Prognostic and immunological roles of heat shock protein A4 in lung adenocarcinoma
Xuan Wu,Shen-Ying Yang,Yi-Hua Zhang,Jin-Zhou Fang,Shuai Wang,Zhi-Wei Xu,Xiao-Ju Zhang
Abstract BACKGROUND Heat shock protein A4 (HSPA4) belongs to molecular chaperone protein family which plays important roles within variable cellular activities,including cancer initiation and progression.However,the prognostic and immunological significance of HSPA4 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) has not been revealed yet.AIM To explore the prognostic and immunological roles of HSPA4 to identify a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for LUAD.METHODS We assessed the prognostic and immunological significance of HSPA4 in LUAD using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database.The association between HSPA4 expression and clinical-pathological features was assessed through Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon signed-rank test.Univariate/multivariate Cox regression analyses and Kaplan-Meier curves were employed to evaluate prognostic factors,including HSPA4,in LUAD.Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was conducted to identify the key signaling pathways associated with HSPA4.The correlation between HSPA4 expression and cancer immune infiltration was evaluated using single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA).RESULTS Overexpressing HSPA4 was significantly related to advanced pathologic TNM stage,advanced pathologic stage,progression disease status of primary therapy outcome and female subgroups with LUAD.In addition,increased HSPA4 expression was found to be related to worse disease-specific survival and overall survival.GSEA analysis indicated a significant correlation between HSPA4 and cell cycle regulation and immune response,particularly through diminishing the function of cytotoxicity cells and CD8 T cells.The ssGSEA algorithm showed a positive correlation between HSPA4 expression and infiltrating levels of Th2 cells,while a negative correlation was observed with cytotoxic cell infiltration levels.CONCLUSION Our findings indicate HSPA4 is related to prognosis and immune cell infiltrates and may act as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for LUAD.
Key Words: Heat shock protein A4;Lung adenocarcinoma;Tumor-infiltration;Prognosis;T helper cells
lNTRODUCTlON
Lung cancer remains a highly prevalent and deadly disease,causing the most cancer-related deaths globally.It is estimated that there are 2 million new diagnosed cases and more than 1.7 million deaths from lung cancer each year[1].Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD),the most prevalent histological subtype of lung cancer,exhibits significant morphological diversity and consists of tumor cells representing various histological subtypes[2].The discovery of actionable oncogenic mutations has revolutionized cancer treatment,leading to the development of targeted therapies that specifically inhibit driver mutations.For instance,epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors have demonstrated superior tumor response and longer progression-free survival in patients with EGFR-mutated LUAD compared to traditional chemotherapy[3-5].However,despite these advancements,advanced-stage LUAD remains largely incurable due to the emergence of therapeutic resistance mechanisms[6-8].Identifying new oncogenic driver genes,and understanding their roles can assist us better comprehend the biological characteristics of the disease and provide new targets for precision therapy[9].Through analyzing large-scale tumor genomic data,the researchers can find new oncogenic driver genes and further study their roles to promote the development of personalized treatments and make therapies more precise and effective[10,11].Additionally,the search for novel prognostic markers is also important avenue to help predict the outcomes and disease progression,and make early predictions of treatment efficacy and prognosis,thereby adjusting treatment strategies and developing personalized treatment plans[12].Some prognostic biomarkers,such as tumor staging and gene expression profiles,are already widely used in clinical practice[13].However,due to the high heterogeneity of LUAD,existing prognostic biomarkers are not sufficient to accurately predict disease progression and prognosis for every individual patient.Therefore,the search for novel prognostic biomarkers is crucial for guiding treatment strategies and evaluating treatment efficacy in LUAD[14].Elevated levels of structurally unstable proteins contribute to the genetic instability and continuous proliferation observed in cancer cells[15].Additionally,cancer cells experience heightened metabolism and protein synthesis,leading to a persistent state of cellular stress that must be counterbalanced[16,17].As a result,tumor cells heavily rely on the maintenance of protein homeostasis through molecular chaperones.As we all know,the 70-kDa heat shock proteins (HSP70s),which are present throughout the cell,play a vital role in the folding and remodeling of all cellular proteins[18,19].In turn,the HSP70s released by cancer cells can affect the malignant characteristics through receptor-mediated signaling