Diabetes mellitus: An overview of the types, prevalence, comorbidity, complication, genetics, economic implication, and treatment
Adekunle Sanyaolu,Aleksandra Marinkovic, Stephanie Prakash,Martina Williams, Yashika Dixon, Chuku
Okorie,Verner N Orish,Ricardo Izurieta
Abstract Diabetes is one of the deadliest diseases.Due to its effects on the lives of people, it has attracted a lot of attention recently.The causes of the various forms of diabetes, including type 1 and type 2, were discussed along with how they affect those who have the disease.Younger people are more prone to type 1 diabetes than older people, who are more likely to develop type 2.The treatment options and strategies for the two forms of diabetes were also discussed in addition to how the disease affects the quality of life of people.Among several factors that were explained, it has been shown that people from low and middle-income countries are more prone to having diabetes.Additionally, the condition is more likely to affect some races more than others.It is associated with obesity.According to statistics, those who are poor are more severely affected by the disease.The progression of the disease over time has been associated with an increase in disability and mortality.
Key Words: Diabetes mellitus; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes; Diabetes; Insulin; Blood glucose
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by abnormalities in insulin secretion or action, or sometimes both[1].Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas that works as the primary messenger for moving glucose from consumed meals to flow from the bloodstream into the body's cells where it is used for energy[2].Diabetes affects the entire system and causes issues in specific organs such as the eyes, nerves, and kidneys[3].It affects 9.0% of the adult population globally, according to the World Health Organization[2,4,5].It is a developing pandemic that may be traced back to the fast rise in obesity and inactivity[3], being classified into two types: Type 1 (insulin-dependent) and type 2 (noninsulin-dependent) (adult-onset)[1].Diabetes causes serious health problems globally, primarily increasing the risk of heart disease and other complications[4].It affects 80.0% of the population in low and middle-income nations, and in wealthy countries, adults between the ages of 35 and 64 years are most affected[4].
Furthermore, the most economically and socially marginalized persons have the heaviest burden of living with the condition and are most financially impacted[4,5].Its consequences are assessed not only by the rise in the prevalence presented every year per capita, but also through the rising number of complications and deaths[4].While the prevalence of most infectious illness continues to diminish as technology improves and life expectancy increases, the impacts of diabetes continue to increase[4].This article reviews diabetes mellitus with an overview of the types, prevalence, comorbidity, complication,genetics, economic implication, and treatment.
METHODOLOGY
The electronic databases PubMed, Google Scholar, and Med Line Plus were searched for the review of literature.The search was limited to peer-reviewed publications between January 1994 and November 2022 for the compiled data.Publications that had keywords including "diabetes mellitus" were chosen.The articles were then included after being evaluated for relevance to the topic (Figure 1).
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DIABETES
Diabetes is a metabolic illness in which insulin plays a central role.There are several pathogenic pathways at work in the etiology of this illness[1].They vary from autoimmune death of pancreatic beta cells, resulting in chronic insulin insufficiency, to a disease inhibiting insulin action[1].The cause of this condition is an aberrant carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism caused by insufficient or even defective insulin activity[1].The major cause of hyperglycemia is a deficiency in either secretion or effect of insulin at one or more sites along its route of action[1].
TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS

Figure 1 Article selection.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is triggered by an autoimmune response in which the body targets insulin-producing cells[1].The level of beta cell breakdown in T1DM varies among patients, being fast in some and exceedingly sluggish in others[1].Keto-acidosis is the most common initial symptom of the illness in most people[1].Others exhibit symptoms such as fasting hyperglycemia as well as ketoacidosis in the context of environmental variables[1].Although some people may preserve adequate beta-cell activity to prevent keto-acidosis, many individuals eventually become insulin dependent and develop keto-acidosis[1].As the condition advances, insulin production decreases, and C-peptide levels become low, and often may become undetectable[1].A variety of reasons, including heredity, environmental factors, and idiopathic causes have been linked to the autoimmune degradation of beta cells[1].Some cases of T1DM have an unclear origin as seen in some people of African or Asian descent[1].
TYPE 2 DIABETES
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) affects 90.0%-95.0% of the diabetic population.T2DM is characterized by a complicated process in which the fundamental issue is a balance between insulin production by beta cells and insulin action, resulting in insulin resistance to insulin-stimulated glucose in the blood[3].Impaired glucose tolerance is the illness' intermediate stage that determines the risk of heart disease[1].Many individuals with T2DM are obese, indicating that obesity may induce some sort of insulin resistance[1].Keto-acidosis occurs spontaneously and gradually in this type of diabetes, and it is frequently triggered by the same conditions that cause T1DM such as stress and illness.Because of the absence of apparent symptoms, T2DM is commonly undiagnosed[3].Most of the symptoms develop slowly and are frequently not severe enough to be detected[1].
REGIONAL OVERVIEWS
The diversity of socioeconomic and geographical parameters, prevalence, associated death, and health expenditure may all be used to assess the Global Perspective[1,2,5].Most diabetics reside in less developed and economically disadvantaged parts of the world[5].Eighty percent of the population is from low- to middle-income nations[1,2,5].Different forms of diabetes are prevalent across the world,yet each has a distinctive impact on different populations[5,6].Infectious diseases, such as human immunodeficiency virus and malaria, as well as poverty are prevalent in Africa[5].A shift in lifestyle in urban and rural regions, has resulted to an increase in obesity."Diabetes has taken precedence in this region" and others[5,6].Europe is grouped into 56 countries, with socioeconomic levels ranging from low to high[7].Age is the most important risk factor for diabetics.Diabetes is expected to affect 56 million people in Europe, with adults accounting for 8.5%[7].The top three nations in the Middle East and North Africa with the highest comparative frequency are Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Qatar[6,7].The rapid rise in economic growth, along with an aging population, has led to a substantial rise in the prevalence of T2DM[4].Rapid urbanization, lower infant mortality, and increasing life expectancy are the primary drivers of the increase in T2DM prevalence[4].North America and the Caribbean have the second-highest comparative prevalence of adult diabetes (9.6%)[4].If the main North American countries of the United States (US), Mexico, and Canada were included in the figure because of their large population, the Caribbean islands would still have the greatest occurrence[4,7].Diabetes affects 38.6 million individuals in this region, with the number anticipated to climb to over 50 million by 2035[7].The US had the highest number of diabetics, at 24.4 million[4].
DIABETES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
Diabetes is one of the most common disorders affecting school-aged children[8].In 2012, around 208000 young persons under the age of 20 years in the US developed diabetes[8].Additionally, during the COVID-19 pandemic, children with newly diagnosed T1DM had higher glucose and HbA1c levels,necessitating specific actions to increase clinician and public awareness[9].T1DM had a global incidence rate of 19.73 per 100000 children in 2019 and 32.39 per 100000 in 2020[9].The number of pediatric cases of new-onset T1DM, diabetic ketoacidosis, and severe diabetic ketoacidosis increased by 9.5% (T1DM),25.0% (DKA), and 19.5% (severe DKA), respectively, during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to pre-pandemic levels[9].
A high proportion of children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes are also susceptible to insulin resistance and have a family history of T2DM[8,10].Certain racial and ethnic groups, including African Americans, American Indians, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and some Asian and Pacific Islander Americans, have higher rates of T2DM[10].Some children and adolescents with T2DM may not exhibit any signs or symptoms at all[10].Other individuals' symptoms may resemble those of T1DM[10].A toddler or teenager may feel tired, thirsty, or sick and urinate more frequently[10].Weight loss, hazy vision, recurring infections, and delayed wound/sore healing are all possible symptoms[10].Because symptoms vary so much, healthcare practitioners must identify and evaluate children and adolescents who are at high risk for the condition[10].The key to controlling T2DM in children is a balanced diet and quantity management, as well as increased physical activity[10,11].Metformin should also be recommended when T2DM is diagnosed[11].However, data indicate that 50.0% of young people with T2DM will be unable to keep their hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) below 8.0% on metformin alone, with or without lifestyle changes[11].If metformin alone is insufficient to normalize blood glucose levels,insulin may be required[11,12].At the time of diagnosis, blood pressure, lipid profile, microalbuminuria evaluation, and dilated eye examination are suggested[12].
DIABETES IN ADULTS
In 2021, diabetes was the eighth leading cause of mortality in the US, affecting more than 100000 people[13].Nearly one-fourth of all US persons with diabetes are undiagnosed, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Diabetes Statistics Report[14].Table 1 shows that this is particularly evident in younger adults aged 18-44 years[14].More than 1/3 of the population with diabetes in this age range are unaware of or did not report having diabetes[14].
Though the trend in the incidence of diabetes among adults has been decreasing significantly since 2008, Table 2 shows that there were still 1.4 million new cases in 2019[15].It is also worth noting that incidence rates are significantly higher among those with a high school education or less[16].This indicates that more effort should be made on health education among those with lower scholastic achievements[15,16].
TREATMENT OF DIABETES AMONG PEOPLE AGED 18 YEARS OR OLDER WITH DIAGNOSED DIABETES IN THE UNITED STATES, 2015-2016
Diabetes management begins with healthy eating habits and physical activity.Since this may be challenging, medications are available to augment the achievement of better treatment results[17].A retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of the 2003-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data was carried out to investigate trends in the use of diabetes medications[17].The study sampled 6323 patients[17].Furthermore, those 18 years and older with an HbA1c greater than 6.4%, or a fasting plasma glucose greater than 125 mg/dL were included [17].The percentage of patients taking any medication increased from 58.0% in 2003-2004 to 67.0% in 2015-2016[17].The use of metformin and insulin analogs increased following American Diabetes Association recommendations in 2007 when metformin was and continues to be the preferred first-line therapy for T2DM[17].Among patients on one therapeutic agent, the use of metformin increased from 33.0% in 2003-2004 to 74.0% in 2015-2016[17].Risk factors for T2DM in adults include: Overweight or obesity, age of 45 years or older, a family history of diabetes, decreased physical inactivity, and history of gestational diabetes[18].Figure 2 shows the distribution of diabetes across races/ethnicity.Diabetes is most prevalent among American Indians and Alaska Natives (14.5%), followed by Blacks (12.1%), people of Hispanic origin (11.8%), Asians(9.5%), and Whites (7.4%)[19].

Table 1 Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes among people aged 18 years or older in the United States, 2019

Table 2 New cases of diagnosed diabetes among people aged 18 years or older in the United States, 2018-2019
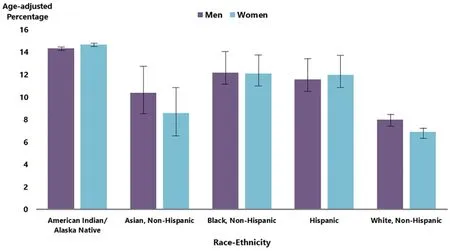
Figure 2 Diabetes by race/ethnicity.The age-adjusted estimated prevalence of diagnosed diabetes by race/ethnicity group and sex for adults aged 18 years or older in the United States, 2018–2019.Data sources: 2018–2019 National Health Interview Survey; 2019 Indian Health Service National Data Warehouse (for American Indian/Alaska Native group only)[19].
CO-MORBID CONDITIONS
The autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT), celiac disease (CD), Addison’s disease,and vitiligo are frequently linked to T1DM[19].In comparison to 0.5% of the general population, CD prevalence in T1DM patients ranges from 1.5% to 10.0%[20].It is important to note that people who develop both illnesses have an earlier age onset for TIDM than patients who just have T1DM[20].Furthermore, 3.4% - 50.0% of people with T1DM also have AIT[20].Anti-thyroid antibodies are developed in 11.0% - 16.9% of T1DM patients within the first year of diagnosis, with females being more frequently impacted[20].Up to 2.0% of T1DM patients may have anti-adrenal autoantibodies[20].It is commonly known that autoimmune diseases like diabetes and vitiligo are related.About 6.0% of diabetic children have vitiligo[20].Additionally, T1DM has been linked to non-autoimmune diseases such as eating disorders[20].
The most common conditions seen in T2DM, according to previous research and American Diabetes Association guidelines, are hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity, depression, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma, coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), arthritis,cancers, neuropathy, heart failure, fractures, peripheral arterial disease, and retinopathy[21].According to a study by Linet al[21], persons over 65 years of age are more likely than those under 65 years to have multiple co-morbid conditions.Additionally, they discovered that older persons were less likely to be obese and depressed but more likely to have hyperlipidemia, hypertension, CAD, CKD, arthritis,malignancy, and heart failure[21].With this information in mind, customized management plans should be created for frequent comorbidity clusters.
COMPLICATIONS
Diabetes can cause long-term harm to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.Smoking cigarettes, being overweight or obese, doing little or no physical activity, having high blood pressure,and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for developing diabetes complications[22].According to a multinational study, heart disease and stroke account for 50.0% of diabetes-related deaths[23].In comparison to adults without diabetes, patients with diabetes over the age of 18 years have 1.7 times higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease[24].In 2011, the CDC found that nearly one-third of diabetics aged 35 years or older had a history of heart disease or stroke.It has been reported that coronary heart disease(21.9%) affects more people than stroke (9.1%)[22].
