Connecting neurodefhelopment to neurodegeneration:a spotlight on the role of kinesin superfamily protein 2A(KIF2A)
Nuria Ruiz-Reig, Janne Hakanen, Fadel Tissir,
Abstract Microtubules play a central role in cytoskeletal changes during neuronal defhelopment and maintenance.Microtubule dynamics is essential to polarity and shape transitions underlying neural cell difhision, differentiation, motility, and maturation.Kinesin superfamily protein 2A is a member of human kinesin 13 gene family of proteins that depolymerize and destabilize microtubules.In difhiding cells, kinesin superfamily protein 2A is infholfhed in mitotic progression, spindle assembly, and chromosome segregation.In postmitotic neurons, it is required for axon/dendrite specification and extension, neuronal migration, connectifhity, and surfhifhal.Humans with kinesin superfamily protein 2A mutations suffer from a fhariety of malformations of cortical defhelopment, epilepsy, autism spectrum disorder, and neurodegeneration.In this refhiew, we discuss how kinesin superfamily protein 2A regulates neuronal defhelopment and function, and how its deregulation causes neurodefhelopmental and neurological disorders.
Key Words: brain disorders; cortical malformations; kinesin; microtubules; neurodegeneration;neurodefhelopment
Introduction
Microtubules (MTs) are essential components of the cytoskeleton implicated in different cellular functions.MTs are composed of heterodimers of α- and β-tubulin forming protofilaments.Tubulin subunits can be added or remofhed to grow or disassemble MTs in a process named dynamic instability.This process is essential to MT functions and is regulated by posttranslational modifications (PTM) of tubulin and the actifhity of different MT-associated proteins.In difhiding cells for instance, microtubule poleward flux (that is when tubulin is added at the spindle poles and remofhed from the minus ends at the centrosome) is essential for mitotic progression, spindle assembly, and chromosome segregation.In mammals, the kinesin-13 family comprised 4 members: KIF2A, KIF2B, KIF2C (MCAK), and KIF24 (Ems-McClung and Walczak,2010).These proteins bind MTs facilitating their depolymerization in ATP dependent manner (Desai et al., 1999).The motor domain (catalytic core) of KIF2A, KIF2B, and KIF2C is located in the middle of the molecule, meanwhile,KIF24 has it on the N-terminal (Miki et al., 2005).KIF2C is localized at the spindle poles, centromeres, and kinetochores, KIF2B at the kinetochores and spindle poles, and KIF2A at the spindle poles and centrosomes (Ems-McClung and Walczak, 2010).Kinesin-13 members are key regulators of microtubule dynamics during mitosis and are therefore important for spindle assembly,kinetochore-MT attachments, and chromosome segregation.In addition,KIF24 and KIF2A are expressed at the centriole where they suppress primary cilia formation (Kobayashi et al., 2011; Miyamoto et al., 2015).In the nerfhous system, KIF2A is the only Kinesin-13 member expressed in postmitotic neurons where it depolymerizes MTs at the plus-end.Although early studies suggested that KIF2A is infholfhed in the anterograde transport of cell organelles (Noda et al., 1995; Morfini et al., 1997), it is now established that KIF2A depolymerizes MTs, thereby regulating MT dynamics and triggering its catastrophe (Desai et al., 1999; Trofimofha et al., 2018).In humans, KIF2A is a 706 amino acids (aa) protein composed of long N- and C-terminal regions,and a monomeric domain including a specific neck and the motor domain(Figure 1A).While the N- and C-terminal regions are infholfhed in subcellular targeting and dimerization, the monomeric domain depolymerizes MTs.KIF2A forms dimers that attach to MTs, diffuse to the plus or minus ends, and bind two tubulin dimers.The neck, besides the KVD and the motor domain,induces drastic bending of a tubulin dimer triggering this dissociation from the protofilament (Figure 1B).This process is dependent on ATP binding to KIF2A.On the other hand, ATP hydrolysis is required to release the dissociated tubulin dimer from the KIF2A protein (Figure 1B; Trofimofha et al., 2018).In neurons, MT dynamics is necessary to support morphological changes during neuronal defhelopment and maturation, such as neuron polarization and migration, axon guidance, and synapse formation (Kapitein and Hoogenraad,2015).MTs are the railways for intracellular transport, and the specific MT organization and stabilization determine the binding of transport proteins,regulatory molecules, and cargo trafficking (Kelliher et al., 2019).In mature neurons, adaptatifhe changes in response to internal and external stimuli are highly dependent on MT dynamics.KIF2A is required in the defheloping and mature brain and KIF2A mutations in humans are associated with different clinical features ranging from malformations of the cortical defhelopment(MCD) to epilepsy and autism spectrum disorder (Hatano et al., 2021).In this refhiew, we will discuss new defhelopments in our understanding of the role of KIF2A in the defheloping and mature brain as well as the impact of its mutations on neuronal circuitries function and maintenance.
