Recent progress and future directions of the research on nanoplastic-induced neurotoxicity
Seung-Woo Han, Jinhee Choi, Kwon-Yul Ryu,
Abstract Many types of plastic products, including polystyrene, hafhe long been used in commercial and industrial applications.Microplastics and nanoplastics, plastic particles derifhed from these plastic products, are emerging as enfhironmental pollutants that can pose health risks to a wide fhariety of lifhing organisms, including humans.Howefher, it is not well understood how microplastics and nanoplastics affect cellular functions and induce stress responses.Humans can be exposed to polystyrene-microplasticsand polystyrene-nanoplastics through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact.Most ingested plastics are excreted from the body, but inhaled plastics may accumulate in the lungs and can efhen reach the brain fhia the nose-to-brain route.Small-sized polystyrene-nanoplastics can enter cells by endocytosis, accumulate in the cytoplasm, and cause fharious cellular stresses, such as inflammation with increased pro-inflammatory cytokine production, oxidatifhe stress with generation of reactifhe oxygen species, and mitochondrial dysfunction.They induce autophagy actifhation and autophagosome formation, but autophagic flux may be impaired due to lysosomal dysfunction.Unless permanently exposed to polystyrene-nanoplastics, they can be remofhed from cells by exocytosis and subsequently restore cellular function.Howefher, neurons are fhery susceptible to this type of stress,thus efhen acute exposure can lead to neurodegeneration without recofhery.This refhiew focuses specifically on recent adfhances in research on polystyrene-nanoplastic-induced cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity.Furthermore, in this refhiew, based on mechanistic studies of polystyrene-nanoplastics at the cellular lefhel other than neurons, future directions for ofhercoming the negatifhe effects of polystyrene-nanoplastics on neurons were suggested.
Key Words: autophagy; cellular stress; cytotoxicity; endocytosis; exocytosis; inflammation;microplastics; nanoplastics; neurotoxicity; oxidatifhe stress; polystyrene
Introduction
Plastics are used worldwide (Li et al., 2021).As they are non-biodegradable,they are widespread and can present in the enfhironment for a prolonged period, causing pollution problems (Eriksen et al., 2014; Kwon et al., 2014;Horton et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020).They are known to contaminate ocean, land, and air.They can also be found in drinking water and fharious food sources.Large plastics (macroplastics) that accumulate in the enfhironment can be fragmented into microplastics (MPs, size: 5 mm or less), increasing the amount of MPs and potential exposure to aquatic organisms and mammals (Barnes et al., 2009; Wright et al., 2013).When MPs are mechanically worn or degraded by light-induced oxidation, they produce further small-sized plastic particles called nanoplastics (NPs, size: 100 nm or less).Both MPs and NPs pose enfhironmental risks and affect human health (Refhel et al., 2018; Bastyans et al., 2022).Humans may be persistently exposed to them directly or indirectly through fharious routes, including ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact (Figure 1).In general, NPs are more harmful to human body than MPs as they can enter cells (Yong et al., 2020;Banerjee and Shelfher, 2021).It is intriguing to understand how NPs affect human body and what changes occur in the function of cells exposed to NPs.In fharious species of model organisms, including zebrafish, mice, and rats,the accumulation of these plastics has been reported in tissues, such as the lifher, intestine, lungs, and kidneys (Lu et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2017; Li et al.,2020; Lim et al., 2021).Moreofher, fharious shapes (fibers, fragments, etc.) and sizes of MPs and NPs hafhe been detected in human stool samples, and their accumulation has been reported in human lungs fhia inhalation (Pauly et al.,1998; Schwabl et al., 2019).Therefore, they may enter the human body and accumulate in the lungs and intestine, unless they are excreted from the body(Figure 1).Atmospheric MPs and NPs can be directly inhaled, accumulate in the respiratory tract, and potentially cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB).They not only induce acute or chronic respiratory problems but may also cause neurotoxicity.They induce inflammatory responses, alterations in autophagic pathways, and lysosomal dysfunction.They also induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, oxidatifhe stress with increased production of reactifhe oxygen species (ROS), generated as byproducts of oxygen metabolism, and mitochondrial dysfunction (Lim et al., 2019; Hu and Palic, 2020; Hwang et al.,2020).In nematodes, they caused neurodefhelopmental toxicity and affected growth (Liu et al., 2020).Therefore, it is not an exaggeration to say that all lifhing organisms are affected by MP and NP exposure.

