Prediction of diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 disease by blood gas parameters using decision trees machine learning model:a retrospective observational study
Mehmet Tahir Huyut,Hilal üstünda?
1 Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics,Faculty of Medicine,Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University,Erzincan,Turkey
2 Department of Physiology,Faculty of Medicine,Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University,Erzincan,Turkey
Abstract The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic went down in history as a pandemic caused by corona-viruses that emerged in 2019 and spread rapidly around the world.The diff erent symptoms of COVID-19 made it diffi cult to understand which variables were more inf luential on the diagnosis,course and mortality of the disease.Machine learning models can accurately assess hidden patterns among risk factors by analyzing large-datasets to quickly predict diagnosis,prognosis and mortality of diseases.Because of this advantage,the use of machine learning models as decision support systems in health services is increasing.The aim of this study is to determine the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 disease with blood-gas data using the Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAID) decision-tree-model,one of the machine learning methods,which is a subf ield of artif icial intelligence.This study was carried out on a total of 686 patients with COVID-19 (n = 343) and non-COVID-19 (n = 343) treated at Erzincan-Mengücek-Gazi-Training and Research-Hospital between April 1,2020 and March 1,2021.Arterial blood gas values of all patients were obtained from the hospital registry system.While the total-accuracyratio of the decision-tree-model was 65.0% in predicting the prognosis of the disease,it was 68.2% in the diagnosis of the disease.According to the results obtained,the low ionized-calcium value (< 1.10 mM) signif icantly predicted the need for intensive care of COVID-19 patients.At admission,low-carboxyhemoglobin (< 1.00%),high-pH (> 7.43),low-sodium (< 135.0 mM),hematocrit (< 40.0%),and methemoglobin(< 1.30%) values are important biomarkers in the diagnosis of COVID-19 and the results were promising.The f indings in the study may aid in the early-diagnosis of the disease and the intensive-care treatment of patients who are severe.The study was approved by the Ministry of Health and Erzincan University Faculty of Medicine Clinical Research Ethics Committee.
Key words: arterial blood gases;artif icial intelligence;carboxyhemoglobin;COVID-19;decision trees;ionized calcium;machine learning models;SARS-CoV-2
INTRODUCTION
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic,which emerged in Wuhan,China at the end of 2019 and caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2),spread rapidly around the world and went down in history as the f irst pandemic caused by corona viruses1.The mechanism of damage caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus in cells,tissues and organs is not fully known.It is characterized by severely atypical respiratory distress in patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia,which may precede radiological changes or other clinical symptoms,including dyspnea.2Hypoxemia in COVID-19 is severe and ultimately is the primary mechanism of multi-organ failure and death.3The underlying pathology is due to the entry of COVID-19 into cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor.This receptor is expressed in many cells,including alveolar epithelial cells and vascular endothelium,which can result in a profound immune response and widespread endothelial dysfunction.4
The diagnosis and treatment of most respiratory system diseases largely depends on an understanding of the basic physiological principles of respiration and gas exchange.
