Short arm cast is as effective as long arm cast in maintaining distal radius fracture reduction:Results of the SLA-VER noninferiority trial
lNTRODUCTlON
Distal radius fractures (DRFs) are a common clinical challenge in orthopaedic trauma care. Traditionally,it was thought that immobilization including the elbow would ensure better control of fracture instability,prevent loss of reduction,and result in better clinical outcomes. However,long arm casts are cumbersome and treatment with lighter short arm casts is generally considered a more comfortable option for patients. Currently,there is no general agreement on how best to immobilize a DRF. Various methods have been described,but no one approach has been identified as being more effective than another[1-4]. According to the latest clinical practice guidelines from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,released in 2009,the evidence available for and against elbow immobilization in patients treated with a cast is “inconclusive” and the choice between them is down to the clinician’s judgment[5]. The hypothesis that short arm casts might perform as well as long arm casts in maintaining the reduction of DRFs has been tested in a number of previous studies. These superiority randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have not found a significant difference in outcome and risk of loss of reduction between below elbow cast (BEC) and above elbow cast (AEC)[6-11]. However,the absence of any significant difference in these studies does not necessarily indicate equivalence[12]. To compare the efficacy and tolerability of these two treatment approaches,we designed a noninferiority randomized trial using predefined minimal clinically important difference thresholds.
In this paper,the terms short arm cast and BEC or long arm cast and AEC are used interchangeably.
The old owl had seen and heard about what happened to people. Some became better and some became worse. But the old owl had become wiser each and every day.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Design
The SLA-VER trial is a prospective,monocentric,randomized,parallel-group,open label,blinded,noninferiority trial (PROBE design),comparing the efficacy of BEC and AEC in maintaining reduction of manipulated DRFs. This study was approved by the local institutional review board (CE1165CESC),conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki,and registered on ClinicalTrials.org (NCT03468023). All patients enrolled gave written informed consent.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was fracture reduction maintenance,measured as variation in radial length (RL),radial inclination (RI),and volar tilt (VT). The secondary outcomes included disability of arm,shoulder and hand (DASH) scores and short form 12 (SF-12) scores as measures of cast tolerability.
Population
All patients admitted to the emergency room with a diagnosis of DRF were enrolled according to the following inclusion criteria:Age ≥ 18 years; candidates for nonoperative treatment; displaced fracture requiring manipulation. The exclusion criteria were:Skeletally immature patients (less than 18); undisplaced fracture; fracture requiring surgical treatment; open fracture; hand/wrist/forehand skin lesion on fractured limb; vascular or neurological deficit; bilateral fracture; association with homolateral upper limb fracture. Patients with any medical comorbidity were included,but pregnant patients or patients requiring urgent or life-saving procedures were excluded. Patients were excluded from the study (
dropouts) if reduction could not be achieved after two attempts (after which surgical treatment was offered),the cast was damaged or removed during treatment,or consent was withdrawn[13].
Procedures
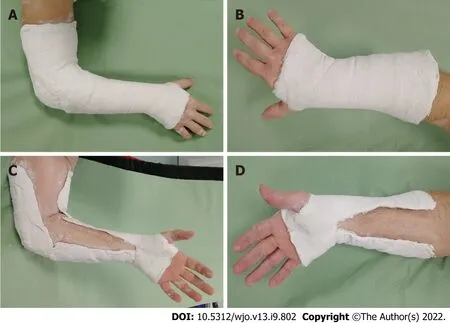
