Prognostic and incremental value of computed tomographybased radiomics from tumor and nodal regions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Bangrong Cao ,Kun Mi ,Wei Dai ,Tong Liu ,Tianpeng Xie ,Qiang Li ,Jinyi Lang,5,Yongtao Han,Lin Peng,Qifeng Wang,5
1Radiation Oncology Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province;2Department of Biobank;3Department of Thoracic Surgery;4Department of Medical Imaging;5Department of Radiation Oncology,Sichuan Cancer Hospital &Institute,Sichuan Cancer Center,School of Medicine,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 610041,China
Abstract Objective:This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of preoperative radiomics and establish an integrated model for esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC).Methods:A total of 931 patients were retrospectively enrolled in this study (training cohort,n=624;validation cohort,n=307).Radiomics features were obtained by contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) before esophagectomy.A radiomics index was set based on features of tumor and reginal lymph nodes by using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression.Prognostic nomogram was built based on radiomics index and other independent risk factors.The prognostic value was assessed by using Harrell’s concordance index,time-dependent receiver operating characteristics and Kaplan-Meier curves.Results:Twelve radiomic features from tumor and lymph node regions were identified to build a radiomics index,which was significantly associated with overall survival (OS) in both training cohort and validation cohort.The radiomics index was highly correlated with clinical tumor-node-metastasis (cTNM) and pathologic TNM(pTNM) stages,but it demonstrated a better prognostic value compared with cTNM stage and was almost comparable with pTNM stage.Multivariable Cox regression showed that the radiomics index was an independent prognostic factor.An integrated model was constructed based on gender,preoperative serum sodium concentration,pTNM and the radiomics index for clinical usefulness.The integrated model demonstrated discriminatory ability better compared with the traditional clinical-pathologic model and pTNM alone,indicating incremental value for prognosis.Conclusions:CT-based radiomics for primary tumor and reginal lymph nodes was sufficient in predicting OS for patients with ESCC.The integrated model demonstrated incremental value for prognosis and was robust for clinical applications.
Keywords:Esophageal squamous cell cancer;radiomics;lymph node;prognosis
Introduction
Esophageal cancer (EC) is one of the most common types of cancer,ranking sixth and seventh in terms of mortality and incidence,respectively,worldwide in 2020 (1).In China,EC is a leading cause of death in cancer patients (2)and ranks fifth in incidence and fourth in mortality (3).In addition,approximately 90% of patients with EC were diagnosed with esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC)(4).Despite the development in diagnosis and multimodal treatment,the prognosis of ESCC is still poor (5).Therefore,a more effective staging system is urgently needed to improve the prognosis of patients with ESCC.
Radiomics is a method to obtain high-dimensional quantitative features using medical imaging and has gained increased importance in diagnosis,prognosis,and treatment response for many types of cancer including EC(6-10).In prognosis analysis,radiomics could be used in predicting postoperative recurrence in patients who achieved pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (11),lymph node metastasis (12),and resectability (13) of ESCC.In the analysis of treatment response,radiomics-based nomograms could help predict radiation pneumonitis (14),the expression of PD-L1 and CD8+tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) (15),and CR to chemoradiotherapy(16);identify patients who do not benefit from chemoradiation (17);and determine neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy treatment response (18,19).Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be performed during the diagnostic assessment of benign and malignant conditions of gastroesophageal tract (20),it still needs improvement and standardization.In clinical practice,contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) is widely used in the preoperative diagnosis,staging and posttreatment monitoring of EC.In addition,the combination of CT-based radiomics and clinical factors has improved the predictive performance in ESCC (15).However,most CT-based radiomics as clinical biomarkers in ESCC was based on tumor signatures with evaluation of region of interest (ROI) usually limited to the primary tumor(11,15,16,19).Lymph node status is complex and changes during progression of tumors (21),and nodal radiomic features may provide detailed phenotype information of lymph nodes.Hence,we hypothesized that additional analysis of lymph node radiomics will improve the prediction ability of prognostic models.
Our study established a radiomics index incorporated both tumor signatures and nodal signatures,which had a similar prediction ability of overall survival (OS)preoperatively with clinicopathological staging in patients with ESCC.The study aimed to develop and validate a prognostic model that integrated this radiomics index with clinicopathological characteristics for better individual prediction of OS in patients with ESCC.
Materials and methods
Patients
The training cohort comprised 624 ESCC patients who received esophagectomy from January 2011 to April 2014 and the validation cohort included 307 patients from May 2014 to March 2016,respectively,at Sichuan Cancer Hospital.Corresponding data including preoperative CT image,clinpathological parameters,postoperative treatment and follow-up information were collected.Histological pathology diagnosis confirmed the histological type of tumors.The 8th edition of American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) classification system was used for pathological tumor-node-metastasis (pTNM)stage.CT-based clinical TNM (cTNM) stage was also determined.This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Sichuan Cancer Hospital (No.SCCHEC-02-2020-015).
The included criteria included:1) aged ≥18 years;2)standard McKeown esophagectomy or Ivor Lewis esophagectomy;3) standard contrast-enhanced CT before surgery;4) histologically confirmed ESCC;and 5) no distant metastases.Patients with primary tumorin situ,adenocarcinoma,small cell carcinoma,or preoperative chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy were excluded from this study.Details of patient recruitment are depicted inSupplementary Figure S1.Patients without preoperative contrast-enhanced CT image,and those with insufficient follow-up information or lack of other clinicopathological data (417 and 480 patients in the training and validation cohorts,respectively) were excluded from further analysis.
Treatment
All patients received surgery alone (training cohort,n=249;validation cohort,n=173) or surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy (AC) or concurrent chemoradiotherapy(CCRT) (training cohort,n=375;validation cohort,n=134).Adjuvant treatment was usually delivered to patients with traditional high-risk factors (eg,T3/T4 stage,lymph nodepositive,neural invasion,vascular invasion,R1/R2 resection or poor tumor grade),except those with physical or other reasons.Platin-based standard chemotherapy was given to patients 4?6 weeks after surgery.Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) was delivered with a total dose of 50?54 Gy/25?30 fractions (5 fractions per week lasting for 5?6 weeks).OS time was defined as the period from surgery date to patient death or the last follow-up date until December 2019,the deadline for follow-up.
CT image and radiomic features
Contrast-enhanced CT images were retrospectively acquired from imaging systems manufactured by either GE Medical Systems or Philips.CT images were scanned within one week before surgery with standard protocols.After administration of iodinated contrast agent by intravenous injection,images were acquired after a 50-second delay with the following parameters:tube voltage of 120 kV,tube current of 230 mA,slice thickness of 5 mm without slice increment,comparable in-slice pixel dimension of 0.98 (range,0.94?0.98) mm,and a convolution kernel with a body filter for all patients.
Segmentation of regions of interest (ROIs) and radiomic feature extraction were performed using the imaging biomarker explorer (IBEX,version 1.0 beta) software (22).On each axial CT image,2D ROIs of primary tumor and lymph nodes were manually delineated,resulting in a 3D volume of interest (VOI).The lymph node VOI was generated by combining all visible lymph nodes with a major axis larger than 5 mm from supraclavicular to the left gastric lymph node region.A total of 1,105 features classified as the following categories were extracted:shape,intensity direct,intensity histogram,neighbor intensity difference 25,grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) 25,and grey level run length matrix (GLRLM) 25.Twenty patients were randomly selected and delineated by two radiologists with more than 5 years of experience for feature stability assay.Other patients were delineated randomly by one of the two radiologists.
Radiomics index
Radiomic features were preselected by performing univariate Cox regression.Multiple tests were adjusted by using the Bonferroni method.Features with adjusted P<0.1 were used to conduct a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression using the R package “glmnet”.The LASSO model is robust to identify the most non-redundant variables based on the parameter lambda (λ) (23).The optimal value of λ was determined by 10-fold cross-validation with a minimum partial likelihood deviance in the training cohort.The final radiomics index was established by a linear combination of features weighted by their coefficients in LASSO regression.
