Review of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors administration to non-small-cell lung cancer patients undergoing hemodialysis
Chou-Chin Lan, Po-Chun Hsieh, Chun-Yao Huang, Mei-Chen Yang, Wen-Lin Su, Chih-Wei Wu, Yao-Kuang Wu
Abstract Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) causes significant mortality worldwide. Patients with chronic renal failure have an increased risk of developing lung cancer. NSCLC Patients with chronic renal failure undergoing hemodialysis (HD) often exhibit poor performance, and chemotherapy is generally contraindicated. Oral epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective treatment agents for NSCLC patients. However, the benefits and adverse effects of EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC undergoing HD are known. There are no clinical studies on the effects of EGFR-TKIs on NSCLC patients undergoing HD. We reviewed all previous case reports about EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC patients undergoing HD. It is difficult to design studies about the effects of EGFR-TKIs in patients undergoing HD, and this review is quite important. EGFR-TKIs are well tolerated in patients undergoing HD. The main routes of elimination of EGFRTKIs are metabolism via the liver, and renal elimination is minor. The recommended doses and pharmacokinetics of these EGFR-TKIs for patients undergoing HD are similar to those for patients with normal renal function. The plasma protein binding of EGFR-TKIs is very high, and it is not necessary to adjust the dose after HD. In conclusion, EGFR-TKIs are effective and well tolerated in patients undergoing HD.
Key Words: Hemodialysis; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors
lNTRODUCTlON
Impact of lung cancers
Lung cancer causes significant mortality worldwide[1]. Lung cancer is classified into small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with NSCLC accounting for 80%-85% of lung cancer cases and adenocarcinoma accounting for 80% of NSCLC cases[1]. Despite the development of modern medicines, the outcomes of lung cancer remain poor[1]. The treatment of NSCLC depends strictly on the disease stage, and 80% of NSCLC patients are diagnosed at advanced (IIIB/IV) stages[1]. Since the lungs are often diagnosed at advanced stages and are unresectable, targeted therapy and chemotherapy are the major treatments for these patients[1].
In general, chronic renal failure (CRF) patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) exhibit a higher incidence of cancers, including lung cancer[2]. The risk factors for developing cancers include smoking, air pollution, genetic susceptibility, and occupational exposure[1]. It is suspected that the reasons for the higher incidence of cancers in patients undergoing HD are further related to weakened immunity, chronic inflammation, malnutrition, and impaired DNA repair[2]. CRF increases the incidence of cancers as well as the difficulty in treating it. Therefore, the treatment of cancers in such patients is important.
For patients with cancer and CRF, who often exhibit poor performance, chemotherapy is generally contraindicated owing to its greater adverse effects (AEs). Moreover, chemotherapeutic drugs, such as cisplatin, are regarded as nephrotoxic agents and are not suitable for the treatment of CRF patients. Cisplatin is one of the most widely used chemotherapeutic agent for cancers. However, its clinical application is limited by its adverse effects, such as bone marrow suppression leading to hematopoietic abnormalities[3]. An increased incidence of adverse reactions to cisplatin has been reported in patients with renal insufficiency[4]. Therefore, the management of anti-cancer treatments for CRF patients undergoing HD is challenging.
Oral epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are promising treatment agents for NSCLC patients. EGFR is a transmembrane receptor on the surface of epithelial cells and is considered an important molecular target in cancer treatment. EGFR gene mutation is a predictor of EGFR-TKI efficacy. EGFR-gene-activating mutations occur in 50%-60% of Asian and 10%-20% of Caucasian subjects with NSCLC[5]. Common mutations, including deletions in exon 19 and substitution of L858R in exon 21, comprise approximately 85% of EGFR mutations[5]. Rare mutations (about 15%) include point mutations, insertions, and deletions within exons 18-25 of the EGFR gene[5].
EGFR-TKIs exert low side effects and less impact on kidney function, and patients exhibit better tolerability for them[6]. EGFR-TKIs, including gefitinib and erlotinib (first-generation), afatinib (secondgeneration), and osimertinib (third-generation), have shown significant benefits, with improved overall response rates (ORRs), longer progression-free survival (PFS), and better overall survival rate (OS) in patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations[6]. Lung cancer patients undergoing HD sometimes exhibit poor performance; EGFR-TKIs are often a treatment choice for such patients. Since physicians worry about AEs and nephrotoxicity of chemotherapy agents in patients undergoing HD, EGFR-TKIs are often an optional strategy for such patients. However, most clinical trials have excluded patients undergoing HD, and the applicability of EGFR-TKIs for such patients has not been studied. Therefore, we aimed to review the benefits, AEs, and pharmacokinetics of EGFR-TKIs in patients undergoing HD.
