A review of the ethnobotanical value,phytochemistry,and pharmacology of Physalis pubescens L.
Xin-Ping Cheng ,Bin Yin ,Qian-Kun Zheng ,Zhen-Peng Xu,Lin-Tao Xu,Guang-Cheng Peng,Xiao-Ning Wang ,*,Tao Shen ,*
1Key Lab of Chemical Biology (MOE),School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Cheeloo College of Medicine,Shandong University,Jinan 250012,People’s Republic of China;
2Poultry Institue,Shandong Academy of Agricultural Science,Jinan 250100,People’s Republic of China;
3Delisi Industrial Park,Zhucheng 262200,Shandong province,People’s Republic of China.
Abstract Physalis pubescens L. (P.pubescens) was widely used for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases,such as sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,and cough in folk medicine.The fruits of P.pubescens are commonly consumed as fruit in many areas of the world.In the past few decades,the phytochemistry and pharmacology of P.pubescens were extensively investigated.About 170 chemical constituents were purified from P.pubescens.The extract and chemical constituents of P.pubescens demonstrate diverse pharmacological effects,including anti-oxidation,anti-inflammation,anticancer,antimicrobial activity,immunomodulation,diuretic effect,hypoglycemic,and hypolipidemic in vitro and in vivo.Herein,we systematically summarized the ethnomedicinal uses,botanical characterization,distribution,phytochemistry,and pharmacology of P. pubescens,and establish the correlation between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects.
Keywords Physalis pubescens L.;Phytochemistry;Withanolides;Pharmacology;Anti-Inflammation
Background
The calyxes and fruits of the plants from the genusPhysalis,commonly known as ‘Suan-Jiang’ (酸漿) in Chinese,were recorded in ‘Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica’ (Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing,神農(nóng)本草經(jīng)),and have been adopted for the treatment of respiratory diseases in China for a long history [1].The well-accepted species for ‘Suan-Jiang’ isPhysalis alkekengivar.franchetii,which has been recorded in Chinese Pharmacopoeia.However,in some areas of China,Physalis pubescensL.(P.pubescens) has been used as a substitute forP.alkekengivar.franchetii,since their similar therapeutic effects against respiratory diseases.P.pubescensis an annual herb of the genusPhysalis(Solanaceae) [2],and has been adopted to treat sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,coughing,and urogenital system diseases in traditional Chinese medicines (TCM) and folk medicine [3].In addition to its medicinal value,the fruits ofP.pubescensare also consumed as edible fruit in many areas of the world since their sweet and sour taste,bright color,and high nutrition.
In recent years,the phytochemistry and pharmacology ofP.pubescenswere investigated extensively.About 170 chemical components including flavonoids,steroids,phenylpropanoids,terpenoids,alkaloids,and organic acids,were identified from the stems,leaves,calyxes,and fruits ofP.pubescens.Its extract and ingredients exerted diverse bioactivities such as anti-oxidation,anti-inflammation,anticancer,antimicrobial,immunomodulation,diuretic,hypoglycemic,and hypolipidemic [4-9].A review written in Chinese has summarized 125 ingredients extracted and purified fromP.pubescensbefore 2017 and briefly described their biological activities [10].However,in the last five years,great progress has been made in the phytochemistry and pharmacology ofP.pubescens.Thus,compared with the published review,our review updated chemical constituents recently discovered inP.pubescensand totally summarized 170 chemical constituents.Moreover,our review analyzed the relationship between the chemical composition and pharmacological effects in more detail,to correlate its ethnomedicinal uses with its modern phytochemistry and pharmacology.Since the fruits have been consumed in large quantities,the nutritional content ofP.pubescenshas also been mentioned in our review.
Botanical characterization and distribution
P.pubescensis an annual herb with a pubescence-covered stem and usually has many densely hairy branches.The leaves are blade broadly ovate,3 - 8 cm long,2 - 6 cm broad,glabrescent or sparsely pubescent,base cordate,often oblique,margin usually unequal dentate,apex acute.Pedicel is 5 - 10 mm in length with densely pubescent.The calyxes are campanulate,densely pilose,lobes lanceolate,acutely pointed.The corollas are light yellow,with purple markings on throat,6 - 10 mm in diameter.The seeds are nearly disc-shaped and about 2 mm in diameter.The fruits are globose,about 1.2 cm in diameter,yellow or purplish which is edible as fruit.The flowering period lasts from May to November.A picture ofP.pubescensis shown in Figure 1.In China,P.pubescenswas mainly distributed in Heilongjiang,Jilin,and Liaoning provinces.

Figure 1 Pictures of P.pubescens (fruits and calyxes)
Ethnomedicinal uses
There are more than 120 species of the genusPhysalis(Solanaceae) in the world,and 5 species and 2 varieties in China,includingPhysalis alkekengiL.,Physalis alkekengiL.var.francheti(Mast.) Makino,Physalis pubescensL.,Physalis minimaL.,Physalis angulataL.,Physalis angulataL.var.villosaBonati,andPhysalis peruvianaL.(http://www.iplant.cn/info/Physalis?t=z).In ancient China,dry calyxes and fruits ofPhysalis,includingP.pubescens,were usually used as TCM herb ‘Suan-Jiang’ (酸漿) [1,3].Presently,P.pubescenshas been distinguished from other plants,and named as ‘Mao-Suan-Jiang’ (毛酸漿).Suan-Jiang was first recorded as a medium-grade herb with the effects of removing heat and clearing the throat in‘Shennong’ s Classic of Materia Medica’ (神農(nóng)本草經(jīng))arisen in the period of the warring states,the Qin and Han Dynasties (B.C.475-A.D.220).Compendium of Materia Medica (本草綱目,A.D.1578) clearly recorded that Suan-Jiang had the effects of removing dampness heat and dampness,reducing phlegm,clearing lungs,and treating cough and gangrene.Many well-known classics of TCM,exemplified by Xin Xiu Ben Cao (新修本草,A.D.659),Zheng Lei Ben Cao (證類本草,A.D.1097),A Supplement to Compendium of Materia Medica (本草綱目拾遺,A.D.1765),have also recorded its medicinal uses.It has the functions of clearing away heat,detoxifying,reducing phlegm,and diuresis,thus was used for symptoms such as sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,coughing,and urine negative embolism.In Chinese folks,P.pubescensis often used internally to treat phlegm,cough,sore throat,hoarse voice or loss of voice,and unpleasant urination,and externally to treat skin diseases such as scars and eczema.In Dan Xi Cuan Yao (丹溪纂要,A.D.1484),Yi Xue Zheng Zhuan (醫(yī)學正傳,A.D.1515),Gui Yang Min Jian Yao Cao (貴陽民間藥草,A.D.1959),it has been recorded as Chinese folk medicines for the treatment of phlegm-heat cough,sore throat,dumb tone,and urination.Moreover,Suan-Jiang was also used as antipyretic and cardiotonic medicine in Japan.
Phytochemistry
The research on chemical composition ofP.pubescenscould be traced back to the 1980s.Until now,170 chemical components have been isolated fromP.pubescens,including steroids,flavonoids,phenylpropanoids,terpenoids,N-containing compounds,organic acids,and miscellaneous constituents.Withanolides and flavonoids were reported to be characteristic and active chemical constituents.
Steroids
About 52 steroids were isolated and identified from the calyxes,fruits,and aerial ofP.pubescens.The steroids isolated from this plant could be mainly divided into two types,withanolides and sterols.Compared to sterols,withanolides are the characteristic and predominant bioactive components inP.pubescens.