Integrated prognostic model
In the training cohort,multivariate Cox regression analysis was conducted with traditional clinicopathological factors.In addition,we also included preoperative hematologic parameters of sodium,mean platelet volume and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as previously reported (24-26).A backward stepwise variable selection procedure was applied to select the optimal variables with P<0.05.The last Cox model was applied to create a nomogram predictor using the ‘rms’ package.The accuracy and discrimination of predictions were measured by calibration curves and the Harrell’s concordance index (C-index),respectively.Internal validation was performed by bootstrap with 1,000 times of resample.The nomogram was further validated to predict death risk of individuals in the validation cohort.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed by using R software version 3.5.1 (https://www.r-project.org/). Categorical variables among subgroups were compared using Chisquared test or Fisher’s exact test.Difference in radiomics index among subgroups was compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test.The stability of radiomic features between two observers was assayed by intraclass correlation coefficients(ICCs).An ICC of greater than 0.75 indicated favorable repeatability.Two concordance indices were compared using the “survcomp” package.Time-dependent receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves,areas under the curves (AUCs) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI),and statistic comparisons were performed using the R package“pROC”.Multiple tests were adjusted by using the Benjamini and Hochberg method when appropriate.Patients were classified as four subgroups by quartiles of total points as predicted by nomogram in the training cohort.Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test.A two-sided P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Characteristics of study cohorts
Figure 1depicts workflow of this study.We studied 624 patients with median age of 61 (range,34?83) years,including 526 males and 98 females,in the training cohort and 307 patients with median age of 62 (range,38?81)years,including 257 males and 50 females,in the validation cohort.The median follow-up time for the living patients was 70.52 [inter-quartile range (IQR),61.17?78.34]months for the training cohort,and 35.50 (IQR,33.13?44.94) months for the validation cohort.Accordingly,the 3-year OS rate was 54.8% (95% CI,51.0%?58.9%) and 51.0% (95% CI,45.4%?57.3%),respectively.Except for the neural invasion rate,there was no statistical difference in other clinicopathological parameters between the training and validation cohorts(Table 1).
Radiomics index
Radiomic features extracted from VOIs of the primary tumor and regional lymph nodes showed good agreement between two observers (Supplementary Figure S2).Univariate Cox regression revealed that 132 tumor features and 209 lymph node features were significantly associated with OS.These candidate features were further identified by selecting features with coefficients in LASSO Cox regression model (Figure 2A,B).Finally,3 tumor features and 9 lymph node features were used to conduct a radiomics index (Supplementary Table S1).The radiomics index was significantly correlated with pathological T and N stage (Figure 2C,D),and clinical T and N stage (Figure 2E,F).Similar results were observed in the validation cohort (Supplementary Figure S3).Moreover,the radiomics index was significantly correlated with gender,resected lymph node number,and cTNM and pTNM stages(Supplementary Table S2,all P<0.05).
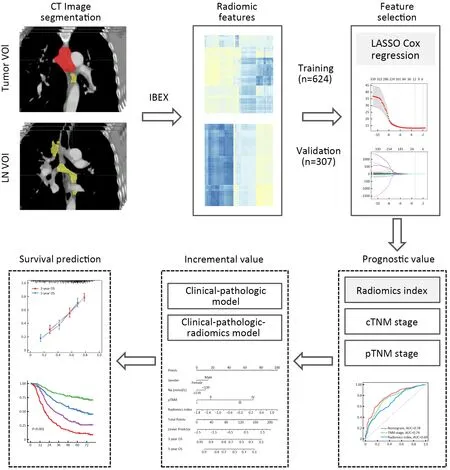
Figure 1 Work flow of present study.LN,lymph node;VOI,volume of interest;CT,computed tomography;IBEX,imaging biomarker explorer;LASSO,least absolute shrinkage and selection operator;cTNM,clinical TNM;pTNM,pathological TNM.
We used the same procedure to establish two radiomic indicators based on tumor and lymph node features,respectively (Supplementary Figure S4).The radiomics index constructed by tumor and lymph node features (Cindex,0.648;95% CI,0.619?0.677) has significantly better discrimination for OS compared with that by tumor features (C-index,0.608;95% CI,0.578?0.638) or lymph node features alone (C-index,0.629;95% CI,0.600?0.658)(Supplementary Table S3).Meanwhile,we also conducted a LASSO Cox regression model using all tumor and lymph node features directly (Supplementary Figure S4E,F).There is no significant difference in C-index between the model and the radiomics index using preselected features(Supplementary Table S3).Therefore,the combined radiomics index was used for further analysis and building an integrated model.
Prognostic value of radiomics index
Cox regression analysis revealed that the radiomics index was significantly associated with OS [hazard ratio (HR),3.54;95% CI,2.72?4.61;P<0.001 in training cohort and HR,2.96;95% CI,1.96?4.48;P<0.001 in validation cohort]. Stratification analyses by different clinicopathological parameters confirmed the prognostic significance of radiomics index in both cohorts(Supplementary Table S4).Multivariable Cox regression indicated that the radiomics index was an independent factor predicting OS (Table 2).
The C-index of the radiomics index was significantly higher than that of cTNM stage in both training and validation cohorts (Table 3,all P<0.001).However,there was no statistically significant difference in C-index between the radiomics index and pTNM stage.Similarly,time-dependent ROC analysis showed that the radiomics index achieved higher 1-year and 3-year AUC values than cTNM stage (Figure 3,Supplementary Table S5).However,there was no significant difference in AUC values between the radiomics index and pTNM stage (Figure 3,Supplementary Table S5).Kaplan-Meier curves confirmed that the radiomics index and pTNM stage were sufficient to predict OS,but the cTNM stage could not significantlypredict OS,especially in the validation cohort(Supplementary Figure S5).These results suggested that the preoperative radiomics index performed better in predicting OS compared with cTNM and achieved comparable performance compared with pTNM stage.

Figure 2 Establishment and clinicopathological association of radiomics index.(A) Feature selection for radiomics index by LASSO Cox regression algorithm with a 10-fold cross validation method.When the λ value was 0.038,with log (λ)=?3.27,the partial likelihood deviance reaches the minimal value;(B) Plot of coefficient profile of LASSO model;(C-F) Boxplot of radiomics index by (C) pT stage (P<0.001);(D)pN stage (P<0.001);(E) CT-based cT stage (P<0.001) and (F) CT-based cN stage (P<0.001) in the training cohort.Statistical significance was calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test.LASSO,least absolute shrinkage and selection operator;pT,pathological T;pN,pathological N;cT,clinical T;cN,clinical N.