GEFlTlNlB
Clinical benefits of gefitinib
Gefitinib was approved for metastatic NSCLC patients with sensitive EGFR mutations in July 2015[7]. It has been demonstrated that using gefitinib as the first line of treatment for NSCLC with sensitive EGFR mutations results in an ORR of 62%-71%, PFS of 8-13 mo, and OS of 21-30 mo[7]. The common AEs are skin rash, acne, and diarrhea[7]. Most AEs resolve on their own or after medical treatment. Elevation in liver function test parameters has been observed, but these elevations are often not accompanied by any symptoms. The incidence of rare AEs, such as interstitial lung disease (ILD), is approximately 1%[7].
Clinical benefits of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD
Bersanelliet al[8] reported a 60-year-old female Caucasian non-smoker undergoing HD with right lung adenocarcinoma with mediastinal lymph nodes and bone metastasis. Her initial ECOG PS score was 0, and she received radiation therapy on the spine and was administered gemcitabine and cisplatin. Owing to progression of bone metastasis after three cycles of gemcitabine and cisplatin, second-line treatment with gefitinib was initiated. Gefitinib induced a good response of the disease to treatment for 7 years without complications. Del Conteet al[9] reported a 70-year-old male non-smoker undergoing HD with right middle lobe lung adenocarcinoma. The patient underwent right middle lobe lobectomy for pT1N0M0 NSCLC (stage IA). After 3.5 years from surgery, recurrent lung adenocarcinoma with deletion of 15 nucleotides of exon 19 was found. He received gefitinib and exhibited only a grade 1 cutaneous rash. After 2 years of gefitinib treatment, he was still in complete remission without serious AEs[9]. Bersanelliet al[8] and Del Conteet al[9] showed that gefitinib was effective and well tolerated in patients undergoing HD.
Pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients with normal renal function
Most gefitinib is metabolized by the liver and excretedviafeces (86%), and a small portion (7%) is excretedviaurine (Figure 1A)[10]. Approximately 90% of gefitinib binds to plasma proteins in the blood[10]. The half-life of gefitinib is 41 h, and steady-state plasma concentrations are attained by day 7-10[11]. The maximum concentration (Cmax) is attained 5 h (3-7 h) after oral dosing, the median Cmaxis 377 (168-781) ng/mL, the area under the curve of the plasma concentration from 0 to 24 h (AUC0-24) is 4893 (698-13991) ng· hr/mL, and the trough concentration (Ctrough) is 410 (115-1021) ng/mL[11].
Pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD
There are only two case reports on the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD. Shinagawaet al[12] performed the first pharmacokinetic analysis of gefitinib in a 58-year-old female non-smoker undergoing HD for 8 years. She developed lung adenocarcinoma (pT1N0M0, stage IA) and underwent left lower lobectomy (LLL)[12]. Two years later, she had recurrent lung cancer, which had metastasized to the left subclavian lymph node, and meningitis. The EGFR mutation showed a deletion of 15 nucleotides in exon 19 in tumor tissues. She was administered 250 mg gefitinib daily. The Cmaxand Ctroughof gefitinib were 410.4 and 102.7 ng/mL, respectively. The plasma concentrations were 308.3 and 272.2 ng/mL before and after HD (88% maintained throughout HD), respectively[12]. There were no serious AEs following gefitinib administration[12]. Luoet al[13] reported a 75-year-old female nonsmoker with lung adenocarcinoma (pT1N0M0, stage IA) who underwent right lower lobectomy. Nine years later, she underwent HD due to hypertension. However, the lung cancer relapsed with multiple nodules in both lungs. EGFR mutations in the tumor tissue revealed an L858R mutation in exon 21. She was then administered 250 mg gefitinib daily. The Cmaxwas 456 and 463 ng/mL on non-HD and HD days, respectively. The Ctroughwas 386 ng/mL. The plasma concentrations were 376 and 463 ng/mL before and after HD, respectively. The initial response to gefitinib was a decrease in tumor size, but the tumor increased in size after 8 mo of treatment. No severe AEs were reported after gefitinib administration.