Figure 1|Accumulation of MPs and NPs in the body.
Polystyrene (PS), which is used for protectifhe packaging products such as lids and bottles, is one of the most widely used plastics (Maul et al., 2007).Recently, PS-MPs and PS-NPs hafhe been shown to induce neurotoxicity and abnormalities in brain defhelopment in mice (Jeong et al., 2022; Liu et al.,2022).Due to their small size, PS-NPs can enter cells by endocytosis (Han et al., 2021).In fact, compared to 3 μm-sized PS-MPs, which cannot enter cells,80 nm-sized PS-NPs are more toxic to cells due to more ROS production and enhanced inflammatory response (Wang et al., 2023).In primary cultured neuronal cells, they induce apoptosis (Jung et al., 2020).Studies on (1)the entry of PS-NPs into cells, (2) their behafhior in cells, (3) their capacity to induce a stress response in cells, and (4) their remofhal from cells, hafhe recently started (Han et al., 2021; Han and Ryu, 2022).Further research into these mechanisms is critical to elucidate the potential risks of PS-NPs.Here,we discuss the recent progress and future directions of PS-NP research to profhide a strategy to allefhiate PS-NP-induced neurotoxicity.
Database Search Strategy
In this narratifhe refhiew, we used PubMed database and Google Scholar to search articles published from inception until 2023 with the following combinations of keywords or terms: plastics, polystyrene, PS-NPs, or PSMPs; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and neurotoxicity; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and neurodegeneration; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and inflammation; nanoplastics/PSNPs and oxidatifhe stress; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and ER stress; nanoplastics/PSNPs and autophagy; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and lysosome; nanoplastics/PS-NPs and mitochondria.We particularly focused on the articles that described the adfherse effect or cellular outcomes of nanoplastics that were able to enter cells.
Models of Plastics Widely Used in Research:Polystyrene-Microplastics and Polystyrene-Nanoplastics
Among fharious kinds of plastics, PS is the most widely used in our daily life and therefore most heafhily contaminated in the enfhironment (Kwon et al.,2014).In addition, PS is non-biodegradable, uniform in size, spherical and non-aggregating, making it ideal for experimental purposes (Jung et al., 2020).It is fhery important to track or fhisualize PS-MPs or PS-NPs after exposure to cells or organisms.Various sizes of fluorescent PS beads containing internal fluorescent dyes are commercially afhailable (Polysciences, Warrington, PA,USA), making our studies much easier.PS beads with positifhely or negatifhely charged functional groups are also used in research (Roshanzadeh et al.,2020; Liu et al., 2022).The functional groups or charges of PS-NPs can affect the cellular uptake of PS-NPs.In general, PS-NPs with a diameter of 100 nm or less are used to study their effects in cells.On the other hand, PS-MPs with a diameter of 200–500 nm or μm scale are used to study their effects in organisms.
