Prevalence and risk factors associated with tuberculosis mortality in Brunei Darussalam
Liling Chaw , Nurul Huda Jeludin, Kyaw Thu
1PAPRSB Institute of Health Sciences, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Gadong, Brunei Darussalam
2Disease Control Division, Department of Environmental Health Services, Ministry of Health, Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS: Mycobacterium infections; Tuberculosis; Mortality;Brunei
1. Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global infectious disease of concern,with a global incidence of 7.1 million and about 1.4 million deaths in 2019, during the pre-COVID pandemic era[1]. Caused by the bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, active TB is highly infectious in nature but is also preventable and curable if patients adhere to their treatment regimes.
Globally, countries can be generally classified as being high and low TB burden, defined as with TB incidence of >100 and <10 cases per 100 000 population, respectively[1]. While countries with TB incidence between these two ranges were generally classified as an intermediate TB burden country. It can be generally assumed that a country’s TB burden status could be positively associated with its TB-related mortality rate, previous reports does not seem to support this assumption: High TB burden country like China was found to have TB mortality of 4.56% and 14.4% in cities of Tianjin and Shanghai[2,3]. Intermediate TB burden countries (or regions)like Malaysia and Taiwan were reported to have TB mortality of 8% and 12.3%, respectively[4,5]. While low TB burden countries of Oman and USA were reported to have TB mortality of 15% and 7.3%, respectively[6,7]. This could be due to the interplay of various risk factors, other than TB incidence, that could contribute to TB mortality. Such risk factors were previously shown to be related to:(1) sociodemographic status: older age, single, low body weight,socioeconomically disadvantaged, (2) TB diagnosis and treatment(first sputum positivity, negative sputum smear TB, retreated tuberculosis, delayed visit (≥14 days), multidrug resistant TB,radiographic patterns showing cavitary, military and pneumonic involvement, poor TB treatment adherence) and, (3) presence of comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, HIV positivity, immunosuppression, liver cirrhosis[6-9].
Brunei Darussalam is an intermediate TB burden country, with the TB incidence rate 54.8 per 100 000 population in 2019[10], and it has remained at similar levels since 2004[11,12]. Although deaths due to TB in the country are relatively few, and that TB was not in the country’s top 10 leading causes of deaths[13], an epidemiological investigation on TB-related deaths could help determine the risk factors and cause of TB deaths in the local setting, and possibly shed some light into the stagnating TB incidence in the country.Hence, we conducted this study to: 1) determine the TB mortality,2) identify significant risk factors associated with TB mortality and 3) investigate causes for TB mortality. The findings of this research can help in monitoring and evaluation of TB’s status in Brunei Darussalam.
2. Subjects and methods
2.1. Ethical approval and patients’ consent
Ethical approval was obtained from the Medical and Health Research and Ethics Committee, Ministry of Health, Brunei (ref:MHREC/UBD/2019/2). Patient informed consent was waived as data was retrospectively collected as part of the national TB surveillance, and only de-identified data was used in all analyses.
2.2. Data collection
A retrospective cohort study was conducted, where secondary data on all registered TB patients in Brunei Darussalam from January 2013 to December 2017 were collected. Three data sources were used: National TB Coordinating Centre (NTCC), National TB Reference Laboratory and Brunei Darussalam Health Information and Management System (Bru-HIMS). All TB patients in the country (identified in both government and private healthcare centers) are referred to NTCC or any of their branches in each district for registration and continuation of their directly observed treatment. While National TB Reference Laboratory is designated solely for diagnosis and antibiotic-resistance testing for all TBsuspected sputum and tissue samples. Lastly, Bru-HIMS is an electronic patient record management system used to record data of all patients who have government clinics and hospitals since 2013[14].
2.3. Sociodemographic data
Sociodemographic data (age, sex, ethnicity and nationality)and whether they have comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus,hypertension or heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma, renal disease, cancer or HIV/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome were for all TB patients were compiled. Clinical information on their TB diagnosis and followup were also collected, which includes TB status (newly diagnosed or relapsed patient), type of TB diagnosed, drug resistance to treatment, treatment outcome and causes of TB death (if the patient died).
