The expression of oxidative stress genes related to myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Qian-lin Gu, Peng Jiang, Hui-fen Ruan, Hao Tang, Yang-bing Liang, Zhong-fu Ma, Hong Zhan
1 Emergency Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510000, China
2 Huangpu District Emergency Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510000,China
KEYWORDS: Acute myocardial infarction; Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; Oxidative stress;TNFSF6; CYP1A1; Unfolded protein response
INTRODUCTION
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a severe stage of coronary heart disease that can cause sudden death and is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity across the world.Timely and effective myocardial reperfusion can reconstruct blood flow and improve myocardial perfusion, which is the most crucial treatment strategy for patients with AMI; however, rapid recovery of coronary blood flow can lead to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI).Until now, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) are not yet completely understood, and the main concentration was about oxidative stress,intracellular Caoverload, inflammation, and impaired metabolism.Research demonstrates that oxidative stress caused by oxygen free radicals, a key early driver,participates in the pathophysiological process of IRI.In the early stage of MIRI, high production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was induced by various ways such as the xanthine oxidase pathway, neutrophil pathway,mitochondrial injury pathway, and catecholamine oxidation pathway. Meanwhile, the injury from an imbalance of oxidant and antioxidant can be inhibited via antioxidants strategies in several clinical and preclinical studies.Additionally, the role that mitochondria play in the pathogenesis of MIRI is essential, since energy supply for cardiomyocytes is mostly derived from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS).The mechanism of mitochondria injury was significantly associated with the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP). As the mitochondrial channel, MPTP opening will further lead to the accumulation of ROS and Ca, exacerbating the myocardial cell microenvironment disorder.What is more, Caoverload is also the primary potential mechanism of MIRI. Through mediating membrane damage (such as mitochondrial membranes and cell membranes) and activating proteases, Caoverload can lead to a vicious cycle of IRI.However, the exact mechanisms of MIRI remain a mystery and a big challenge for clinicians.
Research on cardiovascular disease-specific genes and their gene chip technology has been both a hotspot and an area of difficulty in this field recently.The occurrence and development of IRI are regulated by hundreds of genes. The high throughput and versatility of gene chip technology with the significant advantages of microchemistry and integration provide a powerful tool for systematically studying the molecular mechanisms and prevention of IRI. Meanwhile, with the establishment and gradual improvement of the biological information database, biological information analysis can further increase our understanding of the mechanism,especially at the genetic level. This study aimed to screen the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among oxidative stress genes in patients with AMI following ischemia/reperfusion and provide the potential targets for the management of MIRI.
METHODS
Selection of participants
Patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) were admitted first to the Emergency Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, and then to the Department of Cardiology. Eleven STEMI patients were enrolled,including seven males and four females, with ages of 61.44±13.70 years (range 33-75 years). The control group consisted of 10 healthy volunteers matching the STEMI patient’s age and gender, seven males and three females, with ages of 53.00±6.55 years (range 32-61 years).
The patients enrolled in the study had not been treated previously with coronary heart diseases. The diagnosis of AMI was confirmed by electrocardiogram(ECG), cardiac echocardiogram, coronarography, and serum concentration levels of troponin and its cardiac isoenzyme.
The following inclusion criteria were established:age > 18 years, conscious consent, first-time cardiac incident, absence of previous treatment for coronary heart disease, typical coronary chest pain lasting < 12 h, and ECG changes in ST-T segment and T wave or block of left atrioventricular bundle branch. Exclusion criteria: no consent to participate, acute or chronic inflammatory disease present at the time of admission or in the three months preceding inclusion in the study,renal insufficiency, autoimmune disease, and diabetes.
Specimen collection
10 mL of elbow venous blood was collected on days 3 and 7 after the emergency percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) treatment in the AMI group or after fasting in the morning in the control group.
Materials and reagents
Gel imaging and chemiluminescence image analysis system (FluorChem 8900; Alpha Innotech, USA); total RNA extraction kit, mainly composed of TRIzol reagent(100 mL; Invitrogen, USA); first strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo fisher MBI, USA); RT-PCR kit (Thermo fisher MBI, USA); Taq DNA polymerase (Thermo fisher MBI, USA); PCR primers (Shenggong Biotech, China);diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC)-treated water, DNA marker, and cryogenic high-speed centrifuge (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA), ultra-clean workbench (SIK-202),electrophoresis instrument (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA),temperature gradient PCR instrument (TGGE; Biometra,G?ttingen, Germany), and FeroTec gradient PCR gene amplification instrument (Hangzhou Dahe Thermo-Magnetics, China).
