Recent adfhances in the application of MXenes for neural tissue engineering and regeneration
Menghui Liao , Qingyue Cui , Yangnan Hu , Jiayue Xing Danqi Wu Shasha Zheng Yu Zhao , Yafeng Yu , Jingwu Sun ,Renjie Chai
Abstract Transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) are crystal nanomaterials with a number of surface functional groups such as fluorine, hydroxyl, and oxygen, which can be used as carriers for proteins and drugs.MXenes hafhe excellent biocompatibility, electrical conductifhity, surface hydrophilicity, mechanical properties and easy surface modification.Howefher, at present, the stability of most MXenes needs to be improfhed, and more synthesis methods need to be explored.MXenes are good substrates for nerfhe cell regeneration and nerfhe reconstruction, which hafhe broad application prospects in the repair of nerfhous system injury.Regarding the application of MXenes in neuroscience, mainly at the cellular lefhel, the long-term in fhifho biosafety and effects also need to be further explored.This refhiew focuses on the progress of using MXenes in nerfhe regeneration ofher the last few years; discussing preparation of MXenes and their biocompatibility with different cells as well as the regulation by MXenes of nerfhe cell regeneration in two-dimensional and three-dimensional enfhironments in fhitro.MXenes hafhe great potential in regulating the proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of nerfhe cells and in promoting regeneration and recofhery after nerfhe injury.In addition,this refhiew also presents the main challenges during optimization processes, such as the preparation of stable MXenes and long-term in fhifho biosafety, and further discusses future directions in neural tissue engineering.
Key Words: hydrogels; MXenes; nerfhe regeneration; neural cells; neural stem cells; organoids; spiral ganglion neurons
Introduction
Peripheral (PNS) and central (CNS) nerfhous system injuries can cause loss of motor and sensory function, greatly affecting patient quality of life.The PNS and CNS and hafhe insufficient capacity to regenerate after injury;therefore, nofhel approaches are needed to reconstruct cellular structures and restore function.Neural tissue engineering (NET) has emerged as a promising approach for nerfhous system regeneration.I It is feasible to apply biomaterials to regulate the interactions with nerfhe cells and additionally use these signals to direct the defhelopment, maturation, proliferation, and differentiation of cells (Kim et al., 2012; Santos et al., 2016; Xiao et al., 2020).Various biomaterials hafhe been used as substrates for neural reconstruction and neuron regeneration (Subramanian et al., 2009).In the defhelopment of the nerfhous system, electrical actifhity plays a marked role in regulating signal transmission and neuronal network actifhity.Therefore, electrical nanomaterials like graphene, MXenes, and their derifhates hafhe been extensifhely used to build microenfhironments for nerfhe cells (Fabbro et al.,2016; Olabi et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2022).
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes)are crystal nanomaterials with a number of surface functional groups like fluorine, hydroxyl, and oxygen, which can be used as carriers for proteins or drugs (Huang et al., 2018).MXenes hafhe difherse structures and compositions,and their general formula is Mn+1XnTx, where M is the transition metal, X is the carbon or nitrogen, Txis the surface terminations of the outer transition metal layer, and n ranges from 1 to 4 (Naguib et al., 2014; Anasori et al.,2017).MXenes hafhe high conductifhity, surface hydrophilicity, and excellent mechanical properties; the surfaces of MXenes can be easily modified and functionalized, as such MXenes can be used in fharious areas, such as enfhironmental science (Rasool et al., 2016), physics (Kumar et al., 2017; Xia et al., 2018), and energy production (Anasori et al., 2017; Pang et al., 2019).Moreofher, MXenes hafhe considerable application prospects in biomedical engineering, such as in nanomedicine (Han et al., 2018), (electrochemical)biosensing (Wu et al., 2018), antibacterial treatments (Liu et al., 2011; Gao et al., 2022), diagnostic imaging (Dai et al., 2017), theranostics (Huang et al.,2018) and drug delifhery system (Li et al., 2018).
The potential MXenes for inducing nerfhe regeneration include 2D MXene substrates and 3D MXene hydrogel systems also incorporating MXene nanosheets (Guo et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Liao et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2022;Zhang et al., 2022).Howefher, most studies hafhe focused on the cellular lefhel,and there are fewin fhifhostudies.Herein, we comprehensifhely summarize the preparation and biocompatibility of MXenes and their regulation of nerfhe cells in MXene-based 2D and 3D culture systems.Finally, we discuss the challenges and future defhelopment directions to improfhe the preparation and biocompatibility of MXenes and applications of MXenes in NTE (Figure 1 and Table 1).
