Effects of equine-assisted interventions on older adults’ health: A systematic review
Léa Badin,émilie Alibran,Kristell Pothier,Nathalie Bailly
University of Tours,EA 2114 PAVEA Laboratory,Tours,France
Keywords:Animal assisted therapy Aged Equine assisted therapy Health promotion
ABSTRACT Objective:Equine-assisted interventions (EAI) can improve a variety of health problems in older adults and thus promote their well-being.This systematic review aimed to synthesize studies on EAI to understand better their effects on the health of older adults.Method: A systematic search guided by the PRISMA 2020 approach was performed on specific databases:Medline (PubMed),EMBASE,PsycINFO,and Cochrane Library.Peer-reviewed articles published in the English language from inception to June 2022 were retrieved.Methodological quality was established using the modified version of the Downs and Black checklist.Results:A total of 244 studies were retrieved,and 13 eligible studies were finally included.Three health domains were investigated:physical(balance,gait,and muscular strength),psychological(quality of life and cognitive assessment),and physiological (hormonal measures,cerebral and muscular activity).Among the eight studies investigating the physical dimension,four studies highlighted a positive effect of EAI on balance,four for gait,and three for strength.Regarding the three studies investigating the psychological dimension,two studies showed a positive effect of EAI on quality of life.Lastly,the four studies investigating the physiological dimensions all demonstrated a positive effect of EAI on hormonal measures and cerebral and muscular activity.Conclusion:Nevertheless,this systematic review provides promising findings regarding the positive effects of EAI on physical,psychological,and physiological health in older adults.Research on EAI should therefore be pursued rigorously to promote this non-pharmacological intervention in an older adult population.
What is known?
· Today,equine-assisted interventions (EAI) have been proven to benefit several populations,including youth and especially children with autism.Studies have also shown beneficial outcomes of equine intervention with individuals with psychiatric disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder.
· Studies conducted on older adults specifically address the physical and physiological domains.
· Currently,non-pharmacological interventions are recommended to maintain or improve the quality of life of older adults.
What is new?
· This study proposes a synthesis of EAI with older adults regarding the physical,physiological,and also psychological domains.
· Results contribute to a better understanding of the benefits of EAI on the physical and psychological health of older adults.
· The findings of this systematic review highlight the need for more rigorous studies to promote this type of innovative intervention for older adults to contribute to improving their quality of life.
1.Introduction
Animal-assisted interventions(AAI)are defined as goal-oriented and structured interventions based on human-animal interaction.According to the International Association of Human-Animal Interaction Organizations (IAHAIO,2018),AAI includes different types of interventions such as animal-assisted therapies,animalassociated activities,or animal-assisted education programs [1].Animal-assisted therapies are generally conducted by a health professional (therapists or physicians) with specific therapeutic goals (e.g.improved quality of life),while animal-associated activities and animal-assisted education are more informal and are often conducted by paraprofessionals,or volunteers.Although most of the studies on AAI have focused on dog-assisted interventions [2],equine-assisted interventions (EAI) represent an emerging field of AAI aimed at promoting physical and mental health.EAI involves horses as co-facilitators in a therapeutic or recreational environment.EAI encompasses several activities like horseback riding,but also activities without classic riding such as adapted acrobatics,carriage driving,grooming,and caring for and interacting with horses.Previous studies have demonstrated that EAI seems to alleviate emotional,social,cognitive,and physical disorders in various healthcare settings and has been used to treat neurological disorders[3] and other disabilities such as autism [4]or psychiatric disorders[5,6].
As people age,individuals have to deal with physical,psychosocial,and cognitive changes,and the WHO encourages the development of early interventions that improve behavioral and psychological symptoms,while also enhancing social functioning among older adults.
Most studies on older adults have focused on the physical benefits of horseback riding.Indeed,regular exercise is an important factor for maintaining health in older age and the unique three-dimensional movement involved in horseback riding stimulates movement to maintain balance and activate core muscles which play an important role in postural control among older adults.The beneficial effects of EAI have been demonstrated on balance,gait,muscle strength,and postural coordination compared to conventional walking among older adults [7,9].The metaanalysis conducted by Hilliere [10] with people with disabilities showed a significant improvement in mobility (e.g.step length,velocity,and walking speed)for the equine group compared to the control group.In addition,in a randomized controlled trial,White-Lewis et al.[11] highlighted a significant decrease in physical pain after EAI in older adults with arthritis.These benefits on physical health are important for an aging population because they facilitate the performance of activities of daily life and may reduce the risk of falling.
EAI can also improve psychological domains such as well-being,quality of life,and self-rated health,even in people affected by a variety of diseases [8,12].In a systematic review conducted on adults,White-Lewis et al.[11] highlighted significant improvements in quality of life/self-efficacy/well-being in 91%of the studies(10/11).The same results on quality of life were obtained in a metaanalysis with individuals with disabilities such as cerebral palsy and Parkinson’s disease and intellectual disabilities [13].The benefits of EAI on psychological and behavioral symptoms have also been evaluated,especially in an autistic population [14].For vulnerable older people,for example,those with a neurological disease such as Alzheimer’s,horseback riding is not always appropriate.Nevertheless,it has been reported that EAI without riding(e.g.through grooming)also has beneficial behavioral effects[15,16].For example,it has been demonstrated that activities with horses reduce behavioral problems for older adults diagnosed with dementia [17].Fewer studies have assessed changes in cognitive functions in EAI.In a population with disabilities,some studies have shown no effect of EAI on cognitive function while others have demonstrated an improvement[18,19].
