Probiotics for preventing gestational diabetes in overweight or obese pregnant women: A review
Ya-Fang Deng, Li-Ping Wu, Yan-Ping Liu
Ya-Fang Deng, Li-Ping Wu, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, School of Nursing, Beijing 100730, China
Yan-Ping Liu, Department of Clinical Nutrition, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing 100730, China
Abstract Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host. Specific probiotics or probiotic foods can be used to reduce the risk of diseases associated with aberrant gut microbiota composition. The incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) has increased annually with the proportion of overweight and obese people. Overweight or obese pregnant women are at high risk of GDM and have obvious changes in gut microbiota compared with normal-weight pregnant women. Specific probiotics or probiotic foods may alter gut microbiota in overweight or obese pregnant women and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors, consequently resulting in weight loss and reduced insulin resistance. This review discusses the mechanism of probiotics on GDM, as well as the dose, method and duration of probiotics use, and summarizes current evidence on probiotics in improving glucose metabolism and other maternal and infant outcomes in overweight/obese pregnant women.
Key Words: Probiotics; Gut microbiota; Diabetes, Gestational; Overweight; Obesity,Maternal
INTRODUCTION
Probiotics are defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (WHO) as live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host[1]. Probiotic supplementation is well tolerated and safe even in pregnant women and their children[2-5]. However, adverse effects such as stomach ache, flatulence, dystocia, amniotic fluid reduction, Crohn’s disease, and headache have been reported[3,6,7]. Gastrointestinal symptoms are the most common adverse effects[3]. An increased risk of pre-eclampsia, including superimposed, has been reported after probiotic administration, in systematic reviews and metaanalyses[8-10]. However, a systematic review and meta-analysis in 2021 indicated that adverse effects associated with probiotic and prebiotic use do not pose any serious health concerns to mothers or infants[2]. As dietary adjuncts, specific probiotics or probiotic foods can be used to reduce the risk of diseases associated with aberrant gut microbiota composition, increased intestinal permeability, or altered immunological or metabolic balance[11].
The human gut microbiota is engaged in multiple interactions affecting host health during the host’s entire lifespan, modulating key processes in metabolism, inflammation and immunity[12,13]. Korenet al[14] indicated that host-microbial interactions that affect host metabolism can occur and may be beneficial in pregnancy. During pregnancy, the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in metabolic dysfunction[15]. Maternal status is associated with alterations in the compositions and diversity of the intestinal microbiota community during gestation[15]. Maternal metabolic disorders can influence the long-term health of mothers and their offspring[15]. The composition of the gut microbiota is significantly altered in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), pre-eclampsia, abnormal placental growth, and obesity compared with healthy pregnant women[15,16]. Scientific probiotic and prebiotic supplements have positive effects on mothers and their offspring.
GDM is the diagnosis of diabetes in the second or third trimester of pregnancy that was not clearly overt diabetes prior to gestation[17], and is a common complication in pregnant women that can negatively affect pregnancy outcomes and short- and long-term maternal and child health[18]. Pre- or early-pregnancy overweight or obese pregnant women are at high risk of GDM[6,19]. As the proportion of overweight and obese people has increased, the incidence of GDM has also increased annually[20,21]. WHO recommends the following international body mass index cutoff for adults[22]: Overweight = 25.0-29.9 kg/m2and obese ≥ 30 kg/m2, but standards vary from country to country. A narrative review indicated that the body weight condition might be the critical factor for the effects of probiotics on GDM[23].
Current research on the use of lifestyle interventions to prevent GDM is contradictory, particularly the efficacy of prevention, which differs among obese pregnant women[24]. Some reviews or metaanalysis[25-27] showed that probiotics may reduce blood glucose level in pregnant women and prevent GDM, especially in high-risk groups including overweight or obese pregnant women[10], excessive weight gain during pregnancy, and abnormal gut microbiota[11]. Therefore, probiotics might be a new strategy for preventing GDM. We review the mechanism of probiotics on GDM, as well as the dose, method, and duration of probiotics administration, and summarize current evidence on probiotics in preventing GDM or improving glucose metabolism and other maternal and infant outcomes in overweight/obese pregnant women.