(1) WithanolidesWithanolides are a group of naturally occurring C28 steroids based on an ergostane skeleton,in which C-26 and C-22,or C-26 and C-23,are oxidized to form aδ- orγ-lactone [11].The first withanolide,withaferin A (2),was found in theWithania somniferaby Lavie in 1965 [12].Based on the difference in the substituted groups of C-17 side chain,most withanolides can be divided into two types,those containingδ-lactone orδ-lactol (Type A),and those containingγ-lactone orγ-lactol (Type B) side chain (Figure 2).The number of natural Type B withanolides is far fewer than that of Type A.Most of withanolides isolated fromP.pubescensbelong to the Type-A group (1-39),except for compounds (40-41)belonging to the Types-B group (Table 1).Many withanolides isolated fromP.pubescensexisted in the form of glycosides,e.g.physapubside A (13) as monoglycoside,and physapubside B (14) as diglycoside.Furthermore,the structures of withanolides fromP.pubescensalso contain some heteroatoms.For instance,(20S,22R,24S,25S,26R)-15α-acetoxy-6α-chloro-22,26:24,25-diepoxy-4β,5β,26-trihydroxyergost-2-en-1-one (20) has a molecule of chlorine (Cl),an d(20S,22R,24R,25S)-15α-acetoxy-22,26-epoxy-4β,6α-[oxy(2β-hydroxy-2,1-ethanediyl) thio]-5β,24,25,26-tetrahydroxyergost-2-en-1-one (37) contains sulfhydryl group.Most remarkably,pairs of interconvertible C-26 epimeric isomers were found fromP.pubescens,such as 26S-physapubescin F (15a) and 26R-physapubescin F(15b),26S-physapubside C (16a) and 26R-physapubside C(16b),and so on.

Table 1 Chemical constituents isolated from the plant of P.pubescens

26a (20S,22R,24R,25S,26S)-15α-acetoxy-5,6β:22,26-diepoxy-3β,4β,24,25,26-pentahydroxyergost-1-one fruits [39]26b (20S,22R,24R,25S,26R)-15α-acetoxy-5,6β:22,26-diepoxy-3β,4β,24,25,26-pentahydroxyergost-1-one fruits [39]27 philadephicalactones A calyxes [14]28 virginols A1 calyxes [14]29 physapubenolide calyxes [40]30 nic-2 calyxes [41]31 nic-2 lactone calyxes [40]32 physapubescin K fruits [18]33 physapubescin L fruits [18]34 physapubescin M fruits [18]35 peruvianolide E fruits [18]36 withapubeside B Stems [42]37 physapubescin J fruits [18]38 pubescenin calyxes [40]39 physapubescin G stems and leaves [37]40 withapubeside A stems [42]41 withapubesin stems [42]42 withapubeside C stems [42]43 withapubeside D stems [42]44 alkesterol A fruits [43]45 alkesterol B calyxes and fruits [15,43]46 (22E,24S)-5α,8α-epidioxy-24-methyl- cholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol leaves [15]47(22E,24S)-5α,8α-epidioxy-24-methyl-cholesta-6,9(11),22-trien-3β-ol leaves [15]48 2α,3β-dihydroxy-5α-pregn-16-en-20-one 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside fruits [25](25R)-2α-hydroxy-5α-spirostan-3β-yl O-β-D-glucopyr-49 anosyl-(1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-Dfruits [25]galactopyranoside 50 β-sitosterol calyxes and fruits [1,14,43,44]51 daucosterol calyxes and fruits [1,14]52 stigmasterol fruits [16]Flavonoids 53 luteolin calyxes [19]54 rutin calyxes [14]55 quercetin calyxes [14,19]56 3,7-dimethylquercetin calyxes [44]57 ombuine calyxes and fruits [18,19]58 3′-methoxy ombuine calyxes and fruits [22]59 3,7,3′-trimethylquercetin calyxes and fruits [44]60 quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside calyxes and fruits [1,14]61 quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside calyxes [14]62 quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside calyxes [14]63 quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside calyxes [14]64 quercetin-3-O-(6′-O-trans-coumarinoyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [21]

65 3,7,4′-trimethyl-myricetin calyxes [14]66 3,5,3′,4′-tetrahydroxyl-7-methoxyflavone calyxes [14]67 kaempferol calyxes and fruits [19]68 kaempferide calyxes [44]69 7-methyl kaempferol calyxes [44]70 3,7-dimethyl kaempferol calyxes [44]71 kaempferol-3-glucose-7-rhamnoside calyxes [14]72 kaempferol-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside calyxes [14]73 kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside calyxes [14]74 kaempferol-7-O-β-D-glucose-3-O-β-D-glucosyl-(1→2)-β-D- glucoside calyxes [14]75 kaempferol-3-O-β-D-galactoside calyxes [14]76 kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside calyxes [14]77 kaempferol-3-O-β-D-rutinoside fruits [21]78 kaempferol-3-O-β-D-sophoroside calyxes [14]79 kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnosterin-(1→6)-β-Dglucoside calyxes [14]80 kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnosterin calyxes [14]81 chrysoeriol fruits [1]82 3′,5′,5-trihydroxy-3,4′,7-trimethoxyflavone calyxes [22]83 oxyayanin A calyxes [44]84 physalis pubescens flavones A calyxes [44]85 quercetin-3,5,7-trimethyl ether 3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [21]86 3′,5-dihydroxy-3,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone calyxes [14]87 4,4′-dihydroxy-2′-methoxychalcone fruits [21]88 genistein-7-O-β-D-glucoside-4′-O-α-L-rhamnose-(1→2)-β-D-glucoside calyxes [14]Phenylpropanoid 89 trans-cinnamoyl β-D-glucoside fruits [18]90 1-O-trans-cinnamoyl-β-Dglucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [20]91 1-O-caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [1]92 1-O-p-ferulyl-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [1]93 1-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [1]94 5-O-caffeoyl quinic acid butyl ester fruits [1]95 E-ethyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acrylate calyxes and fruits [21,24]96 E-methyl cinnamate calyxes [24]97 ethyl caffeate fruits [21]98 neo-olivil fruits [1]99 nortrachelogenin fruits [1]100 medioresinol fruits [1]101 pinoresinol fruits [1]102 imperatorin fruits [20]103 xanthotoxin fruits [20]104 bergapten fruits [20]105 isopimpinellin fruits [20]106 osthol fruits [20]107(-)-meranzin hydrate fruits [20]108 auraptenol fruits [20]109 trans-p-coumaric acid ethyl ester calyxes [22]

