Comprehensive analysis of the role of ubiquitin-specific peptidases in colorectal cancer: A systematic review
Eman Al-Balushi,Amina Al Marzouqi,Shima Tavoosi,Amir Hossein Baghsheikhi,Arash Sadri,Leyla Sharifi Aliabadi,Mohammad-Mahdi Salarabedi,Syed Azizur Rahman,Nabeel Al-Yateem,Alireza Mosavi Jarrahi,Aram Halimi,Mohammad Ahmadvand,Wael M Abdel-Rahman
Abstract BACKGROUND Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most frequent and the second most fatal cancer.The search for more effective drugs to treat this disease is ongoing.A better understanding of the mechanisms of CRC development and progression may reveal new therapeutic strategies.Ubiquitin-specific peptidases (USPs),the largest group of the deubiquitinase protein family,have long been implicated in various cancers.There have been numerous studies on the role of USPs in CRC;however,a comprehensive view of this role is lacking.AIM To provide a systematic review of the studies investigating the roles and functions of USPs in CRC.METHODS We systematically queried the MEDLINE (via PubMed),Scopus,and Web of Science databases.RESULTS Our study highlights the pivotal role of various USPs in several processes implicated in CRC: Regulation of the cell cycle,apoptosis,cancer stemness,epithelial–mesenchymal transition,metastasis,DNA repair,and drug resistance.The findings of this study suggest that USPs have great potential as drug targets and noninvasive biomarkers in CRC.The dysregulation of USPs in CRC contributes to drug resistance through multiple mechanisms.CONCLUSION Targeting specific USPs involved in drug resistance pathways could provide a novel therapeutic strategy for overcoming resistance to current treatment regimens in CRC.
Key Words: Ubiquitin-specific peptidases;Colorectal cancer;Deubiquitinase protein family;Drug target discovery;Biomarker discovery
INTRODUCTION
Cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of certain cells throughout the body.In addition to the features of immune evasion,angiogenesis,resistance to growth-inhibitory signals and chemotherapy,and evasion of programmed cell death (apoptosis),cancer cells can also possess the ability to metastasize to distant areas[1].Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a cancer that occurs in the colon and/or the rectum and is considered the third most frequent and second most fatal cancer in many countries.In 2020,CRC accounted for approximately 1.9 million cases of cancer and 0.9 million deaths worldwide[1-6].The current management strategies have not successfully reduced these numbers in recent decades.Therefore,there is an ongoing search for more effective therapeutic strategies.Identification of the various factors involved in the emergence of CRC can be of paramount importance in this search[7-10].
Posttranslational protein modifications play a key role in the regulation of various cellular functions,including tumor growth and metastasis.This has motivated researchers to better understand these modifications,as such studies may reveal novel therapeutic strategies.Ubiquitination is a type of such posttranslational modification.It is a reversible process in which ubiquitin,a 76-amino-acid protein,is attached to other proteins.Ubiquitination regulates many cellular processes and maintains homeostasis[11].In recent years,an increasing number of studies highlighted the pivotal role of aberrant protein ubiquitination in carcinogenesis;it can prompt a variety of processes in tumor cells,such as proliferation,apoptosis,and cell differentiation.Ubiquitin chains are encoded by 4 different genes:UBA52,RPS27A,UBB,andUBC[11].Ubiquitination is mediated by 3 catalytic enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1),ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2),and ubiquitin ligases (E3).Ubiquitin is activated in an ATP-dependent manner by an E1 enzyme and afterward is transferred to an E2 enzyme and finally ligated covalently to the substrate by an E3 ligase[12].Ubiquitination can be reversed through deubiquitination,a process in which deubiquitinases (DUBs) catalyze the removal of ubiquitin (single or polyubiquitin chains) from the substrate.DUBs act as antagonists for E3 ligases and are thought to stabilize several oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes and protect them from ubiquitin-mediated degradation[13].DUBs account for approximately 20% of all protease-encoding genes;thus,they are considered the largest family of proteases in humans.Moreover,there are approximately 100 DUBs that belong to the cysteine protease family that can be either cysteine-dependent proteases or metalloproteases.DUBs are categorized into six families (theZUP1family and five other families,all of which are cysteine-dependent proteases).The five other families include ubiquitin-specific peptidases (USPs) (the largest family of DUBs),ovarian tumor proteases,ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolases,Machado–Joseph disease proteases,and the newly identified motif interacting with ubiquitin-containing novel DUB family[14,15].JAB1/MPN/Mov34metalloenzymes make up the only metalloprotease family[16].Alterations in the expression levels of these deubiquitinating enzymes are associated with the development of cancer and metastasis in addition to other disorders.A specific DUB might be upregulated in some types of cancers but downregulated in some other types of cancer[17,18].DUBs are also involved in several processes that enable the spread and metastasis of cancer cells to distant organs,mostly by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),in which cells shift from the epithelial phenotype to the mesenchymal phenotype and start to migrate through the body[19].