pathways[20,21].Several studies have demonstrated an upregulation of HSP70 expression in various human malignant tumors[22,23].Heat shock protein A4 (HSPA4) is a heat shock protein that acts as a co-chaperone for HSP70.HSPA4 overexpression has been associated with increased cell survival,enhanced metastatic potential,and resistance to apoptosis,and acts as potential prognostic markers in various cancers[24-26].HSPA4 has been found to regulate the function of many immune cells involved in the anti-tumor immune response,and modulates the activity of macrophages,dendritic cells,and natural killer cells,among others,influencing their ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells[26,27].However,the functional role of HSPA4 in LUAD has not been explored.Therefore,we conducted this comprehensive study to explore the prognostic and immunological significance of HSPA4 and the potential molecular mechanisms involved in LUAD development,in order to provide novel prognostic markers and potential therapeutic targets for this malignancy disease.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Data collection and preparation
RNA-Seq profile and related clinical information of 539 LUAD samples and 59 adjacent normal tissues were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).Then,the RNA-seq data in FPKM format was transformed to TPM format.Our analysis strictly adhered to the publication guidelines provided by the TCGA database.
Differentially expressed gene analysis
The LUAD samples included in this study were assigned into two groups according to the median value of HSPA4 expression.Subsequently,we performed further analysis using the student’s t-test through the DESeq2 R package (version 3.6.3) to identify genes that showed differential expression between these two groups.To determine significant differential expression,we applied a threshold of adjustedPvalue < 0.05 and |log2-fold change (FC)| > 1.5.Genes that met the criteria were considered as the differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
Enrichment analysis
To explore the functional implications of DEGs between the above high HSPA4 expression group and the low HSPA4 expression group,we conducted gene ontology (GO) and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) functional enrichment analyses.These analyses were conducted using the ClusterProfiler package in R (version 3.6.3).For GO analysis,which encompasses cellular component,molecular function,and biological process,we identified significantly enriched GO terms associated with these DEGs.GSEA,on the other hand,is a computational method that assesses whether a defined gene set shows concordant differences and statistically significant between two biological states.In our study,we utilized GSEA to identify signaling pathways and gene sets that were enriched in each phenotype.To sort the enriched pathways,we employed the normalized enrichment score and adjusted p-value.In both GO analysis and GSEA,we considered gene sets with an adjustedPvalue < 0.05 and a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.25 as significantly enriched,indicating their potential relevance to the phenotypic differences observed.
Immune infiltration analysis
To examine the association between HSPA4 and the hub genes of 24 different types of the immune cells,we employed single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) within the R GSVA package.This approach allowed us to assess the correlation between HSPA4 expression status and immune cell signatures.Additionally,we systematically analyzed the published literature to investigate the immune infiltrates associated with HSPA4.To compare the immune cell infiltrates between the HSPA4 high and low expression groups,we utilized two statistical methods.Firstly,we conducted the Spearman correlation analysis to evaluate the relationship between HSPA4 expression and the abundance of immunocytes.Secondly,we applied the Wilcoxon rank-sum test to determine any significant differences in immune cell infiltrates between the two expression groups of HSPA4.By employing these methods,we aimed to gain insights into the potential role of HSPA4 in modulating immune cell infiltrates and its implications in the context of the published literature.
Protein-protein interaction network
To explore the protein-protein interactions (PPIs) among co-regulated DEGs,we utilized the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING) database (http://string-db.org).The PPI network was constructed based on the functional interactions between the proteins encoded by these DEGs.In our study,we set a combined score threshold of 0.7 to determine the reliability of the protein interactions.The STRING database provides a comprehensive score for each protein pair relationship,ranging from 0 to 1.The higher total score always indicates the more reliable PPI networks.To visualize and analyze the PPI network,we utilized the STRING database interface,which offers interactive visualizations and various tools for exploring the functional associations among proteins.By employing the STRING database,we aimed to gain insights into the protein interactions and functional associations among the co-regulated DEGs in our study.