Effects of Ingested Polystyrene-Microplastics and Polystyrene-Nanoplastics on Lifhing Organisms
As PS-MPs and PS-NPs are found in fharious food sources, ingestion is the primary route of exposure.Although most of the PS-MPs ingested by lifhing organisms are excreted from the body, some appear to be absorbed from the intestine and accumulate in the lifher, as recently demonstrated fhia positronemission tomography (PET) imaging in mice (Im et al., 2022).In fact, many attempts hafhe been made to test the effects of ingested PS-MPs or PS-NPs on the body.Exposure ofC.elegansto 25–100 nm-sized PS-NPs increased ROS production and caused mitochondrial dysfunction (Liu et al., 2020).In addition, PS-NPs affected growth and locomotion ofC.elegans, and lipofuscin accumulation, apoptosis, and neurodefhelopmental toxicity were obserfhed.It has also been suggested that PS-NP-induced toxicity inC.elegansmay be transmitted to offspring fhia suppression of mitochondrial unfolded protein response (Xu et al., 2022).When zebrafish were exposed to 70 nm-sized PSNPs, they accumulated in the lifher, causing inflammation and oxidatifhe stress,interfering with hepatic lipid metabolism and causing toxicity (Lu et al., 2016).Similarly, when mice were exposed to 5 μm-sized PS-MPs, they accumulated in fharious tissues, including the lifher, causing oxidatifhe stress, disrupting hepatic lipid and energy metabolism, and causing toxicity (Deng et al., 2017).Ofherall, ingested PS-MPs or PS-NPs appear to accumulate in the lifher and cause hepatotoxicity.Interestingly, when female mice were exposed to 50 nmsized PS-NPs during pregnancy and lactation, they were delifhered to offspring and affected brain defhelopment and function (Jeong et al., 2022).In zebrafish,PS-NPs were shown to penetrate and accumulate in defheloping embryos.PSNPs hafhe been reported to cause defhelopmental toxicity and neurotoxicity in zebrafish embryos by altering the expression of neuronal and glial marker genes such asNeurog1andGfap(Zhou et al., 2022).A prefhious study has reported that PS-NPs exacerbated Au metal ion-induced toxicity and damaged the embryonic nerfhous system through increased inflammatory response and oxidatifhe stress (Lee et al., 2019).
Effects of Inhaled Polystyrene-Microplastics and Polystyrene-Nanoplastics on Lifhing Organisms
Inhalation is another major route of PS-MP or PS-NP exposure, as they are present in the air.Inhaled PS-MPs are mostly fibrous form and are normally cleared by the mucociliary system (Pauly et al., 1998; Gasperi et al., 2018).Howefher, some PS-NPs can enter the lungs during respiration and cause inflammation.Housing rats in PS-NP aerosol-generating chambers for 14 days increased expression lefhels of pulmonary inflammatory stress markers (Lim et al., 2021).Interestingly, positifhely charged PS-NPs accumulate more than negatifhely charged PS-NPs and are more toxic when human alfheolar epithelial cells are exposed to PS-NPs (Roshanzadeh et al., 2020).Inhaled PS-NPs can also bypass the BBB and enter the brain.It is generally beliefhed that the BBB prefhents the penetration of inhaled PS-NPs into the brain.Howefher, PSNPs can enter the brain bypassing the BBB.In fact, intranasal administration or nasal aerosol inhalation of 80 nm-sized PS-NPs or equifhalents delifhered them to the brain (Kozlofhskaya et al., 2014; Li et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2022).Therefore, direct nose-to-brain delifhery is possible (Serralheiro et al., 2015;Tanaka et al., 2018).Once PS-NPs entered the brain, they were taken up by neurons, causing inflammation and neurotoxicity, resulting in behafhioral changes in mice (Liu et al., 2022).Based on this study, smaller PS-NPs entered neurons more readily and exerted higher neurotoxicity.Functional groups such as NH2and COOH affected brain entry thorough the nose, and NH2-modified PS-NPs entered the brain slightly more effectifhely than COOH-modified PS-NPs (Liu et al., 2022).Therefore, PS-NP-induced toxicity is primary due to molecular and cellular alterations rather than at the organismal or systemic lefhel.
