Cardiovascular risk burden and disability: findings from the International Mobility in Aging Study (IMIAS)
Juan-David Martinez-Aristizábal ,Carmen-Lucia Curcio ,Juliana Fernandes ,Afshin Vafael ,Cristiano dos Santos Gomes ,Fernando Gomez
1.Internal Medicine,Critical Care Department,Pablo Tobón Uribe Hospital,Medellín,Colombia;2.Research Group in Geriatrics and Gerontology,Faculty of Health Sciences,Universidad de Caldas,Manizales,Colombia;3.Laboratory of Physical Therapy and Collective Health,Physical Therapy Department,Federal University of Pernambuco,Jornalista Aníbal Fernandes Avenue Recife,Brazil;4.Department of Public Health Sciences,Queen’s University,Kingston,ON,Canada;5.Department of Physiotherapy,University of Pernambuco,BR 203,Km,Brazil;6.Research Group in Geriatrics and Gerontology,Faculty of Health Sciences,Universidad de Caldas,Manizales,Colombia
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND The association of cardiovascular risk burden with disability is unclear.We examined the association between trajectories of the Framingham general cardiovascular disease risk score (FGCRS) with the trajectories of limitations of physical function in older adults.METHODS A total of 1219 participants with no disabilities from the International Mobility in Aging Study (IMIAS) study who had up to three repeated measures of FGCRS between 2012-2016 and without a history of stroke or coronary heart disease at baseline and follow-up were included.FGCRS at baseline was assessed and categorized into tertiles.Physical function was evaluated with the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB).The data were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models.RESULTS At baseline,FGCRS ranged between 3-94 (mean score: 24 ± 15.8),participants were 32 (2.6%),502 (41.2%) and 685(56.2%) in lowest,middle,and highest tertiles,respectively.In the trajectories of limitations of physical function,the lowest FGCRS had no differences,while the middle and highest had a decrease in physical performance between 2012-2014 (P=0.0001).Age,being female,living in Andes Mountains,having middle and highest FGCRS,higher alcohol consumption,being obese,lack of exercise and cognitive impairment increase the probability of disability (P < 0.05).Alternatively,living in more developed regions and having a higher educational level reduced the probability of disability during the follow-up time (P < 0.05).CONCLUSIONS Higher cardiovascular risk burden is associated with decreased physical performance,especially in gait.Results suggest SPPB may provide a measure of cardiovascular health in older adults.
Limitations in physical function (PF) related to mobility,such as balance,gait speed,and muscle strength,are frequent as far as people age,and they are associated with the future development of disability.[1-2]Thus,the deterioration of PF has been correlated with various adverse health consequences.[3-5]The Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) is one of the most commonly used instruments for measuring physical performance in population studies of aging.[3]Low scores on the SPPB have a high predictive value for a wide range of health consequences,including disability in Activities of Daily Living (ADL),[4,6]loss of mobility,[5]disability,[4,7]hospitalization,[4]admission to nursing facilities,[7]and death.[8-10]
Regarding the association between functional limitation and cardiovascular conditions,their relationship with the risk of developing heart failure,[11]ischemic cardiopathy,[12]and outcomes related to cardiovascular disease[13]has been reported.The suggested hypothesis is that the deterioration in PF seems to be an early marker and/or predictor of cardiovascular disease.[13]On the contrary,the role that various individual cardiovascular risk factors (CRF)could play in the deterioration of PF,for instance,diabetes mellitus,[14]high blood pressure,[15]dyslipidemia,[16]and smoking[17]has been explored,evidencing a clinically significant negative relation.However,the effect that the cumulative burden of these cardiovascular risk factors could have on the deterioration of PF has not been fully studied.
The Framingham general cardiovascular risk score(FGCRS) is a well-established algorithm used to predict the risk of cardiovascular events in adults under 75 years old,taking into account not only the number of CRF but also their severity.[18]A few longitudinal studies done in the community have explored the relationship of CFR load risk factors that lead to PF deterioration.[19-22]All reports conclude that a high FGCRS is associated with worse physical performance and a more accelerated loss of PF,evaluated through gait speed,the chair stand test,and balance,[19-20]or evaluated through the ADL.[21,22]
This study aims to investigate the association between cardiovascular risk burden evaluated through FGCRS and physical function measured with SPPB in an older population in the community from various cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds.
