Clinical eff ectiveness of a pneumatic compression device combined with low-molecular-weight heparin for the prevention of deep vein thrombosis in trauma patients: A single-center retrospective cohort study
Peng-chao Guo, Nan Li, Hui-ming Zhong, Guang-feng Zhao
1 Emergency Department, the Second Affi liated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
2 Plastic Surgery Department, the Second Affi liated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
KEYWORDS: Deep vein thrombosis; Pneumatic compression device; Low-molecular-weight heparin; Trauma; Logistic regression analysis
INTRODUCTION
Trauma remain a problem worldwide, and the incidence of work-related injuries and traffic injuries resulting in fractures and brain trauma has also increased. In treating patients with multiple injuries, emergency physicians initially focused on addressing potentially fatal injuries. When the patient’s vital signs have initially stabilized, fractures are addressed. The risk of postoperative deep vein thrombosis(DVT) is significantly higher in patients with multiple traumatic injuries than that in other patients.As the number of injuries increases, the incidence of DVT increases. More than 50% of all hospitalized patients have a risk of developing DVT, and patients undergoing surgery are at higher risk than medical patients.DVT after trauma can be life-threatening;thus, the prevention of DVT is critical for the treatment of trauma patients.This study aims to compare the eff ectiveness of a pneumatic compression device (PCD) combined with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) and LMWH alone in trauma patients and provide basis for the development of a clinical anticoagulation strategy.
METHODS
Study design and grouping
This study retrospectively analyzed 286 patients with mild craniocerebral injury and clavicular fractures who were admitted to our department from January 2016 to February 2020. After excluding 34 patients who did not meet the inclusion criteria or were lost to follow-up,patients treated with LMWH alone served as a control group (=126), and patients treated with a PCD and LMWH as an observation group (LMWP+PCD) (=126).The incidence of DVT, postoperative changes in visual analogue scale (VAS) score, and coagulation function were observed. The research procedure was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: age <75 years;Caprini risk score indicating high risk or very high risk;indications for surgical treatment of clavicular fracture; no surgical contraindications; no history of preoperative DVT;Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 13–15 points;and mild craniocerebral injury with disordered consciousness<30 min.
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria were as follows: age ≥75 years;GCS <13 points; fracture surgery contraindications;malignant tumor; severe organ dysfunction; severe coagulopathy; preoperative vascular ultrasound indicating DVT; allergy to the drug used in this study; refusal to provide informed consent; failure to meet the experimental ethical standards; a history of mental disorders or a history of craniotomy; or pregnancy.
Clinical treatment
None of the patients included in the study required neurosurgical treatment for mild craniocerebral injury, and all were treated conservatively with nutritional support and antineuro-degenerative drugs. The clavicular fractures were treated with open reduction and internal fixation(supplementary Figure 1). All patients were treated with anticoagulation medication based on their scores on the Caprini risk assessment model. In the control group, 4,000 U of LMWH calcium was subcutaneous injected once daily after surgery for 7 d. In the observation group, subcutaneous injections of 4,000 U LMWH calcium were administered daily after surgery combined with the use of a PCD on the lower limbs twice daily for 7 d after surgery.
Observation indices
The general characteristics of the patients, their past medical histories, Caprini scores, GCS scores, anticoagulant medication, and type of clavicular fracture were recorded.The VAS was used to assess the pain experienced by the patients before and after surgery.Both groups of patients underwent deep venous color Doppler ultrasonography before and after surgery, and each patient received an ultrasound examination every two weeks. Outpatient followup visits continued after discharge. Platelet (PLT) counts,fibrinogen (FIB), plasma activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma prothrombin time (PT), and D-dimer were recorded for the patients in both groups. The blood coagulation parameters of all patients before, 1 d after,and 7 d after surgery were observed. The postoperative GCS scores, the amount of bleeding that occurred during clavicular fracture internal fixation, the postoperative infection rate, and the length of hospital stay were recorded.
Statistical analysis
The measurement data of continuous variables that conformed to a normal distribution or an approximately normal distribution were expressed as the mean±standard deviation, and comparisons between the two groups were performed using independent Student’s-test. Classif ication data such as Caprini scores, fracture classifications, and GCS scores were compared using nonparametric ranksum tests. The Chi-square () test was used to compare the count data between the groups.<0.05 was considered significant. The independent variables were whether the patient experienced DVT after the operation, sex, age,medication use, Caprini score, length of stay, type of clavicular fracture, preoperative GCS score, intraoperative blood loss, postoperative infection rate, and blood coagulation function index, while the use of PCD was treated as dependent variables, and a multivariate logistic analysis was conducted. Odds ratios and corresponding 95% confidence intervals were calculated for each variables. According to the receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) for single-factor variables, the sensitivity and specificity of coagulation fuction index and other variables were evaluated in the addition of PCD. All statistical tests were performed at a signif icance level of α=0.05. The statistical software IBM SPSS (version 26) was used.