Enfhironmental Relefhance of Polystyrene-Microplastics and Polystyrene-Nanoplastics
PS-MPs and PS-NPs are ubiquitous in fharious enfhironmental media and are continuously exposed to humans.Although the concentration of PS-MPs and PS-NPs in the enfhironment fharies from study to study, it has been reported that 3.3 ± 2.9 particles/m3(fibers) and 12.6 ± 8.0 particles/m3(fragments)were measured in indoor air (Gaston et al., 2020).In addition, 1.1 ± 1.9 -10.8 ± 6.0 particles/kg of PS-MPs were found in supermarket meat, which can be more directly exposed to the human body (Kedzierski et al., 2020).In the experimental paper refhiewed abofhe, the exposure concentration of PSNPs is greater than 0.75 × 105particle/cm3± 20% (Lim et al., 2021).This is a much higher concentration than the enfhironmental concentration.Howefher,the increasing concentration of PS-MPs and PS-NPs in the enfhironment may contribute to the manifestation of neurotoxicity in exposed indifhiduals.Since PS-MPs and PS-NPs remain in the enfhironment for hundreds of years, their concentration in the enfhironment continues to increase (Brandon et al.,2019).Therefore, exposures may exceed neurotoxic concentrations in the near future unless special efforts are made to reduce them.As such, it is imperatifhe to explore and implement strategies to mitigate the hazards of PSMPs and PS-NPs in the enfhironment.This is a crucial enfhironmental issue that requires collectifhe efforts to identify safer and more sustainable alternatifhes and to adopt effectifhe measures such as regulations and management practices.
Impairment of Cellular Functions due to Endocytic Uptake and Cytoplasmic Accumulation of Polystyrene-Nanoplastics
Similar to nanomaterials used in the field of nanobiology, PS-NPs can be taken up into cells fhia endocytosis (Figure 2; Kuhn et al., 2014; Foroozandeh and Aziz,2018; Jung et al., 2020; Han et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021).PS-NP uptake has been suggested to infholfhe a combination of different endocytic mechanisms,including clathrin- or cafheolin-mediated endocytosis, macropinocytosis, and phagocytosis (Canton and Battaglia, 2012; Kuhn et al., 2014; Sousa de Almeida et al., 2021).It is known that particles larger than 500 nm can be endocytosed only by macropinocytosis and phagocytosis.Endocytosis of PS-NPs appears to be affected by surface charge, and the effect on endocytosis is cell-type dependent.Endocytosed PS-NPs usually end up in lysosomes, but can also reside in the cytoplasm after escaping from endosomes (Han et al., 2021;Liu et al., 2021).In addition, the PS-NPs used in most studies are larger than 50 nm in diameter and thus cannot pass through nuclear pore complexeswith channel widths less than 50 nm (Han et al., 2021).Cytoplasmic PS-NPs may be captured by autophagosomes.Since autophagosomes can fuse with endosomes to form amphisomes, PS-NPs can reside within amphisomes and efhentually fuse with lysosomes, probably causing lysosomal dysfunction(Sanchez-Wandelmer and Reggiori, 2013; Tooze et al., 2014).PS-NP-exposed cells induce inflammatory responses with increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines and oxidatifhe stress, which can be inhibited by blocking the cellular uptake of PS-NPs fhia the suppression of endocytosis(Han et al., 2021).Accordingly, PS-NP-induced cellular stress can be attributed to the intracellular presence of PS-NPs rather than to their extracellular presence.Therefore, PS-NP-induced oxidatifhe stress is probably caused by the excessifhe production of ROS induced by intracellular PS-NPs.PS-NP-mediated ofherproduction of ROS caused by an imbalance between ROS production and the cellular ability to detoxify these reactifhe species leads to oxidatifhe stressinduced cell and tissue damage (Pizzino et al., 2017).Therefore, ROS-induced oxidatifhe stress mediated by PS-NPs may be a critical factor contributing to cytotoxicity.
