Impact of X-radiation in the management of COVID-19 disease
INTRODUCTION
Coronaviruses are a diverse group of viruses that infect both animals and humans.The existence of coronavirus and its infection to humans is not new;since the beginning of this century,severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus(SARS-CoV)and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus are infecting humans and are of concern to public health[1].The coronavirus infection is majorly associated with an array of clinical symptoms,which range from upper respiratory tract infection of moderate clinical concern to lower respiratory tract including bronchiolitis and pneumonia leading to fatality,especially in the elderly,and individuals with compromised immunity.The 2019-novel coronavirus(nCoV)outbreak leads to a lower respiratory tract disease called novel coronavirus pneumonia and renamed this beta-corona virus SARS-CoV-2,the established etiology for COVID-19 disease.
COVID-19 disease
The World Health Organization(WHO)has declared 2019-nCoV infection as a global health emergency,because,within a few months not only did several thousand individuals test positive for the virus infection but also resulted in a significant number of deaths worldwide.That was because of the disease burden,the WHO officially characterized the global COVID-19 flare-up as a pandemic on 11 March 2020.Important clinical features of COVID-19 spread documented were:(i)An infection rate of 83% within the family;(ii)Mild to moderate with more systematic symptoms and severe radiological abnormalities as clinical manifestations seen in older patients;and(iii)Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from asymptomatic carriers to others[2].Given the rapid spread of the disease and asymptomatic carriers,it remains a major health problem throughout the world.Although genetic evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 is a natural virus that likely originated in animals,there is no conclusion yet about when and where the virus first entered humans.However,these viruses are known to constantly change through mutation and result in a new variant of the virus;such a new variant is known to affect the virus properties,such as infection rate,the severity of disease,the performance of vaccines,therapeutic medicines,diagnostic tools,or other public health and social measures.Of late many variants form of the virus has been reported with a higher infection rate(Omicron)despite the severity of the disease and the need for hospitalization is less when compared to that of earlier variants(beta and delta coronavirus as SARS-CoV-2)and COVID 19 disease[3].Even the variant reported causing less severe disease,in general,an increase in the total number of cases could lead to an upsurge in hospitalizations,laying more strain on healthcare resources.
Symptoms and Pathogenesis of the disease
The most common symptoms after COVID-19 infection are fever,fatigue,and dry cough.Less common symptoms include sputum production,headache,hemoptysis,diarrhea,anorexia,sore throat,chest pain,chills,nausea,and vomiting[2,4-7]olfactory and taste disorders[8].The majority of infected people showed signs of disease for about fourteen days(frequently around five days),and dyspnea and pneumonia developed within a median time of eight days from illness onset[9,10].The pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans manifests itself as mild symptoms to severe respiratory failure.Upon entry of the virus in the nasal route,the virus binds to epithelial cells in the respiratory tract,starts replicating and migrating down to the airways,and goes into alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs.Owing to the hasty replication of SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs,activate a strong immune response,and cascade into a cytokine storm,resulting in acute respiratory distress syndrome and then respiratory failure,which is considered the notable cause of death in patients with COVID-19 infection[2,5].Even multiple organ failure has also been reported in some COVID-19 cases.Despite the range and severity of the disease,clinical manifestations differ with age;men >60 years with co-morbidities are more prospective to develop a severe respiratory disease that required hospitalization or even death,whereas most young people and children had only mild diseases and/or are asymptomatic[7,11].Moreover,regardless of evidence of trans-placental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected mother to a neonate,the risk of disease was not higher for pregnant women[4,12].Thus,the disease caused a major burden on the individual and society i.e.,anxiety,fear of infection,struggle and extreme competition for hospitalization,and more importantly financial liability.
Diagnosis of COVID-19
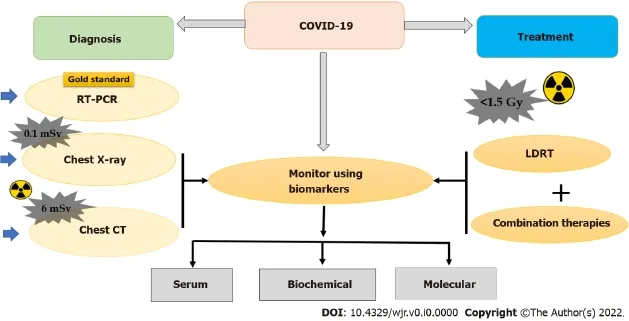
Given the rapid spread of infection,early diagnosis is crucial for controlling the spread of COVID-19.Choice of diagnosis options is(i)detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid;(ii)detecting antibodies to N or S protein;and(iii)imaging by simple chest X-ray and high-resolution computed tomography(CT)with X-rays.The detection time ranges from several minutes to hours depending on the technology used for the diagnosis[13-18].Among those tools,a quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR)test is the current standard of test and remains the “gold standard” to confirm the COVID-19 infection.RT-PCR has also its challenges such as delays in result turnaround time and interpretation of the results.Another major hurdle is the dynamic conversion of RT-PCR results from either negative to positive or vice-versa.Serology tests detecting antibodies to N or S protein could complement molecular diagnosis,particularly in late phases after disease onset or for retrospective studies[19-21].
In alternate,imaging using X-rays such as conventional chest X-rays(CXR)and high-resolution CT was used to quickly identify a patient when the capacity of molecular detection was overloaded as well as to identify the disease severity.CXR examination after two days of RT-PCR tests revealed that the yield of improved heatmaps of influential regions contributed to deep learning prediction scores
machine learning[22].CT,a routine imaging modality is being performed for immediate diagnosis which is even effective in asymptomatic patients whose RT-PCR test results reveal to be negative as the CT scores give better disease findings and long-term follow-up with 29% increased sensitivity in comparison with chest radiography[23].CT scanning combined with repeated swab tests was used for individuals with high clinical suspicion of COVID-19.Thus,combining RT-PCR with CT of the chest in an appropriate clinical setting is considered the best modality to investigate any patient.Ai
[24],2020 suggested a higher sensitivity of CT chest(98%)than RT-PCR(71%)in diagnosing COVID-19.In addition to CXR and CT,Infrared thermography has been useful in the identification of asymptomatic carriers
the detection of true core body temperature but its thermal cameras are insufficient for screening the disease[25].The single-photon emission computerized tomography,and
molecular imaging allows the observation of patient-specific and disease-specific characteristics for physiological models of COVID-19 patients[26,27].
Therapy and management of COVID-19 infection
Until the introduction of vaccines,test-positive subjects were isolated/ quarantined and provided with medication and supplements to boost their immune mechanism to overcome the disease.Initially,in the absence of proven effective therapies for COVID-19 or antivirals against SARS-CoV-2,researchers and manufacturers are conducting large-scale clinical trials to evaluate various therapies for COVID-19.Some of the existing options are to prevent viral entry,inhibition of virus replication,immunomodulatory agents,immunoglobulin therapy,vaccines,and potential control measures using ultraviolet radiation,and low-dose ionizing radiation[28].The illustration of the use of X-rays in the diagnosis and therapy for COVID-19 has been provided in Figure 1.Absence of knowledge on the COVID-19 disease,screening,and specific treatment regimes,multiple approaches were tried to contain the spread of infection in the early time of the pandemic.Thus,the X-radiation technology was used in the early diagnosis,management,and containment of COVID-19 disease.The present review focused on consolidating the role of X-radiation in various stages of COVID-19 infection and disease manifestations:Screening,diagnosis,and management.Also,concerns associated with the use of X-rays in those phases of disease management were discussed.
CXR AND CT IMAGING OF COVID-19 PATIENTS
Aishwarya T A,Mohan DK,Nandhini K contributed to review of literature and preparation of the draft;Raavi V contributed to conceptualization and design of the work,revision,and editing;Perumal V contributed to conceptualization and approval of the final version of the manuscript
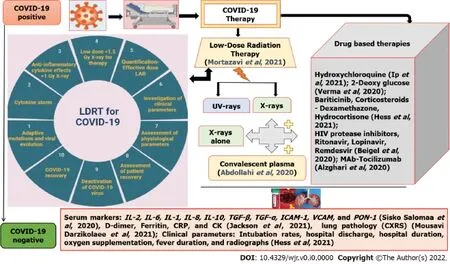
LOW DOSE X-RADIATION THERAPY(LDRT)FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COVID-19 PATIENTS
COVID-19 patients are associated with mucormycosis,shortly referred to as CAM,being one notifiable disease in India with a 50% fatality rate for which administering anti-fungal drugs(amphotericin-B)is the treatment[50].This CAM condition had been observed in 79% of males,either with 59% active COVID-19 or with 41% COVID-19 recovered status[44].Further CAM studies were inquisitive for COVID-19 variants with mucor-immunity-associated disturbances,population-associated genetic susceptibilities,and the presence of virulent strains or influence of environmental factors.In such cases,LDRT is a hope in reducing CAM as it can increase CD3,CD4,and CD8 cells thereby transforming them to CD8 cells that can destroy acute respiratory syndrome-infected cells.An example of this LDRT was its implementation in treating tinea captitis till the discovery of griseofulvin[44].
All the authors declared that there is no conflict of interest
The inclusion criteria for LDRT adopted in recent studies were COVID-19 +ve patients,age > 18 years,both genders,and national early warning score of ≥ 5,and the exclusion criteria were healthy volunteers,patients on mechanical ventilatory support,and hemodynamically unstable patients[48].The mechanisms proposed in these recent studies are that the LDRT could inhibit the cytokine storm,activation of immune and endothelial cells,and inhibition of subsequent virus-induced pulmonary dysfunction in COVID-19 patients[49].Despite many clinical trials being ongoing,three studies reported the prognosis of COVID-19 patients treated with LDRT as 80% to 90%[45,46,48].The guidelines routinely used for whole-lung-irradiation of patients undergoing radiotherapy have been applied for COVID-19 patients treated using LDRT[49].
The sudden outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 infections results in COVID-19 disease,which is associated with compromised immunological defense and lung damage[38].Therefore,the COVID-19 patients were isolated/quarantined and provided with medication and supplements to boost their immune mechanism to overcome the disease[39].In addition to the boosters to immune mechanisms,several therapy strategies were tested to prevent viral entry,inhibition of virus replication,immunomodulatory agents,immunoglobulin therapy,vaccines,and potential control measures[28].The schematic representation of the possible therapy has been provided in Figure 2.One of those therapy strategies is the use of LDRT for COVID-19-infected patients because it has been proven to cure pneumonia in the early 20
century[40].The treatment with low-dose X-rays complements other treatment modalities and has a profound role in minimizing COVID-19 infection severity[39].Low dose comprises doses below 100 mGy as defined by UNSCEAR and has the characteristics such as accelerated immune senescence,altered immune fitness,a shift in peripheral lymphocyte,balance in favor of B-cells,and pro-inflammatory responses[39].The first attempt on the use of LDRT for COVID-19-related pneumonia was made by Italian and American scientists for which the patients received a single dose of either 0.10,0.18 or 0.25 Gy[38].Since then,many studies have attempted to exploit the potential of radiation in the management of COVID-19 disease.The list of major studies(animal models,isolated studies,and multicentric clinical trials)related to LDRT and their salient findings are presented in Supplementary Table 2.