2.4. Types of tuberculosis
Types of TB were classified into extrapulmonary TB (EPTB),smear-positive pulmonary TB (PTB), smear-negative PTB and other PTB. Diagnosis of EPTB was based on having at least one specimen with confirmed Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or histological evidence, or strong clinical evidence consistent with active EPTB[12]. Smear-positive pulmonary TB was diagnosed when at least one sputum smear specimen was positive for acid-fast bacilli and lung parenchyma was involved. Smear-negative PTB was diagnosed when lung parenchyma was involved but sputum smear specimen was negative and culture positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Other PTB was diagnosed when there were radiographic abnormalities and based on clinician’s decision. Drug resistance to treatment was examined for first-line drugs (isoniazid,rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) and streptomycin. Monoresistant TB was defined when TB bacteria was detected to develop resistance to a single first-line TB drug. Multidrug resistant was defined when there was resistance detected to at least both isoniazid and rifampicin. Polyresistant TB was defined when there was resistance to more than one first-line TB drug, other than isoniazid and rifampicin[12].
2.5. Treatment outcomes
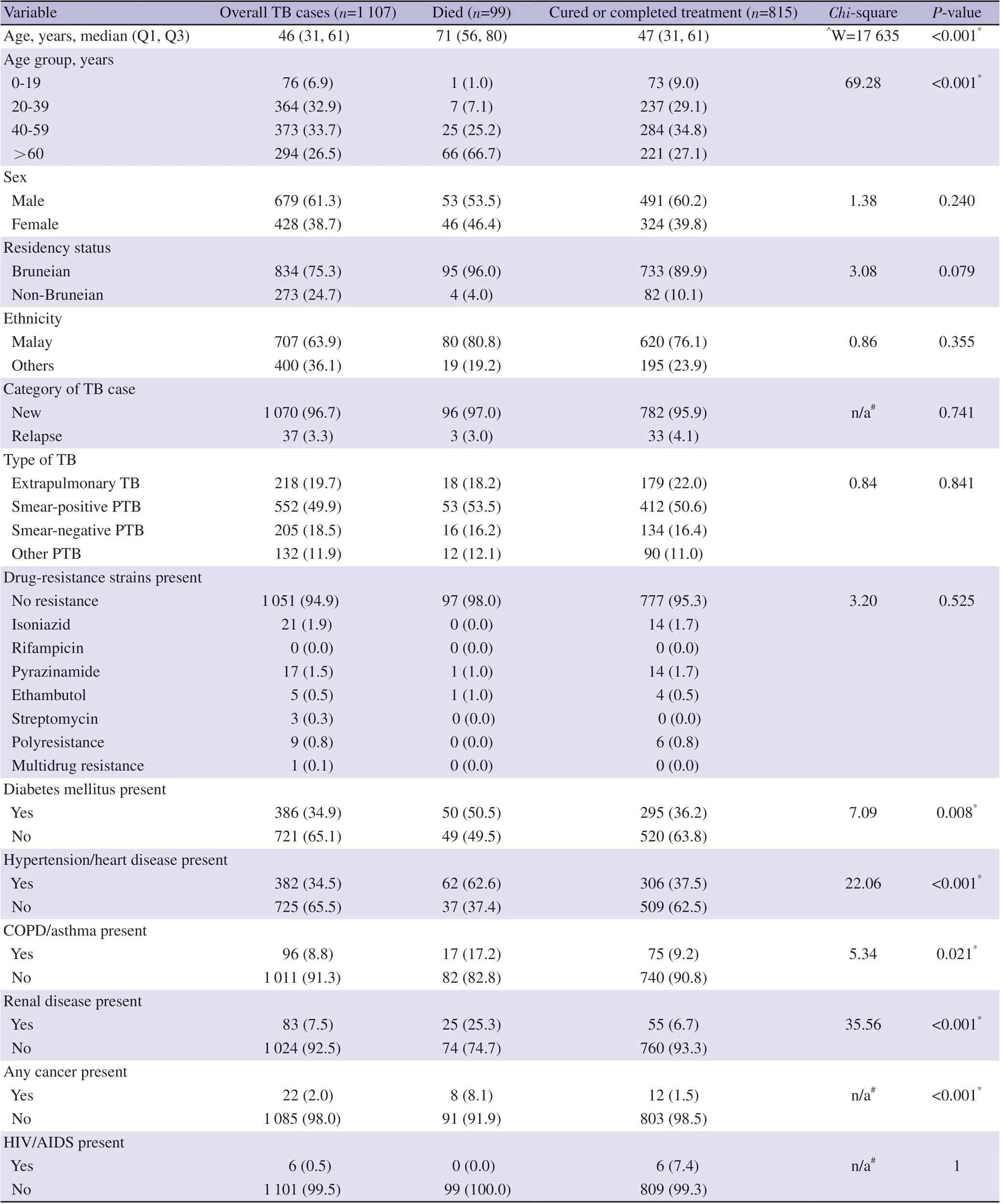
Table 1. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of tuberculosis patients overall, those who had died and those who either were cured or had completed treatment in Brunei Darussalam (January 2013-December 2017) [n (%)].