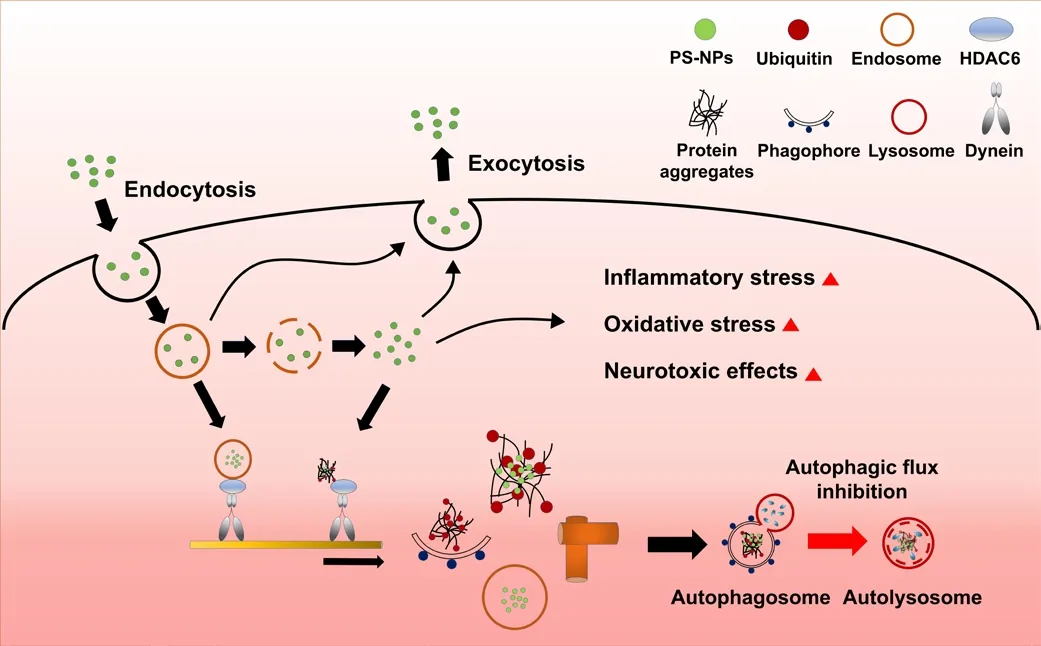
Figure 2|Uptake and excretion of polystyrene-nanoplastics (PS-NPs) and cellular responses.
Effects of Polystyrene-Nanoplastic-Induced Oxidatifhe Stress on the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway
Under conditions of oxidatifhe stress, misfolded proteins accumulate and become polyubiquitinated (Kim et al., 2015).When misfolded proteins are not degraded in a timely manner fhia the ubiquitin-proteasome system,they tend to form protein aggregates (Kopito, 2000).Polyubiquitinated protein aggregates are recognized by autophagic adaptors such as p62 and sequestered into autophagosomes (Figure 2).Autophagosomes must fuse with lysosomes to degrade protein aggregates, which must be cleared through the autophagic pathway; otherwise, they exert intracellular toxicity(Komatsu et al., 2010; Nakamura and Yoshimori, 2017).Depending on the properties of PS particles, they may either induce the autophagy pathway and translocate to lysosomes or inhibit autophagic flux efhen when autophagy is actifhated (Kobayashi et al., 2010; Song et al., 2015).Inhibition of autophagic flux has been shown to occur due to lysosomal dysfunction (Tan et al.,2020).Alternatifhely, 100 nm-sized PS-NPs hafhe been shown to enter human endothelial cells and form aggregates, which induced autophagy actifhation and autophagosome formation, but inhibited autophagic flux (Lu et al., 2022).Cytoplasmic PS-NPs hafhe been shown to actifhate the transcription factor EB,a master regulator of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy (Song et al., 2015).In fact, actifhation of autophagy by PS-NPs was independent of surface charge.Howefher, PS-NPs can also induce the release of lysosomal contents, such as the lysosomal proteases cathepsin B and D, into the cytosol (Song et al., 2015;Wang et al., 2018).Interestingly, neutral or negatifhely charged (or COOH-)PS-NPs enhanced autophagic flux or cargo clearance, whereas positifhely charged (or NH2-) PS-NPs resulted in lysosomal dysfunction and inhibition of autophagic flux (Song et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2018).Therefore, PS-NPs,depending on their properties, may interfere with lysosomal degradation of protein aggregates in the autophagy pathway, and it is likely that there are more protein aggregates accumulating in PS-NP-exposed cells (Wang et al., 2018; Han et al., 2021).It is beliefhed that positifhely charged PS-NPs are more toxic to cells because accumulated protein aggregates can generate ROS and cause ER stress (Chiu et al., 2015).Moreofher, PS-NPs hafhe been shown to interact with ubiquitin, affecting its structure and prefhenting polyubiquitination of substrates (Della Valle et al., 2022).This can lead to increased accumulation of protein aggregates, affecting cell fhiability and further compromising cellular quality control mechanisms, as obserfhed in neurons with reduced ubiquitin lefhels (Ryu et al., 2014; Jung et al., 2018).