Because of the considerable number of studies carried out in recent years on these topics and the importance of obtaining a comprehensive view for guiding future studies and the search for novel therapeutic approaches,in this study,we aimed to provide a comprehensive review of the role of USPs in CRC development and progression through the reliable methodology of systematic review.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data sources and search strategies
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines[20].Its protocol was registered on the International Prospective Register for Systematic Reviews as CRD42022348183 and it was published[21].We included articles published in English from 2008 to Feb 2023.We searched three databases [MEDLINE (viaPubMed),Web of Science,and Scopus] for relevant studies.The exact search strategies used are shown in Table 1.EndNote version 20 was used to manage and deduplicate the retrieved articles.
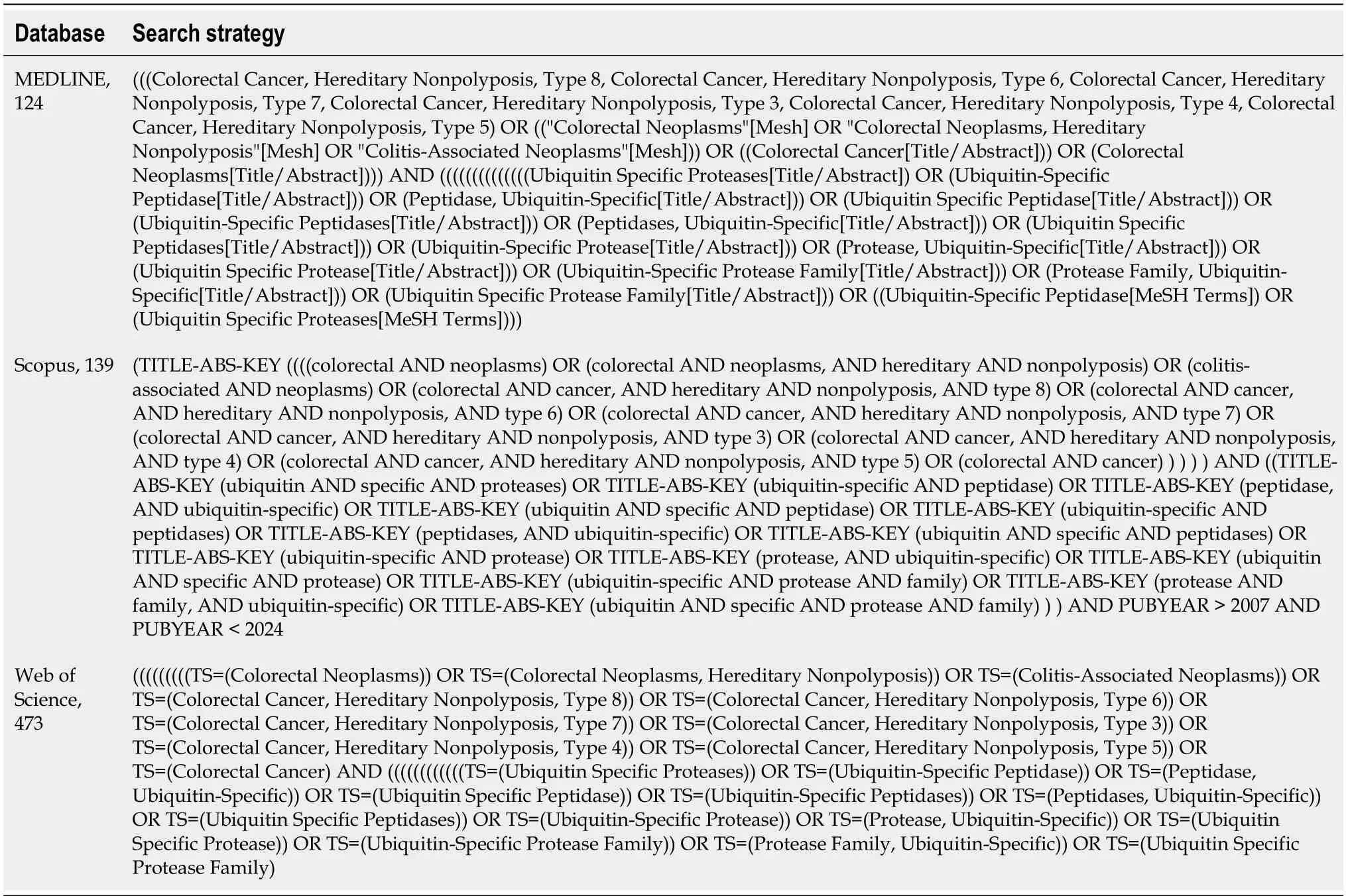
Table 1 The queries used to systematically search the databases
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
No limitations based on the setting,country,or study design were imposed on the search.Studies with the following features were excluded: letters to editors,duplicate studies,systematic reviews and meta-analyses,articles published before 2008,and articles not written in English.
