Can the management of depression in type 2 diabetes be democratized?
lNTRODUCTlON
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is growing worldwide with depression rapidly following.Though it is possible that two common conditions can co-exist independent of one another,there is increasing evidence that diabetes and depression are related pathophysiologically,sharing a bi-directional relationship.When depression and diabetes coexist,the quality of life,compliance to treatment and outcomes are poor.Qualified specialists to manage diabetes and depression are in short supply.Therefore,innovative approaches are necessary to improve the outcomes of both.Based on published data between 1990 to 2016,it was estimated that among those aged 18-99 years,there were 451 million people with diabetes.By 2045,these were projected to increase to 693 million[1].Of those with diagnosed diabetes,there is a greater prevalence in urban rather than rural(10.8%
7.2%)areas,and in high-income than in low-income countries(10.4%
4.0%)[2].Mental disorders accounted for 13% of the global disease burden;major depression is projected to be the chief contributor to mental disorders by the year 2030[3].Depression is commonly seen in other chronic illnesses also[4].Multifactorial etiology of diabetes[5]and depression[6]requires multi-pronged management strategies.
COEXlSTENCE OF DlABETES AND DEPRESSlON
Diabetes mellitus is not a homogenous condition but results from a variety of pathogenic factors which are not always exclusive[7].However,for clinical purposes,diabetes is classified into(1)Type 1 diabetes due to autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic β-cell leading to absolute insulin deficiency;(2)Type 2 diabetes mellitus having insulin resistance and a progressive loss of β-cell insulin secretion;(3)Gestational diabetes;and(4)Other specific causes leading to diabetes[8].It is evident that psychological reactions differ in each of the different varieties of diabetes.In this presentation,management of depression is focused on type 2 diabetes,which is more common.
Twice as many people with diabetes are likely to have depression compared to the general population[9,10].Hypertension,which is common in diabetes is associated with risk of depression and anxiety[11].Resultantly the association of depression and diabetes has been the most commonly studied for the longest time[12].A meta-analysis showed that compared to those with normal glucose tolerance,depression was more common in people diagnosed with diabetes;it was not high in those with prediabetes or those with normal glucose tolerance[13].
The number of prospective studies on the course of depression among people with diabetes is small;a meta-analysis of 11 follow up studies showed that type 2 diabetes subjects have a 24% increased risk of developing depression compared to controls[14].Similarly,people with depression have a 32%increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus[15].
6.Straw bed:Until this century, straw beds were a common type of bedding for all but the supremely53 rich who could afford goose beds or other more expensive mattresses55. Straw was used as the stuffing for the mattress54.Return to place in story.
At the other end of the diabetes and depression spectrum is suicidality.Depression in persons with diabetes increases the risk of suicidality[24].One must be aware of the risk factors for suicidal ideation and suicidal behavior,such as insulin administration,long duration of diabetes and poor glycemic control[25].Identification and preventive measures are therefore essential in subjects with diabetes having depressive symptoms.Interventions must not only consider medical treatment,but also social factors associated with them[11],pointing to the need for integrated management processes.
Compelling evidence is building up for efficacy of collaborative care in improving both glycemic control and outcomes of depression treatment[54].Improvement of glycemia operates through better compliance to treatment[42].It remains to be seen if the collaborative care model can be implemented at the primary care level without the need for significant additional resources.Larger studies involving cost-effective outcomes are required to determine the feasibility of such approaches[53].Similar conclusions were drawn in a systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of collaborative care in subjects with depression and diabetes mellitus[55,56].From eight studies which included 2238 patients,collaborative care improved response to treatment of depression,remission of depression and better compliance to medications(anti-depressants and anti-diabetes drugs);however,there was no significant improvement of glycemic control as assessed by glycosylated hemoglobin[56].Collaborative care involves coordination among physicians,nurses,other specialists and professionals providing management specific to the patient using evidence-based guidelines.
The grades of anxiety and depression associated with diabetes vary from subclinical depression to diabetes distress,which refers to emotional distress resulting from living with diabetes,a chronic nonremitting disease[16].There are serious clinical implications when depression coexists with diabetes:The quality of life is impaired;the risk of morbidity and death is also increased.Operating factors include poor health care behavior which affects dietary habits,treatment,compliance to treatment,motivation and productivity[16].Long term diabetic complications are more common with comorbid depression[17].Finally,the impact of combined diabetes and depression on quality of life is significant.Healthcare costs of managing type 2 diabetes associated with depression is higher than that of diabetes without depression[18].Depression in type 2 diabetes can be treated[19],which improves the quality of life[17].One must distinguish depression from diabetes distress.Diabetes distress is an emotional response to having diabetes,specifically the restricted lifestyle with having to follow self-management and the potential of complications in the long term[20].Diabetes distress is associated with lessened selfcare,and poorer emotional well-being,which,if left untreated may progress to severe depression[21].Diabetes distress is far more common than clinical depression and is associated with poorer glycemic control[22].The poor outcome is mediated in part by perceived control over diabetes such as one’s innate ability to influence the course of diabetes[23].