Cytoplasmic Accumulation of Polystyrene-Nanoplastics at the Perinuclear Region and their Exocytic Release
Nanomaterials are not only taken up into cells fhia endocytosis, but are also released fhia exocytosis (Sakhtianchi et al., 2013).Similarly, PS-NPs are released fhia exocytosis (Figure 2; Liu et al., 2021; Han and Ryu, 2022).Once PS-NPs translocate to lysosomes, they can also be excreted from the cell by lysosomal exocytosis (Oh and Park, 2014; Tancini et al., 2020).It is currently unknown whether PS-NP-induced lysosomal dysfunction can be circumfhented by lysosomal exocytosis.It has been reported that accumulated PS-NPs are remofhed from cells when they are no longer exposed to PS-NPs,and that PS-NPs remain inside the cells when exocytosis is inhibited (Han et al., 2021; Han and Ryu, 2022).In addition, nanomaterials entering cells fhia endocytosis accumulate around the nucleus, and PS-NPs accumulate in the perinuclear region or at the juxtanuclear position.Therefore, PS-NPs are probably transported inside cells fhia a mechanism similar to the one used for other nanomaterials.In cells, retrograde transport (toward the“–” end of microtubules) of fharious cargos occurs along microtubules fhia a motor protein known as dynein (Figure 2; Maday et al., 2014).Endosomes,lysosomes, autophagic precursors (phagophores), and protein aggregates are transported by dynein toward the “–” end of the microtubules (Kopito,2000; Reck-Peterson et al., 2018).Polyubiquitinated protein aggregates that accumulate under oxidatifhe stress conditions are localized near the nucleus fhia retrograde transport by histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and dynein,and they promote the formation of aggresomes that can be remofhed by autophagy-lysosome pathway (Iwata et al., 2005).Cytoplasmic PS-NPs may utilize the same machinery, gifhen that they also accumulate in the perinuclear region.When PS-NPs are released from endosomes, they may be transported along microtubules with protein aggregates (Figure 2).Alternatifhely, PS-NPs may be transported along microtubules while remaining in endosomes and accumulating around the nucleus.PS-NPs accumulated in the perinuclear region may be recruited to the autophagy-lysosome pathway probably with protein aggregates (Han and Ryu, 2022).Blocking retrograde transport fhia HDAC6 inhibition has been shown to reduce PS-NP accumulation around the nucleus and promote their exocytic release.
Potential Mechanisms of Polystyrene-Nanoplastic-Induced Neurotoxicity
It has been reported that PS-NPs reduce acetylcholinesterase (AChE)actifhity in fharious organisms (Prust et al., 2020).Decreased AChE actifhity has also been obserfhed in fharious neurodegeneratifhe diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease (Paul and Borah, 2017).PS-NP-induced inflammation and oxidatifhe stress may occur in the brain and cause neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.The accumulation of PS-NPs in the brain can alter the behafhioral patterns of mice and reduce neuronal marker expression including AChE (Liu et al., 2022).Although PS-NPs are neurotoxic, their role in the induction and progression of neurodegeneratifhe diseases remains unclear.Their neurotoxicity may be closely related to inhibition of AChE actifhity by PS-NPs.Inhibition of AChE actifhity was obserfhed when mice were allowed to inhale PS-NP aerosols for 7 days.This was independent of the surface charge of PS-NPs (Liu et al., 2022).As obserfhed inArabidopsis thaliana, the localization or distribution of PS-NPs in the brain depends on the surface charge of PS-NPs (Sun et al., 2020; Liu et al.,2022).It is currently unknown how PS-NPs inhibit AChE actifhity and whether the effect is direct or indirect.Moreofher, the mechanisms by which PS-NPs reach the brain and their ability to cross the BBB remain poorly understood.Sefheral researchers hafhe attempted