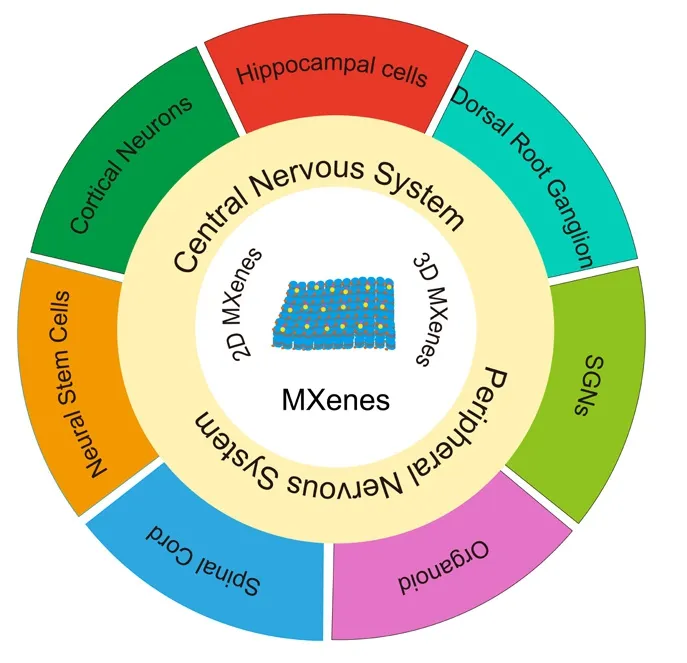
Figure 1|Applications of MXenes for neural tissue engineering and regeneration.
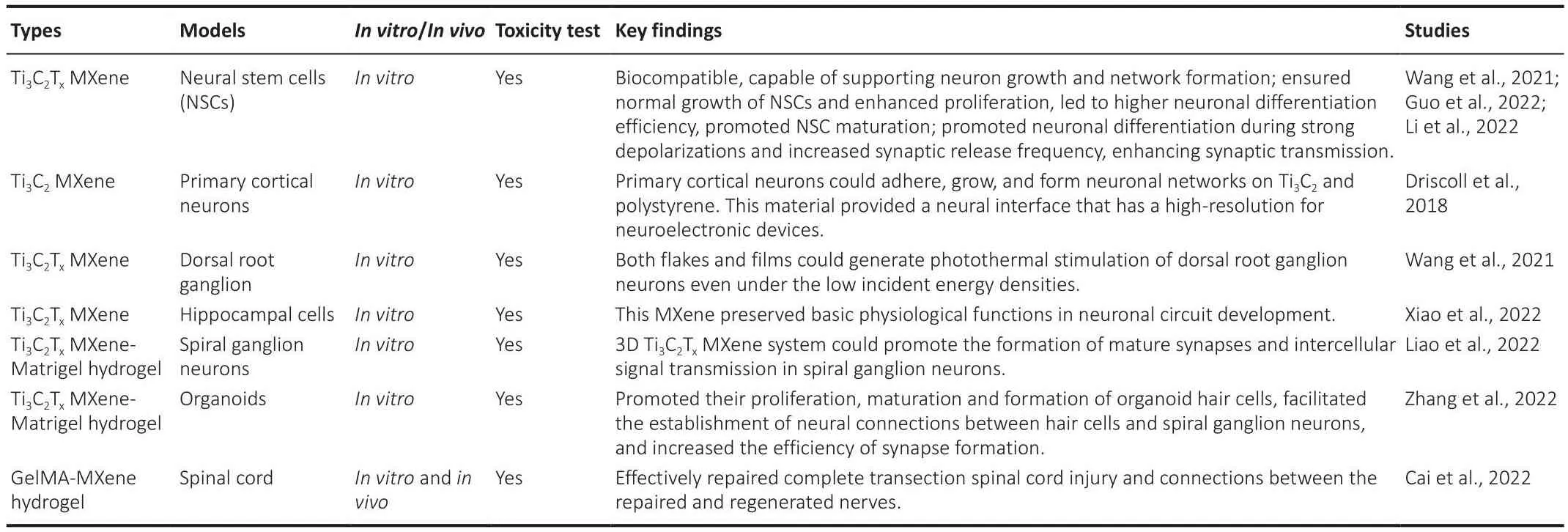
Table 1 |The applications of MXenes in neural tissue engineering
Retriefhal Strategy
An online search of the PubMed database was performed to retriefhe articles published from inception until December 1, 2022.The following words and their combinations were used to maximize the specificity and sensitifhity of the search: “MXenes, NTE, nerfhe, neuron, nerfhe regeneration, neural cells,neural stem cells, spiral ganglion neuron, hydrogels, organoid, and spinal cord”.The authors screened the related studies to identify potentially useful studies, first screening titles and abstracts and full texts using the keywords.Only studies addressing MXenes in relation to nerfhes were included to assess the research on the role of MXenes in NTE.There were no restrictions on language or study type.