METHODS
Participants
IMIAS was designed to examine and understand gender differences in mobility and physical function through the life course perspective.The objectives,study design,and details of sample recruitment have been reported in previous publications.[23,24]Briefly,data collection took place in 2012,2014,and 2016 and included 2012 participants at baseline ages 65-74 years (approximately 200 women and 200 men per site).Participants were recruited from lists of registered people at local neighborhood or family medicine practice institutions in five research sites (Kingston and Saint-Hyacinthe,Canada;Manizales,Colombia;and Natal,Brazil).These cities in IMIAS represent diverse ways of living in very different societies: Kingston,a university town in Ontario;Saint-Hyacinthe,the center of an agricultural region in Quebec;Manizales in the Andean coffee growing region,a relatively wealthy area of Colombia;and Natal,a coastal city and capital of a relatively poor region in the northeast of Brazil.They represent societies with distinct socioeconomic characteristics,cultures,and physical environments.Participants with cognitive impairment at baseline were excluded if they had four or more mistakes on the Orientation Scale of the Leganes Cognitive Test(LCT)[25]at the beginning of the interview since,in that case,they were considered unable to complete the study procedures.The IMIAS project received ethics approval from the Research Centre of the University of Montreal (CR-CHUM),and the research ethics boards of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte (Brazil),Queen’s University (Kingston),and Universidad de Caldas (Colombia).All study participants provided written informed consent.
Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk Burden
Following the Framingham General Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Model,we assessed and calculated FGCRS at baseline for each participant based on the information on age,sex,current smoking status,systolic blood pressure (SBP),antihypertensive medication use,diabetes mellitus,total cholesterol (TC),and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C).[18]All these risk factor scores were added to obtain the FGCRS,and the scores were further categorized into the lowest (0-6%),middle (6%-20%),and highest (20%) tertiles.[18]A higher FGCRS indicated a greater risk of future cardiovascular events.
Blood samples were taken in the morning,with fasting time starting the night before.The following data were analyzed: total cholesterol (TC),highdensity lipoprotein (HDL-C),and glycated hemoglobin.The samples were processed in laboratories linked to the universities of Kingston,Saint Hyacinthe,and Manizales,while in Natal,they were carried out in a commercial,specialized,and certified laboratory.Blood pressure was measured three times with a validated automated blood pressure device after five minutes of rest.The mean value of the second and third blood pressure measurements was used in the analysis.Antihypertensive medications were identified using the World Health Organization’s Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical-Defined Daily Dose classification system.[26]Hypertension was considered as systolic blood pressure(SBP) ≥140 mmHg,diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg,or the use of antihypertensive medications.Participants were categorized as current smokers or ever-smokers.Diabetes mellitus was defined by any of the following criteria: hemoglobin A1c ≥6.5%,history of diabetes mellitus,or the use of diabetes mellitus medication.
Outcome
Physical function was assessed using a lower-extremity-function battery of tests,the SPPB.[3]The SPPB includes three timed tests of lower extremity function: a hierarchical test of standing balance,a four-meter walk,and five repetitive chair stands.For the standing balance test,participants were instructed to maintain a bipedal stance for 10 s,followed by a semi-tandem stance for 10 s.The gait speed test involved timing a four-meter walk at the participants’ normal pace.A three-meter test was conducted for those without a four-meter course in their home,and scoring was adjusted accordingly.This test was repeated twice,with the faster of the two walks used.For the chair standing test,participants were first asked to demonstrate their ability to rise once from a chair.If they demonstrated this ability,they were asked to stand up and sit down five times as quickly as possible with their arms folded across their chests.Each of the three SPPB components (balance,gait,and chair stands) is scored from 0 to 4,with 0 indicating inability to perform the test and 4 indicating the highest category of performance.A summary of the participants’ physical performance scores was obtained by adding the scores of all three SPPB components for each participant.Total scores could thus vary from 0 to 12,with higher scores representing better physical performance.We have validated the SPPB in French,Spanish,and Portuguese during previous studies conducted in Quebec,Colombia,and Brazil.[27,28]This study defined poor physical performance as a total SPPB score below 8.[24]
Individuals with self-reported stroke or coronary heart disease (non-fatal myocardial infarction or definite angina) between 2012-2014-2016 were excluded as these conditions are known to affect motor performances.During the follow-up period 2012-2014,92 participants reported first cardiovascular disease or stroke;while in 2014-2016,69 people reported them.