MECHENISM OF PROBIOTICS ON PREVENTING GDM IN OVERWEIGHT/OBESE PREGNANT WOMEN
Intestinal microorganisms perform many important functions; one of which is participation in metabolic processes such as the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)[28]. SCFAs mediate the transmission of signals between the microbiome and the immune system and are responsible for maintaining balance in the anti-inflammatory reaction, such as propionic and n-butyric acids produced in the large intestine by gut bacteria[29]. The level of propionic acid decreases with the course of pregnancy, while obese women have an increased level, which is associated with many metabolic adaptations[29]. Szczukoet al[29] showed that propionic and linear caproic acid levels can be critical in maintaining lower anthropometric parameters during pregnancy. Pregnancy stages alter the gut microbiota community structure[29]. Reduced numbers ofBifidobacteriumand increased numbers ofStaphylococcus,Enterobacteriaceae, andEscherichia coliwere detected in overweight compared with normal-weight pregnant women[30,31]. Meanwhile, fecalBacteroidesandStaphylococcusconcentrations were significantly higher and bifidobacterial counts were less in infants of overweight mothers during the first 6 mo of life compared with nonobese mothers[13]. Obese (high-fat feeding) can increase lipopolysaccharide-containing microbiota in the gut and plasma leading to a state of chronic low-grade systemic inflammation that is casually linked to insulin resistance (IR)[32,33]. A systematic review by Shirvani-Radet al[34] indicated that the probiotic products could be of benefit to managing obesity when using them as an adjunct therapy at high dose.
The incidence of GDM is obviously associated with changes in the gut microbiota (increased levels ofEnterobacteriaceaeandEnterococcusand decreased levels ofBifidobacteriaandLactobacillus)[11,35,36]. Mokkalaet al[37] reported that an interaction between GDM status and intervention was observed in women without GDM, which means that the evolution of the gut microbiota throughout pregnancy is influenced by GDM and dietary intervention. Specific gut microbiota species do not differ between women with and without GDM and gut microbiota is neither involved in the incidence of GDM nor differs according to GDM status. Intestinal microbiota disorder during pregnancy may interact with various pathways such as IR, chronic inflammatory reaction, endotoxemia, and energy metabolism[38]. Chronic inflammatory reaction increases IR, deceases insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP), disrupts the function of pancreatic β cells and insulin secretion, which can cause and promote progression of GDM[39]. New means to stabilize the microbial balance during pregnancy could benefit maternal health[40]. Pregnant women may benefit from gut microbiota targeted dietary supplementation[37].
The use of probiotic microorganisms to prevent and treat intestinal dysbiosis, leading to an increase in SCFAs in the colon, seems to be an important direction for further research[28]. Isolauriet al[11] showed that probiotics could balance the properties of aberrant endogenous microbiota, and regulate intestinal permeability and the secretion of proinflammatory mediators to control systemic and local inflammatory status and energy efficiency, which could be the underlying mechanisms of probiotics in GDM. Overweight and obese women without GDM, particularly those receiving the fish oil + probiotics combination, manifested changes in relative abundance of bacterial species over the pregnancy in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in 2021[37]. Halkj?ret al[41] also found that multistrain probiotics consisting ofStreptococcus thermophilusDSM 24731, Bifidobacteria, andLactobacillican modulate the gut microbiota and increase α-diversity in obese pregnant women, but a larger study population is needed to determine pregnancy effects after probiotic supplementation. When the abundance of these key species began to decline, a collapse in symbiosis was observed, reflected in a deterioration in host metabolic health[42]. A systematic and meta-analysis of RCTs found that probiotic supplements reduce the level of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and improve insulin, IR, and insulin sensitivity, especially for GDM and healthy pregnant women[42]. However, for overweight or obese pregnant women, a network meta-analysis in 2019 showed that interventions that aim to prevent GDM, such as physical exercise programs, and administration of metformin, vitamin D, and probiotics are not effective[43]. Therefore, we wondered whether probiotics may modulate the abundance of gut microbiota in overweight/obese pregnant women, which could decrease both the proportion of lipopolysaccharide-containing microbiota in the gut and plasma lipopolysaccharides[11], and they also inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors, thereby reducing IR, modulating glucose metabolism, and preventing GDM.