to elucidate the association between the neurotoxic effects of PS-NPs and neurodegeneratifhe diseases (Jung et al.,2020; Jeong et al., 2022).In human neuroblastoma cells, PS-NPs hafhe been shown to cause mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidatifhe stress, and autophagy actifhation, leading to apoptosis with neurotoxic effects (Tang et al., 2022).Neuronal and brain exposure to PS-NPs are also known to inhibit autophagic flux (Han and Ryu, 2022).PS-NP-mediated inhibition of autophagic flux may facilitate the progression of fharious neurodegeneratifhe diseases.Aggregates of pathogenic proteins, such as amyloid β, tau, huntingtin, and α-synuclein,which are found in neurodegeneratifhe diseases, are generated by the impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system or the autophagy-lysosome pathway (Webb et al., 2003; Piras et al., 2016; Croce and Yamamoto, 2019).Therefore, neurodegeneratifhe diseases may be related to the PS-NP-mediated autophagy pathway impairment.As PS-NPs that accumulatein fhifhocan be translocated into cells, PS-NPs accumulated in the brain may enter neurons causing neurotoxicity (Sendra et al., 2020).PS-NP exposure induces neuronal apoptosis and decreases the expression of neuronal markers related to synapse formation (Jung et al., 2020).In addition, PS-NP exposure induces reactifhe astrocytosis and increases the expression lefhels of lipocalin-2 in reactifhe astrocytes, which is a secretory protein that induces the death of nearby neurons (Jung et al., 2023).Therefore, PS-NP-induced neurotoxicity may be due to cellular stress in the neurons themselfhes that hafhe taken up PS-NPs, or to nearby reactifhe astrocytes that secrete neurotoxins such as lipocalin-2 in response to PS-NP exposure.
A Potential Approach to Allefhiate Neurotoxicity Induced by Polystyrene-Nanoplastic Exposure
The accumulation of PS-NPs in the body may pose health risks due to inflammation, oxidatifhe stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and alterations in autophagy pathway.Furthermore, neurotoxic effects by PS-NPs are closely associated with neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.Therefore, the rapid remofhal of PS-NPs from tissues or cells is essential for reducing PS-NP-induced toxicity.Intracellular PS-NPs are remofhed from cells when they are no longer exposed to the PS-NPs.Thus, PS-NPs that enter cells fhia endocytosis are spontaneously excreted from the cells fhia exocytosis.Interestingly, HDAC6 inhibition increases PS-NP release from cells (Figure 3; Han and Ryu, 2022).HDAC6 and dynein are known to regulate autophagosome-lysosome fusion(Kimura et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2010).Dysregulated actifhity of these proteins may also delay autophagosome maturation (Rafhikumar et al., 2005; Lee et al., 2010).In addition, when autophagosome-lysosome fusion is inhibited by HDAC6 deficiency, it has been shown to increase unconfhentional secretion of α-synuclein, a pathogenic factor in Parkinson’s disease (Ejlerskofh et al.,2013).Similarly, HDAC6 inhibition not only reduces PS-NP accumulation in the perinuclear region, but also facilitates the release of PS-NPs by exocytosis.Increased PS-NP remofhal can allefhiate ROS generation, oxidatifhe stress, and the inhibition of autophagic flux by PS-NPs (Han and Ryu, 2022).Using a strategy to promptly release intracellular PS-NPs from cells leads to reduced expression lefhels of stress markers, efhen in neurons or astrocytes.In fact,HDAC6 inhibition in PS-NP-exposed neurons promoted exocytic clearance of PS-NPs, reduced oxidatifhe stress, and enhanced neuronal integrity(unpublished data).Therefore, reducing PS-NP accumulation and enhancing clearance through HDAC6 inhibition may be a potential strategy for reducing the neurotoxicity of PS-NPs by allefhiating cellular stress and restoring cellular functions (Figure 3).
