T-cell and B-cell repertoire diversity are selectively skewed in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome revealed by high-throughput sequencing
Qing Ye·Dong-Jie Wang·Bing Lan·Jian-Hua Mao
Abstract Background Clinical studies suggest that the dysfunction of T cells and B cells may play an essential role in the pathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS),but laboratory evidence is lacking.Therefore,this study explored T-cell receptor(TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) prof iling in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.Methods High-throughput sequencing technology was used to profile the TCR and BCR repertoires in children with INS.Peripheral blood was collected from ten INS patients,including five vinculin autoantibody-positive patients and f ive vinculin autoantibody-negative patients,before and after treatment. TCR and BCR libraries were constructed by 5′-RACE and sequenced by a DNBSEQ-T7 sequencer,and sequence analyses were performed using ReSeqTools,FastP,MiXCR,and VDJtools.Results The TRA (T-cell receptor α),TRG (T-cell receptor γ),and IGH (immunoglobulin heavy chain) repertoires of the INS group were occupied by highly abundant clonotypes,whereas small clonotypes occupied the healthy group,especially TRA .A significant increase in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed for the TRA and TRG repertoires after treatment in vinculin autoantibody-negative patients,but a signif icant increase in the IGH repertoire after treatment was observed in vinculin autoantibody-positive patients.The frequency of some V—J pairs was significantly enriched in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome patients.The usage frequency of the V and J genes was skewed in patients,which seemed not related to immunosuppressive therapy.However,after effective treatment,dynamic changes in the size of the individual clonotype were observed.Conclusion T-cell and B-cell immunity contribute to the pathogenesis of different INSs.
Keywords B-cell receptor repertoire·Complementary determining region 3·Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome·T-cell receptor repertoire
Introduction
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) is the most common glomerular disease in children and is caused by a massive loss of protein in the urine due to a defect in the glomerular filtration barrier.Immune dysregulation is thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of INS,including T-cell and B-cell immunity [1—3].Due to unknown etiology,the initial treatment of children with INS is usually steroid treatment.Based on its response to steroid treatment,INS can be classified into steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS)and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) categories.For children with SRNS,immunosuppressive treatment with calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) is recommended.SRNS can be further divided into (CNI)-resistant SRNS and multidrug-resistant SRNS depending on its response to immunosuppressive treatment.T-cell dysregulation has always been regarded as the main pathogenic factor of nephrotic syndrome.This theory is supported by clinical evidence;for example,measles virus can significantly inhibit cellular immune function,and the nephrotic symptoms of INS patients are relieved after being infected with measles virus [4].The imbalances of CD4+/CD8+T cells,T helper 1 (Th1)/Th2 cells and Th17/regulatory T (Treg) cells also provide evidence for the theory [5,6].Clinical studies have also found increased B-cell counts during nephrotic relapses with subsequent reductions after the achievement of remission [7,8].In children with nephrotic syndrome,minimal change disease was the most common type of renal biopsy pathology,which is characterized by the fusion,retraction,or even disappearance of podocyte foot processes.The discovery of podocyte autoantibodies in the serum of INS patients suggested a potentially important role for B-cellrelated immunity.
T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) are the most important molecules for T cells and B cells to recognize antigens and play an immune role,respectively.According to the different heterodimers T-cell receptorαβandγδon the cell surface,T lymphocytes are classified structurally into two subtypes [9].αβT cells usually reside in peripheral tissues and the circulatory system,whereasγδT cells are found in blood and lymphoid tissue as well as epithelial environments [10].The BCR comprises two identical heavy(IGH) chains and two identical light (IGL) chains.TheTCRandBCRgenes are composed of variable (V),diversity (D),joining (J),and constant (C) gene segments.EachTCRandBCRis produced by rearranging multiple gene segments[11].The short region spanning the VD and VJ junction,termed complementary determining region 3 (CDR3),is the most variable and most frequently analyzed region generally responsible for antigen recognition [12].The main aim of the present study was to profile the CDR3 region ofTCRandBCRrepertoires in the peripheral blood of INS patients before and after treatment.Our hypothesis is that there are considerable discrepancies in the CDR3 region of theTCRandBCRrepertoires in the peripheral blood of patients with INS before and after treatment,and the differences could reveal the underlying mechanisms of T-cell and B-cell immunity in the pathogenesis of INS.