While some of the respiratory system diseases are caused by ventilation failure;others result from the pulmonary membrane,diff usion disorders,or defects in the transport of gases in the blood between the lungs and tissues.5Blood partial pressure of oxygen,partial pressure of carbon dioxide,and pH values obtained from blood gases,which are frequently preferred in the diagnosis,treatment and follow-up of respiratory and metabolic diseases,are among the important tests used to examine lung functions.5-7
Today,machine learning (ML) is used in many f ields such as object recognition,image processing,face recognition,virtual reality,augmented reality,voice recognition,iris recognition,marketing,health,customer service,satellite images,earth science,fraud detection (fraud).It is a subfield and the largest branch of artif icial intelligence (AI).It is seen that AI technologies,which have been used with great success in many f ields in recent years,have started to be used frequently in the diagnosis,prognosis and treatment processes of diseases,especially in the f ield of medicine.The most important reason for this is the power of ML algorithms,which are under AI technologies and accepted as an important part of data mining,to reveal hidden relationships between patterns.In this way,serious success can be achieved in the diagnosis of diseases that show similar symptoms,have intense uncertainties and are diffi cult to distinguish from each other.For example,data mining approaches applied to medical science topics are rapidly being developed due to their high performance in predicting outcomes,reducing drug costs,improving patient health,improving healthcare value and quality,and making real-time decisions to save people’s lives.8
In developed countries,AI research departments associate with hospital to carry out the studies on the “Research and Development,” because the developments in AI technologies not only impacts patients and doctors but also the entire health system.In particular,“Artif icial Intelligence in Medicine” has been def ined as a branch of computer science it has the capacity to analyze complex medical data and help physicians improve patient outcomes.Considering the number of data constantly included in the system in hospitals,information processing capabilities beyond human capacity are needed in order to manage such large data.Today,thanks to AI technologies,predictive discoveries can be made by processing blood,urine and other laboratory samples from patients with powerful learning algorithms.Thanks to these discoveries,the physician can now be more accurate and safe when making a decision about the patient.
In this study,the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 disease was determined by blood gas data using decision trees model from ML algorithms,which is a subf ield of AI.It is thought that the results obtained from this study will guide clinicians in diagnosis and prediction of disease progression and useful strategic issues.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective observational study was conducted taking into account theDeclaration of Helsinkiand was approved by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Turkey and the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University Faculty of Medicine (Ruling No.E-21142744-804.99-70855) on March 23,2020.Between May 1,2020 and March 1,2021,data in accordance with our criteria were collected from the information system of Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University Mengücek Gazi Training and Research Hospital and included in the study.The study only included individuals over the age of 18 years.The laboratory information of the patients participating in the study was the f irst blood values measured at hospital admission.Informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in this study.This study follows the STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement (Additional f ile 1).
Study design,study workflow and participants criteria
Three diff erent patient groups who applied to the Training and Research Hospital of our university between May 2020 and March 2021 were included in this study.First group:those diagnosed with COVID-19 and admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU);Second group:Those diagnosed with COVID-19 and treated in wards outside the intensive care unit (non-ICU);Third group:Patients who were not diagnosed with COVID-19 but had diff erent etiologies and respiratory distress (Control group).Blood gas laboratory data of all patient groups were retrospectively analyzed by f ile scanning.A total of 686 patients,including 131 treated in the ICU unit,212 treated in non-ICU units,and 343 individuals in the control group,were included in the study according to the criteria determined.COVID-19 was diagnosed in our hospital only in cases where SARS-CoV-2 was detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction in nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs during the dates covered by this study.
The workf low of this study consists of two stages.In the f irst step,Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAID)decision tree algorithm was run to predict the prognosis of the disease (separating non-ICU from ICU) with blood gas parameters.In the second stage,CHAID decision tree algorithm was run to predict the diagnosis of the disease (diff erentiating patients with COVID-19 from patients with non-COVID-19)using blood gas parameters.Blood gas biomarkers that are eff ective in the diagnosis and prognosis of the disease were determined by decision tree regression analysis and cut-offvalues were calculated.
Measurements
Age,gender and arterial blood gas;P50 (oxygen tension when hemoglobin is 50% saturated with oxygen),bicarbonate plasma,bilirubin,deoxyhemoglobin,glucoce,HCO3,hematocrit,hemoglobin,carboxyhemoglobin,chlorine,lactate,methemoglobin,oxyhemoglobin,oxygen saturation,osmalarite,pH,potassium,sodium,standard base,total O2,partial pressure of carbon dioxide,partial pressure of oxygen,ionized calcium (iCa) values of the patient and control groups in this study were obtained.Arterial blood gas samples were analyzed and digitally recorded on ABL 700 (Radiometer,Copenhagen,Denmark).