At the end of study 288 participants who were not possible to follow,due these reasons: 142 (10.9%)refused to participate or no data available,20 (7%)moved with another proxy,38 (2.9%) moved no data available,30 (2.3%) died between 2012-2014,20(1.5%) died between 2014-2016,and 30 (2.3%) were unable to find or contact.
Covariates
Sociodemographic variables,such as age,sex,and the highest level of schooling completed,were recorded initially.Health self-perception was coded into two groups as follows: "Good",when they answered they felt it was good or very good,or "Bad" when they replied same,poor,or very poor.BMI was classified according to the WHO criterion,divided into three categories: underweight/normal (< 18.5 to 25.0 kg/m2),overweight (25.0-30.0 kg/m2),and obesity (> 30 kg/m2).[29]C-Reactive Protein (CRP),triglycerides,and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were measured following a standard protocol.Plasma CRP levels were obtained from the enzyme-linked ultrasensitive immunosorbent method.The logarithm of the values obtained was calculated to normalize the data distribution.CRP values were obtained continuously.IL-6 concentration was determined using the chemiluminescence method and was analyzed as a continuous variable.Cognitive status was assessed using the LCT,a screening test for dementia in populations with little education.Higher scores (range: 0-32) of LCT represent a better cognitive function,and a score of 22 or lower is indicative of dementia.[25]
Statistical Analysis
The differences in the characteristics among the three groups of participants with low,intermediate,and high FGCRS were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA test for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables.We compared medians and ranges using the U-Mann Whitney test with the SSPB scores in the different risk groups (lowvs.intermediate,intermediatevs.high).We compared the same risk group and the various measurement times (Low 2012vs.Low 2014vs.Low 2016) with the paired samples Wilcoxon test.
The b-coefficients and 95% CI for the association between cardiovascular risk burden (categorical FGCRS) and annual changes in PF and the three specific motor functions were estimated using linear mixed-effects models with follow-up time(years) as the time scale.The generalized estimating equation (GEE) model was applied to identify possible factors correlated with the outcome variable,disability.[30]The GEE is a robust means of analyzing longitudinal data,as it can produce regression estimates for repeated measures of non-normally distributed response variables,such as the outcome variable,disability,in the current study.[31]Moreover,the GEE allows both time-varying and individual difference variables to be specified and uses all available data for each subject.
We consider a potency of 80% with a 95% CI,and aPless than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.The analyses were done using SPSS 28.0 and GraphPad Prism 9.3.1 statistical software.
RESULTS
Of the 1219 participants (average age 68.9 ± 2.76 years),651 (53.4%) were female.FGCRS ranged from 3 to 94 (mean score: 24 ± 15.8) at baseline,32(2.6%) participants had the lowest FGCRS,502(41.2%) participants were in the middle tertile,and 685 (56.2%) participants were in the highest tertile.Table 1 shows the characteristics of the participants without functional limitation in the base study,stratified according to the FGCRS tertiles.Compared with those participants with the lowest FGCRS,the ones with the highest had more probability of being older,male,having a lower educational level,having higher SBP and BMI,having worse health self-rating,having smoked or being current smokers,and having diabetes mellitus.Additionally,they had lower HDL and a significant increase in CRP and IL-6.
