Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals the regulatory effects of artesunate on splenic immune cells in polymicrobial sepsis
Jiyun Chen ,Xueling He ,Yunmeng Bi ,Jing Liu ,Yin Kwn Wong ,Lulin Xie ,Qin Zhng ,Pio Luo ,Peng Go ,Liwei Gu ,Qiuyn Guo ,Gungqing Cheng ,Chen Wng ,**,Jigng Wng ,,*
a State Key Laboratory for Quality Ensurance and Sustainable Use of Dao-di Herbs,Artemisinin Research Center,and Institute of Chinese Materia Medica,China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing,100700,China
b Department of Nephrology,Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Kidney Diseases,and Shenzhen Clinical Research Centre for Geriatrics,Shenzhen People's Hospital,The First Affiliated Hospital,Southern University of Science and Technology,Shenzhen,Guangdong,518020,China
c Department of Gastroenterology,Shenzhen Hospital,Southern Medical University,Shenzhen,Guangdong,518020,China
Keywords: Artesunate Sepsis Single-cell RNA sequencing Immunomodulatory activity
ABSTRACT Sepsis is characterized by a severe and life-threatening host immune response to polymicrobial infection accompanied by organ dysfunction.Studies on the therapeutic effect and mechanism of immunomodulatory drugs on the sepsis-induced hyperinflammatory or immunosuppression states of various immune cells remain limited.This study aimed to investigate the protective effects and underlying mechanism of artesunate(ART)on the splenic microenvironment of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model mice using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and experimental validations.The scRNA-seq analysis revealed that ART inhibited the activation of pro-inflammatory macrophages recruited during sepsis.ART could restore neutrophils’ chemotaxis and immune function in the septic spleen.It inhibited the activation of T regulatory cells but promoted the cytotoxic function of natural killer cells during sepsis.ART also promoted the differentiation and activity of splenic B cells in mice with sepsis.These results indicated that ART could alleviate the inflammatory and/or immunosuppressive states of various immune cells involved in sepsis to balance the immune homeostasis within the host.Overall,this study provided a comprehensive investigation of the regulatory effect of ART on the splenic microenvironment in sepsis,thus contributing to the application of ART as adjunctive therapy for the clinical treatment of sepsis.
1.Introduction
Sepsis is defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated response of the host immune system to polymicrobial infection,leading to high mortality in patients [1,2].It is also characterized by the complex interplay of host proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes,manifesting as disturbed homeostasis of the immune microenvironment in multiple organs [3].Previous studies have demonstrated that sepsis infection directly or indirectly impairs the function of canonical immune cell types,including T and B lymphocytes,natural killer(NK) cells,neutrophils (Neutro),and macrophages/monocytes(Macro/Mono) within immune-relevant organs and/or tissues [3].Therefore,the immunotherapeutic strategies targeting sepsisinduced hyperinflammation and/or immunosuppression are gradually gaining attention from researchers [4].
As the largest peripheral immune organ of the host,the spleen is the main site where immune cells reside and produce immune responses to both endogenous and exogenous antigens[5].The spleen is divided into red and white pulps based on cellular composition and structure.Many innate immune cells including Neutro and Macro/Mono reside in the red pulp,releasing immune effector substances such as complements and cytokines that can enhance phagocytosis in response to infection.Meanwhile,the lymphocytes in the white pulp can recognize and engulf the invading bacteria and viruses,filtering the circulating blood and protecting the host from infection.Previous studies have demonstrated the fundamental role of the spleen in bacterial clearance via an antibody response or macrophage bactericidal capacity,contributing to bacterial endotoxin detoxification[6].Studying the dynamic changes in various immune cells in the spleen during sepsis can thus be invaluable for further understanding the mechanism of sepsis and developing immunomodulatory therapy.
In recent years,the therapeutic effects of artemisinin derivatives such as artesunate (ART) and dihydroartemisinin (DHA) on the immune system in disease settings have been highlighted[7-9].In addition to the immunomodulatory therapeutic effects of these derivatives on systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis,a recent study revealed that DHA could regulate the immune system via the promotion of CD8+T lymphocytes and the suppression of B cell responses in the spleen of both healthy and Plasmodium berghei-infected mice[10].More importantly,ART has also been reported to be effective in treating sepsis,including septic neuroinflammation and lung damage [11-13].These findings suggest that ART can regulate the host-immune systems during sepsis progression.However,the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms still need further elucidation.
With the development of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq)technology,researchers were able to unbiasedly capture gene expression profiles at single-cell resolution,contributing to our understanding of cellular state and functional heterogeneity,and uncovering the cellular response and dynamic reprogramming in normal,disease,and therapy conditions[14].This methodology has been successfully employed to reveal the immune cell composition and transcriptomics profiles from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in clinical patients with sepsis as well as multiple tissues in the experimental sepsis model [15-17].Therefore,the scRNA-seq technology can provide further novel insights into the molecular mechanisms and therapy development for sepsis.
In the present study,we applied scRNA-seq approach along with bioinformatic analysis,to elucidate the immunomodulatory effects of ART within various immune cell subsets of the spleen on the cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)mouse model.This strategy allowed us to systematically investigate the cellular response and transcriptomic heterogeneity among various immune cells of the spleen during sepsis and after ART treatment,highlighting the immunoregulatory function of ART as adjunctive therapy for sepsis treatment.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Animal experiments
BALb/c male mice (weighed 20-22 g,and aged 6-8 weeks)were purchased from Beijing Vatalriver Laboratory Animal Technology Co.,Ltd..The mice were fed adaptively for 1 week in a specific pathogen-free facility.Then,they were randomly divided into three groups(n=8 per group):Sham,Model,and ART groups.Sepsis was established through CLP as previously described [18].After the surgery in 4 h,10 mg/kg ART solution was intraperitoneally injected into the mice in the ART group,and the mice in other groups were injected with equal volumes of normal saline.All the mice were sacrificed and the spleen samples were collected after 12 h.The mice were observed every 12 h in the 4 days and survival rates were recorded.The experimental protocols were approved by the animal ethics committee of the China Academy of Chinese Medical Science (Approval No.:2022B003).
2.2.Evaluation of spleen pathology
The mouse spleens were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,dehydrated,and paraffin-embedded.Subsequently,they were cut into slices with a thickness of 4 μm.The slices were dewaxed with xylene,rehydrated with graded ethanol,and stained with hematoxylin and eosin orderly.The cytomorphology of spleen tissues in each group was observed under an optic microscope.
2.3.Luminex instruments and multiplex assays
The spleen samples were collected and stored at -80°C.The soluble factors in the spleen were quantified on the Luminex FLEXMAP 3D multiplexing platform.A mouse premixed multi-analyte kit(LXSAHM-11;R&D Systems,Shanghai,China) was used to measure the concentrations of a panel of soluble factors,including interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α),IL-2,IL-4,IL-10,IL-17 A,C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2),CCL3,CCL4,interferon-gamma (IFN-γ),tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α),and granzyme B (GZMB) in one sample at the same time.Luminex assays were performed as the manufacturer's protocol suggested,and each group contains 6 biological replicates.The samples were read on a Luminex FLEXMAP 3D System.The raw data were processed with the Milliplex Analyte program by using a five-parameter logistic regression analysis.
2.4.Western blot (WB) assay
The mouse spleens were lysed with radio immunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer and a 1% protease inhibitor cocktail.The bicinchoninic acid assay kit was used to determine the protein concentrations.Equal amounts of proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on a polyacrylamide gel.The proteins were then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and blocked with 5% (m/V) skimmed milk powder for 1 h.The membranes were labeled with primary antibodies,including pP65 (3033;Cell Signaling Technology,Beverly,MA,USA),P65 (10745-1-AP;Proteintech Group,Inc.,Wuhan,China),programmed death 1 (PD-L1) (ab 213480;Abcam,Cambridge,UK),and KLRD1(PA5- 102559;Thermo Fisher Scentific Inc.,Waltham,MA,USA) overnight at 4°C and with secondary antibodies for 1 h.The immunoblots were exposed to enhanced chemiluminescence reagent and the resulting area and intensity of the bands were quantified using Image J software.
2.5.Biochemical kit assay
The spleen tissue samples were homogenized with normal saline on ice using a homogenizer.Several determination kits(Nanjing Jiancheng Corp.,Nanjing,China) were used to assess the activities of catalase(CAT;A007-2-1),superoxide dismutase(SOD;A001-3),glutathione reduced (GSH;A006-2-1),nitric oxide (NO;A013-2-1),and malondialdehyde (MDA;A003-2) following the manufacturer's protocols.
2.6.Flow cytometry
The mouse spleens were dissociated into single cells,then the red blood cells(RBCs)were removed from the lysate.The cells were subjected to incubation with antibodies: CD19 (551,001;BD Biosciences,San Jose,CA,USA),CD79a(561,942;BD Biosciences),JUN(40,502;Cell Signaling Technology),F4/80 (566,787;BD Biosciences),CD11b(558,123;BD Biosciences),and CD86(560,582;BD Biosciences) for 30 min.They were then rinsed two times using phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and evaluated using flow cytometry (BD FACSCanto?II;BD Biosciences).
2.7.Processing of splenic tissue and isolation of cells
The mouse spleens were placed in Petri dishes containing 5 mL of Hanks'Balanced salt solution(Gibco,Waltham,MA,USA)buffer.The spleen samples were carefully cut into small pieces and transferred to a cellular strainer placed above a 50-mL conical tube.The samples were mashed or pressed through the filter with the plunger end of the syringe,and the cells were washed through the strainer with excess PBS three times.
2.8.scRNA-seq analysis of the splenic cells in sepsis model mice
The splenic cells were suspended to 1000 cells/μL and captured using the 10x Genomics platform (Pleasanton,CA,USA) and the Chromium Next GEM single-cell 3′Kit v3.1 from 10x Genomics,following the manufacturer's protocols.Microfluidic technology was used to encase microbeads and single cells with cellular barcodes in droplets.The cells were then lysed in individual droplets,and the mRNA was linked to the cellular barcode on the beads to form single-cell GEMs.A reverse-transcription reaction was carried out in droplets to construct a complementary DNA library.The single-cell RNA libraries were sequenced using an NovaSeq 6000 sequencer(Illumina,Inc.,San Diego,CA,USA)with 150-bp paired-end reads.
2.9.Pre-treatment of the scRNA-seq dataset
Raw data from each sample were processed with Fastp [19](version 0.20.0)for quality control to remove low-quality reads from sequencing adapters and default settings.Then,the raw gene expression matrix was generated using the cell ranger(version 6.0.1)pipeline coupled with the mouse reference genome (mm10) and analyzed using the Seurat R package (version 4.0.4) [20] in R software(version 4.1.1).Next,Seurat'sSCTransformfunction was used to normalize and scale the nine samples.All cells were integrated into a matrix,and cell clustering was carried out based on common characteristics.Finally,all the clustered cells were subjected to principal component analysis (PCA) for dimensional reduction and uniform manifold approximation and projection(UMAP)for visualization.
2.10.Cell subtype annotation and cell state scores
Seurat'sFindAllMarkersfunction was conducted to identify the expressed markers in each cluster.Besides,each cluster was annotated according to the expression level of canonical markers of specific cell types.As for the subtype dataset,the procedures of PCA,clustering,and cell subtype annotation were performed as previously described.Seurat'sAddModuleScorefunction was used to evaluate the cell state scores,indicating the average expression of genes from a certain predefined expression geneset,which represented the cellular state of individual cells.
2.11.Differentially expressed genes and gene functional enrichment analyses
Seurat'sFindMarkersfunction was used to identify the significant differentially expressed genes(DEGs)between two conditions(min.pct=0.1,P<0.05,and avg_log2(fold change) ≥0.25).Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was performed using the clusterProfiler R package(version 3.18.1),according to the up-and down-regulated protein identified by DEGs analysis.Pvalues were generated from the hypergeometric test model and adjusted using Benjamini-Hochberg method.The biological process (BP) category was selected to represent the functional profiles and visualized based on the count of enriched genes and the adjustedP<0.05.
2.12.Pseudotime analysis
The Monocle2 R package(version 2.20.0)was applied in pseudotemporal analysis to discover the cell-state transitions of the Macro_C1 subgroup and Neutro cells,respectively[21].The Seurat object was first converted into the CellDataSet object,then the genes with significantly changed expression were determined with adifferentialGeneTestfunction.Subsequently,theplot_cell trajectoryfunction was used to plot the lineage trajectories,indicating the differential cell states.
2.13.Cellular communication analysis
The cellular communication analysis was performed using the CellChat R package(version 1.1.3)based on the ligand-receptor(LR) interactions in different cell types [22].First,the normalized gene expression matrix and major cell types in the Sham,Model,and ART groups served as input for CellChat.ThemergeCellChatandcompareInteractionsfunctions were then used to calculate the differential numbers of pairs between Sham,CLP,and ART groups.We further explored the cells with significant changes in the same way using thesubsetCellChatfunction.Finally,we obtained several L-R pairs with differentially expression levels among three groups,and the results were displayed as bubble plots using thenetVisual_bubblefunction.
2.14.Statistical analysis
The differences between groups were evaluated using unpaired one-way analysis of variance with GraphPad Prism software.The data were presented as means ± standard error of the mean.Pvalues less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant unless otherwise specified.
2.15.Data and code availability
The data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Open Archive for Miscellaneous Data,China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics,Chinese Academy of Sciences(https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/omix;Accession No.:OMIX002221).
3.Results
3.1.ART treatment alleviated the inflammatory syndrome of CLPinduced sepsis
We primarily monitored the survival condition of CLP-induced mice with or without ART treatment (10 mg/kg) for 4 days to examine the therapeutic effects of ART treatment on sepsis-related mortality.As shown in Fig.1A,ART treatment significantly improved the survival of mice compared with untreated mice with sepsis (P=0.0375).CLP-induced injury caused a reduction in mouse weight and increased spleen indexes,indicating the successful establishment of the CLP model.However,ART treatment did not significantly reverse these indexes to baseline levels.(Figs.1B and C).As for histological changes,some necrotic and apoptotic bodies were found in the red pulp in the spleen sample of the CLP group.These CLP-induced features in the spleen tissue were partially alleviated in the ART group(Fig.1D).
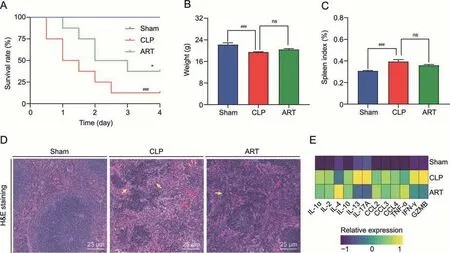
Fig.1.Cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)-induced spleen injury in septic mice and artesunate(ART)therapy.(A)The survival rates of septic mice in three groups were recorded over 4 days(n=12).(B)Body weight in mice of each group(n=6).(C)Spleen index in mice of each group(n=6).(D)Hematoxylin and eosin(H&E)staining diagram(40×)of the spleen tissues in each group.The yellow arrows indicate the white pulp that had started to enlarge and fuse,and the red arrows indicate some necrotic and apoptotic bodies.(E)Heatmap of Luminex liquid suspension chip analysis indicates the relative expression level of various cytokines and chemokine in splenic interstitial fluid derived from mice of each group(n=6).*P <0.05 and ###P <0.001;ns: no significance;IL: interleukin;CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand;TNF: tumor necrosis factor;IFN: interferon;GZMB: granzyme B.
Furthermore,we performed Luminex liquid chip analysis to evaluate the inflammatory state in spleen tissues.We found that the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and GZMB were up-regulated under septic induction (Fig.1E).In contrast,we noticed the down-regulation of these cytokines in the ART group,supporting the anti-inflammatory effect of ART on the septic spleen.We also observed the up-regulation of antiinflammatory cytokines such as IL-4 after ART treatment,which contributed to the suppression of cell-mediated immunity and death associated with polymicrobial sepsis [23,24].Therefore,the results of this study indicated that the inflammatory state in the septic spleen was alleviated after ART treatment,revealing the immunoregulatory effect of ART on the spleen during sepsis.
3.2.Single-cell profiling of the cellular landscape of the spleen in sepsis and after ART-treatment
As demonstrated in the workflow chart(Fig.2A),we isolated the cells from spleen tissue samples and performed scRNA-seq (each group had three biological replicates) via the 10x Genomics platform,to investigate the cellular and transcriptomic alterations in the splenic microenvironment upon sepsis induction and after ART treatment.After quality control(Fig.S1A),86,671 high-quality cells(31,231 in the Sham,28,085 in the CLP,and 27,355 in the ART)were integrated into a normalized and un-batched dataset,and then subjected to PCA for dimensional reduction and UMAP for visualization (Fig.2B).Totally,we identified 11 major cell types based on the expression levels of canonical marker genes:T cell(Cd3e+),NK cell (Nkg7+),B cell(Cd79a+),RBC(Hba-a1+),Macro(C1qb+),Mono(Lyz2+),mDC(Ccr7+),pDC(Siglech+),Mast(Cpa3+),Plasma(Jchain+),and Neutro(S100a8+) (Figs.2C and S1B).
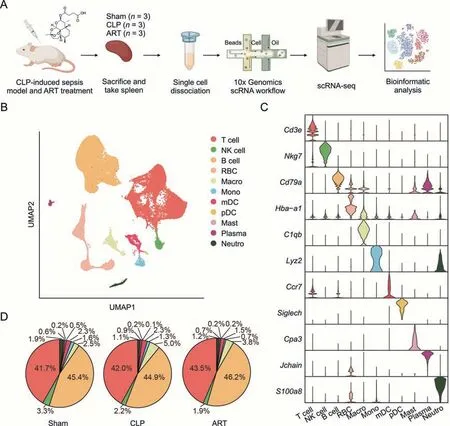
Fig.2.Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of mouse spleen of sepsis induction and after artesunate(ART)treatment.(A)Schematic workflow depicts the single-cell transcriptomics experiment design and analysis of the current study.(B)The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection(UMAP)visualization shows unsupervised single-cell RNA sequencing(scRNA-seq)clustering,revealing 11 distinct cellular identities.(C)The violin plot shows the expression levels of the respective selected markers across 11 clusters.The y-axis shows the log-scale normalized reads count.(D)The pie charts show the cellular proportion among 10 immune types except for red blood cell(RBC),accompanied by cellular percentage in each group,colored according to cell types.CLP: cecal ligation and puncture;NK: natural killer;Macro: macrophage;Mono: monocyte;mDC: myeloid dendritic cell;pDC: plasmacytoid dendritic cell;Mast: Mast cell;Plasma: plasma cell;Neutro: neutrophil.
Next,we visualized the cellular proportions of immune cells across three groups.However,we did not observe evident changes in the cellular composition in the CLP and ART groups compared with the Sham group,suggesting that the regulatory effect of ART on the septic spleen might not directly promote the proliferation or apoptosis of principal immune cells(Fig.2D).Therefore,we further evaluated the enrichment score of two inflammatory pathways:TNFA_SIGNALING_VIA_NKFB and IL6_JAK_STAT3_SIGNALING across the main immune cells in three groups based on gene set variation analysis (GSVA).Our findings demonstrated that most of the immune cells in the CLP group had higher enriched scores than those in the Sham group,consistent with previous reports [16,17].We also found that the enriched scores of two pathways across immune cells were significantly reduced after ART treatment(Fig.S1C).These results demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effect of ART on various immune cells.In the follow-up analysis,we will perform an in-depth investigation into the transcriptomic alterations and BPs across the representative immune cell types.
3.3.ART alleviated M1-like Macro recruitment and activation in mice with CLP-induced sepsis
To explore the landscape of Macro/Mono cells from Sham,CLP,and ART-treated mice,we first subset 2,741 Macro and 893 Mono from the whole scRNA-seq dataset,and re-clustered them into five subtypes based on the expression level of representative markers.The Macro/Mono subgroups include three Macro subtypes and two Mono subtypes: Macro_C1,Macro_C2,Macro_C3,Mono_C1,and Mono_C1 (Figs.3A and B).Among them,we found that the Macro_C1 subtype was characterized by M1-like Macro markers such as Cd80 and Cd86.The cellular proportion of Macro_C1 cells was increased in the CLP group compared with the Sham and ART groups,suggesting that the recruitment of M1-like Macro during sepsis progression was alleviated after ART treatment (Fig.3C).
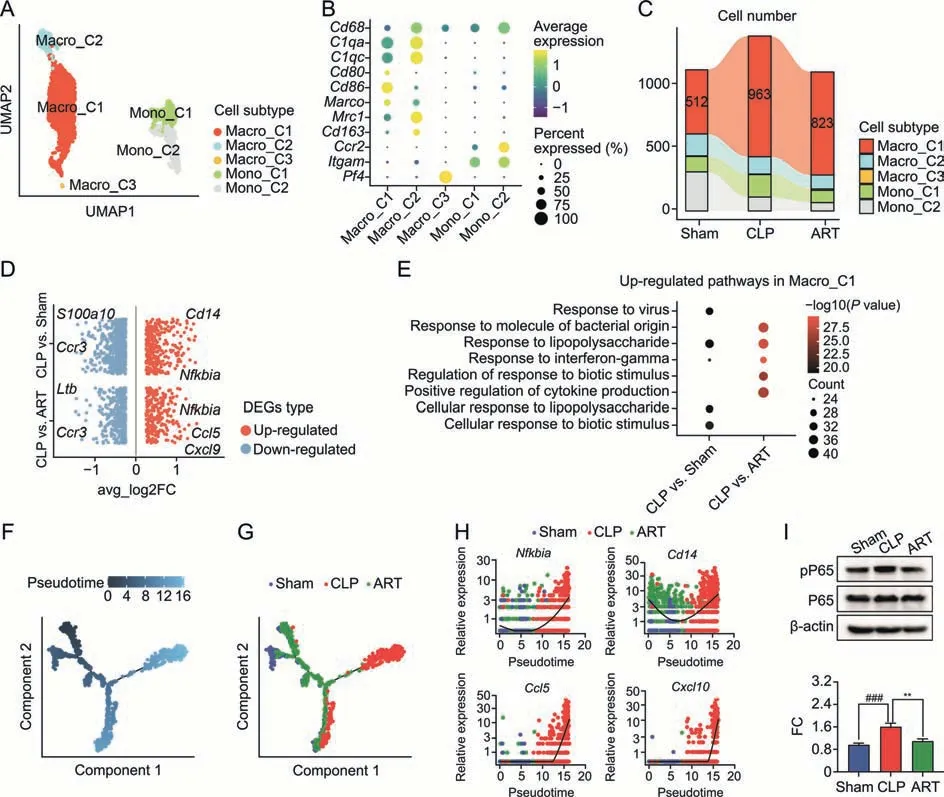
Fig.3.Artesunate(ART)effectively inhibits the recruitment and activation of macrophages in the cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)-induced sepsis mice.(A)The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection(UMAP) visualization shows unsupervised clustering,revealing 5 distinct subtypes of macrophage cells: Macro_C1,Macro_C2,Macro_C3,Mono_C1,and Mono_2.(B) The bubble plot depicts the cell markers expression of each macrophage subtype.(C) The Sankey plot shows the cellular proportion among five macrophage subtypes in each group,colored according to subtypes.(D) The visualization shows the scatter plot of the average log2 fold change (FC) value in both up-regulated and downregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of CLP vs.Sham and CLP vs.ART in Marco_C1 subtype,respectively.(E) Pathway enrichment analysis of overlapping upregulated DEGs in the CLP group compared with the Sham group,as well as in the CLP group compared with the ART group in the Macro_C1 subtype.(F,G) Pesudotime trajectory inference traces a path of pesudotime(F)and three group types(G).(H)The scatter plot shows the relative gene expression level of 4 representative genes(Nfkbia,Cd14,Ccl5,and Cxcl10) in pseudotime,colored according to group types.(I) The expression of pro-inflammatory factors phospho-nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) P65 (pP65) and NF-κB P65(P65) proteins by Western blot (WB) assay (up) and quantitative statistics of the FC of pP65/P65 proteins' expression level among three groups (down) (n=3).**P <0.01 and###P <0.001.Macro: macrophage;Mono: monocyte.
To profile the transcriptomic pattern changes of Macro_C1 cells among the Sham,CLP,and ART groups,we performed DEGs of CLP versus Sham (CLP vs.Sham) and CLP versus ART (CLP vs.ART)groups,respectively.A total of 983 CLP vs.Sham DEGs (327 upregulated and 656 down-regulated) and 651 CLP vs.Sham DEGs(256 up-regulated and 395 down-regulated) were detected(Fig.3D).Compared with the other two groups,the representative up-regulated genes in the CLP group includedNfkbia,Cd14,andCcl5,indicating that these inflammatory genes activated in the CLP group were down-regulated in the ART group.We further subjected the up-regulated DEGs to the GO enrichment analysis.Our results revealed that several biological pathways,including response to lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma,were activated during sepsis and restored to baseline levels after ART treatment (Fig.3E).
Furthermore,the pseudotime analysis was performed on the Macro_C1 subtype to investigate its dynamic gene expression along the trajectory.The distribution of cells in the pseudotime trajectory indicated their relative cellular states(Fig.3F).We found that most Macro_C1 cells from the Sham and ART groups were distributed at the starting locations of the trajectories.In contrast,those in the CLP group were mainly positioned in the end parts of trajectory branches (Fig.3G).Meanwhile,we also investigated the relative expression level of representative genes includingNfkbia,Cd14,Ccl5,andCxcl10.We found that the expression level of these genes decreased first (most of which were from the Sham and ART groups) and then increased (most of which were from the CLP group) along the pseudotime trajectory,which is consistent with our previous results(Fig.3H).As for the expression levels of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) among these genes,the differentially regulated expression ratios of phospho-NF-κB P65/NF-κB P65(pP65/P65) proteins across three groups were validated by WB assay (Fig.3I).Based on these results,we summarized that ART treatment inhibited the recruitment and activation of M1-like Macro,so as to restrict the inflammatory response from Macro during sepsis.
3.4.ART regulated immune dysfunctions and reactive oxygen species of Neutro during sepsis
As critical members of the innate immune system,Neutro was recruited to infected regions during sepsis,releasing Neutro extracellular traps to provide immune protection against pathogens.In our scRNA-seq dataset,we first profiled 1,062 Neutro cells from mouse spleens and divided them into three subtypes: Neutro_S1(Il1b+,Cxcl2+,Cxcl10+,andIcam1+,mainly associated with chemotaxis activity),Neutro_S2 (Spp1+,Ifitm3+,andIfitm6+,mainly involved in the induction and production of interferons),and Neutro_S3(Aldh2+,Top2a+,Ncam1+,andSlc16a7+)(Figs.4A and B).We observed that the cellular proportion of Neutro_S1 was decreased in the CLP and ART groups compared with the Sham group,while the proportion of Neutro_S2 increased in the ART group (Fig.S2A).According to the DEGs of the CLP vs.Sham and CLP vs.ART,the GO enrichment analysis revealed that sepsis up-regulated the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway,cytokine-mediated signaling pathway,and response to inflammatory regulation in Neutro_S1 and Neutro_S2 but not Neutro_S3.However,ART treatment down-regulated the activation of these pathways on Neutro subtypes,indicating the anti-inflammatory effect of ART on Neutro (Fig.S2B).
Next,we examined the expression levels of Neutro effector genes across the three groups to explore the immunoregulatory effects of ART on Neutro during sepsis (Fig.4C).The expression of immunoregulation-related genes,includingIl10rb,Tnf,andTlr2,were upregulated in sepsis compared with that in the Sham and ART groups.Further,ART down-regulated the expression level ofCd274(encoding PD-L1)genes but had no evident regulatory effect on the expression of major histocompatibility complex-II components (H2-Ab1andH2-Aa) in Neutro.We also found the downregulated expression level of chemotaxis-related genes such asCcr1andCxcr2in sepsis,which was restored to baseline after ART treatment.Furthermore,we conducted the pseudotime inference on Neutro and found the cellular distribution of the trajectory(Fig.S2C),and the expression level of effector genes was consistent with the results above (Fig.S2D).
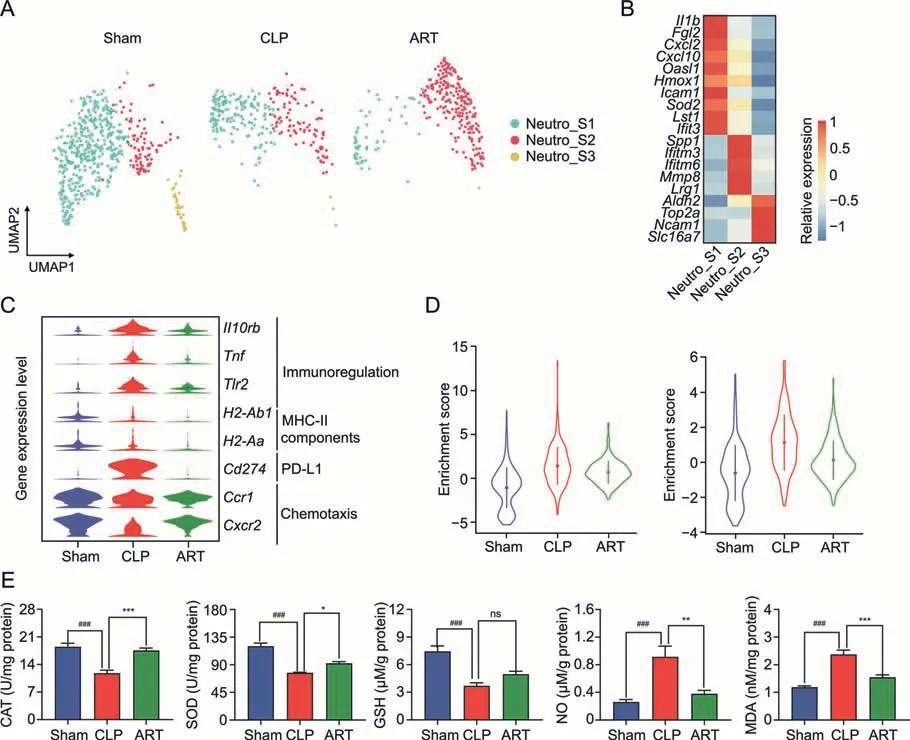
Fig.4.Artesunate(ART) regulates cellular dysfunctions and reactive oxygen species of neutrophils (Neutro) in the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis mice.(A) The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection(UMAP)plots show unsupervised clustering,revealing the distribution of 3 Neutro subtypes in three groups.(B)The heatmap plot depicts the cell markers expression of 3 Neutro cell subtypes.(C)The violin plot shows the relative expression levels of representative genes of Neutro of each group.(D)The violin plot shows the relative expression levels of apoptosis(left)and reactive oxygen species(ROS)(right)pathways of Neutro in three groups.(E)The barplots show the expression level of reactive oxygen products in three groups.*P <0.05;**P <0.01;***P <0.001;and ###P <0.001;ns: no significance.MHC-II: major histocompatibility complex-II;PD-L1: programmed death;CAT: catalase;SOD: superoxide dismutase;GSH: glutathione;NO: nitric oxide;MDA: malondialdehyde.
Previous studies reported that sepsis-induced oxidative stress led to Neutro infiltration and inflammatory reactions [25].Therefore,we evaluated the GSVA enrichment scores of APOPTOSIS and REACTIVE_OXYGEN_SPECIES_PATHWAY pathways of Neutro across three groups,indicating that Neutro in the CLP group manifested a higher score compared with those in the other groups (Fig.4D).Regarding the gene expression patterns of the reactive oxygen species(ROS)and apoptosis in Neutro_S1 and Neutro_S2 subtypes,we found that most ROS-and apoptosis-associated genes were activated in the CLP group but down-regulated after ART treatment(Fig.S2E).Moreover,we used biochemical kits to measure the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen products to further explore the ROS pathway alterations in the spleen tissue,including CAT,SOD,GSH,NO,and MDA.These results suggested that ART could increase the activities of antioxidant substances (CAT,SOD,and GSH) and decrease the activities of oxidant substances (NO and MDA) (Fig.4E).These results demonstrated the immunomodulatory and anti-ROS effect of ART on Neutro during sepsis.
3.5.ART inhibited the activation of Treg while promoted the activation of NK cells in the septic spleen
Both T lymphocytes and NK cells play important roles in maintaining homeostasis and immune response [5,26].We reclustered and further categorized 31,611 T lymphocytes and 1,865 NK cells into seven subtypes based on their marker gene expression(Fig.5A).These cell types included CD4_C1 (CD4+T na?ve,Cd4+Sell+Ccr7+),CD4_C2 (CD4+T memory,Cd4+Cxcr3+Cd40lg+),CD4_C3 (CD4+T regulatory,Cd4+Foxp3+Ctla4+),CD4_C4 (CD4+T effector,Cd4+Il2+),CD8_C1(CD8+T na?ve,Cd8+Sell+Ccr7+),CD8_C2(CD8+T na?ve,Cd8+Gzmk+),and NK(Ncr1+Nkg7+)(Fig.5B).Among these seven lymphocyte subtypes,we observed an increased cellular proportion of CD4_C3(8.64%in the Sham group and 10.02%in the CLP group),as well as a decreased abundance of NK(7.43%in the Sham group and 4.99%in the CLP group).However,the cellular proportion of these subtypes did not change obviously after ART treatment (Fig.5C).
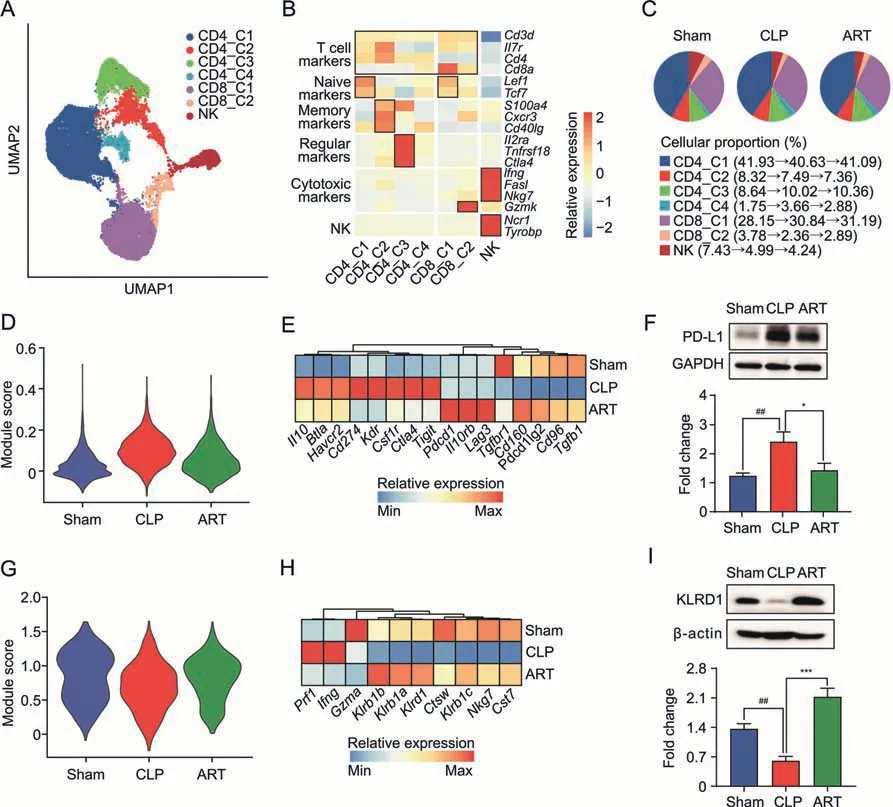
Fig.5.Artesunate(ART)regulates the immune reaction of T lymphocytes and natural killer(NK)cells in the cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)-induced sepsis mice.(A)The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) visualization shows unsupervised clustering,revealing 7 distinct subtypes of T lymphocytes and NK cells: CD4_C1,CD4_C2,CD4_C3,CD4_C4,CD8_C1,CD8_C2,and NK.(B)The heatmap plot depicts the cell markers expression of each subtype in T lymphocytes and NK cells,including T cell,na?ve,effector,memory,regulatory,cytotoxic,and NK markers.(C)The pie charts show the cellular proportion among seven T lymphocytes and NK subtypes in each group,colored according to subtypes.(D) The violin plot shows regulatory module scores of the CD4_C3 subtype in the Sham,CLP,and ART groups.(E) The heatmap plot depicts representative genes of regulatory modules in the CD4_3 subtype across three groups.(F)The protein expression level of PD-L1 by Western blot(WB)(up) and quantitative statistics among three groups(down) (n=3).(G) The violin plot shows cytotoxic module scores of the NK subtype in the Sham,CLP,and ART groups.(H) The heatmap plot depicts representative genes of cytotoxic modules in the NK subtype across three groups.(I) The protein expression level of KRLD1 by WB (up) and quantitative statistics among three groups (down) (n=3).*P <0.05;***P <0.001;and ##P <0.01.PD-L1: programmed death 1;GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
To further determine the transcriptomic patterns of CD4_C3 and NK cells in the three mouse groups,we evaluated the regulatory module in the CD4_C3 subtype and found that CD4_C3 in the CLP group manifested a higher score compared with that in the other groups(Fig.5D).In the regulatory module-related genes,we found increased expression levels of T regulatory genes,such asCd274andCsf1rin the CLP group,most of which down-regulated after ART treatment (Fig.5E).The protein expression change of PD-L1 was confirmed by the WB experiments(Fig.5F).Based on the CLP vs.ART DEGs in the CD4_3 subtype,the GO enrichment analysis results indicated that the biological pathways,such as regulation of T cell proliferation and lymphocyte differentiation,were up-regulated.In contrast,the regulation of response to biotic stimulus and cytokine production was down-regulated after ART treatment,suggesting that ART inhibited the cellular response and cytokine production of T regulatory subtype cells in the spleen of mice with sepsis(Fig.S3A).
Likewise,we evaluated the cytotoxic module score in the NK subtype,finding that NK in the CLP group manifested a lower cytotoxic score compared with that in the other two groups(Fig.5G).We also found that the down-regulated cytotoxic modulerelative genes includingNkg7,Cst7,andKlrd1were up-regulated after ART treatment (Fig.5H).The protein expression level of KLRD1 across the three groups was consistent with the transcriptomic results (Fig.5I).GO enrichment analysis results also revealed that pathways such as the regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity and lymphocyte proliferation were up-regulated,while mRNA processing and cytoplasmic translation were downregulated in the NK cells of mice in the ART group (Fig.S3B).These results suggested that ART treatment could activate the cytotoxic function of splenic NK cells,which was inhibited in the CLP group.
3.6.ART promoted the activation of splenic B cells in mice with sepsis
To decipher the underlying mechanisms of the effects of ART on B cells,we subset 33,941 B cells in total and classified them into four subpopulations based on cellular markers: B_C1 (Sell+Mef2c+),B_C2 (Ms4a1+Cr2+Cd19+),B_C3 (Ldha+Cd83+),and Plasma(Igkc+lghm+)(Figs.6A and B).The GO enrichment analysis based on the cellular marker profiles across four subtypes indicated that the B_C1 subtype was mainly involved in lymphocyte cell differentiation and cell-cell adhesion,the B_C2 subtype in cytoplasmic translation and antigen receptor-mediated signaling,the B_C3 subtype in ATP metabolic and rRNA processing,and Plasma in protein targeting and protein catabolic process (Fig.6C).The abundance of the B_C1 subtype was lower in the CLP group(72.0%)compared with the other two groups (75.9% and 77.8%,respectively),indicating the impaired differentiation and activation of the B_C1 subtype during sepsis infection (Fig.6D).
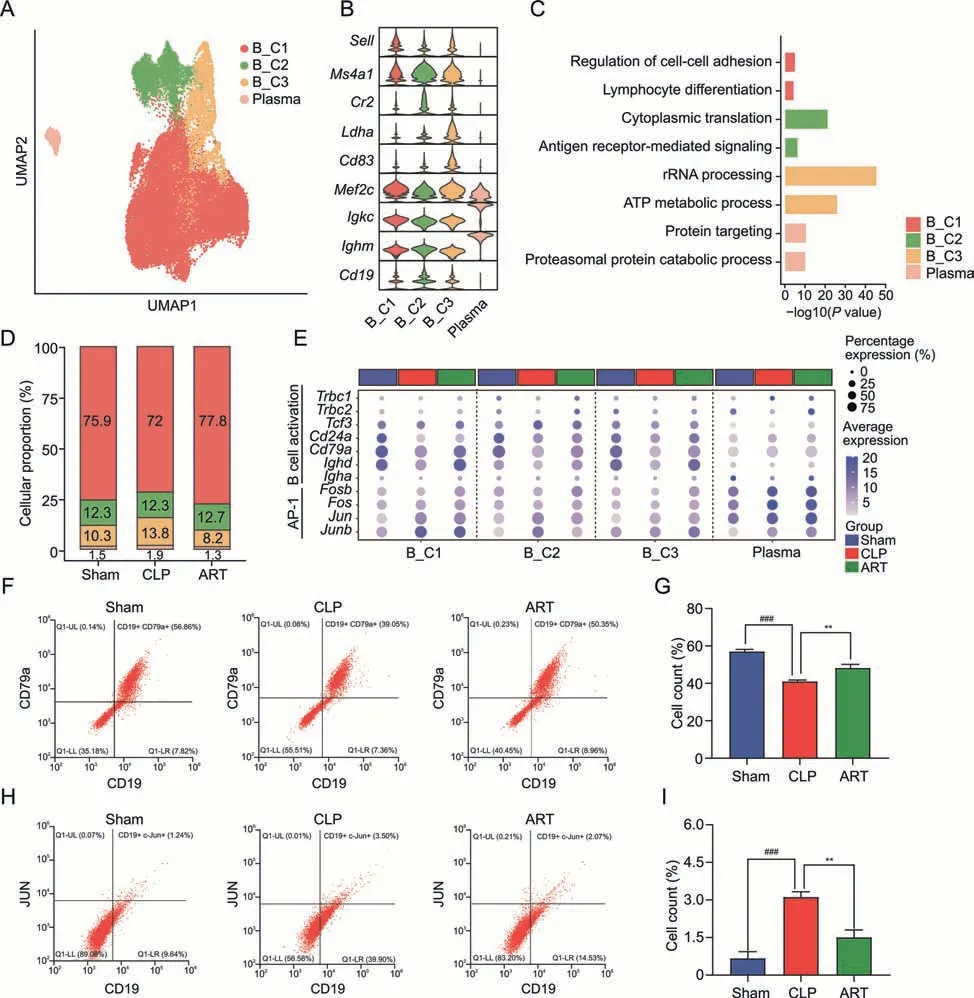
Fig.6.Artesunate(ART)influences the differentiation and activation of B cells in cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)-induced sepsis mice.(A)The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection(UMAP)visualization shows the B cells populations in the spleen,and colors indicate the cell types.(B)Violin plots show the relative expression levels of the B cells marker gene in each subtype.(C)The bar plot shows enriched pathways based on the up-regulated DEGs among B cell subtypes,colored by each subtype.(D)The bar chart shows the subtype proportion of B cells in three groups,colored by subtypes.(E)The dot plot displays the expression level of genes involved in B activation,and activator protein-1(AP-1)gene families of different B cell subtypes across three groups.(F,G)Flow cytometry analysis shows the proportion(F)and cell counts(G)of activated B cells among three groups.(H,I) Flow cytometry analysis shows the proportion and cell counts of AP-1 positive B cells among three groups.**P <0.01 and ###P <0.001.Plasma: plasma cells;ATP:adenosine.triphosphate;UL: upper left;LL: lower left;LR: lower right.
Besides,we profiled the up-regulated DEG patterns of mice in the Sham vs.CLP groups and CLP vs.ART groups among four subtypes of B cells,revealing that the levels of most activated DEGs were restored to baseline after ART treatment (Fig.S3C).GO enrichment analysis revealed that the activated pathways such as RNA splicing and response to virus were down-regulated after ART treatment across most B cell subtypes.We observed the downregulation of response to biotic stimulus,innate immunity,and IFN-γ in the ART group compared with the CLP group (Fig.S3D).These results highlighted the regulatory effects of ART on the activation of splenic B cells in mice with sepsis.
Furthermore,we found that the B cell activation markers such asCd24aandCd79aandimmunoglobulin heavy constant alphawere down-regulated in four B cell subtypes in the CLP group.However,these genes were up-regulated after ART treatment,indicating that ART might promote the activation of B cells(Fig.6E).We then used flow cytometry to validate the cellular states of B cells among the three groups,which were consistent with the analysis results(Figs.6F and G).Activator protein-1 (AP-1) was reported to play vital roles in regulating the immune system during disease progression and lead to the release of various inflammatory cytokines and immune modulators [27].Thus,we also profiled the gene expression patterns of AP-1 gene families of B cells across three groups(Fig.6E).We found that the up-regulated expression of AP-1 family members includingJun,andJunbin the CLP group was downregulated after ART treatment.These findings suggested that ART could inhibit the inflammatory states of B cells,which was confirmed by cytometry experiments (Figs.6H and I).
3.7.ART mediated the intercellular crosstalk in the microenvironment of the septic spleen
To explore the intercellular interactions of sepsis-induced splenic immunologic dissonance and investigate the regulatory effect of ART on the microenvironment,we constructed a cellular communication network among different cell types.Next,we examined the cell-cell interaction strength in the Sham,CLP,and ART groups,revealing that the CLP and ART groups had higher cellular interaction numbers compared with the Sham group(Fig.7A).In comparison with the Sham group,we found increased interaction strength among Neutro,NK,and Macro,but decreased strength among Mono and mDC in the CLP and ART groups(Fig.7B).
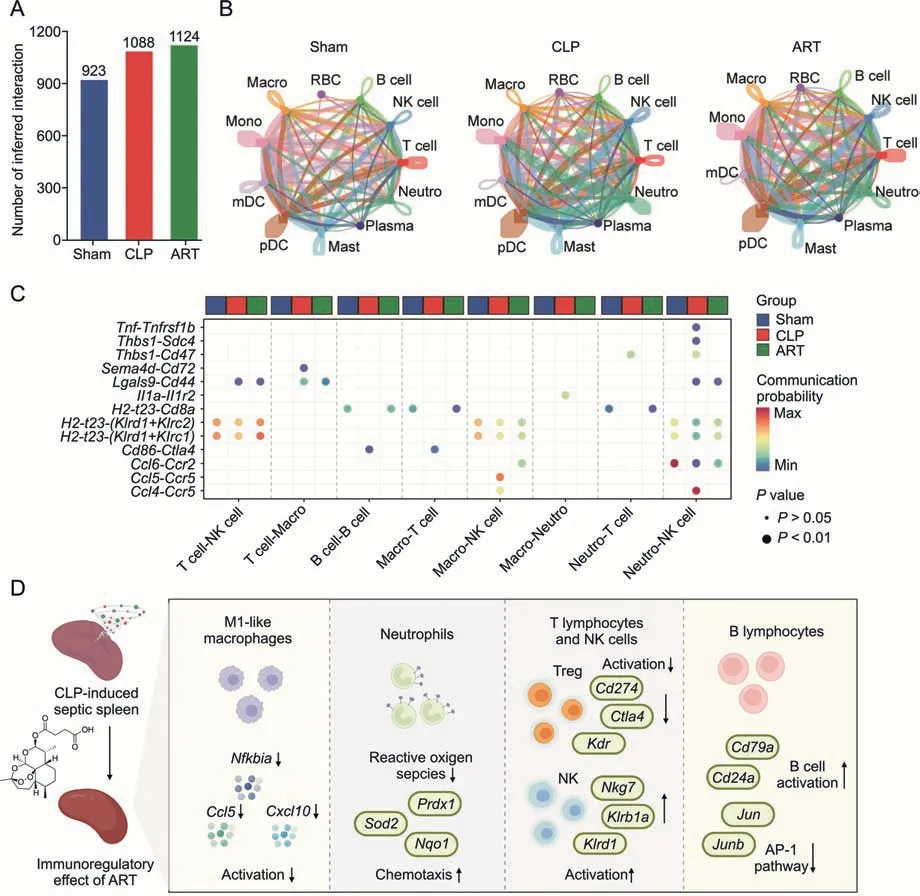
Fig.7.Artesunate(ART)regulates the imbalanced cell-cell communication in the cecal ligation and puncture(CLP)-induced sepsis mouse spleen.(A)The bar plot shows the number of inferred intercellular interactions in three groups.(B) The chordal graphs show the total cell-cell interaction patterns across various cell types among the Sham,CLP,and ART groups,colored by each cell type.(C) The bubble plot shows the communication probability of ligand-receptor pairs among various cell types,colored by group types.(D) The schematic diagram shows the cellular and molecular mechanisms of artesunate in the treatment of sepsis-induced splenic immunologic dissonance.RBC:red blood cell;NK:natural killer;Neutro: neutrophil;Macro: macrophage;Mono: Monocyte;mDC: myeloid dendritic cell;pDC: plasmacytoid dendritic cell;Mast: Mast cell;Plasma: Plasma cell;AP-1:activator protein-1.
Furthermore,we identified the significant L-R pairs (P<0.01),determining 13 L-R pairs in total (Fig.7C).The communication probabilities ofTnf-Tnfrsf1bandCcl4-Ccr5pairs between Neutro and NK cells,andIl1a-Il1r2pairs between Macro and Neutro increased in the CLP group.A previous study has reported thatTnfandIl1were pro-inflammatory cytokines [28],suggesting that the activation ofTnf-Tnfrsf1b and Il1a-Il1r2pairs between Neutro and other immune cells might promote the inflammatory reaction of Neutro during sepsis.These findings were in line with the inflammatory state of these cells in the septic spleen.More importantly,we found that ART might inhibit the inflammation of Neutro via down-regulating intercellular communications.
We also found the increased immune checkpoint interactions such as theCd86-Ctla4pair(from Macro or B cells toT lymphocytes)in the CLP group compared with the other two groups,indicating that the immunosuppression of T cells through this L-R pair during sepsis was alleviated after ART treatment.Moreover,the interaction strength ofH2-t23-(Klrd1+Klrc2)andH2-t23-(Klrd1+Klrc1)L-R pairs from T lymphocytes,Macro,and Neutro to NK cells were decreased in the CLP group but increased in the ART group,indicating that ART treatment might promote the activation of NK cells in the spleen to protect the host from sepsis.These findings demonstrated that the imbalance of the intercellular network during sepsis was effectively alleviated after ART treatment.
4.Discussion
Exploring the immune response alterations during sepsis is the foundation of the discovery of potential therapeutic strategies[29].Several single-cell transcriptomic studies have profiled the immune cell landscape generated from septic patients admitted to intensive care units as well as from CLP-induced or lipopolysaccharideinduced experimental mouse models [15,17,30].Most of these studies have explored the heterogeneity of immune cells and identified key immune subtypes during sepsis,while providing valuable scRNA-seq data resources.However,the reports on the therapeutic effect of specific medicines on sepsis-induced hyperinflammation and/or immunosuppression based on the scRNA-seq method are few.Our in vivo results showed that,although ART treatment did not completely recover mouse weight loss and spleen index to a healthy baseline,the immune response dysfunctions in the septic spleen at the histological and cytokine expression levels were alleviated after ART treatment.Furthermore,we constructed a single-cell atlas of mouse spleens during CLP-induced sepsis and after ART treatment,exploring the therapeutic effect of ART on the septic spleen.The novelty of our study was that we illustrated the regulatory effect of ART on various immune cells at single-cell resolution and demonstrated the potential mechanism via scRNA-seq analysis and experimental verification(Fig.7D).
During the early stages of sepsis (within 24 h),M1-like Macro have been reported to be activated and recruited to inflammatory tissues/regions,eliminating microorganisms via phagocytosis or the production of pro-inflammatory mediators,including IFNs,TNFs,and ILs.However,the over-activation of M1-like Macro and many inflammatory factors can also cause uncontrolled inflammatory reactions in the body,resulting in severe immune dysfunction in tissues.We found that ART treatment alleviated the recruitment and activation of M1-like Macro in mice with CLP-induced.During sepsis,signal transduction and pro-inflammatory gene expression provoke the activation of the downstream NF-κB pathway.Previous studies have also demonstrated that the pathophysiology of sepsis involves complex cytokine and inflammatory mediator networks,and NF-κB activation is a central event leading to the activation of these networks that promote M1 polarization in Macro[31-33].In our results,ART might act by down-regulating the expression levels ofNfkbia,Cd14,Ccl5,andCxcl10,accompanied by down-regulated pathways such as the response to lipopolysaccharides and IFN-γ.These results suggested that ART could regulate the overactivation of pro-inflammatory Macro,reducing the damage to septic organs and thus improving the outcomes of sepsis-related symptoms.
In both animal models and sepsis patients in the immunosuppressed phase of sepsis,the presence of large amounts of pathogenassociated molecular patterns results in an altered state of Neutro,including impaired bacterial clearance,decreased reactivity,ROS production,and significantly reduced numbers of Neutro recruited to infected tissues [25,34].We found that ART could potentially regulate the production of cytokines,but had limited effects on the chemotaxis of Neutro during sepsis.Furthermore,the inhibition of the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway and cytokine-mediated signaling pathway by ART reflected the anti-inflammatory effect of ART on Neutro.Furthermore,the down-regulation of ROS pathways as well as ROS-associated genes also demonstrated the antioxidative effect of ART on Neutro during sepsis.
Previous studies have reported that the increased abundance of T regulatory cells is associated with not only poor prognosis,but also the impaired proliferation and function of effector T cells and other innate immune cell types[35,36].As for NK cells,the number of circulating NK cells in animal models and patients with sepsis is significantly reduced in the immunosuppressed phase,accompanied by dysfunctional cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion,which are all associated with increased mortality[37].Our results showed that ART treatment inhibited the cellular response and cytokine production of the T regulatory subtype in the spleen,accompanied by a reduced regulatory module score.In contrast,we found increased cytotoxic module score and expression of module-related genes,as well as the increased regulation of leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and lymphocyte proliferation in NK cells after ART treatment.Our findings suggested that ART treatment activated the cytotoxic function of splenic NK cells while inhibiting the functionality of T regulatory cells.B cells are considered as the mediators of humoral immune responses and are involved in antibody-mediated immune responses during sepsis,affecting the long-term immune health of the infected host[38].Our findings also revealed that ART activated and regulated cell growth and differentiation of splenetic B cells during sepsis.However,the direct binding protein targets of ART and their mediated signaling pathways on these cell types still needed further elucidation.Thus,methods such as activity-based protein profiling and cellular thermal shift assay,which allow us to profile the engagement of drug probe-proteins,should be considered to be employed in future studies[39,40].
Regarding cellular communication,our dataset deciphered that a complicated network and L-R pairs involving Macro/Mono,Neutro,T cell,and B cell,contributed to the development of CLP-induced sepsis.At the same time,ART treatment could effectively alleviate the imbalance of the intercellular network resulting from sepsis.However,the regulatory mechanisms of cell-cell interaction were not validated experimentally due to methodological limitations.On one hand,isolating these immune cell subpopulations and coculturing them to validate their interactions is difficult.On the other hand,determining a specific L-R pair among ligands and their receptor genes for intervention is challenging.Further studies are warranted to explore the cellular interaction network during sepsis and after ART treatment with more comprehensive experimental and bioinformatics technologies.
Collectively,our study demonstrated the complex landscape of splenic immune cells in sepsis-induced mice in response to ART treatment.Our findings provide new insights into the immunoregulatory effect of ART on splenic immune dysfunction during sepsis.This study also supported the further application of ART as an adjunctive therapy for sepsis treatment,to reduce the damage to septic organs and thus improve the outcomes of sepsis-related symptoms.
5.Conclusions
We employed scRNA-seq to investigate the immune regulatory effect and mechanism of ART treatment on various immune cells in CLP-induced septic model mice.scRNA-seq analysis revealed that ART inhibited the activation of pro-inflammatory Macro recruited during sepsis.Besides,ART could restore the chemotaxis and immune function of Neutro in the septic spleen.Moreover,ART inhibited the activation of T regulatory cells but promoted the cytotoxic function of NK cells in the septic spleen.Finally,ART also promoted the differentiation and activity of splenic B cells in sepsis mice.These results indicated that ART could alleviate the inflammatory and/or immunosuppression states of various cell types involved in the sepsis course,so as to balance the immune homeostasis of the host.
CRediT author statement
Jiayun Chen:Investigation,Software,Bioinformatic analysis,Visualization,Writing -Reviewing and Editing;Xueling He:Investigation,Validation,Resources,Writing -Original draft preparation,Reviewing and Editing;Yunmeng BaiandJing Liu:Investigation,Visualization,Software,Writing -Reviewing and Editing;Yin Kwan Wong: Investigation,Resources,Visualization,Software;Lulin Xie: Resources,Writing -Original draft preparation;Qian ZhangandPiao Luo:Software,Investigation,Resources;Peng Gao,Liwei Gu,Qiuyan Guo,andGuangqing Cheng:Investigation,Validation,Resources;Chen Wang:Investigation,Bioinformatic analysis,Resources,Visualization;Jigang Wang:Supervision,Writing -Reviewing and Editing,Project administration.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the Establishment of Sino-Austria “Belt and Road” Joint Laboratory on Traditional Chinese Medicine for Severe Infectious Diseases and Joint Research,China (Grant No.: 2020YFE0205100),the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos.:2020YFA0908000 and 2022YFC2303600),the Distinguished Expert Project of Sichuan Province Tianfu Scholar(Grant No.:CW202002),the Innovation Team and Talents Cultivation Program of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine,China (Grant No.:ZYYCXTD-C-202002),the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant Nos.:82141001,82274182,82074098,and 82173914),the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (CACMS) Innovation Fund,China(Grant Nos.:CI2021A05101 and CI2021A05104),the Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences(Grant No.:CI2021B014),the Science and Technology Foundation of Shenzhen,China (Grant No.:JCYJ20210324115800001),the Science and Technology Foundation of Shenzhen,China(Shenzhen Clinical Medical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases),the National Key R&D Program of China Key Projects for International Cooperation on Science,Technology and Innovation (Grant No.: 2020YFE0205100),the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes,China(Grant Nos.:ZZ14-YQ-050,ZZ14-YQ-051,ZZ14-YQ-052,ZZ14-FL-002,ZZ14-ND-010,and ZZ15-ND-10),Shenzhen Governmental Sustainable Development Fund,China (Grant No.:KCXFZ20201221173612034),Shenzhen key Laboratory of Kidney Diseases,China (Grant No.: ZDSYS201504301616234),and Shenzhen Fund for Guangdong Provincial High-level Clinical Key Specialties,China(Grant No.:SZGSP001).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.02.006.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2023年7期
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2023年7期
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Preface for Special Issue: Single-Cell and Spatially Resolved Omics
- A Scd1-mediated metabolic alteration participates in liver responses to low-dose bavachin
- The role of signaling crosstalk of microglia in hippocampus on progression of ageing and Alzheimer's disease
- Discovering metabolic vulnerability using spatially resolved metabolomics for antitumor small molecule-drug conjugates development as a precise cancer therapy strategy
- Single-cell analysis of cellular heterogeneity and interactions in the ischemia-reperfusion injured mouse intestine
- Cux1+ proliferative basal cells promote epidermal hyperplasia in chronic dry skin disease identified by single-cell RNA transcriptomics