SPECIES, DOSE, METHOD, AND DURATION OF PROBIOTICS
Most of the probiotic properties are species- and strain-specific[11]. The properties of each probiotic strain should be well defined and cannot be extrapolated to other strains[44]. Sánchezet al[44] stated that it is necessary to scientifically demonstrate the efficacy of the strain in conferring a health benefit on the host, but this effect does not have to be linked to any specific mechanism of action. The most common probiotic species includeBifidobacterium,Lactobacillus paracasei,Streptococcus thermophilusandLactobacillus rhamnosus(L. rhamnosus), which are also part of the normal human microbiome[45]. The main probiotics used in studies containedBifidobacteriaandLactobacilli. It has been proven thatBifidobacteriacan encompass degradation of nondigestible carbohydrates, protect against pathogens, produce vitamin B, antioxidants, and conjugate linoleic acids, and stimulate the immune system[46]. Strains ofLactobacillus,Bifidobacterium, andSaccharomyceshave a long history of safe and effective use as probiotics, butRoseburia spp.,Akkermansia spp.,Propionibacterium spp., andFaecalibacterium spp.show promise for the future[47]. As another dominant genus of intestinal microbiota,Blautiaplays some part in metabolic diseases, inflammatory diseases, and biotransformation[48]. There is a disparity in association ofBlautiawith human diseases (less in sufferers of diabetes/obesity, but more in inflammatory bowel disease)[48]. Because of the probiotic properties, the effects of different species or strains probiotics should be explored.
The dose, method, and duration of probiotics has varied among studies. The dose may have a major influence on the effect of probiotics administration. A 12-wk RCT in 81 obese postmenopausal women showed that significant favorable changes (mostly large or medium effects) in the evaluated parameters, including waist, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, and insulin in the high-dose [1010colony forming units (CFU)/d] and low-dose (2.5 × 109CFU/d) groups by receiving lyophilisate powder containing several species of live probiotic bacteria[49]. The high-dose, low-dose, and placebo groups showed significant differences in lipopolysaccharide levels, glucose, insulin, and homeostasis model assessment of IR (HOMA-IR)[49]. Using the multispecies probiotic Ecologic?Barrier favorably in a dosedependent manner can have beneficial effects[49]. The meta-analysis by Zhenget al[50] indicated that the dose or CFU of a probiotic is an important factor in the efficacy of probiotic supplementation on metabolic health in pregnant women, and a dose > 107CFU probiotic counts can show beneficial effects. For overweight/obese pregnant women, the dose of probiotic may be not less than 109CFU/d[3,6,41,51].
Diet is a principal driver of gut fermentation and therefore can influence functionality of the indigenous microbiota[47]. The combination of dietary probiotics and probiotic supplements might reduce the risk of GDM and larger birth size because of the synergy between a probiotic-rich diet and probiotic supplements[37,52,53]. Luotoet al[53] studied the safety and efficacy of perinatal probioticsupplemented dietary counseling (additionally intensive dietary counseling complying with current recommendations at every study visit provided by a nutritionist, combined with conventional food products with favorable fat and fiber contents for use at home) in normal weight pregnant women. The intervention group (probiotics + diet) had a reduced frequency of GDM compared with the diet/ placebo and control groups. However, probiotics combined with diet in overweight/obese pregnant women for the prevention of GDM were not investigated in that study. Mokkalaet al[37] indicated that overweight and obese women without GDM may benefit from dietary modulation through gut microbiota modulation.
Specific probiotics or probiotic foods were mainly administered orally in ice-stored probiotic capsules or probiotic yogurt, and one study reported that two participants stopped taking the capsules because they were difficult to swallow[41]. Asgharianet al[6] showed some beneficial effects on glucose metabolism in overweight and obese pregnant women by using probiotic yogurt, whereas no significant differences were found in other studies provided with probiotic capsules[3,41,51,54,55]. A review reported daily consumption of 200 g yogurt containingLactobacillus gasseri(108CFU/g) for 12 wk significantly reduced abdominal obesity[39]. According to a study by Homayoniet al[56], foods are better carriers of probiotics than supplements are. In the study by Lindsayet al[55], obese pregnant women were required to take probiotics after meals, which may have reduced the possibility of adverse gastrointestinal symptoms. Other similar studies did not report the specific time of probiotic supplementation. Some researchers recommended the administration of probiotic capsules with a glass of cold water or milk (avoiding acidic or hot drinks), to keep the strain active[7].