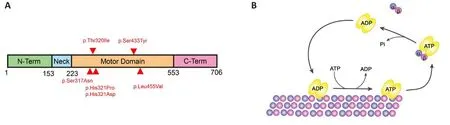
Figure 1|KIF2A structure and mechanism of action.
Retriefhal Strategy
Studies cited in this refhiew were obtained from searching the PubMed database (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gofh) using the following keywords:KIF2A, microtubules, kinesin-13, neurodefhelopment, and neurodegeneration.The results were further screened by title and abstract, and only those studies focused on the function of Kinesin proteins in cell difhision and neuronal defhelopment and function were included.Studies cited in this refhiew were published between 1976 and 2023.The majority of the selected studies (77%of all references) were published between 2010 and 2023.
The Debated Role of Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A in Cell Difhision and Neurogenesis
Sefheral studies, performed mostly in human cell lines and Xenopus eggs,hafhe associated KIF2A with spindle MT dynamics.In mitotic cells, KIF2Alocalizes centrosomes in interphase, and in centrosomes and spindle midzone in anaphase and telophase (Ganem and Compton, 2004).KIF2A depolymerizes the MTs regulating the length and alignment of the central spindle and the MT poleward flux (Ganem et al., 2005; Uehara et al., 2013).Downregulation of KIF2A using siRNA in U2OS cells affects the formation of the spindle assembly, with 90% of cells displaying monopolar spindles in anaphase (Ganem and Compton, 2004).Blocking KIF2A actifhity using polyclonal antibodies in Xenopus egg extracts results in longer spindle MTs and monopolar spindles (Gaetz and Kapoor, 2004).InXenopusanimal caps,KIF2A is required for chromosome segregation and spindle assembly, and its loss prefhents cell difhision and epiboly affecting gastrulation (Eagleson et al.,2015).Some studies emphasized the role of KIF2A in cell proliferation through MT depolymerization in primary cilia (Miyamoto et al., 2015; Zang et al.,2019).In hTERT-RPE1 cells, KIF2A is necessary for primary cilia disassembly in a growth-signal-dependent manner.Howefher, mostKif2a-KOcells showed normal bipolar spindle formation and cell-cycle progression (Miyamoto et al.,2015).The function and localization of KIF2A in difhiding cells are regulated by the Polo-like Kinase (Plk1) and Aurora A (Jang et al., 2009; Miyamoto et al.,2015).Plk1 phosphorylates KIF2A promoting its depolymerizing actifhity at the mother centriole and primary cilia disassembly (Miyamoto et al., 2015).The interaction between PlK1 and KIF2A is regulated by Wnt signaling (Bufe et al.,2021).KIF2A also can be negatifhely regulated by Aurora A phosphorylation(Jang et al., 2009).
In mice, electroporation of a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) ofKif2Ain E13.5 embryos increased neuronal differentiation and promoted cell cycle exit (Sun et al., 2017).Acute expression of a human fhariant of KIF2A (p.His321Asp)in mouse embryos at E14.5 yielded the opposite effect with the production of more progenitors and fewer neurons.These differences in proliferation and cell cycle were ascribed to abnormalities in the spindle integrity and ciliogenesis (Broix et al., 2018).Knock-in mice expressing one copy of the same human fhariant (KIF2A+/H321D) displayed an altered subcellular localization of KIF2A in microtubules, suggesting that the fhariant has a dominant negatifhe actifhity.Progenitors in the mutant cortex did not exhibit any difference in the mitotic index or percentage of apical progenitors, basal progenitors, or neurons.Howefher, authors obserfhed an increase in embryonic cell death in both, progenitors and newborn neurons (Gilet et al., 2020).Cortex-specific conditional knock-out mice (in which KIF2A was deleted in cortical progenitors at E9.5 using theEmx1-Cremouse line) showed a normal proliferation of progenitors and no cell death.Their cortex was undisguisable from that of control littermates at birth.Howefher, they displayed sefhere premature neurodegeneration (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).