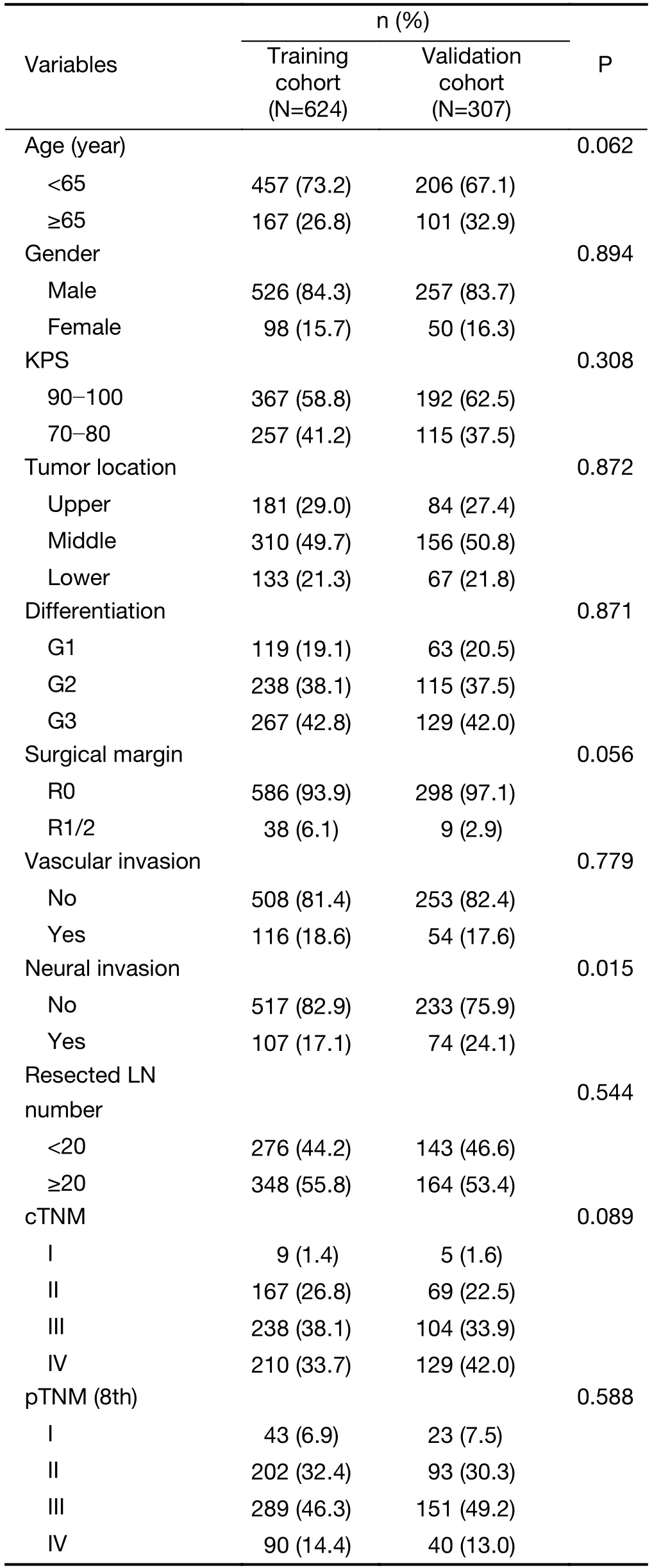
Table 1 Characteristics of study cohorts
Integrated model and incremental value of radiomics index
Regarding the clinical and pathologic factors,gender,preoperative sodium concentration and pTNM stage were independent factors in predicting OS (Table 2).The clinical-pathologic model achieved a C-index of 0.669(95% CI,0.642?0.695) and 0.657 (95% CI,0.641?0.700) in the training and validation cohorts,respectively (Table 3).The difference in C-index between the clinical-pathologic model and the radiomics index was marginally significant(training cohort,P=0.076;validation cohort,P=0.072).The radiomics index together with the clinical-pathologic risk factors was used to build an integrated model.The integrated model yielded a significant improvement in Cindex [the training cohort:C-index,0.694 (95% CI,0.667?0.720);the validation cohort:C-index,0.674 (95%CI,0.630?0.718)] as compared with the clinical-pathologic model or pTNM or the radiomics index alone (all P<0.05,Table 3).