Radiation as the choice of COVID-19 infection containment
LDRT also regulates lymphocyte counts,and bacterial co-infections in COVID-19 patients by modulating excess inflammatory responses[5].The use of UV or γ-rays for sanitization will effectively kill viral particles[51].Thus,deactivating COVID-19 viral cells and not allowing the infection to recur by implicating minimal dose radiation therapy by assessing the patient's condition can cure COVID-19[52].The LDRT was also tested by combining with 2-deoxy glucose(2-DG),which has a potential adjuvant to enhance the efficacy of LDRT in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia[53].Anti-inflammatory effects in LDRT are found to be associated with anti-viral or anti-bacterial effects[53].Targeting the glycolytic pathway by 2-DG has been well established for its radio- and chemo-sensitizing effects in both
and
conditions.The 2-DG has been suggested as a therapeutic for the management of COVID-19 patients[53].The 2-DG in combination with LDRT may also protect other virus-sensitive tissues and organs leading to a reduction in mortality and morbidity[53].Azido-2-DG will produce the electronmediated formation of oxidizing aminyl radicals,thus an adjuvant to LDRT[53].
BIOMARKERS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF COVID-19 INFECTION AND DISEASE
The biomarkers for the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease have been categorized into hematological[lymphocyte count,neutrophil count,and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio(NLR)],inflammatory(CRP,Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate,and procalcitonin),immunological(cytokines),and biochemical(Ddimer,troponin,creatine kinase,and aspartate aminotransferase),coagulation cascades in disseminated intravascular coagulation in most of the studies[54].Retrospective studies conducted in COVID-19 patients admitted in intensive care unit(ICU)and post-recovery had been assessed for levels of several biomarkers wherein interleukins(IL)-2,IL7,IL10,GCSF,IP10,MCP1,MIP1A,and TNFα were higher in ICU patients than non-ICU patients[2].Elevation of glomerular filtration function markers such as serum urea,CREA,and Cys C had been observed in severe COVID-19 patients more than in mild COVID-19 patients[55].In comparison with the recovered group,the deceased group had an elevation in levels of leukocytes,neutrophils,high-sensitivity C-reactive protein(hsCRP),prothrombin,D-dimer,serum ferritin,IL-2,and IL-6[56].Elevated levels of LDH,CRP,ferritin,and D-dimer had been found in most of the cases.IL-6 significantly increased in severe type,also IL-6,CRP,LDH,and ferritin were the most commonly elevated biomarkers and were associated with the severity of COVID-19[57].On the other hand,a decrease in the density of natural killer cells and CD3+ T cells,including all T cell subsets had been observed in patients.Multiplex gene expression analysis showed an up-regulation of genes involved in type-I IFN signaling(
,
,and
)contrasting with a striking down-regulation of
-stimulated genes(
,
,and
)in critical SARS-CoV-2 patients[58].Lymphocytopenia was found to be the most common marker of infection in most critically ill COVID-19 patients[59].These biomarkers are thus significant in the early identification of COVID-19 disease;hence disease prognosis can be improved and also helpful to monitor the LDRT.
Then he recognized Gerda, and said, joyfully10, “Gerda, dear little Gerda, where have you been all this time, and where have I been?” And he looked all around him, and said, “How cold it is, and how large and empty it all looks,” and he clung to Gerda, and she laughed and wept for joy
LIMITATIONS/ FUTURE IMPROVEMENTS ON USING X-RAYS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF COVID-19 DISEASE
Although,exposure to radiation from these X-ray imaging is a concern,due to its wide application in delivering intense structures of the organs which are been reliably used for the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease.However,the use of this X-ray-based imaging should be done with the most precaution since it might result in stochastic effects later in the life span of the exposed individual.Also,the concerns associated with the use of radiation in terms of risk for carcinogenesis were evaluated using phantom models[60].The stochastic effects are seen with low doses in LDRT and thus quantifying the effective dose and Lifetime Attributable Risk will help in the effective treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia[41].Delivering radiotherapy by giving quality assurance is impossible as the system conditions of portable X-ray machines delivering low-dose radiation therapy are not compatible.The concept of being as low as reasonably achievable is the basis of the radiation protection approach[61].Targeting the whole lung requires vast knowledge about the biological mechanisms and hence deliverance of a low dose for an appropriate target volume is highly challenging.Examining LDRT in a trial setting in the case of COVID-19 treatment can be beneficial for patients and can be taken to the next level for scientific scrutiny.Shortening overall therapy time by giving multiple fractions/weeks may enhance COVID-19 management[62].Based on the previous clinical trials,the effectiveness of LDRT in treating COVID-19 was up to 80%;therefore,the Food and Drug Administration recommended LDRT(by irradiating 0.5 Gy)as a treatment for COVID-19[63].Thus,the contribution of X-ray-based imaging is enormous and its use is inevitable in modern-day health care including the COVID-19 pandemic.Despite the beneficial effects,the ethical concerns to use LDRT in the management of COVID-19 were the risk of spread of infection,time frame for a patient,and inconvenience in treating an intubated patient[64].Even though medical imaging is widely used,divergent thoughts existed on the health effects of low-dose IR in scientific communities/stakeholders[65,66].An “enhanced risk of stochastic effects due to radiation dose received by the patients during CT imaging” and “clarifications” from professional associations and regulatory authorities during this COVID-19 pandemic raised the anxiety among the public at the national level[67,68].Any technology is not devoid of risk/side effects.Nevertheless,the improvements/advancements in technology contribute to minimizing the risk while enhancing the benefits.The same is the case for CT imaging;a recent low-dose chest CT protocol has been proposed to reduce the dose up to 89% when compared to the standard-dose protocol without compromising the diagnostic accuracy of COVID-19-induced pneumonia in CT images[69].Despite those developments,the medical uses of IR are not devoid of criticism owing to the projected risk for different health effects.The reported studies suggest that CXR contributed significantly toward initial rapid diagnosis and CT- imaging to monitor the disease.