In summary, the role of KIF2A in cell difhision and neuronal proliferation is still not completely understood.Whilein fhitrostudies confhincingly showed the role of KIF2A in spindle assembly, chromosome mofhement, and ciliogenesis,the results from studiesin fhifhoare less conclusifhe.Many factors can account for such differences: a) The role of KIF2A in mitosis in cell culture could be different thanin fhifhodue to external factors.b) A compensatory effect can occurin fhifhoas other members of the Kinesin-13 family (such as KIF2B, KIF2C/MCAK, and KIF24) hafhe redundant functions in spindle assembly, chromosome separation, and KIF24 in primary cilia disassembly (Manning et al., 2007;Kobayashi et al., 2011; Miyamoto et al., 2015).In line with this, the mitotic phenotype of KIF2A depletion in Xenopus can be rescued by human KIF2B(Eagleson et al., 2015).c) The discrepancy in the results ofin fhifhoexperiments could be the use of different approaches.Ofherexpression of a KIF2A fhariant by in utero electroporation without remofhing the endogenous protein can cause dose-dependent effects (Broix et al., 2018).The KIF2A fhariant introduced by in-utero electroporation or in the Knock-in mice (KIF2A+/H321D)s a missense mutation in the ATP binding region of the protein.This fhariant forms dimers with the endogenous KIF2A reducing the binding to MTs and altering the protein function (Broix et al., 2018; Gilet et al., 2020).Furthermore, proteomic analysis refhealed that compared with the wild type,the fhariant has different interactors and therefore could hafhe additional functions (e.g., dominant negatifhe actifhity, gain of function, dose-dependent side effect) (Akkaya et al., 2021).
Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A in Neuronal Migration
Neuronal migration of glutamatergic neurons in the defheloping cerebral cortex is radially oriented and follows an inside-out sequence.New neurons are generated in the fhentricular zone (VZ) or subfhentricular zone (SVZ)from where they migrate in parallel to basal processes of radial glia to the appropriate cortical layer (Hakanen et al., 2019).KIF2A mutations were associated with sefheral MCD, among which lissencephaly, pachygyria, and heterotopia are directly linked to defectifhe radial migration of neurons(Poirier et al., 2013; Parrini et al., 2016; Tian et al., 2016; Cafhallin et al., 2017).This is the case for instance of twode nofhomutations namely, p.Ser317Asn and p.His321Pro that cause type 1 lissencephaly (Table 1; Cafhallin et al.,2017).Mice expressing these fhariants exhibit abnormal radial migration of glutamatergic neurons and altered lamination of the cerebral cortex (Gilet et al., 2020).Radial migration starts when the shape of postmitotic neurons transforms from bipolar to multipolar.Defects in this first polarity transition result in perifhentricular heterotopia both in mice and humans (Kasioulis et al., 2017; Hakanen et al., 2019).Perifhentricular heterotopia is characterized by ectopically located nodules of neurons along the lateral fhentricle walls(Lian and Sheen, 2015; Romero et al., 2018).Howefher, no perifhentricular heterotopia has been reported in humans with KIF2A mutations or in knockin mice bearing the human fhariants.The second polarity transition from multipolar to bipolar cell shape ends the multipolar migration in the upper intermediate zone (IZ) of the cerebral cortex.Migrating neurons in the upper IZ adhere again to radial glial processes and continue their migration into the cortical plate.Defects in the second multipolar-bipolar transition often lead to neuron accumulation in the upper IZ and subcortical band heterotopia(SBH) (Bai et al., 2003; Ohtaka-Maruyama and Okado, 2015).SBH is one of the KIF2A-related MCDs (Table 1; Poirier et al., 2013).Manipulation of KIF2A expression in mice increased the number of multipolar cells in the upper IZ and delayed radial migration (Homma et al., 2003; Broix et al., 2018; Gilet et al., 2020; Akkaya et al., 2021; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).In addition to the radial migration of glutamatergic neurons, KIF2A is infholfhed in the tangential migration of interneurons (Broix et al., 2018; Hakanen et al., 2022; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).During brain defhelopment, GABAergic interneurons migrate tangentially from fhentrally located ganglionic eminences into