fixation of the pubic symphysis plus two sacroiliac joint screws internal fixation in their study,which could guarantee an adequate stability.With regard to the anterior pelvic ring fixation,Wanget al19considered that if the posterior pelvic ring had the forceful internal fixation,the anterior pelvic ring could not be fixed.If the displacement of the anterior pelvic ring was larger than 10 mm,T-shape nickelclad should preferentially be chosen to be used for the fixation.With reference to the unstable pelvic fracture (pubic symphysis disassociation,superior and inferior ramus fracture of the ischiopubic,sacroiliac joint disassociation and its moving vertically upward),the researchers in the external fixation area usually considered that making only use of the anterior pelvic ring external fixation could not provide an adequate forceful fixation,and adding a posterior pelvic ring internal fixation could make the pelvis remain its normal position and also avoid the unequally long lower extremity,pelvic obliquity,lower lumbar part pain,and other complications.20Considering this research’s results,we can conclude that the main reason of developing such complications as lower lumbar part pain,pelvic band pain,pelvic obliquity,unequal long lower extremity,and abnormal gait in the convalescence after the ischiopubic resection is the sacroiliac joint unsteadiness and the sacroiliac joint strain enlargement caused by the loss of the pubic symphysis connection function.For young patients doing heavy manual jobs and meeting the clinical reconstruction guiding principle,it is suggested that the restoration and reconstruction of the anterior pelvic ring be done in order to reach the purpose of decreasing the incidence rate of complications and raising patients’ life quality.
Biomechanical change of the acetabular roof and its clinical significance
The unilateral hip joint bears 20%-31% pressure of whole body weight in a bipedal standing position.The area of the acetabular roof is 2/5 of the acetabular,and is the biggest weight-bearing part of facies lunata acetabuli.In a normal condition,this area’s cartilage surface bears the biggest compressive stress,and it decreases progressively peripherally.The body’s weight passes here and transfers to the femur head and the femur neck.The biomechanical change of the acetabulum affects not only the intrinsic movement function of the hip joint,but also the homolateral sacroiliac joint.The pubic symphysis,lumbosacral articulation,and hip joint are the sacroiliac joint’s main assistant stable structures.Moedet al21indicated that the acetabular subchondral bone would form a maldistributed osteosclerotic zone when the hip joint’s stress changed,and the osteosclerotic zone located in the lateral part of the acetabular roof was the most harmful for the acetabulum,which was related with the shortening of the lower extremity.This study showed that after the unilateral ischiopubic resection,the stress and strain values of the acetabular roof was significantly increased,and the stress and strain area expanded obviously and already involved the surrounding bone structure of the acetabulum.The bigger the stress of the acetabular roof was,the bigger the contact and friction of the femur head and acetabular roof cartilage surface were,and the more easily the femur head and acetabular roof cartilage would be injured.Meanwhile,this area’s stress concentration could produce articular cartilage degeneration and lead to the secondary arthritis,which was an important reason for huckle pain and protective posture in the recovery stage.On the other hand,the augmentation of the stress and strain of the acetabular roof was also one of the reasons of the homolateral sacroiliac joint dysfunction.The disappearance of the stabilization and connection function of the pubic symphysis and superior ramus of pubis,the stress and strain changes of the acetabular roof,the augmentation of the movement range,and the occurrence of the sacroiliac joint dysfunction were the main reasons of the occurrence of complications during the recovery stage after the unilateral ischiopubic resection.These three factors affected and reacted on one another.
Clinical significance of the reconstruction of the anterior pelvic ring
The pelvic tumor resection and pelvic reconstruction are still a big challenge that the orthopedist faces.Pre-,post-,and intraoperations had many contingent problems,such as bleeding,difficulty of the tumor body ablation,instability,and complication of the reconstruction.The ways of the pelvic reconstruction depended on types of the pelvic resection to a large extent.There was no need to reconstruct it when the pelvic ring was intact.In the condition of benign tumors and main metastatic tumors,the marginal excision style was usually used and the autogenous bone,variant bone,bone cement,and other bone fillers were used to reconstruct the pelvis.This study showed that the main consequence after the unilateral ischiopubic resection was the removal of the connection function of the pubic symphsis,which led to the disappearance of the tensile force that closed the anterior pelvic ring,accordingly,the destabilization of the homolateral sacroiliac joint and the stress augmentation of the acetabular roof.Its biomechanical change was similar to the separation of the symphysis pubis caused by the trauma.After the unilateral ischiopubic resection,the pelvic stability mainly depended on the support of the pelvic cavity bottom muscles and cicatrices,and part of the effect of the pelvic ligaments disappeared because of the loss of their adhesion.So a series of factors,such as patient’s age,occupation,operation’s extent,tumor’s category,etc.,have to be considered to decide whether the bone graft reconstruction is clinically needed in this case.In a biomechanical consideration,the reconstruction of the structural bone graft of the superior ramus of pubis is beneficial for closing the pelvic ring,lightening the pressure of the pelvic weightbearing arch,decreasing the occurrence of complications in the convalescence,and raising the patient’s life quality,which has an important meaning to young persons and manual workers.