CONCLUSION
Aishwarya T A 0000-0001-7818-3386;Divya K Mohan 0000-0001-8283-6343;Nandhini K 0000-0002-6066-1826;Venkateswarlu Raavi 0000-0002-7858-1664;Venkatachalam Perumal 0000-0003-2152-2003.
FOOTNOTES
X-ray-based imaging is being used for the diagnosis of numerous health conditions for several decades.In the sudden outbreak of COVID-19,X-ray-based imaging was considered a relevant and rapid modality in the diagnosis of patients with COVID-19 disease,especially if the availability of other diagnostic methods like RT-PCR becomes limited due to a large number of infected patients and the time required for the reporting.CXR and high-resolution chest CT are the two important non-invasive examinations for the diagnosis of lung damage caused by COVID-19 infection[29].Because of its intense resolution capacity and also clarity of organizational structures,these two X-ray imaging modalities have been used for the diagnosis of COVID infection and severity of disease in several countries.The prominent chest CT imaging findings of COVID-19 patients were found to be bilateral lung involvement and Ground Glass Opacities(GGO).Since then,many hospitals from different countries used both chest X-ray and chest CT imaging for the initial diagnosis of lung damage and published at a rapid pace.An overview of the published articles on the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection using chest X-ray and chest CT imaging were shown in Supplementary Table 1.The finding from all those studies suggests that the radiographic findings seem to be good predictors for assessing the progress of COVID-19 disease.It was found that the chest CT has high sensitivity and lower specificity for diagnosis and severity of COVID-19 disease.CXR was used as a primary imaging technique for the initial screening of COVID-19 in many hospitals[30,31].However,few studies sounded controversial that chest CT detected a combination of lung abnormalities that were not observed in CXR[32].The enhanced use of CT substantially improved diagnostic performance over CXR in COVID-19 infections and diseases.Age-dependent variations on CT features were associated with clinical manifestation and also with patient prognosis[33].Therefore,CT was considered for the initial assessment of suspected COVID-19 infections compared to CXR.In general,the CT features and scores ranging between,mild(0-7),moderate(8-17),and severe(18 or more)are usually associated with clinical manifestation and COVID-19 disease prognosis[34].CT imaging had good diagnostic value in symptomatic infections and was insufficient to justify its use as a first-line screening approach in asymptomatic infections[35].CXR severity was correlated with known laboratory markers of disease such as higher lactate dehydrogenase(LDH),higher C-reactive protein(CRP),and lower lymphocyte count[36].In a similar study,CT findings showed characteristics of GGO,which were correlated with biochemical markers such as CRP,erythrocyte sedimentation rate,and LDH to the severity of COVID-19 infection[37].Although the gold standard RT-PCR has been the primary source of diagnosis of COVID-19 infection,chest CT imaging has a high sensitivity for diagnosis and finding the severity of COVID-19 disease when compared to RT-PCR[24].Both RT-PCR and X-ray-based imaging has been used extensively throughout the world to contain the spread of COVID-19 infection and disease severity in COVID-19 patients.
India
The range of doses employed in the LDRT among the published literature varies between 0.5-1.5 Gy of X-rays[39].Whole lung LDRT may serve as a better option as it presents a low-risk treatment for COVID-19 pneumonia patients[38].The LDRT is possible by using LINAC equipment that can deliver an appropriately low dose[39].A recent study with nine clinical trials used the dose range between 0.5-1 Gy in a single fraction to investigate the effect of whole-lung irradiation of COVID-19 patients by analyzing the parameters such as CRP,IL-6,D- dimer,and ferritin as it can affect the lung macrophages at these doses[39].The therapeutic benefits of LDRT for pneumonitis were evaluated based on the percentage of recovery and the extent of severity[41].The most commonly evaluated outcome parameters were ventilator-free numerous hematologic,cardiac,hepatic,and inflammatory markers.Few parameters such as the probability of intubation rates,hospital discharge,hospital duration,oxygen supplementation,fever duration,radiographs,clinical recovery ,SatO2/FiO2 index,and lung inflammation[42,43].The radiation toxicity effects had also been studied apart from other parameters[44].Physiological parameters such as blood oxygen level,clinical recovery rate,mean oxygen saturation,improvement in oxygenation SF ratio,and demand for supplemental oxygen in postradiotherapy[45].Clinical parameters such as overall survival,response rate,and X-ray severity score were mainly considered[46].The level of serum biomarkers such as CRP,CK,and inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2,IL-6,IL-1,IL-8,IL-10,TGF-beta,TGF-alpha,ICAM-1,VCAM,and oxidative marker(PON-1)had been evaluated in previous studies[42].LDRT can increase interferon-γ production,activates natural killer cells,stimulates antigen processing and antigen presentation to T- cells and activates natural killer T-cells(NKT),γδ T cells,and αβ CD8+ T-cells[47].The results of these initial studies highlight that the LDRT can be used as one of the treatment options to treat pneumonia in COVID-19 patients.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See:https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Now, said he, you must each of you tie a stone to your necks, so that you may be sure to go deep enough, for I found the pigs that you saw very deep down indeed
Overall the review of the literature suggests that the chest CT has high sensitivity(98%)and less specificity for COVID-19 disease diagnosis compared to RT-PCR.The LDRT therapy for COVID-19 patients compliments the drug therapy in the early recovery stage by maintaining the physiological parameters better than the drug therapy alone.All the recent studies results demonstrated that X-raybased technology continues to evolve and play a significant role even during the COVID-19 pandemic.
He therefore went to the queen, and told her everything, at the same time showing her the king s letter containing the command to burn her and the princes
Liu JH
He now had plenty of time to reflect on thedifference of fortune on earth, and to wonder why this fate had beenallotted to him; yet he felt sure that all would be made clear inthe next life, the existence that awaits us when this life is over
A
Come with me , the man said. Over that hill is an old cellar hole, from somebody s farm of years ago, and there are lilacs all round it. The man who owns this land said I could poke12 around here anytime. I m sure he won t mind if we pick a few lilacs.