Finally,some studies on EAI have focused on physiological changes such as stress hormone levels.Cho et al.[20] highlighted an increase in serotonin and a decrease in cortisol levels following 8 weeks of EAI among older adults compared to a control group.The same results were observed in an autistic population [21].In addition,it has been demonstrated that EAI enhances brain function[22,23].For example,Cho et al.[23]showed that the power of the relatively fast alpha band increased in the equine compared to the horseback riding machine group after 12 weeks of the intervention.These findings suggested that EAI provides psychological benefits by improving brain function,increasing comfort and concentration,and reducing stress.
Although a growing number of studies support the positive physical and psychological impact of EAI among young adults,little attention has been paid to EAI for older populations [17].In addition,their efficacy remains to be proved completely.Thus,the purpose of this systematic review is to synthesize evidence from EAI studies among older adults and to better understand the benefits of EAI on their health.
2.Methods
2.1.Search strategy
The present study was conducted according to the PRISMA[24].The authors of the study conducted a comprehensive literature search using the following electronic databases: Medline(PubMed),EMBASE,PsycINFO,and Cochrane Library.The review was carried out using the following medical subject heading(MeSH) terms and keywords: [“equine assisted therapy” OR“therapeutic horse riding” OR “therapeutic horseback riding” OR“hippotherapy” OR “equine psychotherapy” OR “equine facilitated therapy” OR “equus” OR “horse therapy” OR “equine assisted intervention”] AND [aged “older adult*” OR aged OR elderly].The final search date was the inception of each database to June 2022.
Study eligibility criteria for this systematic review are as follow:1)60 years old or older.2)Interventions focused on EAI i.e.,interventions based on IAHAIO guidelines (https://iahaio.org/iahaio-international-guidelines-on-care-training-and-welfarerequirements-for-equines-in-equine-assisted-services). These guidelines include EAT-with a therapeutic aim conducted by a health professional and Equine Assisted Activities (EAA-with recreational or educative aims).All these interventions aim to improve human health and well-being.3) Health outcome measures(physical,psychological,or physiological).4) Experimental or quasi-experimental (random controlled trials,non-random controlled trials,pre-post test design,etc.).5) Peer-review articles published in English.Articles that were excluded include opinion papers,editorial reviews,literature reviews,EAI guidelines,or studies with only mechanical horses.Two of the authors of this systematic review(N.Bailly and L.Badin)independently extracted the data and agreed after discussion.The PRISMA flow diagram(Fig.1) summarizes the systematic review process.
2.2.Data evaluation
Two of the review authors (N.Bailly and E.Alibran) assessed independently the methodological quality of the studies included using the modified version of the Downs and Black checklist for assessing randomized controlled trials (RCT) and non-randomized controlled trials (NRCT) [25].This is one of the two most useful tools for quality scoring [26].It consists of 27 items distributed across five subscales: reporting (10 items),external validity (3 items),internal validity bias(7 items),internal validity confounding(6 items),and power(1 item).In the modified instrument,answers are scored 0 or 1,except for one item in the reporting subscale,which is scored 0 to 2.The power score was calculated by one of the authors (N.Bailly) and was based on the sample size calculation with the effect size determined for each article.The total maximum score is 28 with higher scores indicating better study quality.