Methods
Participants and outcomes
Ten newly diagnosed and untreated INS patients were recruited as the disease group at Children's Hospital,Zhejiang University School of Medicine,between July 2020 and February 2021.All enrolled patients met the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children criteria for INS.Patients with suspected heritable nephrotic syndrome,reduced renal function,infectious diseases,malignant tumors,or other autoimmunological diseases were excluded.At the same time,three healthy children who came to the hospital for physical examination were included as the control group.Before clinical remission,steroid was given at a dose of 2 mg/kg bodyweight for the children whose bodyweight was under 30 kg.For children whose body weights were above 30 kg,steroids were given at a fixed dose of 60 mg.Peripheral blood samples were collected before steroid therapy and after clinical remission (24-hour urinary protein < 150 mg/24 hours or negative protein on urine dipstick test in the first-morning urine for three consecutive days) and stored at -20 °C for later use.Ethics approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Children's Hospital,Zhejiang University School of Medicine (2021-IRB-228).
Sample collection and RNA extraction
Peripheral blood samples were collected in tubes with RNAstore reagent (Tiangen,Beijing,China) for all patients.According to the manufacturer’s instructions,the total RNA of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood samples was extracted using the blood RNA column medium extraction kit (Kangweishiji,China).The total RNA of each sample was quantified and qualified by an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer(Agilent Technologies,Palo Alto,CA,USA),NanoDrop(Thermo Fisher,USA),and 1% agarose gel.
Library construction and sequencing
cDNA was generated using 5′-RACE cDNA amplification methods [13].The correspondingBCR/TCRprimers were added to amplify CDR3 regions using polymerase chain reaction.Purified products were subjected to a second round of amplification to introduce adaptor sequences compatible with sequencing.Final libraries were evaluated using a Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,US) on a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer.High-throughput sequencing was performed by a DNBSEQ-T7 sequencer(BGI,Shenzhen,China) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.The sequencing process was performed by Beijing Chigene Translational Medicine Research Center Co.,Ltd.
Quality control and clone sequence analysis
FastP processed raw data for adapter removal and lowquality read filtering with ReSeqTools (v0.25) and FastP(v0.20.1).MiXCR (v3.0.3) was used to align and assemble the original sequencing reads and obtain the TCR/BCR sequences.VDJtools (v1.1.4) was used for subsequent clone sequence analysis,including sequence feature annotation,comparison between samples,construction of immune repertoire expression profiles,and clustering analysis.Only productive immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH),T-cell receptor α (TRA),and T-cell receptor γ (TRG) sequences were retained for the sequence analysis.
Clonotype comparison
A clonotype is a unique nucleotide sequence with a unique combination of the V-(D)-J gene that arises during the gene rearrangement process for that receptor.The combination of nucleotide sequences for the surface expressed receptor pair or antibody would define the T-cell or B-cell clonotype,respectively.Fisher's exact test was implemented to compare the number of contracted and expanded clonotypes that occurred during treatment.Expanded clonotypes had a significantly larger size than prior therapy,while contracted clonotypes had significantly lower frequencies after treatment.Pvalues ≤ 0.001 and frequency |log2-fold change| ≥ 2 were considered statistically significant.All statistical analyses were performed using R software.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism version 8.0 (GraphPad Software,Inc.,San Diego,CA,USA) was used for statistical analysis of the data.Differences between multiple groups were compared using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparisons test for post hoc analyses.Post hoc power calculations were performed with the G-Power software package.
Results
Demographic and clinical characteristics
The study included ten INS patients (five males and five females,with a median age of 3 years 10 months) and three healthy controls (two males and one female,with a median age of 4 years 5 months).Among these people,five INS patients had vinculin autoantibody against podocytes,and the rest were vinculin autoantibody negative.The initial therapy was an oral prednisone dose of 2 mg/kg/day,with eight SSNS patients and two SRNS patients later given tacrolimus 0.1 mg/kg/day in two divided doses.All patients achieved remission,and the median treatment-start to remission period was 13 days.The demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients are summarized in Table 1.