“Moths are the most beautiful animals in the animal kingdom. At one time they were more colorful than the butterflies. They have always been helpful, kind, and generous creatures. One day the angels up in heaven were crying. They were sad because it was cloudy and they couldn’t look down upon the people on earth. Their tears fell down to the earth as rain. The sweet little moths hated to see everyone so sad. They decided7 to make a rainbow. The moths figured that if they asked their cousins, the butterflies, to help, they could all give up just a little bit of their colors and they could make a beautiful rainbow.
Liu JH
1 Cui J,Li F,Shi ZL.Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses.
2019;17:181-192[PMID:30531947 DOI:10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9]
2 Huang C,Wang Y,Li X,Ren L,Zhao J,Hu Y,Zhang L,Fan G,Xu J,Gu X,Cheng Z,Yu T,Xia J,Wei Y,Wu W,Xie X,Yin W,Li H,Liu M,Xiao Y,Gao H,Guo L,Xie J,Wang G,Jiang R,Gao Z,Jin Q,Wang J,Cao B.Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan,China.
2020;395:497-506[PMID:31986264 DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5]
3 Na W,Moon H,Song D.A comprehensive review of SARS-CoV-2 genetic mutations and lessons from animal coronavirus recombination in one health perspective.
2021;59:332-340[PMID:33624270 DOI:10.1007/s12275-021-0660-4]
4 Chen H,Guo J,Wang C,Luo F,Yu X,Zhang W,Li J,Zhao D,Xu D,Gong Q,Liao J,Yang H,Hou W,Zhang Y.Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women:a retrospective review of medical records.
2020;395:809-815[PMID:32151335 DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30360-3]
5 Mehta P,McAuley DF,Brown M,Sanchez E,Tattersall RS,Manson JJ;HLH Across Speciality Collaboration,UK.COVID-19:consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression.
2020;395:1033-1034[PMID:32192578 DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0]
6 Wang D,Hu B,Hu C,Zhu F,Liu X,Zhang J,Wang B,Xiang H,Cheng Z,Xiong Y,Zhao Y,Li Y,Wang X,Peng Z.Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan,China.
2020;323:1061-1069[PMID:32031570 DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.1585]
7 Guan WJ,Ni ZY,Hu Y,Liang WH,Ou CQ,He JX,Liu L,Shan H,Lei CL,Hui DSC,Du B,Li LJ,Zeng G,Yuen KY,Chen RC,Tang CL,Wang T,Chen PY,Xiang J,Li SY,Wang JL,Liang ZJ,Peng YX,Wei L,Liu Y,Hu YH,Peng P,Wang JM,Liu JY,Chen Z,Li G,Zheng ZJ,Qiu SQ,Luo J,Ye CJ,Zhu SY,Zhong NS;China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19.Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China.
2020;382:1708-1720[PMID:32109013 DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032]
8 Giacomelli A,Pezzati L,Conti F,Bernacchia D,Siano M,Oreni L,Rusconi S,Gervasoni C,Ridolfo AL,Rizzardini G,Antinori S,Galli M.Self-reported Olfactory and Taste Disorders in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2 Infection:A Cross-sectional Study.
2020;71:889-890[PMID:32215618 DOI:10.1093/cid/ciaa330]
9 Lauer SA,Grantz KH,Bi Q,Jones FK,Zheng Q,Meredith HR,Azman AS,Reich NG,Lessler J.The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19)From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases:Estimation and Application.
2020;172:577-582[PMID:32150748 DOI:10.7326/M20-0504]
10 Wu Z,McGoogan JM.Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19)Outbreak in China:Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
2020;323:1239-1242[PMID:32091533 DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.2648]
11 Lu X,Zhang L,Du H,Zhang J,Li YY,Qu J,Zhang W,Wang Y,Bao S,Li Y,Wu C,Liu H,Liu D,Shao J,Peng X,Yang Y,Liu Z,Xiang Y,Zhang F,Silva RM,Pinkerton KE,Shen K,Xiao H,Xu S,Wong GWK;Chinese Pediatric Novel Coronavirus Study Team.SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children.
2020;382:1663-1665[PMID:32187458 DOI:10.1056/NEJMc2005073]
12 Vivanti AJ,Vauloup-Fellous C,Prevot S,Zupan V,Suffee C,Do Cao J,Benachi A,De Luca D.Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
2020;11:3572[PMID:32665677 DOI:10.1038/s41467-020-17436-6]
13 Bordi L,Nicastri E,Scorzolini L,Di Caro A,Capobianchi MR,Castilletti C,Lalle E; On Behalf Of Inmi Covid-Study Group And Collaborating Centers.Differential diagnosis of illness in patients under investigation for the novel coronavirus(SARS-CoV-2),Italy,February 2020.
2020;25[PMID:32127123 DOI:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.8.2000170]
14 Chan JF,Yip CC,To KK,Tang TH,Wong SC,Leung KH,Fung AY,Ng AC,Zou Z,Tsoi HW,Choi GK,Tam AR,Cheng VC,Chan KH,Tsang OT,Yuen KY.Improved Molecular Diagnosis of COVID-19 by the Novel,Highly Sensitive and Specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay Validated
and with Clinical Specimens.
2020;58[PMID:32132196 DOI:10.1128/JCM.00310-20]
15 Corman VM,Landt O,Kaiser M,Molenkamp R,Meijer A,Chu DK,Bleicker T,Brünink S,Schneider J,Schmidt ML,Mulders DG,Haagmans BL,van der Veer B,van den Brink S,Wijsman L,Goderski G,Romette JL,Ellis J,Zambon M,Peiris M,Goossens H,Reusken C,Koopmans MP,Drosten C.Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus(2019-nCoV)by realtime RT-PCR.
2020;25[PMID:31992387 DOI:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045]
16 Konrad R,Eberle U,Dangel A,Treis B,Berger A,Bengs K,Fingerle V,Liebl B,Ackermann N,Sing A.Rapid establishment of laboratory diagnostics for the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in Bavaria,Germany,February 2020.
2020;25[PMID:32156330 DOI:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.9.2000173]
17 Lu R,Wu X,Wan Z,Li Y,Zuo L,Qin J,Jin X,Zhang C.Development of a Novel Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2.
2020;35:344-347[PMID:32239445 DOI:10.1007/s12250-020-00218-1]
18 Cordes AK,Heim A.Rapid random access detection of the novel SARS-coronavirus-2(SARS-CoV-2,previously 2019-nCoV)using an open access protocol for the Panther Fusion.
2020;125:104305[PMID:32143123 DOI:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104305]
19 Zhang W,Du RH,Li B,Zheng XS,Yang XL,Hu B,Wang YY,Xiao GF,Yan B,Shi ZL,Zhou P.Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients:implication of multiple shedding routes.
2020;9:386-389[PMID:32065057 DOI:10.1080/22221751.2020.1729071]
20 Guo L,Ren L,Yang S,Xiao M,Chang,Yang F,Dela Cruz CS,Wang Y,Wu C,Xiao Y,Zhang L,Han L,Dang S,Xu Y,Yang QW,Xu SY,Zhu HD,Xu YC,Jin Q,Sharma L,Wang L,Wang J.Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease(COVID-19).
2020;71:778-785[PMID:32198501 DOI:10.1093/cid/ciaa310]
21 To KK,Tsang OT,Leung WS,Tam AR,Wu TC,Lung DC,Yip CC,Cai JP,Chan JM,Chik TS,Lau DP,Choi CY,Chen LL,Chan WM,Chan KH,Ip JD,Ng AC,Poon RW,Luo CT,Cheng VC,Chan JF,Hung IF,Chen Z,Chen H,Yuen KY.Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2:an observational cohort study.
2020;20:565-574[PMID:32213337 DOI:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30196-1]
22 Hu Q,Drukker K,Giger ML.Role of standard and soft tissue chest radiography images in deep-learning-based early diagnosis of COVID-19.
2021;8:014503[PMID:34595245 DOI:10.1117/1.JMI.8.S1.014503]
23 Pal A,Ali A,Young TR,Oostenbrink J,Prabhakar A,Deacon N,Arnold A,Eltayeb A,Yap C,Young DM,Tang A,Lakshmanan S,Lim YY,Pokarowski M,Kakodkar P.Comprehensive literature review on the radiographic findings,imaging modalities,and the role of radiology in the COVID-19 pandemic.
2021;13:258-282[PMID:34630913 DOI:10.4329/wjr.v13.i9.258]
24 Ai T,Yang Z,Hou H,Zhan C,Chen C,Lv W,Tao Q,Sun Z,Xia L.Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19)in China:A Report of 1014 Cases.
2020;296:E32-E40[PMID:32101510 DOI:10.1148/radiol.2020200642]
25 Khaksari K,Nguyen T,Hill B,Quang T,Perreault J,Gorti V,Malpani R,Blick E,González Cano T,Shadgan B,Gandjbakhche AH.Review of the efficacy of infrared thermography for screening infectious diseases with applications to COVID-19.
2021;8:010901[PMID:33786335 DOI:10.1117/1.JMI.8.S1.010901]
26 Barrett HH,Caucci L.Stochastic models for objects and images in oncology and virology:application to PI3K-AktmTOR signaling and COVID-19 disease.
2021;8:S16001[PMID:33313340 DOI:10.1117/1.JMI.8.S1.S16001]
27 Giger M.Medical imaging of COVID-19.
2021;8:010101[PMID:34754885 DOI:10.1117/1.JMI.8.S1.010101]
28 Hu B,Guo H,Zhou P,Shi ZL.Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19.
2021;19:141-154[PMID:33024307 DOI:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7]
29 Benmalek E,Elmhamdi J,Jilbab A.Comparing CT scan and chest X-ray imaging for COVID-19 diagnosis.
2021;1:100003[PMID:34786568 DOI:10.1016/j.bea.2021.100003]
30 Rousan LA,Elobeid E,Karrar M,Khader Y.Chest x-ray findings and temporal lung changes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
2020;20:245[PMID:32933519 DOI:10.1186/s12890-020-01286-5]
31 Stephanie S,Shum T,Cleveland H,Challa SR,Herring A,Jacobson FL,Hatabu H,Byrne SC,Shashi K,Araki T,Hernandez JA,White CS,Hossain R,Hunsaker AR,Hammer MM.Determinants of Chest X-Ray Sensitivity for COVID-19:A Multi-Institutional Study in the United States.
2020;2:e200337[PMID:33778628 DOI:10.1148/ryct.2020200337]
32 Das KM,Alkoteesh JA,Al Kaabi J,Al Mansoori T,Winant AJ,Singh R,Paraswani R,Syed R,Sharif EM,Balhaj GB,Lee EY.Comparison of chest radiography and chest CT for evaluation of pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia:Does CT add diagnostic value?
2021;56:1409-1418[PMID:33631061 DOI:10.1002/ppul.25313]
33 Niu R,Ye S,Li Y,Ma H,Xie X,Hu S,Huang X,Ou Y,Chen J.Chest CT features associated with the clinical characteristics of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
2021;53:169-180[PMID:33426973 DOI:10.1080/07853890.2020.1851044]
34 Hefeda MM,Elsharawy DE,Dawoud TM.Correlation between the initial CT chest findings and short-term prognosis in Egyptian patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
2022;1-17[DOI:10.1186/s43055-021-00685-w]
35 De Smet K,De Smet D,Ryckaert T,Laridon E,Heremans B,Vandenbulcke R,Demedts I,Bouckaert B,Gryspeerdt S,Martens GA.Diagnostic Performance of Chest CT for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Individuals with or without COVID-19 Symptoms.