RESULTS
Comparison of basic data
There were no significant differences between the two groups in sex, age, hypertension, diabetes, antiplatelet therapy, oral anticoagulant therapy, Caprini risk scores, GCS scores, or clavicular fracture types (all>0.05) (Table 1).
Comparison of VAS scores
There were no significant differences between the two groups in the VAS score before surgery (5.1±1.4 vs.5.0±1.5) or in the VAS score 7 days after surgery (2.7±1.1 vs. 2.8±0.9). However, the postoperative VAS scores of both groups were significantly lower than those before surgery,indicating that the effect of surgery on clavicular fracturerelated pain in trauma patients is significant (<0.05)(supplementary Figure 2).
Comparison of the incidence of DVT
Deep venous color Doppler ultrasonography of both lower limbs was recorded after the operation, and the incidences of DVT in the two groups were compared.The incidence of DVT was significantly lower in the observation group than that in the control group (5.6%[7/126] vs. 15.1% [19/126], respectively;=4.605,<0.05).
Comparison of coagulation function indicators
A comparison of the coagulation parameters of all patients showed no significant difference in preoperative coagulation function between the two groups.
Repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA)showed signif icant diff erences in the APTT, PT, PLT count,and FIB level before the operation, and 1 d and 7 d after the operation. The PLT count and FIB level were significantly higher in the control group than those in the observation group, and the APTT and PT were signif icantly lower in the control group than those in the observation group. These findings indicated that coagulation ability was significantly greater in the observation group than that in the control group and the combined anticoagulant effect was better in the observation group. The difference was significant(<0.05) (Figure 1, supplementary Table 1).
Comparison of other related indicators during hospitalization
There were no significant differences between the two groups in preoperative or postoperative GCS scores,intraoperative blood loss, postoperative infection rate, or length of hospital stay (supplementary Table 2).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of thrombosis
Taking the occurrence of DVT after the operation as the dependent variable (supplementary Table 3), the basic data were used as the independent variable in a binary multivariate logistic analysis. The results showed that the postoperative risk of DVT in patients who received LMWH alone was 1.764 times greater than that of patients who received the combination of LMWH+PCD (<0.05). This finding indicated that the combined anticoagulation effect of LMWH+PCD was superior to that of LMWH alone (Table 2).
ROC curve analysis
According to the variables of the multivariate logistic regression model, the ROC curve was constructed (Figure 2), the AUC was calculated, and the Youden index was calculated based on the sensitivity and specif icity of AUC.
It can be seen that thevalues of the two indicators are both less than 0.05, and the difference is statisticallysignificant (Table 3). The AUC of APTT and PLT were both greater than 0.5, indicating that they were the inf luence indicators of adding PCD to prevent DVT. The cut-off values of APTT and PLT were 37.5 s and 124×10/L. When the indices were higher than these two cut-off values, the addition of PCD could better prevent DVT.