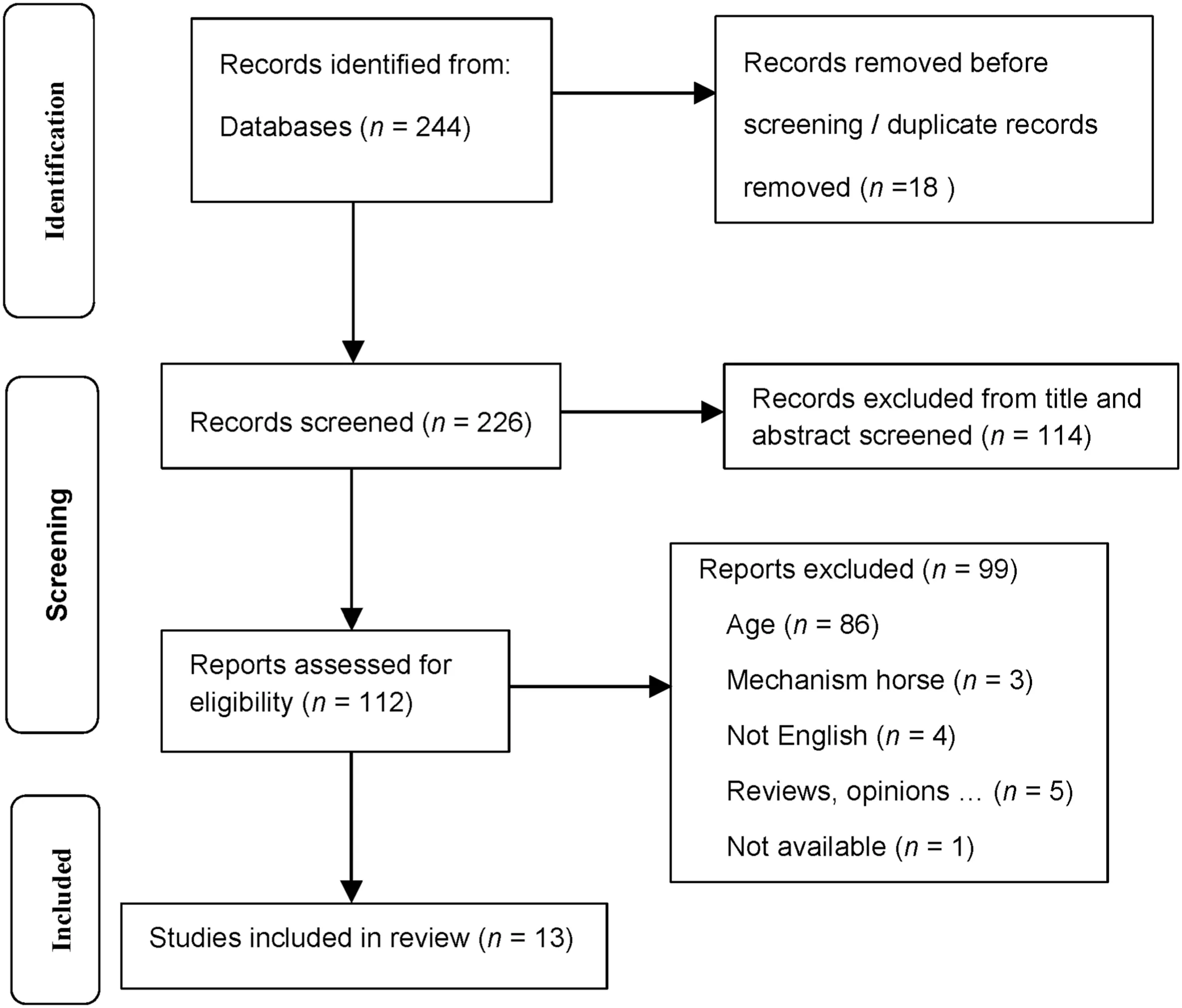
Fig.1.The PRISMA flow diagram for search strategy.
2.3.Data analysis
The description of each study’s aim,characteristics of participants,organization of equine intervention (frequency,number of sessions,etc.),contents of interventions,health measures assessed,and results were summarized in a review matrix.For each study and according to the health outcome measures (physical,psychological,or physiological),the statistical results before and after EAI were screened.For studies with control groups (and when data were available),a group by time interaction was screened.Discussions between authors(L.Badin,N.Bailly,and K.Pothier)were held to validate the conclusions and clarify any discrepancies to reach a mutual consensus.The summary tables of evidence are classified according to research design,as shown in Table 1 (randomized control trial studies),Table 2 (non-randomized control trial studies),and Table 3 (single group studies).
3.Results
A total of 244 articles were identified from the search.Out of the 244,18 were excluded (duplicate records) and 114 were excluded after screening titles and abstracts.The remaining 112 full-text articles were reviewed,and 99 were excluded based on being out-of-scope,reviews on EAI,participants younger than 60 years old,or use of mechanical horses only.Finally,13 articles met the inclusion criteria.The authors organized the extracted data in the following way:1)author’s name;2)purpose of the study;3)details of the population;4)details of the interventions;5)health outcome measures and 6) major results of outcomes.Studies are summarized in Tables 1-3.
3.1.Study and subject characteristics
Regarding the 13 studies,five were carried out in Brazil[7,27,28,30,31],four in Korea [20,22,23,29],three in the USA[8,12,16],and one in Spain[9].The total sample included 265 older adults ranging from 60 to 95 years old.Sample sizes of groups ranged from 9 to 38 participants.A large majority of studies(n=10)were conducted on healthy individuals [7,9,12,20,22,23,27-29,31],and two studies were conducted on older adults suffering from neurocognitive impairment [16,30] and one study on people with balance deficit [8].
3.2.Study design
Of the 13 studies:five were RCT[9,23,27-29];eight were quasiexperimental,four of which were non-randomized controlled trials[7,12,20,22];three were single groups with pre-test and post-test studies [8,30,31];one study was based on a mixed method including observational quantitative data on a single group but without pre or post-test [16].
3.3.Intervention characteristics
Among the 13 equine intervention groups,nine were based on Equine Assisted Therapy (EAT),i.e.conducted by a health professional with specific health goals [7,8,12,16,27-31] while the other four were EAA [9,20,22,23].A summary of the interventions conducted in each study is presented in Tables 1-3.The duration of these six different equine assisted interventions was from 1 to 12 weeks and they were conducted one to three times per week for 15-60 min per session.