Validation analysis
We evaluated the prognostic value of HSPA4 expressions in three independent datasets (GSE31210,GSE13213,and HARVARD-LC).
Statistical analysis
We performed the analyses in this study by R 3.6.3.First,Wilcoxon rank-sum test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test were performed to evaluate HSPA4 expression between LUAD tissues and the adjacent normal lung tissues.The correlationbetween clinicopathological factors and HSPA4 expression was assessed by Welch one-way ANOVA.Univariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the effect of clinicopathological features on HSPA4 expression.Moreover,univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses in this study were used to evaluate the prognostic significance of clinicopathological features and HSPA4 expression on survival of LUAD patients.The prognostic significance of HSPA4 was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier curves.Two-tailedP≤ 0.05 was considered as the statistical significance.
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics
The clinical information,including the age,gender,T stage,pathologic stage,primary therapy outcome,and overall survival (OS) event,of 539 LUAD samples was shown in Table 1.After excluding the samples without complete information,a total of 539 samples were analyzed in this study.The result of Fisher’s exact test revealed that HSPA4 was significantly associated with the OS event of LUAD patients (P=0.02).And the result of chi-square test showed that HSPA4 significantly correlated with N stage (P=0.028),pathologic stage (P=0.012),and primary therapy outcome (P< 0.001).However,no significant correlation was observed between HSPA4 expression and other clinicopathological variables.
Differential expression analysis of HSPA4 in LUAD
Based on the HTSeq-Counts data of HSPA4-related genes obtained from TCGA,we conducted a differential expression analysis to identify DEGs using a cut-off criterion of |logFC| > 1.5 and adjustedPvalue < 0.05.A total of 150 DEGs were detected,with 40 genes upregulated and 110 genes downregulated.To visually represent the expression patterns of these DEGs,we created a volcano plot (Figure 1A).Further analyses were conducted to explore the expression of HSPA4 specifically.Both unpaired and paired differential expression analyses were conducted to compare HSPA4 expression between the normal and LUAD groups.The results indicated that HSPA4 was significantly upregulated in tumor samples compared with normal tissues (Figure 1B and C).To investigate the correlation between HSPA4 and other genes,we generated a heatmap depicting the expression levels of HSPA4 along with 25 selected genes (Figure 1D).This heatmap provides a visual representation of the relationship between HSPA4 and these genes.

Figure 1 The results of differentially expressed genes analysis. A: The volcano plot of differentially expressed RNAs;B and C: The different expressions of HSPA4 between lung adenocarcinoma and adjacent normal tissues;D: Heatmap of the 25 genes correlated to HSPA4.Statistical significance is expressed as cP < 0.0001.
In addition,we also evaluated the protein level of HSPA4 between LUAD samples and adjacent normal tissues based on the UALCAN database which provides protein expression analysis option using data from CPTAC and ICPC datasets.The results showed that both the total-and phosphor-protein levels of HSPA4 were significantly increased in LUAD tissues than those in adjacent normal tissues (Supplementary Figure 1).
Functional enrichment analysis of DEGs
GO analysis suggested that the DEG-related HSPA4 had important regulation on neutrophil extracellular trap formation,alcoholism,systemic lupus erythematosus,olfactory receptor activity,protein-DNA complex,DNA packaging complex,nucleosome,protein-DNA complex assembly,nucleosome organization,nucleosome assembly,protein heterodimerization activity,and bitter taste receptor activity (Figure 2A).And,the PPI network of HSPA4 and the potential coexpression genes in HSPA4-related DEGs were exhibited in Figure 2B.

Figure 2 Enrichment analysis of HSPA4 in lung adenocarcinoma. A: Biological process enrichment related to HSPA4-related genes;B: A network of HSPA4 and its 10 potential co-interaction proteins;C and D: The results of enrichment analysis from gene set enrichment analysis.