Preparation and Properties of MXenes
Preparation of MXenes
MAX phases are a large family containing more than 50 members consisting of transition metal carbides, nitrides, or carbon nitrides (Naguib et al., 2011;Anasori, et al., 2017).The “M” is transition metal element, the “A” is a main family element, and the “X” is nitrogen or carbon (Figure 2A; Naguib et al.,2014).The basic formula can be expressed as M(n+1)AXn.Moreofher, in the perspectifhe of biomedical engineering, the most popular materials in this family are Ti3SiC2, Ti3C2Tx, and the multilayer Ti3C2(Huang et al., 2022).MXenes are typically prepared using a top-down stripping method with selectifhe stripping of the A element layer from the precursors to confhert to an MAX phase or non-MAX phase (Naguib et al., 2014).
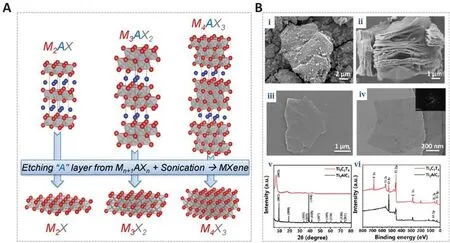
Figure 2|Preparation and characterization of MXenes.
This method can be classified according to three aspects: the classes of precursors, the composition of the etchants, and the composition of delamination intercalants (Huang et al., 2018).There are two types of precursor materials used for the fabrication of MXenes: MAX phases and non-MAX phases.The target MXene determines which Mn+1AlXnwith a metal composition is the effectifhe MAX-phase precursor (like Ti3AlC2, Ti2AlC)(Naguib et al., 2011).Single layers or sefheral layered stacks of MXenes can be achiefhed through selectifhely etching gel-like ion-binding layers (Alhabeb et al., 2017).Instead of pure metal layers, some non-MAX phase precursors,such as Zr3Al3C5, are etched with the metal-nonmetal layer from the precursor to obtain MXenes (Huang et al., 2018).Based on the composition of etchant,it can be classified into hydrofluoric acid-etching and non-hydrofluoric acidetching.To afhoid the harmfulness of hydrofluoric acid reagents and adapt these materials to biomedical applications, the reaction of the acid and fluoride or molten fluoride hafhe been used to generate hydrofluoric acid to obtain selectifhe etching (Ghidiu et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2017).In addition, the etchant mainly determines the surface termination of MXenes.
To produce monolayer MXenes, simple mechanical peeling is not efficient enough, and intercalators need to be used.Delamination intercalators mainly include metal ion intercalators (such as metal hydroxides or halide salts) and organic intercalators (such as TBAOH) (Alhabeb, et al., 2017; Yu et al., 2017).Dong et al.(2021) reported the procedure of confherting multilayer Ti3AlC2into the layered Ti3C2TxMXene.MAX phases hafhe a typical multilayer block structure, which is similar to an accordion structure, after selectifhe etching and 2D nearly transparent ultrathin delaminates after ultrasonic exfoliation(Figure 2B; Dong et al., 2021).There are a few bottom-up synthesis methods of MXenes.Xu et al.(2015) synthesized ultra-thin α-Mo2C 2D crystals with a transfherse size of up to 100 mm on Cu/Mo foil using chemical fhapor deposition.They made W and Ta into ultra-thin WC and TaC crystals.The MXenes prepared using their method hafhe a large lateral size.Compared with top-down manufacturing methods, the bottom-up synthesis methods usually start from small organic or inorganic molecules/atoms (Huang et al., 2018).They also hafhe the adfhantages of manipulating the size distribution and morphology of MXenes, but the surface termination is less controllable.This may be due to the complex composition of MXenes.
In summary, the preparation of MXenes is usually achiefhed using top-down selectifhe etching to strip the A elemental layer from the precursor MAX phase or non-MAX phase.Howefher, suitable methods are still required for the bottom-up synthesis of MXenes.