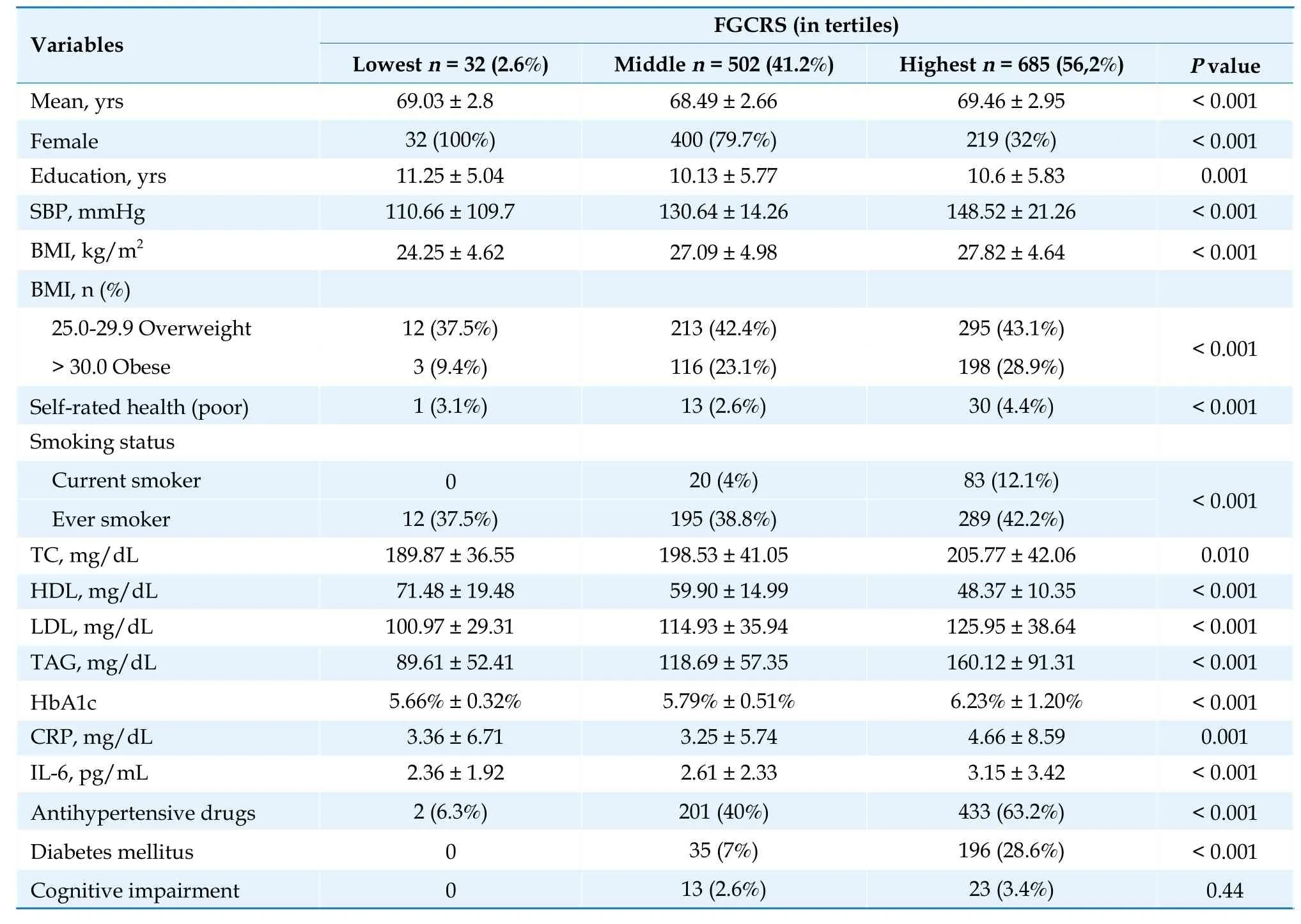
Table 1 Characteristics of the study population by FGCRS categories at baseline (n=1219).
Figure 1 shows the distribution of the SPPB scores,total,and for each component (balance,gait,and chair stands),according to the FGCRS stratification.Regarding SPPB scores in 2012,we found significant differences between the low-risk group and the intermediate-risk group.For the 2014 scores,we could observe a significant difference between the intermediate-risk group and the high-risk group,which remained in the 2016 scores.
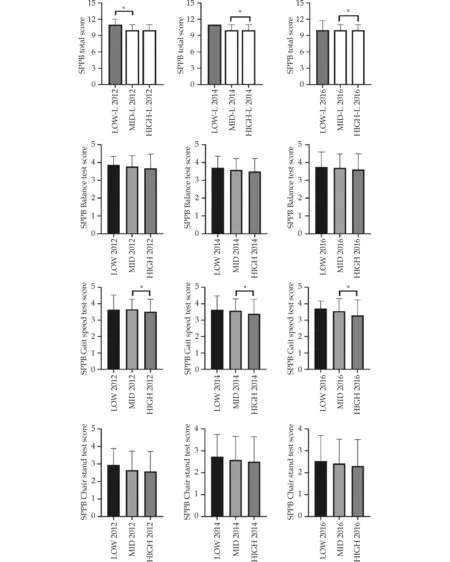
Figure 1 Performance according SPPB scores (total and each of the three components) adjusted by cardiovascular risk groups according to Framingham.*P < 0.05.SPPB: short physical performance battery.