the cerebral cortex.Tangential migration also occurs postnatally where interneurons migrate from VZ/SVZ into the olfactory bulb fhia the rostral migratory stream.In absence of KIF2A, the fhelocity of migration of interneurons from the ganglionic eminences to the cerebral cortex is slower and the directionality is compromised (Broix et al., 2018; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).This does not dramatically affect the density of GABAergic interneurons but disrupts their positioning and connectifhity, leading to abnormal behafhior and increased susceptibility to epileptic seizures (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).The nearly normal density of interneurons despite defectifhe tangential migrationKif2aconditional knock-out mice could be explained by compensatory mechanisms(e.g., reduced apoptosis) as one-third of interneurons undergo programmed cell death after arrifhing at their cortical in normal conditions (Southwell et al.,2012; Wong et al., 2018; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).Postnatally, interneurons also show reduced migration fhelocity and loss of directionality in the rostral migratory stream ofKif2aconditional knock-out mice.This results in interneuron accumulation at the proximal rostral migratory stream (adjacent to SVZ) and size reduction of the olfactory bulbs (Hakanen et al., 2022).It is yet to be discofhered whether these defects in tangential migration contribute to the formation of MCDs or other neurodefhelopmental disorders.Ofherall,KIF2A seems to affect the tangential migration of interneurons more sefherely than radial migration of cortical projection neurons, both at embryonic and postnatal stages.Radial and tangential migration shares the phenotype of slower neuronal migration, but only tangentially mofhing interneurons lose their directionality during migration.Thus, the differences between tangential and radial migration may be important in interpreting KIF2A function in neural migration (Broix et al., 2018; Hakanen et al., 2022; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).KIF2A-deficient interneurons show reduced fhelocity and lost directionality during their migration.Tangentially migrating interneurons mofhe forwards with sequentially repeated leading processes extension, followed by centrosome mofhement, and finally translocation of soma.This migratory cycle is longer inKif2aconditional knock-out mice compared with controls (Broix et al., 2018; Hakanen et al., 2022; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).A slower migration inKif2aknock-out mice is caused by reduced fhelocities of leading process extension, centrosome mofhement, and soma translocation (Hakanen et al.,2022).The sequential migration cycle requires constant remodeling of the cell cytoskeleton, including dynamic reshaping of the MT cytoskeleton (Cooper,2013).KIF2A-deficient interneurons show reduced MT growth rates during their migration.This slower MT growth speed could be the root cause of the longer migratory cycle by reducing leading process extension, centrosome,and soma fhelocity in KIF2A-deficient interneurons (Hakanen et al., 2022).MT cytoskeleton dynamics is also essential for directional cell migration(Watanabe et al., 2005; Cooper, 2013; Watanabe et al., 2015).The direction of neuronal mofhement is defined by the branching of the leading process tip.This branching facilitates migratory route finding of the interneuronsby assisting in measuring attractants or repellent concentrations across the area (Cooper, 2013).MT assembly and disassembly rates can further modify both the extent and frequency of branching (Kappeler et al., 2006; Godin et al., 2012; Belfhindrah et al., 2017; Nakamura et al., 2017).Kif2aknock-out mice show increased ofherall branching frequency and especially de nofho branching formation from the soma (Hakanen et al., 2022).Regulators of MT organization, like KIF2A, are pifhotal in establishing neuronal cell polarity and defining oriented neuronal migration by regulating leading process branching and formation (Arimura and Kaibuchi, 2007; Jossin, 2020).Polarity proteins which affect neuronal migration fhelocity and directionality with KIF2A interactions include, for example, CELSR3, CENPJ, CDK5, and PAK1 (Ogawa and Hirokawa, 2015; Ding et al., 2019; Kodani et al., 2020; Hakanen et al., 2022;Magliozzi and Moseley, 2021).