Outcome criterion
The f irst aim of this study is to predict the prognosis of the disease (diff erentiating out of ICU and intensive care unit) by blood gas parameters.Our secondary aim is to predict the diagnosis of the disease (diff erentiating patients with COVID-19 from patients with non-COVID-19) with blood gas parameters.With this methodology,the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 is determined by the blood gas values measured at the time of admission of the patients.
CHAID decision tree analysis
CHAID decision tree method is a non-parametric method that can analyze nominal and quantitative variables together,provides highly reliable predictions on large data sets,and can be used as an alternative to logistic regression models.Besides these benef its,it can detail the relationship structures between predictive variables and provide effi cient and understandable tree-like outputs even in complex data structures.With this superiorty,CHAID decision tree method has a large range of uses.9,10
Preparation of the data set
After data completion,training and test sets were determined by 10-fold cross validation on the measured properties dataset.In addition,the advantage of cross validation was used to minimize the risk of overf itting in the evaluation of training and test sets.This procedure allowed for unbiased generalization estimation while determining the parameters of the decision tree model.9Then,the optimum hyperparameters of the decision tree model were determined by grid search.Non-ICU and ICU patients with COVID-19 were selected as the dependent variable when predicting the prognosis of the disease.When determining the diagnosis of the disease,groups with COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 (Control group)were selected as dependent variables.In addition,a balanced data set was created to increase the success performance of the decision tree model in the diagnosis of COVID-19,and an equal number of patients were included in the COVID-19 group and the non-COVID-19 (Control) group.
Statistical analysis
SPSS Statistics 25 (IBM,Armonk,NY,USA) software was used for statistical analysis.Categorical variables were analyzed with the chi-square test and continuous variables were analyzed with the Mann-WhitneyUtest.The CHAID algorithm,one of the Decision Trees analysis methods,was used.P< 0.05 was considered statistically important.All blood gas parameters obtained as a result of the measurement and age and gender variables of the patients were included in the decision tree model,which was run to determine the variables aff ecting the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19.
RESULTS
Demographic data of patients
The demographic data of this study population are summarized in Figure 1.Of the 131 ICU group patients included in the study,80 (61.1%) were male and 51 (38.9%) female;of the 212 non-ICU group patients,122 (57.5%) were male and 90(42.5%) female;of the 343 control group patients,209 (60.9%)were male and 134 (39.1%) female (Figure 1).

Figure 1:Flowchart of demographic data of this study population.
The gender variable was not found to be signif icant among the patient groups (P> 0.669).Data regarding the age distribution of the study groups are summarized in Table 1.The mean age of the patients in the ICU and non-ICU groups was higher than the control group (P< 0.05).However,there was no signif icant diff erence between the ages of the ICU and non-ICU groups (P> 0.15) (Table 1).
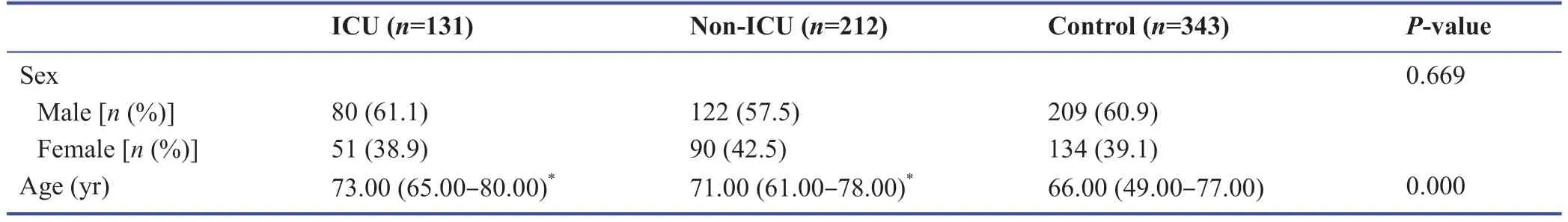
Table 1:Demographic characteristics of the study groups
Predictive blood gas variables affecting the prognosis of the disease
In this research,the CHAID decision tree diagram obtained to identify the blood gas predictors that ?nf luenced the prognosis of COVID-19 disease (separating non-ICU from the ICU)is presented in Figure 2.When the decision tree diagram in Figure 2 was investigated,212 (61.8%) of the COVID-19 patients included in the study were non-ICU and 131 (38.2%)were ICU patients.The “ionized calcium” blood gas parameter was found to be the most effi cient predictor of the prognosis of the disease (χ2= 25.027,P< 0.001;Figure 2).Accordingly,COVID-19 patients are divided into two diff erent groups according to the ionized calcium variable whose cut-off value is determined.According to these f indings,1.10 and lower“ionized calcium” values increases the prognosis of patients COVID-19 signif icantly (27.1%vs.53.9%).In addition,constructing our decision tree with the “ionized calcium”variable to determine disease progression demonstrated the clinical accuracy of our interpretable decision tree (Figure 2).

Figure 2:Tree structure of predictive variables aff ecting the progression of COVlD-19.
The classif ication success rate of the decision tree model,which was created to predict the prognosis of the disease with only the “ionized calcium” variable,was 65.0% and it was found to be statistically signif icant (Table 2).Accordingly,69.3% of non-ICU patients and 58.0% of ICU patients were predicted correctly by considering only the cut-off value of the “ionized calcium” variable (Table 2).
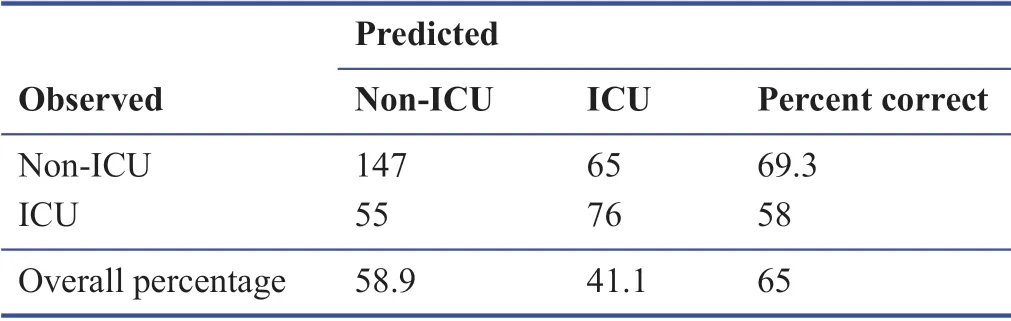
Table 2:Prediction accuracy of “ionized calcium”parameter in prognosis according to CHAID decision tree model among COVID-19 patients
Predictive blood gas variables affecting the detection of COVID-19
In this manuscript,the CHAID decision tree diagram was constructed to identify the blood gas predictors that inf luence the detection of COVID-19 (separating the COVID-19 patients from the Control group) (Figure 3).When the decision tree diagram in Figure 3 was investigated,343 (50.0%) of 686 patients were in the COVID-19 group and 343 (50.0%) were in the Control group.It was seen that the most eff ective blood gas variable on the diagnosis of the disease is “carboxyhemoglobin” (χ2= 76.698,P< 0.001;Figure 3).The presence of Carboxyhemoglobin (and subsequently pH,sodium,hematocrit,methemoglobin) at the root of the decision tree ensures the clinical accuracy of our interpretable Decision Tree (Figure 3) regarding the robustness of the approach to determining the diagnosis of the disease.

Figure 3:Tree structure of predictive variables affecting the diagnosis of the disease.
According to the diagnosis of COVID-19,the “carboxyhemoglobin” variable was divided into three diff erent groups in our decision tree.While the “carboxyhemoglobin” value of 7.3% of the individuals in the study could not be reached,92.7% were classif ied according to cut-off values of ≤ 1.00,(1.00-1.60) and > 1.60.When Figure 3 was examined,62.0%of individuals with a “carboxyhemoglobin” value of ≤ 1.00,43.9% of (1.00-1.60),and 24.0% of individuals with > 1.60 were COVID-19 patients,respectively.According to these f indings,low Carboxyhemoglobin value was found to be an important biomarker in the diagnosis of the disease.In addition,the most inf luential variables in the diagnosis of COVID-19 in individuals with three diff erent “carboxyhemoglobin” values were pH (χ2= 21.765,P< 0.001),sodium (χ2= 10.574,P<0.05) and hematocrit (χ2= 10.574,P< 0.05).In three diff erent“carboxyhemoglobin” groups,individuals with > 7.43 pH,≤135.00 mM sodium and ≤ 40.0% hematocrit values,respectively,had more COVID-19 disease (84.7%,59.2%,37.0%,respectively).In addition,“methemoglobin” was the most inf luential variable in the diagnosis of COVID-19 diseases in individuals with a carboxyhemoglobin value of ≤ 1.00 and a pH value of ≤ 7.43 (χ2= 9.585,P< 0.05).In accordance with the f indings,the rate of having COVID-19 in individuals with a methemoglobin value of ≤ 1.30 was 65.9%,while this rate was 43.4% in individuals with a value of > 1.30.According to this,high pH,low sodium,hematocrit and methemoglobin values were found to be the most important biomarkers in the diagnosis of COVID-19 after low “carboxyhemoglobin” value.
The classif ication success of the decision tree model obtained in order to predict the COVID-19 diagnosis of individuals within the scope of the study is presented in Table 3.The overall classif ication success rate of the decision tree model,which was created with only f ive variables,was 68.2% and it was statistically signif icant (Table 3).In addition,59.5% of 343 COVID-19 individuals and 77.0% of 343 non-COVID-19 individuals were predicted correctly,considering the cut-offvalue of carboxyhemoglobin,hematocrit,sodium,pH and methemoglobin variables with the decision tree model established for the diagnosis of the disease (Table 3).
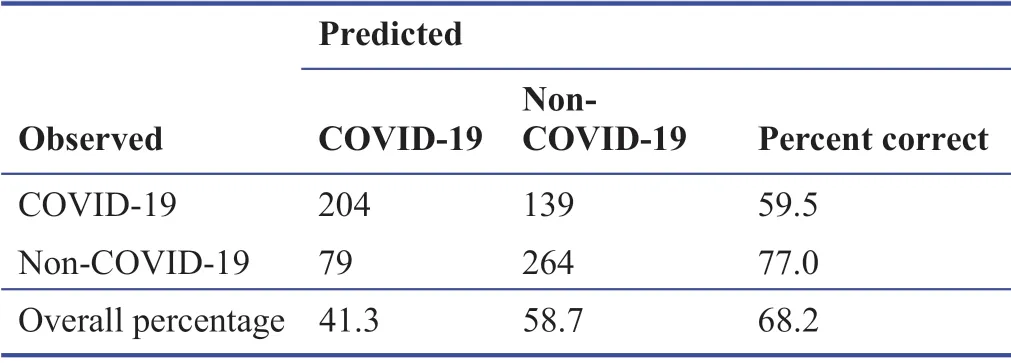
Table 3:Prediction accuracy in diagnosis according to five blood gas parameters of the CHAID decision tree model between COVID-19 (patient group) and non-COVID-19 (control group)
DISCUSSION
The symptoms of COVID-19 are very similar to the common f lu,which includes fever,cough and nasal congestion.11As the pandemic spread,other symptoms emerged,such as loss of taste and smell (anosmia).12,13Severe cases can lead to serious respiratory illness and pneumonia.Those most at risk are the elderly and people with underlying medical problems/comorbid diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.14,15As the disease spreads around the world,more symptoms and features are being noticed that aff ect patient deaths.Having such a broad set of features aff ected by the disease makes it diffi cult to understand which variables have a greater impact on disease mortality.ML models can analyze large datasets to identify diseases,predict progression and mortality,and can be used to help accurately assess risk factors.