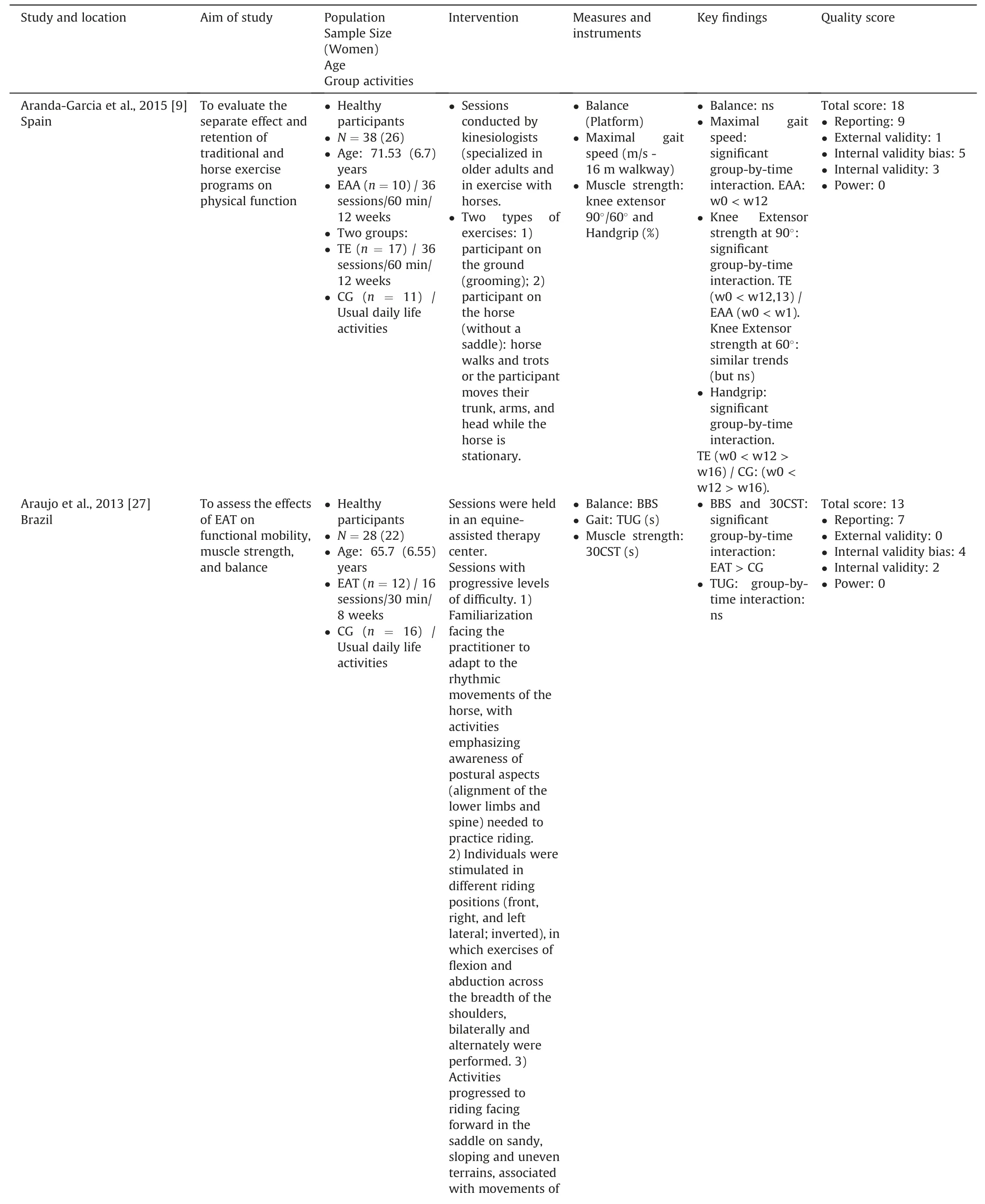
Table 1Summary table of evidence for Randomized Control Trials studies (n=5).

Table 1 (continued)
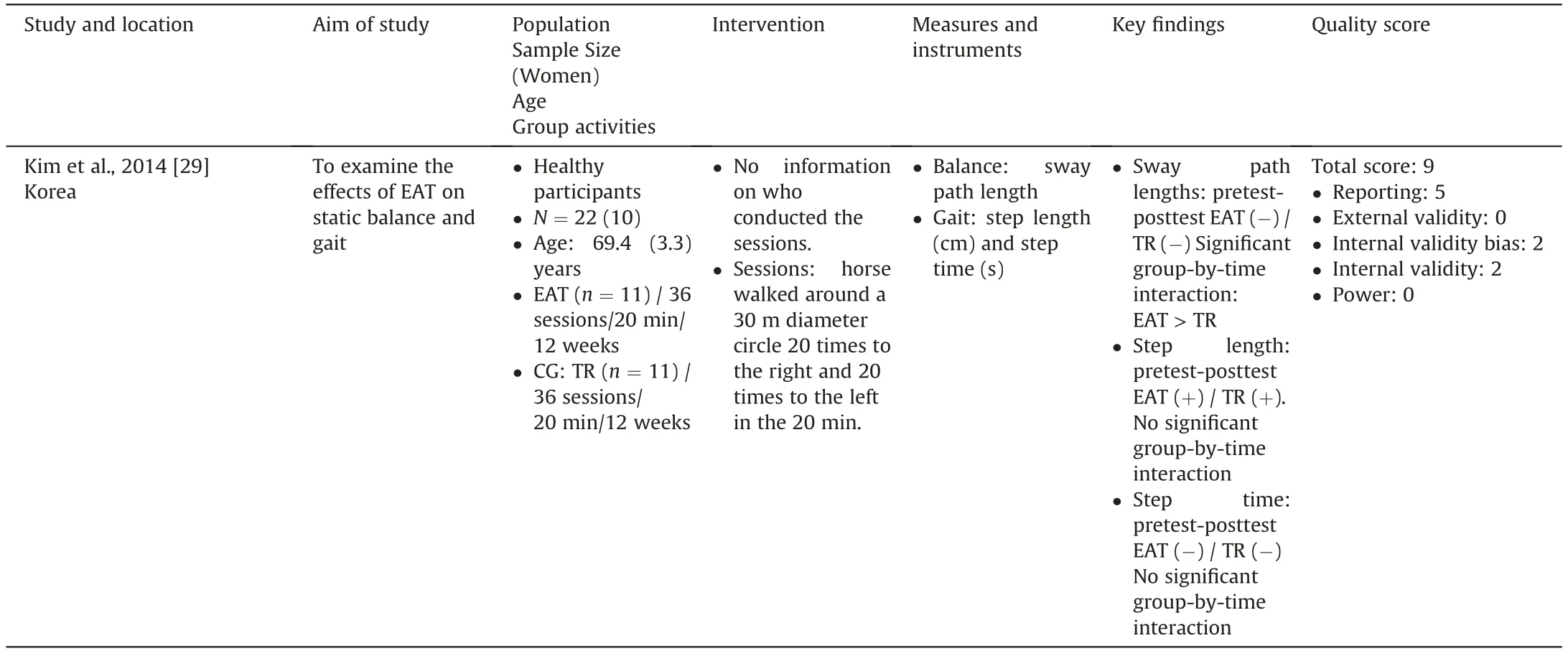
Table 1 (continued)
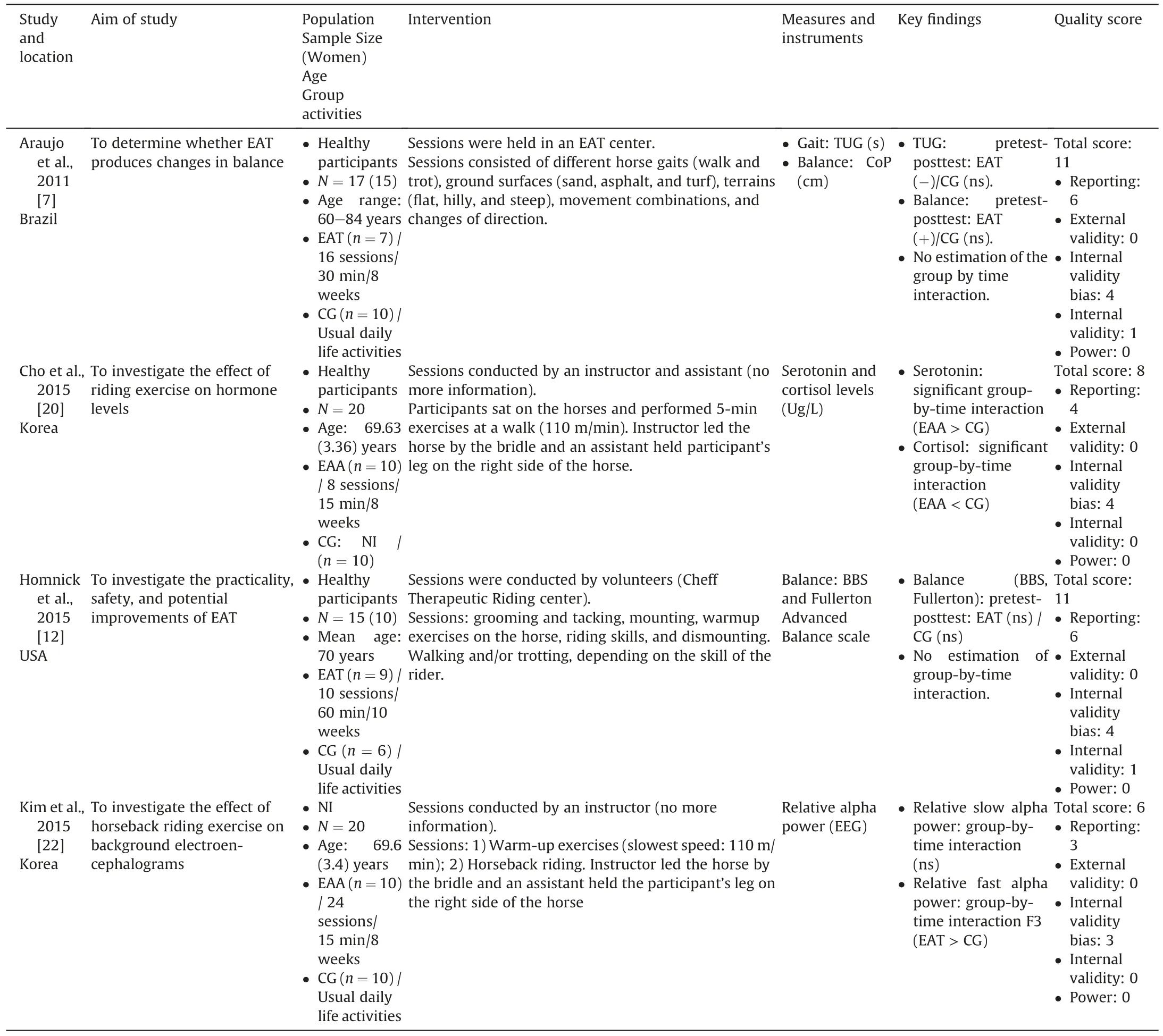
Table 2Summary table of evidence for Non-Randomized Control Trials studies (n=4).