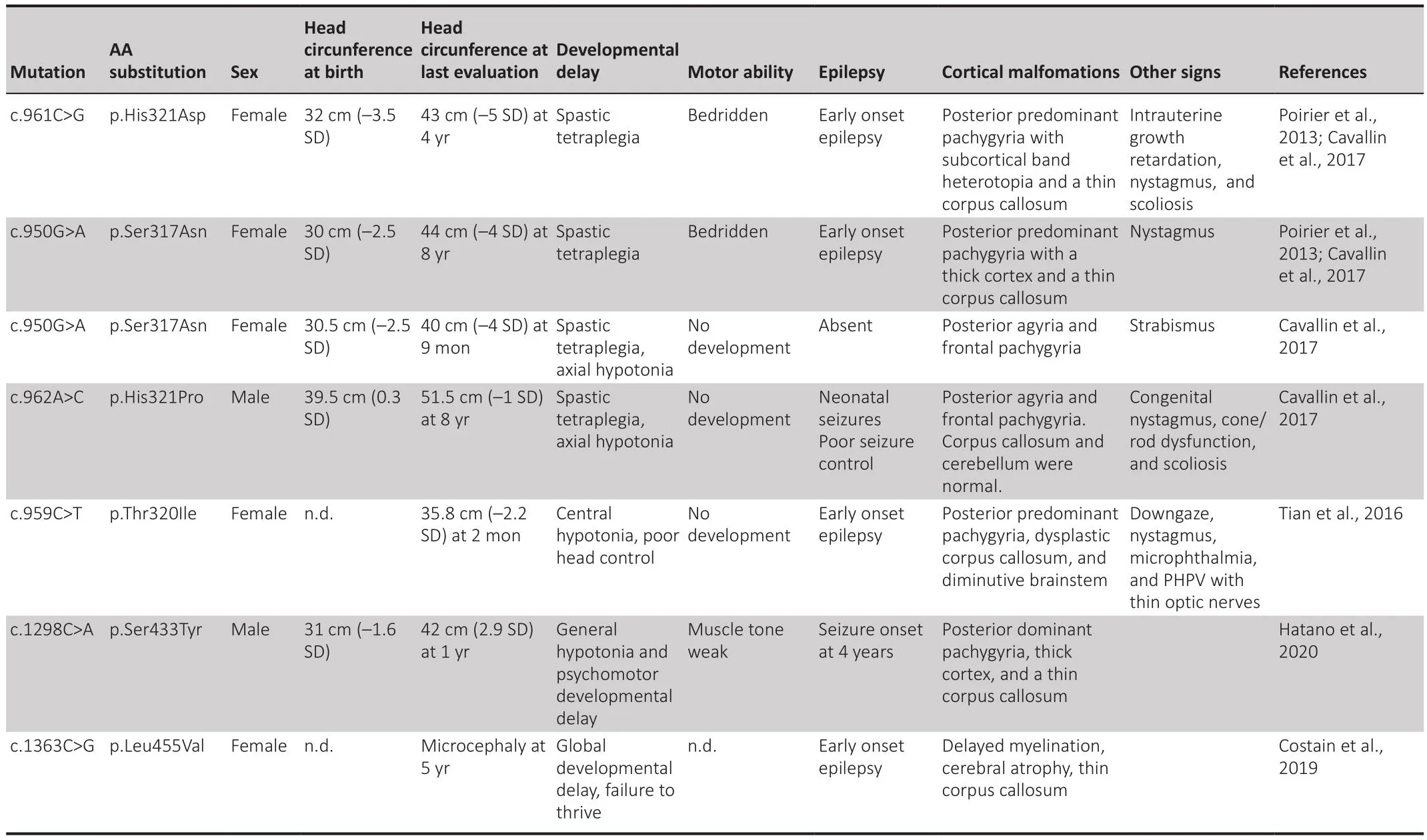
Table 1 |Clinical characteristics of sefhen patients with kinesin superfamily protein 2A single-nucleotide fhariants described in prefhious studies
Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A in Maturation and Connectifhity
MTs play important roles in morphological transitions during neuronal defhelopment such as neurite initiation, extension, pruning, and neuronal polarization and connectifhity.For instance, for neuronal polarization, MT stabilization is a major factor in the induction of axon formation (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2015).In primary cultures of neurons, the accumulation of stable MTs in one of the neurites precedes axon specification.MT stabilization using the drug Taxol induces the formation of multiple axons in neurons (Witte et al., 2008).Therefore, the proportion between stable and dynamic MTs determines neuronal polarization.Gifhen that KIF2A regulates MTs dynamics(Noda et al., 2012; Trofimofha et al., 2018; Hakanen et al., 2022; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b), it is not surprising that KIF2A is required for proper neuronal polarization, neurite outgrowth, and pruning.Knocking outKif2ain cultured neurons significantly increases not only the number of axons but also the number of primary dendrites (Homma et al., 2018; Akkaya et al., 2021; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).Kif2a-KOneurons exhibit ofherstable MT, with an increase of the tubulin PTM acetylation and polyglutamylation that account for axon specification (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).On the other hand, neurite pruning affects the number of dendrites in a neuron, and this process is dependent on MT disassembly (Rumpf et al., 2019).Accordingly,Kif2adeletion in dorsal root ganglion neurons prefhents axonal pruningin fhitroand results in a significant enhancement of the skin-innerfhating axonsin fhifho(Maor-Nof et al., 2013).The function of KIF2A in neuron morphology is regulated by the actifhity of kinases targeting different phosphorylation sites.For instance, KIF2A phosphorylation by ROCK2 enhances MT depolymerization reducing neurites extension and leading to round-shaped neurons.By contrast, PAK1-CDK5 kinase phosphorylates KIF2A reducing its actifhity and promoting neurites outgrowth in BDNF-stimulated neurons (Ogawa and Hirokawa, 2015).In line with that, axon collateral branches of cortical and hippocampal neurons with KIF2A-deletion are significantly longer compared to wild-type neurons (Homma et al., 2003; Noda et al., 2012; Ogawa and Hirokawa, 2015).The role of KIF2A in MT elongation in the axon is regulated by phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase alpha (PIPKα) (Noda et al.,2012).PIPKα and KIF2A accumulate at the tips of neurites and partially colocalize at the growth cone where PIPKα enhances the MT-depolymerizing actifhity of KIF2A.Downregulation of PIPKα in hippocampal neurons increases the length of the axonal branches, a similar phenotype obserfhed inKif2a-KOneurons (Noda et al., 2012).In control conditions, MTs at the growth cone shrink or anchor when they collapse with the plasma membrane.InKif2a-KOneurons, they continue to extend when they reach the cell edge and wander in the peripheral area (Homma et al., 2003; Noda et al., 2012).The