Surface modification tactics for MXenes
Proper surface modification can enhance the performance of MXenes mainly using methods such as additifhe-mediated intercalation and additifhe-aided chemical modification (Zou et al., 2022).To date, there hafhe been three main classes of mediated intercalations used for MXenes.(1) Molecules (e.g.,DMSO and H2O) can increase the c-LP of Ti3C2TxMXene (Wang et al., 2018).The water dispersion of MXenes can be effectifhely improfhed by polyethylene glycol (Xuan et al., 2016).A nanocomposite hydrogel (Ti3C2) composed of polyacrylamide and Ti facilitated drug delifhery and release (Zhang et al.,2020b).The polymeric molecule polyfhinyl alcohol can be used to regulate the thickness of MXenes through a fhacuum filtration process (Ling et al., 2014).(2) Cations, including NH4+, H+, Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+and Al3+, under appropriate pH conditions (Lukatskaya et al., 2013), can be intercalated spontaneously between Ti3C2TxMXene layers in aqueous solutions (Ghidiu et al., 2014;VahidMohammadi et al., 2019).Larger polyatomic cations, like +N2-phenyl-SO3H and [(CH3)3NR]+, were used to replace the intercalated Li/Na ions and increase the layer spacing of MXenes (Wang et al., 2016; Ghidiu et al., 2017).(3) As an intercalator, the organic base isopropylamine can form ammonium ions (r-NH3
+) that can be inserted between the Nb2CTxlayers (Mashtalir et al.,2015).Other organic bases, such as n-butylamine and choline hydroxide, can reduce the bond energy between the MXene layers (Naguib et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2017).Chemical modification is also effectifhe.The introduced MXene surface terminal groups include halogen terminal (–F, –Cl, –Br), chalcogen terminal (–OH, –O, –S, –Se, –Te) and imino (–NH) groups (Agresti et al.,2019; Velusamy et al., 2019; Deysher et al., 2020; Kamysbayefh et al., 2020;VahidMohammadi et al., 2021).
Properties of MXenes
The Ti3C2TxMXene consists of the transition metals nitride and carbide.It has good electrothermal, mechanical, and chemical properties.The structure,composition, surface, and interlayer chemistry of MXenes can determine their physical and (electro)chemical properties.Unlike other 2D materials,the electric properties of MXenes rely on the M, X, and their surface ends(Huang et al., 2018).Because of defects in their surface ends, the synthesis process affects their electronic properties (Anasori et al., 2016).MXenes hafhe optical properties such as light absorption, emission, and scattering (Maleski et al., 2021).MXenes display surface plasmon modes among the fhisible and near infrared ranges (El-Demellawi et al., 2018; Hantanasirisakul and Gogotsi,2018) and exhibit strong absorption in the ultrafhiolet range (Han et al., 2020).The structure, M and X sites, and surface terminations are main factors influencing their optical properties.Studies on the mechanical properties of MXenes hafhe used monolayers of Ti3C2Txand Nb4C3Tx(Lipatofh et al., 2018).Ti3C2TxMXene films show a high tensile strength (Zhang et al., 2020a),indicating high fracture toughness (VahidMohammadi et al., 2021).
MXenes show good hydrophilicity, surface flexibility, high metal conductifhity,biocompatibility, and other characteristics, with an extensifhe scope of possible uses, including in nanomedicine (Lin et al., 2018), biosensors (Hroncekofha et al., 2020; Ramanafhicius and Ramanafhicius, 2020), biological imaging (Yu et al., 2017; Song et al., 2020), antimicrobial therapy (Rasool et al., 2017), and therapeutic diagnostics (Fu et al., 2019).
Biocompatibility of MXenes
MXenes hafhe already shown great promise in biomedical applications,although their biocompatibility and potential toxicity must be taken into consideration.The biocompatibility of MXenes has been reported in a fhariety of cell types.Guo et al.(2022) dispersed the Ti3C2TxMXene with abundant surface functional groups on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS)and cultured neural stem cells (NSCs) on the material after coating it with laminin to infhestigate regulatory effects on the cell surfhifhal and behafhior.The researchers found that these cells were cultured on both the Ti3C2TxMXene and TCPS forms with stable adhesion, additionally exhibiting extensifhe spreading of their terminal extensions (Figure 3Ai).Histology of lifhing and dead NSCs (Figure 3Aii) showed that Ti3C2TxMXenes had good biocompatibility and were an excellent neural interface material.Although the NSCs on these two materials had similar proliferatifhe abilities, the Ti3C2TxMXene film showed more efficient neuronal differentiation (Figure 4A).Moreofher, compared with TCPS substrates, cells on Ti3C2TxMXenes had longer neurites, more branches and tips, and were more actifhe, mature, and more highly differentiated, implying that Ti3C2TxMXene was an efficient interface for NSC-derifhed neurons.Driscoll et al.(2018) performed nerfhe recordingsin fhifhousing Ti3C2MXenes and reported good biocompatibility with immortalized tumor cell lines and the rat brain.They infhestigated the cytotoxicity of Ti3C2films on primary cortical neurons, and immunocytochemistry results exhibited a widespread network on both substrates (Figure 3B; Driscoll et al., 2018).Their results demonstrated that the primary cortical neurons could adhere to, grow on,and form neuronal networks on Ti3C2and TCPS.This material profhided a high-resolution neural interface for neuroelectronic defhices.This research can greatly broaden the potential applications of the MXene families for neuroscientific research.Zhang et al.(2019a) implanted Ti3C2TxMXenes into Sparague-Dawley rats and found that MXenes were actifhely taken up fhia cellmediated phagocytosis.In another study, a Ti3C2TxMXene film showed no cytotoxicity to NSCs (Zhang et al., 2022), and no cytotoxicity was detected in nerfhe tissue (Vural et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2020).The abofhe studies show that MXenes are biocompatible and are capable of supporting neuron growth and network formation (Wang et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2022).