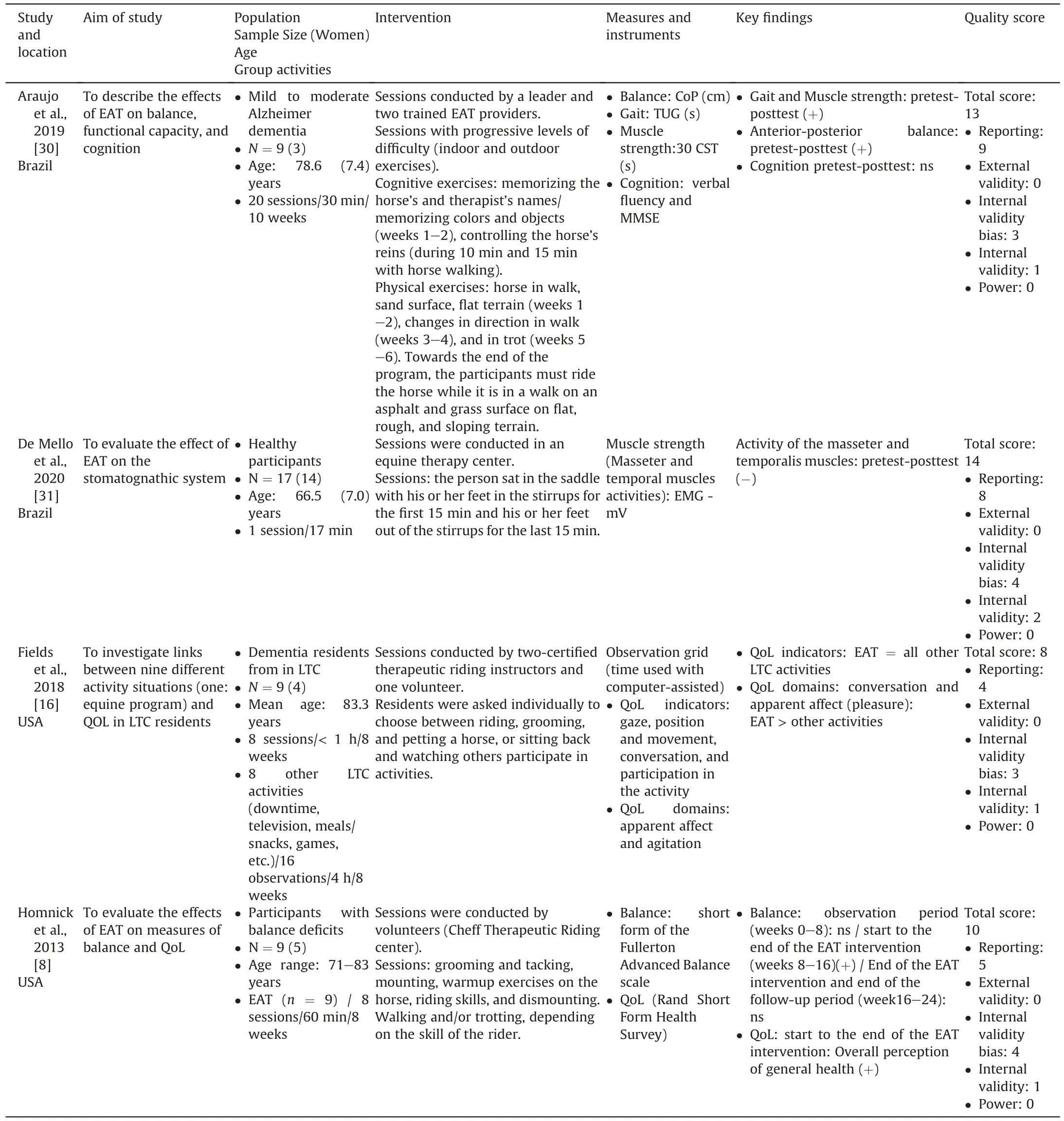
Table 3Summary table of evidence for single group(pre/post-test) studies (n=4).
Concerning the 10 studies with a control group (CG),interventions were usual daily life activities (i.e.with no intervention) for six studies [7,9,12,22,27,28],and one study each fortraditional physical exercise (i.e.cardiovascular exercise involving different movements of the whole body [9]),a mechanical horse[23] and a treadmill [29].One study did not include information about the control group[20].In one study,Field et al.[16]compared the effect of different types of activity in a single group(EAT versus eight care activities: downtime,television,meals/snacks,games,jokes and riddles,music group,bus time,and physical therapy).
3.4.Measurements
In these 13 studies,the authors investigated three main domains: physical,psychological,and physiological.
3.4.1.Physical measures
Eight articles studied the effect of the equine intervention on physical outcomes [7-9,12,27-30].Three main domains were investigated:balance,gait,and strength.Balance was assessed in all these studies.Instruments were: Berg Balance Scale [12,27,28],Fullerton Advanced Balance scale [8,12],the Functional Reach Test[28],sway path length[29]or platform utilization for estimation of balance [7,30].Gait was measured in six studies [7,9,27-30].The Timed Up &Go test was the most frequently used [7,27,28,30].In addition,Aranda-Garcia et al.[9]used maximal gait speed(m/s)on a marked 16-m walkway,and Kim et al.(2014)[29]measured step length and step time using a gait analyzer.Four studies focused on muscle strength [8,27,28,30].The Chair-Stand-Test (30s-CST) was reported in two studies [27,30] and the Sit and Reach Test in one study [28].Aranda-Garcia et al.[9] assessed muscle strength of arms and legs using handgrip and knee extensor.
3.4.2.Psychological measures
One study focused on cognitive measurements (measures of global cognition with the mini mental state examination (MMSE)and semantic fluency test[30]and two studies focused on quality of life [8,16].
3.4.3.Physiological measures
Physiological measurements were evaluated in four studies.Serotonin and cortisol levels were considered in one study as a measure of emotional state [20].Moreover,the Alpha power spectrum was measured in two studies using EEG [22,23].Finally,masseter and temporalis muscle activity was assessed using EMG in one study [31].
