Myeloid checkpoints for cancer immunotherapy
Yixin Qian ,Ting Yang ,Huan Liang ,Mi Deng1,,3
1Peking University International Cancer Institute,Health Science Center,Peking University,Beijing 100191,China;2 School of Basic Medical Sciences,Health Science Center,Peking University,Beijing 100191,China;3Peking University Cancer Hospital&Institute,Peking University,Beijing 100142,China
AbstractMyeloid checkpoints are receptors on the myeloid cell surface which can mediate inhibitory signals to modulate anti-tumor immune activities.They can either inhibit cellular phagocytosis or suppress T cells and are thus involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases.In the tumor microenvironment,besides killing tumor cells by phagocytosis or activating anti-tumor immunity by tumor antigen presentation,myeloid cells could execute protumor efficacies through myeloid checkpoints by interacting with counter-receptors on other immune cells or cancer cells.In summary,myeloid checkpoints may be promising therapeutic targets for cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Cancer;immune checkpoint;myeloid checkpoint;MDSC;TAM;immunotherapy
Introduction
Anti-tumor immunotherapies,conventionally referred to as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs),target T-cell immune checkpoints and have elicited impressive therapeutic responses in the treatment of human cancers (1).Despite achieving the long-term survival of 10%-30% of treated individuals,immunotherapies are not effective for most patients suffering from cancer (2).A primary challenge of this strategy for extensive anticancer application remains the cell complexity of the tumor immune microenvironment.In addition to many endeavors to seek intrinsic factors to enhance the efficacy of immune therapy in both tumor and T cells (3-5),many studies have revealed that the therapeutic efficacy could be improved by targeting immune regulatory cells,including myeloid cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) (6,7).
Myeloid cells are the most abundant hematopoietic cells in the human body and have diverse functions.All myeloid cells arise from multipotent hematopoietic stem cells(HSCs) that develop into mature myeloid cells through sequential steps of differentiation (Figure 1) (6).Various tumors show abundant infiltration of myeloid cells.More specifically,tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are constitutive of several myeloid lineages,including mast cells,plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) (8),conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) (9),monocytes (10),macrophages(11),and granulocytes (12).A pan-cancer single-cell transcriptional atlas of TIMs across 15 human cancer types showed that monocytes and macrophages accounted for the largest proportion of TIMs,with an average of above 50%in most tumors,and the proportion of cDCs was relatively stable (approximately 10%-20%) across tumor types,while the proportion of mast cells showed great variation across different types of tumors (13).
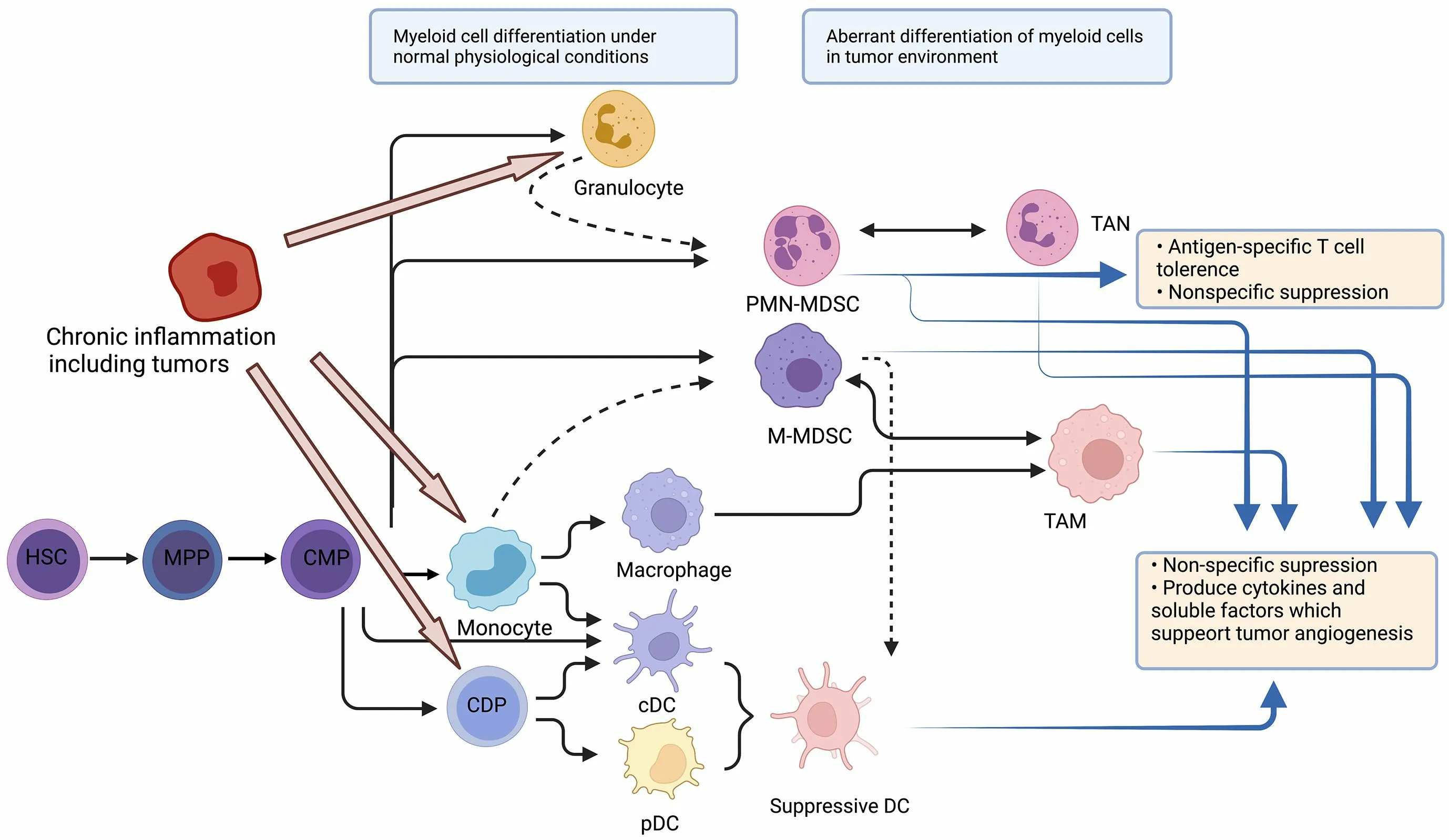
Figure 1 Stages of myelopoiesis differentiation.Myeloid cells originate from HSCs and MPPs.Myelopoiesis is amplified during chronic inflammation to assist tumor progression and dissemination.HSCs differentiate into CMP,which can further differentiate through hematopoietic system.In physiological conditions,CMP can differentiate into neutrophils or monocytes,and subsequently into DCs or macrophages.However,with chronic inflammation,pro-inflammatory cytokines can skew monocytopoiesis of CMP into M-MDSC and TAM,and granulopoiesis into PMN-MDSC and TAN.HSC,hematopoietic stem cell;MPP,multipotent progenitor cell;CMP,common myeloid progenitor;DC,dendritic cell;M-MDSC,monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell;TAM,tumor-associated macrophage;PMN-MDSC,polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cell;TAN,tumor-associated neutrophil;CDP,common DC progenitor;cDC,conventional DC;pDC,plasmacytoid DC.
Single-cell RNA-seq also indicated that in the TME,myeloid cells experience continuous reprogramming (14).Following TME-specific cues,monocytes can differentiate into inflammatory macrophages (M1-like type) and monocyte-derived DCs,whose functions are anti-tumor,or alternatively activated macrophages (M2-like type) with immunosuppressive capacity.The differentiation from monocytes to M2 macrophages may be the predominant path in the process of myeloid reprogramming (15).
These cells have a profound impact on anti-tumor effect and could influence neoangiogenesis,and sustain cancer cell proliferation,metastasis and immunotherapy resistance(16).On the one hand,myeloid cells can directly kill tumor cells by phagocytosis (17) or activate anti-tumor immunity by tumor antigen presentation (6).On the other hand,a group of myeloid cells,including tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs),tumor-associated neutrophils(TANs),myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and inhibitory DCs,support tumor development and metastasis by suppressing infiltrating cytotoxic lymphocytes (18).The activities and functions of these myeloid cells are regulated by stimulatory or inhibitory signals mediated by receptors on the cell surface,and inhibitory signals are considered myeloid checkpoints,which may contain an immunereceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)/immunereceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) to transduce immune modulatory signals in myeloid cells or interact with counter-receptors on other immune cells to modulate their activities or on cancer cells to execute pro-tumor efficacies.A new type of immunotherapeutic strategy targeting myeloid cells has also emerged (19).
In this review,we will discuss the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of myeloid checkpoints below.
Checkpoints expressed by myeloid cells
We briefly introduce CD47,signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family,programmed cell death 1 (PD-1),sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin(Siglec) family,leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B(LILRB) family,triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2),neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and common lymphatic endothelial and vascular endothelial receptor-1(Clever-1) in this chapter (Figure 2).