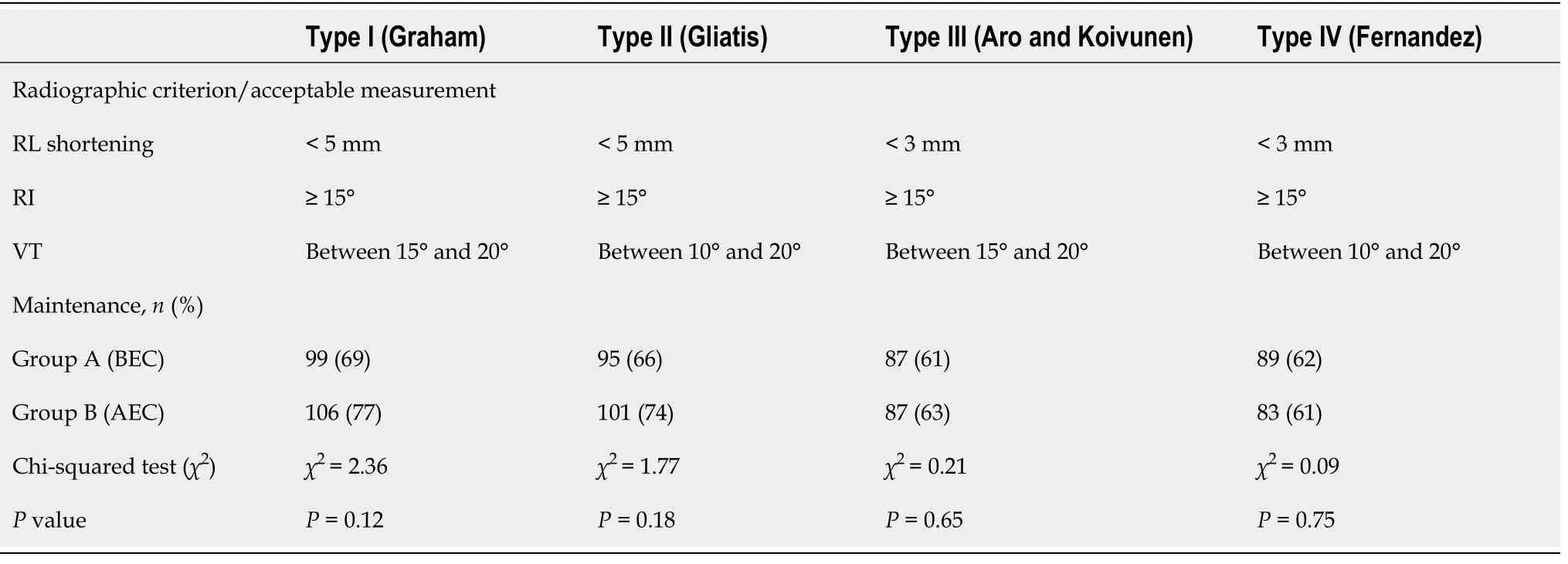
Randomization was carried out by a statistician with no involvement in the clinical care of patients. Software random allocation in blocks of 4 resulted in 353 sequentially numbered opaque sealed envelopes. When a patient was eligible for enrollment,an envelope was opened to assign the participant to a treatment group. Closed manipulation was performed under hematoma block,and the forearm was immobilized in an opposite-to-dislocation position. The arm cast was a radial gutter made of plaster of Paris (POP) that was left open on the volar side to allow for swelling and then circumferentially closed 5-7 d later by applying an extra layer of POP (Figure 1). BEC patients were treated with a BEC extending from the metacarpal heads to 2-4 cm from the elbow crease. AEC patients were treated with an AEC extending from the metacarpal heads to the middle third of the arm. Posteroanterior (PA) and lateral view X-rays were taken pre and post manipulation and at 7 and 35 d. The radial gutter was closed at the first office visit and removed at the final visit. If closed manipulation failed to achieve satisfactory reduction,patients were offered surgical treatment and excluded from the study. If reduction was lost at 7 d,patients were offered surgical treatment. These patients were still considered for analysis as subjects who did not maintain satisfactory reduction at the final follow-up. Radiographic parameters were determined at each X-ray examination. RL was measured on the PA view as the distance between two lines drawn perpendicularly to the radial shaft long axis:one at the tip of the radial styloid and one at the ulnar border of the radius articular surface at the central reference point,which is a point midway between the volar and dorsal ulnar corners to eliminate variation caused by dorsal angulation as described by Slutsky[14]. RI was measured on the PA view by determining the angle between a line passing through the tip of the radial styloid and the medial corner of the articular surface of the radius and a line perpendicular to the shaft of the radius. VT was measured on the lateral view by the angle between the line of the distal articular surface (passing through the two most distal points of the dorsal and volar lips of the radius) and the longitudinal axis of the radius[14,15]. Fracture stability was assessed according to Lafontaine (dorsal angulation > 20°,dorsal comminution,articular involvement,associated ulnar fracture,and age > 60 years):If three or more of these criteria were present,the fracture was defined unstable[16]. The casting technique was assessed by means of cast index and three-point index[17,18]. Reduction was considered to be maintained when the following criteria,described by Graham,were met[13]:Loss of radial length < 5 mm,radial inclination ≥ 15°,and volar tilt between +15° and -20°. Given the variability of the criteria used to assess acceptability of reduction,we decided to further test the dataset against three other sets of criteria (combinations of different thresholds of RL,RI,and VT). All measurements were performed by three investigators,none of whom were involved in patient recruitment and all of whom were blinded to patient group assignment. Patients were stratified by age,sex,presence of osteoporosis (indirectly assessed by osteoporosis-specific drug consumption),fracture type (according to AO classification),and fracture stability (according to Lafontaine’s criteria)[19]. At the final follow-up visit,patients were asked to complete DASH and SF-12 questionnaires and elbow range of movement (ROM) after cast removal was also recorded[20,21]. Protocol details have been published previously[22] and are available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03468023.