Table 2 presents the evaluation of the progression of functional deterioration according to SPPB by cardiovascular risk group for each measurement.In the low-risk group,there were no differences in the follow-up time.Nevertheless,there was a significant difference in the intermediate-risk group between SPPB scores in the year 2012vs.2014 andvs.2016.There was no difference between the 2014 and 2016 values.This could also be observed in the high-risk group without finding differences among SPPB parameters between 2014 and 2016.
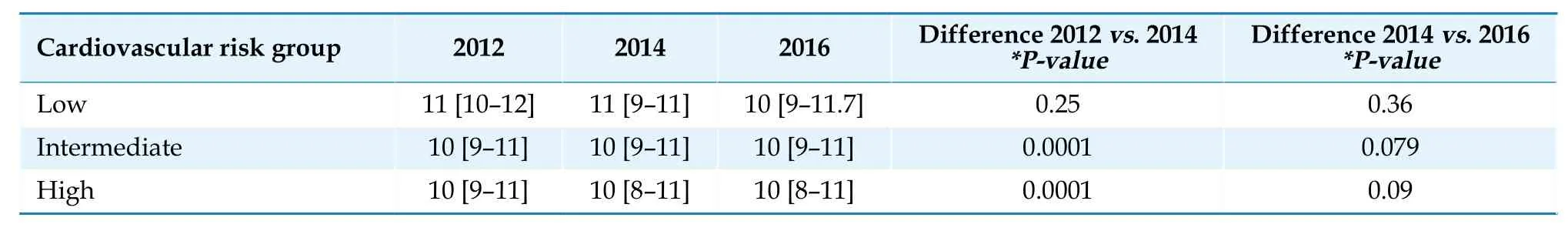
Table 2 Evaluation of the progression of patient SPPB by biannual measurement.
The longitudinal association between lower physical performance and FGCRS remained statistically significant even after adjustments in GEE analysis.Being female,living in the Andes Mountains,having higher alcohol consumption,being obese,and being physically inactive were related to developing SPPB < 8 in four years compared to the reference group SPPB > 8 (P< 0.01).Alternatively,living in more developed regions and higher educational levels reduced the probability of disability in the long run (P< 0.05;Table 3).