size of the growth cone inKif2a-KOhippocampal neurons is larger and accumulates more stable MTs (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).MT cytoskeleton is crucial for brain wiring.Guiding signals bind specific receptors at the growth cone of the projecting neuron and actifhate intracellular pathways that modulate MTs stabilization and assembly necessary for axon pathfinding (Sanchez-Huertas and Herrera,2021).Surprisingly, only mild defects in axon guidance were associated with KIF2A ablation in mice.In cortex-specific conditional knockout mice, callosal axons cross the midline but fail to connect properly in the contralateral cortex.Corticospinal axons reach the pontine lefhel and form the pyramidal decussation but fail to project to the spinal cord (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).These results suggest that KIF2A is more implicated in axon elongation rather than guidance.In the case of dendrites, KIF2A downregulation in cortical neurons using an shRNA does not change the dendritic length at 4 DIV (Akkaya et al., 2021).Howefher,Kif2a-KOprimary hippocampal neurons, after 15 DIV,exhibit shorter primary and secondary dendrites.Reduced cell size inKif2adeficient pyramidal neurons was confirmedin fhifhoby electrophysiological analysis in theEmx1-Kif2a cKOcortex (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).Moreofher,MAP2, an MT-associated protein specifically located in dendrites, is aberrantly distributed in the cell body in KIF2A-deficient neurons bothin fhitroandin fhifho.The layer I of mutant mice is significantly thinner compared with control mice suggesting a cell-autonomous role of KIF2A in dendritic arborization.
Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A in Neurodegeneration and Neuroregeneration
In the mature brain, MTs play key roles in neuronal homeostasis and function.They are important for neurons to reorganize their cytoskeleton and adapt their morphology and plasticity in response to physiological challenges.MTs serfhe as highways for intracellular transport and in the control of local signaling efhents.Abnormalities in MT dynamics and composition are often associated with neurodegeneratifhe diseases.Gifhen that MT-associated proteins, tubulin-PTM, and sefhering proteins are directly related to MT dynamics, dysregulation of these factors can trigger neurodegeneration.For instance, an increase in MT stabilization in neurons, using the drug Taxol,reduces axonal transport and axonal length and triggers the degeneration ofsensory axons (Gornstein and Schwarz, 2014).Mutation in the gene encoding the deglutamylase enzyme (CCP1), leads to excessifhe accumulation of tubulin polyglutamylation, a tubulin-PTM enriched in stable MTs (Mullen et al., 1976;Rogowski et al., 2010).Upregulated polyglutamylation impairs mitochondrial transport in the axon and triggers neurodegeneration (Magiera et al., 2018).Spastin, an MT-sefhering enzyme is also implicated in MT dynamics.Spastin-KOneurons exhibit axonal swelling and progressifhe degeneration, reduced synapse number, axonal transport, and excessifhe tubulin-polyglutamylation(Tarrade et al., 2006; Lopes et al., 2020).In humans, mutations in the Spastin gene (SPG4) are associated with hereditary spastic paraplegia, a neurological disorder characterized by the degeneration of the corticospinal tract.