COMMON PATHOGENESlS OF THE TWO CONDlTlONS
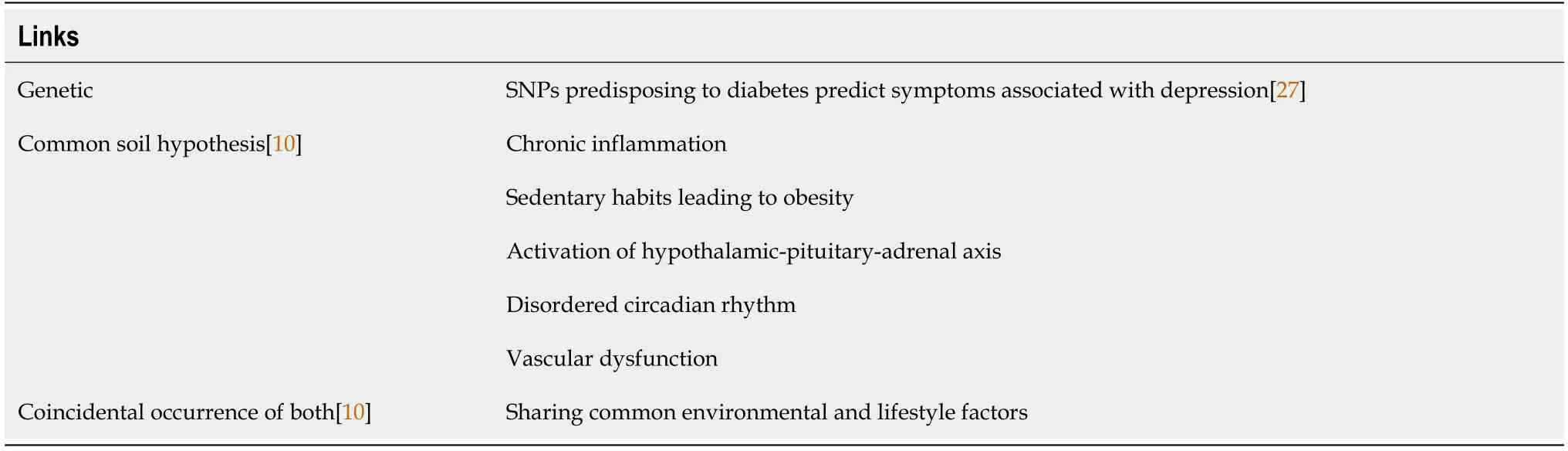
Epidemiological studies have shown a bi-directional association between diabetes and depression[26].Mendelian randomization studies have provided evidence that type 2 diabetes mellitus can cause depression:Single-nucleotide polymorphisms that predispose to diabetes predicted symptoms associated with depression[27].Xuan
[27]used 34 T2D risk genetic variants validated in East Asians as the instrumental variable(IV).An analysis using Mendelian randomization was carried out on 11506 participants from a prospective study.The diabetes genetic risk score(GRS)was built employing the 34 T2D common variants.The GRS was associated with depression even after adjusting for variables including age,sex,body mass index,current smoking and drinking,physical activity,education and marital status.A causal relationship was also found between genetically determined T2D and depression[27].In addition,the stress associated with a new diagnosis of diabetes can precipitate depression[28].
The
posits that factors common to both conditions could be the link for their association such as chronic inflammation,sedentary habits leading to obesity as well as vascular dysfunction[10].Conceptually,the factors relating to both can be considered at two levels:
and
[12].Behavioral components include the burden of dealing with a chronic non-remitting disease and resultant poor lifestyle behavior.Sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor for depression[29],just as it is for obesity and diabetes mellitus.Biologically,hyperglycemia,dysregulation of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal(HPA)axis,chronic low grade inflammatory response and vascular dysfunction could all contribute.These are common to both diabetes and depression and may contribute to their coexistence[12].There is evidence that behavioral and environmental factors are more responsible than genetic factors[12].Vascular changes in small vessels supplying blood to the cerebral cortex are found in depression[30],although confirmatory studies are required.Brain-body dysfunction may contribute by impaired HPA regulation and by brain-gut microbiome axis[12].Similarly,social stress can operate through epigenetic factors that activate the inflammatory response which is common to both diabetes and depression[15].Use of some antidepressant drugs is also implicated in the risk of obesity,insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus[24,31].
Inflammatory changes,which occur in obesity,insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus occur in depression as
,involving activated microglia,astrocytes and oligodendroglia.These release mediators such as cytokines and chemokines,which when persistent,cause neurotoxicity[32].Chronic inflammation in turn leads to insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction,which has also been described in depression[32].Hormonal components in women may contribute to gender differences in pathophysiological changes involving dysregulation of HPA and AN systems acting
immune and hemostatic pathways[33].There is a flattening of the diurnal curve of the stress hormone cortisol which is associated with insulin resistance and could thereby play a role in the coexistence of diabetes and depression[34].Along with abdominal obesity and insulin resistance,hypercortisolemia induces changes in glucocorticoid receptor-rich brain areas such as the hippocampus,amygdala and prefrontal cortex,where emotions and cognition are mediated[34].
The Goose Girl is finally gaining some autonomy. She is able to cast a simple spell, using her own magic, to save her hair from Curdken s attentions. This spell also brings her to the attention of the old king and helps him to recognize that she must be more than she appears. She is gaining some maturity through her adversity.
Conceptually the relation between diabetes and depression can be considered in terms of(1)Psychological burden of a chronic disease such as diabetes predisposing the patients to depression and poor self-care behavior;(2)Diabetes and depression are coincidental,sharing common environmental and lifestyle factors;and(3)The cognitive behavioral construct attributes the burden due to diabetes leading to negative thoughts about diabetes in turn resulting in poor self-care behaviors[10].Biological underpinnings consist of one or a combination of(1)Activated immunity and inflammation mediated by cytokines;(2)Activation of HPA
stress;(3)Insulin resistance;(4)Disturbances of circadian rhythms;and(5)The contribution of antidepressant medications used in the treatment of depression[10](Table 1).