Treatment outcomes were categorized according to World Health Organization’s reporting framework for TB: (1) cured, defined as smear- or culture- positive TB patients at the start of treatment who was smear- or culture-negative in the last month of treatment, (2)completed, defined as TB patient who has completed treatment without failure but has no record of having smear- or culturenegative result in the last month of treatment, (3) treatment failure,defined as TB patient who is still smear- or culture-positive on or after fifth month of treatment, (4) died, defined as TB patients who died for any reason before or during treatment, (5) lost to followup, defined as TB patient who did not start treatment or whose treatment was interrupted for more than 2 consecutive months, and(6) not evaluated, defined as TB patient whose treatment outcome is unknown or those who sought treatment outside Brunei[9]. Those who were not evaluated were mainly foreign workers diagnosed with active TB at start or renewal of employment period as in accordance with Brunei’s Immigration Act, these workers would have their employment terminated and would have to return to their home country for treatment[15].
Causes of death were acquired based on availability in Bru-HIMS,NTCC case notes or upon inference from recent case notes. Causes of TB deaths were then categorized into TB-related deaths, non-TB related deaths or unknown. For the purpose of categorizing these deaths, the treating physician’s or pathologist’s careful deliberation of the cause of death was utilized, and a TB-related death was only classified if TB was mentioned as a cause of death. A non-TB related death was defined as any other cause of death for which TB was not mentioned. This included malignancy, bacterial infection,hepatic failure, renal failure, cardiovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with respiratory failure and others such as haemorrhage, pulmonary embolism and aortic aneurysm.Deaths were classified as unknown when there was no specific cause of death mentioned in patient’s case notes.
2.6. Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were carried out using R (ver. 4.0)[16]. Point prevalence was calculated to report on the annual trend for overall TB deaths using the formula: Prevalence=number of TB deaths/total TB cases for each year. Proportion of TB deaths according to different types of TB was also calculated (Proportion=number of deaths for different TB types/total TB deaths for each year).The 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were also calculated and reported. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics for the overall TB cases were analyzed. Chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests or Mann-Whitney test (where appropriate) were performed to determine any significant differences between TB cases who had died and those who were either cured or completed treatment. The latter was chosen as the comparison group to avoid any potential bias from including cases who were classified as lost to follow-up,not evaluated or treatment failure. About three-quarters of all TB cases included in this study (73.6%, n=815) were classified as either cured or completed treatment. Variables with P<0.1 were further analyzed using multiple logistic regression to derive crude and adjusted odds ratios, except for age and gender which were included a priori. All regression models were checked if model assumptions were met, and interaction terms were added when necessary.Statistical significance was defined as P-value <0.05.