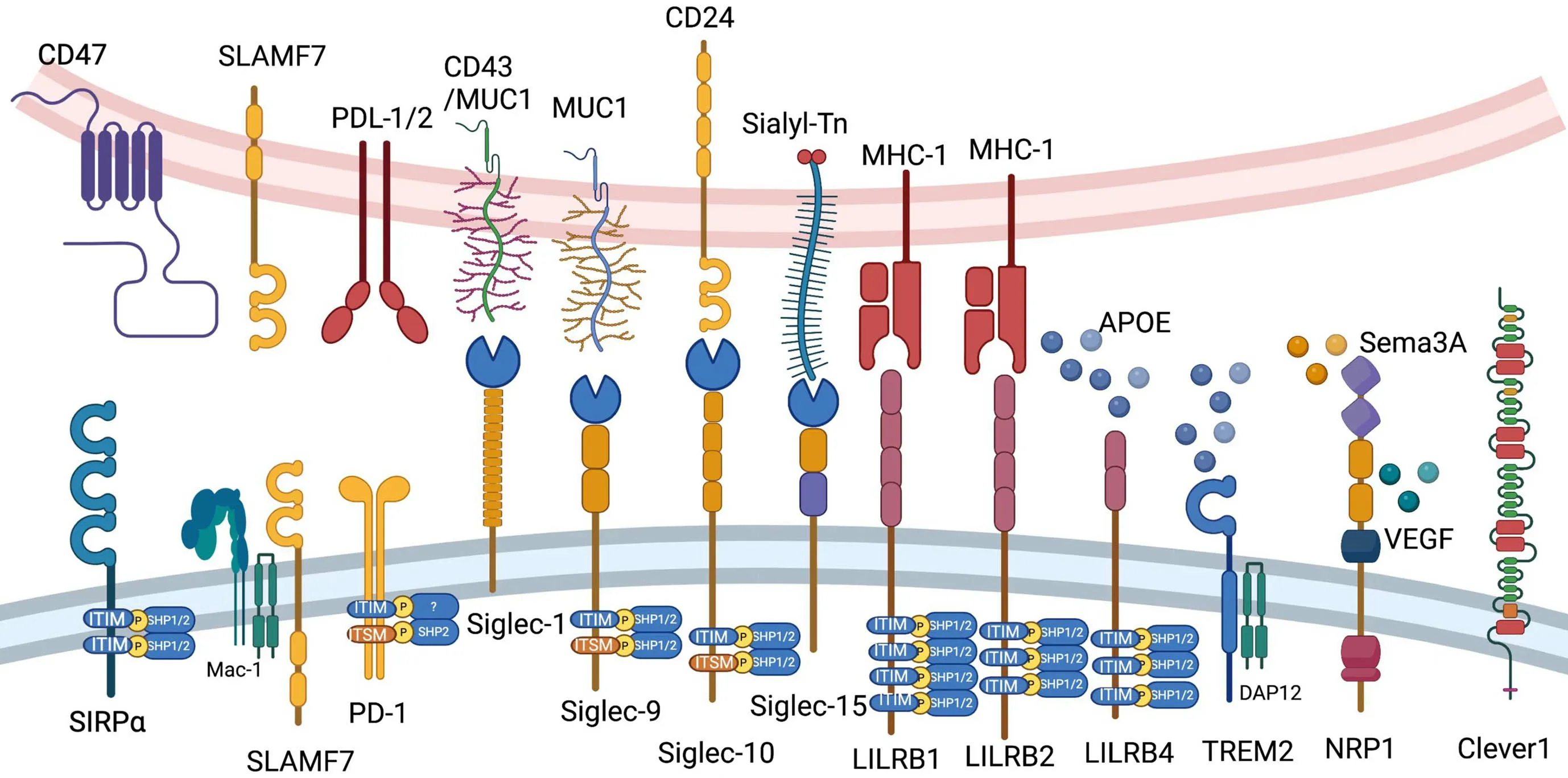
Figure 2 Current myeloid checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.Ligands and elementary structures of CD47,SLAMF7,PD-1,LILRB1,LILRB2,LILRB4,Siglec-1,Siglec-9,Siglec-10,Siglec-15,TREM2,NRP1 and Clever1 are shown in this figure.PD-1,programmed cell death 1;LILRB,leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B;Siglec,sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin;TREM2,triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2;NRP1,neuropilin-1;Clever1,common lymphatic endothelial and vascular endothelial receptor-1.
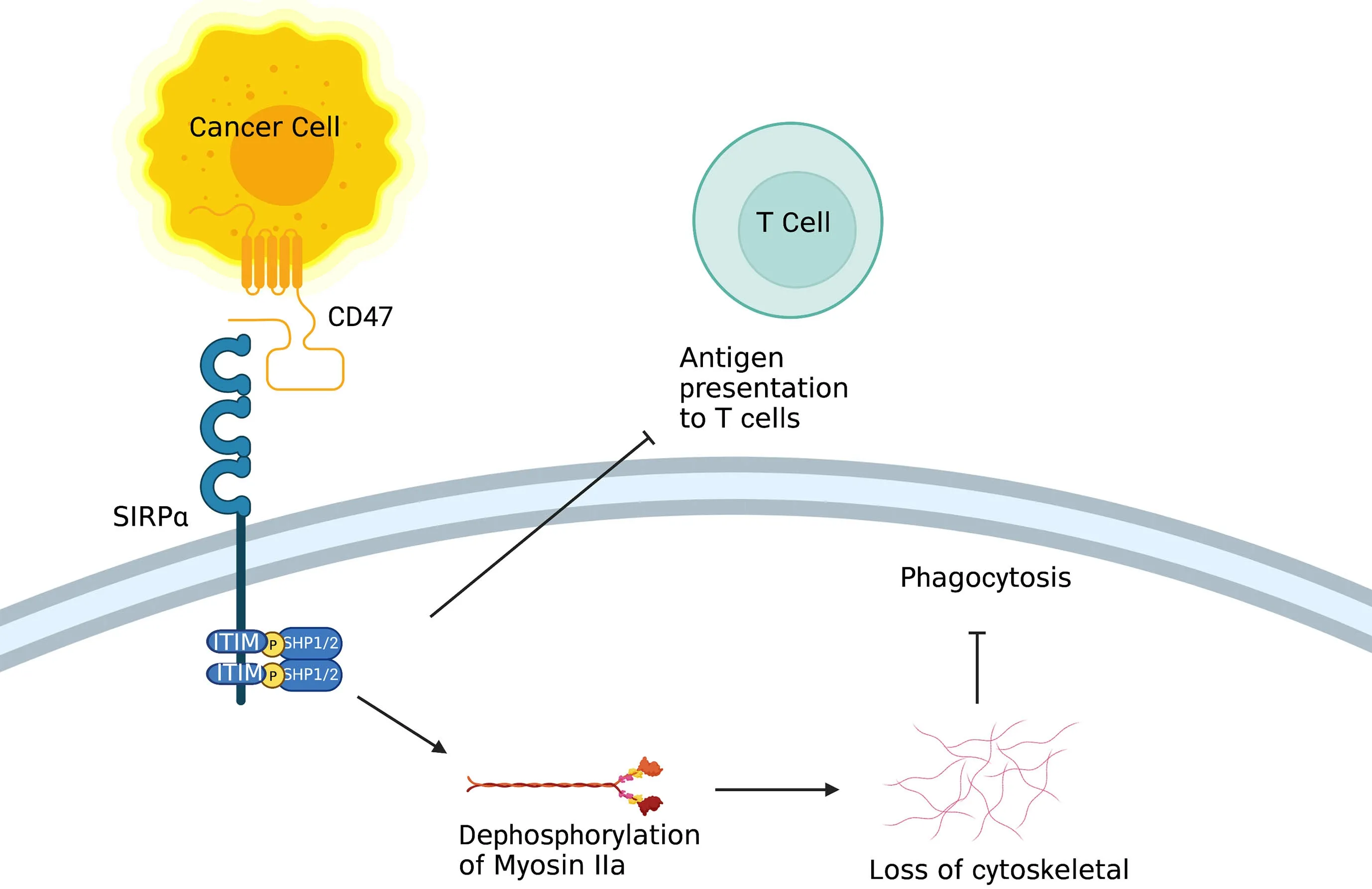
Figure 3 Role of CD47/SIRPα.On the one hand,after binding to CD47,ITIM in the cytoplasmic tail of SIRPα on macrophage activates inhibitory tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2,resulting in inhibition of the actin cytoskeleton rearrangement required for phagocytosis.On the other hand,SIRPα on DC inhibits the antigen presentation of tumor cells.ITIM,tyrosine-based inhibitory motif;DC,dendritic cell.
CD47/SIRPα
CD47 (also known as inhibitor of apoptosis protein,IAP) is a red blood cell signal that serves to discriminate self and non-self (20).Upon engagement of CD47 by signal regulatory protein alpha [SIRPα;also known as SH2-domain bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)substrate-1 (SHPS-1) or CD172a] on macrophages and DCs,the ITIM in the cytoplasmic tail of SIRPα activates the inhibitory tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2,resulting in inhibition of the actin cytoskeleton rearrangement required for phagocytosis (Figure 3).CD47 is upregulated on the surface of several cancer cell types,enabling these cells to evade phagocytic removal by immune cells (21).In accord with this,high CD47 expression is negatively correlated with disease prognosis and survival in acute myeloid leukemia (AML),non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (21-24).Furthermore,therapeutic reagents that antagonize the CD47-SIRPα axis in macrophages inhibit the growth of several types of tumors,including AML and non-Hodgkin lymphoma,by enhancing cellular phagocytosis (25-28).Furthermore,CD47 blockade has been shown to robustly increase immune responses against tumor antigens by activating DCs but not macrophage cross-presentation of tumor antigens (29).In recent years,combined therapies of a CD47-SIRPα axis inhibitor and other anticancer therapeutics [e.g.,PD-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) blockade] have been investigated in the context of potentiating anti-tumor immunityin vitro(25,30).
SLAM family
The SLAM family of receptors is expressed on the majority of immune cells.These receptors often serve as self-ligands and play important roles in cellular communication and adhesion,thus modulating immune responses (Figure 4)(31,32).SLAM family receptors (SFRs) play a key role in inhibiting macrophage phagocytosis. SFR deficiency triggers macrophage phagocytosis of hematopoietic cells,resulting in severe rejection of donor hematopoietic grafts in recipient mice (33).