3.5.Effects of interventions on outcome measures
3.5.1.Physical effect of EAI
Eight studies investigated the effects of the equine intervention on balance in older adults [7-9,12,27-30].Among them,four studies demonstrated that there was a significant positive effect of EAI on balance [7,27,29,30],two studies showed mixed results[8,28] and two studies demonstrated no effect [9,12].Concerning the positive effects of EAI on balance,it should be noted that two controlled studies highlighted a significant group by time interaction[27,29],while Araujo et al.(2011)[7]highlighted no significant group by time interaction,but only a positive pre-post EAI effect on balance.Two studies conducted on a single group with vulnerable participants(Alzheimer’s dementia and balance deficit)indicated a positive pre-post test effect on balance.Diniz et al.[28] obtained mixed results with a significant effect on the Balance Berg Scale but no effect on the Functional Reach test.Finally,Homnick et al.[8]reported no significant change in the observation period (weeks:0-8) and the follow-up period (weeks: 16-24) but highlighted a significant improvement in balance score from the beginning to the end of the EAI intervention (weeks: 8-16).
Gait was considered in six studies [7,9,27-30].Among them,two studies indicated no effect of EAI on gait[27,29].Only one study showed a significant group by time interaction [9].The other studies indicated a positive effect of EAI on gait only on pre-post tests[7,28,30].
Four studies looked at muscle strength [8,27,28,30].Among them,three demonstrated a significant positive effect of EAI[27,28,30]with the group by time interaction for Araujo et al.(2013)[27] or positive pre-post test effects [28,30].According to Aranda-Garcia et al.[9],significant positive results were observed in the horse exercise group and the traditional exercise group in kneeextensor strength,but only the horse exercise group had significantly faster gait speed.However,the traditional exercise group showed greater improvements in handgrip than the horse exercise group.
3.5.2.Psychological effect of EAI
The only study which measured a cognitive dimension with Alzheimer’s disease showed no effect of EAI [30].Concerning the assessment of the quality of life,Homnick et al.[8],indicated the improved quality of life and Fields et al.[16]showed an increase in conversational social interaction and pleasure.
3.5.3.Physiological effect of EAI
Two studies investigated the effects of the equine intervention on cortical electrical activity effects (with EEG frequency bands[22,23]).They investigated the relative alpha power index which indicates concentration and relaxation.Kim et al.[22]showed that EAI activated faster relative alpha power in all brain domains analyzed.Furthermore,there was a positive significant difference between the horseback riding group and the control group in the prefrontal activity.Similar results were obtained in Cho’s study[23]which compared horseback riding exercises with mechanical horseback riding exercises.Repeated measures analysis of variance showed that the horseback riding group increased the power of fast relative alpha power compared to the mechanical horseback riding group after 12 weeks of intervention.One study analyzed the hormonal effects(serotonin and cortisol levels in blood samples)of horseback riding in older adults [20].The horseback riding groupshowed a significant increase in serotonin and a decrease in cortisol levels between the pre and post-test indicated a better emotional state.Only one study documented masseter and temporalis muscle activity [31].The intervention involving a horse highlighted a significantly lower electromyographic activity for these two muscles.
3.6.Quality of studies
The summary of the quality scores is displayed in Tables 1-3.The quality scoring descriptive statistics include a mean of 11.46([6,18],ET:3.4)[9]scored the highest with 18/28 points.Overall,the findings indicate that the majority of studies were of low quality,particularly for the two items: external validity and power.
4.Discussion
4.1.Effects of EAI on older adults’ health
Three health domains were investigated: physical,psychological,and physiological.Concerning the physical domain,the main findings of this review are that EAI is an effective intervention that improves physical functioning (including balance,gait,and strength)of older adults even in older adults with disabilities.Our results are similar to previous systematic reviews conducted on healthy older adults or people with disabilities [10,11,13].Nowadays,we know that physical activity is beneficial for the health of older adults [32,33],so it is coherent that greater benefits were found in the older adults participating in EAI,than in those who had a daily life routine without any activity.However,a more striking result is the comparison of EAI versus physical activities.Aranda-Garcia et al.[9] for gait and Kim et al.[29] for balance found a greater effect of EAI than for traditional physical activities.Firstly,this difference could be explained by the fact that more dynamic and complex movements were performed during the EAI sessions;the whole body is more involved during an EAI session than for a simple activity (e.g.stooping,turning,etc.).Secondly,during the EAI session,other ancillary and body-stimulating activities were taken into consideration;the older adults who performed the exercises with the horse also had to walk much longer distances due to the size of the equestrian center.They had to walk to the stables to collect the horse,then walk to the training site and return the horse to its stable.Thirdly,the sensory and motor stimuli of the horse’s movements transmitted to the older adult while riding could also improve their physical abilities [34].
Concerning physiological effects,EAI changes hormone levels and brain activity.It increases levels of serotonin and decreases the secretion of cortisol,but it also activates faster relative alpha power in all brain domains analyzed.These effects are similar to those observed during other sports activities.
Concerning the effects of EAI on the psychological domain,our review highlights an improvement in the quality of life of older adults,even in people with Alzheimer’s disease.This is in line with results in the literature on people with disabilities[13,35,36].In the present review,two studies[16,28]found a beneficial effect of the equine intervention on the quality of life of older adults with Alzheimer’s disease.Several explanations can be advanced.First of all,equestrian activities are usually performed in groups and group activities promote social interaction among seniors,an important element of well-being in older adults [37].Secondly,EAI is an outside activity,and connection with nature should be taken into account.Indeed,most studies indicate that direct contact with nature benefits the quality of life of older adults [16,38,39].In addition,communication with the horse and the bond with the animal,in general,are also elements underestimated in the literature but are linked to the well-being of older adults [40,41].All these positive results must be interpreted with caution: only two studies concern the quality of life.Thirdly,links between the physical domain and quality of life are well-established [32] and physical activity adapted to the older adult’s capacities is one of the recommendations regarding aging well and tending towards the optimum quality of life [42].Finally,these links can also be explained by hormonal reasons.EAI has similar effects to sports,it increases serotonin levels (a hormone responsible for well-being)and decreases the secretion of cortisol (a stress hormone).This type of intervention has relaxing effects,decreasing stress.This can certainly explain the improvement in the quality of life of older adults who benefited from EAI.
4.2.Study rigor and study quality
The quality assessment of the thirteen studies highlights that the majority of them were of low quality with a minimum total score of 6[22].Only one study[9]was of sufficiently high quality to be able to legitimately claim significant results.The scores were very low in external validity and statistical power.This indicates that all the studies had the insufficient statistical power to detect clinically important effects and none of the findings could be generalized to an older population.Although the studies reported improvement,the current research evidence is compromised by methodological weaknesses in the study design.Serious risk bias can be highlighted such as small samples,no comparison or control group,no systematic randomization,and lack of details regarding the intervention.This low quality of the studies had already been highlighted in a previous systematic review [43].
4.3.Limitations
Although EAI seems to be a beneficial intervention for older adults,there are several limitations to be considered.Firstly,the high degree of heterogeneity of the studies renders interpreting the results difficult and does not allow them to be generalized.The heterogeneity of the programs and interventions impacts the results,making them more difficult to interpret because several variables are taken into account.Indeed,the contents of sessions differed according to the type of intervention (EAT or EAA),some studies had a specific,predefined program with various therapeutic objectives (EAT),while for others the objectives were only recreational (EAA).In addition,the frequency and the duration of the sessions also varied from one study to another (one session to 36 sessions/15 min to 60 min).Secondly,the physical measures assessed refer to different concepts.Regarding balance,some tools measured both static and dynamic balance(e.g.Berg Balance Scale and Fullerton Advanced Balance Scale),while others assessed only static balance (e.g.sway path length test and platform) or the dynamic balance(Functional Reach Test).Concerning gait,some tools evaluated simple walking(e.g.maximal gait speed on straight lines,step length,and time)and others complex walking which involves executive functions(e.g.TUG).Finally,for muscular strength,some tools measured lower limb strength (e.g.30s-CST,Sit and Reach Test,and knee extensor),while others assessed upper limb strength(e.g.handgrip).Moreover,aging is known to be a complex process resulting in a heterogeneous population.Indeed,with advancing age,people's trajectories vary.Thus,it is complicated to generalize the results,particularly since the studies in our systematic review were conducted on healthy older adults or older adults with neurocognitive and balance disorders.
Finally,it is important to mention that conducting EAI depends on several limiting factors: notably the region and more precisely the geographical proximity of an equestrian center.In addition,the culture of the country is also a factor.Nowadays,this innovative activity has been developed more in certain countries such as Korea,Brazil,and the United States[11,43].This cultural difference can be illustrated,for example,by the Native American population who are likely to have stronger relationships with animals,as they focus on the equality and interdependence of all creatures and perceive possibilities for health and healing in the human-animal bond.Regarding the horse,it is a sacred animal that will guide all individuals in the right direction[44-46].Another factor to consider when conducting this type of intervention is the personal experience of the beneficiary,such as a potential phobia of horses which would generally exclude that person from attending a session.Finally,the economic status would also seem to be a variable to be taken into account,since EAI sessions are quite expensive.Although potential beneficiaries may be aware of the advantages of EAI sessions,many may not be able to afford such services in the private sector[3].
5.Conclusion
Currently,there are few systematic reviews evaluating the effect of EAI on the health of older adults.Our findings provide evidence for promising health outcomes in older adults.The benefits of horse interventions are mainly related to the physical capacities of the older adults,but also show certain benefits for quality of life and the physiological domain.Nevertheless,more studies are needed to confirm the effects of EAI on the psychological health of older adults,taking into account additional factors such as general wellbeing,thymic effects,behavioral disorders,cognitive abilities,social interactions,and medication used.Similarly,further studies are required to verify the frequency and duration of interventions necessary to achieve benefits in older adults.To promote this nonpharmacological intervention in an older adult population,and to counter the poor quality of studies to date,more rigorous research on equine mediation should be pursued.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Lˊea Badin: Conceptualization,Methodology,Investigation,Writing-original draft preparation.ˊEmilie Alibran:Investigation,Writing -review &editing.Kristell Pothier: Writing -review &editing.Nathalie Bailly: Writing -reviewing and editing.
Data availability statement
Authors declare the absence of shared data in the present study.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2022.09.008.
 International Journal of Nursing Sciences2022年4期
International Journal of Nursing Sciences2022年4期
- International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- Nurses’ experiences of caring for preterm infants in pain: A metaethnography
- Mothers overcoming remorse to care for self and baby: An emerging concept
- Development and validation of the Nurse’s Workplace Mental Health Questionnaire
- A comprehensive health education plus monitoring support program for older adults with knee osteoarthritis coexisting with overweight and type 2 diabetes
- Nursing undergraduates’ experiences of a simulation-centred educational program in hospice care in Macao: A qualitative research
- Nursing students’ knowledge and attitude toward diabetic ulcer care and their contributing factors in Indonesia