It was studied on patients who were hospitalized in the intensive care unit with the diagnosis of COVID-19,were diagnosed with COVID-19 and were treated in non-ICU services,were not diagnosed with COVID-19,but had a diff erent etiology and respiratory disease (control group).Based on the arterial blood gas test results of these three patient groups,decision trees (Figures 2 and 3) were obtained with the CHAID algorithm,which can be used for guidance in cases of doubt in the detection and progression of COVID-19,by evaluating predictors together.10
In this study,COVID-19 patients were importantly older than the control group.The high correlation between advanced age and disease was found to be consistent with the literature.10In addition,age was included in the decision tree models in the study,as it was found to be an important predictor in the determination and progression of the disease.15-18
Although iCa constitutes about half of the calcium level in the circulatory system,it is a free form that is metabolically active and not bound to proteins.Since the circulating ionized level is a better indicator than the total level,it is a more useful parameter in clinical terms.For this reason,it is requested by clinicians,especially to evaluate the follow-up or treatment of critically ill patients.19In this study,the most important arterial blood gas variable aff ecting the prognosis of COVID-19 disease was “ionized calcium” (Figure 2).The overall classif ication accuracy of the decision tree,which was modeled signif icantly only with the ionized calcium variable to predict the progression of COVID-19,was 65.0%.Accordingly,69.3% of non-ICU patients and 58.0% of ICU patients were predicted correctly (Table 2).Other arterial blood gas values were not found to be important in predicting the progression of COVID-19.In this manuscript,“ionized calcium” values (≤ 1.10 mM) signif icantly predicted the need for intensive care in COVID-19 patients.
Although it was emphasized in one study that “methemoglobin” and “carboxyhemoglobin” levels may be associated with the severity of sepsis,these levels were not associated with the prognosis of COVID-19.20In another study,it was stated that carboxyhemoglobin alone cannot be used to diagnose pneumonia of COVID-19 or to predict disease severity.21In another study,low methemoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin values were observed at the beginning of the disease,and it was stated that these values were expected to increase with the progression of the disease.However,it was stated that both variables and their clinical consequences should be further investigated and followed in severe patients.22In addition,studies on intensive care patients indicated that low carboxyhemoglobin levels were associated with high mortality.In another study,it was stated that low carboxyhemoglobin level at admission in COVID-19 patients is a biomarker that can guide early follow-up and treatment planning to prevent severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and mortality.23
In this study,the most substantial arterial blood gas variable in determining the disease was carboxyhemoglobin.After that,arterial blood values of sodium,pH,hematocrit and methemoglobin were found to be important in determining the disease.Low carboxyhemoglobin (< 1.00%),high pH(> 7.43),low sodium (< 135.0 mM),hematocrit (< 40.0%),and methemoglobin (< 1.30%) values were signif icant independent markers in detecting COVID-19.It was noteworthy that blood gas variables that were found to be important in determining COVID-19 were not considered signif icant in the progression of the disease.Arterial blood gas variables,which were found to be important in detecting COVID-19 and predicting its progression,were above the reference values at the time of admission and this was consistent with the literature.The overall classif ication accuracy of the decision tree modeled with f ive variables in determining COVID-19 was 68.2%.Accordingly,59.5% of patients with COVID-19 and 77.0% of individuals without COVID-19 were predicted correctly,and the results were promising.