Statistical analysis
For the study to have 80% power to show a difference between the treatments with a two-sided type 1 error rate of 5%,we calculated that approximately 150 patients would be required for each group using a 2 mm difference in RL and a 3° difference in RI and VT as noninferiority thresholds. These estimates of minimal clinically important differences were based on previous reports of interobserver variability of up to 3° in radiographic parameter measurement and considerable deterioration of clinical outcome when shortening of RL was > 5 mm[15,23,24]. We included 53 additional patients to make up for a predicted 15% dropout rate. Since our aim was to identify the real treatment efficacy under optimal conditions,we conducted a per-protocol analysis. In noninferiority trials,both intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses are recommended[25]. In this trial,we did not include dropouts in the final analysis,since doing so would have introduced a confounding effect of surgery. We did not use baseline differences to decide whether and which covariates should be used to adjust treatment effect because we assumed that,in RCTs,any baseline difference between the two groups is attributable to chance and thus negligible[26]. The 95%CI was calculated for continuous variables following a normal distribution. Noninferiority
-tests were used to compare radiological parameters,and chi-squared tests were used to compare percentages of loss of reduction between the two groups. DASH and SF-12 scores between the BEC and AEC groups were compared using superiority
-tests. All variables included in the analysis were complete,with no missing data. Analyses were performed using SAS 9.4.
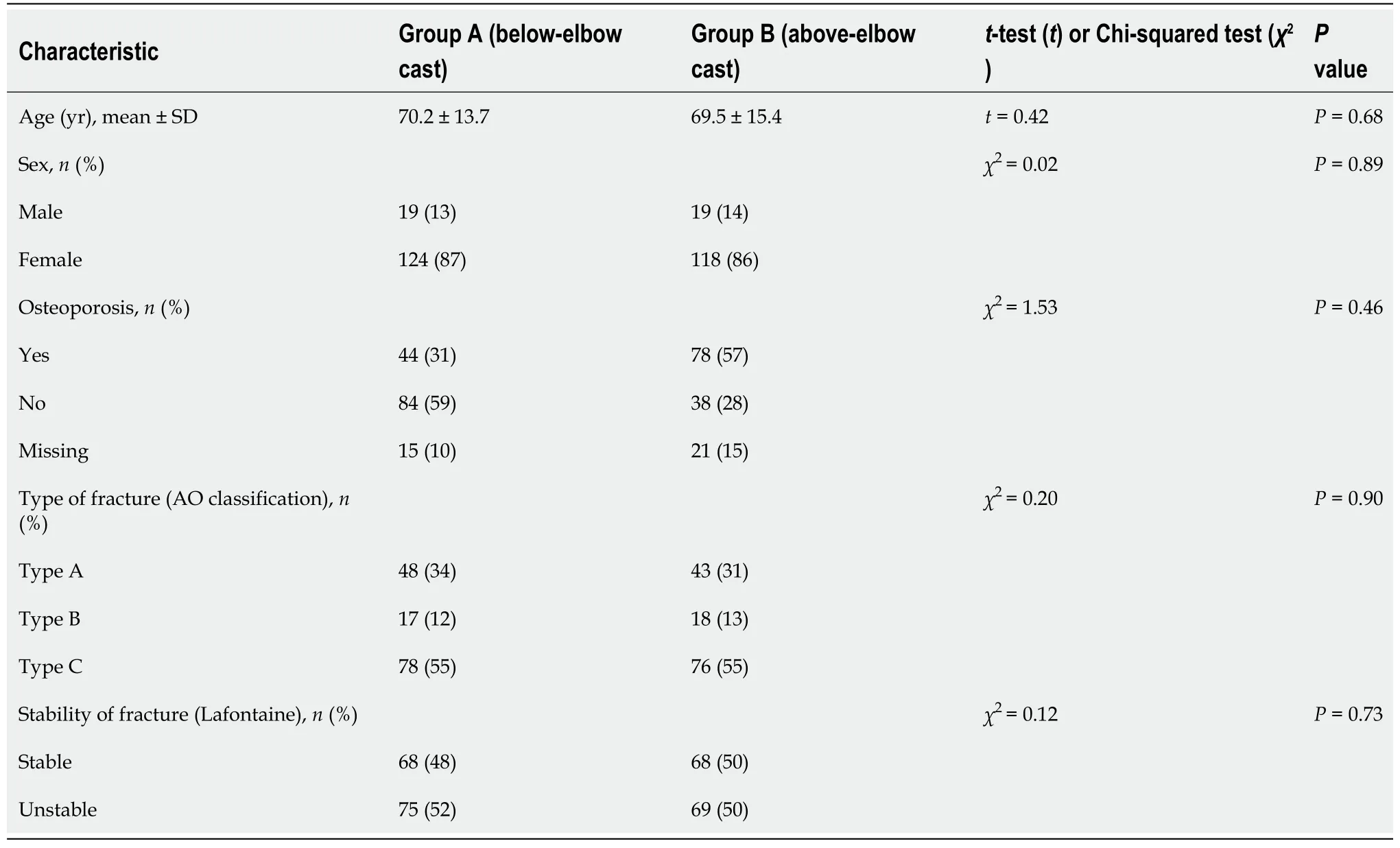
RESULTS
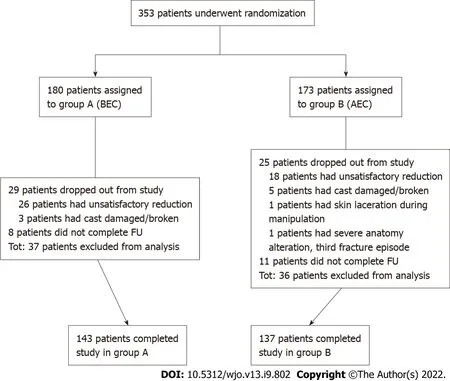
Between March 2017 and February 2020,353 eligible patients were enrolled in the trial. Of these,180 patients were randomly assigned to treatment group A (BEC) and 173 were randomly assigned to treatment group B (AEC). In group A,29 patients dropped out of the study,and 8 did not complete the follow-up. In group B,25 patients dropped out from the study,and 11 did not complete the follow-up (Figure 2). Dropouts (and dropout reasons) were similar between the groups. A total of 280 patients (143 in group A and 137 in group B) completed the study and were included in the analysis. The study groups were similar with respect to age,sex,osteoporosis,type of fracture (AO classification),and stability of fracture,as shown in Table 1. Cast index and three-point index were homogeneous between the groups (
= 1.72,
= 0.19 and
= 0.06,
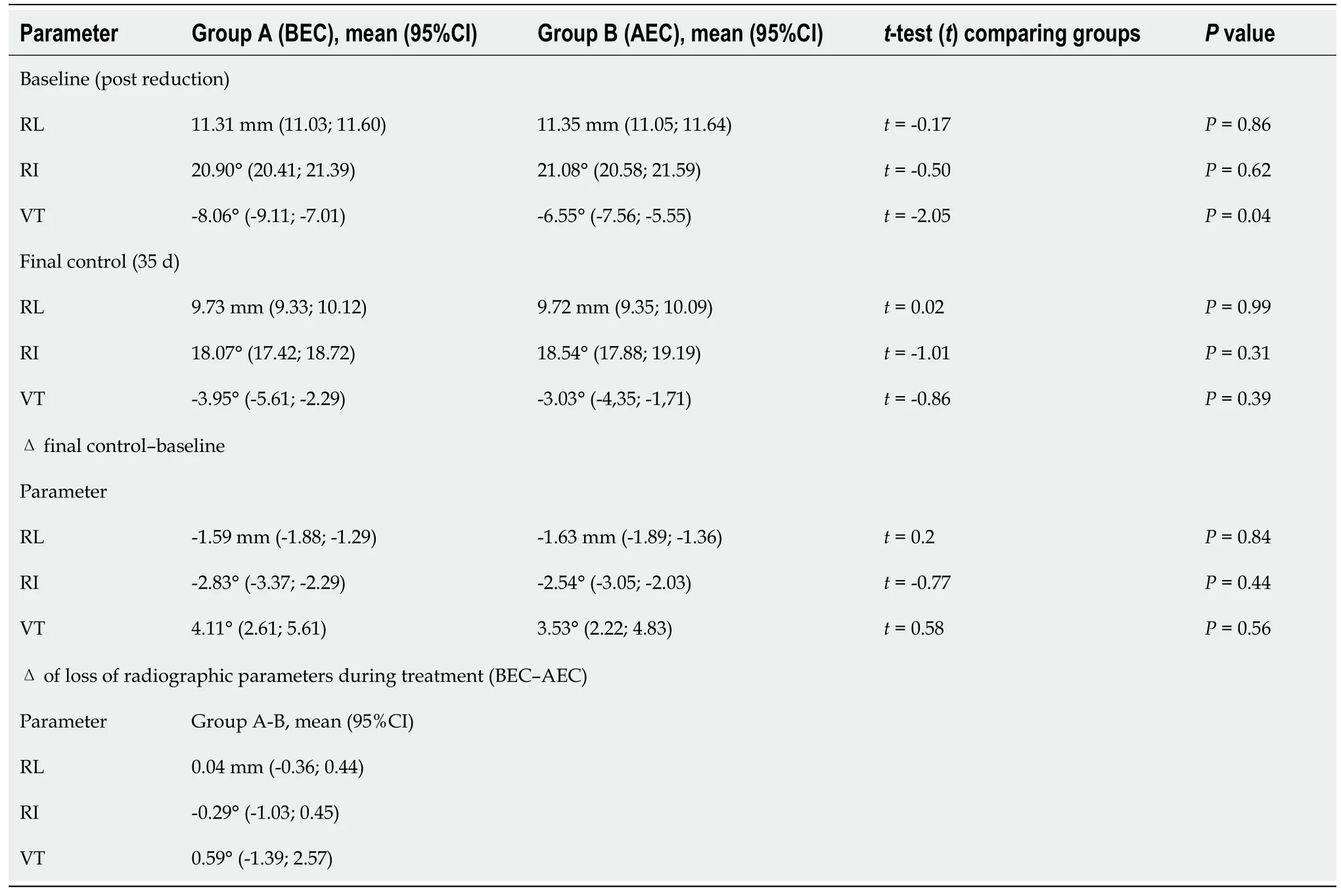
= 0.79,respectively). Randomization resulted in two wellbalanced study groups. The mean time of immobilization was 33 d (95%CI:31.88-34.10) for BEC patients and 32.6 d (95%CI:31.5-33.63) for AEC patients. Nine patients treated with BEC and ten treated with AEC lost reduction at 7 d. Seven were treated surgically,and two continued nonoperative treatment in the BEC group; seven were treated surgically,and three continued nonoperative treatment in the AEC group. Upon removal of cast at the final follow-up,the mean loss of RL was -1.59 mm for BEC
-1.63 mm for AEC (between-group difference:0.04 mm; 95%CI:-0.36-0.44); the mean loss of RI was -2.83° in BEC
-2.54° in AEC (between-group difference:-0.29°; 95%CI:-1.03-0.45); the mean loss of VT was 4.11° in BEC
3.52° in AEC (between-group difference:0.59°; 95%CI:-1.39-2.57). Differences in loss of RL,RI,and VT during treatment between the groups reached statistical significance when tested for noninferiority (
< 0.0001 for RL,
< 0.0001 for RI,and
= 0.0087 for VT),and all differences were below the prefixed thresholds outlined above. Differences between the final and baseline radiographic parameters are reported in Table 2. According to Graham’s criteria,99 (69%) out of 143 patients treated with BEC maintained satisfactory reduction as opposed to 106 (77%) out of 137 patients treated with AEC. This difference was not significant (
= 0.12; Table 3). Considering that the percentage of fractures labelled as “maintained” varies according to the criteria of acceptability of reduction used,we tested a further three sets of criteria as described above. In all cases,no statistically significant difference was observed (66% maintained in BEC
74% in AEC for type 2,61% maintained in BEC
62% in AEC for type 3,and 62% maintained in BEC
61% in AEC for type 4; Table 3). DASH score,SF-12 [physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS)] scores,and elbow ROM were collected for 122 out of 280 patients:55 (38%) patients in group A and 67 (49%) patients in group B. DASH score for BEC patients was 59 (95%CI:53.8-64.2) and 59.9 (95%CI:55.6-64.3) for AEC patients; the mean PCS and MCS scores were 34.9 (95%CI:32.9-36.9) and 43.6 (95%CI:40.5-46.8),respectively,for BEC patients and 36.6 (95%CI:34.9-38.2) and 41.8 (95%CI:39.1-44.5) for AEC patients. No difference was observed between patient groups. Subgroup analysis for dominant side fracture did not change the result. Regarding elbow ROM,BEC patients exhibited a mean flexion of 123.6° (95%CI:117.1-130.1),mean extension of 6.7° (95%CI:2.5-10.8),mean pronation of 69.5° (95%CI:63.8-75.3),and mean supination of 52.5° (95%CI:45.6-59.3). AEC patients had similar ROM,with a mean flexion of 123.9° (95%CI:118.9-128.9),mean extension of 5.5° (95%CI:1.4-9.5),mean pronation of 72.1° (95%CI:66.4-77.9),and mean supination of 52.9° (95%CI:45.5-60.3). Again,no difference was observed between the groups.
DlSCUSSlON
Noninferiority tests are the most appropriate way to evaluate the hypothesis that BEC and AEC have similar efficacy. They are based on minimal clinically important thresholds that are established
by drawing on empirical assumptions. When observed between-treatment differences fall below these thresholds,treatments can be considered equivalent. Statistical superiority tests,for example,the percentage of fractures that maintain reduction
the percentage of fractures that lose reduction,can be misleading since they tell us nothing about equivalence[12]. Therefore,in the current study,we analysed both dichotomic variables (
,percentage of reduction maintenance) and continuous variables (
,radiographic radial parameters) for which noninferiority thresholds could be predetermined. By employing a noninferiority design,the current study showed that the efficacy of BEC in maintaining the reduction of manipulated DRFs is similar to that of AEC. According to our model,when clinicians have to choose between using BEC or AEC to immobilize a DRF,the maximum predictable outcome difference between the two treatments does not exceed 2 mm in terms of RL loss and 3° in terms of RI and VT loss
Maintenance of reduction of DRFs is more likely to depend on factors other than length of cast used,for example,patient age and stability or type of fracture. SLA-VER has some limitations that warrant discussion. Quality of reduction was not assessed and could have potentially influenced the difference between BEC and AEC. Given that no computerized tomography was carried out,we may not have accurately measured every articular gap,and it is possible that its prevalence might be different between the study groups. However,our approach is consistent with general clinical practice. Furthermore,we limited our investigation to radiological outcomes only and did not include clinical outcome measures. SLA-VER aimed only at ascertaining whether the type of casting used affects the likelihood of fracture maintenance. A large amount of data about factors associated with loss of reduction risk and clinical outcome has already been published[16,27-39]. Only a small number of patients completed the DASH and SF-12 questionnaires and received elbow ROM measurements,even though this was a secondary study endpoint. Our data did not reveal a clear difference in patient comfort between BEC and AEC and this remained true even after subgroup analysis of dominant side fractures. Surprisingly,elbow range of motion was not affected by the type of cast as one would have expected. One explanation could be that the time of immobilization may have been too short to result in significant elbow stiffness or that the absence of elbow injury might have contributed to preserving joint mobility. This finding is also reported by Okamura
[11]. Finally,it may be that DASH scores are not the most appropriate way to assess cast comfort. Bong
[7] found better DASH scores in below-elbow splints,although to a lesser degree than expected,suggesting that DASH might not be able to specifically address the comfort level of the two constructs. Furthermore,Caruso
[10] did not find any difference in DASH scores between BEC and AEC at the 4 wk follow-up but reported a significant difference in favour of BEC using the Mayo elbow score. Similarly,Park
[8] did not find any difference in DASH score between BEC and AEC,although they found a correlation with the dominant side and a higher incidence of shoulder pain in the latter group. Nevertheless,BEC is broadly considered more comfortable and preferable than AEC[8].
CONCLUSlON
To test the hypothesis that blocking the elbow is not necessary and that a below arm cast (BEC)performs as well as an above elbow cast (AEC).
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
I hope you get sick when someone blows smoke in your face. I don’t care if you try beer once, but I hope you won’t like it. And if a friend offers you a joint5 or any drugs, I hope you are smart enough to realize that person is not your friend.
Research motivation
Further large population randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses are required to confirm the hypothesis that BEC should become the option of choice for DRF treatment.
Distal radius fracture (DRF) treatment is a common challenge in orthopaedic trauma care. Uncertainty exists on how best to immobilize a DRF.
The words of Proverbs 11 came to mind: “A good man [person] is guided…and directed by honesty…Be sure you know a person well before you vouch9 for his [or her] credit
Research objectives
Data from this trial lead us to conclude that BEC performs as well as AEC in maintaining reduction of a manipulated DRF. When clinicians have to choose between BEC and AEC,the maximum predictable difference does not exceed 2 mm in terms of RL loss and 3° in terms of RI and VT loss. We recommend BEC over AEC for its non-inferior performance and better tolerability.
Research methods
This study was registered on ClinicalTrials.org (NCT03468023).
Research results
Rates of loss of reduction were similar between BEC and AEC. Variation of radiographic parameters (RL,RI,and VT) was similar between BEC and AEC and fell within the predetermined noninferiority thresholds.
Research conclusions
BEC performs as well as AEC in maintaining reduction of a manipulated DRF.
Research perspectives
The necessity of blocking the elbow when immobilizing a DRF is still a matter of debate.
But even now she could not bend her proud heart, and she said, Though he has executed these two tasks, yet he shall not be my husband till he brings me an apple from the tree of life
The authors would like to sincerely thank Dr. Anna Powell,medical writer,for her expertise in proofreading the manuscript and Dr. Giuseppe Palazzolo,MD,for his help in reviewing patients’ radiological records.
The authors have read the CONSORT 2010 statement,and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CONSORT 2010 statement.
This study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (CE1165CESC).
A noninferiority randomized clinical trial was conducted on 280 patients diagnosed with a DRF managed nonsurgically. Loss of reduction was evaluated considering variation in radiographic parameters [radial length (RL),radial inclination (RI),and volar tilt (VT)].
All study participants provided informed written consent prior to study enrollment.
Each author certifies that he or she has no conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Dataset and statistical code is available from the corresponding author on request.
When we had finished our sweetmeats or fruit she would accompany us to the stoep, bidding us thank our mother for her gift and sending quaint11, old-fashioned messages to her and the Father
Dib G and Cengarle M equally conceptualized and designated the research work; Maluta T contributed to organizing and performing the research; Marconato G performed the research and was actively involved together with Dib G and Cengarle M in reviewing patients' X-ray; Bernasconi A analyzed the data; Dib G drafted the manuscript; Magnan B and Corain M revised the manuscript.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See:https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
When he was safe on shore the little hare said to him: Now this is what you have to do: dress yourself like a Breton seeking a place as stable-boy, and go and offer your services to your father
Italy
Giovanni Dib 0000-0002-3213-5204; Bruno Magnan 0000-0002-9112-9349.
Zhang H
Cola-Mattheo rose at dawn, and taking a basket on his arm, he went to the market, and bought all the pomegranates, apricots, cherries, and other fruit he could find there, and sowed the seeds and stones in the palace garden
On Friday morning, Susan took the bus to work as usual. As she was exiting the bus, the driver said, Miss, I sure envy you. Curious, Susan asked the driver why.
Wang TQ
The popular expression There are no atheists in foxholes17 applied18 to our B-17 as well. God spared us above Brunswick; I think we may have been the best-praying crew in the Eighth Air Force.
Zhang H
1 Sarmiento A,Pratt GW,Berry NC,Sinclair WF. Colles' fractures. Functional bracing in supination.
1975; 57:311-317 [PMID:1123382]
2 Sarmiento A. The brachioradialis as a deforming force in Colles' fractures.
1965; 38:86-92 [PMID:5889097]
3 Bünger C,S?lund K,Rasmussen P. Early results after Colles' fracture:functional bracing in supination vs dorsal plaster immobilization.
1984; 103:251-256 [PMID:6391415 DOI:10.1007/BF00387330]
4 Wahlstr?m O. Treatment of Colles' fracture. A prospective comparison of three different positions of immobilization.
1982; 53:225-228 [PMID:7136568 DOI:10.3109/17453678208992206]
5 Lichtman DM,Bindra RR,Boyer MI,Putnam MD,Ring D,Slutsky DJ,Taras JS,Watters WC 3rd,Goldberg MJ,Keith M,Turkelson CM,Wies JL,Haralson RH 3rd,Boyer KM,Hitchcock K,Raymond L. Treatment of distal radius fractures.
2010; 18:180-189 [PMID:20190108 DOI:10.5435/00124635-201003000-00007]
6 Sahin M,Ta?ba? BA,Da?lar B,Bayrakci K,Sava? MS,Günel U. [The effect of long- or short-arm casting on the stability of reduction and bone mineral density in conservative treatment of Colles' fractures].
2005; 39:30-34 [PMID:15805751]
7 Bong MR,Egol KA,Leibman M,Koval KJ. A comparison of immediate postreduction splinting constructs for controlling initial displacement of fractures of the distal radius:a prospective randomized study of long-arm versus short-arm splinting.
2006; 31:766-770 [PMID:16713840 DOI:10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.01.016]
8 Park MJ,Kim JP,Lee HI,Lim TK,Jung HS,Lee JS. Is a short arm cast appropriate for stable distal radius fractures in patients older than 55 years?
2017; 42:487-492 [PMID:28490225 DOI:10.1177/1753193417690464]
9 Gamba C,Fernandez FAM,Llavall MC,Diez XL,Perez FS. Which immobilization is better for distal radius fracture?
2017; 41:1723-1727 [PMID:28578470 DOI:10.1007/s00264-017-3518-y]
10 Caruso G,Tonon F,Gildone A,Andreotti M,Altavilla R,Valentini A,Valpiani G,Massari L. Below-elbow or aboveelbow cast for conservative treatment of extra-articular distal radius fractures with dorsal displacement:a prospective randomized trial.
2019; 14:477 [PMID:31888682 DOI:10.1186/s13018-019-1530-1]
11 Okamura A,de Moraes VY,Neto JR,Tamaoki MJ,Faloppa F,Belloti JC. No benefit for elbow blocking on conservative treatment of distal radius fractures:A 6-month randomized controlled trial.
2021; 16:e0252667 [PMID:34111160 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0252667]
12 Harris AH,Fernandes-Taylor S,Giori N. "Not statistically different" does not necessarily mean "the same":the important but underappreciated distinction between difference and equivalence studies.
2012; 94:e29 [PMID:22398743 DOI:10.2106/JBJS.K.00568]
13 Graham TJ. Surgical Correction of Malunited Fractures of the Distal Radius.
1997; 5:270-281 [PMID:10795063 DOI:10.5435/00124635-199709000-00005]
14 Slutsky DJ. Principles and practice of wrist surgery. Philadelphia PA:Saunders Elsevier,2010
15 Johnson PG,Szabo RM. Angle measurements of the distal radius:a cadaver study.
1993; 22:243-246 [PMID:8316865 DOI:10.1007/BF00197667]
16 Lafontaine M,Hardy D,Delince P. Stability assessment of distal radius fractures.
1989; 20:208-210 [PMID:2592094 DOI:10.1016/0020-1383(89)90113-7]
17 Chess DG,Hyndman JC,Leahey JL,Brown DC,Sinclair AM. Short arm plaster cast for distal pediatric forearm fractures.
1994; 14:211-213 [PMID:8188836 DOI:10.1097/01241398-199403000-00015]
18 Alemdaro?lu KB,Iltar S,Aydo?an NH,Say F,Kilin? CY,Tiftik?i U. Three-point index in predicting redisplacement of extra-articular distal radial fractures in adults.
2010; 41:197-203 [PMID:19782974 DOI:10.1016/j.injury.2009.08.021]
19 Müller ME,Koch P,Nazarian S,Schatzker J. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. Berlin,Heidelberg:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1990
20 Hudak PL,Amadio PC,Bombardier C. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure:the DASH (disabilities of the arm,shoulder and hand) [corrected]. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG).
1996; 29:602-608 [PMID:8773720 DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199606)29:6<602::AID-AJIM4>3.0.CO;2-L]
21 Jenkinson C,Layte R. Development and testing of the UK SF-12 (short form health survey).
1997; 2:14-18 [PMID:10180648 DOI:10.1177/135581969700200105]
22 Maluta T,Cengarle M,Dib G,Bernasconi A,Lavini F,Ricci M,Vecchini E,Samaila EM,Magnan B. SLA-VER:study protocol description and preliminar results of the first italian RCT on conservative treatment of distal radial fractures.
2019; 90:54-60 [PMID:30714999 DOI:10.23750/abm.v90i1-S.8083]
23 DiBenedetto MR,Lubbers LM,Ruff ME,Nappi JF,Coleman CR. Quantification of error in measurement of radial inclination angle and radial-carpal distance.
1991; 16:399-400 [PMID:1861017 DOI:10.1016/0363-5023(91)90004-u]
24 Aro HT,Koivunen T. Minor axial shortening of the radius affects outcome of Colles' fracture treatment.
1991; 16:392-398 [PMID:1861016 DOI:10.1016/0363-5023(91)90003-t]
25 Shah PB. Intention-to-treat and per-protocol analysis.
2011; 183:696; author reply 696 [PMID:21464181 DOI:10.1503/cmaj.111-2033]
26 Senn S. Statistical issues in drug development. 2nd ed. Chichester,England,Hoboken,NJ:John Wiley & Sons,2007
27 Jaremko JL,Lambert RG,Rowe BH,Johnson JA,Majumdar SR. Do radiographic indices of distal radius fracture reduction predict outcomes in older adults receiving conservative treatment?
2007; 62:65-72 [PMID:17145266 DOI:10.1016/j.crad.2006.08.013]
28 Bentohami A,Bijlsma TS,Goslings JC,de Reuver P,Kaufmann L,Schep NW. Radiological criteria for acceptable reduction of extra-articular distal radial fractures are not predictive for patient-reported functional outcome.
2013; 38:524-529 [PMID:23186862 DOI:10.1177/1753193412468266]
29 Cowie J,Anakwe R,McQueen M. Factors associated with one-year outcome after distal radial fracture treatment.
2015; 23:24-28 [PMID:25920638 DOI:10.1177/230949901502300106]
30 Maluta T,Dib G,Cengarle M,Bernasconi A,Samaila E,Magnan B. Below- vs above-elbow cast for distal radius fractures:is elbow immobilization really effective for reduction maintenance?
2019; 43:2391-2397 [PMID:30324309 DOI:10.1007/s00264-018-4197-z]
31 Wadsten M?,Sayed-Noor AS,Englund E,Buttazzoni GG,Sj?dén GO. Cortical comminution in distal radial fractures can predict the radiological outcome:a cohort multicentre study.
2014; 96-B:978-983 [PMID:24986954 DOI:10.1302/0301-620X.96B7.32728]
32 Walenkamp MM,Aydin S,Mulders MA,Goslings JC,Schep NW. Predictors of unstable distal radius fractures:a systematic review and meta-analysis.
2016; 41:501-515 [PMID:26420817 DOI:10.1177/1753193415604795]
33 Leone J,Bhandari M,Adili A,McKenzie S,Moro JK,Dunlop RB. Predictors of early and late instability following conservative treatment of extra-articular distal radius fractures.
2004; 124:38-41 [PMID:14608466 DOI:10.1007/s00402-003-0597-6]
34 Gliatis JD,Plessas SJ,Davis TR. Outcome of distal radial fractures in young adults.
2000; 25:535-543 [PMID:11106514 DOI:10.1054/jhsb.2000.0373]
35 Kodama N,Takemura Y,Ueba H,Imai S,Matsusue Y. Acceptable parameters for alignment of distal radius fracture with conservative treatment in elderly patients.
2014; 19:292-297 [PMID:24338051 DOI:10.1007/s00776-013-0514-y]
36 Mackenney PJ,McQueen MM,Elton R. Prediction of instability in distal radial fractures.
2006; 88:1944-1951 [PMID:16951109 DOI:10.2106/JBJS.D.02520]
37 Makhni EC,Ewald TJ,Kelly S,Day CS. Effect of patient age on the radiographic outcomes of distal radius fractures subject to nonoperative treatment.
2008; 33:1301-1308 [PMID:18929192 DOI:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.04.031]
38 Gutiérrez-Monclus R,Gutiérrez-Espinoza H,Zavala-González J,Olguín-Huerta C,Rubio-Oyarzún D,Araya-Quintanilla F. Correlation Between Radiological Parameters and Functional Outcomes in Patients Older Than 60 Years of Age With Distal Radius Fracture.
2019; 14:770-775 [PMID:29661068 DOI:10.1177/1558944718770203]
39 Nesbitt KS,Failla JM,Les C. Assessment of instability factors in adult distal radius fractures.
2004; 29:1128-1138 [PMID:15576227 DOI:10.1016/j.jhsa.2004.06.008]
 World Journal of Orthopedics2022年9期
World Journal of Orthopedics2022年9期
- World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in a 9-year-old with osteomyelitis of the knee:A case report
- Evolution of evidence in spinal surgery – past,present and future Scientometric analysis of randomized controlled trials in spinal surgery
- Return to work following shoulder arthroplasty:A systematic review
- Fragility of statistically significant findings from randomized clinical trials of surgical treatment of humeral shaft fractures:A systematic review
- Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction:Return to sports at a minimum 5-year follow-up
- Histological difference in ligament flavum between degenerative lumbar canal stenosis and non-stenotic group:A prospective,comparative study