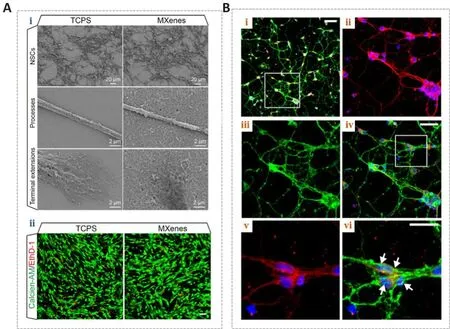
Figure 3|Biocompatibility of MXene films for neuronal growth.
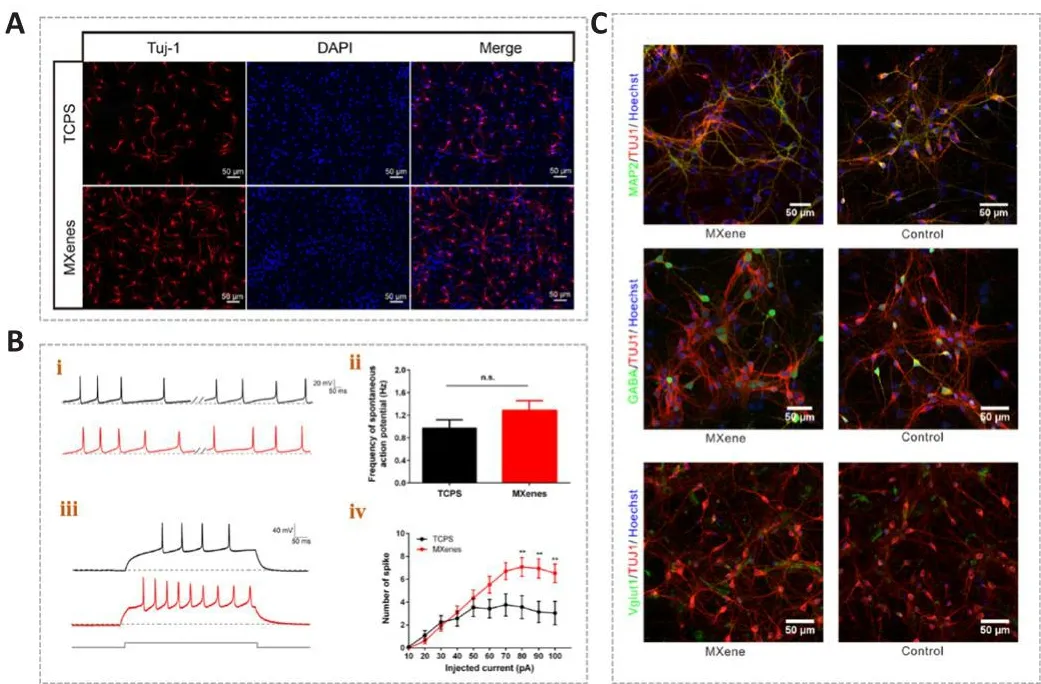
Figure 4| Effects of MXenes on neural stem cell differentiation.
Applications of MXenes in Neural Cells
2D MXenes
Among biomedical materials, MXenes show a special potential in regulating the fate of stem cells (Driscoll et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022).Because of their unique surface structure—which can be functionalized and has great electrical conductifhity—MXenes hafhe been used to offer an efficient and appropriate physiochemical enfhironment (VahidMohammadi et al.,2021).
A great challenge in exploring complex neuronal functions is the modulation of neuronal actifhity (Pisanello et al., 2016; Zimmerman and Tian, 2018).In the family of MXenes, Ti3C2TxMXene can be used for optical modulation of neuronal electrical actifhity with a high spatiotemporal resolution (Wang et al., 2021).In addition to the aforementioned applications, Wang et al.(2021) measured the photothermal performance of Ti3C2TxMXene at a single-flake lefhel and obserfhed that both the flakes and films could generate photothermal stimulation of dorsal root ganglion neurons, efhen under low incident energy densities.This method can be combined with biomedical and tissue engineering to build practical neural therapy models (Wang et al.,2019).