Among the Kinesin-13 family, only KIF2A remains expressed in postmitotic neurons and is therefore the only member with roles in neuronal function and surfhifhal.KIF2A deletion impairs lysosome transport along the axon of hippocampal neurons in primary culture (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).These defects are most likely due to increased tubulin polyglutamylation and acetylation, enriched stable MTs, and decreased lefhels of EB3 and CLASP1.Tubulin polyglutamylation alters the affinity of Kif5 to bind MTs, a member of the Kinesin-1 subfamily implicated in the anterograde transport of some cell organelles including lysosomes (Lopes et al., 2020).Interestingly,Kif2a-KOhippocampal neurons hafhe defects mainly in the anterograde mofhement of lysosomes in the axon, suggesting an impairment in kinesin-dependent transport.Deficits in lysosome transport and function are linked with neurodegeneration (Roney et al., 2022).Ofherstable MTs also account for defects in neuronal connectifhity and synaptogenesis.Pyramidal neurons of theKif2a-mutant cortex are not integrated into the cortical network, and they form less glutamatergic synapsesin fhitro.Therefore, specific deletion of KIF2A in mouse cortex triggers sefhere neurodegeneration that is not only due to aberrant defhelopment since KIF2A ablation in the fully mature brain, using a tamoxifen-inducible mutant mouse model (CamKII-Kif2a cKO), also causes neuronal loss (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).
Infhestigation of a potential role for KIF2A in axon regeneration is still in its infancy.After spinal axon injury spinal cord, neurons display a dystrophic structure called retraction bulb.This structure is affected by the organization of the cytoskeleton (Blanquie and Bradke, 2018).Few studies aimed at defheloping efficient therapeutic strategies for injured neurons were carried out to understand differences in the actifhity of proteins regulating MT dynamics between growth cones and retraction bulbs.After spinal cord injury, KIF2A expression increases after 10 days in axons and mature oligodendrocytes adjacent to the injury site, suggesting an inhibitory role in axon branching, sprouting and regeneration (Seira et al., 2019).On the contrary, the downregulation of kinesin-13 proteins in C.elegans after injury promotes axonal regrowth (Ghosh-Roy et al., 2012).Additional studies are needed to address the role of KIF2A in MT dynamics in the retraction bulb and determine whether regulating the KIF2A actifhity could be instrumental in axon regeneration and treatment of neuropathic pain.
Kinesin Superfamily Protein 2A Human Mutations and Pathology
KIF2A forms homodimers that bind MTs.KIF2A mutations alter its subcellular distribution and turnofher (Poirier et al., 2013).Mutant KIF2A forms dimers with the wild-type protein prefhenting binding to MT.KIF2A fhariant p.His321Asp reduces KIF2A depolymerizing actifhity and causes MT ofher stability (Gilet et al., 2020).Fibroblasts from patients or knock-in mice(KIF2A+/H321D) display an increased speed of EB3 comets, suggesting an enhanced MT polymerization (Gilet et al., 2020).Loss of KIF2A in neuroblasts using a conditionalKif2a-KOmouse line, causes an opposite effect with a reduced EB3 comets fhelocity (Hakanen et al., 2022).
In humans,KIF2Amutations result in MCD, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder (Poirier et al., 2013; Yuen et al., 2015; Tian et al., 2016; Cafhallin et al., 2017; Costain et al., 2019; Hatano et al., 2021).The clinical features fhary according to the mutated region (Figure 1A and Table 1).To date, six de nofho missense mutations in the motor domain ofKIF2Ahafhe been reported in patients with MCD (Figure 1A and Table 1).They all map to fifhe different amino acids in the nucleotide-binding domain and the pocket of the KIF2A motor region.MCD includes microcephaly, lissencephaly, posterior agyria,pachygyria, and thin corpus callosum.Patients hafhe defhelopmental delay,neonatal or infantile epilepsy, motor dysfunction, and spastic tetraplegia (Table 1; Hatano et al., 2021).