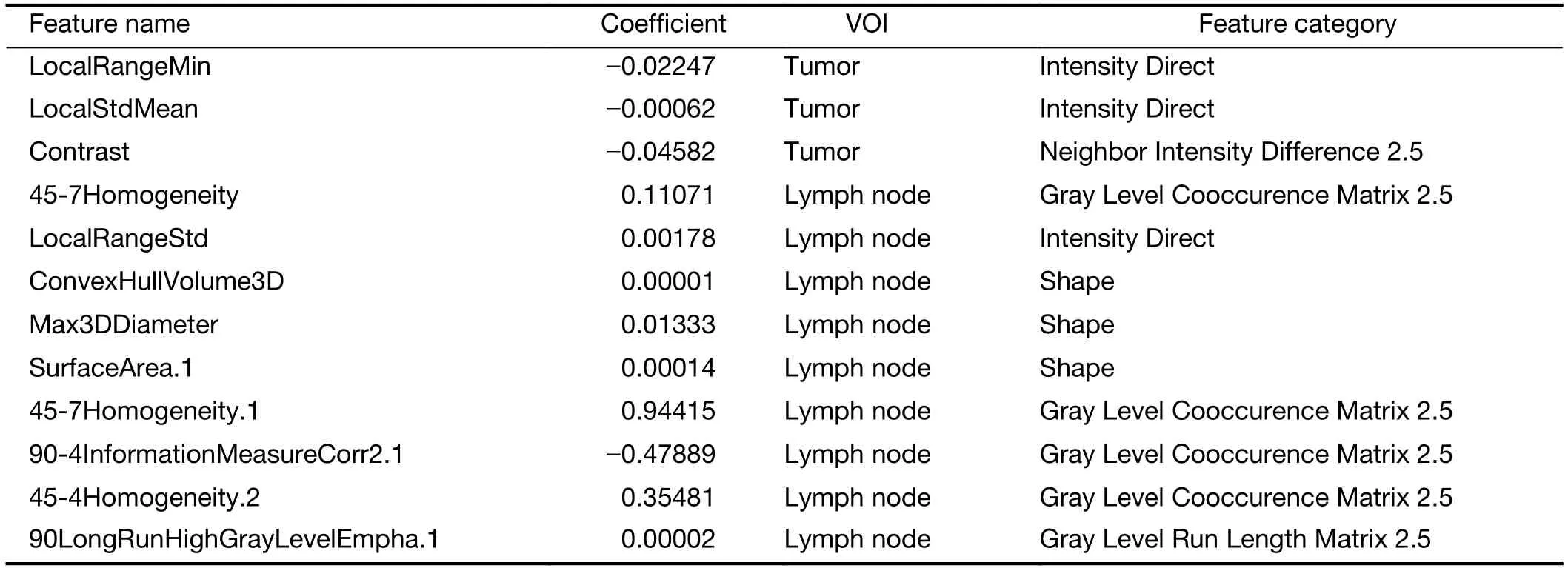
Table S1 Feature information of radiomics index
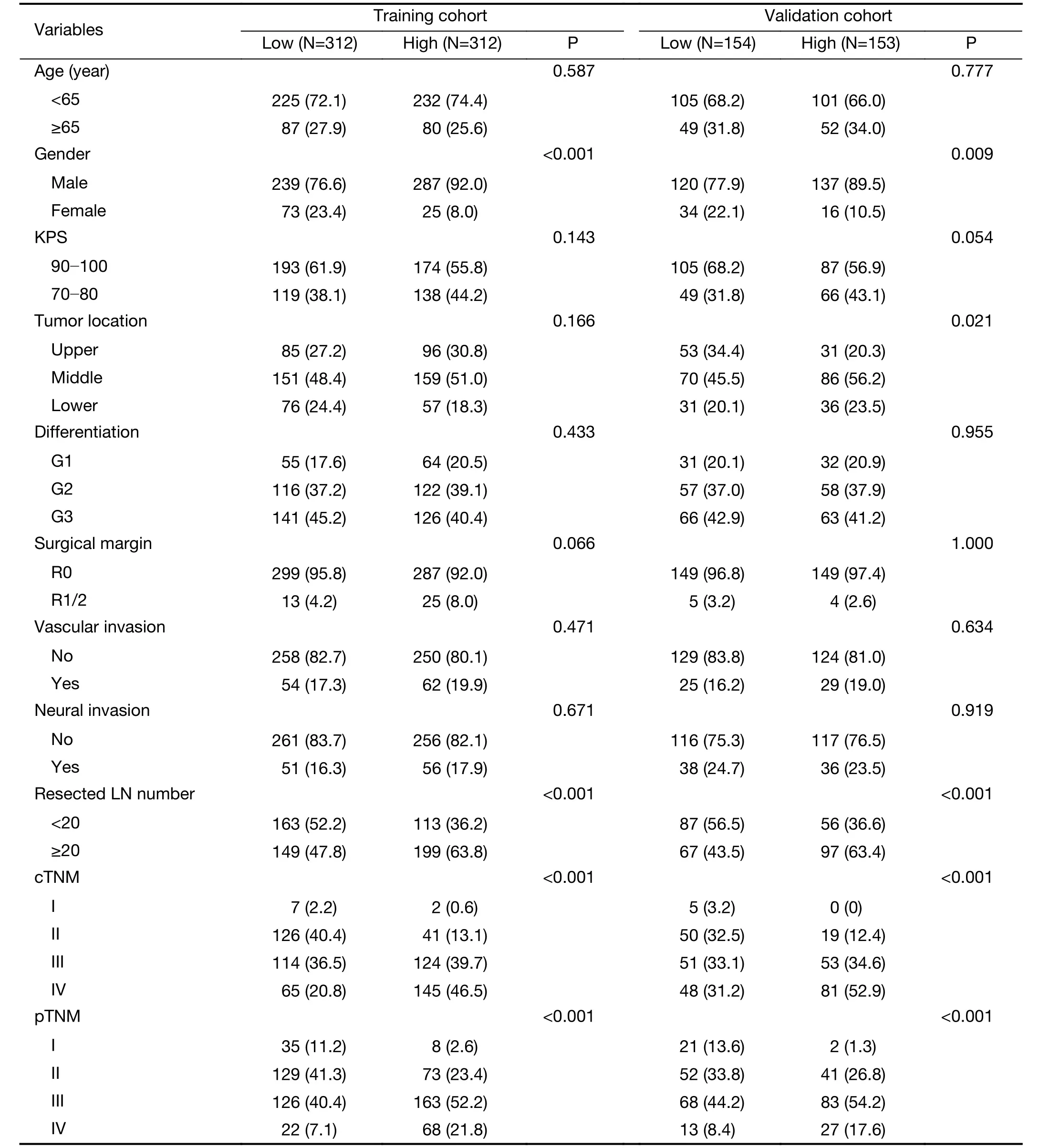
Table S2 Correlation analysis of radiomics index with clinpathological variables

Table 2 Cox regression for training cohort
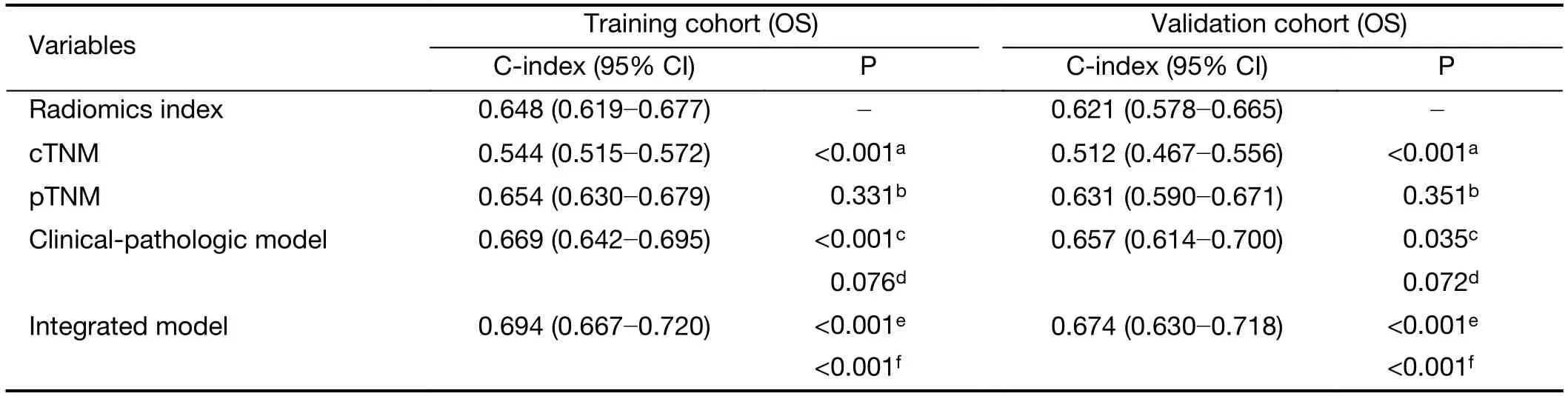
Table 3 C-index analysis for radiomics index,cTNM,pTNM and integrated model
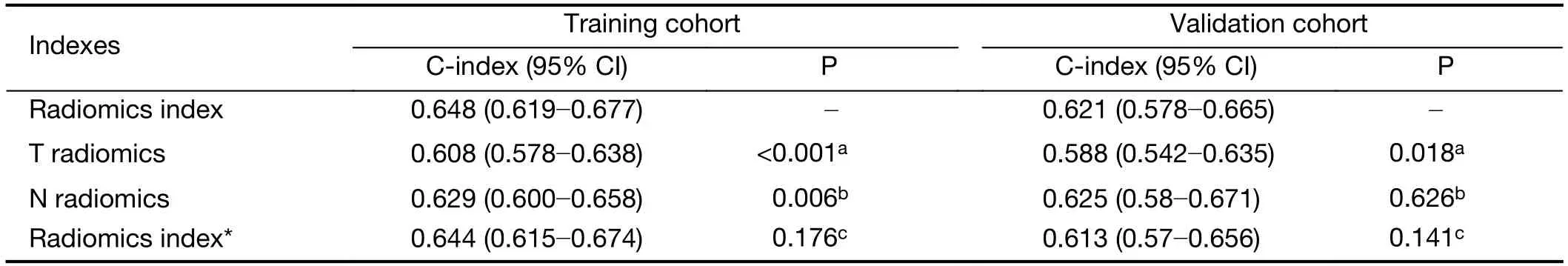
Table S3 C-index analysis for radiomics index
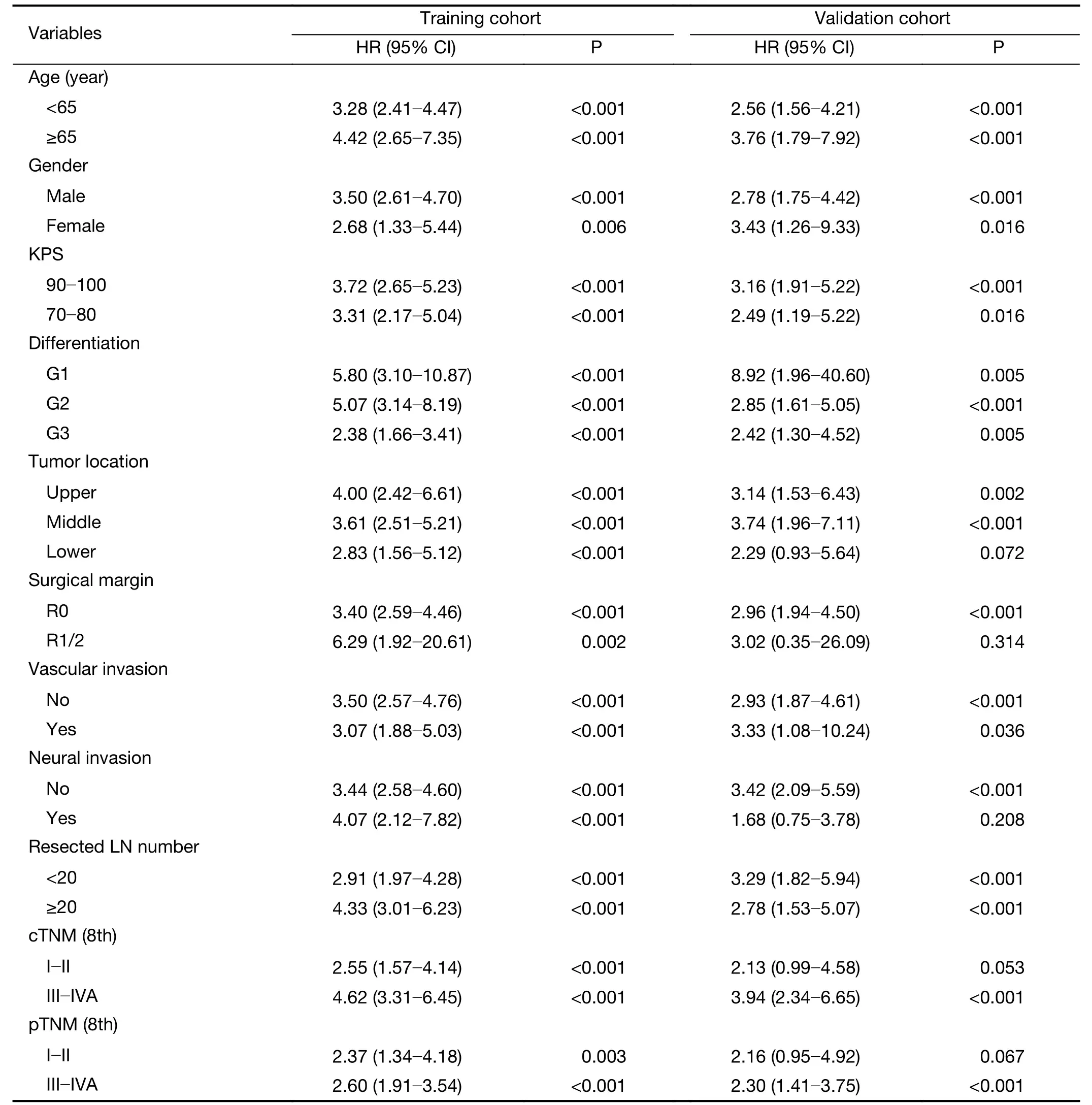
Table S4 Stratified univariable Cox regression analysis of radiomics index
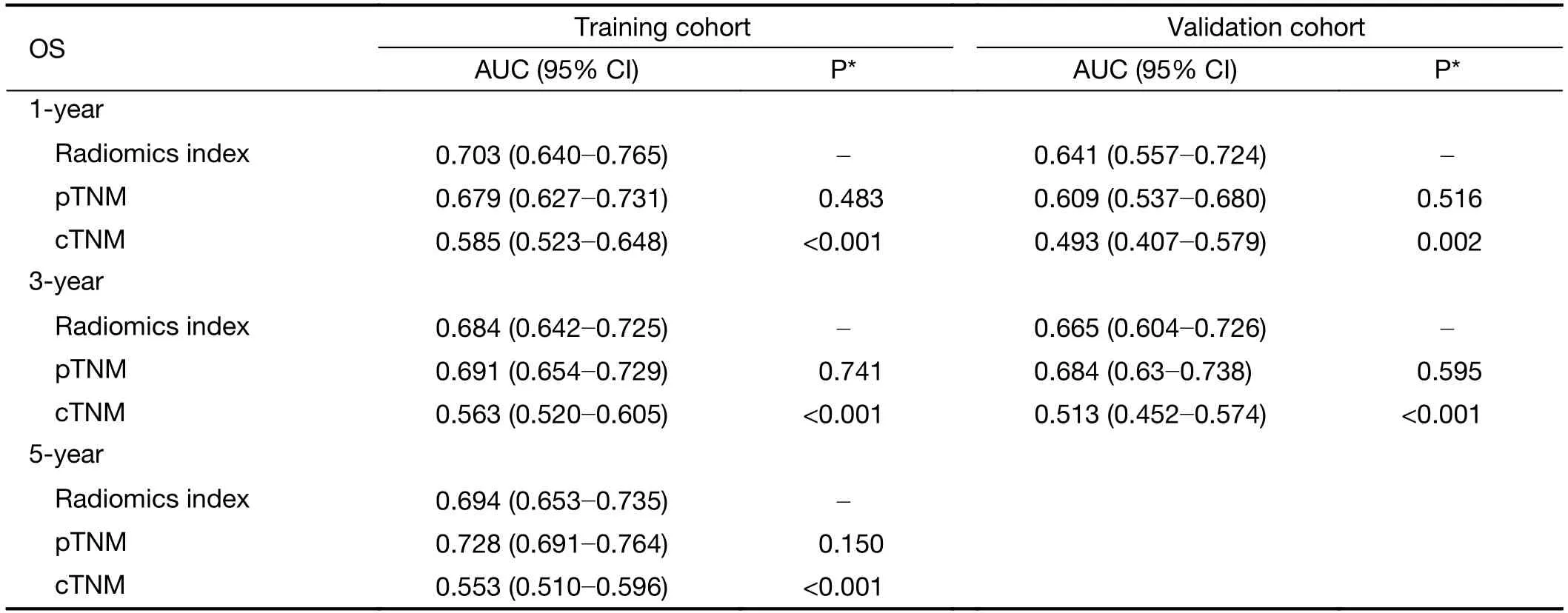
Table S5 Time-dependent ROC analysis for cTNM,pTNM and radiomics index
A nomogram was constructed to estimate the predicted probability of 3-year or 5-year OS in the form of graphic depiction (Figure 4A) for easy-clinic usage.Calibration curves showed that the modeled 3-year or 5-year estimates of OS closely approximated the actual estimates in the training cohort (Figure 4B).Similarly,the predicted 3-year OS in the validation cohort showed good agreement with the actual estimate of the probability of OS (Figure 4C).
Survival analysis
Patients were classified into four subgroups as defined by quartiles of the predicted score of the integrated model.Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the training cohortindicated that OS rate was significantly different across the four subgroups (Figure 4D,P<0.001).The same was true for the validation cohort (Figure 4E,P<0.001).Moreover,stratification analysis by postoperative treatment options showed that the prognostic value of the integrated model was independent of adjuvant AC/CCRT (Supplementary Figure S6).
Figure S1 Recruitment pathway for patients.CT,computed tomography.