ML methods,which are increasingly used eff ectively in Medical Services,have the ability to distinguish useful patterns in large-scale data and can identify predictors that are expected to help decision-making process in studies.As a matter of fact,in many studies for the automatic detection of the diagnosis of COVID-19 with ML models,the routine hematochemical values of patients (white blood cell count and platelet,C-reactive protein (CRP),aspartate aminotransferase,alanine aminotransaminase,lactate dehydrogenase plasma levels) were used.In these studies,it was stated that AST,CRP and lymphocyte levels are parameters to be considered and important predictive features in the diagnosis of the disease.10,24-26
In similar ML studies in the literature,it was reported that COVID-19 positivity was associated with lymphopenia,liver and muscle tissue damage,and signif icantly increased CRP.27In another study,a logistic regression ML model was run to identify risk factors for 4542 COVID-19 patients,and f inal predictors were identif ied and reported.In another study,in which the relationship between many laboratory values and disease was determined using data mining methods,aspartate aminotransferase,alanine aminotransaminase,calcium,sodium,potassium,creatinine and CRP were found to be associated with the risk of death.28Other studies using ML models found elevated neutrophil,CRP,lymphocyte and lactate dehydrogenase levels and advanced age variables as predictors of mortality associated with COVID-19 disease.29,30
In many studies,CHAID analysis from decision tree ML models was used as a predictor of diagnosis,prognosis and mortality in the results of these studies may assist clinicians in the diagnosis and treatment of potential COVID-19 patients.Indeed,in one study,predictors of mortality in COVID-19 patients admitted to the emergency room were determined by CHAID analysis.As a result of the study,it was stated that a high Shock Index (SI) value is an important indicator of COVID-19 mortality.31The SI ratio,def ined as the ratio of heart rate to systolic blood pressure,is a biomarker that can be used to understand changes in cardiovascular status and tissue perfusion level.32Similarly,in another study using the CHAID decision tree model,the CIT (CRP × international normalized ratio × troponin) biomarker was found to be important in the diagnosis of COVID-19,while the CRP level was found to be important in predicting its prognosis.10
The COVID-19 disease has turned into a worldwide health crisis and has caused signif icant problems in emergency rooms and intensive care units.Therefore,it is important to evaluate individuals who need intensive care and have high mortality expectations in the early stage of the disease (at admission),for the health system to work more effi ciently.Findings related to the decision trees obtained in our study may be helpful in the early diagnosis of the disease and in the intensive care treatment of severe patients.In addition,these results are important in terms of maintaining the effi ciency of the health system and reducing the pressure of time,cost and workload.
Since this study is a retrospective study obtained from registries,the inaccessibility of patients’ comorbidity data and the fact that it is a single center are the limitations of this study.Since variables cannot be controlled in retrospective studies,our study data may need to be supported by prospective cohort studies.Moreover,the data used in the study were obtained from populations of COVID-19 patients in diff erent seasons.For this reason,the parameter values in this article may have shown seasonal discrepancy from analogous studies.Studies involving larger patient groups and diff erent centers will further clarify the importance of arterial blood gas laboratory values in the COVID-19 outbreak.
Author contributions
MTH:Conceived the ideas or experimental design of the study,organized the material and methodology,applied the analyses,interpreted,discussed and written,f ixed the revisions;Hü:scanned the literature,contributed to the introduction and discussion,collected the material.
Conflicts of interest
Authors declare no conf lict of interest.
Financial support
The authors did not receive any f inancial support for this study.
Institutional review board statement
This retrospective observational study was conducted in accordance with the 1989Declaration of Helsinkiand was approved by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Turkey and the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University Faculty of Medicin.
Declaration of participant consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in this study.
Reporting statement
This study follows the STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement.
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of Faculty of Medicine,Erzincan Binali Y?ld?r?m University.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by both authors before publication.
Data sharing statement
Datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Additional file
Additional f le 1:STROBE checklist.
- Medical Gas Research的其它文章
- Can united airway disease be the cause of variable severity experience of COVID-19 in health care workers?
- COVID-19 is more dangerous for older people and its severity is increasing:a case-control study
- COVID-19 incidence and local ozone level:is there any association?
- Acute asthma exacerbation after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine(Sinovac?):a case report
- Ozone gas applied through nebulizat?on as adjuvant treatment for lung respiratory d?seases due to COVID-19 infect?ons:a prospective randomized trial
- Effects of Iranian Polyherbal Syrup (Zufa syrup)on oxygen saturation and clinical symptoms in suspected patients with COVID-19:a triple-blinded,randomized,placebo-controlled trial