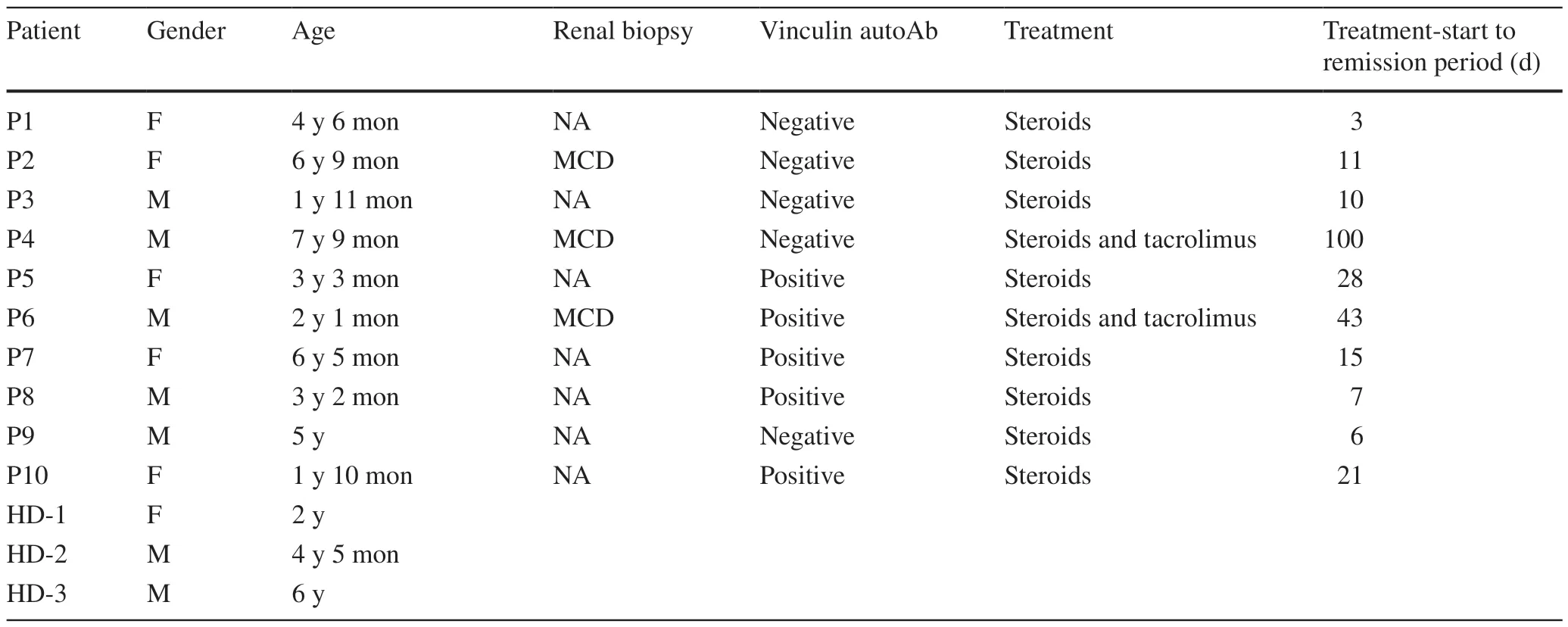
Table 1 The demographic and clinical characteristics of patients and healthy controls
Features of the sequence data
The present study analyzed theIGH,TRA,andTRGrepertoires before and after treatment.The mean number of analyzed sequences for theIGHrepertoire was 382,286(83,864—475,985).The mean number of analyzed sequences for theTRArepertoires was 225,662 (85,206—286,171).In addition,the mean number of analyzed sequences for theTRGrepertoires was 78,033 (24,294—95,040).Next,the number of unique productive clonotypes in the chain repertoires was analyzed.The number of unique clonotypes in theIGHrepertoire was 8783 (1941—34,939).The number of unique clonotypes in theTRArepertoire was 1454(169—7330).Similarly,the number of unique clonotypes in theTRGrepertoire was 163 (15—536).