To further explore the underlying biological function of HSPA4,GSEA analysis between the low and the high HSPA4 expression groups were executed to identify the GO terms and KEGG pathways related to HSPA4.A total of 425 pathways were significantly different in the enrichment of GO terms and KEGG signaling pathways within the high HSPA4 expression samples (FDR < 0.25 and adjustedP< 0.05).The GSEA analysis revealed that retinoblastoma gene in cancer,mitotic spindle checkpoint,ATR pathway,PLK1 pathway,and cell cycle were positively associated with high expression levels of HSPA4 (Figure 2C).HDACS deacetylate histones,DNA methylation,ERCC6 CSB and EHMT2 G9A positively regulate RRNA expression,activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR androgen receptor regulated genes KLK2 AND KLK3,SIRT1 negatively regulates RRNA expression were negatively associated with high expression levels of HSPA4 (Figure 2D).These results showed that the signaling pathways that regulated the immunoglobulin complex,DNA methylation,and cell cycle control were strongly related to HSPA4 expression.
Correlation between HSPA4 expression and immune cell infiltration
The correlation between the HSPA4 expression and the immune cell infiltrates quantified as the ssGSEA score was evaluated by Spearman correlation analysis.Both the infiltration levels of T cells and CD8 T cells display a significantly negative correlation with HSPA4 expression (P=0.001) (Figure 3A and B).The infiltration levels of B cells and cytotoxic cells also display a significantly negative correlation with HSPA4 expression (P< 0.001) (Figure 3C and D).On the other hand,the infiltration levels of Th2 cells and T helper cells showed a significantly positive correlation with HSPA4 expression (P< 0.05) (Figure 3E and F).Th2 cells,Tcm,T helper cells,dendritic cell (DC),aDC,neutrophils,macrophages,and eosinophils,have also shown a positive relation with HSPA4.Treg,natural killer (NK) CD56dim cells,NK cells,Tgd,mast cells,Tem,Th1 cells,iDC,Th17 cells,CD8 T cells,T cells,NK CD56bright cells,cytotoxic cells,TFH,pDC,and B cells were negatively related to HSPA4 expression (Figure 3G).These above results showed the significant value of HSPA4 in immune cell infiltration of LUAD tissues.A heatmap was used to evaluate and visualize the varying degrees of correlation between 24 subtypes of tumor-infiltrating immune cells (Figure 3H).

Figure 3 The results of analysis between HSPA4 expression and immune infiltration. A: The negative correlation between HSPA4 expression and T cells;B: CD8 T cells;C: B cells;D: Cytotoxic cells;E: The negative correlation between HSPA4 expression and Th2 cells;F: T helper cells;G: Correlation between HSPA4 expression level and the relative abundances of 24 immune cells;H: Heatmap of 24 immune infiltration cells in lung adenocarcinoma.
Correlation between HSPA4 expression and clinicopathological variables
The result of Welch one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction analysis demonstrated that increased HSPA4 expression was significantly associated with advanced pathologic TNM stages (Figure 4A-C).And,the t-test also showed that high HSPA4 expression indicated advanced pathologic stage,and PD of primary therapy outcome (Figure 4D and E).Thus,increased HSPA4 expression indicated advanced tumor stage and poor primary therapy outcome.In addition,the female patients with LUAD had increased HSPA4 expression levels compared with male patients with LUAD (Figure 4F).

Figure 4 Correlation between the HSPA4 expression and different clinicopathologic characteristics. A: Correlation between the HSPA4 expression and the pathologic T stage;B: N stage;C: M stage;D: Pathologic stage;E: Primary therapy outcome;F: Gender.Statistical significance is expressed as a P < 0.05,bP < 0.01,cP < 0.0001.
In this Cox regression analysis model,the univariate Cox regression analysis revealed that the TN stage,pathologic stage,and HSPA4 expression significantly correlated with poor survival of patients with LUAD (P< 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2 The COX regression analysis about clinicopathological characteristics associated with the survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients
Multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that T,N stage,pathologic stage and HSPA4 expression were independent factors for the survival of LUAD patients (P< 0.05) (Figure 5A).