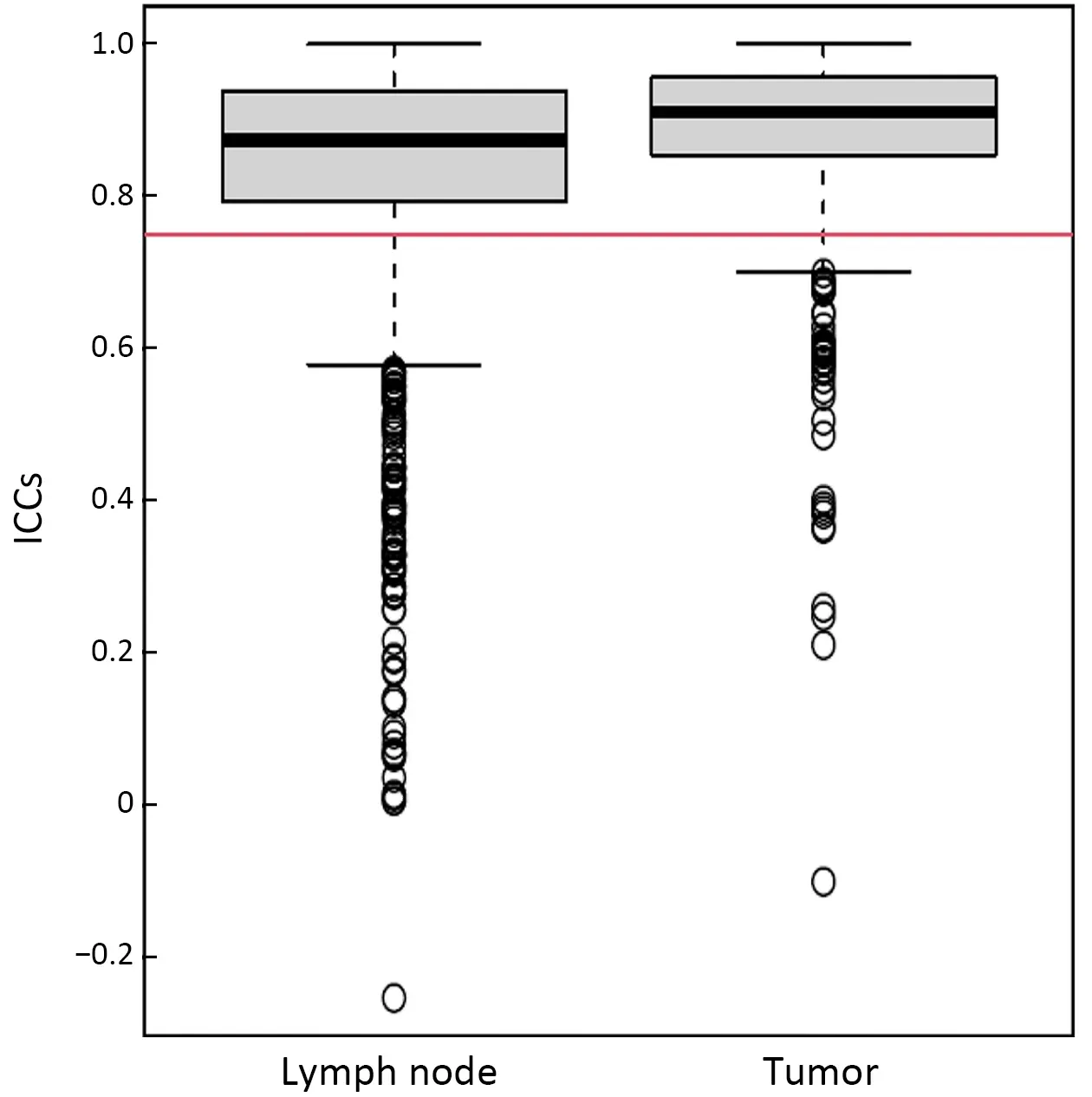
Figure S2 Boxplot of ICCs of features extracted from lymph node and tumor.ICCs of greater than 0.75 (red line) present good agreement.ICC,intraclass correlation coefficient.
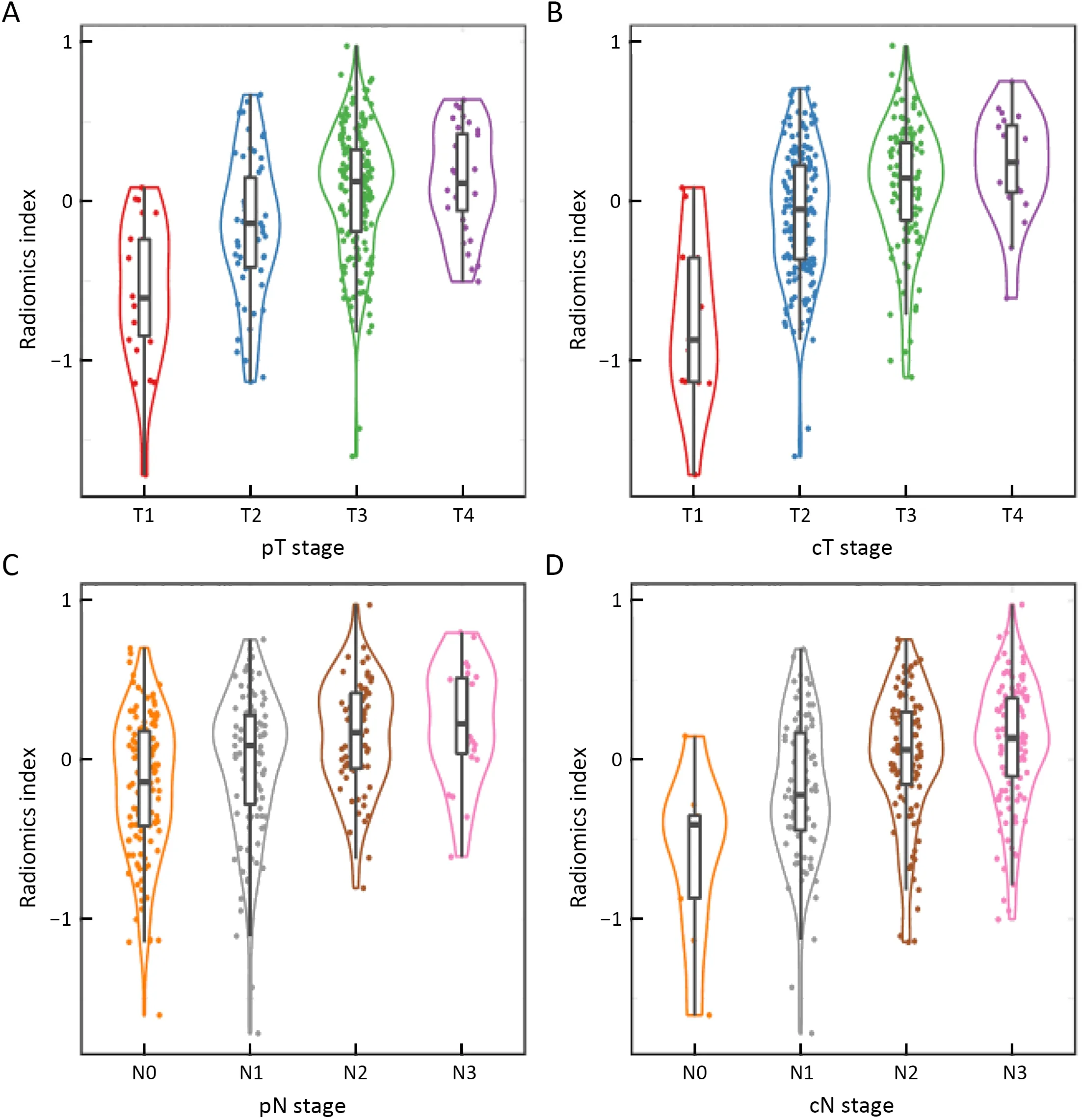
Figure S3 Correlation analysis of radiomics index in validation cohort.(A) pT (P<0.001);(B) cT (P<0.001);(C) pN (P<0.001);and (D) cN(P<0.001) stages.pT,pathological T;cT,clinical T;pN,pathological N;cN,clinical N.Statistical significance was calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test.

Figure 3 Time-dependent ROC curves for OS in respect to the radiomics index (RadIndex),pTNM stage and CT-based cTNM stage.(A)1-year (RadIndex,AUC=0.70;pTNM,AUC=0.68;cTNM,AUC=0.59);(B) 3-year (RadIndex,AUC=0.68;pTNM,AUC=0.69;cTNM,AUC=0.56);and (C) 5-year (RadIndex,AUC=0.69;pTNM,AUC=0.73;cTNM,AUC=0.55) ROC curves in the training cohort;(D) 1-year(RadIndex,AUC=0.64;pTNM,AUC=0.61;cTNM,AUC=0.49) and (E) 3-year (RadIndex,AUC=0.66;pTNM,AUC=0.68;cTNM,AUC=0.51) ROC curves in the validation cohort.ROC,receiver operating characteristic curve;AUC,area under the ROC curve;pTNM,pathological TNM;cTNM,clinical TNM.