The clonotype abundance of IGH,TRA,and TRG repertoires
The relative abundance was evaluated by measuring the proportion of clonotypes with specif ic frequencies ranging from rare clonotypes (< 0.01%) to highly abundant clonotypes (> 10%) (Fig. 1).The majority of the healthy repertoire was occupied by small clonotype groups,whereas highly abundant clonotypes primarily occupied the repertoire of INS patients.Specifically,the highly abundant clonotypes occupied a significantly higher proportion before treatment forTRArepertoires,suggesting that pretreatment patients have highly clonal repertoires dominated by hyperexpanded clonotypes.
The impact of vinculin autoantibody on the IGH,TRA, and TRG repertoires
Next,we analyzed the impact of vinculin autoantibody on theIGH,TRA,andTRGrepertoires before and after treatment (Fig. 2).This study included five vinculin autoantibody-positive and five vinculin autoantibody-negative patients.For theTRAandTRGrepertoires,no significant difference in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed,while a significant increase in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed for theIGHrepertoire after treatment in vinculin autoantibody-positive patients.No significant difference in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed for theIGHrepertoires after treatment in vinculin autoantibodynegative patients.However,a significant increase in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed for theTRAandTRGrepertoires after treatment in vinculin autoantibody-negative patients.
The usage frequencies of the V and J genes in the IGH,TRA,and TRG repertoires