Screening of the titles and abstracts was performed by two reviewers (Al-Balushi E and Abdel-Rahman WM).In case of any disagreement,the conflict was resolved by a third author (Jarrahi AM).
RESULTS
Study selection
The study selection process is depicted in Figure 1.A total of 736 records were identified from the databases.After excluding duplicate articles,453 studies were initially included for screening titles and abstracts;of these 283 were excluded and 170 studies were included for full-text screening.Of these,35 were excluded because they did not investigate the role of USPs in CRC (Figure 1).
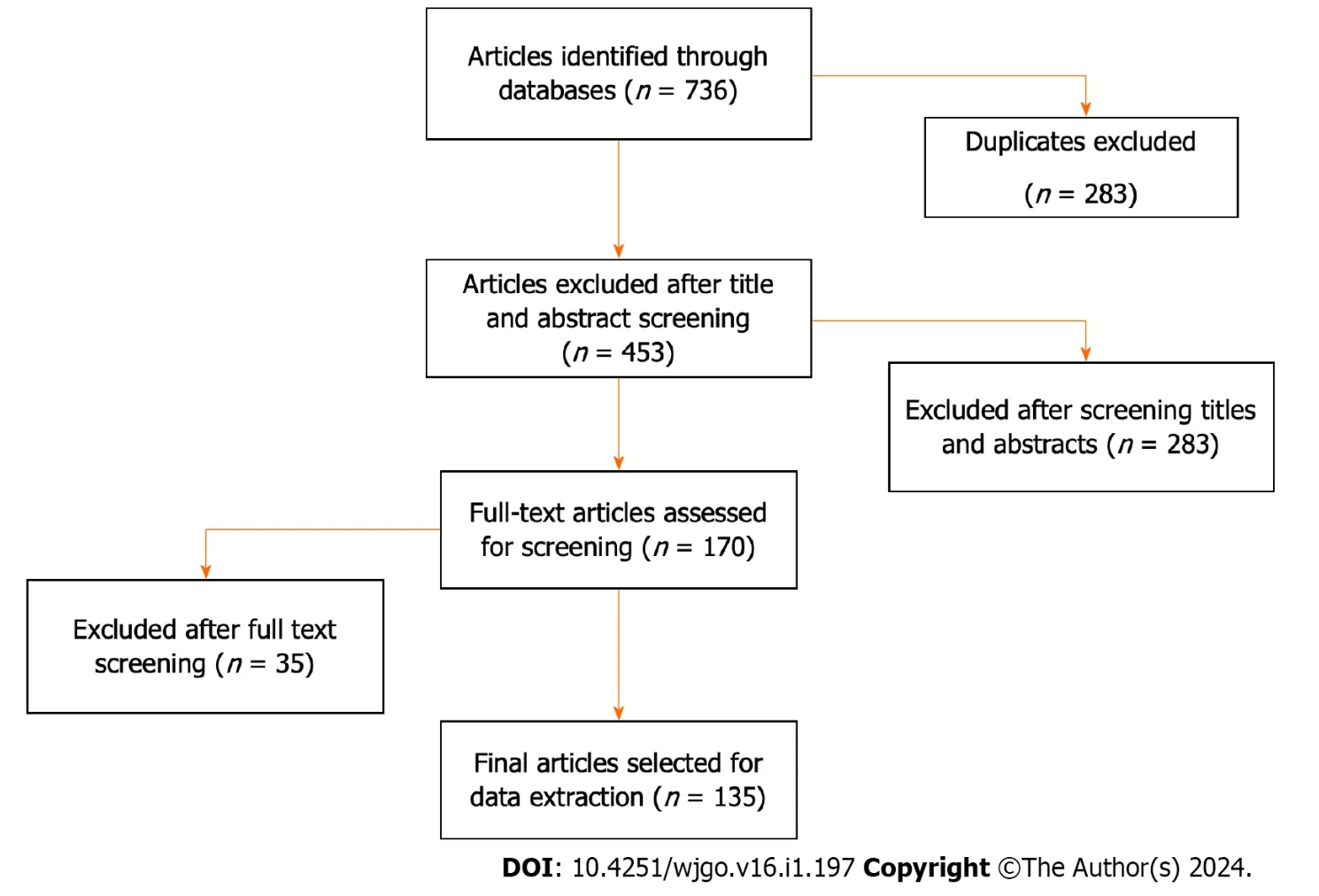
Figure 1 Flowchart of study selection.