Figure 5 The prognostic value of HSPA4 in lung adenocarcinoma. A: Multivariate Cox regression visualized in the forest plot;B: HSPA4 expression distribution and survival status.0: dead,1: alive;C: Nomogram with the HSPA4 expression and traditional clinical prognostic factors.
Additionally,we evaluated the association between survival status and distribution of HSPA4 expression,and expression profile among LUAD samples.The plot features blue dots to depict surviving samples,while red dots represent dead samples.The upper line signifies the median risk score,with the left side denoting low-risk group characterized by less HSPA4 expression (Figure 5B).Conversely,right side of dotted line indicates high-risk samples,displaying higher levels of HSPA4 expression.As the risk score increases,there is a gradual rise in the number of orange dots,indicating an increase in deceased LUAD patients.This observation suggests that individuals categorized in the high-risk group face inferior survival outcomes and a heightened risk of mortality.
Furthermore,to assess the potential clinical use of HSPA4 expression,we developed a nomogram with the HSPA4 expression and traditional clinical prognostic factors,including TN stage,pathologic stage,and age,to predict the survival status in patients with LUAD (Figure 5C).
The Kaplan-Meier survival curve was drawn to assess the prognostic value of HSPA4 in patients with LUAD by R package survminer.LUAD samples were subsequently assigned into low and high HSPA4 expression groups based on the median expression value.The increased HSPA4 expression group tend to be significantly related to poor overall survival (HR=1.51,P=0.056) and disease specific survival (HR=1.40,P=0.071) (Figure 6A and B).

Figure 6 The prognostic value of HSPA4 in the different subgroups. A and B: The prognostic value of HSPA4 in overall survival and disease specific survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients;C-H: High expression of HSPA4 was associated with worse overall survival in different subgroups.
The increased HSPA4expression of was also related to worse survival in the T2 subgroup of T stage (P=0.038),M0 subgroup of M stage (P=0.006),age > 65 subgroup (P=0.003),female subgroup (P=0.021),smoker subgroup (P=0.03),and stage III subgroup of pathologic stage (P=0.061) (Figure 6C-H).
Data validation
In all three independent datasets,Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that high HSPA4 mRNA expression group exhibited a significantly poor survival compared to the low HSPA4 mRNA expression group (P< 0.05) (Figure 7).
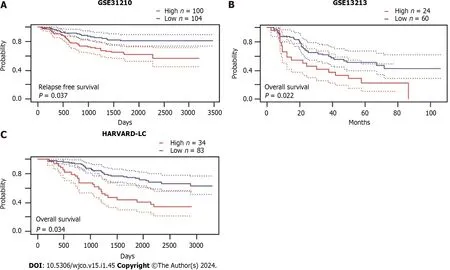
Figure 7 The prognostic value of HSPA4 in three independent datasets. A: The prognostic value of HSPA4 in GSE31210 database;B: GSE13213 database;C: HARVARD-LC database.
HSPA4 methylation in patients with LUAD
The MethSurv tool was utilized to examine the association between DNA methylation levels of HSPA4 and the prognostic value of individual CpG sites.The analysis identified 13 methylation CpG sites,with cg05996250 and cg07474441 displaying the highest levels of DNA methylation (Figure 8).Among these CpG sites,seven of them,namely cg02067788,cg23946014,cg05996250,and cg07474441,exhibited a significant correlation with prognosis (P< 0.05) (Figure 8).Patients with decreased methylation levels of these CpG sites in HSPA4 experienced poorer overall survival compared to those with elevated HSPA4 methylation levels.Since increased methylation level means low expression of HSPA4,which indicates that patients with elevated expression of HSPA4 have a poor prognosis,which is consistent with the results in Figures 6 and 7.

Figure 8 Visualization between the methylation level and HSPA4 expression.