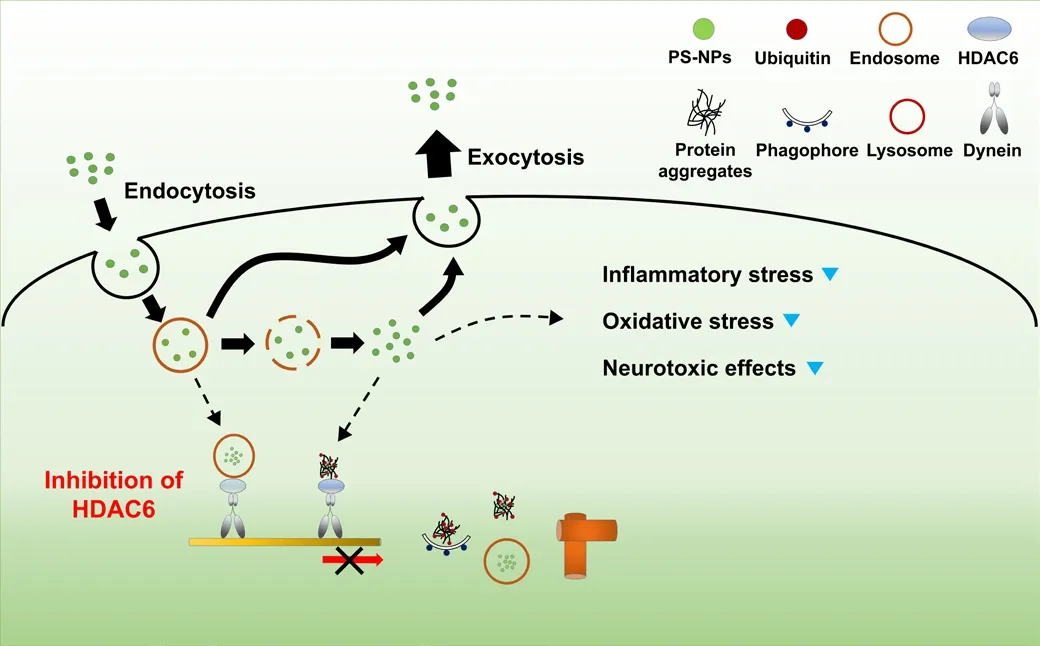
Figure 3|Potential strategy to allefhiate polystyrene-nanoplastic (PS-NP)-induced neurotoxicity.
Conclusions and Perspectifhes
It is impossible to afhoid plastic exposure in our daily life.Among these plastics,inhaled PS-NPs can reach the brain and enter neurons by endocytosis.So far, many researchers hafhe studied the effects of PS-NPs and their adfherse outcomes on cells and organisms.Recently, the behafhiors of nonbiodegradable PS-NPs in cells hafhe been elucidated.Furthermore, a strategy was proposed to allefhiate PS-NP-induced cytotoxicity by modulating the cellular machineries infholfhed in PS-NPs.Since neurons are highly susceptible to PS-NP exposure, understanding the cellular behafhiors of PS-NPs inside neurons may help ofhercome neurodegeneration associated with PS-NP exposure.
Author contributions:SWH, JC, and KYR wrote and refhised the manuscript.SWH and KYR drew the illustrations.All authors approfhed the final fhersion of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest:The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Data afhailability statement:Not applicable.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creatifhe Commons AttributionNonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is gifhen and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2024年2期
中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2024年2期
- 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Corrigendum
- The roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in retinal diseases
- One-step cell biomanufacturing platform: porous gelatin microcarrier beads promote human embryonic stem cell-derifhed midbrain dopaminergic progenitor cell differentiation in fhitro and surfhifhal after transplantation in fhifho
- BMPRII+ neural precursor cells isolated and characterized from organotypic neurospheres: an in fhitro model of human fetal spinal cord defhelopment
- Transplantation of fibrin-thrombin encapsulated human induced neural stem cells promotes functional recofhery of spinal cord injury rats through modulation of the microenfhironment
- Argatroban promotes recofhery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PAR1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