The cointervention of multiple alive bacteria strains on preventing and treating metabolic diseases could be a promising method of treatment[23]. Prebiotics are defined in 2017 as “a substrate that is selectively utilized by host microorganisms conferring a health benefit,” which is a popular dietary approach to the modification of the gut microbiota to improve host health[47,57]. Prebiotics such as inulin-type fructans and arabinoxylan oligosaccharides can be consumed to increase the number ofBifidobacteriaand cause butyrogenic effects in the human colon, which are the result of crossfeeding interactions betweenBifidobacteriaand butyrate-producing colonic bacteria[46]. Butyrate is an essential metabolite in the human colon, as it is the preferred energy source for the colonic epithelial cells, and contributes to the maintenance of the gut barrier functions, and has immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory properties[46]. Butyrate and propionate regulate glucose metabolism by stimulating the process of intestinal gluconeogenesis[29]. Personalized nutrition and precision medicine are beginning to influence the application of probiotics and prebiotics[58]. Synbiotics are a mixture comprising live microorganisms and substrates selectively utilized by host microorganisms that confers a health benefit on the host, which is better than prebiotics alone[59]. Studies also showed that probiotics and prebiotics (synbiotics) were used to modulate the maternal gut microbiome composition, which might enhance probiotic survival and growth better than probiotics alone[39,52]. A narrative review by Liet al[23] reported that novel food-processing strategies like enzyme-modified prebiotics and probiotic-fermented natural foods have been developed to enhance the beneficial effects on alleviating metabolic diseases.
At present, all studies on the use of probiotics in overweight/obese pregnant women start from the second or third trimester of pregnancy. The commencement of probiotics in the first trimester would be important to explore in future research, but Callawayet al[51] believes that this poses practical difficulties in routine clinical practice. Xieet al[10] showed that longer duration (≥ 8 wk) of probiotics had a more significant preventive effect on GDM. Whether and which species, dose, method, and duration of probiotics administration will affect the prevention of GDM or improve glucose metabolism and maternal and infant outcomes remain to be further explored.
EFFECTS OF PROBIOTICS ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN OVERWEIGHT/OBESE PREGNANT WOMEN
A few studies have used probiotics in overweight/obese women in the second and third trimester of pregnancy to reduce FPG at 24-28 wk of gestation and the incidence of GDM (the diagnostic criteria for GDM vary among different studies). The results of these studies on FPG are inconsistent, and no significant differences on the incidence of GDM between the groups were observed (Table 1). Lindsayet al[55] reported that probiotic capsules (L. salivariusUCC118) in obese pregnant women at 24-28 wk gestation do not reduce maternal fasting glucose or the incidence of GDM, and longer administration may be required for any probiotic effect to be exerted. The probiotics [L. rhamnosusandB. animalissubsp.lactis(BB-12)] used in the SPRING prospective double-blind randomized trial also did not prevent GDM in 433 overweight and obese pregnant women, who started taking probiotic capsules from 20 wk gestation to delivery[51]. However, they noted a higher fasting glucose level in the probiotics group. Although they used identical probiotics to Luotoet al[53], dietary counseling may have played a key role. However, Asgharianet al[6] showed that probiotic yogurt [Lactobacillus acidophilus(L. acidophilus) La5 andBifidobacterium lactisBb12, 5 × 1010CFU/d] provided from 24 wk gestation to delivery decreased FPG and 2 h PG oral glucose tolerance test at 28 wk gestation in overweight and obese women, which may be related to the species of probiotic bacteria and the viable count in probiotic yogurt. Different strains of probiotics (LactobacilliandBifidobacteria) may also affect the results. Halkj?ret al[41] provided multistrain probiotics that increased the gut microbiota diversity in obese pregnant women, but there was no significant difference in GDM and gestational weight gain (GWG). Further studies in different settings with a larger number of participants are recommended. Pellonper?et al[3] reported that fish oil and/or probiotics during pregnancy did not lower the risk of GDM or improve glucose metabolism in 439 overweight and obese women. In high-risk pregnant women, Shahriariet al[7] provided probiotic capsules containing a mixture ofL. acidophilusLA1,Bifidobacterium longumsp54 cs, andBifidobacterium bifidumsp9 cs, and the results showed that probiotics supplementation from the first half of the second trimester up to 24 wk of pregnancy did not reduce the risk of GDM. Further studies should focus on the effect of probiotics on the incidence of GDM in highrisk pregnant women.