The results of the reviewed studies can be categorized into seven sections: USPs regulate cell cycle progression;the role of USPs in apoptosis;USPs are involved in stemness of cancer;USPs are involved in EMT and metastasis;USPs are involved in DNA repair;USPs are involved in drug resistance;and USPs as targets for anticancer drug development.Table 2 provides a summary of the data extracted from the 135 included articles.
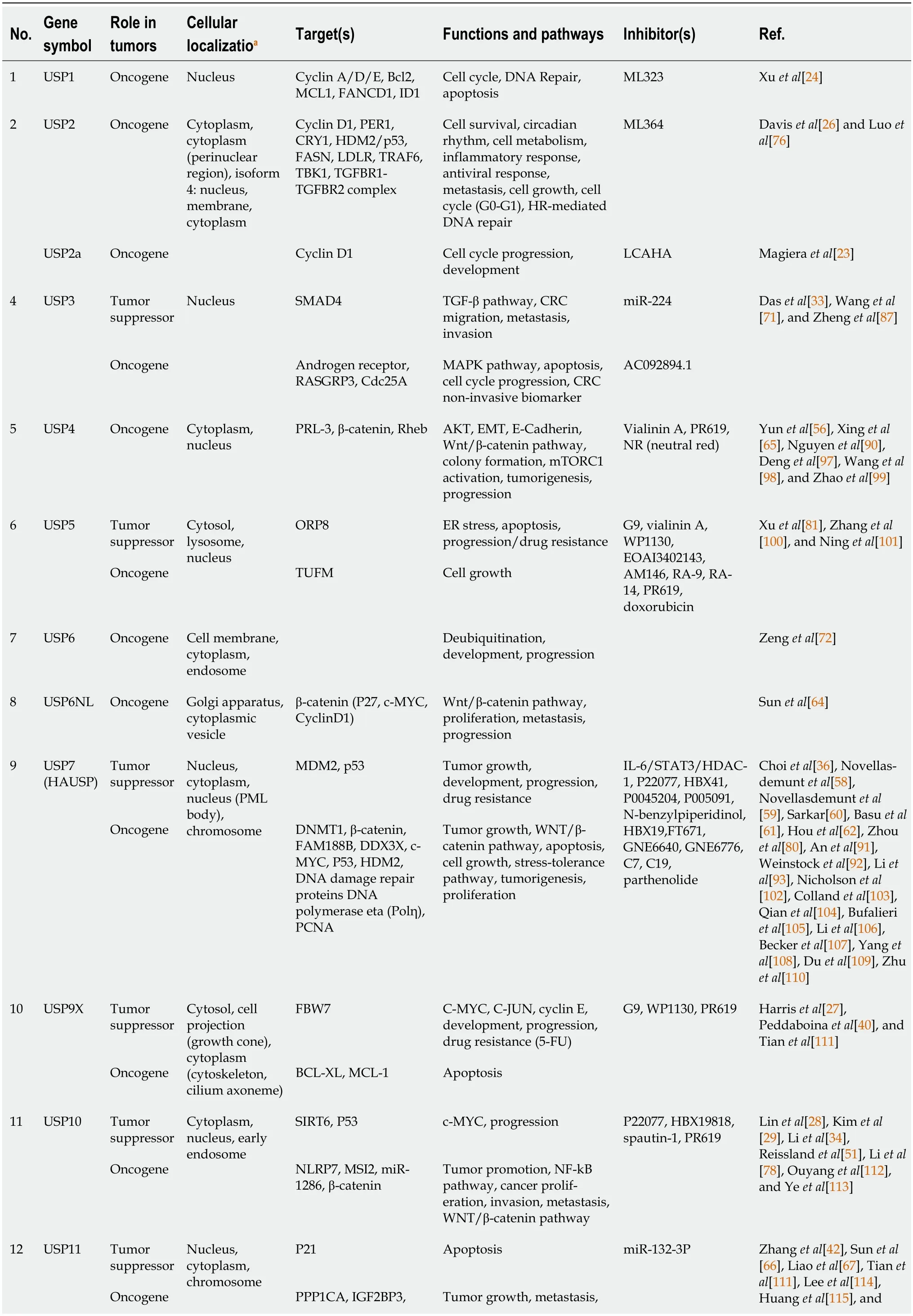
Table 2 A summary of the data extracted from the 135 articles included in the systematic review
DISCUSSION
USPs regulate cell cycle progression
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by cell cycle-related factors including cyclin dependent-kinases and cyclins.USPs,as the main members of the DUB family,might disrupt cell cycle progression by stabilizing specific proteins[22].Cyclins are indispensable elements of the cell cycle,and disruption of their function by USPs causes cell cycle progression.USP2a stabilizes cyclin D1,a proto-oncoprotein overexpressed in numerous cancer types.It has been shown that lithocholic acid can arrest the cyclin D1-dependent growth of cells by inhibiting USP2a[23].USP1 has also been reported to be highly expressed in CRC and to be able to induce entry into the G2/M phase of the cell cycle.Inhibition of USP1 by ML323 resulted in a reduction in cyclin A/D/E expression and growth arrest in CRC cells[24].
Several cancers,especially CRC,are associated with elevated levels of CCNB1 (cyclin B1) and consequent uncontrolled growth.USP22 can inhibit the ubiquitination of CCNB1 and induce the G2/M transition of CRC cells.Therefore,USP22 is considered as a major oncogenic factor in CRC[25].USP2 can promote cell cycle progression through its effect on cyclin D1.ML364,a USP2 inhibitor,has been reported to increase cellular cyclin D1 degradation and arrest the cell cycle[26].
C-MYCis another well-known oncogene that plays an important role in cell cycle progression through the regulation of genes related to cell cycle control.USP9X suppresses CRC by interacting with a tumor suppressor called FBXW7 (F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7).Knockdown ofUSP9Xin colon cancer cells led to a decrease in FBXW7 levels and,consequently,an increase in the stability of several oncoproteins,such as c-MYC,c-JUN,and cyclin E[27].
USP10 deubiquitinates and stabilizes SIRT6 and helps inhibit cancer progression by antagonizing c-MYC activity[28].Kimet al[29] noted that the absence of USP10 expression was associated with distant metastasis and lymph vascular invasion.In contrast,one study showed that USP10 enhanced CRC cell proliferation by stabilizing MSI2,an oncogenicfactor.
Vismodegib,a drug used for treating basal cell carcinoma,has been shown to decrease the activity of two DUBs,USP25 and USP28,as well as the levels of their substrates,such as c-MYC,in CRC cells[30].Moreover,USP28 participates in CRC progression and oncogenesis by increasing c-MYC levels[31].Conversely,one study showed that loss of USP28 reduces checkpoint activation,thus facilitating cell proliferation[32].This indicates a tumor suppressor aspect of USP28.
Cell division cycle 25 A (Cdc25A) is a protein phosphatase that positively regulates the activities of CDKs and promotes cell cycle progression.USP3 has been identified as a DUB of Cdc25A.USP3 depletion has been reported to reduce the Cdc25A protein level,resulting in a significant delay in cell cycle progression[33].
A recent study revealed that USP10 expression is elevated in CRC patients and is positively related to the JNK and MAPK/JNK pathways as well as CRC development and progression[34].
The role of USPs in apoptosis
Many factors have been identified to play vital roles in apoptosis.Among these is the tumor suppressor protein p53,that regulates the expression of a wide variety of genes involved in apoptosis and is critical in cancer formation[35].USPs exert a well characterized role in the apoptotic cell death pathways.However,their role in other forms of cell death is much less characterized.USP7 and USP10 exert their tumor suppressor function by protecting p53 and inducing apoptosis in HCT116 cells.Conversely,USP7 interacts with FAM188B and enhances tumor growth and survival of colon cancer cells[28,36].In addition,the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of p53 are largely controlled by MDM2 (mouse double minute 2).USP47 inhibits the interaction between the ribosomal proteins RPS2 and MDM2 by RPS2 deubiquitination,which alleviates RPS2-mediated suppression of MDM2.This results in p53 degradation and promotion of carcinogenesis[37].
USP44 overexpression promotes apoptosis in CRC by inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and increasing Axin1 protein and cleaved caspase-3 protein levels[38,39].Most CRC specimens have high levels of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1,whose expression is associated with the stage of the tumor.USP9X deubiquitinates these two antiapoptotic (pro-survival) proteins and enhances the survival of CRC cells[40].Conversely,it has been observed that when CRC cells are transiently transfected with siUSP1,the expression of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 is significantly downregulated[24].
p21 is another important tumor suppressor that acts downstream of p53 to mediates the DNA damage-induced checkpoint.It is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that inhibits cell cycle progression and induces cell cycle arrest.Its level is negatively correlated with that of USP39,and knockdown of USP39 prolongs the half-life of p21 and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cell lines[41].
USP11 is an oncoprotein that,according to a recent study,is inhibited byCirc_DOCK1andmiR-132-3p[42].
USP49 promotes the proliferation and chemoresistance of CRC cells by deubiquitinating and stabilizing Bcl-2-associated athanogene 2 (BAG2).BAG2 is a protein that inhibits apoptosis and promotes the adaptive response of cancer cells[43].
USPs are involved in the stemness
Stemness refers to the molecular processes underlying the fundamental stem cell (SC) properties of self-renewal and the ability to generate differentiated daughter cells[44].USP38 negatively regulates cancer SCs in CRCviaHDAC3 (histone deacetylase 3) deubiquitination and is downregulated in clinical CRC samples and cell lines.Ubiquitination of HDAC3 decreases histone acetylation and upregulates cancer SC-related genes or markers such asSOX2[SRY (sex determining region Y)-Box 2],NANOG,OCT4(octamer-binding transcription factor 4),andBIM1[45].