DlSCUSSlON
LUAD is a common malignant tumor with prognosis influenced by various factors.Treatment options for patients with LUAD are limited,especially for those without actionable drug targets.However,some immunotherapy approaches,including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs),and adoptive cellular therapy,have been shown effective for some LUADs.Nevertheless,there are also many challenges,including the lack of initial response and resistance overtime to ICIs in certain subgroups of cancers,that need to be addressed in order to broaden the application[28].Therefore,it is necessary to study the molecular mechanisms underlying ICIs resistance to develop strategies to enhance Immunotherapy response.
In this study,we found that LUAD patients with high HSPA4 expression had worse overall survival and diseasespecific survival,which is consistent with previous research evidences,supporting HSPA4 as a potential biomarker for evaluating the prognosis of LUAD patients.Previous evidences have shown that abnormal expression of HSPA4 is related to the occurrence and development of various tumors[23,29].
In addition,further subgroup analysis showed a positive correlation between high HSPA4 expression and worse survival in the T2 stage,M0 stage,age > 65 years,female,smoker,and pathological stage III subgroups.This indicates that HSPA4 may have promising predictive value in these specific subgroups and provide important information for individualized treatment decisions.For example,more aggressive treatment strategies may be needed for those with higher pathological stages in response to the malignant biological behavior represented by high HSPA4 expression.
When it comes to immune regulation in LUAD,the functional enrichment analysis demonstrated that HSPA4 plays crucial roles in the antigen presentation process,which is essential for the activation of T cells and the initiation of an immune response against cancer cells.It assists in the proper folding and assembly of antigens,facilitating their presentation on major histocompatibility complex molecules.This process enables immune cells to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively[30].Furthermore,in our study,HSPA4 has been found to regulate the function of various immune cells involved in the anti-tumor immune response.It modulates the activity of dendritic cells,macrophages,and natural killer cells,among others,influencing their ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.HSPA4 can promote antigen cross-presentation by DCs and enhance the cytotoxicity of natural killer cells,thus improving the immune response against cancer.HSPA4 expression in the tumor microenvironment can influence immune cell infiltration.It has been observed that high levels of HSPA4 are associated with decreased infiltration of immune cells,such as cytotoxic T cells and CD 8 T cells,into tumors.This infiltration is linked to improved prognosis in certain cancers[31].
Overall,HSPA4 plays a multifaceted role in immune regulation in LUAD.It facilitates antigen presentation,promotes immunogenic cell death,modulates immune cell function,and influences the tumor microenvironment.Further research is still needed to fully understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the correlation between HSPA4 and immune regulation in LUAD.
Subsequently,we developed a Nomogram model that combines HSPA4 expression with traditional clinical prognostic factors such as TNM stage,pathological stage,and age.This Nomogram model provides clinicians with an intuitive tool to more accurately assess the prognosis of LUAD patients and tailor individualized treatment strategies.The comprehensive predictive model integrating clinical and molecular biology information allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of patient prognostic risk and provides robust support for clinical decision-making.The HSPA4 expression and the combined nomogram model were of great significance in prognostic prediction for LUAD patients.The increased HSPA4 expression had been shown to indicate an immunosuppressive microenvironment,which maybe contribute to the immunotherapy resistance in the treatment of LUAD patients.The HSPA4 inhibitor addition may enhance the therapeutic response to immune checkpoint blockade,thereby optimizing treating strategies and drug application.
Although this study provides preliminary exploration of the potential of HSPA4 as a prognostic biomarker for LUAD patients,there are still some limitations.Firstly,our study is based on retrospective analysis and may have selection bias.Further prospective and multicenter validation studies will help better define the prognostic value of HSPA4.Moreover,this study only focused on the expression level of the HSPA4 gene and did not investigate its regulatory mechanisms and functions.Future research can delve into the biological characteristics of HSPA4 to reveal the specific role in the initiation and progression of LUAD.
CONCLUSlON
Above all,this study suggests that HSPA4 is a potential prognostic indicator,with high expression correlating with worse prognosis in LUAD patients.The expression level of HSPA4 may have differential predictive value in different subgroups and can be used in combination with traditional clinical prognostic factors through the Nomogram model.The findings provide new clues for better evaluating prognostic risk and devising individualized treatment strategies for LUAD patients and serve as useful references for relevant clinical practice and research.Future studies should explore the biological functions and regulatory mechanisms of HSPA4 and validate its clinical applicability as a prognostic biomarker.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 (HSPA4) is a member of the HSP110 family.Previous studies showed HSPA4 is significantly associated with prognosis and immune regulation in different cancer types.However,the role of HSPA4 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) has not been revealed yet.