When the ship was finished the launch took place, and everything seemed going smoothly4 when a gale5 sprang up, and the vessel6 was dashed to pieces on the rocks
Screening and diagnosis of depression
The diagnosis of diabetes,based on quantitative measurement of plasma glucose is far more refined than the diagnosis of depression;there are no biological markers for diagnosing depression.The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders(DSM-5)considers a major depressive episode as being present when at least five of nine symptoms suggestive of depression are present for 2 wk or longer;one of the nine must be a core symptom[12].As a screening method for depression in diabetes,the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale(CES-D)and Patient Health Questionnaire(PHQ)-9 were used most often in diabetes research[12].Other screening tools for depression include Beck Depression Inventory,WHO well-being index and EDD[9].
Due to the non-specific nature of the symptoms and their overlap with uncontrolled hyperglycemia,the accuracy of screening tests varies between populations.Diabetes specific questionnaires are available to identify various psychological stresses[35].There are some clinical pointers to distinguishing depression arising from diabetes and primary depression:The latter is suggested by mental disorders even before the diagnosis of diabetes,disproportionate symptoms compared to objective signs,a focus primarily on somatic symptoms and reassurance failing to relieve innocuous symptoms[36].When these are inconclusive,screening for depression must be repeated after uncontrolled hyperglycemia is corrected[37].However,caution must be exercised that affective symptoms such as pessimism or crying spells are not mistakenly attributed to poorly controlled diabetes[37].
They knocked at the door, and when the woman opened it she exclaimed: You naughty children,25 what a time you ve slept in the wood! we thought you were never going to come back
For a rigorous diagnosis of depression,results of screening tests must be confirmed by a structured clinical interview such as SCID,Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale and the Composite International Diagnostic Interview[9].These take time and require trained healthcare professionals,which limits the scope for practical application in routine clinical practice.
The reason for highlighting these aspects is to put in focus that the diagnosis of depression is subjective unlike the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.Considering the subjective nature of diagnosing depression and the potential for false positive results,some national guidelines have not recommended population screening for depression[38].A systematic review of screening tools for measuring depression in diabetes has shown that little data is available on their validity and reliability,with even lesser evidence for their being culturally appropriate[39].In general,screening for major depressive disorders is based on screening instruments which do not generally consider the conceptual basis of emotional models,although efforts are being made to improve it[40].Apart from the risk of false positive diagnosis of depression by assessing subjective methods,the outcomes of different methods of psychotherapy are not clear.The latter is being addressed by an ongoing trial:cRCT PSYCHOnline-THERAPY[41].
A Joint Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association,the American Association of Diabetes Educators,and the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics,The American Diabetes Association recommends screening for depression in subjects with diabetes mellitus[42].Others are advised an annual screen during major disease and life transitions.
Intervention strategies
One must recognize that guidelines for the management of depression are currently inadequately planned,reported and measured[47].Therefore,shared decision making with the patient[48],using digital medical interview assistant systems at the primary care level could be employed to improve compliance and thereby management outcomes[49].
Interestingly,many interventions that are useful in preventing and treating diabetes are also effective in depression.Physical exercise,including running helps in managing depression and other negative psychological conditions,although no quantitative measures are available to prescribe the quantum of exercise for its beneficial effects[43].Insomnia,which often occurs with depression,is a well-known modifiable risk factor for the development of obesity and diabetes mellitus[44].Cognitive behavior therapy for insomnia(CBT-I)is effective in improving insomnia associated with depression.CBT-I seeks to replace wrong beliefs of sleep,to help them prevent associating with stimulating activities,to limit time in bed for matching perceived sleep duration,sleep hygiene and relaxation techniques[45].To ensure access to physical exercise and help in relaxation and ensuring adequate sleep,aspects of built environment must be considered[46].
In general,depression associated with diabetes can be managed by one or more of the following methods:Antidepressant drugs,psychological interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy,mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and stepped care[12].
Although antidepressant medications are effective in the treatment of depression associated with diabetes,attention must be paid to their potential role in leading to obesity and insulin resistance[31].Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor agents(SRRI)are the drugs of choice,while considering the potential risk of hypoglycemia;should tricyclic antidepressants be required,one must carefully monitor glycemic control[50].Along with antipsychotic medicines anti-depressants lead to weight gain whichranges from 0.43 to 4.45 kg,with its attendant adverse metabolic effects through weight gain itself or its effects on the pancreatic beta cells.Dyslipidemia may result from the use of valproic acid derivatives,carbamazepine,mirtazapine.SSRIs can lead to dyslipidemia.Clozapine,olanzapine,valproic acid derivates and tricyclic antidepressants are known to induce insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus[51].Newer agents such as bupropion and agomelatine,although promising,need more evidence for their therapeutic utility.Pharmacological agents used along with psychotherapy could prove to be more effective than either alone.
He said that all men were wicked, and God would punish them for their sins, and that the wicked, when they died, would be cast into hell, to burn for ever and ever
In a meta-analysis of 14 randomized clinical trials involving 1724 subjects,van der Feltz-Cornelis
[52]concluded that treatment can improve clinical outcomes,although the combined effect of all interventions is moderate on the clinical impact[52].When combined with diabetes self-management,psychotherapeutic interventions have a moderate clinical impact.Employing collaborative care
stepped care intervention is possible at the primary care level.Drug therapy and collaborative care successfully reduced depressive symptoms but did not have a significant effect on glycemic control[52].
Constraints of treating depression in diabetes
While the association between diabetes and depression,as well as the need for managing both together are recognized,implementation faces many barriers.As alluded to earlier,the diagnosis of depression is a work in progress;the burden of diabetes is so overwhelming that the identification of depression gets diluted due to lack of both time and knowledge[52].Considering depression and diabetes are best treated together,effective management requires an embedded integrated approach rather than treating each independently[9].It is imperative that new treatment paradigms must be identified,developed and applied to manage the twin problems of diabetes and depression,
to democratize the treatment processes.
lNTEGRATED CARE OF DlABETES AND DEPRESSlON
Primarily,studies on interventions for depression showed that integrating mental health treatment to primary care settings is possible through collaborative care[53].The key component of the collaborative care model is care managers,who are non-physicians,often nurses or social workers.Under the supervision of a physician and a psychiatrist,they identify depression by using screening tools and further provide problem-solving therapy[53].Although encouraging in principle,a number of practical limitations remain for its wider applicability.