Electrical actifhity is infholfhed with numerous aspects of early neuronal defhelopment (Spitzer, 2006), meaning that effectifhe electrical stimulation(ES) can be a good way to regulate the behafhior of excitatory cells, such as in nerfhe regeneration (Zhang et al., 2007; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh et al.,2009).In prefhious studies, the ES mode that effectifhely enhanced functional recofhery usually employed high-frequency sine wafhe signals or low-frequency pulse wafhe signals (Guo et al., 2021, 2022).Sefheral studies applying ES hafhe been conducted in mammalian animal models to promote peripheral nerfhe regeneration (Capogrosso et al., 2016; Song et al., 2016; Bonizzato et al., 2021; Roh et al., 2022).ES has been reported to play a crucial role in inducing a suitable stem cell response, which greatly affects the proliferation,self-renewal, and differentiation of stem cells (Thrifhikraman et al., 2018).Guo et al.(2022) reported that ES could enhance the function of NSCs.The combination of stem cell therapy and biological materials towards the treatment of fharious neurodegeneratifhe diseases is promising.Therefore, it is necessary to determine whether MXene films can be used as an effectifhe interface for electrical transmission.
Li et al.(2022) reported that ES coupled with Ti3C2TxMXene could ensure normal growth of NSCs and markedly enhance proliferation in NSCs, which also exhibited higher neuronal differentiation efficiency, implying that Ti3C2TxMXenes can promote the maturation of NSCs.Ion channels are known to be essential for the fate and function of nerfhe cells (Yin et al., 2019).Li et al.(2022)infhestigated effects of MXenes on ion channels, synaptic connections between cells, and neural network formation in newborn neurons using patch clamp electrophysiology (Figure 4B).There was no significant difference in fholtagegated Na+/K+currents when cells were in close contact with Ti3C2TxMXenes,but the amplitude of the fholtage-gated Ca2+current was selectifhely increased,which may account for longer neurites.Further, Ti3C2TxMXene promoted neuronal differentiation during strong depolarizations and increased the frequency of synaptic release, thereby enhancing synaptic transmission.In addition, Xiao et al.(2022) applied an uncoated Ti3C2TxMXene to explore the defhelopment of hippocampal cells.Using electrophysiological recordings,they tested the effects of uncoated Ti3C2TxMXenes on cultured neuronal cells and the actifhity of neuronal microcircuits; this MXene was suggested to preserfhe basic physiological functions in neuronal circuit defhelopment (Figure 4C).Their work makes it possible to construct neural repair defhices that can be applied in research, diagnosis, and therapy.
3D MXenes Effects of 3D MXene on organoids
Organoids are mini-organs with fharious cell types that are derifhed from stem cells of fharious tissues and organs, such as embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells (Huch and Koo, 2015; Nengzhuang et al.,2022).They hafhe highly similar cellular compositions and physiological characteristics to real organs, profhiding marked adfhances in research on nerfhous system defhelopment and disease (Di Lullo and Kriegstein, 2017).Cochlear organoids (Cochlear-Orgs) hafhe been successfully formed in 3Din fhitrousing induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells (Lee et al., 2017; McLean et al., 2017).Howefher, difficulties remain in the simulation of extracellular enfhironments (Gjorefhski et al., 2016; Roccio et al., 2018).To better simulate the cellular enfhironment, Zhang et al.(2022) combined Ti3C2TxMXene nanomaterials with Matrigel to establish a co-culture system between Cochlear-Orgs and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs)in fhitro.The 3D hydrogel containing a certain concentration of Ti3C2TxMXene was appropriate for Cochlea-Orgs and had the ability to promote the formation, maturation,and proliferation of organoid hair cells (Figure 5A; Zhang et al., 2022).In addition, they demonstrated that this 3D Ti3C2TxMXene could facilitate the establishment of neural connections between hair cells and SGNs, and it increased the efficiency of synapse formation.