2021;298:E30-E37[PMID:32776832 DOI:10.1148/radiol.2020202708]
36 Hui TCH,Khoo HW,Young BE,Haja Mohideen SM,Lee YS,Lim CJ,Leo YS,Kaw GJL,Lye DC,Tan CH.Clinical utility of chest radiography for severe COVID-19.
2020;10:1540-1550[PMID:32676371 DOI:10.21037/qims-20-642]
37 Xiong Y,Sun D,Liu Y,Fan Y,Zhao L,Li X,Zhu W.Clinical and High-Resolution CT Features of the COVID-19 Infection:Comparison of the Initial and Follow-up Changes.
2020;55:332-339[PMID:32134800 DOI:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000674]
38 A R M,J J B,S A R M,S M J M.COVID-19:Introducing Low Dose Radiation as an Effective Treatment for Pneumonia that Shouldn't Induce Selective Pressure and New Mutations.
2020;10:247-250[PMID:32637368 DOI:10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2005-1114]
39 Mortazavi SMJ,Shams SF,Mohammadi S,Mortazavi SAR,Sihver L.Low-Dose Radiation Therapy for COVID-19:A Systematic Review.
2021;234-249[DOI:10.3390/radiation1030020]
40 Lara PC,Burgos J,Macias D.Low dose lung radiotherapy for COVID-19 pneumonia.The rationale for a cost-effective anti-inflammatory treatment.
2020;23:27-29[PMID:32373721 DOI:10.1016/j.ctro.2020.04.006]
41 Jackson MR,Stevenson K,Chahal SK,Curley E,Finney GE,Gutierrez-Quintana R,Onwubiko E,Rupp A,Strathdee K,Williams K,MacLeod MKL,McSharry C,Chalmers AJ.Low-Dose Lung Radiation Therapy for COVID-19 Lung Disease:A Preclinical Efficacy Study in a Bleomycin Model of Pneumonitis.
2022;112:197-211[PMID:34478832 DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.08.029]
42 Hess CB,Nasti TH,Dhere VR,Kleber TJ,Switchenko JM,Buchwald ZS,Stokes WA,Weinberg BD,Rouphael N,Steinberg JP,Godette KD,Murphy DJ,Ahmed R,Curran WJ Jr,Khan MK.Immunomodulatory Low-Dose Whole-Lung Radiation for Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Pneumonia.
2021;109:867-879[PMID:33340603 DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.12.011]
43 Ganesan G,Ponniah S,Sundaram V,Marimuthu PK,Pitchaikannu V,Chandrasekaran M,Thangarasu J,Kannupaiyan G,Ramamoorthy P,Thangaraj B,Shree Vaishnavi R.Whole lung irradiation as a novel treatment for COVID-19:Interim results of an ongoing phase 2 trial in India.
2021;163:83-90[PMID:34391759 DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2021.08.001]
44 Sharma DN,Welsh J,Kumar R.Can low-dose radiation therapy reduce the risk of mucormycosis in COVID-19 patients?
2021;17:1294-1296[PMID:34916356 DOI:10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_2011_21]
45 Ameri A,Rahnama N,Bozorgmehr R,Mokhtari M,Farahbakhsh M,Nabavi M,Shoaei SD,Izadi H,Yousefi Kashi AS,Dehbaneh HS,Taghizadeh-Hesary F.Low-Dose Whole-Lung Irradiation for COVID-19 Pneumonia:Short Course Results.
2020;108:1134-1139[PMID:32707264 DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.07.026]
46 Hess CB,Eng TY,Nasti TH,Dhere VR,Kleber TJ,Switchenko JM,Weinberg BD,Rouphael N,Tian S,Rudra S,Taverna LS,Daisson AP,Ahmed R,Khan MK.Whole-lung low-dose radiation therapy(LD-RT)for non-intubated oxygendependent patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia receiving dexamethasone and/or remdesevir.
2021;165:20-31[PMID:34653525 DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2021.10.003]
47 H A,I S,J J B,A J,A R,H Z,S A R M,S M J M.Low Dose Radiation Therapy and Convalescent Plasma:How a Hybrid Method May Maximize Benefits for COVID-19 Patients.
2020;10:387-394[PMID:32802787 DOI:10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2006-1125]
48 Sharma DN,Guleria R,Wig N,Mohan A,Rath G,Subramani V,Bhatnagar S,Mallick S,Sharma A,Patil P,Madan K,Soneja M,Thulkar S,Singh A,Singh S.Low-dose radiation therapy for COVID-19 pneumonia:a pilot study.
2021;94:20210187[PMID:34545760 DOI:10.1259/bjr.20210187]
49 Prasanna PG,Woloschak GE,DiCarlo AL,Buchsbaum JC,Schaue D,Chakravarti A,Cucinotta FA,Formenti SC,Guha C,Hu DJ,Khan MK,Kirsch DG,Krishnan S,Leitner WW,Marples B,McBride W,Mehta MP,Rafii S,Sharon E,Sullivan JM,Weichselbaum RR,Ahmed MM,Vikram B,Coleman CN,Held KD.Low-Dose Radiation Therapy(LDRT)for COVID-19:Benefits or Risks?
2020;194:452-464[PMID:33045077 DOI:10.1667/RADE-20-00211.1]
50 Aranjani JM,Manuel A,Abdul Razack HI,Mathew ST.COVID-19-associated mucormycosis:Evidence-based critical review of an emerging infection burden during the pandemic's second wave in India.