Research methods
The ficoll method was conducted to separate PBMCs. The blood was lightly spread on the surface of the lymphocyte separation solution, followed by centrifugation at 2,500 r/min for 30 min, and five layers were formed in the centrifuge tube. The PBMC layer was transferred to a sterile centrifuge tube and washed twice with 10 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Finally,PBMCs were adjusted to 1×10cells/mL.
One milliliter blood from subjects was taken in heparin containing vacutainer for estimation of plasma total antioxidant capacity by the ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) assayaccording to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Peripheral blood samples (2 mL) were collected from two groups and processed with 2 mL TRIzol reagent,stored at -80 °C, and finally sent to Shanghai Kangcheng Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (China) for gene chip detection.The chip used in this experiment was a human wholegenome chip developed by SABiosciences (Frederick,USA): the stress and toxicity pathway gene chip, article number OHS-053. The chip expression spectrum was constructed by Shanghai Kangcheng Bioengineering Co.,Ltd.
PMCs were transferred to an Eppendorf tube, and the supernatant was centrifuged for RNA extraction following the manufacturer’s instructions (RNA extraction kit, Omega). Finally, the RNA sample was performed for electrophoresis and 1 μL was used for UV spectrophotometer analysis. RNA samples with an/value between 1.8 and 2.0 were considered acceptable.
The ReverTra Ace kit was used for performing cDNA synthesis (Toyobo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Following cDNA synthesis, the labeled probe and the high-density genomic chip were hybridized under standard conditions.
-
Fluorescence quantification was performed by fluorescence quantitative premixed reagent. A 20 μL system was established. The reaction procedure was as follows: an initial incubation at 95 °C for 3 min; followed by 30 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s and 62 °C for 30 s. All procedures were performed under the manufacturer’s instructions.
For the data obtained by the gene chip, the value collected by each chip was first subtracted from the minimum value of the original value of the chip, and then divided by the value of the housekeeping gene to obtain standard values for each gene. The standard values of several chips from one patient were averaged and compared to the standard values of the control to obtain a ratio of the changes in gene expression.
Image acquisition was performed with a GenePix 4000B chip scanner (Molecular Devices, USA), which scanned the fluorescence intensity of the chips and converted the experimental results into digital data.
Data analysis and DEGs identification,biological function and pathway enrichment analysis
The sequencing data set was normalized and analyzed by the DESeq package (1.10.1). The criteria of a false discovery ratio (FDR) <0.01 and log fold change |logFC| >2 was set as the threshold. Visualization of the heat map was done with R software. The up-regulated genes and downregulated genes among the 114 oxidative stress genes were chosen for producing the heat map.
In gene networks conforming to scale-free distribution, genes with similar expression patterns could be co-regulated, functionally related or pathway shared.Through calculating the corresponding topological overlap, genes in the above selected module positively associated with oxidative stress genes were found out and subjected to gene ontology (GO) analysis (GOSeq,Release 2.12) to determine clusters of DEGs with enriched molecular functions. Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis was performed via the “clusterProfiler” package in R/Bioconductor software to acquire the enriched biological process and KEGG pathway for subsequent analysis.A-value <0.05 and counts ≥ 4 were considered as significant. Our samples were divided into two groups(AMI and control). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)online tool (http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp) was applied in the two groups to verify the results of GO and KEGG analysis. The cut-off criteria for GSEA were<0.05.
Data processing and statistical methods
All data are expressed as the mean with standard deviation. Differences between groups were analyzed by-test and analysis of variance, and correlations were analyzed by simple correlation analysis. All data were analyzed with SPSS 10.0 software. A-value<0.05 was considered statistical significance.
RESULTS
Clinical outcome
The total numbers of WBC, neutrophil counts, and lymphocyte counts in the AMI group were higher than those in the control group (Table 1).
The total number of WBC in the AMI group was positively correlated with the CK-MB value (day 1)(=0.018,<0.05) (Figure 1).
The T-AOC was significantly lower in AMI group comparing to control (12.80±1.79 U/mL vs. 20.48±2.55 U/mL,<0.05) (Table 1).
Gene analysis
A total of 114 oxidative stress genes were analyzedto identify the significant DEGs between the AMI and control groups. A total of eight genes were up-regulated and four genes were down-regulated. The heat map of DEGs (Supplementary Figure 1) as shown in Table 2,the up-regulated DEGs included one cell growth arrest/senescence-related gene (), one oxidative and metabolic stress-related gene (), three heat shock-related genes (,, and),one DNA damage and repair gene (), and two apoptosis signaling-related genes (and). The down-regulated DEGs consisted of one cell proliferation/carcinogenesis gene (), two oxidative and metabolic stress genes (and),and one DNA damage and repair gene ().