110 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid butyl ester fruits [1]111 1-ferulylglucose fruits [18]112 caffeic acid fruits [1]113 3,4-dihydroxybenzenepropionic acid fruits [20]114 p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid fruits [20]115 ferulic acid fruits [45]116 cinnamic acid fruits [45]117 sinapic acid fruits [45]118 1′-O-β-D-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4′-O-caffeoyl glucoside fruits [1]119 calceolarioside A fruits [1]Terpenoids 120 oleuropein fruits [21]121 blumenol A fruits [1]122 5-O-(E-feruloyl) blumenol calyxes [22,24]123 arjunolic acid fruits [1]124 pulsatilla saponin A fruits [1]125 pulsatilla saponin D fruits [1]126 3,6,11-trimethyl-3-hydroxyl-1,6E,10-dodecatriene-8-Oβ-D-glucoside calyxes [14]127 8-hydroxylinalool fruits [18]128 betulalbuside A fruits [18]129 capsidiol fruits [18]130 lubimin fruits [18]131(6S,9R)-roseoside fruits [25]132 (6S,9S)-roseoside fruits [25]133(1′S,6′R)-8′-hydroxyabscisic acid β-D-glucoside fruits [25]134 p-menth-4(8)-ene-12-diol 1-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [25]135 1β,3α-dihydroxy-7α-eremophila-9,11-dien-3-O-[α-Larabinopyranosyl-(l→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [25]N-containing compounds 136 N-trans-ferulogltyramine fruits [20]137 uridine fruits [1]138 adenosine fruits [1]Organic acids 139 4-hydroyl-3-methoxy benzoic acid fruits and calyxes [1,44]140 3-hydroxyl-4-methoxy benzoic acid calyxes [14]141 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid calyxes [44]142 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetic acid fruits [20]143 dihydroxysuccinic acid calyxes [45]144 citric acid calyxes [45]145 malic acid calyxes [45]146 butanedioic acid calyxes [45]147 cis,cis-muconic acid calyxes [44]Miscellaneous constituents 148 syringic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester fruits [1]149 1-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl) ethanone fruits [20]150 isovanillin fruits [24]151 4-methoxy-3-propoxybenzaldehyde fruits [9]
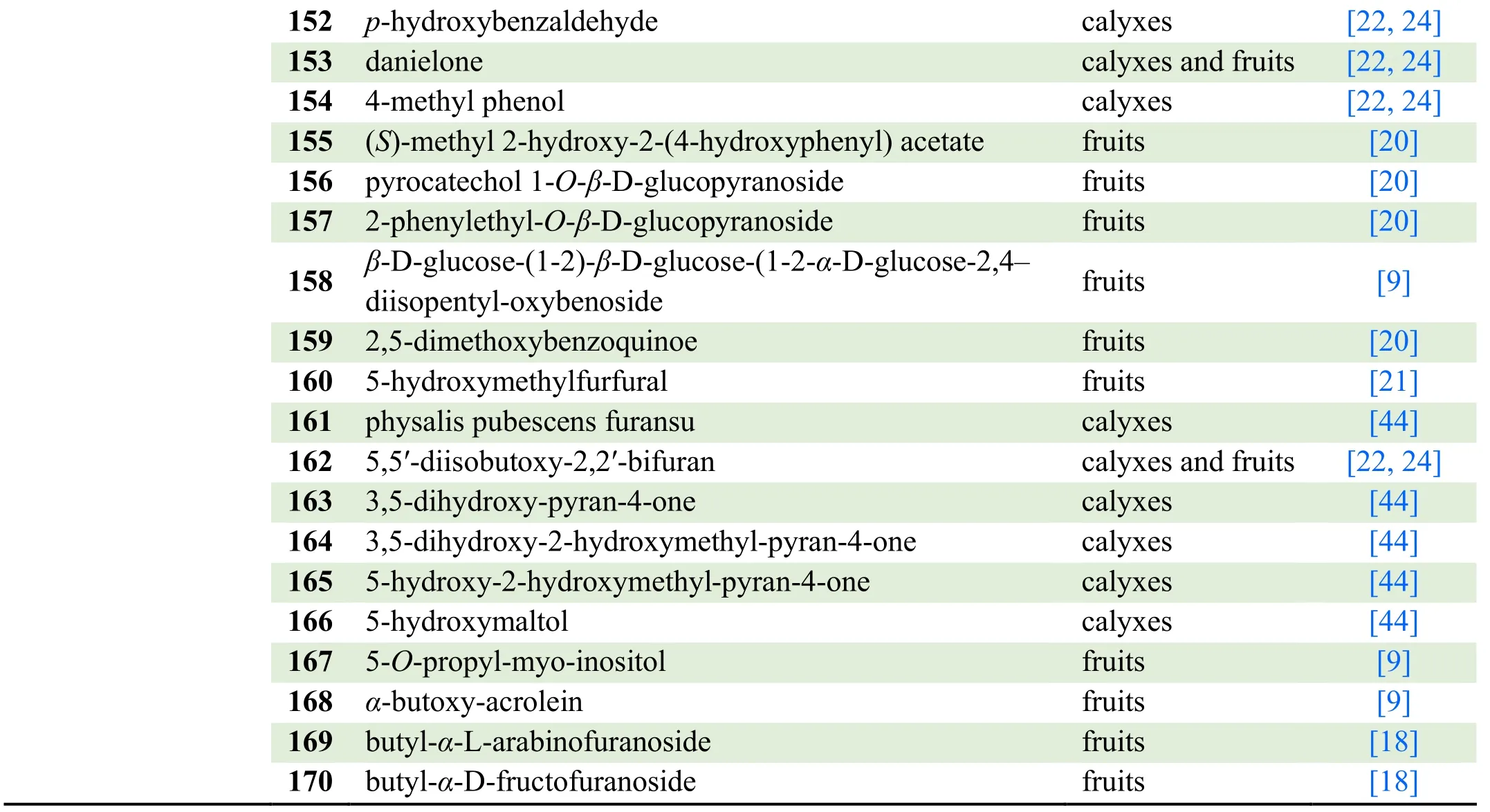
152 p-hydroxybenzaldehyde calyxes [22,24][22,24]154 4-methyl phenol calyxes [22,24]153 danielone calyxes and fruits[20]156 pyrocatechol 1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits [20]155(S)-methyl 2-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetate fruits[20]158 β-D-glucose-(1-2)-β-D-glucose-(1-2-α-D-glucose-2,4-diisopentyl-oxybenoside fruits [9]157 2-phenylethyl-O-β-D-glucopyranoside fruits[20]160 5-hydroxymethylfurfural fruits [21]159 2,5-dimethoxybenzoquinoe fruits[44]162 5,5′-diisobutoxy-2,2′-bifuran calyxes and fruits [22,24]161 physalis pubescens furansu calyxes[44]164 3,5-dihydroxy-2-hydroxymethyl-pyran-4-one calyxes [44]163 3,5-dihydroxy-pyran-4-one calyxes[44]166 5-hydroxymaltol calyxes [44]165 5-hydroxy-2-hydroxymethyl-pyran-4-one calyxes[9]168 α-butoxy-acrolein fruits [9]167 5-O-propyl-myo-inositol fruits[18]170 butyl-α-D-fructofuranoside fruits [18]169 butyl-α-L-arabinofuranoside fruits

Figure 2 Structures of two important groups of withanolides (Types A and B)
Among these withanolides,physapubescins,which count up to 0.033% of the hairy groundcherry,are considered as representative ingredients ofP.pubescens[13].Physapubescins are a group of withanolides which usually contain 24,25-epoxy or ring opening at 24,25-epoxy to form two hydroxyl groups.Since the complexity of their structures,the absolute configuration of physapubescins,such as physapubescin A (8) and physapubescin B (9),were identified using single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis or ECD data analysis.
(2) SterolsAt present,some sterols have been separated from theP.pubescens,exemplified by withapubeside C(42),withapubeside D (43),alkesterol A (44),alkesterol B(45),β-sitosterol (50),daucosterol (51),and stigmasterol(52) [14-16].In addition,(22E,24S)-5α,8α-epidioxy-24-methyl-cholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (46) and (22E,24S)-5α,8α-epidioxy-24-methyl-cholesta-6,9(11),22-trien-3βol (47) containing peroxidic bond,as well as two glycosides 2α,3β-dihydroxy-5α-pregn-16-en-20-one 3-Oβ-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactop yranoside (48)and (25R)-2α-hydroxy-5α-spirostan-3β-ylO-β-Dglucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (49) have been isolated from this plant.All structures of steroids fromP.pubescenswere summarized in Figure 3.



Figure 3 Steroids isolated from P.pubescens
Flavonoids
About 36 flavonoids have been separated from the calyxes and fruit ofP.pubescens(Figure 4).These isolated flavonoids are quercetin (55) and its derivatives (56,59-64,85),luteolin (53) and its glycoside rutin (54),kaempferol glycosides (67-80) [1,14,17-21].Moreover,one chalcone[4,4′-dihydroxy-2′-methoxychalcone (87)] and one isoflavone [genistein-7-O-β-D-glucoside-4′-O-α-L-rhamnose-(1→2)-β-D-glucoside (88)] were obtained from the fruits and calyxes of this plant [14,21].In addition,three flavonol analogues,ombuine (57),3′-methoxy ombuine(58),and oxyayanin A (83),were obtained from calyxes ofP.pubescens[19,22].