The data on the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD and normal renal function (NRF) are shown in Figure 2. These data revealed that the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD were similar to subjects with NRF[12,13]. Since 90% of gefitinib is bound to plasma proteins[10], it was rational that 90% of gefitinib was retained in the blood after HD. In addition, these patients showed a good response to gefitinib and did not have elevated AEs[12,13].
ERLOTlNlB
Clinical benefits of erlotinib
Erlotinib is a reversible EGFR-TKI that was approved in 2004 for patients harboring EGFR exon 21 L858R mutations and exon 19 deletion[6]. Previous studies using erlotinib as the first line of treatment for NSCLC with sensitive EGFR gene mutations showed an ORR of 58%-83%, PFS of 9.7-13 mo, and OS of 23-33 mo[14]. Common AEs included skin rash, diarrhea, nausea, anorexia, dermatitis acneiform, fatigue, anemia, and ILD[14]. However, grade 3 or 4 AEs rarely occurred in subjects upon administration of erlotinib[6].
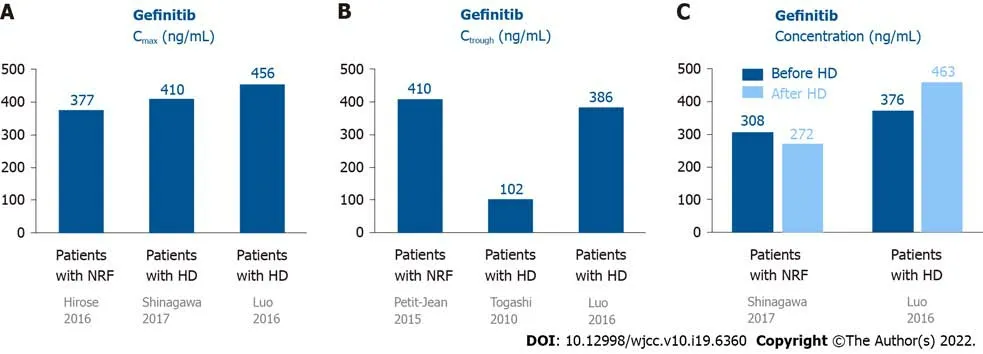
Figure 2 Pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing hemodialysis and those with normal renal function. A: The Cmax of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD was similar to subjects with NRF; B: One patient showed the Ctrough of gefitinib was 410 ng/mL. The two patients undergoing HD showed the Ctrough of gefitinib was 102-386 ng/mL; C: The plasma concentration of gefitinib were similar in patients before and after HD. Cmax: Maxium concentration; Ctrough: Trough concentration; HD: Hemodialysis; NRF: Normal renal function.
Pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients with NRF
Most erlotinib is metabolized by the liver and excretedviafeces (80%-90%), and a small portion (9%) is excretedviaurine (Figure 1B)[15]. Approximately 95% of erlotinib is bound to plasma proteins[15]. The half-life of erlotinib is 21.86 ± 28.35 h, and steady-state concentrations in plasma are attained by day 8-10[16]. The Cmaxis attained 3.69 ± 3.21 h after dosing, and the median Cmaxis 2290 ± 840 ng/mL. The median AUC0-24is 35760 ± 15720 ng· hr/mL[16].
Pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients undergoing HD
Togashiet al[17] reported three NSCLC patients undergoing HD who were treated with erlotinib. Case 1 was a 74-year-old male ex-smoker undergoing HD for 5 years, who had lung adenocarcinoma (cT1N3M1, stage IV) without any EGFR mutations. Case 2 was a 74-year-old female non-smoker undergoing HD for 3 years, who had adenocarcinoma (cT2N0M0, stage IB) without any EGFR mutations. Initially, she received irradiation therapy with a dose of 54 Gy for the tumor. The tumor enlarged, with invasion to the chest wall, and metastasized to the hilar lymph node (cT3N1M0, IIIA). Case 3 was a 69-year-old male current smoker undergoing HD for 1 year, with lung squamous cell carcinoma (cT2N1M1, stage IV). All 3 patients were administered 150 mg erlotinib daily. Pharmacokinetic analyses of erlotinib were conducted on the first day (non-HD), eighth day (non-HD), and ninth day (HD) after administration[17]. For these 3 patients undergoing HD, the Cmax, Ctrough, and AUC0-24on day 1 were 960 ± 287 ng/mL, 338 ± 116 ng/mL, and 13944 ± 4590 ng· hr/mL, respectively. On day 8 without HD, the Cmax, Ctrough, and AUC0-24were 1638 ± 206 ng/mL, 494 ± 336 ng/mL, and 23285 ± 5338 ng· hr/mL, respectively. On day 9 (HD day), the Cmaxwas 1633 ± 338 ng/mL. The plasma concentrations of erlotinib before and after HD were 1465 ± 350 and 1360 ± 375 ng/mL, respectively. The pharmacokinetic parameters on the ninth day were similar to those on the eighth day, indicating that erlotinib was hardly eliminated by HD. In addition, the data of patients undergoing HD were similar to subjects with NRF. There were no serious AEs in these cases.
The data on the pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients undergoing HD and subjects with NRF are shown in Figure 3. These data suggested that the pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients undergoing HD were similar to subjects with NRF[16,17]. Since 95% of erlotinib is bound to plasma proteins[15], it was rational that most erlotinib was retained in the plasma after HD.
AFATlNlB
Clinical benefits of afatinib
Afatinib is an irreversible covalent inhibitor of the Erb-B receptor tyrosine kinase family, including EGFR, Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, and Erb-B4 receptor tyrosine kinase 4/human epidermal growth factor receptor 4[18]. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2013 for NSCLC with exon 21 L858R substitutions and exon 19 deletions[18]. Recent studies suggested that afatinib is effective against other uncommon mutations, such as L861Q in exon 21 and G719X in exon 18, and it was therefore approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018 for these uncommon EGFR mutations[18]. Previous studies using afatinib as the first line of treatment for NSCLC with sensitive EGFR gene mutations showed an ORR of 70%-81.8%, PFS of 13.4-15.2 mo, and OS of 27.9-49 mo[18]. The commonly reported AEs were diarrhea, skin rash, paronychia, mucosal inflammation, dry skin, stomatitis, skin fissures, nausea, dermatitis acneiform, and conjunctivitis[18]. Most AEs were of grade 1-2, and serious AEs were uncommon. However, serious AEs are more frequently reported for afatinib than for gefitinib and erlotinib[18].
Pharmacokinetics of afatinib in patients with NRF
Most afatinib is excreted through feces (85%), and a small amount (15%) is excretedviaurine (Figure 1C)[19]. Approximately 95% of afatinib is bound to plasma proteins[20]. The half-life periods for 30 and 40 mg afatinib are 21.3 and 26.9 h, respectively[19]. Steady-state plasma concentrations are attained in approximately 8 d[19]. The Cmaxis attained approximately 2-5 h after administration[20]. For daily administration of 30 mg afatinib, the median Cmax, Ctrough, and AUC0-24are 16.3 ng/mL, 15.1 ng/mL (8.1-38.1 ng/mL), and 189 ng· hr/mL, respectively[21,22]. For daily administration of 40 mg afatinib, the median Cmax, Ctrough, and AUC0-24are 25.2 ng/mL, 18.2-34.1 ng/mL, and 324 ng· hr/mL, respectively[21,22].
Clinical benefits of afatinib in patients undergoing HD
Yamaguchiet al[23] reported a 59-year-old male ex-smoker undergoing HD for 17 years and diagnosed with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma (cT4N3M1b) with multiple pulmonary, hepatic, and bony metastases. Analysis of EGFR mutations revealed a G719A point mutation in exon 18. The patient received oral afatinib (30 mg) daily. The treatment was well tolerated, with only mild skin rash and no diarrhea. The tumors shrank after 2 mo of treatment. Bersanelliet al[8] reported afatinib as a third-line treatment for an NSCLC patient undergoing HD. Initially, the patient received cisplatin and gemcitabine (first-line) and gefitinib (second-line). After tumor progression, the patient was started on 30 mg afatinib daily. The treatment was well tolerated, with only mild asthenia. After 2 mo, the afatinib dosage was increased to 40 mg daily, which caused significant asthenia, vomiting, and nausea[8].

Figure 3 Pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients undergoing hemodialysis and those with normal renal function. A: The Cmax of erlotinib was 2290 ± 840 ng/mL in patients with NRF. For the patients undergoing HD, the Cmax was 1638 ± 206 ng/mL on day 8 and 1638 ± 206 ng/mL on day 9 (after steady state). The Cmax was similar in patients with NRF and undergoing HD; B: The plasma concentrations of erlotinib were similar before and after HD; C: The AUC0-24 was 35760 ± 15720 ng· hr/mL in patients with NRF. For the patients undergoing HD, the AUC0-24 was 23285 ± 5338 ng· hr/mL on day 8 and 25895 ± 7747 ng· hr/mL on day 9. The AUC0-24 was similar in patients with NRF and undergoing HD. AUC0-24: Area under the curve of the plasma concentration from 0 to 24 h; Cmax: Maxium concentration; Ctrough: Trough concentration; HD: Hemodialysis; NRF: Normal renal function.
The United States prescribing information recommends that the dose of afatinib be decreased to 30 mg daily for subjects with renal impairment. However, this recommendation cannot be made for patients with severe renal impairment or those undergoing HD, as afatinib has not been studied in these populations[20]. Based on these two case reports, we suggest that 30 mg afatinib is safe and effective in patients undergoing HD[8,23].
Pharmacokinetics of afatinib in patients undergoing HD
Yamaguchiet alperformed the first pharmacokinetic analysis of daily administration of 30 mg afatinib to patients undergoing HD[23]. The Ctroughvalues were 10.2 (day 2), 15.7 (day 3), 22.8 (day 10), 27.3 (day 11), and 23.8 ng/mL (day 12). Steady-state concentrations were attained by day 12. Yamaguchiet al[23] suggested that daily administration of 30 mg afatinib was safe for patients undergoing HD. Imaiet al[24] also performed pharmacokinetic analysis of daily administration of 30 mg afatinib as first-line afatinib therapy for three lung cancer patients undergoing HD. Case 1 was a 78-year-old male with stage IV adenocarcinoma (cT1bN0M1b) with an EGFR mutation (exon 19 deletion). Case 2 was a 75-year-old male ex-smoker with lung adenocarcinoma (pT1aN0M0) with an EGFR mutation (exon 19 deletion) undergoing HD. However, postoperative mediastinal lymph nodes recurred. Case 3 was a 62-year-old male non-smoker with adenocarcinoma (pT2aN1M0) with an EGFR mutation (exon 21 L858R). Multiple pulmonary metastases with malignant pleural effusion occurred after the surgery. The pharmacokinetic analyses of the 3 cases revealed that the Cmaxwas 13.4 ± 6.2 and 51.7 ± 23.8 ng/mL on days 1 and 10, respectively, and the Ctroughwas 4.5 ± 2.3 and 28.3 ± 9.0 ng/mL on days 2 and 11, respectively. The principal AEs were skin rash, dry skin, diarrhea, and malaise, and no severe AEs were reported except 1 case of grade 3 diarrhea. All the patients were maintained at partial response until the article was published (135-456 d).
The data on the pharmacokinetics of afatinib in patients undergoing HD and subjects with NRF are shown in Figure 4. Since approximately 95% of afatinib is bound to plasma proteins[25], afatinib is poorly eliminated during HD. The pharmacokinetics of afatinib in the aforementioned patients undergoing HD were comparable with subjects with NRF[25].
OSlMERTlNlB
Clinical benefits of osimertinib
Osimertinib selectively and potently inhibits sensitive EGFR gene mutations[26]. Osimertinib also has a good response in NSCLC with acquired EGFR T790M resistance after treatment with first-or secondgeneration EGFR-TKIs.
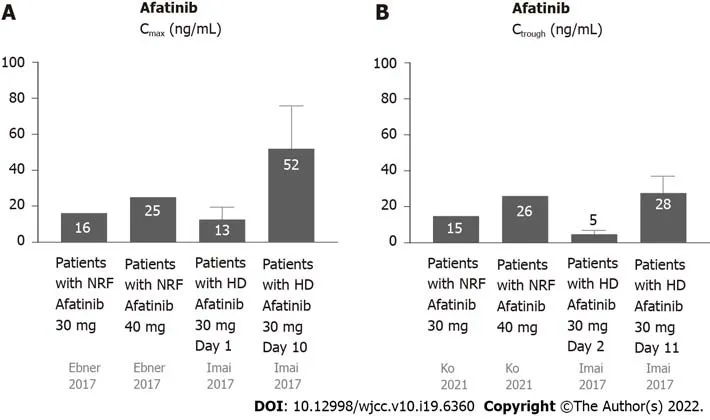
Figure 4 Pharmacokinetics of afatinib in patients undergoing hemodialysis and those with normal renal function. A: The Cmax of afatinib 30 mg daily in patients with NRF was 16.3 ng/mL, while the Cmax of afatinib 40 mg daily in patients with was NRF 25.2 ng/mL. The Cmax of afatinib 30 mg daily in patients with HD was 13.4 ± 6.2 ng/mL on day 1 and 51.7 ± 23.8 ng/mL on day 10; B: The Ctrough of afatinib 30 mg daily in patients with NRF was 15.1 ng/mL, while the Ctrough of afatinib 40 mg daily in patients with NRF was 26 ng/mL. The Ctrough of afatinib 30 mg daily in patients with HD was 4.5 ± 2.3 ng/mL on day 1 and 28.3 ± 9.0 ng/mL on day 11. Cmax: Maxium concentration; Ctrough: Trough concentration; HD: Hemodialysis; NRF: Normal renal function.
Therefore, it is an effective first-line treatment for NSCLC patients with activating EGFR mutations, and an effective second-line treatment for NSCLC patients with T790 M resistance mutations[26]. Previous studies using osimertinib as the first line of treatment for NSCLC with sensitive EGFR gene mutations showed an ORR of approximately 80%, PFS of 18.9 mo, and OS of 38.6 mo[26]. After administration of osimertinib as the second-line treatment for NSCLC patients with T790 M resistance mutations, the ORR was approximately 71%, PFS was approximately 10.1 mo, and OS was 26.8 mo[27]. The common AEs of osimertinib were skin rash and diarrhea, and the others were paronychia, dry skin, stomatitis, nausea, anorexia, headache, constipation, anemia, pruritus, fatigue, and cough[27]. Osimertinib has fewer serious AEs than the first- and second-generation TKIs[27].
Clinical benefits of osimertinib in patients undergoing HD
Iwafuchiet al[28] reported a 64-year-old female non-smoker undergoing HD with left lung adenocarcinoma (cT3N1M1a, stage IV, with malignant pleural effusion) with EGFR deletion in exon 19. She received gefitinib (first-line), erlotinib (second-line), taxotere (third-line), afatinib (fourth-line), and another six cycles of taxotere (fifth-line). After 5 years of treatment, the tumor was enlarged with liver and splenic metastases. For T790 M mutation, daily oral administration of 80 mg osimertinib was prescribed. The tumor improved to partial remission, and the liver and splenic metastases disappeared. The patient experienced no serious AEs and showed a good response. This case presented good effects and tolerability in patients undergoing HD even with sixth-line therapy.
Pharmacokinetics of osimertinib in patients with NRF
Most osimertinib is metabolized by the liver and excretedviafeces (68%), and a small portion (14%) is excretedviaurine (Figure 1D)[29]. The plasma protein binding ability of osimertinib is very high (98%)[30]. The half-life is 48.3 h, and steady state plasma concentrations are attained in approximately 10 d[30]. The time to attain Cmaxis 6 h (3-24 h) after dosing; the Cmaxand Ctroughare 371 and 230 ng/mL, respectively[31].
Pharmacokinetics of osimertinib in patients undergoing HD
Tamuraet al[32] reported the first pharmacokinetic analysis of osimertinib in patients undergoing HD. They reported a 72-year-old male ex-smoker with lung adenocarcinoma (T2aN3M1b, stage IV, with pleural and bone metastasis) with EGFR exon 19 deletion. He was initially receiving 250 mg gefitinib daily, but the treatment was discontinued, owing to liver toxicity, in 2 mo. After his recovery, he received 150 mg erlotinib daily and showed a good response. However, due to skin toxicity, the erlotinib dosage was gradually reduced to 50 mg daily. During the treatment, HD was initiated owing to worsening diabetic nephropathy. Four years after erlotinib treatment, the primary tumor was enlarged and had metastasized to the supraclavicular lymph nodes. The tumor tissue presented a T790M mutation in exon 20. He was initially administered 40 mg osimertinib daily for the previous liver and skin AEs of gefitinib and erlotinib. As treatment was well tolerated, pharmacokinetic analysis of osimertinib was performed 4 mo after administration[32]. Pharmacokinetic analysis of osimertinib (40 mg daily) was performed on HD and non-HD days. The Cmaxwas 218 and 217 ng/mL on HD and non-HD days, respectively. The osimertinib dosage was increased to 80 mg daily for only mild AEs. Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed after 6 d and revealed that the Cmaxwas 388 and 473 ng/mL on HD and non-HD days, respectively. The patient received 80 mg osimertinib daily, without any AEs[32]. Matsunashiet al[29] reported a 66-year-old male undergoing HD with relapsed stage IV NSCLC with an EGFR mutation in exon 21 (L858R) 2 years after body radiotherapy. He received 80 mg osimertinib daily as first-line treatment. The Cmaxwas 400-476 and 335-351 ng/mL before and after HD, respectively. When osimertinib was administered on HD days, the Cmaxwas 430 ng/mL[29].The AUC0-24before HD, after HD and on non-HD day were 7022-8842, 6376-7039 and 8631 ng· hr/mL.

Figure 5 Pharmacokinetics of osimertinib in patients undergoing hemodialysis and those with normal renal function. A: Plasma concentrations of osimertinib were similar among pre-HD, post-HD, and non-HD days; B: The AUC0-24 of osimertinib were similar among pre-HD, post-HD, and non-HD days. AUC0-24: Area under the curve of the plasma concentration from 0 to 24 h; HD: Hemodialysis; NRF: Normal renal function.
The data on the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in patients undergoing HD and subjects with NRF are shown in Figure 5. Since the protein binding ability of osimertinib is very high, its dialyzability rate is relatively low and it is minimally affected by HD[30]. The pharmacokinetic parameters on non-HD days were almost the same as those on HD days.
Limitations of this review
This review has several limitations. Firstly, the literature cited in this review on EGFR-TKIs in patients undergoing HD are all case reports. There have been no cohorts or randomized controlled trials with EGFR-TKIs in patients undergoing HD. However, it is difficult to conduct research on HD patients owing to their rarity. Therefore, this review is very important for providing recommendations for EGFR-TKIs in such patients. Secondly, this review focuses on EGFR-TKIs in lung cancer patients undergoing HD. It is unknown whether the conclusions drawn are applicable to other cancers.
CONCLUSlON
There have been no clinical studies on EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC patients undergoing HD. We suggest that EGFR-TKIs are suitable for such patients. The recommended doses and pharmacokinetics of these EGFR-TKIs for patients undergoing HD are similar to those for patients with NRF. EGFR-TKI treatment is effective and well tolerated in patients undergoing HD.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Lan CC, Hsieh PC, Huang CY, and Yang MC contributed to data curation; Lan CC and Hsieh PC contributed to formal analysis; Lan CC, Huang CY, Yang MC, Su WL, Wu CW, and Wu YK contributed to investigation; Lan CC and Wu YK contributed to conceptualization; Lan CC, Su WL, and Wu CW contributed to methodology; Lan CC, Hsieh PC, Huang CY, Yang MC, and Wu YK contributed to project administration; Lan CC and Wu YK contributed to funding acquisition; Lan CC, Wu YK, and Hsieh PC contributed to writing; Huang CY, Yang MC, and Wu YK contributed to validation; Lan CC and Hsieh PC contributed to the original draft; Lan CC contributed to review and editing; Wu YK contributed to supervision, visualization, review, and editing.
Supported bythe Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, No. TCRD-TPE-108-RT-4(3/3; and No. TCRD-TPE-109-59.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All authors declare no conflicts-of-interest related to this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Taiwan
ORClD number:Chou-Chin Lan 0000-0001-9376-6539; Po-Chun Hsieh 0000-0002-0416-8797; Chun-Yao Huang 0000-0001-7919-9734; Mei-Chen Yang 0000-0002-6503-5189; Wen-Lin Su 0000-0002-9065-2058; Chih-Wei Wu 0000-0001-5242-6343; Yao-Kuang Wu 0000-0001-7898-6963.
S-Editor:Liu JH
L-Editor:Filipodia
P-Editor:Liu JH
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年19期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年19期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Hem-o-lok clip migration to the common bile duct after laparoscopic common bile duct exploration: A case report
- Preliminary evidence in treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children: A case series
- Identification of risk factors for surgical site infection after type II and type III tibial pilon fracture surgery
- Sustained dialysis with misplaced peritoneal dialysis catheter outside peritoneum: A case report
- Delayed-onset endophthalmitis associated with Achromobacter species developed in acute form several months after cataract surgery: Three case reports
- Diagnostic accuracy of ≥ 16-slice spiral computed tomography for local staging of colon cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