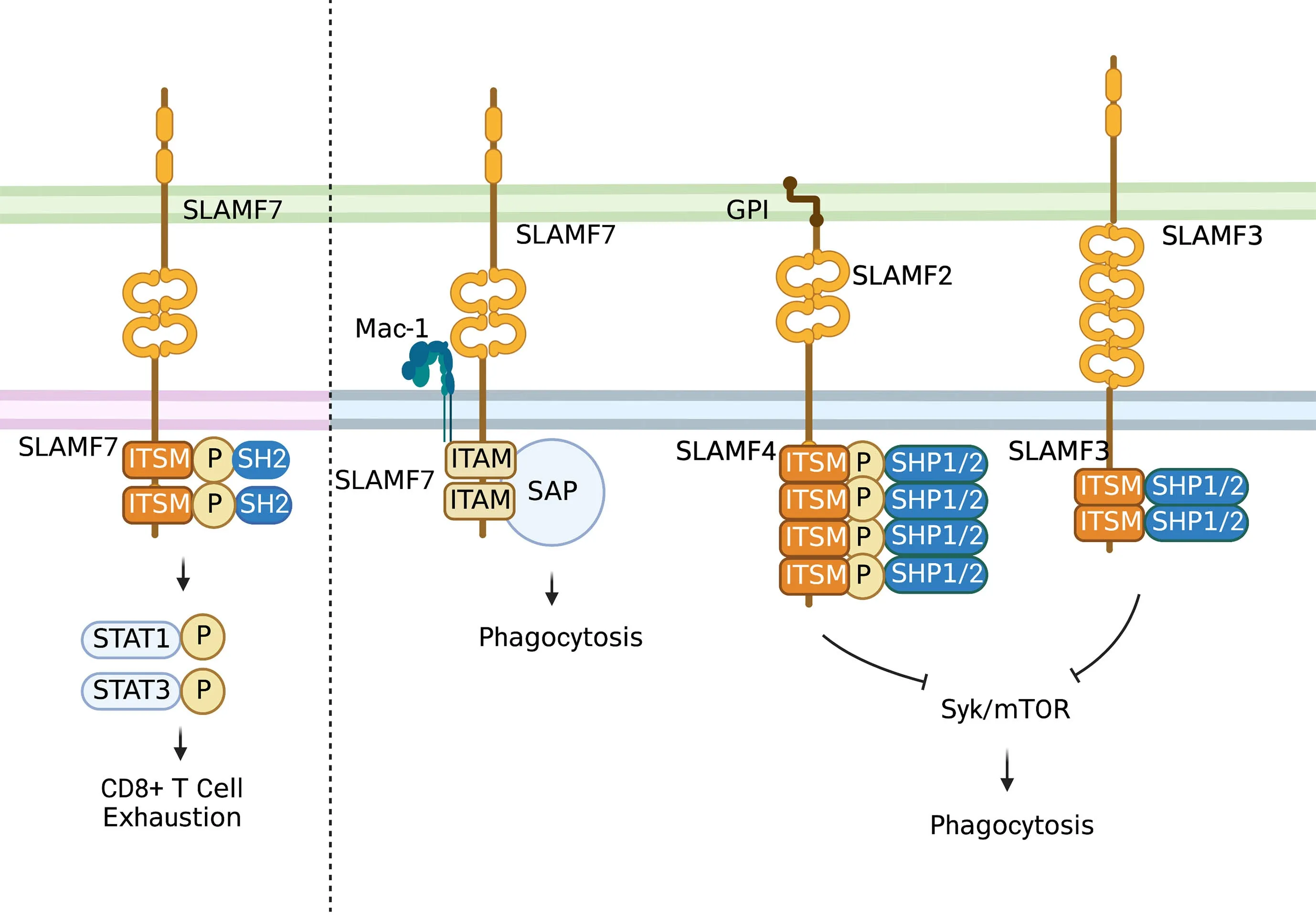
Figure 4 Role of SLAM family.In T cells,the activation of self-ligand SLAMF7 immune receptor could induce phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 and expression of various inhibitory receptors and transcription factors associated with T cell exhaustion.In macrophages,SLAMF7 could mediate phagocytosis interacting with integrin Mac-1 and do with signals involving immune-receptor tyrosine-based activation motifs.While most SLAM-mediated phagocytosis functions depend on SAP adaptors.SLAMF3 and SLAMF4 are identified as“don’t eat me” receptors on macrophages which inhibit “eat-me” signals such as LRP1-mediated activation of mTOR and Syk through SH2 domain-containing phosphatases.STAT,signal transduction and activator of transcription;SAP,signaling lymphocyte activation moleculeassociated protein;GPI,glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol.
SLAMF7
The SLAMF7 [also acknowledged as CD2-like receptoractivating cytotoxic cell (CRACC),CS1 and CD319]receptor belongs to the SLAM family of receptors (34),presenting at diverse periodicities on different types of immune cells,such as macrophages,and restrictively expressed on hematopoietic cells (32,34,35).Except for SLAMF4 (2B4),SLAM family members function as homotypic receptors,which recruit different SH2 domaincontaining proteins to their cytoplasmic immune-receptor tyrosine-based switch motifs when activated (34) so that SLAMF7 can regulate immune cell-specific functions across diverse types of immune cells (34-36).SLAM family receptors are correlated with T-cell exhaustion.SLAMF6 is a marker of the progenitor of exhausted CD8+T cells (37),and both SLAMF6 and SLAMF4 (2B4) are reported as inhibitory receptors of CD8+T cells (34).As reported,SLAMF7 is also expressed on a CD8+T-cell subset enriched in melanoma patients who are not responsive to checkpoint blockade immune therapy (38).Moreover,SLAMF7 is expressed on certain kinds of memoryprecursor and effector CD8+T cells,which respond to checkpoint blockade in an indirect way (39).A recent study showed that activation of the self-ligand SLAMF7 immune receptor on T cells could induce phosphorylation of signal transduction and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) and STAT3,and expression of various inhibitory receptors and transcription factors associated with T-cell exhaustion(31,40).High SLAMF7 expression is reported to indicate poor survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC)(31).Moreover,SLAMF7highCD38highTAMs show strong relations with exhausted T cells and are an independent prognostic factor of ccRCC (31).Apart from the role of SLAMF7 in modulating T-cell function in the TME,SLAMF7 could mediate phagocytosis by interacting with integrin Mac-1 (41) and with signals involving immunereceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (42). Most SLAM-mediated phagocytosis functions depend on signaling lymphocyte activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) adaptors (34,43).What’s more,it has been shown that patients whose tumors express SLAMF7 are more likely to respond to SIRPα-CD47 blockade therapy (33).
SLAMF3 & SLAMF4
Specifically,SLAMF3 (Ly-9,CD229) and SLAMF4 (2B4,CD244) were identified as “do not eat me” receptors on macrophages (44). These receptors inhibit “eat-me”signals,such as LRP1-mediated activation of mTOR and Syk,through SH2 domain-containing phosphatases.SFRs bind to but are independent of CD47 to alleviate macrophage phagocytosis,and combined deletion of SFRs and CD47 results in reduced hematopoietic cells in mice.This SFR-mediated tolerance is compromised in patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis,a syndrome characterized by inappropriate phagocytosis of hematopoietic cells.Thus,SFR-mediated inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis is critical for hematopoietic homeostasis,and SFR may represent a previously unknown tumor immunotherapy target (44).
PD-1/PD-L1
PD-1 (also known as CD279) is one of the bestcharacterized immune checkpoint targets for cancer immunotherapy,and PD-1 blockade has proven to be the most successful immunotherapy strategy to date (45).It has been reported that increased galectin-9+M-MDSCs in the peripheral blood of NSCLC patients are involved in resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy (46).Therefore,the presence of MDSCs in the TME is detrimental for the anti-PD-1/PD-L1 response.As expected,several studies revealed the relationship between MDSC infiltration and PD-1 blockade resistance,and selective depletion of MDSCs could restore anti-PD-1 efficacy (47,48).
In addition,it has been found that PD-1 is expressed in TAMs but not in circulating monocytes or splenic macrophages and that it can negatively regulate cancer cell phagocytosis (30).In addition,as reported,blockade of PD-1 or PD-L1 enhanced the phagocytic activity of TAMs towards tumor cellsin vivoand inhibited tumor growth in a macrophage-dependent fashion,suggesting that the PD-1/PD-L1 axis is an immune checkpoint for regulating both innate and adaptive immunity.They further found that PD-1 blockade also changed the nature of TAMs from immunosuppressive M2-like cells to pro-inflammatory M1-like cells.The presence of TAMs in pancreatic cancer exaggerates immunosuppression within the microenvironment and leads to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade resistance.Inhibition of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) on TAMs can upregulate the expression of PD-L1 and increase CD8+T-cell infiltration,which ablates anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistance (49).PD-1-expressing macrophages exhibit an anti-inflammatory-like surface profile in tumor settings.PD-1 expression is negatively correlated with the phagocytic ability of macrophages,and blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 enhances antitumor responses and prolongs survival by inhibiting pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization (50,51).PDL1 antibody treatment promoted the proliferation of cultured bone marrow-derived macrophages,which was related to the activation of the AKT-mTOR pathway(Figure 5) (52).The transcriptomic profiles of macrophages were switched to inflammatory phenotypes following PDL1 antibody treatment (53).The interaction between the immune checkpoint molecules PD-1 and PD-L1 may also be responsible for TAN-mediated immune suppression.In human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and HCCbearing mice,PD-L1 and PD-1 were expressed in peritumoral neutrophils and T lymphocytes,respectively,and PD-L1+neutrophils from patients with HCC effectively suppressed the proliferation and activation of T cells by utilizing PD-1/PD-L1 interactions (54).