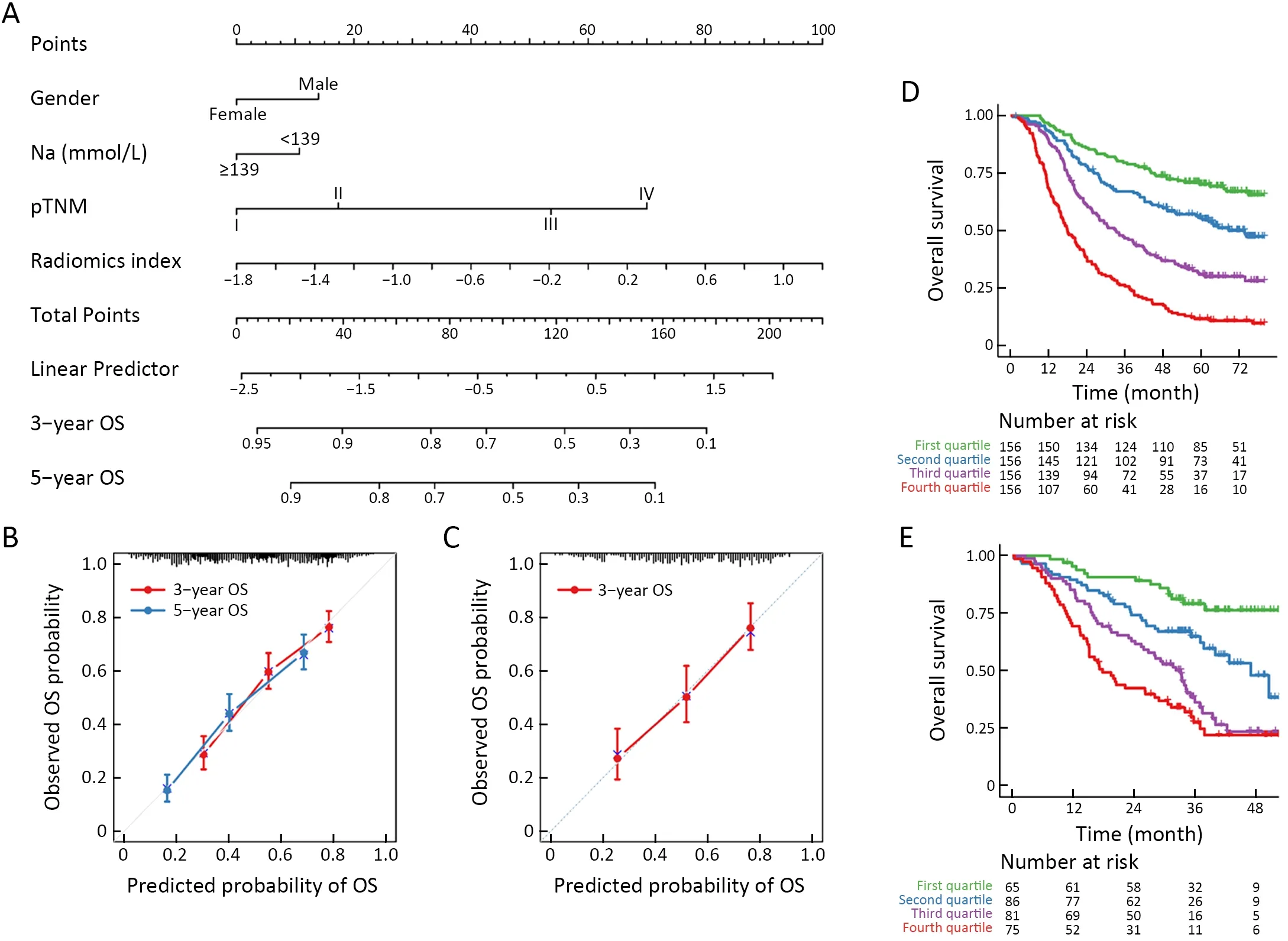
Figure 4 Integrated prognostic model for ESCC patients.(A) Nomogram of the integrated model for ESCC.For each individual patient,the corresponding value is located on each variable axis,and a line is drawn upward to determine the number of points received for each variable value.Total points axis represent the sum of these numbers,and two lines are drawn downward to the 3-or 5-year survival axes;(B)Calibration curves for predicting patients’ 3-year or 5-year OS in the training cohort;(C) Calibration curves for 3-year OS in the validation cohort;(D,E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for all patients in (D) training cohort (P<0.001) and (E) validation cohort (P<0.001).Patients are grouped by quartiles of the nomogram score.P is calculated by using the log-rank test.ESCC,esophageal squamous cell cancer;OS,overall survival;pTNM,pathological TNM.
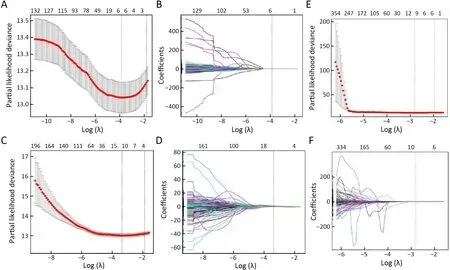
Figure S4 LASSO regression based on different sources of radiomics.Two radiomics indicators were built based on (A,B) tumor features;(C,D) LN features;and (E,F) using all tumor and LN features directly.LASSO,least absolute shrinkage and selection operator;LN,lymph node.

Figure S5 Kaplan-Meier curve analysis for radiomics index (RadIndex),pTNM,cTNM.OS by (A) RadIndex (P<0.001);(B) pTNM(P<0.001);and (C) cTNM (P=0.007) in training cohort and (D) RadIndex (P<0.001);(E) pTNM (P<0.001);and (F) cTNM (P=0.860) in validation cohort.OS,overall survival;pTNM,pathological TNM;cTNM,clinical TNM stage.