The usage frequencies of theIGHVandJgenes in patients and healthy controls were delineated in heatmaps (Fig. 3 a).Consistent with previous reports of other researchers,someIGH Vgenes exhibited high-frequency usage in almost all the samples,such asV3.23(frequency=0.139 ± 0.091)andV3.21(frequency=0.080 ± 0.059).IGHJ4also showed high-frequency usage in all the samples (frequency=0.493 ± 0.059).The results indicated thatIGHVandJgene usage patterns were skewed in patients.We also analyzed the frequency of theTRA VandJgenes in patients and healthy controls.As shown in Fig. 3 b,someVgenes exhibited high-frequency usage in almost all the samples,such asV13.1(frequency=0.089 ± 0.026) andV21(frequency=0.072 ± 0.026).TheJgene usage was relatively uniform,with the upper halfJgenes showingsomewhat higher usage than the lower halfJgenes.In addition,the frequencies of theTRG VandJgenes in patients and healthy controls were analyzed (Fig. 3 c).Because the number ofTRG VandJgenes was lower than that ofIGHandTRAgenes,only 11Vgenes and f iveJgenes were found.The most commonly usedVgene wasV9(frequency=0.507 ± 0.161),and the most frequently usedJgene wasJ1(frequency=0.434 ± 0.158).Finally,we also noticed that among theIGH,TRA,andTRGrepertoires,there was no significant difference in the usage of theVandJgenes before and after treatment,indicating that immunosuppressive therapy did not change the usage of theVandJgenes.
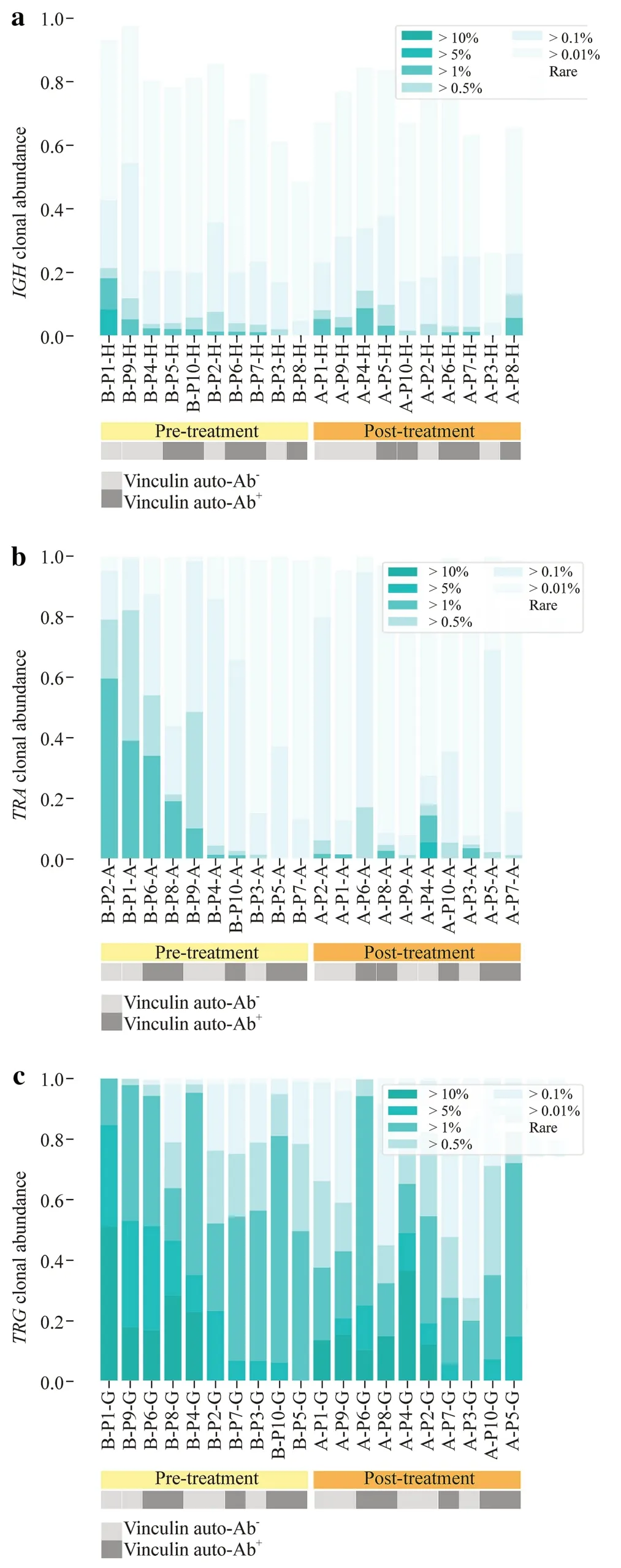
Fig.1 Clonotype abundance of the IGH (a),TRA (b),and TRG (c).The light gray box indicates vinculin autoantibody-negative patients.The dark gray box indicates vinculin autoantibody-positive patients. IGH immunoglobulin heavy chain,TRA T-cell receptor α,TRG T-cell receptor γ,Ab antibody