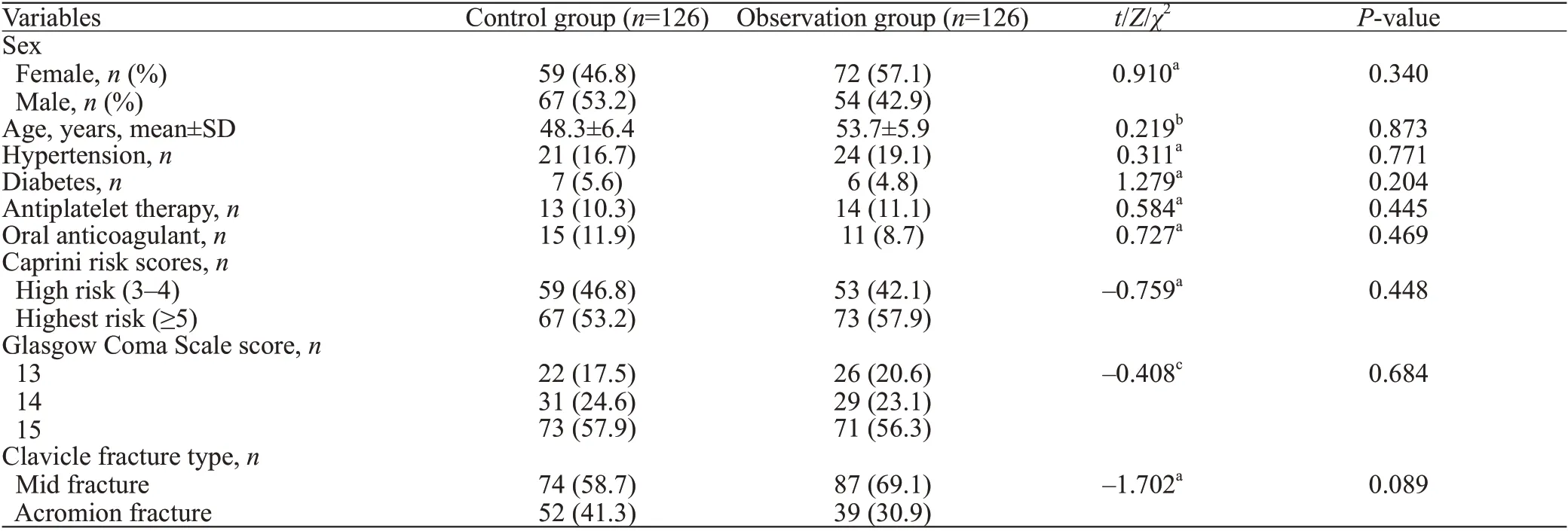
Table 1. Comparison of basic data between groups
DISCUSSION
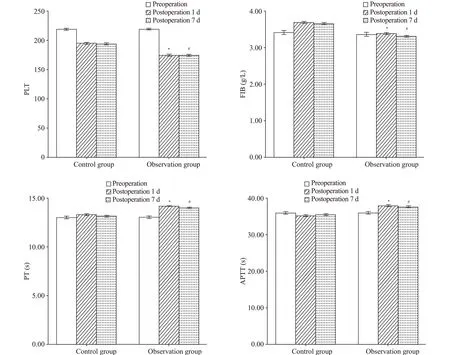
Figure 1. Comparison of PLT, FIB, PT, and APTT between groups. Compared with before surgery within the two groups, *P<0.05; compared with after surgery between the two groups, #P<0.05. PLT: platelet; FIB: f ibrinogen; PT: plasma prothrombin time; APTT: plasma activated partial thromboplastin time.
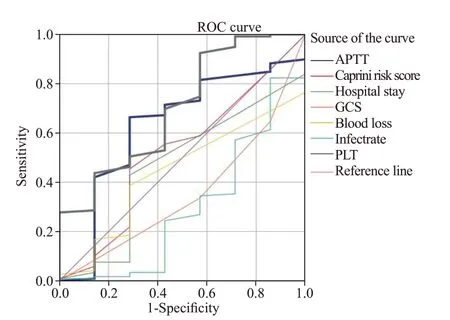
Figure 2. The ROC curves of the inf luencing factors for preventing deep venous thrombosis by pneumatic compression device. APTT: plasma activated partial thromboplastin time; GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; PLT:platelet.
In patients with multiple trauma, potentially fatal injuries are treated first. Early internal fixation should adhere to the principle of the preservation of life as the first goal.When the patient’s vital signs have been initially stabilized,other treatments can be started. Epiphyseal growth is rapid in patients with brain trauma. A large number of epiphyses in the subclavian region may compress the subclavian structure, stimulate the brachial plexus nerve, and cause traumatic arthritis. Thus, internal fixation of fractures should be performed early.However, the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with trauma is high,and this condition can be life-threatening and cause various complications.Therefore, the prevention of DVT is very important in the treatment of trauma patients. DVT and pulmonary embolism (PE) are both referred to as VTE events.In clinical experience, chest fractures, pelvic fractures, limb fractures, craniocerebral trauma, and bed rest are high-risk factors for VTEs.This study analyzed various factors of VTEs in trauma patients and provided a theoretical basis for the clinical anticoagulation strategies.
In patients with multiple trauma, death is most often caused by traumatic brain injury (TBI). According to the GCS, clinical TBI can be divided into mild, moderate, and severe. The related permanent disability rates are 10%, 60%,and 100%, respectively.This study included patients with mild injuries who had GCS scores of 13 or higher only. The occurrence of VTE and its related complications increase the length of hospital stay and medical costs; it is also one of the most common preventable cause of death among hospitalized individuals.The prevalence of DVT in trauma and orthopedic patients is about 1.16%. With the development of medical knowledge and treatment methods,DVT can be controlled and prevented.In this study, some patients experienced DVT of the lower limbs. Despite the use of drugs and mechanical anticoagulation, craniocerebral injury, chest trauma, and bed rest are still high-risk factors for DVT. Although hospitalization for acute trauma is an independent risk factor for incident VTE, taking measures to prevent VTE increases the risk of bleeding in patients with acute trauma.Based on previous experience, there is concern regarding the worsening of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with brain trauma, and drugs are not usually used in the early stage of treatment after injury.According to a 2011 study of 812 patients with craniocerebral trauma,the incidence of VTE was lower in patients who received preventive drugs than in those who did not receive preventive drugs.Phelanproposed that low-risk TBI patients should start enoxaparin treatment within 24 h after injury. Piccinini et alreported that if the injury was stable and the benef it of prevention outweighed the risk of bleeding progression, preventive drugs should be administered.Thus, all patients at high or very high risk were treated with anticoagulation drugs in this study.
Many risk factors for venous thrombosis that alter blood flow, activate the endothelium, and increase blood coagulation have been identified. Three important factors aff ecting thrombosis are blood f low, blood composition, and blood velocity. Severe trauma often leads to the emergence of the Virchow's triad (hypercoagulability, endothelial damage, and venous stasis), and this increases the risk of thromboembolism.Prolonged bed rest and limb fractures in the patients in this study promoted venous stasis. Increased hematocrit, FIB levels, and decreased clotting time in trauma patients can lead to local accumulation of coagulation activation products and cause hypercoagulability.In this study, patients’ blood coagulation was monitored to determine whether there was thrombosis in the blood.
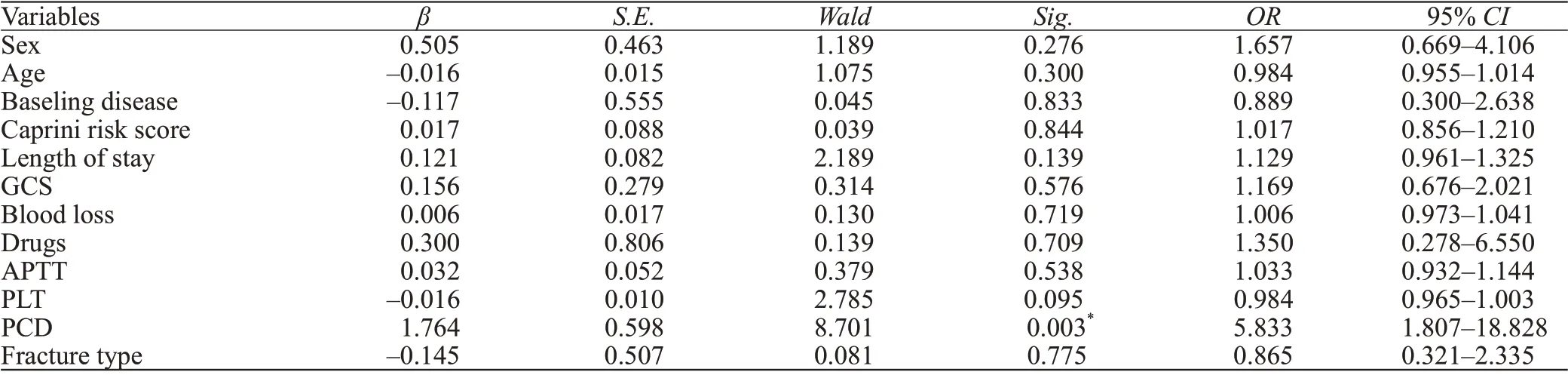
Table 2. Multivariate logistic regression analysis results of DVT in trauma patients
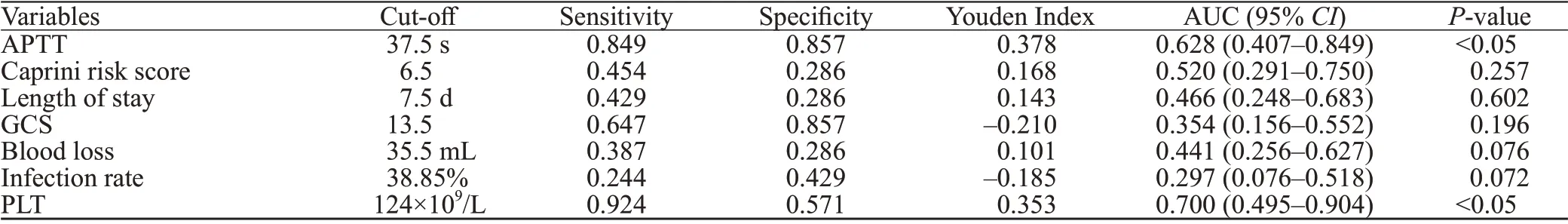
Table 3. ROC curve analysis of variables in the prevention of deep vein thrombosis by PCD
The contraindications in cases of brain injury often limit the strategies for preventing VTE in trauma patients. This study explored the choice of methods for preventing DVT in trauma patients. The available methods for thrombosis prevention in trauma patients can be divided into pharmacological anticoagulation,mechanical prevention, and the use of inferior vena cava filters (IVCs).LMWH was used for anticoagulation in this study. It has the advantages of rapid pharmacokinetics,convenient administration, and few adverse reaction, and it has strong activity against factor Xa because of its low molecular weight and charge.LMWH became the most(or only) effective method for preventing DVT in trauma patients in the late 1990s.A previous studyhas shown that LMWH reduces the incidence of DVT in trauma patients. Due to the need for safer and more effective preventive measures in patients with high-risk trauma, both drugs and mechanical anticoagulation were used in the observation group in our study. Conventional mechanical prevention includes the use of graded compression socks(GCS), sequential PCD, and pneumatic sole (A-V) foot pumps.These devices reduce the risk of thrombosis and related bleeding by reducing the luminal diameter of the veins, causing an increase in venous blood f low velocity,and they are often used in the treatment of trauma patients.Kurtoglu et alprospectively randomized enrolled 120 trauma patients and compared the eff ectiveness of PCDs and LMWH in preventing VTE; they concluded that PCDs could be used to prevent DVT safely. The treatment of LMWH combined with intermittent pneumatic pressure devices is recommended. Based on our results, a combination of PCD and LMWH may be a potential way to prevent DVT in patients with multiple trauma.
According to the 2008 American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) guidelines for the prevention of VTE,LMWH should be administered to patients with severe trauma as soon as possible; an acceptable alternative is to combine LMWH with the best mechanical methods.For patients with severe trauma, the ACCP recommends therapy to prevent thrombosis until discharge. The patients in this study received therapy for the duration of their hospitalizations. The Eastern Association of Trauma Surgery(EAST) recommends secondary LMWH for patients with multiple trauma as an anticoagulation therapy. The level III recommendation is that PCD alone can be used in patients with partial head injuries.The 9ACCP guidelines only suggest the “use of low dose unfractionated heparin (LDUH), LMWH, or mechanical prophylaxis over no prophylaxis” in major trauma patients and give this recommendation the lowest grade of evidence.Based on the latest guidelines for the prevention of traumatic DVT, the clinical effectiveness of LMWH combined with PCD was analyzed and compared with that of LMWH alone in this study. Obviously, VTE is one of the main problems in trauma patients. Despite the extensive literature on this topic, there is currently a lack of high-quality clinical evidences supporting the selection of VTE prevention methods. It is clear that when precautionary measures are not taken, the incidence of DVT could be higher, and this may increase the risk of VTErelated morbidity and mortality. Although LMWH was used in all patients in this study, the best strategy for preventing VTE in trauma patients remains controversial. Largescale, randomized prospective clinical studies are needed to provide evidence regarding the optimal measures that can be taken in clinical practice to prevent VTE.
This study has some limitations. We included the retrospective data from outpatient databases with a small sample size and a short study period. Further research with a longer study period in which more cases are collected is needed. Multicenter follow-up in a prospective study is also needed. In addition, the changes in index values at multiple time points, the risk of thrombosis over a long period, and the dosage eff ect of drugs should be investigated.Embedding the VTE risk assessment scale in electronic medical records and guiding intervention based on those scores can eff ectively improve VTE prevention and control strategies, and reduce the incidence of VTE. Although angiography is the golden standard for diagnosing DVT,vascular Doppler ultrasound was used in this study because of its noninvasive nature and relatively low cost. In addition,our records allowed the calculation of infection rates during hospitalization.
CONCLUSIONS
Compared with LMWH alone, PCD combined with LMWH may improve blood rheology and coagulation function in patients with traumatic brain injury and clavicular fracture, reduce the DVT incidence, shorten the lenght of stay, and improve the clinical eff ectiveness of treatment.
None.
The research procedure was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital.
No benef its in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
PCG proposed the study, and wrote the f irst draft.All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts.
All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