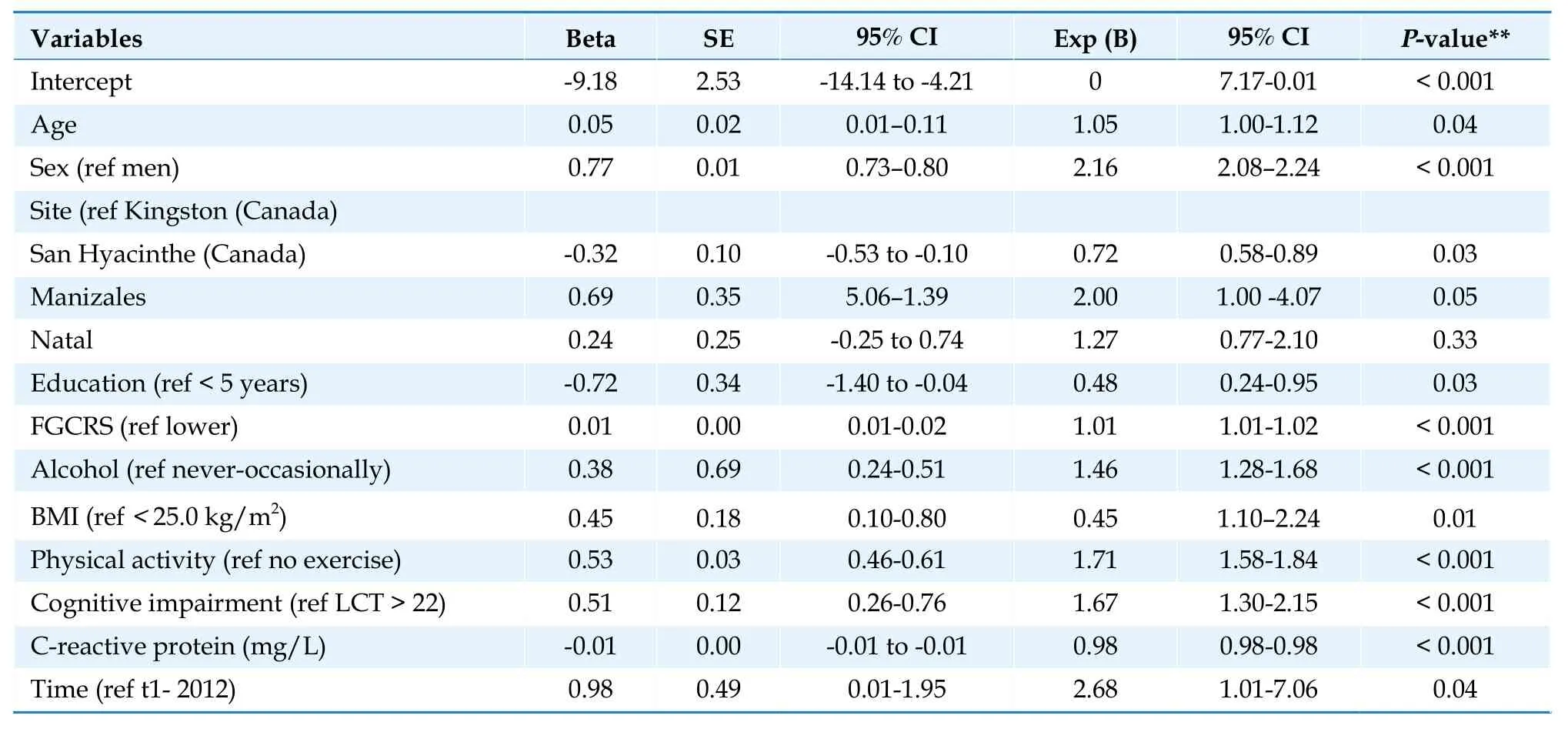
Table 3 Generalized estimating equations model: estimating the effect of factors affecting an SPPB less than 8.
DISCUSSION
This study among older adults from diverse settings that differed in social,cultural,socioeconomic aspects and healthcare systems shows the burden relationship of cardiovascular risk factors evaluated using the FGCRS with an objective measure of physical function tool such as the SPPB.Consequently,high scores in FGCRS are associated with a decline in the future PF.In the four-year follow-up,we observed that older people with intermediate and high risk deteriorate progressively,while those with low risk maintain their physical function.In addition,factors like age progression,being female,living in the Andes Mountains,having an intermediate or high FGCRS,high consumption of alcohol,being obese,not having exercising habits,and cognitive deterioration increase the probability of having functional limitations in the future.On the other hand,living in more developed regions and having a high educational level reduces the probability of long-term disability.