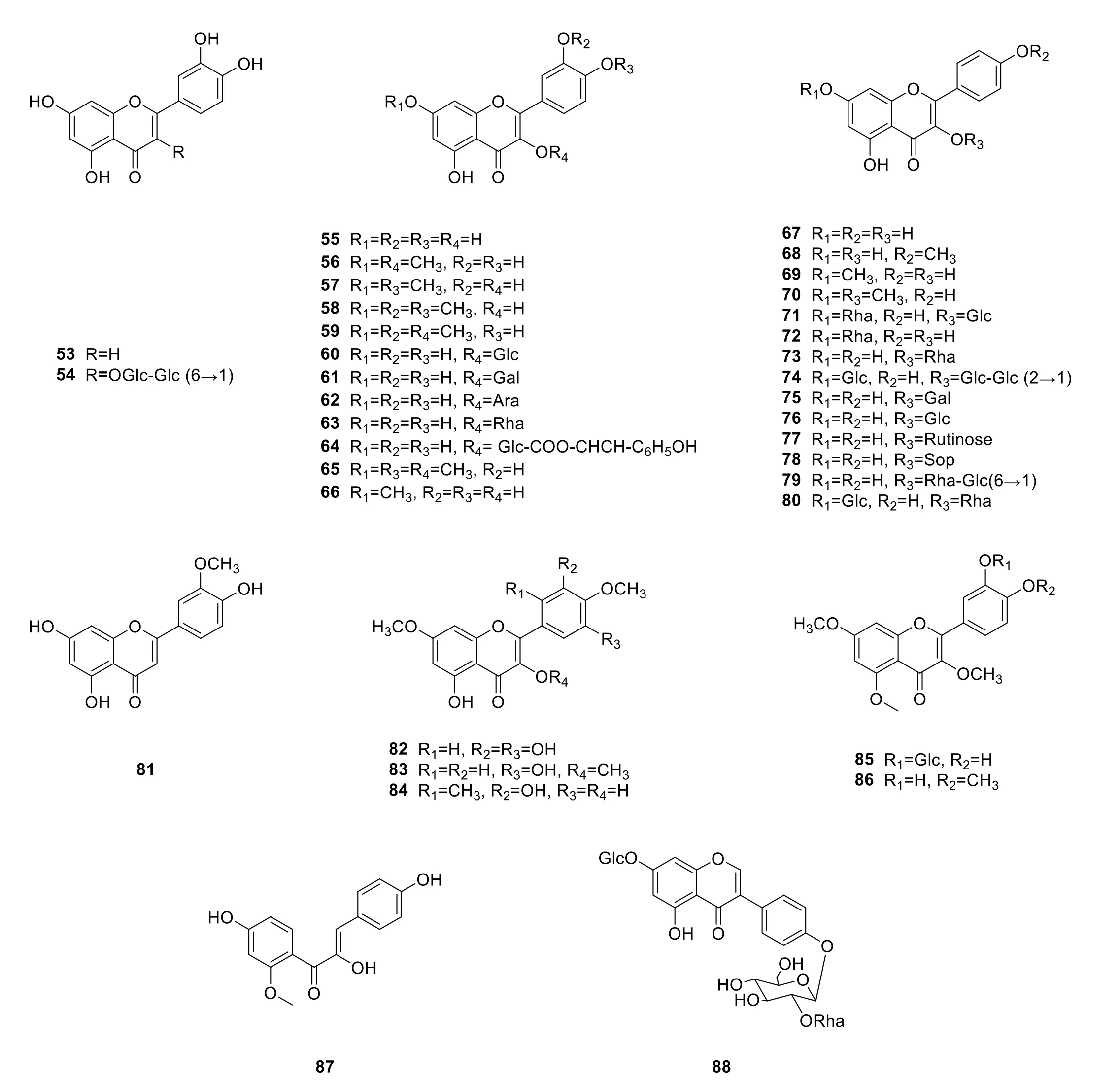
Figure 4 Flavonoids isolated from P.pubescens
Phenylpropanoids
At present,about 31 phenylpropanoids,including simple phenylpropanoids,coumarins,and lignans,have been separated fromP.pubescens(Figure 5).Among these phenylpropanoids,lignans have the activities of scavenging free radicals and anti-oxidation such as neoolivil (98),nortrachelogenin (99),medioresinol (100),and pinoresinol (101) [1,17].Meanwhile,coumarins are also important members of phenylpropanoids fromP.pubescens,such as imperatorin (102),xanthotoxin (103),bergapten (104),isopimpinellin (105),osthol (106),(-)-meranzin hydrate (107),and auraptenol (108) [20].Furthermore,some phenylpropanoids are substituted by benzoethanol glycoside moiety,for instance,1′-O-β-D-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)-4′-O-caffeoyl glucoside (118) and calceolarioside A (119).


Figure 5 Phenylpropanoids isolated from P.pubescens
Terpenoids
About 16 terpenoids have been discovered,covering sesquiterpenes,triterpenes (Figure 6) [1,14,19-22,24].Although the amounts of terpenoids isolated fromP.pubescenswere limited,there are still some compounds with distinctive structures.For example,5-O-(E-feruloyl)blumenol (122) was regarded as the product of esterification reaction between sesquiterpene and phenylpropanoid.Some terpenoids isolated fromP.pubescensexisted in the form of glycosides,such as oleuropein (120),pulsatilla saponin A (124),pulsatilla saponin D (125),and 3,6,11-trimethyl-3-hydroxyl-1,6E,10-dodecatriene-8-O-β-D-glucoside (126).Moreover,lubimin (130) is a rare vetispirane-type sesquiterpenoid which has been isolated fromP.pubescensin 2020 [18].
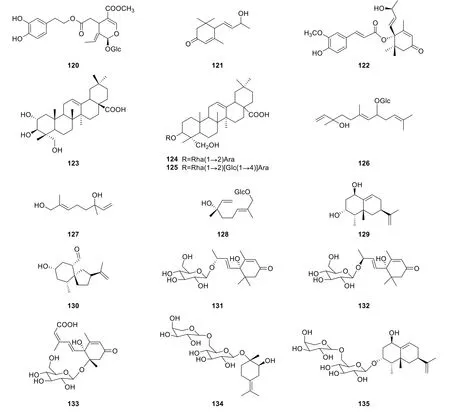
Figure 6 Terpenoids isolated from P.pubescens
N-containing compounds
Three N-containing compounds have been separated from the roots ofP.pubescens.(Figure 7),which are two alkaloids,uridine (137) and adenosine (138),and one amideN-trans-ferulogltyramine (136) [1,17,20].

Figure 7 N-containing compounds isolated from P.pubescens
Organic acids
Natural organic acids fromP.pubescensare mainly classified as aliphatic organic acids and aromatic organic acids(Figure 8).At present,four aromatic organic acids are isolated fromP.pubescens,which are 4-hydroyl-3-methoxy benzoic acid (139),3-hydroxyl-4-methoxy benzoic acid (140),3,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid (141),and 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetic acid (142) [1,14,19,20].Aliphatic organic acids are dihydroxysuccinic acid (143),citric acid (144),malic acid (145),butanedioic acid (146)andcis,cis-muconic acid (147) [19].