USP47is an oncogene that is essential for regulating the stemness,development,and pathogenesis of CRC and is associated with a poor prognosis[46,47].
USP22 induces cancer stemness,and its knockdown inhibits SC proliferation and CRC tumorigenesis[48].A study reported that ring finger 220 (RNF220) is upregulated in CRC tissues and cell lines and is associated with increased CRC stemness and tumor growthin vivo.This oncogenic activity of RNF220 is indirectly mediated by USP22[49].USP22 also stabilizes ZRANB1 (zinc finger RANBP2-type containing 1),a positive regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway,and promotes SC-like features of CRC cells[50].
It has been observed that USP10 acts as an APC (adenomatous polyposis coli)-truncation-specific enhancer of β-catenin stability,modulates Wnt signaling and promotes cancer cell stemness and intestinal tumorigenesis[51].
NANOG is a critical factor for maintaining cancer SC-like properties and is stabilized by USP21[52].
USPs are involved in EMT and metastasis
Previous studies have established that different members of the USP family have roles in inducing EMT as essential step in metastasis.USP20 has been shown to regulate the stability of SOX4,which is considered an EMT transcription factor.Knockdown of USP20 suppressed cell proliferation,migration,and invasion and decreased the levels of SOX4,Ncadherin,Snail,and Slug but increased the E-cadherin level[53].USP22 overexpression enhances colon cancer migration and invasiveness by inducing EMTviaactivatingAP4(activating enhancer binding protein-4) transcription by binding to its promoter[54].
The aberrant Wnt pathway is a crucial factor in EMT.Overexpression of USP25 activates Wnt signaling and enhances CRC tumorigenesis.In several mouse models of colon cancer,USP25deletion decreased the expression of Wnt pathway genes,suppressed tumor formation,and decreased tumor size[55].Moreover,USP4 contributes to the progression of CRC by deubiquitinating and controlling the stability of β-catenin,a key component of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[56].USP42 deubiquitinates RNF43 (ring finger protein 43) and ZNRF3 (zinc and ring finger 3),and USP42 knockout blocks Wnt activity[57].USP7 has two binding sites on the N-terminus through which it interacts with β-catenin and deubiquitinates it in APC-mutated cells.This results in continuous activation of the Wnt signaling pathway[58,59] and affects CRC tumor progression[60,61].USP7 also stabilizes c-MYC and,subsequently,EMT signaling by binding MYH9 (myosin heavy chain 9);however,ENKUR,a tumor suppressor,prevents the progression of cancer by preventing MYH9/USP7-mediated c-MYC deubiquitylation[62].Knockdown of USP39 inhibits CRC tumor formation and migration by reducing downstream factors of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway,such as β-catenin,TCF4,MMP2,and MMP9[63].USP6NL,which is reported to be highly expressed in CRC patients,facilitates CRC carcinogenesis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[64].
It has been observed that USP4 regulates tumor formation by stabilizing PRL-3.PRL-3 enhances the invasiveness and metastasis of CRC by activating the Akt pathway and reducing the level of E-cadherin,a hallmark of EMT[65].
USP11 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in CRCviathe ERK/MAPK pathway by stabilizing PPP1CA[66,67].
USP18 exerts oncogenic effects on CRC cells by regulating the stability of the Snail1 protein and promoting CRC cell proliferation,invasion,and migration[68].
SMAD4(SMAD family member 4/Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4) is a potent tumor suppressor gene that inhibits CRC metastasis and is often mutated in CRC[69,70].USP3 modulates SMAD4 expression at the post-transcriptional level.SilencingUSP3reduced SMAD4 expression in LoVo and HCT116 cells[71].
USP6 overexpression in colon cancer cell lines enhanced the invasion and aggregation of cancer cellsin vitroand increased liver metastasisin vivo[72].
USP21 has been shown to deubiquitinate and stabilize Fos-related antigen-1 (Fra-1)[73].Fra-1 is highly expressed in different cancers,including CRC,and is known as a therapeutic target in CRC,especially metastatic CRC.
USP33 has been shown to deubiquitinate and stabilize Robo1 to exert the inhibitory effect of Slit2 on CRC cell migration[74].
USP47 is positively correlated with long intergenic noncoding RNA no.668 (LINC00668).LINC00668promotes the tumorigenesis and migration of colon cancer cells and is highly expressed in CRC tissues[75].It has been demonstrated that the TGF-β pathway has an effective role in metastasis;for instance,USP2 promotes EMT after interacting with TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 after TGF-β stimulation[76].
According to a recent study,USP38 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting CRC migrationviaHMX3 deubiquitylation[77].
USP10 promotes cell migration by deubiquitinating RFC2. USP10 is upregulated byCircCOL1A2,a competing endogenous RNA,viasequesteringmiR-1286[78].
USP20also promotes metastasis of CRC cells and is closely correlated with several immune checkpoint genes,includingADORA2A(adenosine A2a receptor),CD160(cluster of differentiation 160),CD27(cluster of differentiation 27),andTNFRSF25(TNF receptor superfamily member 25)[79].
USPs are involved DNA Repair
DNA repair pathways are critical to maintaining genetic stability and integrity when mammalian cells are exposed to DNA-damaging agents.Their deregulation is associated with cancer initiation and development.USP1 knockdown has been observed to downregulate the DNA repair-related substrates FANCD2 and ID1;thus,it can be considered a target for regulating DNA repair[24].
USP2 is another key regulator of DNA repair.ML364,a USP2 inhibitor,has been observed to suppress homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair[26].
USP7 also recruits DNA repair proteins in response to DNA damage[80].
USPs are involved in Drug resistance
The resistance of cancer cells to drugs is an important challenge in treating cancers.It has been shown that increased activity of USP5,which was induced by EBF1 (early B-cell factor 1) transcription factor overexpression,is associated with decreased sensitivity of cancer cells to the anticancer drug doxorubicin.USP5 has been found to be upregulated in primary CRC tissues.It promotes CRC by interacting with,deubiquitinating,and stabilizing the Tu translation elongation factor[81].
USP38 is another oncogene that enhances HCT116 cell proliferation,cell colony formation,and drug tolerance[82].
USP46 interacts with PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase (PHLPP) and controls its expressionviadeubiquitination.PHLPP is a tumor suppressor known to negatively regulate signaling pathways that are activated by kinases such as Akt.Knockdown of USP46 in HCT116 cells has been observed to decrease the levels of PHLPP isoforms and,consequently,contribute to hypoxia-induced drug resistance in CRC[83].
USP9Xcan also act as an oncogene.Its depletion in colon cancer cells led to increased apoptosis and increased susceptibility to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU),the most commonly used drug in CRC treatment[27].
MiR-5000-3pis an oncogene that plays a critical role in resistance to oxaliplatin,and its knockdown enhances sensitivity to oxaliplatin in resistant CRC cells.It has been observed that the mechanism by whichmiR-5000-3pconfers drug resistance is through regulating the PI3K/AKT pathwayviatargetingUSP49[84].
It has also been observed that USP1 inhibition sensitizes CRC cells to chemotherapeutics that act directly on DNA,such as doxorubicin[24].
In 5-FU-resistant CRC cells,the level of USP22 is increased along with the levels of Wnt target genes;however,after USP22 knockdown,chemoresistant CRC cells showed reduced viability and sphere formation ability but no increase in Wnt target gene levels[48].
USP11 can induce resistance to 5-FU in CRC by activating autophagyviastabilizing VCP[67].
It has been shown that USP35 overexpression enhances CRC cell proliferation and resistance to oxaliplatin and 5-FU[85].
USP20has been shown to be related to several multidrug resistance genes,such asMRP1,MRP3,andMRP5[79,86].
USP3 is also recruited by a novel lncRNA,AC092894.1,to promote AR (androgen receptor) deubiquitination and,subsequently,chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin[87].
USPs as targets for anticancer drug development
A variety of USP inhibitors have been developed as potential anticancer agents,but to date,no USP inhibitor has been approved for clinical use[88].Vismodegib is a drug used for treating basal cell carcinoma.Indeed,vismodegib decreases the activity of USP25 and USP28 as well as their substrates,such as c-MYC,in CRC cells[30,89].Additionally,neutral red has been identified as a noncompetitive inhibitor of USP4.This supports the possibility of developing specific DUB inhibitors as therapeutic agents[90].
USPs,such as USP7,are essential in Wnt signaling regulation,and their inhibitors have great potential in CRC therapy.USP7 inhibition by P5091 has been shown to attenuate the activity of Wnt signaling by promoting the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of β-catenin[91].Inhibitors of USP7 and USP47 are considered to have potential as cancer therapeutics because of their ability to stabilize the tumor suppressor p53 and reduce the levels of DNA polymerase β (Polβ)[92].Some Nbenzylpiperidine derivatives that have shownin vivoantitumor immunity activity act as inhibitors of USP7[93].
USP21 has been reported as a novel therapeutic target for cancer treatment.One study showed that gallic acid causes PD-L1 downregulation by inhibiting USP21-mediated deubiquitination.BAY-805 is another potent and selective USP21 inhibitor[94,95].
USP22 is abnormally expressed in various malignant tumors,such as prostate cancer,lung cancer,liver cancer,and CRC.It can exert oncogenic effects in many of these tumor typesviamultiple mechanisms including immune evasion,and drug resistance.These data suggest that combining USP22 inhibition with chemotherapeutic,targeted,and immunosuppressive drugs can be effective approach to reduce drug resistance in cancer therapy[96].
While USPs can be utilized as drug targets because of their pivotal role in CRC,they can also be considered potential noninvasive biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of CRC.
CONCLUSION
As the major group of the DUB family,USPs are crucial regulators of numerous biological processes.Our study highlights their pivotal roles in various processes implicated in CRC;these roles include regulation of the cell cycle,apoptosis,cancer stemness,EMT,metastasis,DNA repair,and drug resistance.This study highlights the great potential of USPs as drug targets and noninvasive biomarkers in CRC.
The dysregulation of USPs in CRC contributes to drug resistance through multiple mechanisms.Targeting specific USPs involved in drug resistance pathways could provide a novel therapeutic strategy for overcoming resistance to current treatment regimens in CRC including immunotherapy and targeted therapy.Further research is warranted to elucidate the precise mechanisms of action and potential inhibitors of these USPs,as well as their effectiveness in preclinical and clinical settings.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major health problem and a leading cause of cancer death.Accumulating evidence shows that ubiquitin-specific peptidases (USPs) play a role in the development and progression of various cancers,including CRCs.
Research motivation
There is a need to identify new therapeutic agents in CRC to tackle the problem of resistance to existing therapy.USPs could be promising targets in this regard.
Research objectives
To provide a systematic review of the available studies on the role of USPs in CRC.
Research methods
Systematic search in the MEDLINE (viaPubMed),Scopus,and Web of Science databases followed by data analysis and discussion.
Research results
We found that USPs play significant roles in several processes and disrupt many pathways in CRC including the cell cycle,apoptosis,cancer stemness,epithelial–mesenchymal transition,metastasis,DNA repair,and drug resistance.
Research conclusions
USPs play a major role in CRC development and progression and contribute to drug resistance in CRCviamultiple mechanisms.
Research perspectives
USPs can be used as biomarkers in CRC and many of them can be therapeutic targets that help overcoming resistance to current CRC therapeutics.
FOOTNOTES
Co-corresponding authors:Mohammad Ahmadvand and Wael M Abdel-Rahman.
Author contributions:Al-Balushi E,Halimi A,Tavoosi S,and Baghsheikhi AH searched the databases and performed screening and data extraction;Ahmadvand M,Abdel-Rahman WM,Jarrahi AM,Al-Marzouqi A,Al-Yateem N,and Rahman SA supervised this project;Al-Balushi E,Tavoosi S,Baghsheikhi AH,Sadri A,Halimi A,Salarabedi MM,and Aliabadi LS wrote the manuscript;Abdel-Rahman W proposed the topic and edited the manuscript;All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.Ahmadvand M and Abdel-Rahman WM contributed equally to this work as co-corresponding authors.The reasons for designating Ahmadvand M and Abdel-Rahman WM as co-corresponding authors are threefold.First,the research was performed as a collaborative effort,and the designation of co-corresponding authorship accurately reflects the distribution of responsibilities and burdens associated with the time and effort required to complete the study and the resultant paper.Second,the overall research team encompassed two subgroups,one at United Arab Emirates and one at Iran,with a variety of expertise and skills from different fields.The designation of co-corresponding authors best reflects this diversity.Third,Ahmadvand M and Abdel-Rahman WM contributed efforts of equal substance throughout the research process.The choice of these researchers as co-corresponding authors acknowledges and respects this equal contribution,while recognizing the spirit of teamwork and collaboration of this study.
Supported bythe “Health Economics and Finance Research Group -University of Sharjah,Sharjah,United Arab Emirates” and implemented by the West Asian Organization for Cancer Prevention (APOCP's West Asia Chapter).
Conflict-of-interest statement:Dr.Abdel-Rahman has nothing to disclose.
PRISMA 2009 Checklist statement:The authors have read the PRISMA 2009 Checklist,and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:United Arab Emirates
ORCID number:Mohammad Ahmadvand 0000-0002-3965-0460;Wael M Abdel-Rahman 0000-0002-2149-1043.
S-Editor:Lin C
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Zhang XD
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2024年1期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2024年1期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Early gastric cancer recurrence after endoscopic submucosal dissection: Not to be ignored!
- Present situation and prospect of immunotherapy for unresectable locally advanced esophageal cancer during peri-radiotherapy
- Comprehensive evaluation of rare case: From diagnosis to treatment of a sigmoid Schwannoma: A case report
- Emerging role of liquid biopsy in rat sarcoma virus mutated metastatic colorectal cancer: A case report
- Application of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy in curative surgery for esophageal cancer: A metaanalysis
- Colorectal cancer’s burden attributable to a diet high in processed meat in the Belt and Road Initiative countries