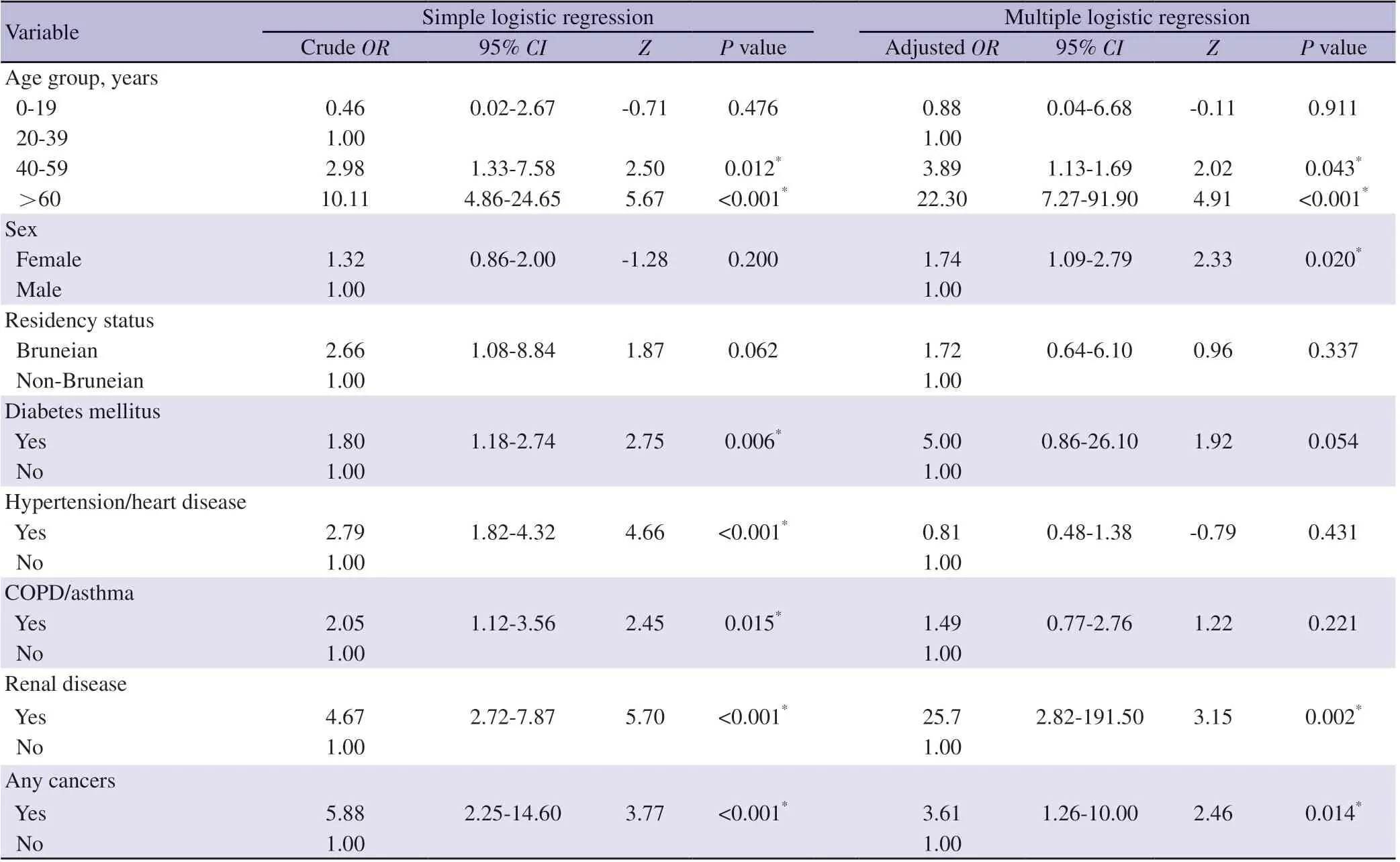
Table 2. Factors associated with overall tuberculosis deaths in Brunei Darussalam (January 2013-December 2017).
3. Results
A total of 1 107 TB cases (PTB and EPTB) were reported between January 2013 and December 2017. Among them, 485 were cured,330 completed treatment, 4 experienced treatment failure, 1 lost to follow up, 188 not evaluated, and 99 deaths occurred during the TB treatment period, giving an overall TB mortality rate of 8.9% (95%CI 7.4-10.8) during the 5-year study period.