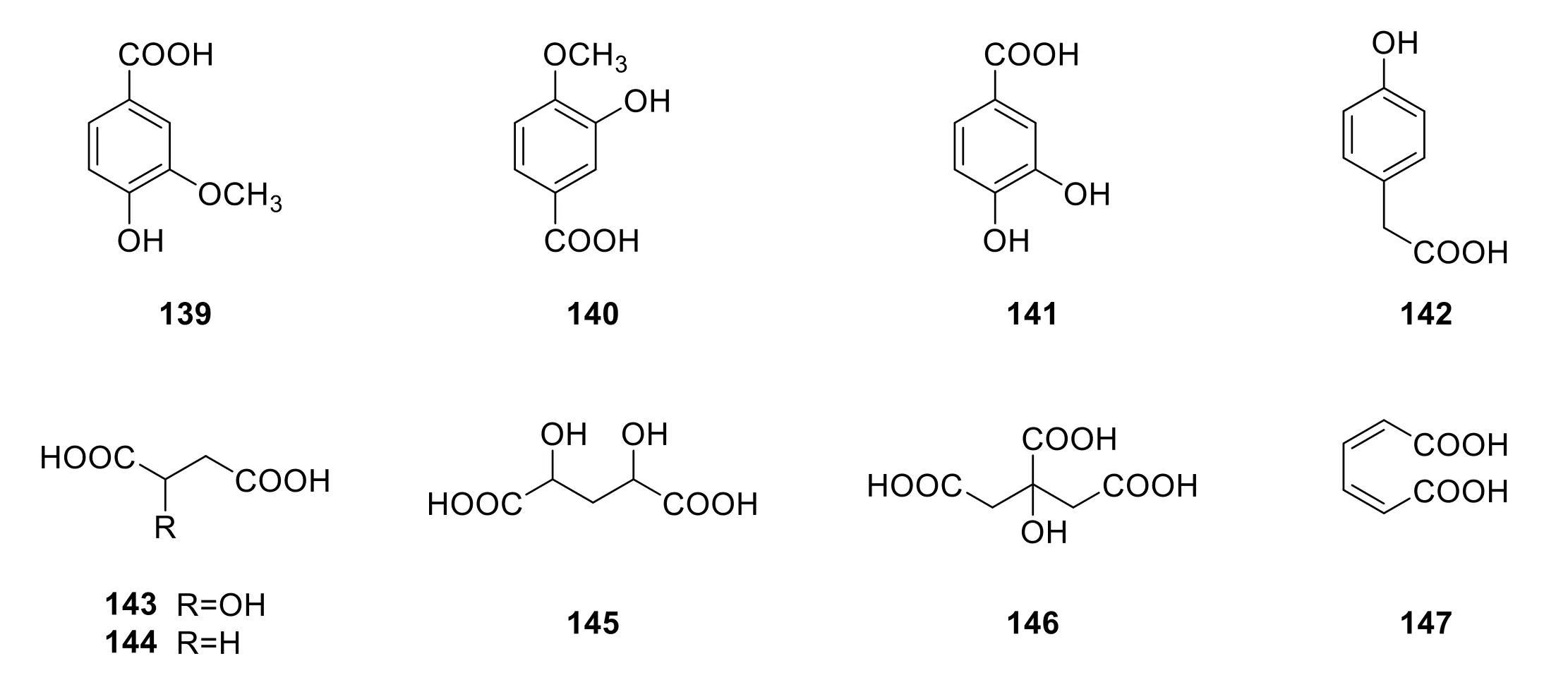
Figure 8 Organic acid isolated from P.pubescens
Miscellaneous constituents
Plenty of other ingredients have been isolated,such as aromatic compounds (148-158),quinones (159),heterocyclic compounds (161-166),and aliphatic derivatives (Figure 9) [1,9,14,18-22,25].Moreover,polyphenols (0.766 g/L) exemplified by tannic acid and pectins were rich inP.pubescens.Catechin,salicylic,paracumaric,and chlorogenic acids are the most abundant phenolic compounds in the juice [26].The content of oil in juice is very low (1.1 g/L),and most of it is unsaturated fatty acid,which makesP.pubescensa healthy fruit [27].

Figure 9 Miscellaneous constituents isolated from P.pubescens
Nutrient content
The fruits ofP.pubescensare consumed as high-quality fruit for their good taste and rich nutrition in many parts of the world.In Egypt,P.pubescensis used by local residents as a good source of vitamin supplements [28].In Northeast China,it is also used to supplement nutrients,provide minerals,and regulate the body health.The contents of potassium,calcium,magnesium,zinc,copper,iron,phosphorus,and manganese in its juice are higher than the lime,lemon,and orange,suggesting thatP.pubescensis an important source of these trace elements [29].There is a high content of natural pigments with anti-oxidation and anti-cancer effects inP.pubescens [30].
The fruits ofP.pubescenscontain more than 18 kinds of amino acids,among which the essential amino acid content is distributed as follows: leucine (3.95%),valine(2.75%),lysine (2.58%),threonine (2.54%),phenylalanine(2.23%),isoleucine (1.91%),histidine (1.52%),methionine (1.02%),and tryptophan (0.51%) [31].Thus,it is a good potential source of essential amino acids such as isoleucine,valine,and tryptophan [(4.2,3.9,and 3.9) g/100 g protein] [28].
Pharmacology
From the perspective of modern medicine,the diseases which were treated byP.pubescensin TCM,such as sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,and coughing,were highly related to inflammation,redox imbalance,and microbial invasion [46].The extracts and the purified compounds ofP.pubescensshowed anti-inflammation,anti-oxidant,and antibacterial activities.Moreover,they also exerted diverse pharmacological activities,such as anticancer,regulating immunological competence,and antihyperglycemic effects.We focused on the pharmacology effects related to the traditional uses ofP.pubescens,particularly on the anti-inflammation,anti-oxidant,and antibacterial activities,and try to establish their correlations.Furthermore,pharmacological effects of the extracts and ingredients were also discussed,which was expected to provide a basis for further investigations(Figure 10).
Anti-inflammatory effect
80% ethanol extract of the fruits ofP.pubescensattenuated acute pyelonephritis.Treatment with ethanol extract of fruits relieved mouse ear edema and rats cotton ball granuloma.Treatment with 0.625 and 1.25 mg/mL ethanol extract significantly decreased the concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) via inhibiting the mRNA and protein levels of nuclear factorκB (NF-κB) [47].Moreover,treatment with 0.3 and 0.6 g/kg ethanol extract of the fruits ofP.pubescenssignificantly attenuated the kidney inflammation caused by ligation and reduced the accumulation of neutrophils [9].The extract of crude polysaccharides (POL) fromP.pubescensfruits ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium salt(DSS)-induced intestinal injury via attenuating the inflammation and oxidative stress in mice.Pretreatment with POL before DSS-stimulation suppressed the neutrophil infiltration and modulated the NF-κB/inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)signal transduction pathway [4].
Steroids isolated fromP.pubescensexert antiinflammatory effects.Withaferin A (2) suppressed NF-κB and Akt and thus inhibiting the production of iNOS and NO in RAW 264.7 macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [48].Treatment with 2 protected kidneys from the inflammation induced by unilateral uretera obstruction (UUO) via inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors [49].Moreover,2 suppressed the inflammatory disease state in several disease models,such as diabetes,obesity,neurodegenerative disorder,cystic fibrosis,and osteoarthritis [50].Physapubescin A (8),physapubescin I (18),and physapubescin M (34) were all able to inhibit the production of NO in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages [18].Withapubeside A (40),withapubeside B (36),withapubeside C (42),and withapubeside D (43) inhibited the production of NO induced by LPS via decreasing the level of iNOS [42].
The anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids isolated fromP.pubescenswas also extensively studied,such as luteolin (53),quercetin (55),kaempferol (67),and chrysoeriol (81).53 inhibited the LPS,nigericin,and adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-induced nod like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation in J774A.1 macrophages via interfering with ASC oligomerization.Treatment with 53 at doses from 5 to 40 μM suppressed the activation of caspase-1 and the secretion of IL-16 derived by NLRP3 inflammasome in J774 A.1 macrophages [51].Moreover,53 exerts antiinflammatory effects in many animal inflammation models.Treatment with 100 mg/kg 53 suppressed the symptom of ulcerative colitis induced by DSS by regulating the SHP-1/ STAT3 pathway in mice [52].Similarly,53 inhibited the inflammation in the ovalbumin (OVA)-stimulated allergic rhinitis rat model [53].In the diabetic nephropathy mouse model,53 exerted anti-inflammatory effects via regulating the STAT3 pathway [54].Treatment with 55 was able to suppress atherosclerosis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [55].55 also dose-dependently suppressed oedema and inhibited acute inflammation induced by monosodium urate (MSU) in rats [56].Moreover,55 attenuated lung and liver injury by suppressing inflammation induced by LPS and nickel[57-59].Treatment with 55 exerted an inhibitory effect on systemic inflammation stimulated by LPS in mice [60].67 suppressed the inflammation in osteoarthritis via regulating the NF-κB pathway and inflammatory factors[61,62].Moreover,67 showed a therapeutic effect in DSSinduced colitis and cisplatin-induced cardiac dysfunction and injury by suppressing inflammation [63,64].Pathogenic microbial invasion is the main cause of inflammation,67 reduced the expression of TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-8,and IL-18 in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells [65].The inhibition of 81 on NF-κB,AP-1,and phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases(PI3K)/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)was related to its potent anti-inflammatory effects [66,67].Collectively,flavonoids are important sources of antiinflammatory activity inP.pubescens.
Phenylpropanoids fromP.pubescens,including ethyl caffeate (97),pinoresinol (101),imperatorin (102),xanthotoxin (103),and caffeic acid (112),showed antiinflammatory effects.97 inhibited the activation of NF-κB and the production of iNOS,COX-2,and PGE in vitro or in mouse skin [68].101 could significantly reduce levels of IL-6 and COX-2 human intestinal Caco-2 cells [69].103 suppressed the production of NO,prostaglandin E2(PGE2),TNF-α,and IL-6 by downregulating the NF-κB,AP-1,and JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways in LPSinduced RAW 264.7 macrophages [70].102 could regulate MRGPRX2 and CamKII/ERK pathway,thus attenuating OVA-induced lung inflammation in mice [71].102 also exerted an anti-inflammatory effect in atherosclerosis by regulating the MAPKs signaling pathway [72] and suppressed the iNOS expression and NO production,which was related to its regulating effect of ERKMAPK/AP1,JAK/STAT,and NF-κB pathway [73-75].Treatment with 102 attenuated the symptoms of ulcerative colitis by regulating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway [76].112 inhibited the secretion of TNF-α,IL-6,and IL-1βvia inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways in the mammary gland [77].Moreover,112 suppressed DSS-induced murine ulcerative colitis through deactivating macrophages [78].
Two terpenoids,oleuropein (120) and arjunolic acid(123),exhibited anti-inflammation activities.120 protected the kidney from the inflammation after acute injury because of its regulatory effect on TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB/MAPK axis [79].120 could suppress the secretion of TNF-α,IL-β,and IL-6 and inflammation-related genes in mice that received LPS injection [80].Treatment with 123 significantly suppressed the expressions of TNF-α,IL-1β,and IL-6 in serum of complete Freund’s adjuvant(CFA)-induced arthritic rats [81].
The anti-inflammatory effects of the calyx and fruit extracts ofP.pubescensand its constituents have been sufficiently evaluated and verified using diverse models in vitroandin vivo.Steroids,flavonoids,terpenoids,and phenylpropanoids are responsible for their antiinflammatory effects.The mechanism for alleviating inflammation have also been investigated,which was related to inhibition of inflammation-regulating pathways(e.g.NF-κB,AP-1,MAPK,and STAT3).Thus,all of the above data supported the ethnomedical uses ofP.pubescensf for treating inflammation-related diseases.
Antioxidant effect
The antioxidant capability of hydroalcoholic extracts of the pulp and seeds ofP.pubescenswas evaluated using a 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging capability assay,and high antioxidant activity of both the pulp (2210.46 μM irgin/g) and seeds (2807.74 μM irgin/g)was observed [82].The Ferric reducing ability of plasma(FRAP),2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS),and superoxide radical scavenging activity of the yellow pigment extracted fromP.pubescenswere 6.11 ± 0.22 mmol/g,2.80 ± 0.27 mmol/g,and 57281.5 ±2749.5 U/g,respectively,which indicated that the yellow pigment enables to maintain redox balance [30].
Steroids ofP.pubescensexhibited antioxidant activity.Withaferin A (2) was reported to be a SIRT3 activator that could suppress the oxidative stress stimulated by CCl4in mice [83].The quinone reductase (QR) induction activities of physapubescin A (8),physapubescin B (9),and physapubescin C (10) were 2.41,2.30,1.86-fold of control at 10 μM which suggested their antioxidative effect [33].
The antioxidant effects of flavonoids extracted fromP.pubescenshave been investigated extensively.As a Nrf2 activator,luteolin (53) alleviates oxidative stress stimulated by ochratoxin A and high blood sugar,thus protecting cells and tissues [84,85].Treatment with 53 at doses of 2.5-50 μM protected cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through regulating MAPK/NF-κB [86].Quercetin (55)could also alleviate oxidative stress induced by D-glucose in human hepatoellular carcinomas HepG2 cells via inducing the activity of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD),catalase (CAT),glutathione peroxidase(GPx),glutathione reductase (GR),and cellular levels of glutathione (GSH) [87].Kaempferol (67) suppressed the oxidative stress induced by different stimulants including Cu2+,clozapine,and radiation in vitro [88-90].67 exhibited potential therapeutic effects in lung ischemiareperfusion injury and skin fibrosis via keeping oxidative balance [91,92].Chrysoeriol (81) reversed retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells dysfunction which is involved in age-related macular degeneration via antioxidant effect,treatment with 2.5-10 μM.81 significantly suppressed cell death and decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS)stimulated by H2O2[93].Quercetin (55),3,7,3′-trimethylquercetin (59),and kaempferol (67) displayed DPPH free radical scavenging ability [19].
Arjunolic acid (123) protected uterine tissue against DNA damage,and counteracted ROS induced by As3+in rats via activating endogenous enzymatic antioxidants [94].Treatment with 123 effectively attenuated oxidative stressinduced I/R injury in rats subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion [95].The EC50values of kaempferol-3-Oβ-D-galactoside (75),bergapten (104),blumenol A (121),and caffeic acid (112) for scavenging DPPH radical were 0.51,1.86,1.47,and 1.75 μg/mL,which indicated that those compounds displayed significant antioxidant effect[17].
Antibacterial effect
Bacterial infestation is an important factor that induces and exacerbates inflammation.The extract of fruits inhibits the proliferation of the standard strain ofEscherichia coli(ATCC 25922),Escherichia colifrom hospital,the standard strain ofStaphylococcus aureus(ATCC 25925),and the clinical isolates ofStaphylococcus aureuswith MICs of 31-125 mg/mL [6].Besides,flavonoids such as quercetin (55),3,7,3′-trimethylquercetin (59),and kaempferol (67) exhibited inhibitory effects on different bacterials [19].Moreover,nortrachelogenin (99) inhibited the survival rate ofEscherichia coliO157 by disorganizing the cytoplasmic membrane [96].
Regulation on immune response
The extract and ingredients ofP.pubescensalso exert regulating effect on the immunological system.The pulp,peel,and seeds extract significantly downregulated cellular immunity in mice through regulating Tlymphocytes.According to the delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH),carbon particle clearance test,and serum agglutination test,40% ethanol extract had the strongest inhibitory effect against immune response.Besides,two flavonoids extracted from the fruits ofP.pubescens,luteolin (53) and quercetin (55) increased the cell viability of natural killer NK-92 cells [97].Ethyl caffeate (97) exerted the effect against arthritis by suppressing the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th1 at a dose of 10 μMin vitro [98].
Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation
Flavonoids extracted fromP.pubescensdemonstrate inhibitory effects against cancer cells.Luteolin (53)inhibited the progression of carcinogenesis such as cell transformation,metastasis,invasion,and angiogenesis[99],induced apoptotic cancer cells death [100],and blocked the cell cycle arrest [101],thus suppressed the proliferation of various kinds of tumor cells [102].Treatment with 55 at 50 μM and 75 μM suppressed the growth of human ovarian teratoma PA-1 cells via suppressing PI3k/Akt,Ras/Raf pathways,and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression [103].Similarly,55 induced apoptosis or cell cycle arrest in human leukemia U937 cells,human breast cancer cells,human cells transformed by human papillomavirus type 16 oncoproteins,and nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells[104-107].Moreover,the IC50values of kaempferol (67)against different cancer cell lines is 19 ± 0.33 μM for human ovarian cancer A2780 cells,38 ± 3.30 μM for human lung cancer H460 cells,46 ± 2.70 μM for human skin cancer A431 cells,45 ± 2.90 μM for human adenocarcinoma HT29 cells,37 ± 3.5 μM for human mammary epithelial MCF10A cells,22 ± 2.10 μM for human glioblastoma SJ-G2 cells,and 26 ± 1.30 μM for mouse glioblastoma SMA cells,respectively [108].The cancer cells growth was suppressed by 67 due to its cell cycle blocking and apoptosis inducing effects [109].67 also exerts its anticancer effect through regulating the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/CDK6/cyclin D1 pathway in human gallbladder cancer cells [110].Kaempferide (68) induced apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells via regulating TGF-β,NF-κB,and MAPK pathways [111].Chrysoeriol (81) could significantly suppress the proliferation of human lung cancer A549 cells with an IC50of 15 μM.The growth of tumor could be suppressed while treated with 81 in xenografted mice models [112].81 inhibited the growth of RPMI 8226 and KM3 cell lines via regulating PI3K pathway [113].
Physapubescin B (9) inhibited human hepatoellular carcinomas HepG2,human prostate cancer PC3,human ovarian cancer SKOV3,human breast cancer MDA-MB-231,human prostate epithelial RWPE-1,and human prostate cancer Du145 cells with IC50values ranging from 1.8 to 16.0 μM by blocking cancer cells in G2-M phase [7],which was related to its inhibitory effect of STAT3 activation [35].9 also promoted the apoptosis and autophagy of cancer cells [114,115].Kidney-type glutaminase (KGA) is crucial for energy supply,thus overexpressed in different cancers.Physapubescin I (20)showed an inhibition effect on human pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells,human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells,and human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells with IC503.34 ±0.04 μM,5.04 ± 0.05 μM,and 2.06 ± 0.03 μM by inhibiting the activity of KGA [116].Similarly,physapubescin A (8)was able to inhibit the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer HCC827 cells and human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells by inhibiting the activity of KGA [117].
As a KGA inhibitor,21 exhibited inhibitory effects on proliferation of human pancreatic cancer SW1990 and human non-small cell lung cancer HCC827 cancer cells by blocking glutamine metabolism [118].21,26,and virginols A1(28) inhibited the growth of four kinds of human cancer cell lines (human renal carcinoma 786-O cells,human renal carcinoma A-498 cells,human clear renal carcinoma Caki-2 cells,and human renal carcinoma ACHN cells).24 was identified to be the inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis ligand (TRIL) belonging to the TNF superfamily [39].
Withanolides exemplified by withaferin A (2) and 2α,3β-dihydroxy-5α-pregn-16-en-20-one3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (48) showed inhibitory effect on proliferation of human cancer cells.2 demonstrated inhibitory effects against cancer cell proliferation,which was verified in several types of cancer[119-121].1β,3α-dihydroxy-7α-eremophila-9,11-dien-3-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(l→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside(135) from the fruit ofP.pubescens,inhibited the proliferation of human prostate cancer C4-2B cells and human melanoma A375 cells with IC50values of 12.8 and 28.3 μM [25].
Moreover,ethyl caffeate (97) inhibited the proliferation,migration and invasion of human ovarian cancer SKOV-3 cells through regulating Akt,ERK,and MAPK [122].Similarly,nortrachelogenin (99) inhibited proliferation of prostate cancer cells through suppressing the membrane localization and activation of growth factor receptors [123].Pinoresinol (101) showed cytotoxic activity and killed human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and human breast cancer MCF-7 cells,which suggested its potential antitumor activity [124].101 suppressed the migration,and invasion of human hepatoellular carcinomas HepG2 cells by regulating E-cadherin,vascular cell adhesion molecule-1,and MMP-9 expression [125] and has an inhibitory effect on human ovarian cancer SKOV-3 cells with an IC50of 20 μM [126].Treatment with 50 μM arjunolic acid (123) exerted inhibitory activity against the proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 and human cervical cancer Hela cells through regulating ROS,NF-κB,and TNF-α [127].Pulsatilla saponin A (124) caused G2 arrest,differentiation,and apoptosis of myeloma cells by regulating MEK/ERK signaling pathway [128].Treatment with 20,50,and 100 nmol/L pulsatilla saponin D (125)inhibited the proliferation of human cervical cancer Hela cells with inhibition rates of 47.16%,17.90%,and 25.28%via regulating the Wnt signaling pathway [129].
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects
In diabetic rats induced by alloxan monohydrate,administration with the juice ofP.pubescensexerts antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effects,which are mainly attributed to its antioxidant potential,regulating β cells of the pancreas and insulin production [8].In streptozocin(STZ)-induced rats,oral administration of 5 mL/kgP.pubescensjuice significantly decreased the blood glucose and protected against diabetes-induced neurodegenerative complications via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation [130].The polysaccharide was able to inhibit the activity of α-glucosidase in vitro.Meanwhile,it improved the oral glucose tolerance in the diabetic mouse model induced by STZ [131].
Treating with kaempferol (67) enhanced the process of glucose metabolism to protect body from damage from diabetes [132].67 promoted β cells survival,insulin secretory function,ameliorates,and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes rats [133,134].Administration of 67 at 10 mg/kg attenuated obesity,hyperlipidemia,hyperglycemia,and insulin resistance via activating PPARγ/LXRα/ABCA1 and PPARγ/PI3K/AKT pathways in high-fat-diet rats [135].In STZ-induced diabetes rats,67 regulated a series of carbohydrate metabolic enzymes to maintain the blood sugar [136].
Withaferin A (2) significantly improved the insulin sensitivity in hepatic metabolic via inhibiting ROS production and inflammation [137,138].Moreover,2 effectively combated STZ-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) through modulating of Nrf2/NF-κB pathway and holding substantial potential for therapy of T1DM [139].
Imperatorin (102) significantly reduced obesity,hypertension,dyslipidemia,and increased insulin sensitivity in fat diet-fed rats.Oleuropein (120)ameliorated diabetes and relieved diabetes complications since its capability of modulating insulin secretion,repairing islet morphology,activating hepatic AMPactivated protein kinase singling,and improving glucose tolerance and insulin resistance [140].Treatment with 120 efficiently reduced blood glucose,insulin,and hepatic glycogen levels in gestational diabetes mellitus mice via regulating oxidant and inflammation [141].Arjunolic acid(123) prevented the over-production of ROS,RNS,advanced glycation end products (AGEs),and decrease oxidative damage induced by hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes [142].Caffeic acid (112) inhibited AGEs formation in vitro,and decreased the inflammatory and oxidative damage in HUVECs exposed to AGEs.112 markedly decreased lipid accumulation in the liver and the levels of ER stress markers,improved glucose intolerance and insulin sensitivity [143].
Diuretic effect
Treatment with 80% ethanol extract ofP.pubescenssignificantly enhanced the urination function of the kidney in rats.The diuretic effect of 0.15,0.3,and 0.6 g/kg ethanol extract ofP.pubescenswas equivalent to hydrochlorothiazide in the 1-2 h measurement period and disappeared after 4 hours [9].