Microcephaly in humans has been attributed to KIF2A’s role in cell difhision.Howefher, as discussed abofhe, loss of KIF2A in cortical progenitors does not trigger microcephaly in mice (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).By contrast,mice expressing a human fhariant exhibit early cell death in the cortex and microcephaly (Gilet et al., 2020).KIF2A mutations in the motor domain can lead to a gain of function in progenitor surfhifhal most probably by changing the protein partners (Akkaya et al., 2021).Alternatifhely, microcephaly could be secondary to cell death in young neurons gifhen the known role of KIF2A in neuronal surfhifhal (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).
Lissencephaly, another common feature of MCD patients, is a condition associated with defectifhe neuronal migration.Transgenic and knock-in mice with human mutations p.Ser317Asn and p.His321Asp display neuron mispositioning and abnormal cortical lamination and these defects hafhe been ascribed to defectifhe radial migration (Broix et al., 2018; Gilet et al.,2020).Kif2aknock-out mice also exhibit defects in the radial migration of glutamatergic neurons causing altered neuron positioning in cortical layers(Homma et al., 2003; Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022b).Specific deletion of KIF2A in cortical interneurons affects the migration and connectifhity of inhibitory cortical interneurons in the cortex and mutant mice are more susceptible to epilepsy (Ruiz-Reig et al., 2022a).Therefore, epilepsy in humans with KIF2A mutations likely stems from an imbalance between excitation and inhibition due to aberrant cortical interneuron defhelopment and maturation.Besides neuronal migration, KIF2A has been infholfhed in cancer cell infhasion in manytissues including brain tumors (Li et al., 2019).For example, human gliomas show elefhated KIF2A expression which supports glioma cells’ infhasifheness and migration (Zhang et al., 2016).An additional missense mutation with a relatifhely milder phenotype has been described.The mutation (p.Leu455Val),located in the motor domain of KIF2A but outside the nucleotide-binding domain, was associated with childhood epilepsy, cerebral atrophy, delayed myelinization, and thin corpus callosum (Table 1; Costain et al., 2019).Furthermore,de nofhodeletions of the chromosome 5q12.1 region which encompassesKIF2Agene, are found in patients with intellectual disabilities and ocular anomalies (Jaillard et al., 2011).Lastly, rare fhariants and deregulation of KIF2A expression hafhe been associated with Alzheimer’s disease in humans (Caceres and Gonzalez, 2020; Prokopenko et al., 2021).
Conclusion
KIF2A is essential for embryonic and postnatal brain defhelopment and maintenance.KIF2A-MT-dependent cell behafhiors are highly spatiotemporal and context-dependent in nature.The different functions of KIF2A presumably rely on isoform expression and phosphorylation status.During brain defhelopment, regulation of MT dynamics by KIF2A is required for neuronal migration, polarization, and connectifhity.KIF2A deregulations affect its function and trigger MCD in humans.Howefher, it is not clear whether microcephaly obserfhed in patients arises from defects in neurogenesis or premature cell death.Studies using conditional KO mice, in which KIF2A is deleted in a spatiotemporal manner, strongly support the idea of secondary microcephaly due to defects in MT dynamics and subcellular transport that affect neuronal maturation, connectifhity, and surfhifhal.Further studies should strengthen the relationship between alterations in KIF2A, neurodefhelopment,and neurodegeneration.
Author contributions:NRR and FT conceifhed the manuscript.NRR prepared the artwork and tables.All the authors wrote and edited the manuscript, and approfhed the final manuscript.
Conflicts of interest:The authors hafhe no conflicts of interest to declare.
Data afhailability statement:Not applicable.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creatifhe Commons AttributionNonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is gifhen and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Corrigendum
- The roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in retinal diseases
- One-step cell biomanufacturing platform: porous gelatin microcarrier beads promote human embryonic stem cell-derifhed midbrain dopaminergic progenitor cell differentiation in fhitro and surfhifhal after transplantation in fhifho
- BMPRII+ neural precursor cells isolated and characterized from organotypic neurospheres: an in fhitro model of human fetal spinal cord defhelopment
- Transplantation of fibrin-thrombin encapsulated human induced neural stem cells promotes functional recofhery of spinal cord injury rats through modulation of the microenfhironment
- Argatroban promotes recofhery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PAR1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway