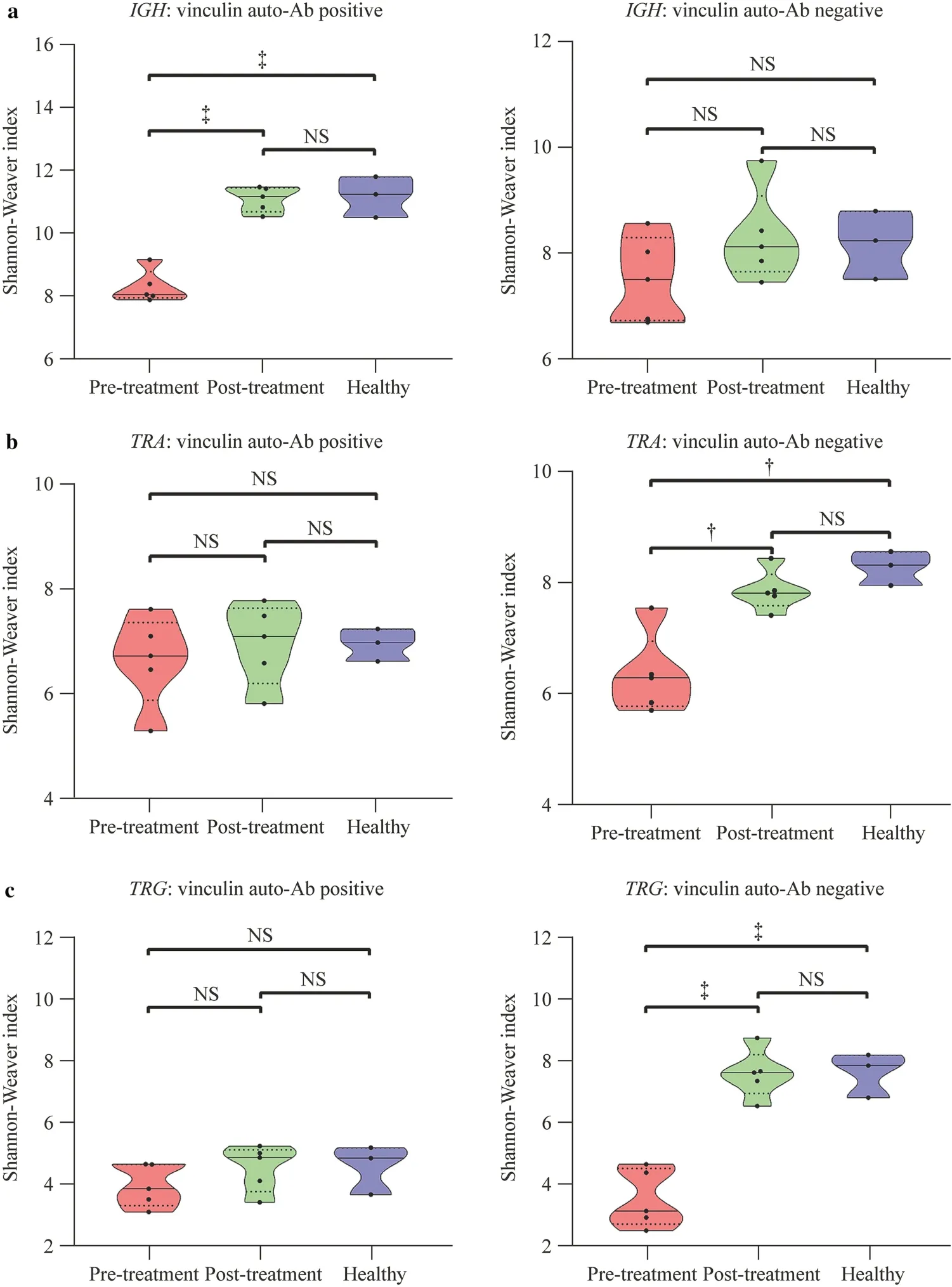
Fig.2 Diversity of the IGH (a),TRA (b),and TRG (c) repertoires in vinculin autoantibody-positive or vinculin autoantibody-negative patients before and after treatment. IGH immunoglobulin heavy chain,TRA T-cell receptor α,TRG T-cell receptor γ,Ab antibody,NS not significant.? P<0.01,? P<0.001
Dynamic changes in individual clonotypes before and after treatment
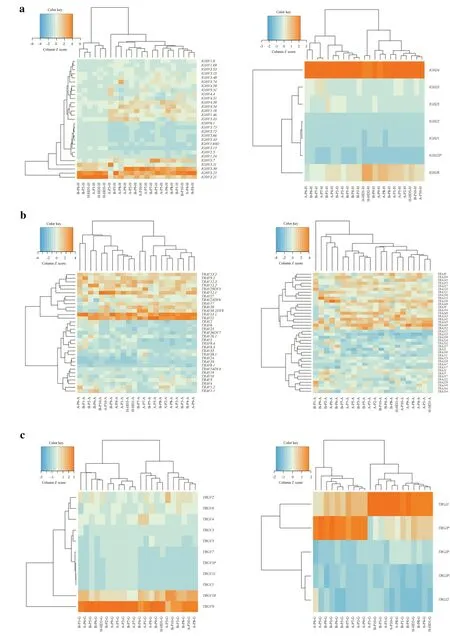
?Fig.3 Heatmaps of V and J gene usage frequencies of IGH (a),TRA(b),and TRG (c) repertoires.The horizontal coordinate is the frequency distribution of the V or J gene in different patients and healthy people,the vertical coordinate is the frequency distribution of the V or J gene,and the horizontal and vertical coordinates are all analyzed by clustering. IGH immunoglobulin heavy chain,TRA T-cell receptor α,TRG T-cell receptor γ
The sizes of each clonotype were measured before treatment versus after treatment to evaluate the dynamic changes in individual clonotypes.In theIGHrepertoire,611 significantly expanded clonotypes and 426 significantly contracted clonotypes were identified (Fig. 4 a).Additionally,136 significantly expanded clonotypes and 137 significantly contracted clonotypes in theTRArepertoire were identified(Fig. 4 b).At the same time,40 greatly expanded clonotypes and 57 significantly contracted clonotypes were identified in theTRGrepertoire (Fig. 4 c).The results showed that after effective treatment,the size of the clonotype changed significantly.