Research motivation
We tried to explore the prognostic and immunological roles of HSPA4 in the Bio informatics methods based on the public databases.We confirmed the role of HSPA4 in LUAD prognosis and verified the correlation between HSPA4 and immune regulation.This study can assist us better comprehend the biological characteristics of the disease and provide new therapeutic target for precision therapy.
Research objectives
We aim to comprehensively analyzed the correlation between HSPA4 expression and the clinical characteristic,prognosis and immunology based on the RNA-seq data from the public database.We showed HSPA4 is significantly associated with prognosis and immune regulation and is a potential prognostic and new therapeutic target in LUAD.
Research methods
The primary research method used in my study was bioinformatics.This technique is an advanced technology used in recent years to study genetics and genomics.It is widely used due to its ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns and relationships that might be difficult to detect using other methods.The novelty of bioinformatics lies in its ability to integrate multiple technologies and methodologies,such as computer science,statistics,and molecular biology,to provide a comprehensive understanding of biological systems.In my study,I applied various bioinformatics tools and algorithms to analyze genomic data and identify potential genetic targets for further investigation.
Research results
The study found that overexpression of HSPA4 was significantly associated with advanced disease stage,progression disease status,and worse survival outcomes in LUAD.Additionally,HSPA4 expression was correlated with alterations in cell cycle regulation,immune response,and the balance of infiltrating immune cells within the tumor microenvironment.These findings suggest that HSPA4 may play a role in tumor progression and immune evasion in LUAD.However,this study only focused on the expression level of the HSPA4 gene and did not investigate its regulatory mechanisms and functions.Future research can delve into the biological characteristics of HSPA4 to reveal the specific role in the initiation and progression of LUAD.
Research conclusions
This study proposed that HSPA4 may play a role in tumor progression and immune evasion in LUAD.This study comprehensively analyzed the correlation between HSPA4 expression and the clinical characteristic,prognosis and immunology in bioinformatics method based on the RNA-seq data from the public database.
Research perspectives
The regulatory mechanisms and functions of HSPA4 and the specific role in the initiation and progression of LUAD are direction of the future research.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Wu X and Yang SY contributed equally to this work;Wu X,Yang SY and Zhang XJ designed the research study;Wu X,Yang SY and Fang JZ performed the analysis;Wu X,Yang SY,and Wang S analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript;all authors have read and approve the final manuscript.
lnstitutional review board statement:This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital.
Clinical trial registration statement:Since our paper is not a clinical research study but a bioinformatics analysis to assess the prognostic and immunological significance of HSPA4 in LUAD using data from public database.So,it is not applicable to provide the Clinical Trial Registration Statement.
lnformed consent statement:Since our paper is not a clinical research study but a bioinformatics analysis to assess the prognostic and immunological significance of HSPA4 in LUAD using data from public database.So,it is not applicable to provide the Signed Informed Consent Form(s) or Document(s).
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Data sharing statement:The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories.The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORClD number:Xuan Wu 0000-0001-8539-6611;Xiao-Ju Zhang 0000-0002-2833-8746.
S-Editor:Liu JH
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Zhang XD
 World Journal of Clinical Oncology2024年1期
World Journal of Clinical Oncology2024年1期
- World Journal of Clinical Oncology的其它文章
- Prognostic factors of breast cancer brain metastasis
- Radiotherapy for hyoid bone metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma: A case report
- What are the changes in the hotspots and frontiers of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma over the past decade?
- Fatty acid binding protein 5 is a novel therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Gene signatures to therapeutics: Assessing the potential of ivermectin against t(4;14) multiple myeloma
- Predicting colorectal cancer prognosis based on long noncoding RNAs of disulfidptosis genes