This study concluded that the significance of the anterior pelvic ring to stabilize the posterior pelvic ring was bigger than that demonstrated by the previous studies.Its conclusions had some guiding direction significances for the pelvic postoperative repair and reconstruction.Along with the sociometric continuing development,the surgical therapy for the purpose of raising the life quality will be increased continually.The limitations of this study were∶(1)the finite element model ignored the viscoelasticity and anisotropic materials characteristics,which would be a development direction of the finite element modeling in the future;(2) the study ignored the effect of pelvic ligaments and muscles and the entire biomechanical change of the postoperative pelvis,which needed to be further lucubrated.The finite element analysis,as a rationale research,still belongs to a qualitative investigation and has its limitations in the aspect of quantitative investigation,so its development depends on the development of basal mathematics and physics theory.Along with the continuing development of the medical simulation technique and finite element modeling,the application of the finite element analysis in the biomechanical area will become more and more extensive,and its development has an obvious potentiality.
1.Papathanasopoulos A,Tzioupis C,Giannoudis VP,et al.Biomechanical aspects of pelvic ring reconstruction techniques∶evidence today.Injury 2010;41∶1220-7.
2.Enneking WF,Dunham WK.Resection and reconstruction for primary neoplasms involving the innominate bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am 1978;60∶731-46.
3.Aboulafia AJ,Buch R,Mathews J,et al.Reconstruction using the saddle prosthesis following excision of primary and metastatic periacetabular tumors.Clin Orthop 1995;314∶200-13.
4.Nobukiro K,Hiroshi T,Hirofumi T,et al.Biomechanical study of load transfer of the pubic ramus due to inclination after hip joint surgery using a three-dimensional finite element model.J Orthop Sci 2004;9∶264-9.
5.Tan R,Fan H,Wu F,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of bone stress distribution around the hip joint prosthesis with stepped stem.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Za Zhi 2011;28∶732-6.
6.Vleeming A,De Vries HJ,Mens JM,et al.Possible role of the long dorsal sacroiliac ligament in women with peripartum pelvic pain.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81∶430-6.
7.Arand M,Kinzl L,Gebhard E.Computer-guidance in percutaneous screw stabilization of the iliosacrai joint.Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;42∶201-7.
8.Jones CB.Posterior pelvic ring injures∶when to perform open reduction and internal fixation.Instr Course Lect 2012;61∶27-38.
9.He YQ,Zhang XL,Tang BH.Construction of threedimensional finite element model of hipbone based on DICOM data.Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong (Chin)2008;37∶251-4.
10.Tile M.Acute pelvic fractures∶caution and classification.JAAOS 1996;4∶143-7.
11.Choy WS,Kim KJ,Lee SK,et al.Anterior pelvic plating and sacroiliac joint fixation in unstable pelvic ring injuries.Yonsei Med J 2012;53∶422-6.
12.Shadmehr A,Jafarian Z,Talebian S.Changes in recruitment of pelvic stabilizer muscles in people with and without sacroiliac joint pain during the active straightleg-raise test.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2012;25∶27-32.
13.Kotsenas AL.Imaging of posterior element axial pain generators∶facet joints,pedicles,spinous processes,sacroiliac joints,and transitional segments.Radiol Clin North Am 2012;50∶705-30.
14.Zelle BA,Gruen GS,Brown S,et al.Sacroiliac joint dysfunction∶evaluation and management.Clin J Pain 2005;21∶446-55.
15.Foleb BS,Buschbacher RM.Sacroiliac joint pain∶anatomy biomechanics,diagnosis,and treatment.Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2006;85∶997-1006.
16.Ebraheim NA,Madsen TD,Xu R,et al.Dynamic changes in the contact area of the sacroiliac joint.Orthopedics 2003;26∶711-4.
17.Li M,Xu RM,Qiu HJ,et al.The study of displacement changes of the sacroiliac joint in unstable pelvic injury.J Pract Orthop (Chin) 2007;13∶81-4.
18.Garcia JM,Doblare M,Seral B,et al.Three-dimentional finite element analysis of several internal and external pelvic fixation.J Biomech Eng 2000;122∶516-21.
19.Wang JC,Wang H,Wang Q,et al.Biomechanical studies and clinical application of interfixation for unstable pelvic fracture.J Clin Med Pract (Chin) 2007;11∶21-5.
20.Cole PA,Gauger EM,Anavian J,et al.Anterior pelvic external fixatiorversussubcutaneous internal fixator in the treatment of anterior ring pelvic fractures.J Orthop Trauma 2012;26∶269-77.
21.Moed BR,Carr SE,Watson JT.Open reduction and internal fixation of posterior wall fractures of the acetabulum.Clin Orthop 2000;377∶57-67.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年3期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年3期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Hypercalcemia Appeared in a Patient with Glucagonoma Treated with Octreotide Acetate Long-acting Release
- Zinc Finger Protein-activating Transcription Factor Up-regulates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Expression in Vitro△
- Comparison of Clinical Effects of Au-Pt Based and Ni-Cr Based Porcelain Crowns
- Clinical Analysis of Placenta Previa Complicated with Previous Caesarean Section△
- Accuracy Validation for Medical Image Registration Algorithms:a Review△
- Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain-1 Ligand Induces Inflammation and Attenuates Glucose Uptake in Human Adipocytes△