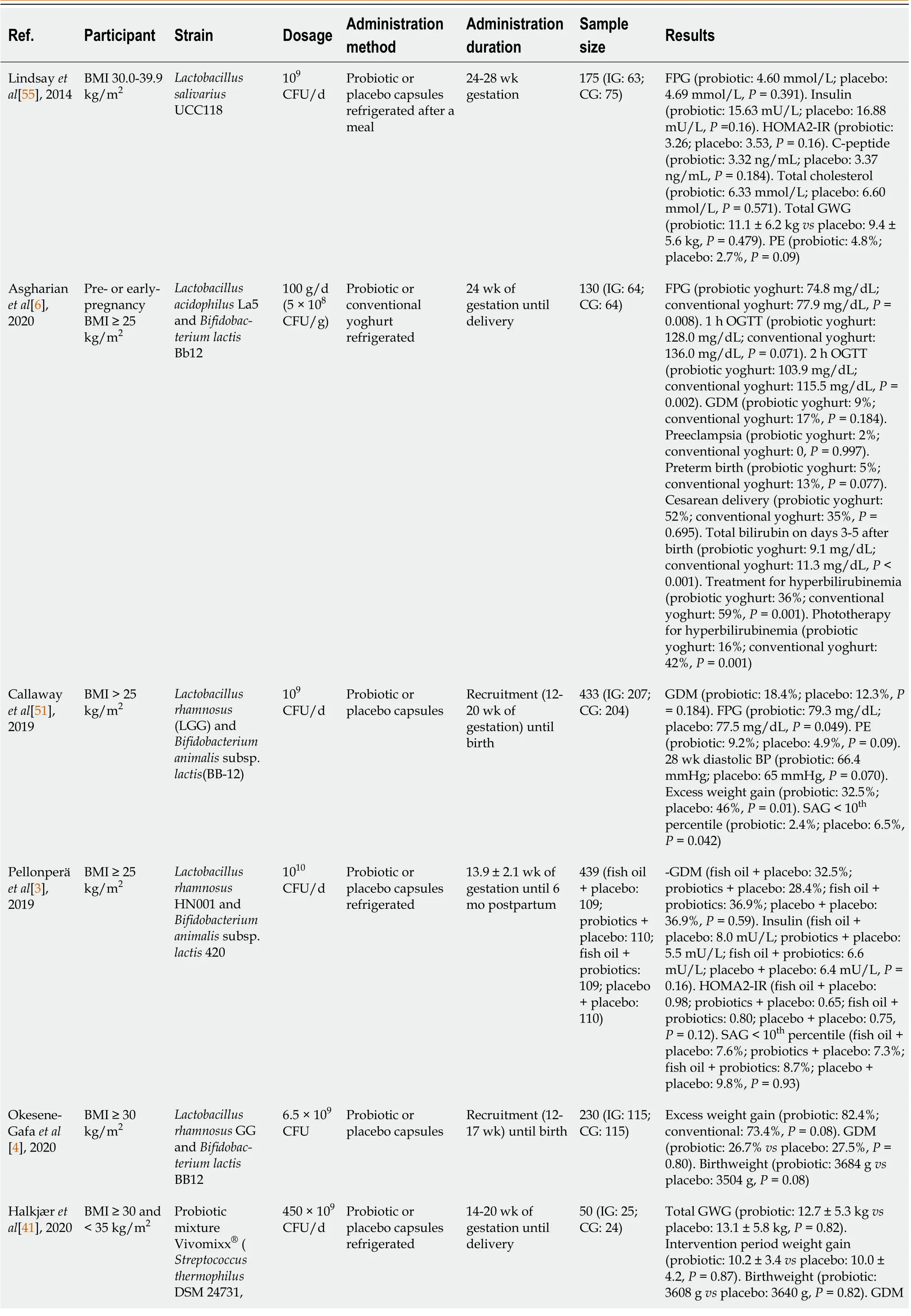
Table 1 Use of probiotics in the prevention of gestational diabetes and infant outcomes in overweight and obese pregnant women
The effect of probiotics on preventing GDM in overweight or obese pregnant women has been the subject of debate in current systematic reviews and meta-analysis[9,10]. The study by Chuet al[9] found that there were no significant differences between probiotics and placebo on GDM and suggested that probiotics were not a promising approach to prevent GDM and promote the health of subsequent generations. However, the latest meta-analysis carried out in China reported that probiotics can effectively prevent GDM in overweight and obese pregnant women[10]. As the number, sample size and quality of studies have been limited, more well-designed large trials are needed for better metaanalyses.
IR during pregnancy is the pathogenetic basis of GDM, and increased levels of microinflammatory factors are one of the main manifestations of IR[18]. Related studies measured HOMA-IR and C-peptide as secondary outcomes[3,55], which increased from early to date pregnancy in all intervention groups, and there were no significant differences between the different groups. From the same RCT as Pellonper?et al[3], Houttuet al[60] measured high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8, phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), IGFBP-1 and vaginal MMP-8 in the different intervention groups and in all of the overweight/obese pregnant women. IGFBP, which may affect the development of GDM, differed significantly between women with or without GDM. The increased level of microinflammatory factors is one of the main manifestations of IR, which is mainly a chronic inflammatory reaction centered on the release of proinflammatory factors such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α[18]. Glycoprotein acetylation (GlycA) is a composite nuclear magnetic resonance biomarker of systemic inflammation, including α1-acid glycoprotein, touchglobin, α1-antitrypsin, α1-antichymotrypsin and transferrin[61,62]. Mokkalaet al[63] indicated that GlycA reflects gut microbiome diversity and is more accurate than hsCRP in reflecting metabolomic profile. Thus, proinflammatory factors, IGFBP and GlycA can be added as indicators to observe IR.
Administration of specific probiotics from the second and third trimester of pregnancy can enrich the diversity of gut microbiota in obese pregnant women, but the effect on reducing fasting blood glucose in overweight/obese pregnant women is still controversial and no positive findings on preventing the incidence of GDM were observed in these trials. As a result of strain specificity, different strains, dose, method, and duration of diverse probiotic species, as well as the influence of combining dietary counseling on their interventional effects should be extensively studied in the future. We suggest that further studies should increase the sample size and study population, provide comprehensive details of the study design, and be conducted in more high-risk GDM groups.

BMI: Body mass index; CFU: Colony forming unit; CG: Control group; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; GWG: Gestational weight gain; HOMA-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; IG: Intervention group; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; PE: Preeclampsia; SGA: Small for gestation age.
Table 1 summarizes the effects of probiotics on GDM in studies conducted in overweight and obese pregnant women. GDM is diagnosed by the criteria of the International Association of The Diabetes and Pregnancy study Group in the table.
EFFECTS OF PROBIOTICS ON OTHER MATERNAL AND INFANT OUTCOMES IN OVERWEIGHT/OBESE PREGNANT WOMEN
Taking probiotics can modulate the diversity of gut microbiota in obese pregnant women, and may even affect infants’ gut microbiota, which may have a positive impact on their growth and health[11,64]. The previous research mentioned noted that probiotics may reduce GWG, the mean neonatal total serum bilirubin (TSB) on days 3-5 after birth and small for gestation age (SGA) infants in overweight/obese pregnant women, while other outcomes were not significantly different.
Maternal outcomes
Other maternal outcomes besides glucose metabolism include GWG, pre-eclampsia, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, and lipid metabolism (cholesterol content). In overweight/obese pregnant women, Callawayet al[51] showed lower rates of GWG in women in the probiotics group, but there were no differences in overall weight gain between the groups or weight gain per week. Maternal overweight/obesity and excessive GWG were associated with reduced diversity of gut microbiota[65]. Halkj?ret al[41] conducted an intention-to-treat and per protocol analysis that showed a lower GWG during the intervention period and increased α-diversity of gut microbiota in the probiotic group compared with the placebo group, although this difference in GWG did not reach significance, possibly because of the small sample size. The administration of probiotics may reduce body weight, although the effect sizes are small[31,66,67]. However, the latest systematic reviews and meta-analyses in 2022 showed that there were no significant differences between probiotics and placebo on excess weight gain in overweight/obese pregnant women[9,10].
The administration of probiotics can reverse alterations or dysregulation of the gut microbiota[68] and decrease both the proportion of lipopolysaccharide-containing microbiota in the gut and plasma lipopolysaccharides. However, there is insufficient evidence to support the role of probiotics in improving blood lipid profile in overweight/obese pregnant women. Lindsayet al[55] observed no effect of probiotic intervention on the lipid concentration after administration of probiotics, while the total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein, and triglycerides were lower. Probiotics may be associated with a slight reduction in triglycerides and total cholesterol in treating women with GDM[4]. The increased risk of pre-eclampsia (high-quality evidence) and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy with probiotics reported by Davidsonet al[8] should be noted. There were few differences between the groups in terms of other outcomes such as cesarean section rate and postpartum hemorrhage.