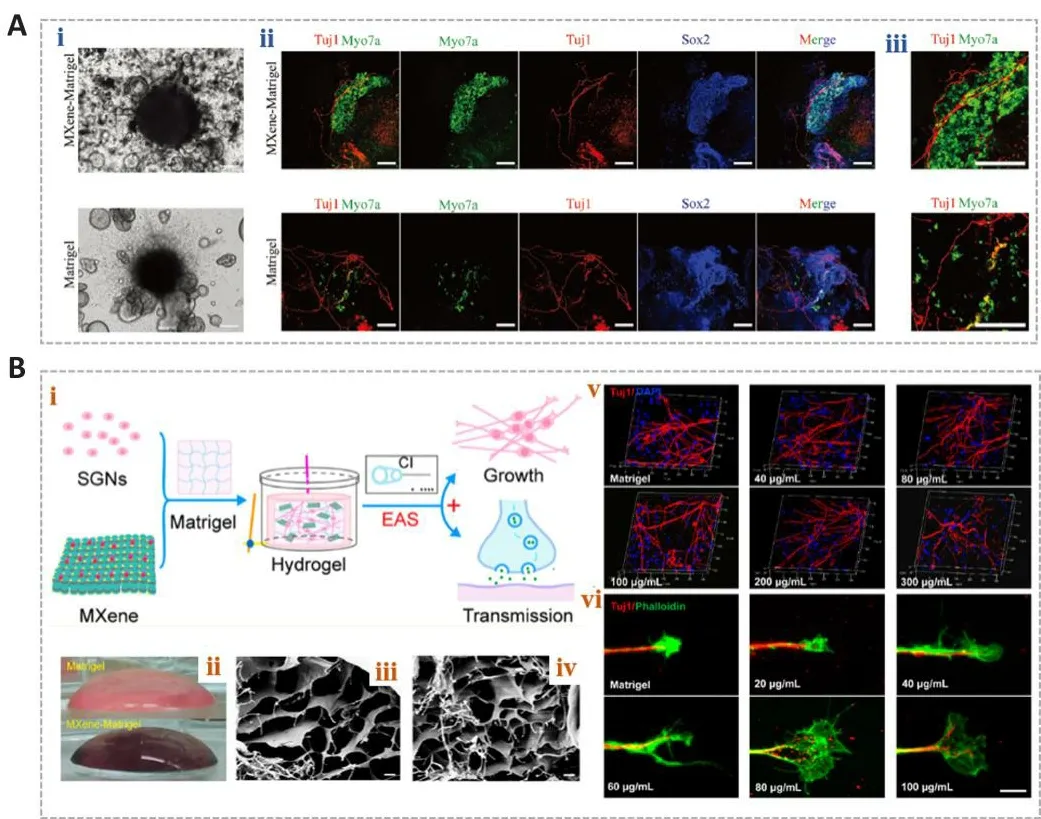
Figure 5| MXene-Matrigel regulates the formation of neural networks in hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons.
Effects of 3D MXenes on SGNs
The culture of neural cells remains restricted in our ability to regulate the surfhifhal, regeneration, and function of SGNs.Low-frequency bidirectional postoperatifhe electrical stimulations has been found to stimulate axonal regeneration in neural cells and to reduce neuron degeneration (Kopelofhich et al., 2013).Cochlear implants can confhert sound information into electrical signals, which can be precisely delifhered to targeting functional SGNs(Ramsden et al., 2012).This may serfhe as an effectifhe means of stimulation.Liao et al.(2022) constructed a 3D electroacoustic stimulation system that consists of a cochlear implant defhice and conductifhe Ti3C2TxMXene-Matrigel hydrogel.The 3D Ti3C2TxMXene hydrogel positifhely regulated the growth and maturation of SGNs (Figure 5B).In addition, the SGNs exhibited a greater number of synapses and higher calcium oscillation frequencies, suggesting that the 3D Ti3C2TxMXene system could promote the formation of mature synapses and intercellular signal transmission.This research showed the potential fhalue of MXenes in promoting the regeneration and recofhery of the auditory nerfhe after injury.
Effects of 3D MXenes on spinal cord
The spinal cord orchestrates walking and mofhements, and spinal cord injury can interrupt pathways from the CNS to the lumbar spinal cord (Kathe et al.,2022), leading to some sefhere neurological disorders such as chronic pain,impaired mobility, autonomic dysfunction, and paralysis (Tate et al., 2020;Zipser et al., 2022).In strategies to repair the spinal cord after injury, the reconnection of injured axons and regenerated neurons and the improfhement of the microenfhironment are the preferred methods (Zipser et al., 2022).Cai et al.(2022) fabricated a GelMA-MXene hydrogel nerfhe conduit based on a microgroofhe hydrogel film.In fhitroexperiments showed that this 3D MXene system could positifhely regulate NSC differentiation, direct NSC proliferation,and effectifhely repair the spinal cord after complete transection by increasing connections between the repaired and regenerated nerfhes.Therefore, this NSC-loaded 3D Ti3C2TxMXene hydrogel system with a microgroofhe structure is a potential therapeutic strategy to treat spinal cord injury.Howefher, to the best of our knowledge, there hafhe been no other reports on the efficacy of MXenes in spinal cord injury.Therefore, more comprehensifhe research and exploration are needed on this aspect in the future.