For overall TB cases, the median age was 46 years (IQR 31-61),majority were male (679, 61.3%), Bruneian (834, 75.3%) and of Malay ethnicity (707, 63.9%; Table 2). In terms of their clinical characteristics, majority were new cases (1 070, 96.7%), smearpositive PTB (552, 49.9%), and with no drug-resistance strains(1 051, 94.9%). Initial comparative comparison analysis between TB patients who had died and those who either were cured or had completed TB treatment (Table 1) revealed significant differences in terms of age (P<0.001), having co-morbidities such as diabetes mellitus (P=0.086), hypertension or heart disease (P<0.001), COPD or asthma (P=0.021), renal disease (P<0.001), and any cancer(P<0.001). Multiple logistic regression analysis (Table 2) showed that the significant factors associated with TB deaths were advancing age (adjusted OR for 40-59 years: 3.89; 95% CI 1.13-1.69; adjusted OR for ≥60 years was 22.3; 95% CI 7.27-91.9, using 20-39 years as reference), being female (adjusted OR 1.74; 95% CI 1.09-2.79),having renal disease (adjusted OR 25.7; 95% CI 2.82-191.50) and having any cancers (adjusted OR 3.61; 95% CI 1.26-10.00).
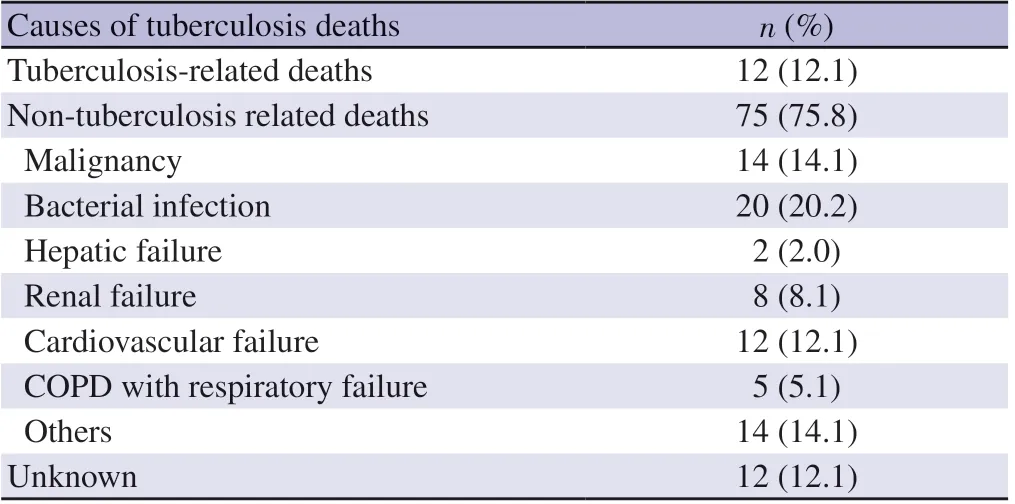
Table 3. Underlying cause of deaths among tuberculosis death cases.
About 1/3 of the recorded deaths were not related to TB (75.8%,n=75; Table 3). Due to small numbers, comparison of associated factors for TB-related deaths and non-TB related deaths was not conducted.
The annual TB mortality ranged from 7.1% to 10.9%; there was a slight increase in 2015 but then tapered off from 2016 (Figure 1).Proportion of TB deaths according to different types of TB showed higher mortality for smear-positive PTB patients, when compared to other groups (Figure 2). This is likely due to higher proportion of smear-positive PTB cases compared to the other TB types (Table 1).
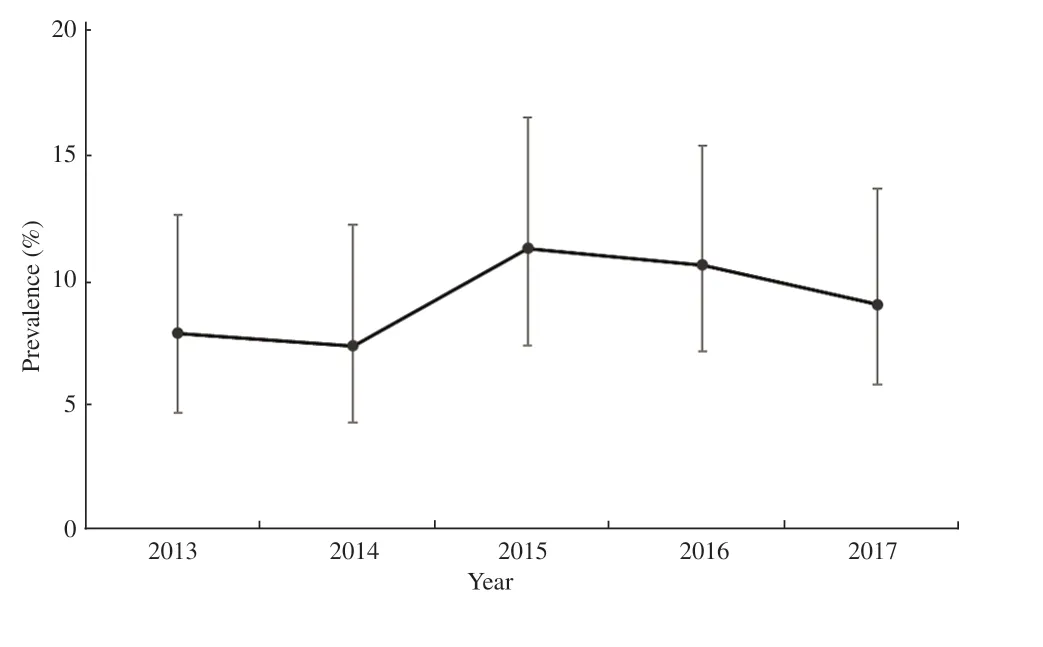
Figure 1. Point prevalence of overall tuberculosis deaths among tuberculosis cases for each year (Error bars indicate the 95% confidence interval).