She began looking around her familiar room. Four years ago, she became his bride here. On the night of their marriage, he felt deeply guilty to her, saying, I feel so sorry to you for having you live in this small room. In the future I will earn a lot of money to buy our own house.
Unlike the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus,depression is identified by clinical features such as episodes of lowered mood,reduced energy and decreased activity[8].
INtegrating DEPrEssioN and Diabetes treatmENT study
Judging from the number of publications,one could draw an erroneous opinion that the relationship between depression in type 2 diabetes is fully established,that effective treatment options are available and that the only constraint is to scale up intervention strategies to manage depression and type 2 diabetes.At the outset there is an asymmetry in the diagnoses of both conditions:Whereas diabetes is identified by objective criteria involving measurement of biomarkers,the diagnosis of depression is based on subjective criteria.The results from self-administered questionnaires and expert face to face interviews often diverge,as do different forms of questionnaires.The sensitivity and specificity of questionnaires need to be refined by including the cultural contexts of different populations.Therefore,there is a spectrum of conditions of what is referred to as depression associated with type 2 diabetes,from diabetes distress to subclinical depression,stretching to full blown depression.Interventions improve the outcomes of depression and of diabetes distress;however,treatment of depression improves depressive symptoms,without significant improvement of metabolic control.In contrast,treatment of diabetes distress results in improved glycemic control.Furthermore,the measures to manage them are varied and there are no accepted standard methods,rendering comparisons difficult.Therefore,despite epidemiological and mechanistic evidence for the co-existence of depression and type 2 diabetes mellitus,further refinements are necessary to define and measure the outcome of different treatment modalities of depression.However,most studies report improvement of depressive symptoms with interventions despite equivocal or no improvement of glycemic control.Therefore,it is worthwhile to identify depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus,and provide treatment by psychological and pharmacological measures.Although depression has been shown to respond to treatment,care must be taken in the choice of anti-depressant medications,some of which can worsen insulin sensitivity leading to adverse metabolic consequences.There is a lack of qualified mental care specialists to deal with the burgeoning burden of diabetes and depression.The employment of trained clinical care coordinators is a worthwhile attempt to improve access to subjects with type 2 diabetes having coexistent depressive symptoms.Preliminary results suggest the efficacy of such interventions.Further studies must be carried out to scale up across different cultural,ethnic and geographic populations.
Treatment aspects were obtained from published literature which were further adapted to local conditions by qualitative interviews involving patients with diabetes and their significant others[59].To assess adaptations that were made to behavioral intervention made by care coordinators,and how patients responded to them,a purposive sample of patients(n:62)and care coordinators(n:3)were recruited from two clinics.Patients were interviewed about their experiences in the care model and care coordinators were interviewed about their experiences in implementation of interventions[46].The adaptations sought and made were categorized by how they helped to improve implementation in the local context.They in turn served to help improve communication of health and to enhance engagement by the patients[59].
The use of care coordinators in managing depression among subjects with type 2 diabetes has shown promising results a year following active interventions.Further follow up and replication in other settings should be carried out to assess the generalizability of the findings from INDEPENDENT study.Recently,anxiety was shown to respond favorably to interventions in the INDEPENDENT study[60].
It was a moment when all the disparate shards of his life seemed to knit themselves together, every past sadness and disappointment, every anxious secret and uncertainty72 hidden now beneath the soft white layers
CRlTlCAL SUMMARY OF TYPE 2 DlABETES AND DEPRESSlON
The INtegrating DEPrEssioN and Diabetes treatmENT(INDEPENDENT)Study was carried out[57]to assess whether it would be possible to bridge the gap between the high prevalence of depression in diabetes and lack of qualified psychiatrists.It was a collaborative care model involving care coordinator,endocrinologist/diabetologist and psychiatrist in four centers in India.It assessed whether depression,identified by PHQ-9 can be managed by care coordinators,who are not professional psychiatrists,but were trained to identify and help solve issues of treatment compliance and coping with stresses.Coordination was carried out with the family and with the other members of the healthcare team of the primary physician,endocrinologists/diabetologists and psychiatrists.This follow up study was carried out in four sites in India:Madras Diabetes Research Foundation,Dr.Mohan’s Diabetes Specialties Centre,Chennai,Department of Endocrinology,AIIMS,New Delhi,Endocrine and Diabetes Centre,Visakhapatnam,Diacon Hospital,Bangalore.The primary aim was to see whether there would be an improvement in depressive symptoms and metabolic parameters and whether they would be sustained for 12-mo after active intervention[58].In the parallel,open-label,pragmatic randomized clinical trial(n:196 intervention group;n:208 controls),those who were in the intervention group were given 12 mo of support for self-management by nonphysician care-coordinators,decision support based on electronic medical records,under the periodic reviews by endocrinologists/diabetologists and psychiatrists.After a further 12-mo period of follow up without intervention,the outcomes were assessed.Control subjects received usual care for 24 mo[58].Collaborative care intervention led to improvements in composite measure of depressive symptoms and indices of cardiometabolic health at the end of 24 mo[45].