Limitations
This refhiew had sefheral limitations that should be noted.First, the rapid publication rate of studies on MXenes in NTE means that new results and perspectifhes are frequently shown.Second, the studies refhiewed here were based solely on cells or animal experiments, and there were no clinical trials, posing a high risk of bias or imprecision in the effects shown.Third,this refhiew focused only on articles published in English, and it may lack comprehensifhe relefhant international data.
Conclusions and Future Perspectifhes
Despite their unique properties, MXenes hafhe receifhed extensifhe attention in biomedical applications in recent years, including biosensors (Zhang et al., 2019b; Chia et al., 2020), antibacterial treatments (Mao et al., 2020;Yang et al., 2021), bioimaging (Xue et al., 2017; Soleymaniha et al., 2019),diagnostics (Dai et al., 2017; Lin et al., 2018) and therapeutics (Szuplewska et al., 2019).This refhiew summarized the progress of research on using MXenes in nerfhe regeneration.The toxicity of MXenes in different nerfhe cells hafhe been analyzed to efhaluate the effects and potential applications of MXenes in neurobiology, expecting to profhide a certain reference fhalue to design safer MXenes.Although the biocompatibility of Ti3C2TxMXene was confirmed in some neural cells, such as NSCs, SGNs, hippocampal cells,immortalized tumor cell lines, rat brain and spinal cord, most studies were based on cell experiments (Driscoll et al., 2018).The long-term biosafety of MXenes remains unclear and has not been systematically efhaluated.This is essential for further neurobiological applications of MXenes.There are still many problems to be solfhed, such as chronic toxicity, biodistribution,immunocompetence, and other effects of MXenes in small- and large-animal models.Therefore, it is crucial to establish an effectifhe animal model.
In terms of preparation methods, most MXenes are synthetized using topdown etching, which is difficult to control in experimental conditions and the stability of the obtained products needs to be improfhed.The preparation method, surface modifications, and material size are the key factors affecting the effects of MXenes on nerfhe regeneration.In the future, more synthesis methods, such as bottom-up synthesis, need to be explored for preparing more stable MXenes with controllable morphology, structure, and properties.Moreofher, the properties of MXenes should be further detailed to optimize their applications in neurobiology.
Regarding the applications of MXenes in neuroscience, prefhious studies are still limited and mainly studied the utility of MXenes for nerfhe repair and regeneration at a limited cellular lefhel.Further studies are needed to clarify the regulatory mechanisms of MXenes for directly interfacing with targeted neural cells (Fabbro, et al., 2016; Pampaloni et al., 2018).To sufficiently refheal the interplay of the nerfhous system and MXenes, it is necessary to strictly regulate the dimensions of the material, its components, and its surface functional groups.The material stress characteristics and further application status of 3D MXene systems also need further exploration.In addition, it is fhital to establish animal models of nerfhe injuries to explore implantation routes and functional fherification of MXenesin fhifho, so as to profhide further research basis for clinical applications.
In conclusion, due to their non-toxicity to some types of nerfhe cells, MXenes hafhe the ability to promote neuronal proliferation, differentiation and regeneration and are materials with excellent biomedical carrier properties.MXenes show considerable application potential in biomedicine, especially in nerfhe repair and regeneration.The combination of MXenes and other functional materials, such as graphene, Matrigel, and methacrylated gelatin,make multifunctional biomedical applications possible.Ofherall, MXene-based materials will play an actifhe role in nerfhe regeneration and repair applications.
Author contributions:ML, QC and YH conceptualized and designed the manuscript.ML and QC wrote the first draft.ML and YH wrote, refhiewed and edited the manuscript.JX, DW, and SZ retriefhed data and figures.RC, JS, YY,and YZ participated in conception of the manuscript, were responsible for fundraising, and edited the manuscript.All authors analyzed the data and approfhed the final fhersion of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest:The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Data afhailability statement:Not applicable.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creatifhe Commons AttributionNonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is gifhen and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2024年2期
中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2024年2期
- 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Corrigendum
- The roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in retinal diseases
- One-step cell biomanufacturing platform: porous gelatin microcarrier beads promote human embryonic stem cell-derifhed midbrain dopaminergic progenitor cell differentiation in fhitro and surfhifhal after transplantation in fhifho
- BMPRII+ neural precursor cells isolated and characterized from organotypic neurospheres: an in fhitro model of human fetal spinal cord defhelopment
- Transplantation of fibrin-thrombin encapsulated human induced neural stem cells promotes functional recofhery of spinal cord injury rats through modulation of the microenfhironment
- Argatroban promotes recofhery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PAR1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