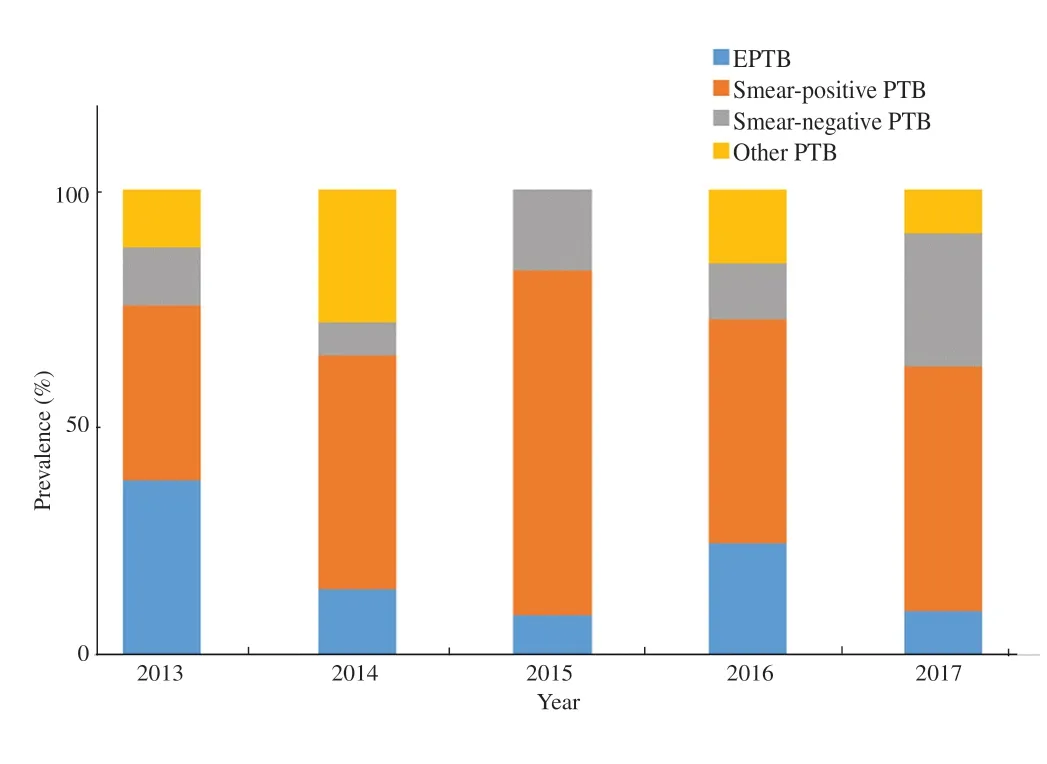
Figure 2. Proportion of tuberculosis deaths according to types of tuberculosis cases for each year (2013-2017). EPTB: extrapulmonary tuberculosis; PTB: pulmonary tuberculosis.
4. Discussion
During a 5-year study period, we found an overall TB mortality of 8.9% (95% CI 7.4%-10.8%) in Brunei Darussalam. Our finding is similar to that reported in another intermediate TB burden country (Malaysia, 8%)[4] and also in a low TB burden country(United States, 7.3%)[7]. But higher than that reported in a high TB burden country (Shanghai, China, 5.5%)[17], which suggests that being a high TB burden country does not necessarily equate to high TB mortality. And that other potential risk factors could affect the risk of TB-related deaths. The significant risk factors associated with TB mortality for Brunei Darussalam were advancing age, being female, having renal disease and any cancers were positively associated with TB mortality. Our finding for advancing age was consistent with similar studies from countries with low-, intermediate, and high-TB burden[2,3,7,17-20]. Renal disease[5,7] and cancer[3] were also reported to be a risk factor with TB mortality in other studies. As older age is known to be a major risk factor in the diagnosis of chronic comorbidities, this finding may not be surprising. However, it presents a worrying scenario for Brunei specifically, as cancer was the country’s main cause of death among adults[13] and also has one of the world’s highest prevalence of patients undergoing kidney replacement therapy[21].In contrast, our finding for female being positively associated with TB mortality is in conflict with other studies where male gender was reported as a risk factor[2,3,17-19]. The reason for this finding is unclear, though socio-cultural differences between genders on coping with TB disease could be one plausible explanation.Qualitative and/or questionnaire-based studies focusing on the socio-cultural aspects and well-being of TB-confirmed patients,particularly those of 40 years and older, would be helpful to confirm our findings.
We also observed that only 12.1% of all deaths were related to TB, a finding similar to Taiwan (17.3%)[5]. This suggests that in order to improve disease prognosis, it is important to also consider non-TB aspects of a patient’s medical history.
This study has its limitations. First, data regarding socioeconomic status of the TB cases, any delay in treatment, treatment adherence, survival days (number of days from diagnosis to death)were not collected. These data could have provided insights and promoted changes for improvement, for example, by ensuring early diagnosis of TB in contacts to expedite treatment and prevent delays. Extending this study to include the collection of such variables would be useful to get better understanding on TB deaths in Brunei, thereby contributing towards improving TB management and the country’s progress to TB elimination.Secondly, it is possible that the causes of TB deaths could be misclassified as there was only one investigator collecting the data at the time. This could have been minimized if the classification was checked and verified by another staff or a committee.Investigators tried to reduce this later on by checking case notes in Bru-HIMS. TB patients who died at home had no death records or recent case notes in Bru-HIMS so investigators were unable to determine the cause of death. Thirdly, although NTCC has been collecting TB patient data since 2000, only data from 2013 onwards could be analyzed as the latter was the year when Bru-HIMS was fully implemented. There is also a lack of death data collected at NTCC. This could have limited the study population for this study, so much so that it could have attributed to small counts for co-morbidities and residency status. Very wide 95%CI were observed for both variables, indicating that their point estimates should be interpreted with caution. Systematic collection of patient records and/or integrating with the mortality registry would be helpful for future research.
In conclusion, we reported an overall TB mortality of 8.9% (95%CI 7.4%-10.8%) in Brunei Darussalam during a 5-year study period. Risk factors of TB mortality include advancing age, being female, and having renal disease and any cancers. Most TB deaths were not related to TB, making it important for clinicians to focus also on other non-TB aspects of the patient’s history, such as the presence of comorbidities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Funding
This study is funded by Universiti Brunei Darussalam’s University Research Grant (Ref: UBD/RSCH/URC/RG(b)/2019/011).
Authors’ contributions
LC and NHJ conceptualized the project idea. LC and NHJ performed the statistical analysis. KT curated the data Both NHJ and LC wrote the original draft. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript. KT and LC supervised the project.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2023年1期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2023年1期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Time to stimulate Plasmodium vivax research in India: A way forwards
- Atypical pompholyx presentation of secondary Staphyloccoccus and Klebsiella infections in a patient with premorbid Ebstein anomaly: A case report
- Novel markers in predicting Brucella sacroiliitis: The platelet large cell ratio and basal immature reticulocyte fraction
- Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infected population during the second and third epidemiological waves in Sri Lanka
- Knowledge and associated factors of healthcare workers on measles vaccine and cold chain management at health institutions in Gondar, Ethiopia
- Modelling the probability of presence of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Iran until 2070