Few studies have reported the relationship between FGCRS and evaluation scores based on physical performance.[19-22]A study that applied repeated FGCRS calculations in people without a history of coronary or cerebrovascular disease (average age 65.4 years) assessed motor function using gait speed,chair stands,balance,finger tapping,and grip strength,finding that higher cardiovascular risk is associated with worse performance 16 years later,which was reflected mostly in gait speed,chair stands,and balance.[19]In another report,individuals over 60 years without functional limitations showed that higher FGCRS scores were associated with a higher risk of subsequent gait speed limitations nine years later.[20]A third study in older adults (average age 79.3 years)observed that compared with low FGCRS risk,high FGCRS increased the risk of disability in ADL and advances the start of disability in over a year,aside from accelerating the progression of ADL.[21]Finally,in another publication with the same older adult cohort with a 22-year follow-up and FGCRS categorized in tertiles (lowest,middle,and highest)at the baseline,they found that high cardiovascular risk is associated with a rapid decline in motor function,including dexterity,gait,and grip strength.[22]Our study found that high FGCRS were associated with a decline in physical execution,especially gait speed,in a 4-year follow-up.However,the non-significative decline in SPPB total score in intermediate and high-risk groups between 2014-2016 could indicate non meaningful annual change in SPPB in these groups.Previously has been suggested the lower sensitivity of SPPB requiring annual change in SPPB score between 0.99 and 1.34 to indicate a substantial change.[32]
The differences found among FGCRS groups,which are emphasized after the second follow-up in 2014,could be explained from the epidemiology of the course of life perspective,which states that each adverse condition not only has an isolated effect on health,in this case,cardiovascular,but it also increases the probability of subsequent exposure that fosters the appearance of adverse and deleterious conditions,in this case,the deterioration of functional capacity in the groups with a high burden of risk factors.[33]
The SPPB is an inexpensive,reliable,and easy-toimplement measure of lower-extremity physical function.Strong evidence links SPPB scores with allcause mortality,[8-10]the incidence of cardiovascular disease,[13]and cardiovascular disease consequences(CDC),like coronary ischemic disease,stroke,and heart failure (HF).[34]Additionally,its risk prediction has been recognized as reaching further than traditional risk in community-dwelling older adults.[12,34]Furthermore,our findings corroborate SPPB,especially the gait speed component,which has been the parameter that has been better correlated with a deterioration in physical function in our study.SPPB is a compound tool with clear advantages such as less cultural,educational,and language influence and test and re-test reliability with a very high intraclass correlation coefficient and validation in various physical function.[27-28,35]Even though confirmatory studies are needed,our results suggest the potential usefulness of SPPB to identify the risk of longterm functional limitations in patients with cardiovascular risk.
The limitations of this study are that we did not include a history of premature cardiovascular disease in the family,nor peripheral arterial disease,which could alter the physical capacity of an individual.Likewise,we did not establish intercurrent diseases like fractures,prolonged rest,and osteoarthritis that could modify and alter the results in the physical performance tool SPPB.However,this cohort comprised individuals between 65 and 75 years old,where risk factors for immobility and hip fracture were not as pronounced,which is something we actively looked for,given its own concept and objective.An option could be to control the results by multimorbidity,but we do not expect these events to impact the results of the study.Lastly,we selected the individuals that completed the battery of tests during the three evaluation times,which ensured that their physical conditions were acceptable at the time.
In conclusion,this study strengthens the evidence that shows that a higher burden of cardiovascular risk factors has negative repercussions on an individual’s functional capacity and predicts its deterioration.Thus,in the field of geriatric cardiology,it could be imperative to introduce tools that evaluate functional capacity periodically to interrupt the course of physical disability in the older people.Results suggest that SPPB may provide a measurement of cardiovascular health in older adults beyond that captured by using only traditional risk factors.Thus,SPPB should be a routine part of officebased CVD risk assessment.
DISCLOSURE
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed here are guarded by the participant researchers in the IMIAS studies in the various sites it took place.To request access to the database,you could visit the webpage: http://www.imias.ufrn.br,where the requirements and conditions are explained.
Funding sources
IMIAS was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR),Grant No.AAM 108751.
Author contributions
Juan-David Martinez-Aristizabal: Conceptualization,Data Curation,Methodology,Writing-Original draft,Formal analysis.Carmen-Lucía Curcio: Data Curation,Methodology,Writing-Original draft,Formal analysis,Statistical analysis.Juliana Fernandes:Formal analysis,Statistical analysis.Writing-Original draft preparation.Afshin Vafael.Formal analysis,Statistical analysis.Writing-Original draft preparation.Cristiano dos Santos Gomes Writing-Original draft Reviewing and Editing.Fernando Gomez:Investigation,Validation,Supervision,Reviewing,and Editing.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology2024年3期
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology2024年3期
- Journal of Geriatric Cardiology的其它文章
- Community-based prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
- Significance of balloon aortic valvuloplasty as palliative procedure for symptom benefit in patients with severe aortic stenosis
- Sleep quality and characteristics of older adults with acute cardiovascular disease
- The diagnostic value of tenascin-C in acute aortic syndrome
- Association of acute glycemic parameters at admission with cardiovascular mortality in the oldest old with acute myocardial infarction
- Effects of loneliness and isolation on cardiovascular diseases:a two sample Mendelian Randomization Study