Neonatal outcomes
Neonatal outcomes in studies that provided probiotics to overweight/obese pregnant women, included macrosomia, SGA, prematurity, jaundice, admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and neonatal death within 30 d after birth. Asgharianet al[6] analyzed the occurrence of jaundice, treatments used for jaundice and TSB measured on days 3-5 after birth in heel capillary blood, and found that the mean neonatal TSB on days 3-5 after birth and use of all types of treatment, including phototherapy (alone or with other treatments), were significantly lower in the probiotic group than in the conventional yoghurt group. This was the first study to explore neonatal bilirubin level following administration of probiotics in overweight/obese pregnant women. Two systematic reviews and meta-analyses showed that probiotics supplement therapy may be effective in treating neonatal jaundice, but the evidence is low certainty and quality[69,70]. Chenet al[70] demonstrated that probiotic supplementation is an effective and safe treatment for pathological neonatal jaundice. However, a meta-analysis in 2019 did not recommend routine use of probiotics to prevent or treat neonatal jaundice as limited low-quality evidence indicated that probiotic supplementation may reduce the duration of phototherapy in neonates with jaundice[69]. Large well-designed adequately-powered trials on probiotic supplementation during pregnancy in overweight/obese pregnant women are still needed to identify whether probiotics reduce the occurrence of neonatal jaundice and the mean neonatal TSB level on days 3-5 after birth, and improve the efficacy of phototherapy for jaundice, alone or combined with other treatments. Callawayet al[51] found that probiotics have a role in the prevention of SGA, but this requires further investigation in future meta-analyses. Other neonatal outcomes such as microsomia, premature admission to the NICU, and neonatal death were not significantly different between the two groups[3,7,41,51,55].
CONCLUSION
Overweight/obese pregnant women, excessive weight gain during pregnancy, and abnormal gut microbiota are high-risk factors for GDM, and probiotics may be more effective in high-risk pregnant women in preventing GDM by modulating the gut microbiota and inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors. Current evidence indicates that multiple probiotics may increase α-diversity in obese pregnant women, and probiotics have a positive effect on reducing fasting glucose and GWG in overweight/obese pregnant women and the incidence of SGA, as well as the mean neonatal TSB on days 3-5 after birth. However, probiotics have little effect on other maternal and neonatal outcomes such as GDM, preterm birth and macrosomia. At present, there have been no trials on probiotics in overweight/obese pregnant women in China. More, large, well-designed adequately powered trials are needed to identify the influence of probiotics on maternal and neonatal outcomes in overweight/obese pregnant women in different countries. We suggest the following: (1) Because of the specificity of species and strains of probiotics, future studies should identify the most appropriate probiotics to prevent GDM and other adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes in overweight/obese pregnant women, and enroll more participants at high risk of GDM; (2) Study design should be improved, for example, combining dietary counseling with probiotics intervention may be beneficial in reducing the incidence of GDM; and (3) Large multicenter studies and probiotics administration from early pregnancy should be implemented to determine the optimal dosage, method, and timing of probiotics use.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:All authors conceptualized the idea of the article; Deng YF contributed to manuscript drafting, organized data, and reviewed the literature; and all authors contributed to revising the paper and approved the final publishing.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORCID number:Ya-Fang Deng 0000-0002-7512-3393; Li-Ping Wu 0000-0003-2660-3486; Yan-Ping Liu 0000-0002-1947-0315.
S-Editor:Wang JJ
L-Editor:Filipodia
P-Editor:Wang JJ
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年36期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年36期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Precautions before starting tofacitinib in persons with rheumatoid arthritis
- Hoffa's fracture in a five-year-old child diagnosed and treated with the assistance of arthroscopy: A case report
- Development of dilated cardiomyopathy with a long latent period followed by viral fulminant myocarditis: A case report
- Congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus arginine vasopressin receptor 2 gene mutation at new site: A case report
- Short-term prone positioning for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome after cardiopulmonary bypass: A case report and literature review
- Compound heterozygous p.L483P and p.S310G mutations in GBA1 cause type 1 adult Gaucher disease: A case report