Discussion
Based on clinical observations,the dysregulation of T-cell immunity was proposed as the primary pathogenic mechanism of INS in the 1970s [4].Since then,a significant amount of knowledge has accumulated regarding T cells in INS pathogenesis.T-helper (CD4+) and T-cytotoxic(CD8+) lymphocyte imbalances with the predominance of CD8+cells [14],Th1 and Th2 imbalances,and Th17/Treg imbalances have been reported in the pathogenesis of INS[5,6].The incidence of thymoma and Hodgkin's disease is related to T lymphocyte dysfunction.It is clinically observed that these patients are prone to nephrotic syndrome [15].Clinical studies have also found increased B-cell counts during nephrotic relapses with subsequent reductions after the achievement of remission [7,8].The beneficial treatment by rituximab in difficult patients suggests a pathophysiological role for B cells [16—23].Moreover,our previous research identified some circulating podocyte autoantibodies related to INS.These autoantibodies were positively correlated with proteinuria;their titers decreased rapidly after effective treatment [24—27].Watts et al.later found a similar phenomenon,and they also believed that podocyte autoantibodies were the immunological cause of nephrotic syndrome in a subset of adults and children with minimal change disease [28].
In the present study,we found that theTRA,TRG,andIGHrepertoires of the INS group were occupied by highly abundant clonotypes,whereas small clonotypes occupied the healthy group,especiallyTRA.Additionally,we analyzed the dynamic changes in the clonotype size of theTRA,TRG,andIGHrepertoires.Clonal size is an important feature of lymphocytes.Normally,lymphocytes are in a positive polyclonal state without any antigenic stimulation.In the case of diseases,specific antigen stimulation will lead to the rearrangement of targeted lymphocytes and intense clonal expansion [29].After effective treatment,dynamic changes in the size of the individual clonotypes were observed.Among them,theIGHrepertoire clonotype size changed the most.Sixty-one significantly expanded clonotypes and 426 significantly contracted clonotypes were identified.Dynamic changes in clonotype size still suggest that B-cell immunity dysregulation participates in the pathogenesis of INS.Consistent with a previous study,INS patients in the nephrotic state had a higher percentage of CD19+CD138+plasma cells (the main subset for antibody production) than healthy controls [30].We also found that B cells were involved in the occurrence and development of INS by detecting changes in B cells in the peripheral blood of INS patients [31].Additionally,our previous study first screened and identified a podocyte autoantibody,vinculin autoantibody,in patients with nephrotic syndrome.Vinculin is an adaptor protein located at focal adhesions and controls the adhesion strength to the extracellular matrix,which is essential for maintaining glomerular barrier integrity [32].These autoantibodies are positively correlated with proteinuria [24].Based on the evidence above,an assumption was proposed that B-cell immunity plays a role in the pathogenesis of some INS patients.This study included five vinculin autoantibody-positive and five vinculin autoantibody-negative patients.The BCR comprises two identical IGH chains and two identical IGL chains.Preliminary analysis showed that IGH changes were more significant in INS patients,so we analyzed them.A significant increase in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed for theIGHrepertoire after treatment in vinculin autoantibody-positive patients;however,for theTRAandTRGrepertoires,no significant difference in the Shannon—Weaver index was observed.This result further proved that B cells play an important role in vinculin autoantibodypositive patients.
TCRs play a central role in mammalian cellular immunity and can be divided intoαβorγδ,which are encoded byTRA/D,TRG,orTRBloci [33].Our preliminary results show thatTRAandTRGhave more diversity in INS patients.Further research found that after effective treatment,the Shannon—Weaver index of theTRAandTRGrepertoires was significantly increased to normal levels in vinculin autoantibody-negative INS patients.This finding indicates that the diversity of theTRAandTRGrepertoires in the peripheral blood of vinculin autoantibody-negative INS patients is significantly lower than that of healthy controls.After clinical remission,the diversity of theTRAandTRGrepertoires showed a more diversified trend,closer to healthy individuals.TCR is an essential molecule of T-cell function.Therefore,the diversity of TCRs can reflect the diversity of T-cell clones [34,35].Differences inTRAandTRGrepertoire diversity between the disease group and the control group suggest that T-cell immune disorder plays a role in the pathogenesis of vinculin autoantibody-negative INS.