Discussion
P.pubescenshas been recorded as an important herbal medicinal plant for treating sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,coughing,and urogenital system diseases in TCM and folk medicine for a long history [1,3,25].In the present review,we have summarized the ethnomedicinal use,nutrition,phytochemistry,and pharmacology aspects ofP.pubescens,which helps to explain its mechanisms of treating the diseases,and thus supports the ethnomedicinal use and establish a basis for future investigations.
The present review summarized 170 constituents including steroids (1-52),flavonoids (53-88),phenylpropanoids (89-119),terpenoids (120-135),Ncontaining compounds (136-138),organic acids (139-147),and miscellaneous constituents (148-170),which were derived from calyxes,stems,leaves,and fruits ofP.pubescens.Of which,steroids,flavonoids,and phenylpropanoids were the main constituents.Those constituents and crude extract exhibited diversity of bioactivities,such as anti-inflammation,anti-oxidation,antibacterial,regulating immunological competence,and diuretic effects which support its ethnomedicinal use [4,6,30,130].In TCM systems,P.pubescenswas often used together with other plants of the SolanaceaePhysalis,but differences in constituents betweenP.pubescensand other plants have been found.Physalins and withaferins which are representative and common compounds in otherPhysalisplants were rarely reported in the phytochemical research ofP.pubescens.Instead,physapubescins,exemplified by physapubescin A and physapubescin B are rich and representative ingredients inP.pubescens[7,33].Moreover,compared to other plants of the same genus,P.pubescensis more consumed as fruits now.
In the present review,we tried to establish the connection between the modern survey of phytochemistry and bioactivities with the ethnomedicinal use ofP.pubescens.The diseases of sore throat,aphonia,phlegm,heat,and coughing,are usually accompanied by the inflammation in trachea,throat,or lung [144,145].The previous review didn’t focus on the anti-inflammatory effect ofP.pubescens,which is essential for its ethnomedicinal use.The constituents derived fromP.pubescens,especially steroids,flavonoids,and phenylpropanoids exert anti-inflammatory effects in vitro andin vivo.Moreover,inflammation is also closely related to the oxidative stress and infection of bacterial [146,147].Active molecules represented by flavonoids and steroids exhibit the potential to scavenge free radicals,maintain redox balance,and attenuate microbial infections.All the observed evidences have indicated that the pharmacological effects supporting the ethnomedicinal use ofP.pubescensin TCM and folk medicine are produced by flavonoids,steroids,and phenylpropanoids.In addition to respiratory diseases,inflammation is also involved in many chronic diseases,such as neurodegenerative disorders,diabetic nephropathy,heart failure,and so on[148-151].Among those anti-inflammatory constituents,withaferins and physapubescins exhibited strong antiinflammatory activity as characteristic components ofP.pubescens,which suggested the potential ofP.pubescensto be a therapeutic agent for these chronic diseases.
Since long history of ethnomedical application and remarkable therapeutic effects,TCM herbs are an important source for drug discovery and development for various diseases.Besides the pharmacological activities ofP.pubescenswhich are closely related to the ethnomedicinal use in TCM and folk medicine,other bioactivities are also discussed in the present review,such as effect on immunological competence,anticancer,antihyperglycemic,antihyperlipidemic,and diuretic effects.Initially,these pharmacological activity studies focused on the extracts ofP.pubescens,and with continuous in-depth research on the components and pharmacology,a series of components represented by flavonoids,steroids,and phenylpropanoids with those activities have been discovered inP.pubescens.Those activities observed in modern research not only confirm the medicinal value ofP.pubescens,but also broadened his medicinal use,which provides the basis for the further development and utilization of this medicinal herb.Among those activities,anticancer,antihyperglycemic,and antihyperlipidemic effects ofP.pubescensare more outstanding.The active flavonoids,steroids,and phenylpropanoids possessing above mentioned biological effects are potential lead compounds to explore agents for the therapy of cancer or diabetes.
Moreover,in addition to the medicinal herb,the fruitsP.pubescensare also consumed as high-quality fruits with good taste and rich nutrition in many areas.Its fruits are excellent supplements of trace elements,especially for zinc and magnesium.The organic acids,such as tartaric acid,malic acid,citric acid,succinic acid,which promote digestion and absorption,were high content in the fruits.In addition,the rich natural pigments in fruits exert antioxidant activity.Taken together,the fruits ofP.pubescensare excellent fruits with rich trace elements,organic acids,and flavonoids.
Phytochemistry research onP.pubescensindicated that the major bioactive constituents ofP.pubescensare flavonoids,steroids,and phenylpropanoids.In recent decades,much important research has been performed to support its traditional applications.However,problems aboutP.pubescenswhich need further study and discussion still remains.
(ⅰ) The phytochemistry research aboutP.pubescenshave been going on for a few decades.However,the understanding of the chemical composition inP.pubescensis not sufficient.the further phytochemistry research onP.pubescensis needed,especially the research on the water-soluble part ofP.pubescens,because water decoction is the main method of administration in TCM clinic.
(ⅱ) In folk medicine,P.pubescenswas totally used with the same pharmacological effect as plants from the genus ofPhysalis,such asPhysalis alkekengiL.var.franchetii(Mast.) Makino.With the development of modern botany,we now know that they are different plants.Further clarifying the similarities and differences between those plants in phytochemical and pharmacological activities is of great significance for the development and utilization of the resources of the medicinal plants.
(ⅲ)P.pubescensis a medicinal and edible plant,the fruits ofP.pubescensare consumed and eaten as fruits in many areas.However,the benefits or therapeutic effects of long-term consumption ofP.pubescensfruits on the human body have not been fully revealed.More attention is needed for the direction in the future research onP.pubescens,which has guiding significance for the food processing ofP.pubescens.
Data availability or Code availability
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to shentao@sdu.edu.cn (Prof.Tao Shen).
Abbreviations
ABTS,2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid;AGEs,advanced glycation end products ;AP-1,activating protein-1;ARE,antioxidant response element;ATP,adenosine triphosphate;CAT,catalase;CFA,complete freund's adjuvant;CDK,cyclin-dependent kinase;COX-2,cyclooxygenase-2;DPPH,2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl;DSS,dextran sulfate sodium salt;EGFR,epidermal growth factor receptor;FRAP,ferric reducing ability of plasma;GPx,glutathione peroxidase;GR,glutathione reductase;GSH,glutathione;HO-1,heme oxygenase-1;IL,interleukin;iNOS,inducible nitric oxide synthase;KGA,kidney-type glutaminase;LPS,lipopolysaccharide;MAPK,mitogen-activated protein kinase;MSU,monosodium urate;NK,natural killer;NLRP3,nod like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3;NO,nitric oxide;Nrf2,nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2;OVA,ovalbumin;PGE2,prostaglandin E2;PI3K,phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases;polysaccharides,POL,polysaccharides;QR,quinone reductase;ROS,reactive oxygen species;RPE,retinal pigment epithelium;SHP-1,src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1;SOD,superoxide dismutase;STAT3,signal transducer and activator of transcription 3;T1DM,type 1 diabetes mellitus;TCM,traditional Chinese medicines;TNF-α,tumor necrosis factor-α.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NNSF of China(81673558).
Author contributions
Xin-Ping Cheng,Xiao-Ning Wang,and Tao Shen conceived and designed the review.Xin-Ping Cheng,Bin-Yin,and Qian-Kun Zheng collected and analyzed literatures.Xin-Ping Cheng,Lin-Tao Xu,and Guang-Cheng Peng drafted the manuscript.Xiao-Ning Wang,Zhen-Peng Xu,and Tao Shen revised the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2022年3期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2022年3期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Effects of Euphorbiasteroid on gene expression in lung cancer cells based on gene chip
- Standardization and Quality control parameters of Kayam Churna
- Niaoduqing granules inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells
- The genus Strobilanthes: phytochemistry and pharmacology
- Traditional Chinese medicine as monotherapy or combined with oseltamivir in the treatment of H1N1 influenza: a systematic review and meta-analysis