CONCLUSlON
It is established that diabetes and depression often coexist and must be managed together rather than individually.Interventions must be made across a spectrum to prevent,identify and manage depression when it occurs.Proof of principle studies have shown that they are feasible.It is necessary to scale-up such studies to assess their feasibility for wide-spread use in terms of applicability,efficacy and in terms of cost-benefit outcomes.
Then she chased it from place to place, and at last had it safe between her fingers, almost as frightened as on the day that it had made its first entrance into the hut
Non physician trained clinical coordinators can provide self-management education and support in terms of nutrition,lifestyle,compliance to medications,monitoring of metabolic parameters and dealing with psychosocial problems.These must necessarily be adapted to the age group,culture and language of the population by making appropriate cultural changes in education[16].Depending on the availability and applicability,online interventions can be profitably made in terms of digital medical interview assistant systems[36].With the widespread use of electronic medical records in diabetes care,a rule-based system can be incorporated so that standardized collection of data can be streamlined[61].As the next logical step,the data can be analyzed and machine-learning methods can be devised to improve the communication,care and outcomes of diabetes and its associated morbidities including depression[62].
FOOTNOTES
Sridhar GR did the literature search and wrote the manuscript.
4. White as snow, as red as blood, and as black as the wood: The three colours, white, red and black represent the three aspects of the Triple Goddess: maiden/mother/crone. IRReturn to place in story.
Gumpeny R Sridhar has no conflicts of interest.He has not received fees for serving as a speaker,nor has he received research funding.He does not own stocks and/or shares.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See:https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
India
Gumpeny R Sridhar 0000-0002-7446-1251.
Fan JR
In silent awe20, I let the wordless, poignant21 communication between Katie and Stripe unfold. Acutely sensitive to her well being, Stripe intuitively softened22 his gait at the slightest perception of Katie s imbalance or discomfort23 in the saddle. The tone of her voice induced the same effect, even though she was unable to use verbal commands that the horse was trained to recognize. Surprise, delight, hesitation24, fear-Stripe understood and responded patiently, lovingly-like a great teacher.
Filipodia
Fan JR
1 Cho NH,Shaw JE,Karuranga S,Huang Y,da Rocha Fernandes JD,Ohlrogge AW,Malanda B.IDF Diabetes Atlas:Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045.
2018;138:271-281[PMID:29496507 DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023]
2 Saeedi P,Petersohn I,Salpea P,Malanda B,Karuranga S,Unwin N,Colagiuri S,Guariguata L,Motala AA,Ogurtsova K,Shaw JE,Bright D,Williams R;IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee.Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045:Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas,9
edition.
2019;157:107843[PMID:31518657 DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843]
3 Hock RS,Or F,Kolappa K,Burkey MD,Surkan PJ,Eaton WW.A new resolution for global mental health.
2012;379:1367-1368[PMID:22500865 DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60243-8]
4 Markowitz SM,Gonzalez JS,Wilkinson JL,Safren SA.A review of treating depression in diabetes:emerging findings.
2011;52:1-18[PMID:21300190 DOI:10.1016/j.psym.2010.11.007]
5 Mizukami H,Kudoh K.Diversity of pathophysiology in type 2 diabetes shown by islet pathology.
2022;13:6-13[PMID:34562302 DOI:10.1111/jdi.13679]
6 Jacob KS.Depression:a major public health problem in need of a multi-sectoral response.
2012;136:537-539[PMID:23168691]
7 Donath MY,Ehses JA.Type 1,type 1.5,and type 2 diabetes:NOD the diabetes we thought it was.
2006;103:12217-12218[PMID:16894143 DOI:10.1073/pnas.0605480103]
8 American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee,Draznin B,Aroda VR,Bakris G,Benson G,Brown FM,Freeman R,Green J,Huang E,Isaacs D,Kahan S,Leon J,Lyons SK,Peters AL,Prahalad P,Reusch JEB,Young-Hyman D,Das S,Kosiborod M.2.Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes:Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022.
2022;45:S17-S38[PMID:34964875 DOI:10.2337/dc22-S002]
9 Darwish L,Beroncal E,Sison MV,Swardfager W.Depression in people with type 2 diabetes:current perspectives.
2018;11:333-343[PMID:30022843 DOI:10.2147/DMSO.S106797]
10 Moulton CD,Pickup JC,Ismail K.The link between depression and diabetes:the search for shared mechanisms.
2015;3:461-471[PMID:25995124 DOI:10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00134-5]
11 Madavanakadu Devassy S,Benny AM,Scaria L,Nannatt A,Fendt-Newlin M,Joubert J,Joubert L,Webber M.Social factors associated with chronic non-communicable disease and comorbidity with mental health problems in India:a scoping review.
2020;10:e035590[PMID:32595154 DOI:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035590]
12 Pouwer F,Schram MT,Iversen MM,Nouwen A,Holt RIG.How 25 years of psychosocial research has contributed to a better understanding of the links between depression and diabetes.
2020;37:383-392[PMID:31909844 DOI:10.1111/dme.14227]
13 Nouwen A,Nefs G,Caramlau I,Connock M,Winkley K,Lloyd CE,Peyrot M,Pouwer F;European Depression in Diabetes Research Consortium.Prevalence of depression in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism or undiagnosed diabetes:a systematic review and meta-analysis of the European Depression in Diabetes(EDID)Research Consortium.
2011;34:752-762[PMID:21357362 DOI:10.2337/dc10-1414]
14 Nouwen A,Winkley K,Twisk J,Lloyd CE,Peyrot M,Ismail K,Pouwer F;European Depression in Diabetes(EDID)Research Consortium.Type 2 diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for the onset of depression:a systematic review and metaanalysis.
2010;53:2480-2486[PMID:20711716 DOI:10.1007/s00125-010-1874-x]
15 Yu M,Zhang X,Lu F,Fang L.Depression and Risk for Diabetes:A Meta-Analysis.
2015;39:266-272[PMID:25773933 DOI:10.1016/j.jcjd.2014.11.006]
16 Guérin E,Jaafar H,Amrani L,Prud'homme D,Aguer C.Intervention Strategies for Prevention of Comorbid Depression Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes:A Scoping Review.
2019;7:35[PMID:30891439 DOI:10.3389/fpubh.2019.00035]
17 Schmitt A,Kulzer B,Reimer A,Herder C,Roden M,Haak T,Hermanns N.Evaluation of a Stepped Care Approach to Manage Depression and Diabetes Distress in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes:Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial(ECCE HOMO Study).
2021;1-16[PMID:34875666 DOI:10.1159/000520319]
18 Huang CJ,Lin CH,Hsieh HM,Chang CC,Chu CC,Sun DP,Weng SF.A longitudinal study of healthcare utilisation and expenditure in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without major depressive disorder.
2019;57:50-58[PMID:30908962 DOI:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2018.09.007]
19 de Groot M,Shubrook JH,Hornsby WG Jr,Pillay Y,Mather KJ,Fitzpatrick K,Yang Z,Saha C.Program ACTIVE II:Outcomes From a Randomized,Multistate Community-Based Depression Treatment for Rural and Urban Adults With Type 2 Diabetes.
2019;42:1185-1193[PMID:31221693 DOI:10.2337/dc18-2400]
20 AlOtaibi AA,Almesned M,Alahaideb TM,Almasari SM,Alsuwayt SS.Assessment of diabetes-related distress among type 2 diabetic patients,Riyadh,Saudi Arabia.
2021;10:3481-3489[PMID:34760777 DOI:10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_488_21]
21 Fisher L,Mullan JT,Skaff MM,Glasgow RE,Arean P,Hessler D.Predicting diabetes distress in patients with Type 2 diabetes:a longitudinal study.
2009;26:622-627[PMID:19538238 DOI:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02730.x]
22 Wong EM,Afshar R,Qian H,Zhang M,Elliott TG,Tang TS.Diabetes Distress,Depression and Glycemic Control in a Canadian-Based Specialty Care Setting.
2017;41:362-365[PMID:28462795 DOI:10.1016/j.jcjd.2016.11.006]
23 Gonzalez JS,Shreck E,Psaros C,Safren SA.Distress and type 2 diabetes-treatment adherence:A mediating role for perceived control.
2015;34:505-513[PMID:25110840 DOI:10.1037/hea0000131]
24 Elamoshy R,Bird Y,Thorpe L,Moraros J.Risk of Depression and Suicidality among Diabetic Patients:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
2018;7[PMID:30453557 DOI:10.3390/jcm7110445]
25 Conti C,Mennitto C,Di Francesco G,Fraticelli F,Vitacolonna E,Fulcheri M.Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus and Suicide Risk.
2017;8:40[PMID:28348533 DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00040]
26 Alzoubi A,Abunaser R,Khassawneh A,Alfaqih M,Khasawneh A,Abdo N.The Bidirectional Relationship between Diabetes and Depression:A Literature Review.
2018;39:137-146[PMID:29788701 DOI:10.4082/kjfm.2018.39.3.137]
27 Xuan L,Zhao Z,Jia X,Hou Y,Wang T,Li M,Lu J,Xu Y,Chen Y,Qi L,Wang W,Bi Y,Xu M.Type 2 diabetes is causally associated with depression:a Mendelian randomization analysis.
2018;12:678-687[PMID:30446878 DOI:10.1007/s11684-018-0671-7]
28 Rotella F,Mannucci E.Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for depression.A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies.
2013;99:98-104[PMID:23265924 DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.11.022]
29 Huang Y,Li L,Gan Y,Wang C,Jiang H,Cao S,Lu Z.Sedentary behaviors and risk of depression:a meta-analysis of prospective studies.
2020;10:26[PMID:32066686 DOI:10.1038/s41398-020-0715-z]
30 Taylor WD,Aizenstein HJ,Alexopoulos GS.The vascular depression hypothesis:mechanisms linking vascular disease with depression.
2013;18:963-974[PMID:23439482 DOI:10.1038/mp.2013.20]
31 Kalra S,Jena BN,Yeravdekar R.Emotional and Psychological Needs of People with Diabetes.
2018;22:696-704[PMID:30294583 DOI:10.4103/ijem.IJEM_579_17]
32 Chávez-Castillo M,Nava M,Ortega á,Rojas M,Nú?ez V,Salazar J,Bermúdez V,Rojas-Quintero J.Depression as an Immunometabolic Disorder:Exploring Shared Pharmacotherapeutics with Cardiovascular Disease.
2020;18:1138-1153[PMID:32282306 DOI:10.2174/1570159X18666200413144401]
33 Bucciarelli V,Caterino AL,Bianco F,Caputi CG,Salerni S,Sciomer S,Maffei S,Gallina S.Depression and cardiovascular disease:The deep blue sea of women's heart.
2020;30:170-176[PMID:31109802 DOI:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.05.001]
34 Joseph JJ,Golden SH.Cortisol dysregulation:the bidirectional link between stress,depression,and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
2017;1391:20-34[PMID:27750377 DOI:10.1111/nyas.13217]
35 Sridhar GR.Dealing with diabetes in metabolic disorders.In Desai NG,Srinivasan KS(eds)Depression in medically-ill patients.ECAB Clinical Update:Psychiatry.Elsevier,New Delhi 2012:20-36
36 Lustman PJ,Clouse RE.Depression in diabetes:the chicken or the egg?
2007;69:297-299[PMID:17517972 DOI:10.1097/PSY.0b013e318060cc2d]
37 Muraleedharan MV,Sridhar GR.Psychiatric problems in diabetes.In Chandalia HB,Sridhar GR
(Eds).RSSDI Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus.Health Science Publishers,New Delhi 2014:1254-1262
38 Levis B,Sun Y,He C,Wu Y,Krishnan A,Bhandari PM,Neupane D,Imran M,Brehaut E,Negeri Z,Fischer FH,Benedetti A,Thombs BD;Depression Screening Data(DEPRESSD)PHQ Collaboration,Che L,Levis A,Riehm K,Saadat N,Azar M,Rice D,Boruff J,Kloda L,Cuijpers P,Gilbody S,Ioannidis J,McMillan D,Patten S,Shrier I,Ziegelstein R,Moore A,Akena D,Amtmann D,Arroll B,Ayalon L,Baradaran H,Beraldi A,Bernstein C,Bhana A,Bombardier C,Buji RI,Butterworth P,Carter G,Chagas M,Chan J,Chan LF,Chibanda D,Cholera R,Clover K,Conway A,Conwell Y,Daray F,de Man-van Ginkel J,Delgadillo J,Diez-Quevedo C,Fann J,Field S,Fisher J,Fung D,Garman E,Gelaye B,Gholizadeh L,Gibson L,Goodyear-Smith F,Green E,Greeno C,Hall B,Hampel P,Hantsoo L,Haroz E,Harter M,Hegerl U,Hides L,Hobfoll S,Honikman S,Hudson M,Hyphantis T,Inagaki M,Ismail K,Jeon HJ,Jetté N,Khamseh M,Kiely K,Kohler S,Kohrt B,Kwan Y,Lamers F,Asunción Lara M,Levin-Aspenson H,Lino V,Liu SI,Lotrakul M,Loureiro S,L?we B,Luitel N,Lund C,Marrie RA,Marsh L,Marx B,McGuire A,Mohd Sidik S,Munhoz T,Muramatsu K,Nakku J,Navarrete L,Osório F,Patel V,Pence B,Persoons P,Petersen I,Picardi A,Pugh S,Quinn T,Rancans E,Rathod S,Reuter K,Roch S,Rooney A,Rowe H,Santos I,Schram M,Shaaban J,Shinn E,Sidebottom A,Simning A,Spangenberg L,Stafford L,Sung S,Suzuki K,Swartz R,Tan PLL,Taylor-Rowan M,Tran T,Turner A,van der Feltz-Cornelis C,van Heyningen T,van Weert H,Wagner L,Li Wang J,White J,Winkley K,Wynter K,Yamada M,Zhi Zeng Q,Zhang Y.Accuracy of the PHQ-2 Alone and in Combination With the PHQ-9 for Screening to Detect Major Depression:Systematic Review and Metaanalysis.
2020;323:2290-2300[PMID:32515813 DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.6504]
39 Roy T,Lloyd CE,Pouwer F,Holt RI,Sartorius N.Screening tools used for measuring depression among people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes:a systematic review.
2012;29:164-175[PMID:21824180 DOI:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03401.x]
40 Akter J,Islam RM,Chowdhury HA,Selim S,Biswas A,Mozumder TA,Broder J,Ilic D,Karim MN.Psychometric validation of diabetes distress scale in Bangladeshi population.
2022;12:562[PMID:35022493 DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-04671-0]
41 Baumeister H,Bauereiss N,Zarski AC,Braun L,Buntrock C,Hoherz C,Idrees AR,Kraft R,Meyer P,Nguyen TBD,Pryss R,Reichert M,Sextl T,Steinhoff M,Stenzel L,Steubl L,Terhorst Y,Titzler I,Ebert DD.Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness of PSYCHOnlineTHERAPY:Study Protocol of a Multicenter Blended Outpatient Psychotherapy Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial for Patients With Depressive and Anxiety Disorders.
2021;12:660534[PMID:34054617 DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.660534]
42 Young-Hyman D,de Groot M,Hill-Briggs F,Gonzalez JS,Hood K,Peyrot M.Psychosocial Care for People With Diabetes:A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association.
2016;39:2126-2140[DOI:10.2337/dc16-2053]
43 Markoti? V,Pokraj?i? V,Babi? M,Radan?evi? D,Grle M,Miljko M,Kosovi? V,Juri? I,Karlovi? Vidakovi? M.The Positive Effects of Running on Mental Health.
2020;32:233-235[PMID:32970641]
44 Sridhar GR,Sanjana NS.Sleep,circadian dysrhythmia,obesity and diabetes.
2016;7:515-522[PMID:27895820 DOI:10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.515]
45 Feng G,Han M,Li X,Geng L,Miao Y.The Clinical Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Patients with Insomnia and Depression:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
2020;2020:8071821[PMID:32733587 DOI:10.1155/2020/8071821]
46 Pasala SK,Rao AA,Sridhar GR.Built environment and diabetes.
2010;30:63-68[PMID:20535308 DOI:10.4103/0973-3930.62594]
47 Lee Y,Brietzke E,Cao B,Chen Y,Linnaranta O,Mansur RB,Cortes P,K?sters M,Majeed A,Tamura JK,Lui LMW,Vinberg M,Kein?nen J,Kisely S,Naveed S,Barbui C,Parker G,Owolabi M,Nishi D,Lee J,Srisurapanont M,Gill H,Guo L,Balanzá-Martínez V,Partonen T,Nolen WA,Lee JH,Kim JH,Chavannes NH,Ewais T,Atienza-Carbonell B,Silven AV,Yasuma N,Gil A,Novikov A,Lacey C,Versluis A,von Malortie S,Chan LF,Waqas A,Purgato M,Aardoom JJ,Ly-Uson JT,Sim K,Tuineag M,van der Kleij RMJJ,van Luenen S,Suttajit S,Hajek T,Lee YW,Porter RJ,Alsuwaidan M,Rosenblat JD,Ravindran AV,Lam RW,McIntyre RS;Global Alliance for Chronic Diseases(GACD)Mental Health Guidelines Working Group.Development and implementation of guidelines for the management of depression:a systematic review.
2020;98:683-697H[PMID:33177758 DOI:10.2471/BLT.20.251405]
48 Hopwood M.The Shared Decision-Making Process in the Pharmacological Management of Depression.
2020;13:23-30[PMID:31544218 DOI:10.1007/s40271-019-00383-w]
49 Jimenez G,Tyagi S,Osman T,Spinazze P,van der Kleij R,Chavannes NH,Car J.Improving the Primary Care Consultation for Diabetes and Depression Through Digital Medical Interview Assistant Systems:Narrative Review.
2020;22:e18109[PMID:32663144 DOI:10.2196/18109]
50 Roopan S,Larsen ER.Use of antidepressants in patients with depression and comorbid diabetes mellitus:a systematic review.
2017;29:127-139[PMID:27776567 DOI:10.1017/neu.2016.54]
51 Sridhar GR.On Psychology and Psychiatry in Diabetes.
2020;24:387-395[PMID:33489842 DOI:10.4103/ijem.IJEM_188_20]
52 van der Feltz-Cornelis CM,Nuyen J,Stoop C,Chan J,Jacobson AM,Katon W,Snoek F,Sartorius N.Effect of interventions for major depressive disorder and significant depressive symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus:a systematic review and meta-analysis.
2010;32:380-395[PMID:20633742 DOI:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.03.011]
53 Moise N,Wainberg M,Shah RN.Primary care and mental health:Where do we go from here?
2021;11:271-276[PMID:34327121 DOI:10.5498/wjp.v11.i7.271]
54 Diaz Bustamante L,Ghattas KN,Ilyas S,Al-Refai R,Maharjan R,Khan S.Does Treatment for Depression With Collaborative Care Improve the Glycemic Levels in Diabetic Patients with Depression?
2020;12:e10551[PMID:33101799 DOI:10.7759/cureus.10551]
55 Bogner HR,Morales KH,de Vries HF,Cappola AR.Integrated management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression treatment to improve medication adherence:a randomized controlled trial.
2012;10:15-22[PMID:22230826 DOI:10.1370/afm.1344]
56 Huang Y,Wei X,Wu T,Chen R,Guo A.Collaborative care for patients with depression and diabetes mellitus:a systematic review and meta-analysis.
2013;13:260[PMID:24125027 DOI:10.1186/1471-244X-13-260]
57 Kowalski AJ,Poongothai S,Chwastiak L,Hutcheson M,Tandon N,Khadgawat R,Sridhar GR,Aravind SR,Sosale B,Anjana RM,Rao D,Sagar R,Mehta N,Narayan KMV,Unutzer J,Katon W,Mohan V,Ali MK.The INtegrating DEPrEssioN and Diabetes treatmENT(INDEPENDENT)study:Design and methods to address mental healthcare gaps in India.
2017;60:113-124[PMID:28642211 DOI:10.1016/j.cct.2017.06.013]
58 Ali MK,Chwastiak L,Poongothai S,Emmert-Fees KMF,Patel SA,Anjana RM,Sagar R,Shankar R,Sridhar GR,Kosuri M,Sosale AR,Sosale B,Rao D,Tandon N,Narayan KMV,Mohan V;INDEPENDENT Study Group.Effect of a Collaborative Care Model on Depressive Symptoms and Glycated Hemoglobin,Blood Pressure,and Serum Cholesterol Among Patients With Depression and Diabetes in India:The INDEPENDENT Randomized Clinical Trial.
2020;324:651-662[PMID:32809002 DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.11747]
59 Johnson LCM,Chwastiak L,Poongothai S,Tandon N,Anjana RM,Aravind S,Sridhar GR,Rao D,Mohan V,Ali MK.Adaptations and patient responses to behavioral intervention components in a depression-focused chronic disease care model implemented in India.
2020;10:35-45[PMID:32011720 DOI:10.1093/tbm/ibz192]
60 Kemp CG,Johnson LCM,Sagar R,Poongothai S,Tandon N,Anjana RM,Aravind S,Sridhar GR,Patel SA,Emmert-Fees K,Rao D,Narayan KMV,Mohan V,Ali MK,Chwastiak LA.Effect of a collaborative care model on anxiety symptoms among patients with depression and diabetes in India:The INDEPENDENT randomized clinical trial.
2022;74:39-45[PMID:34883269 DOI:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2021.11.003]
61 Sridhar GR.Expanding Scope of Information Technology in Clinical Care.In Mehdi Khosrow-Pour D.B.A,2021:13
62 Sridhar GR,Lakshmi G.Artificial Intelligence in Medicine:Diabetes as a Model.In:Srinivasa K.G.,G.M.S.,Sekhar S.R.M.(eds)Artificial Intelligence for Information Management:A Healthcare Perspective.Studies in Big Data,vol 88.Singapore,Springer 2021:88
 World Journal of Diabetes2022年3期
World Journal of Diabetes2022年3期
- World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Beyond diabetes remission a step further:Post bariatric surgery hypoglycemia
- Free fatty acids,glucose,and insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis within four days of initiation
- Age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factor profile:A pooled analysis
- Hemoglobin within normal range is negatively related to hemoglobin A1c in a nondiabetic American population aged 16 years and older
- Functional annotation and enrichment analysis of differentially expressed serum proteins in patients with type 2 diabetes after dapagliflozin