2021;15:e0009921[PMID:34793455 DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0009921]
51 Dua V,Shishir V.Effect of ultraviolet c radiation,radiation &heat treatment on disinfection rate of SARS-COVID virus-2.
2021;206-213 Available from:https://www.ijsdr.org/papers/IJSDR2105035.pdf
52 Venkatraman P,Sahay JJ,Maidili T,Rajan R,Pooja S.Breakthrough of COVID-19 using radiotherapy treatment modalities.
2020;148:225-226[PMID:32342867 DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.024]
53 Verma A,Adhikary A,Woloschak G,Dwarakanath BS,Papineni RVL.A combinatorial approach of a polypharmacological adjuvant 2-deoxy-D-glucose with low dose radiation therapy to quell the cytokine storm in COVID-19 management.
2020;96:1323-1328[PMID:32910699 DOI:10.1080/09553002.2020.1818865]
54 Ponti G,Maccaferri M,Ruini C,Tomasi A,Ozben T.Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression.
2020;57:389-399[PMID:32503382 DOI:10.1080/10408363.2020.1770685]
55 Xiang J,Wen J,Yuan X,Xiong S,Zhou X,Liu C,Min X.Potential biochemical markers to identify severe cases among COVID-19 patients.
2020[DOI:10.1101/2020.03.19.20034447]
56 Zhou S,Chen C,Hu Y,Lv W,Ai T,Xia L.Chest CT imaging features and severity scores as biomarkers for prognostic prediction in patients with COVID-19.
2020;8:1449[PMID:33313194 DOI:10.21037/atm-20-3421]
57 Liu T,Zhang J,Yang Y,Zhang L,Ma H,Li Z,Cheng J,Zhang X,Wu G.The potential role of IL-6 in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019.SSRN 3548761:2020[DOI:10.2139/ssrn.3548761]
58 Hadjadj J,Yatim N,Barnabei L,Corneau A,Boussier J,Smith N,Péré H,Charbit B,Bondet V,Chenevier-Gobeaux C,Breillat P,Carlier N,Gauzit R,Morbieu C,Pène F,Marin N,Roche N,Szwebel TA,Merkling SH,Treluyer JM,Veyer D,Mouthon L,Blanc C,Tharaux PL,Rozenberg F,Fischer A,Duffy D,Rieux-Laucat F,Kernéis S,Terrier B.Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients.
2020;369:718-724[PMID:32661059 DOI:10.1126/science.abc6027]
59 Yang X,Yu Y,Xu J,Shu H,Xia J,Liu H,Wu Y,Zhang L,Yu Z,Fang M,Yu T,Wang Y,Pan S,Zou X,Yuan S,Shang Y.Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan,China:a single-centered,retrospective,observational study.
2020;8:475-481[PMID:32105632 DOI:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5]
60 García-Hernández T,Romero-Expósito M,Sánchez-Nieto B.Low dose radiation therapy for COVID-19:Effective dose and estimation of cancer risk.
2020;153:289-295[PMID:33065184 DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.09.051]
61 Boon IS,Au Yong TPT,Boon CS.Radiotherapy for COVID-19:Primum non nocere.
2020;149:236-237[PMID:32505723 DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.05.046]
62 Lancia A,Bonzano E,Bottero M,Camici M,Catellani F,Ingrosso G.Radiotherapy in the era of COVID-19.
2020;20:625-627[PMID:32552073 DOI:10.1080/14737140.2020.1785290]
63 Hahn SM,Hahn DD.Low-dose radiotherapy,0.5 Gy to the lungs,for COVID-19 pneumonia.2020[DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.27967.33441]
64 Venkatesulu BP,Lester S,Hsieh CE,Verma V,Sharon E,Ahmed M,Krishnan S.Low-Dose Radiation Therapy for COVID-19:Promises and Pitfalls.
2021;5:pkaa103[PMID:33437924 DOI:10.1093/jncics/pkaa103]
65 Oakley PA,Harrison DE.Are Continued Efforts to Reduce Radiation Exposures from X-Rays Warranted?
2021;19:1559325821995653[PMID:33746654 DOI:10.1177/1559325821995653]
66 Rühm W,Harrison RM.High CT doses return to the agenda.
2020;59:3-7[PMID:31844985 DOI:10.1007/s00411-019-00827-9]
67 Randeep Guleria.(2021,May3).
Randeep Guleria said asymptomatic patients with normal oxygen saturation should not go for CT scans.All India.Available from:https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/aiims-director-randeep-guleria-says-ct-scan-being-misused-cant-detect-mild-covid-cases-2427262
68 A R Sundararajan.(2021,May 13).“How safe are CT,X-Rays as first-line tools to screen for Covid-19?”.Unlike the swab tests which can diagnose Covid-19 accurately,imaging findings are not specific enough to confirm Covid-19.Deccan Herald.Available from:www.deccanherald.com/opinion/how-safe-are-ct-x-rays-as-first-line-tools-to-screen-for-covid-19-985344
69 Azadbakht J,Khoramian D,Lajevardi ZS,Elikaii F,Aflatoonian AH,Farhood B,Najafi M,Bagheri H.A review on chest CT scanning parameters implemented in COVID-19 patients:bringing low-dose CT protocols into play.
2021;1-10[DOI:10.1186/s43055-020-00400-1]
 World Journal of Radiology2022年7期
World Journal of Radiology2022年7期
- World Journal of Radiology的其它文章
- Catheter-based renal sympathetic nerve denervation on hypertension management outcomes
- Type 2 dynamic curves:A diagnostic dilemma
- Radiological review of rhinocerebral mucormycosis cases during the COVID-19 Pandemic:A single-center experience
- Molecular imaging as a tool for evaluation of COVID-19 sequelae–A review of literature
- Expanding utility of cardiac computed tomography in infective endocarditis:A contemporary review