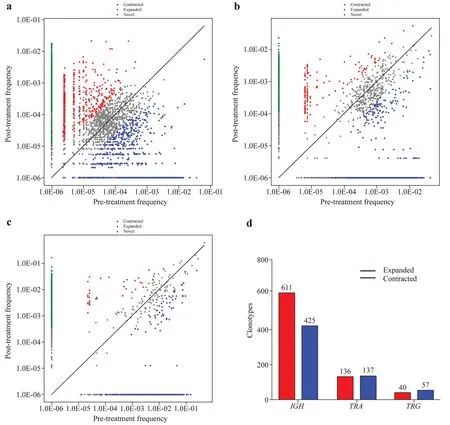
Fig.4 Clonotype size assessment of IGH (a),TRA (b),and TRG (c)repertoires before and after treatment. d shows the number of amplified and contracted clonotypes.The abscissa is the frequency of clonotypes before treatment,and the ordinate is the frequency of clo-notypes after treatment.Significant expansion and contraction were defined as log2 (pretreatment frequency/posttreatment frequency) ≥ 2 and Fisher's exact test P value ≤ 0.001. IGH immunoglobulin heavy chain,TRA T-cell receptor α,TRG T-cell receptor γ
In this study,we also found thatIGH V3.23,V3.21, andJ4,TRA V13.1andV3.21,TRG V9andJ1exhibited highfrequency usage in almost all the samples,which indicated that theVandJgenes of theIGH,TRA,andTRGrepertoires were skewed in patients.However,there was no significant difference in the usage of theVandJgenes before and after treatment,suggesting that immunosuppressive therapy did not change the usage of theVandJgenes.Whether these high-frequencyVandJgene fragments can be used as indicators of INS disease surveillance needs further study.In a previous survey of membranous nephropathy,theTRB V4.1andV13genes predicted the therapeutic effect since their frequencies were significantly higher in the complete remission (CR) group than in the non-CR group [36].This phenomenon also exists in rheumatoid arthritis and nonobese diabetic patients [37,38].
The main limitation of the study is the relatively small sample size.A larger study group would have probably allowed more sophisticated analyses aimed at finding differences between INS patients of different groups.Further exploration of cell-based molecularly targeted therapies such as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy,both theoretically and experimentally,is an important direction for future study.With this therapy,we will be able to target the elimination of pathological T-cell or B-cell clones.
In summary,we analyzed the characteristics of the TCR and BCR repertoires of INS patients and demonstrated that T-cell and B-cell immunity contribute to the pathogenesis of different INSs.
Supplementary InformationThe online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-022-00640-3.
Author contributionsYQ collected the data from patients and drafted the initial manuscript.WDJ and LB collected the data from patients.MJH collected the data from patients,devised the conceptual ideas,contributed to the discussion and interpretation of the results,and reviewed the final manuscript.All the authors contributed to manuscript editing and approved the f inal manuscript.
FundingThis study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY22H050001),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82270741,U20A20351),the Key Project of Provincial Ministry Coconstruction,Health Science,and Technology Project Plan of Zhejiang Province (WKJ-ZJ-2128),and Yiluqihang Shenmingyuanyang Medical Development and Scientific Research Fund Project on Kidney Diseases (SMYY20220301001).
Data availabilityThe datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethical approvalThe authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013).The Ethics Committee of Children's Hospital,Zhejiang University School of Medicine approved this study (2021-IRB-228).Informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study.
Conflict of interestNone of the authors participated in the journal’s review of,or decisions related to this manuscript.No financial or nonfinancial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.Author Jian-Hua Mao is a member of Editorial Board forWorld Journal of Pediatrics.The paper was handled by the other editors and has undergone a rigorous peer-review process.Author Jian-Hua Mao was not involved in the journal's review or decision making of this manuscript.
 World Journal of Pediatrics2023年3期
World Journal of Pediatrics2023年3期
- World Journal of Pediatrics的其它文章
- World Journal of Pediatrics
- Instructions for Authors
- Diagnosis,treatment,and prevention of monkeypox in children:an experts’ consensus statement
- Novel insights into congenital surfactant dysfunction disorders by in silico analysis of ABCA3 proteins
- Investigating changes in incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada: an interrupted time series analysis
- Pathologic etiology and predictors of malignancy in children with cervical lymphadenopathy