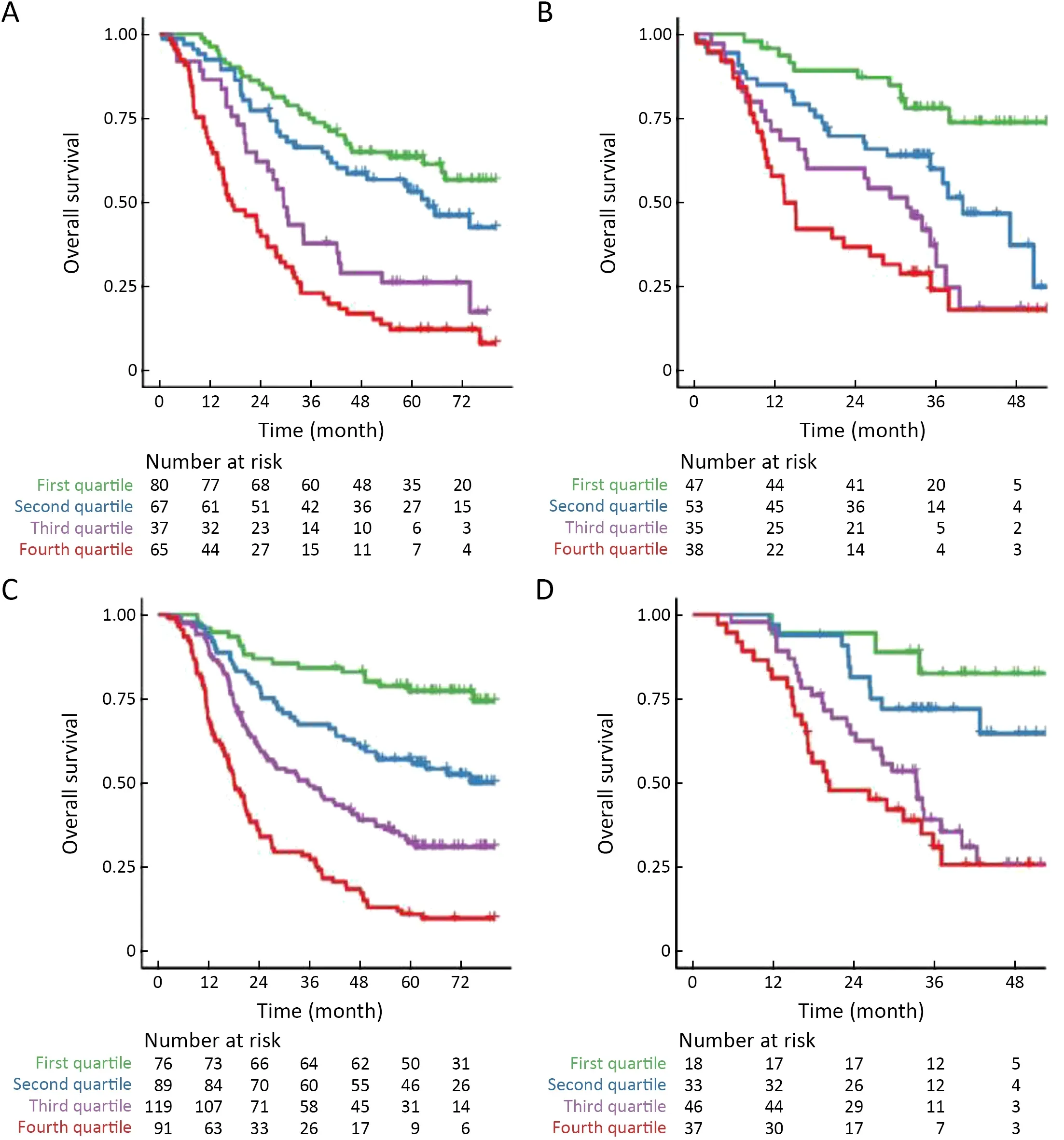
Figure S6 Kaplan-Meier curve analysis for nomogram score in subgroups of patients.Patients receiving surgery alone in (A) training cohort(P<0.001) and (B) validation cohort (P<0.001) or surgery followed by adjuvant AC/CCRT treatment in (C) training cohort (P<0.001) and(D) validation cohort (P<0.001).AC,adjuvant chemotherapy;CCRT,concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
Discussion
In the present study,we developed and validated a CTbased radiomics index based on features from both tumor and nodal area.The radiomics index performed better robust prognostic value compared with cTNM stage and achieved comparable performance compared with pTNM stage.The radiomics index also demonstrated significantly incremental value in predicting survival when being added to the clinical-pathologic model.
Great attention has been given to radiomics in cancer research.However,most of the radiomics analyses focused on tumor signatures,disregarding lymph nodes that keep changing during the tumor progression.Recently,Yang and colleagues incorporated tumor and nodal radiomics to predict lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer (27).Their study developed and validated a radiomics signature based on multi-step feature selection to identify preoperative nodal status in gastric cancer.ESCC prognosis was highly correlated with progression of primary tumor and lymph node metastasis,and thus except primary tumor,lymph node status should also be considered in radiomics model construction.However,many radiomic studies on the progression of ESCC considered only the primary tumor(9-13,28).In this study,we evaluated the added value of lymph nodal radiomics in OS prediction and demonstrated that the performance of combined tumor and nodal radiomics was superior to those of either tumor radiomics or nodal radiomics alone.To the best of our knowledge,we made the first attempt to study the lymph nodal features and extracted them to construct the radiomics index combined with tumor features for ESCC prognosis.
For the integrated radiomics index,75% (9/12) of features were extracted from lymph node area,indicating a pivotal role of nodal radiomics in prognosis.Nodal features of Max3DDiameter,ConvexHullVolume3D and SurfaceArea belong to the category of shape features representing a measure of the maximum dimension,volume and surface areas of the lesion evaluated in 3-diamension.These may more accurately define the lesion size than the maximum axial diameter (29).Homogeneity belongs to the category of GLCM,which represents the local homogeneity of textural features (7).Long-Run High Gray-level Emphasis (LRHGLE) represents the distribution of the long homogeneous runs with high-grey levels (30).It was reported that higher texture homogeneity might indicate more homogeneous uptake of iodine contrast in hypervascular tumors with fewer acellular and necrotic areas (31).That may biologically explain our findings that the homogeneity-related features such as GLCM and LRHGLE were correlated with poor outcome.
The accuracy of CT-reported lymph node metastasis number was quite low (32).Hence,our study included all the lymph nodes regardless of whether they were positive or not,in order to ensure the objectivity and accuracy.Our results showed that the addition of nodal features significantly improved the prognostic performance of radiomics in ESCC.Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and esophagectomy are recommended for patients with locally advanced EC due to significant OS improvement compared with surgery alone (33-36).Conversely,accurate preoperative clinical stage has an important impact on the choice of treatment and patient prognosis.In our study,the preoperative radiomics index demonstrated much better discrimination for OS compared with the cTNM stage and achieved comparable prediction ability compared with pTNM stage.Therefore,we suggested that the radiomics index might serve as a predictive marker for neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy although further study is warranted.
We also developed and validated a predictive nomogram that incorporated the radiomics index with gender,preoperative serum sodium and pTNM stage.The integrated model showed good discrimination and calibration,demonstrating better performance than the clinical-pathologic model and pTNM stage alone in predicting OS.Application of the nomogram in the validation cohort still gave good discrimination and calibration.The nomogram score was sufficient to predict OS in patients receiving surgery plus AC/CCRT or those with surgery alone despite patients in this study received different treatment options.These results indicated that the nomogram constructed with radiomics index and clinical-pathologic parameters performed satisfactory prognostic value,which was independent of postoperative treatment.
Both unenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT scans have been used in radiomics studies (36,37).Although radiomic features were sensitive to contrast medium,which could mask the lesions intrinsic variability in patients with esophageal and esophago-gastric cancer,contrast-enhanced CT remains the most common step performed first in stage due to the high prevalence of metastatic disease (38).It is recommended to explore the potential effects of contrast medium on radiomic features of CT imaging of ESCC in future work.
There are some limitations in our study.First,the nomogram was based on data obtained from a single institution in China,although another large number population was included for validation in a consecutive patient cohort,future multi-center studies should provide high-level evidence for our model.Second,manual target delineation still had deviations and artificial intelligence should be used to achieve more objective and accurate results.Third,this study was retrospectively designed,so prospective studies are suggested to prove its effectiveness.Fourth,a proportion of patients were excluded from analysis due to lack of CT data,which might partially influence the representativity and generalization of the results.Moreover,this study focused on ESCC,the dominant histologic type of EC in China.Hence,further studies are needed to investigate other types of EC,such as esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Conclusions
Our results indicated that expanding radiomics analysis of lymph nodes improves model performance of the nomogram for predicting OS in patients with ESCC.The nomogram based on the radiomics index established in this study incorporated the tumor and nodal signatures,which could be used to fill gaps in the staging system for patients with ESCC and help the clinicians to make treatment decisions and predict patient prognosis more effectively.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No.22NSFSC1483,2019YFS0378 and 2018JY0277) and CSCO-Genecast Oncology Research Found (No.Y-2019Genecast-041).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest:The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2022年2期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2022年2期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Pan-cancer tumor-infiltrating T cells:A great hallmark in cancer immunology research
- Current status and perspectives of conversion therapy for advanced gastric cancer
- CSCO guidelines for colorectal cancer version 2022:Updates and discussions
- Current situation of programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors in advanced triplenegative breast cancer
- Establishment of an optimized CTC detection model consisting of EpCAM,MUC1 and WT1 in epithelial ovarian cancer and its correlation with clinical characteristics
- Genomic landscape of T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma