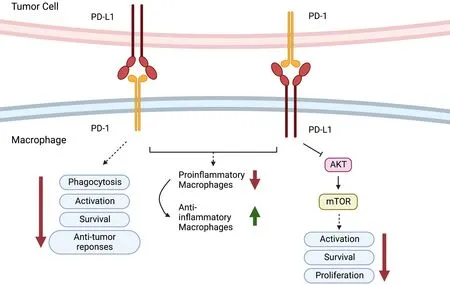
Figure 5 Role of PD-1/PD-L1.PD-1-expressing macrophages exhibit an anti-inflammatory-like surface profile in tumor settings.PD-1 expression is negatively correlated to phagocytic ability of macrophages.PD-L1 antibody treatment promotes cell proliferation of cultured bone marrow-derived macrophages,which is related to the activation of the AKT-mTOR pathway.PD-1,programmed cell death 1;PDL1,programmed cell death ligand 1.
In addition to PD-L1,B7 superfamily member 1 (B7S1)(also known as B7-H4,B7x,or VTCN1) is expressed by tumor-infiltrating antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and triggers dysfunction and exhaustion of activated CD8+TILs by Eomes upregulation (55).Murine experiments indicated that B7S1 inhibition suppresses the development of liver cancer and enhances antitumor CTLs and that the combination of B7S1 and PD-1 blockade could inhibit tumor growth in a synergistic way (55).
In summary,together with PD-1,B7S1 could be an intriguing target to reverse T-cell exhaustion and maximize immunotherapeutic efficacy in cancer.
Siglec family
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins (Siglecs)contain a family of cell surface proteins playing an essential role in regulating immune homeostasis (Figure 6).The dysregulation of Siglecs is reported to be correlated with various diseases,including autoimmunity diseases,infections and cancer (56). Siglecs are type I transmembrane proteins with one V-set immunoglobulin(Ig) domain,including a sialic acid-binding site,and one or more C2-set Ig domains in the extracellular region.Most Siglecs,such as CD22 (Siglec-2) and most CD33 (Siglec-3)-related Siglecs,have ITIMs and/or ITIM-like motifs in the intracellular domain and convey signaling mediated by inhibitory receptors (57).Each Siglec prefers a different kind of sialic acid expressed on all mammalian cells to distinguish self and non-self (58).Mammalian cells have a relatively high density of sialoglycans on their surface in comparison to most pathogens.This high density of sialoglycans,which can be considered self-associated molecular patterns (SAMPs),can lead to the inhibition of immune responses against the self (59).Siglec is mainly expressed on hematopoietic cells,almost on myeloid cells and B cells or other types of cells,such as neurons (56,58).
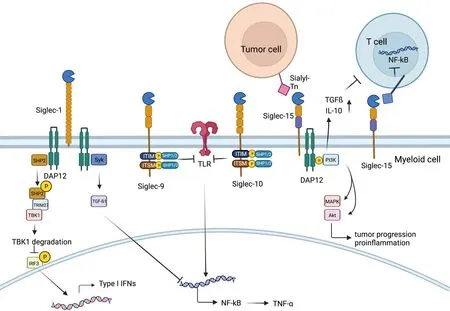
Figure 6 Role of Siglec family.On the one hand,Siglec-1 could associate with DAP12 to recruit and activate SHP2,which then could recruit E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM27,inducing TBK1 degradation.Therefore,type I IFN production is inhibited and innate immune response could be suppressed.On the other hand,Syk activation occurs when Siglec-1 binds to DAP12,leading to increased production of TGF-β1,which could inhibit production of NF-kB,Siglec-9 and Siglec-10.Membrane-proximal ITIM of Siglec-9 and Siglec-10 could offer docking sites for SHP-1/2 once tyrosine is phosphorylated,which could inhibit the role of Toll-like-receptor,resulting in increased production of NF-kB.SHP,SH2-domain bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase;IFN,interferon;TGF,transforming growth factor;Siglec,sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin.
CD169
CD169,which is also called sialoadhesin or Siglec-1,is expressed mostly on macrophages conserved among mammals (60,61).The CD169 molecule consists of 17 Iglike domains,including an N-terminal V-set domain and 16 C2-set domains (62).CD169 can serve as a functional ligand,different from most Siglecs,which work as receptors (57).The functions of CD169 are involved in cell-to-cell adhesion and cell-pathogen interactions (63)including sialylated pathogen uptake,antigen presentation,and modulating self-antigen tolerance (64).CD169 could potentially contribute to both the damping and the facilitation of antitumor immunity (65).On the one hand,Siglec1 can recognize and bind surface polysaccharides,such as CD43,on T cells to implement cell-to-cell communication (66).CD169+macrophages in the marginal zone of the spleen recognize phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic cells,acting as APCs to present apoptotic cell antigens so that Tregs are recruited to exhibit their immune tolerance role (67).On the other hand,CD169 in lymph nodes plays an immunoregulatory role by interacting with MUC-1 binding on the surface of breast cancer tumor cells (68).A high density of CD169+macrophages in the regional lymph nodes of colorectal,endometrial carcinoma and malignant melanoma patients indicates a better clinical prognosis,perhaps owing to an increase in the number of tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic immune cells (69,70).CD169+macrophages can also directly contact CD43-expressing CD8+T cells (71).In endometrial carcinoma patients,a high density of CD169+cells in the regional lymph nodes of the tumor is associated with a higher density of CD8+T cells and NK cells in the tumor tissue (69,70).The number of intratumoral cells expressing CD169 also positively correlates with the number of infiltrating CD8+T cells in the tumor and with patient survival (71).In contrast,the subcapsular sinus macrophages in regional lymph nodes of patients with advanced-stage endometrial carcinoma or metastatic carcinoma bear lower levels of CD169 or are completely dismissed from this molecule (70).Furthermore,some results suggested that upon vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)infection,Siglec1 can associate with DAP12 and SHP2,triggering suppression of type I IFN production (72).There is also evidence that Siglec-1 can interact with and activate the DAP12-Syk pathway to increase the production of TGF-β1,which plays an essential role in sepsis and endotoxin tolerance (73).
Siglec-9
Siglec-9 is expressed on various kinds of human blood leukocytes,including lymphocytes and myeloid cells such as B cells,small groups of T cells,monocytes,neutrophils,and NK cells (74).Siglec-9 is mainly expressed on neutrophils in peripheral blood (75) and on NK cells,B cells and monocytes afterwards (76).As plentiful evidence indicates,Siglec-9 plays inhibitory roles in modulating immune homeostasis (77) by interacting with the membrane-proximal ITIM.ITIMs can offer docking sites for SHP-1/2 once tyrosine is phosphorylated (78).Siglec-9 could also link with transmembrane epithelial MUC,a kind of strongly glycosylated protein basically produced by epithelial tissues,which could trigger immune evasion (79).MUC1 overexpressed on adenocarcinomas and hematological cancers could recruit β-catenin binding to its C-terminal domain to give rise to the growth of tumor cells(80).MUC1-sialylated O-linked glycan binding to Siglec-9 could induce calcium flux,leading to the activation of MEK-ERK kinases instead of recruiting SHP-1/2 (81).Siglec-9 could also interact with MUC16 expressed on epithelial ovarian cancer cells,which protects tumor cells from immune clearance (82).
Siglec-E
Siglec-E is the mouse orthologue of human Siglec-9.Similar to Siglec-9,Siglec-E was first found on neutrophils,macrophages and monocytes (83).Siglec-E could stop inflammatory responses mediated by immune cells when binding to sialoglycan ligands in its extracellular region(83).A Siglec-E-deficient mouse model (84) was utilized to explore the role of Siglecs in myeloid cells (85).As reported,neutrophil-associated Siglec-E could promote extravasation and colony formation of tumor cells in the lungs.The tumoricidal effect and reactive oxygen species(ROS) production mediated by neutrophils are shown to be enhancedin vitrowith the deficiency of Siglec-E (85,86).TAMs in mice with Siglec-E deficiency have a higher preference for polarization into M2 macrophages and could enhance subcutaneous tumor growth (85).
Siglec-10
CD24 (also known as heat stable antigen or small-cell lung carcinoma cluster 4 antigen) is a heavily glycosylated glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored surface protein (87).It is reported to interact with the inhibitory receptor sialicacid-binding Ig-like lectin 10 (Siglec-10) on innate immune cells to dampen damaging inflammatory responses to infection (88),sepsis (89),liver damage and chronic graftvs.host diseases (87,90).The binding of CD24 to Siglec-10 triggers an inhibitory signaling cascade,which is mediated by Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatases,SHP-1 and/or SHP-2.The phosphatases are associated with the two immune-receptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of Siglec-10,thereby blocking Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammation and the cytoskeletal rearrangement required for cellular engulfment by macrophages (58,91,92).Moreover,the role of CD24 in modulating tumor immune responses has been reported.CD24 is a potent antiphagocytic “don’t eat me”signal that is capable of directly protecting cancer cells from attack by Siglec-10-expressing macrophages.Many tumors overexpress CD24,and TAMs express high levels of Siglec-10.Genetic ablation of either CD24 or Siglec-10,as well as blockade of the CD24-Siglec-10 interaction using monoclonal antibodies,robustly augmented the phagocytosis of all CD24-expressing human tumors and led to macrophage-dependent reduction of tumor growthin vivoand an increase in survival time (93).Studies have shown that CD24 is expressed by several solid tumors,such as ovarian cancer and breast cancer (94,95),which demonstrate weaker responses to anti-PD-L1/PD-1 immunotherapies than other cancers (52,96),suggesting that an alternative strategy may be required to achieve responses across a wide range of cancers.
Siglec-15
Among the Siglec family members,Siglec-15 has been identified as a very unique member,selectively expressed on myeloid cells and osteoclasts (a bone-specific myeloid lineage) and generally absent in other immune cells and tissues (97,98).Siglec-15 was identified as a novel T-cellinhibitory molecule,which was originally characterized as an osteoclast modulator (99).The expression of Siglec-15 is normally limited to cells in the myeloid lineage but can be upregulated in many human cancers (97).As a recent study indicated,Siglec-15 strongly suppresses antigen-specific Tcell responsesin vitroandin vivoand can mediate immune evasion in the TME (100).As an immune suppressive molecule,the Siglec-15 pathway is nonredundant to the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway (100,101). Siglec-15 can be upregulated by macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF) released by diverse cell types in response to inflammatory cytokines or by tumor cells,while under physiological conditions,it is expressed on macrophages at a low level (102).
Apart from Siglec-15’s unique induction mechanism by M-CSF,IFNγ,the major inducer of PD-L1 (101),is significantly demonstrated to suppress the expression of Siglec-15 on macrophages (100).Unlike the majority of Siglec members,there are no typical ITIMs or ITIM-like motifs in the intracellular domain of Siglec15 (58).Instead,it was reported to be associated with the adaptors DAP12 and DAP10,which contain an immunoreceptor tyrosinebased activation motif (ITAM) (103).DAP12 can recruit PI3K (104) and then promote an inflammatory response by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK)pathway (105).Furthermore,Siglec-15 could inhibit T cell NF-κB/NFAT signaling in a direct way once binding and could suppress the proliferation of T cells and the production of cytokines,and the inhibitory function could be mediated by IL-10 (99).In addition,Siglec-15 could behave as a macrophage receptor and produce TGFβ when binding with its sialic acid ligand Sialyl-Tn on tumor cells(101).When the levels of IL10 and TGFβ rise in the TME,the immune-suppressive effect of Siglec-15 is magnified (100).
LILRB family
The LILR family comprises a set of paired immunomodulatory receptors expressed among human myeloid and lymphocyte cell populations.The leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LILR,LIR,ILT,CD85)family can be divided into two classes: the inhibitory LILR subfamily B (LILRB1-5) and the activating LILR subfamily A (LILRA1-6).Inhibitory LILRB receptors were first identified in 1997 (106).Expression is enriched in myeloid cell populations and is primate specific,reflecting rapid gene duplication and evolution within the leukocyte receptor complex of chromosomes (106).LILRs are closely linked to the human killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR)family,and both LILRs and KIRs share similar Ig-like structures and cytoplasmic signaling domains.Whereas KIR expression is restricted to natural killer (NK) cells,LILRs are expressed on various immune cells,including NK,T,and B lymphocytes and myelomonocytic cells(monocytes,macrophages,DCs and granulocytes).LILRB expression has also been reported in other cell types,including osteoclasts (107),leukemia ,stromal and endothelial cells,and various cancers (108).LILRB expression in cancer has been associated with enhanced tumor growth and correlates with poor survival outcomes.LILRB1 is broadly expressed on myeloid cells,B cells and subsets of NK cells and T cells.LILRB2-5 are more restricted to cells of myeloid origin and DCs.LILRB receptors contain cytoplasmic (S/I/V/LxYxxI/V/L) ITIM domains to recruit the Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase SHP1/SHP2/SHIP,leading to inhibited immune signaling cascades. SHP/SHIP phosphatase activity is critical in maintaining immune homeostasis(Figure 7) (109).LILRBs act as both immune checkpoint molecules and tumor sustaining factors but may not affect normal development. Thus,they have potential as attractive targets for cancer treatment.
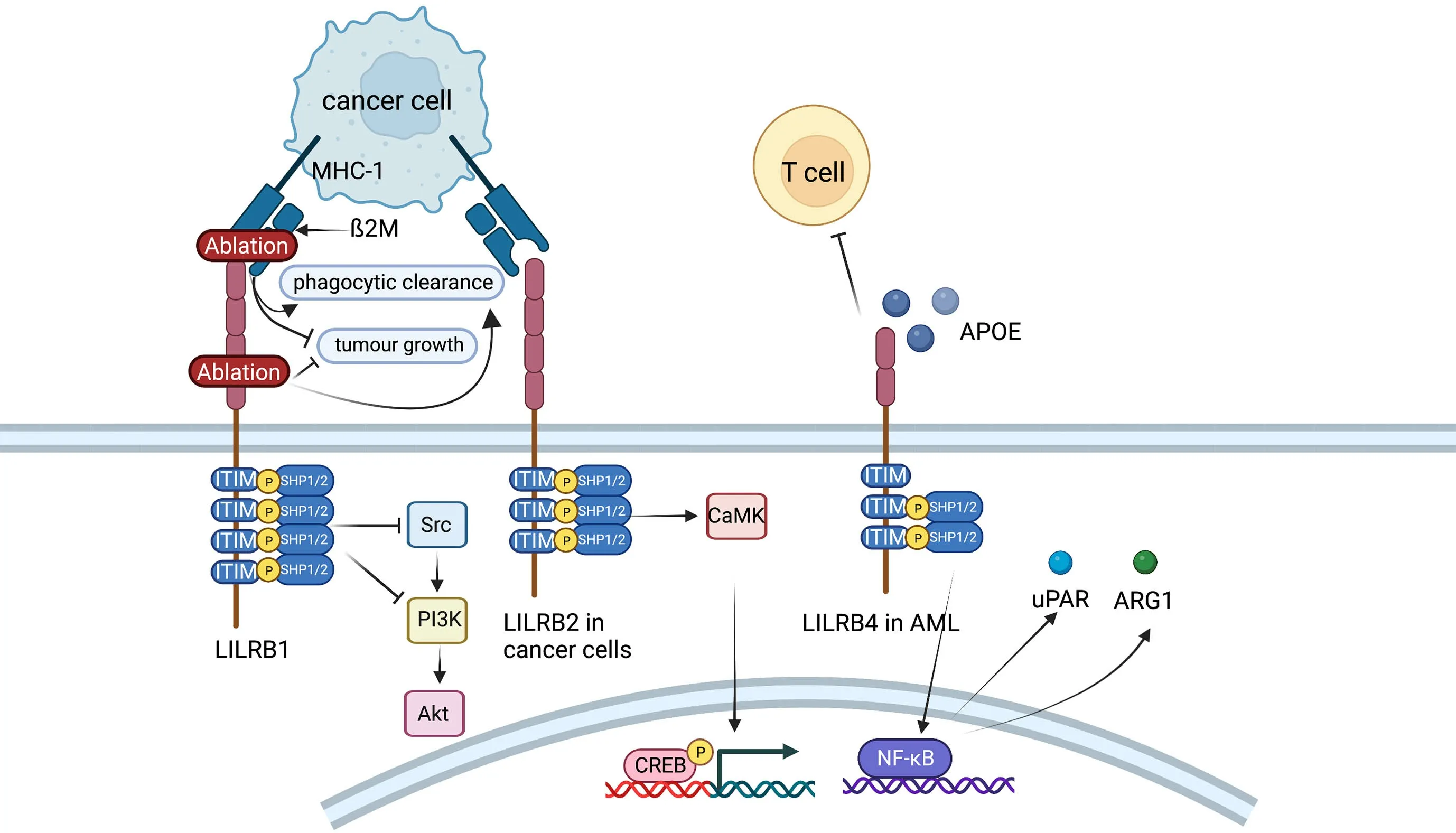
Figure 7 Role of LILRB family.LILRB1 inhibits Fc receptor-mediated signaling in NK cells and monocytes and possibly plays an antitumor effect in hepatocarcinoma cells by activating SHP-1,which could then inhibit PI3K/Akt pathway.In endometrial cancer cells,LILRB2 could enhance the SHP2/CaMK1/CREB signaling pathways.LILRB4 supports tumor cell infiltration into tissues and suppresses T cell activity possibly via APOE,LILRB4,SHP-2,uPAR and ARG1 in AML cells.LILRB,leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B;SHP,SH2-domain bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase;NK,natural killer;AML,acute myeloid leukemia.
LILRB1
LILRB1,an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif-containing receptor,is widely expressed on human immune cells,including B cells,monocytes and macrophages,dendritic cells and subsets of NK cells and T cells (110).The ligands of LILRB1,such as major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules,activate LILRB1 and transduce a suppressive signal,which inhibits immune responses (111).The MHC class I component β2-microglobulin (β2M) has been found to act as a potential antiphagocytic signal in cancer cells (110).MHC-I on the cancer cell surface is sensed by LILRB1 on TAMs,resulting in negative regulation of cancer cell phagocytosis.LILRB1 is an immunoglobulin-like receptor for the gene product of human cytomegalovirus UL18,a homolog of cellular MHC class I antigens (112).LILRB1 in NK cells inhibits Fc receptor-mediated signaling in monocytes by activating the inhibitory phosphatase SHP-1(113).It has been reported that LILRB1 possibly plays an antitumor role in hepatocarcinoma cells by interacting with SHP1 (114).Ablation of MHC-I on cancer cells or LILRB1 on macrophages has been reported to promote the phagocytic clearance of tumor cells and inhibit tumor growth in anin vivomouse model (110).
LILRB2
LILRB2 is known as an immune inhibitory receptor that suppresses the immune system.CD8+CD28-alloantigenspecific T suppressor cells could trigger the expression of LILRB2 on monocytes and DCs,leading to the tolerance effect on these APCs (115).LILRB2highDCs could give rise to the anergy of CD4+CD45RO+CD25+T cells and suppress their further differentiation into regulatory T cells(116).As recent studies have reported,LILRB2 is highly expressed on hematopoietic stem cells or leukemia stem cells and is critical for the maintenance of stemness supporting hematopoiesis or leukemogenesis (117).LILRB2 is also reported to be expressed in many types of solid cancers.For instance,LILRB2 is linked with fewer infiltrating lymphocytes and more lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer (117).LILRB2 can be detected on the cell membrane and in the intracellular region of NSCLC and enhances progression (118).LILRB2 plays a vital role in sustaining epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the early metastatic behavior of pancreatic adenocarcinoma(119).Furthermore,LILRB2 is shown to be highly expressed in endometrial cancer,and the expression levels are conversely correlated with overall survival of patients(119).In vitroexperiments indicate that knockdown of LILRB2 leads to a significant decrease in proliferation,colony formation and migration in several endometrial cancer cell lines. LILRB2 could enhance the SHP2/CaMK1/CREB signaling pathways,which supports the expansion and migration of endometrial cancer cells (119).
LILRB4
LILRB4 (also known as CD85K,ILT3,LIR5,and HM18)has two extracellular Ig-like domains (D1 and D2) and three ITIMs.On the one hand,LILRB4 is a marker for monocytic AML (120).Further demonstration is that LILRB4 is more highly expressed on monocytic AML cells than on their normal counterparts and that LILRB4 expression inversely correlates with overall survival of patients with AML (120).Experiments in mouse models and human cells show that LILRB4 supports tumor cell infiltration into tissues and suppresses T-cell activity via a signaling pathway that involves APOE,LILRB4,SHP-2,uPAR and ARG1 in AML cells (120).Furthermore,LILRB4 represents a compelling target for the treatment of monocytic AML.It has been reported that a LILRB4-targeted humanized mAb,which blocks the LILRB4/APOE interaction in a competitive manner,inhibits monocytic AML cell tissue infiltration and reverses T cell suppression (121).On the other hand,LILRB4 is expressed on MDSCs and TAMs (122).Expression of LILRB4 on PMN-MDSCs and M-MDSCs in NSCLC is associated with poor patient outcomes (123).In vitro,the capacity of M-MDSCs from normal human monocytes to induce IL-10-producing Treg cells could be potentiated by prostaglandin E2 through LILRB4 on M-MDSCs (124).Anti-LILRB4 antibodies impaired the T cell suppression induced by M-MDSCs (122).Furthermore,fibronectin expressed by stromal cells in the TME can bind and activate LILRB4 on MDSCs,which recruits SHP-1 to inhibit Syk-mediated FcγR signaling and the immunosuppressive activities of MDSCs (125).Apart from MDSCs,studies have indicated that LILRB4 is expressed on TAMs in various human cancers and mouse models,including melanoma,lung cancer,colon carcinoma and pancreatic carcinoma (108).Blocking LILRB4 or gp49b deficiency could increase the infiltration of antineoplastic immune cells into the TME and lessen the inhibitory effect of Treg cells by regulating IL-1b and iNOS production from TAMs (126).In summary,LILRB4 expressed on MDSCs and TAMs may be an interesting target for cancer immunotherapy.
TREM2
TREM2 was originally recognized in Alzheimer’s disease as a myeloid receptor that transmits intracellular signals to maintain microglial responses.TREM2 is also expressed on TAMs,acting as an activating receptor of the Ig superfamily and transmitting intracellular signals when binding to the adaptor DNAX-activating protein of 12 kDa(DAP12) (127).DAP12,which recruits the protein tyrosine kinase Syk,could conduct a tyrosine phosphorylation cascade activating downstream mediators such as PLCγ2,PI-3K,mTOR and MAPK,finally triggering cell activation(Figure 8).Mouse models show that TREM2-/-mice are more resistant to the growth of diverse kinds of cancers than wild-type mice and are more responsive to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy (128).Moreover,treatment with an anti-TREM2 monoclonal antibody suppresses tumor growth and raises regression when combined with anti-PD-1 (128).Moreover,in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and triplenegative breast cancer,TREM2 expression is reported to have a converse correlation with higher overall survival and relapse-free survival (128,129).
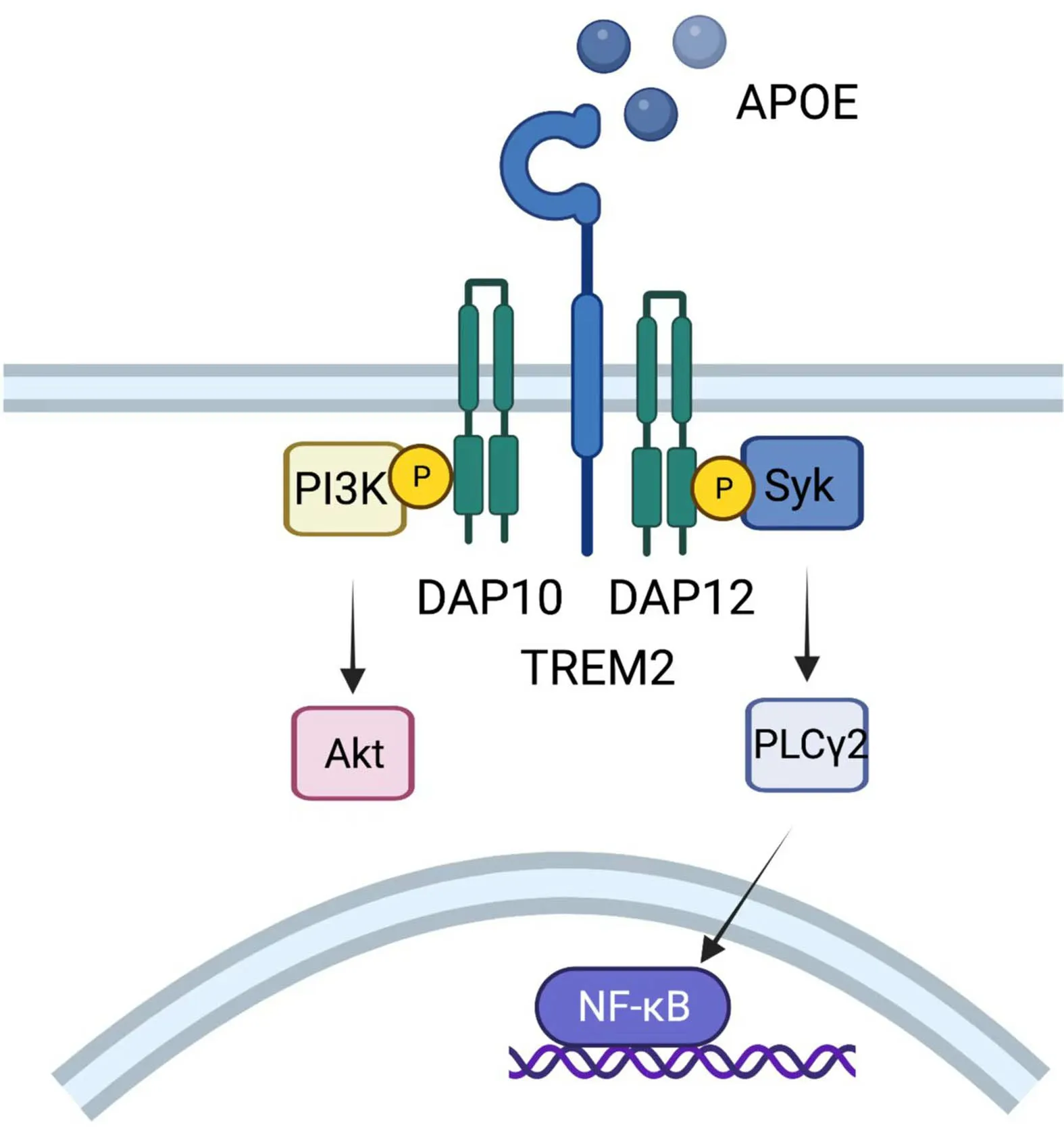
Figure 8 Role of TREM2.TREM2 expressed on TAMs could transmit intracellular signals when binding to DAP12,which recruits the protein tyrosine kinase Syk,conducting a tyrosine phosphorylation cascade activating downstream mediators such as PLCγ2,PI-3K,mTOR and MAPK,and finally triggers cell activation.TREM2,triggering receptor expressed on myeloidcells 2; TAM,tumor-associated macrophage; MAPK,mitogenactivated protein kinases.
NRP1
NRP1 was originally distinguished as an adhesion molecule in the frog nervous system and found as a transmembrane glycoprotein located on axons of nerve fibers (130).NRP1 located on the cell surface acts as a nontyrosine kinase transmembrane glycoprotein and plays a role as a coreceptor of secreted Semaphorin-3A (Sema-3A)(Figure 9).TheNRP1gene is widely expressed in various kinds of cells,tissues and organs,such as endothelial cells,and the heart,liver,lung,kidney,pancreas,and skeletal muscle (131),playing an essential role in promoting angiogenesis,neural development,cytoskeleton remodelling,inflammation,the initial immune response,and tumor development (132,133).The expression of NRP1 in the immune system is more restricted and regulated.NRP1,which is also known as blood DC antigen 4 (BDCA4,or CD304),was identified as a human DC marker expressed in all pDCs (134).Other types of APCs,including monocytes and macrophages,also express NPR1(135).NRP1 expressed in monocytes and macrophages generally plays proangiogenic and anti-inflammatory roles,contributing to tissue remodelling and wound healing(136).As recently reported,NPR1 is also expressed in CD8+T cells in mice and humans and is mainly detected in intratumoral CD8+T cells marked by high expression of PD-1 (137).
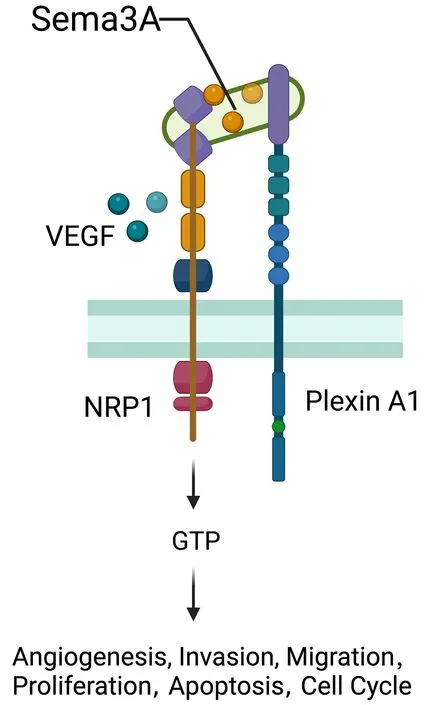
Figure 9 Role of NRP1.NRP1 located on the cell surface acts as a non-tyrosine kinase transmembrane glycoprotein and plays a role as a co-receptor of secreted Semaphorin-3A (Sema-3A).NRP1 gene widely expresses over various kinds of cells,tissues and organs such as endothelial cells,the heart,liver,lung,kidney,pancreas,and skeletal muscle,playing an essential part in promoting angiogenesis,neural development,cytoskeleton remodeling,inflammation,initial immune response,and tumors development.VEGF,vascular endothelial growth factor.