Diabetes has major complications that may be fatal, such as hyperglycemic crises, which include diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar condition[20].Death rates have progressively decreased over time, but 17.3 per 100000 people still die each year[24].In 2011, 44.0% of all new cases of renal failure were caused by diabetes.In the same year, 228924 people of all ages were undergoing diabetes-related dialysis or a kidney transplant, while 49677 people of all ages started therapy for kidney failure[24].The minor blood vessels in the retina are harmed by diabetic retinopathy, which causes blindness.Diabetes is responsible for 1.0% of blindness worldwide[23].Furthermore, diabetes may result in amputations.Foot neuropathy raises the risk of developing foot ulcers, getting infected,and ultimately leading to an amputation[23].Around 73000 non-traumatic lower limb amputations occurred in 2010 for adult diabetics.Overall, these patients comprise about 60.0% of all non-traumatic lower-limb amputations in adults over the age of 20 years[24].
GENETIC ROLE IN DIABETES MELLITUS: TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
One of the factors associated with the risk of T1DM is genetic variation.Some families have an inherited propensity for T1DM development[25].It has been shown that the immune system can distinguish between proteins produced by the body's own cells and those produced by foreign invaders with the aid of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex[25].An increased risk of T1DM exists with some HLA variations on chromosome 6[25].Hundreds of genes that are known to play a role in the immune system are found in the genetic sequence area.The genes frequently linked to T1DM have been identified to be part of the HLA class II genes.These genes includeHLA-DQA1,HLA-DQB1, andHLADRB1[25].
An estimated 40.0%–50.0% of the heritable risk for T1DM is attributed to HLA class II genes[26].Researchers discovered a significant link between T1DM and the haplotypes DQA1*0501-DQB1*0201 and DQA1*0301-DQB1*0302 in Caucasian populations[26].A haplotype is a group of single nucleotide polymorphisms that are located on the same chromosome[26].Further research revealed that different races have different high-risk haplotypes for T1DM, such as DRB1*07-DQA1*0301-DQB1*0201 for African Americans, DRB1*09-DQA1*0301-DQB1*0303 for Japanese people, and DRB1*04-DQA1*0401-DQB1*0302 for Chinese people[26].Additionally, it was discovered that DRB1*15-DQA1*0602-DQB1*0102 were protective and linked to a lower incidence of T1DM in most populations[26].Recent studies reveal that independent of HLA class II genes, other genes in the central, class I, and extended class I areas may also enhance the risk of T1DM[26].
People with high-risk DRB1-DQA1-DQB1 haplotypes are substantially more likely to develop T1DM than people without such a haplotype[25].It is reported that there is an approximately 6.0% absolute risk for Caucasian people with two susceptibility haplotypes to develop T1DM by the time they are 35 years old.However, in populations where T1DM is uncommon, this number is much lower (1.0%among Asians).Two other genes, insulin (INS) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated 4 (CTLA-4), are also known to affect the risk of T1DM as shown in Table 3[27,28].
GENETIC ROLE IN DIABETES MELLITUS: TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
The metabolic illness T2DM is characterized by hyperglycemia and a lack of insulin in the blood.One of the many factors contributing to T2DM is a genetic anomaly[26].In 2011, several studies found that about 36 genes were connected to an elevated risk of T2DM.Due to these hereditary variables, only 10.0% of T2DM cases are clinically present[26].Table 4 lists the genes that are susceptible to T2DM[29].
Due to its function in adipose tissue and lipid metabolism, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors γ (PPARγ) gene is crucial for study[30].The PPARγ gene's (Pro) function lowers insulin sensitivity while simultaneously raising the risk of T2DM[30].In most populations, this gene is regarded as being prevalent[30].At least one copy of the Pro allele is carried by 98.0% of Europeans.As a result, it probably accounts for a sizable part (25.0%) of T2DM in the Caucasian population[30].
Humans and most other mammals contain the proteins known as ATP binding cassette, subfamily C,member 8 (ABCC8)[31].Sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) protein is made with the help of this gene[31].This protein and the Kir6.2 sub-unit, which is encoded by KCNJ1, are components of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel, which participate in a wide range of physiologic responses, such as controlling the release of insulin and glucagon from the beta cells of the pancreas[31].Insulin secretion and potassium channel function can both be impacted by a gene abnormality[31], finally leading to T2DM.Intriguingly,the distance between ABCC8 and KCNJ11—which is only 4.5 KB—is close to that of the INS gene[31].ABCC8(Ala)and KCNJ11(Lys) gene variants have been linked to T2DM[30].
A ubiquitously expressed intracellular calcium-dependent cysteine protease known as calpain 10,which is prevalent in humans, is encoded by the CAPN10 gene[32].An intrinsic adenine (A) to glycine(G) mutation at position 43 of a haplotype that was previously associated with T2DM appears to be important in CAPN10 transcription[32].According to physiological research, the differences in chaplain 10 activities' effects on insulin secretion increase the risk of T2DM[32].Studies from various ethnic groups suggest that Mexican American communities may be considerably more likely than Caucasian populations to have an increase in T2DM risks because of this locus[32].
COST OF DIABETES
Diabetes economic expenses in the US rose by 26.0% between 2012 and 2017, after accounting for inflation, because of rising diabetes prevalence and per-person costs[33].The population aged 65 and older is most affected by the rise in diabetes prevalence and medical expenses, which adds to the rising financial burden on the Medicare program[33].The estimated $327 billion total cost of diabetes diagnosis in 2017 includes $237 billion in direct medical expenses and $90 billion in lost productivity[33].Average annual medical costs for individuals with diabetes are $16750, of which diabetes-related expenses account for $9000 of that total[33].Medical costs for those with diabetes are, on average, 2.3 times more expensive than that for people without the disease[33].The indirect costs of diabetes include increased absenteeism ($3.3 billion) and decreased productivity at work ($26.9 billion) for the employed population, as well as decreased productivity for those who are not in the labor force ($2.3 billion)[33].In addition, indirect costs include the inability to work due to disease-related disability ($37.5 billion)and lost output as a result of 277000 premature deaths that can be directly linked to diabetes ($19.9 billion)[33].
TREATMENT
The course of treatment for diabetes varies from patient to patient depending on the laboratory test results, particularly the levels of blood glucose[34].Blood glucose control is the main objective of every treatment plan to avoid associated problems[34].The primary treatment modalities targeting T1DM are insulin therapy, oral hypoglycemic agents, exercise, and a regulation/monitoring of diet[34].The primary goals of T2DM are weight loss and dietary advice.In the severe event where the aforementioned techniques fail to regulate blood glucose levels, oral medication will be administered [34].

Table 3 Estimated relative risk of genes that affect type I diabetes mellitus

Table 4 Estimated relative risk of genes that affect type II diabetes mellitus
CONCLUSION
Diabetes has been associated with significant financial loss for the families that are affected.It has also been associated with severe complications which could leads to death.l.T1DM and T2DM are the two types of diabetes mellitus.The former is more prevalent among children, whereas the latter is more prevalent among adults.However, there are risk factors that have been identified in children that could lead to the development of T2DM and have a negative impact on their health.Diabetes is known to cause other severe complications in patients, resulting in even more misery and premature death.Individuals' chances of developing diabetes are also affected by their race, ethnicity and lifestyle.Perhaps this is related to the social and economic factors among these races.In people suffering from this disease, fortunately, interventions as well as treatment options are available.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Sanyaolu A contributed to conceptualization and methodology; Marinkovic A, Prakash S,Williams M, and Dixon Y contributed to writing – original draft preparation; Izurieta R, Okorie C, and Orish VN contributed to writing – review & editing; Sanyaolu A contributed to project administration.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Nigeria
ORCID number:Adekunle Sanyaolu 0000-0002-6265-665X; Aleksandra Marinkovic 0000-0002-3672-0777; Stephanie Prakash 0000-0003-2664-9775; Martina Williams 0000-0001-5136-4179; Yashika Dixon 0000-0003-4007-9481; Chuku Okorie 0000-0001-5483-0032; Verner N Orish 0000-0002-8345-423X; Ricardo Izurieta 0000-0003-1256-5896.
S-Editor:Liu JH
L-Editor:Ma JY
P-Editor:Liu JH
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2023年5期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2023年5期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- Evidence relating cigarette, cigar and pipe smoking to lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Meta-analysis of recent data from three regions
- Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as promising therapy in the improved survival of pediatric patients with leukemias and myelodysplasias
- Real-world effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in the elderly during the Delta and Omicron variants: Systematic review
- Pulmonary cytomegalovirus infection: A case report and systematic review
- Advances in the mechanism of action of metformin in pituitary tumors
- Vitamin D deficiency among outpatients and hospitalized patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