A recent study indicated the role of NRP1 in the emergence and development of human malignant tumors(138).Higher expression or mutations of NRP1 are linked with the initiation,progression,and prognosis of human malignant tumors such as hepatocellular carcinoma (139),gastric cancer (140,141),breast cancer (142),prostatic cancer,and pancreatic cancer (143).Overexpression of NRP1 significantly reduces the survival rate in NSCLC patients.The reduction of NRP1 expression by utilizing NRP1 monoclonal antibody,RNA interference or NRP1 inhibitor could inhibit tumor cell growth and tumor angiogenesis (144).Overexpression of NRP1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma shows more spindle filaments,reduces the expression of EMT epithelial markers and increases the expression of mesenchymal markers (145).As studies report,NRP1 promotes the presence of EMT in breast cancer cells by augmenting signaling molecules such as TGF-β (146).
Clever-1
Clever-1,also known as stabilin-1 or FEEL-1,is a multifunctional glycoprotein expressed on a subset of antiinflammatory macrophages involved in scavenging,angiogenesis and cell adhesion,which are involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis and recycling,intracellular sorting and transcytosis (147,148).Additionally,it is the first adhesion molecule implicated in transmigration through the lymphatic arm of the immune system (147).Attenuated progression of melanoma tumor growth and metastasis has been observed in Clever-1-knockout mice and those treated with anti-Clever-1 therapy (149).Clever-1+macrophages are found in human cancers and are associated with poorer disease-free survival in colorectal cancers of advanced stage and overall survival in bladder cancer (149). Circulating monocytes and tissue macrophages show higher expression of Clever-1 in an immunosuppressive environment,such as pregnancy and cancer,which could suppress Th1 lymphocyte activation(148).Meanwhile,according to a phase 1/2 clinical trial,bexmarilimab,a novel anti-Clever-1 antibody,has shown significant efficacy in 10 patients with hard-to-treat solid tumors (150).
Clinical application
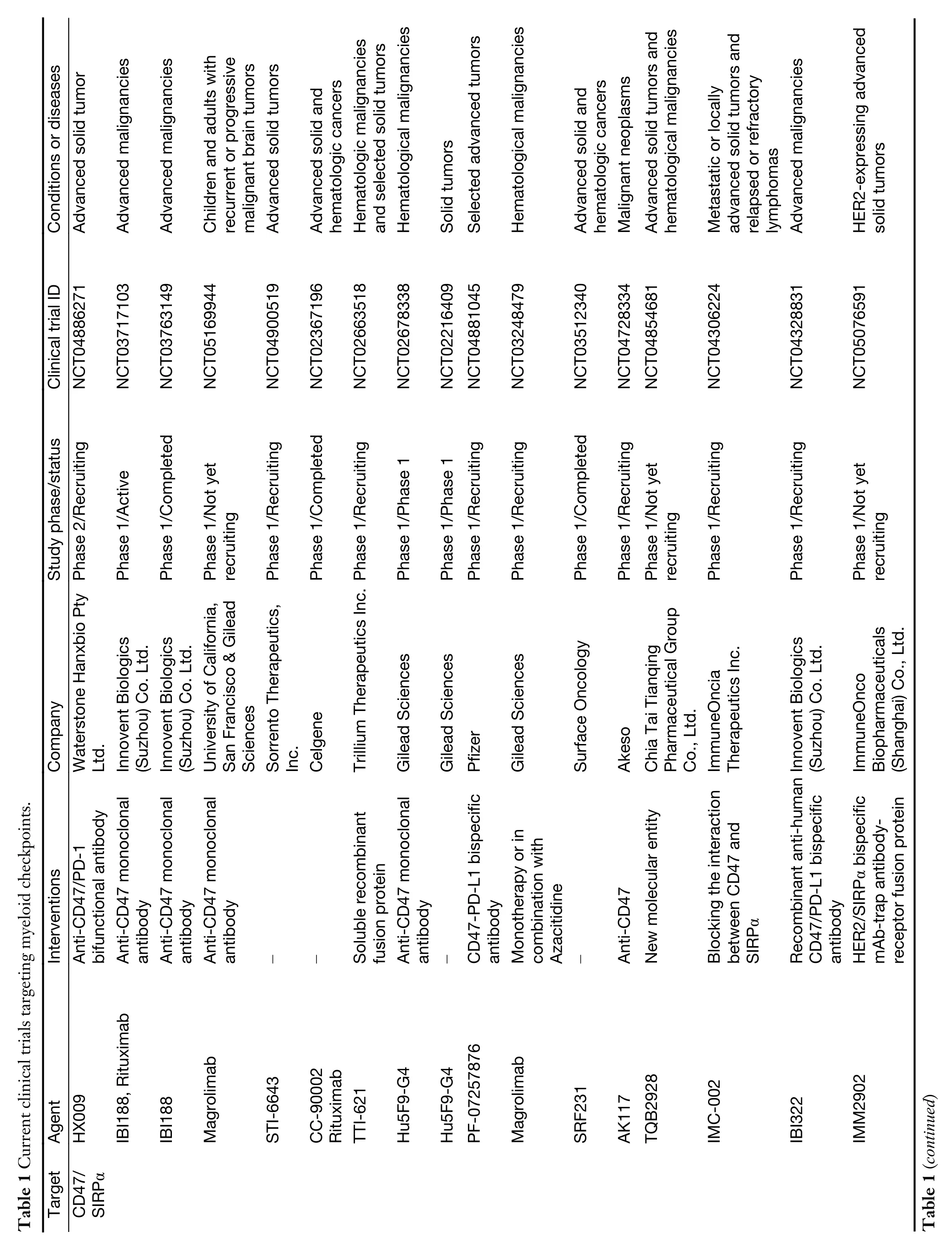
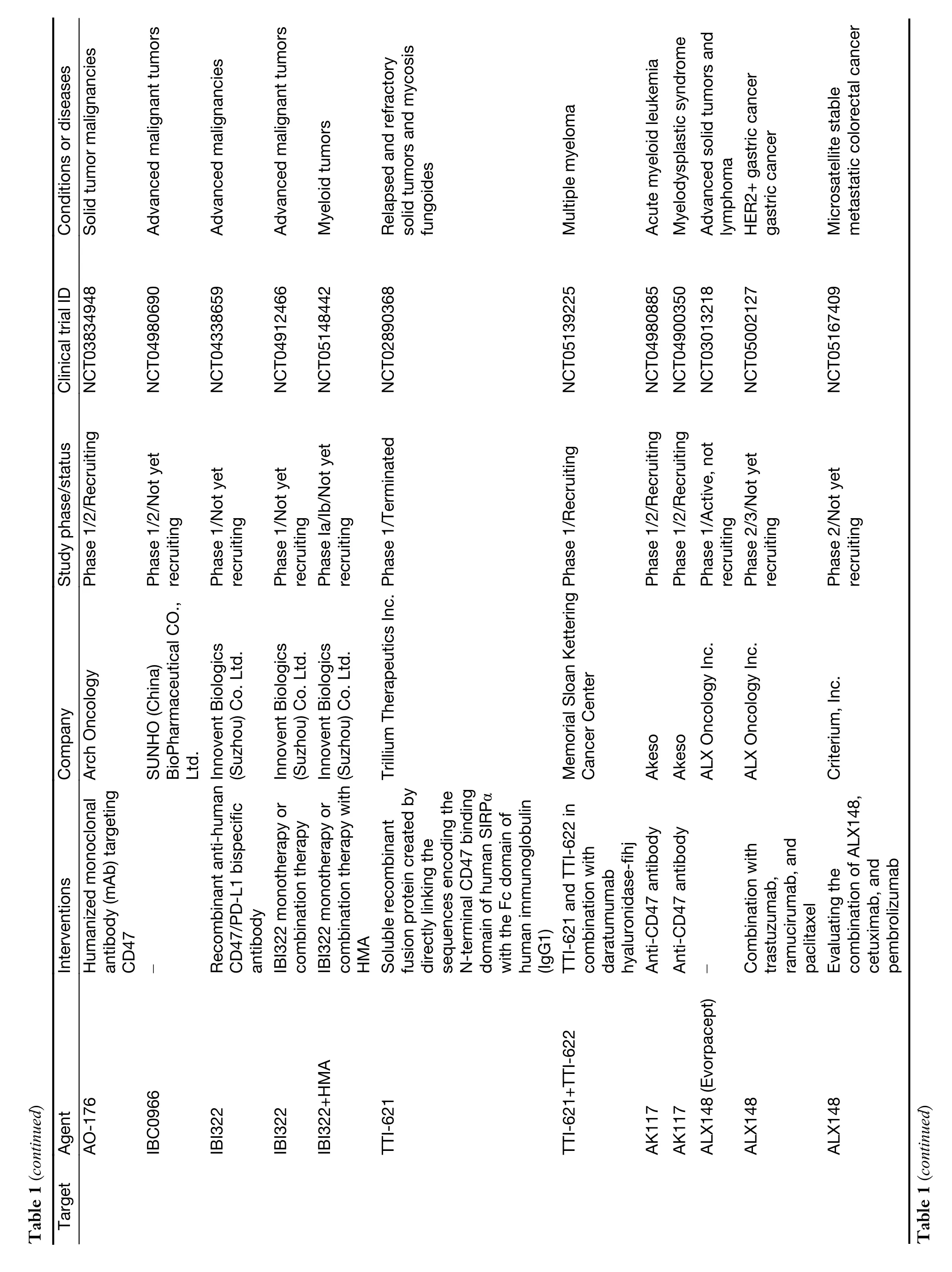
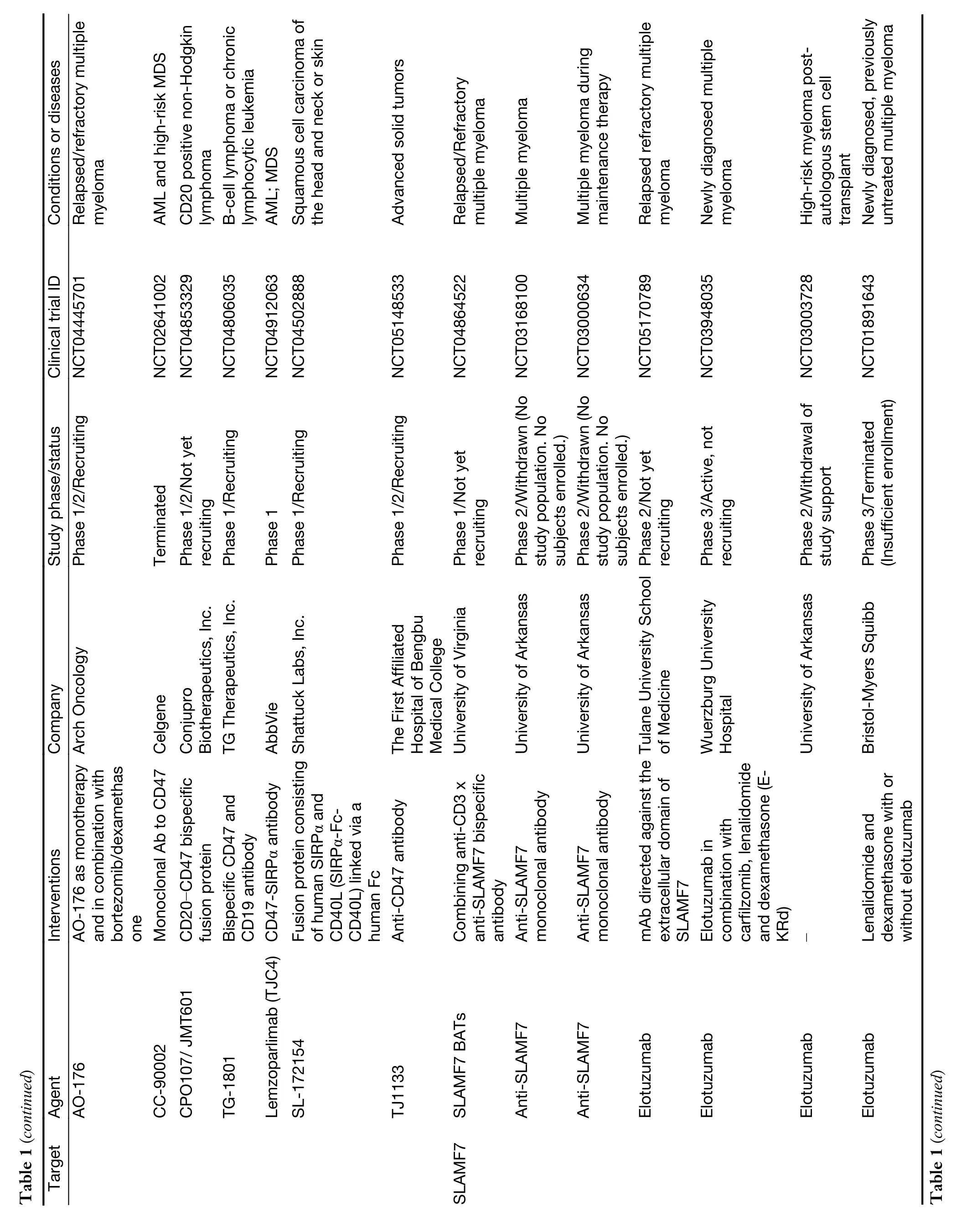
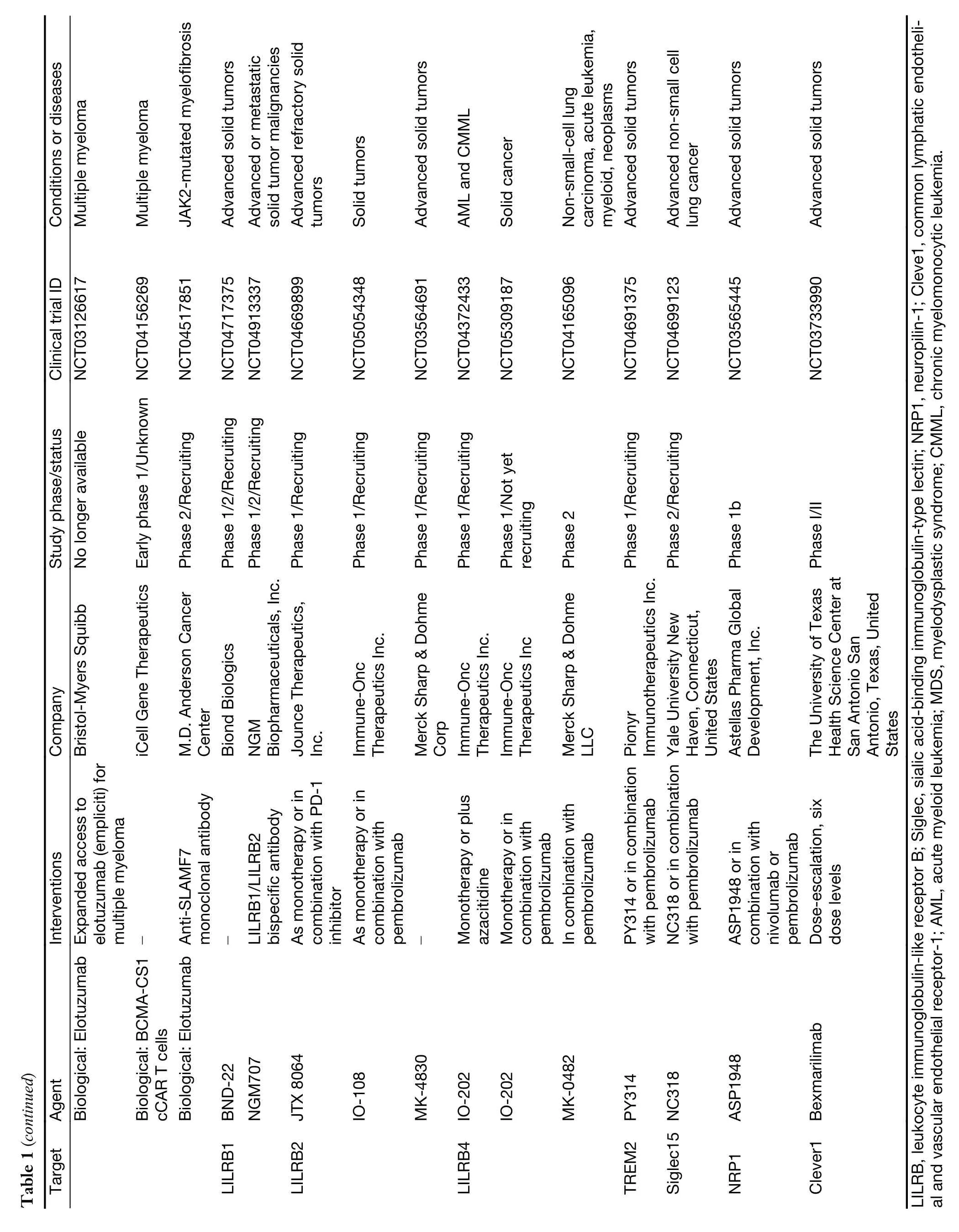
While myeloid checkpoints have been increasingly recognized as a potentially hopeful target to develop novel immunotherapeutic strategies,several monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting myeloid checkpoints have recently been under development,and clinical trials are ongoing.Here,we labelled the recent advanced antibodies targeting those myeloid checkpoints below (Table 1).
Summary and prospects
In this review,we briefly summarized the biological functions of different kinds of myeloid checkpoints expressed on various myeloid cells,which has greatly advanced cancer treatment.To overcome the immune escape mechanisms of tumors and to improve the versatility and raise the efficiency of current immunotherapies,it is necessary to understand myeloid checkpoints in more details and explore novel approaches based on these kinds of checkpoints.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Imported Scholar Project and Startup from Peking University Health Science Center(BMU2021YJ063 to MD);the Biotechnology Innovation Plan from Beijing Sungen Biomedical Technology Co.,Ltd(2022066 to MD);and the Excellent Young Scientists Fund Program (overseas) from National Natural Science Fund(HY2021-7 to MD).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.Figures are created with BioRender software (https://biorender.com/).
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2022年5期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2022年5期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Characteristics of lymph node stations/basins metastasis and construction and validation of a preoperative combination prediction model that accurately excludes lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer
- Correlation between imaging features on computed tomography and combined positive score of PD-L1 expression in patients with gastric cancer
- Evaluation of triage strategies for high-risk human papillomavirus-positive women in cervical cancer screening: A multicenter randomized controlled trial in different resource settings in China
- Colorectal cancer burden,trends and risk factors in China:A review and comparison with the United States
- National guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of malignant lymphoma 2022 in China (English version)
- Beyond images: Emerging role of Raman spectroscopy-based artificial intelligence in diagnosis of gastric neoplasia