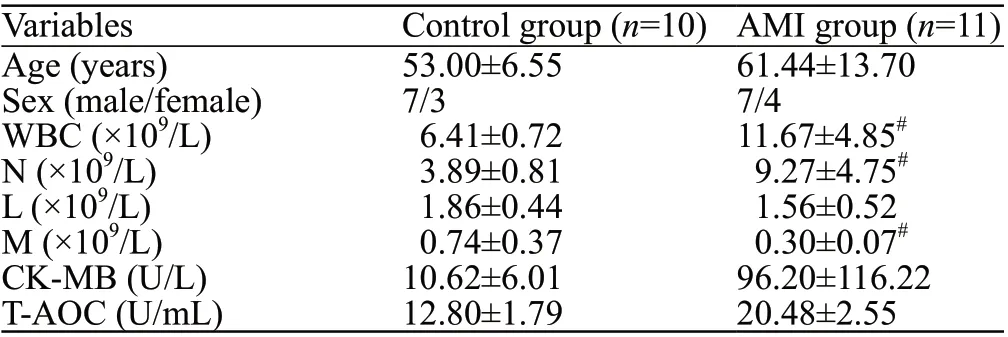
Table 1. Comparison of clinical data between the control and AMI(STEMI type) groups

Figure 1. The correlation between white blood cell counts and CKMB concentration on first day in the STEMI group.
The GO/KEGG enrichment analysis was performed with the DAVID website, and the top 10 enrichment results for each term are plotted in Figure 2. GO analysis results showed that changes in the biological process(Figure 2A) of genes were significantly enriched in protein folding, temperature stimulus, unfolded protein,topologically incorrect protein and cellular response to abiotic stimulus. Changes in cellular component(Figure 2A) were mainly enriched in cytoplasmic vesicle lumen, vesicle lumen, cytosolic part, secretory granule lumen and chaperone complex, etc. Changes in the molecular function (Figure 2A) were mainly enriched in unfolded protein binding, ubiquitin protein ligase binding, ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding, heat shock protein binding, and cytokine receptor binding.KEGG pathway analysis (Figure 2B) demonstrated that human cytomegalovirus infection, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, apoptosis and NF-κB signaling pathway.
RT-PCR results
After corrected by the internal reference gene,the relative expression ofin the AMI group was significantly higher than that in the control group(1.67±0.24 vs. 1.00±0.13;<0.05), while the expression ofwas significantly lower (0.66±0.08 vs.1.00±0.11;<0.05). Correlation analysis showed thatwas negatively correlated with(=0.227,<0.05) (Figure 3).
During the observation period of the AMI group, theexpression ofwas higher than that in the control group (0.78±0.23 vs. 0.45±0.03;<0.05), while the relative expression ofwas lower (0.09±0.07 vs.0.19±0.03;<0.05), and the expression levels at different time points showed no significant difference (>0.05)(Figure 4).

Table 2. Genes significantly differentially expressed in the AMI group compared with the control group
DISCUSSION
Our study showed that the total numbers of WBC and neutrophils in the AMI group were significantly higher than those in the control group, and it was positive correlated with CK-MB on day 1. A previous study has found that activated neutrophils can directly cause reperfusion injury by releasing proteolytic enzymes or exacerbate tissue damage by hydrolyzing cells.Respiratory bursts occur in neutrophils during ischemia/perfusion, and cellular oxygen consumption significantly increases, which produce and release large amounts of ROS, interleukins, and other vasoconstrictors. These changes destroy the fine structure of cardiomyocytes,leading to increased ion permeability of the cell membrane, calcium overload, oxidative phosphorylation dysfunction, and ultimately, cell death. Romson et alshowed that 2 h after myocardial infarction, the number of WBC in the infarcted myocardium increased 17-fold and 70% of the oxygen was consumed to produce ROS. Granfeldt et alreported that inhibition of central granulocytes can significantly reduce myocardial infarct size and protect the heart in animal experiments.Recently, Shimizu et alreported that plasma pentraxinrelated protein (PTX3) produced by bone marrowderived cells plays a crucial role in the protection against IRI by reducing neutrophil infiltration, ROS, and inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, WBC may play an important role in the IRI.
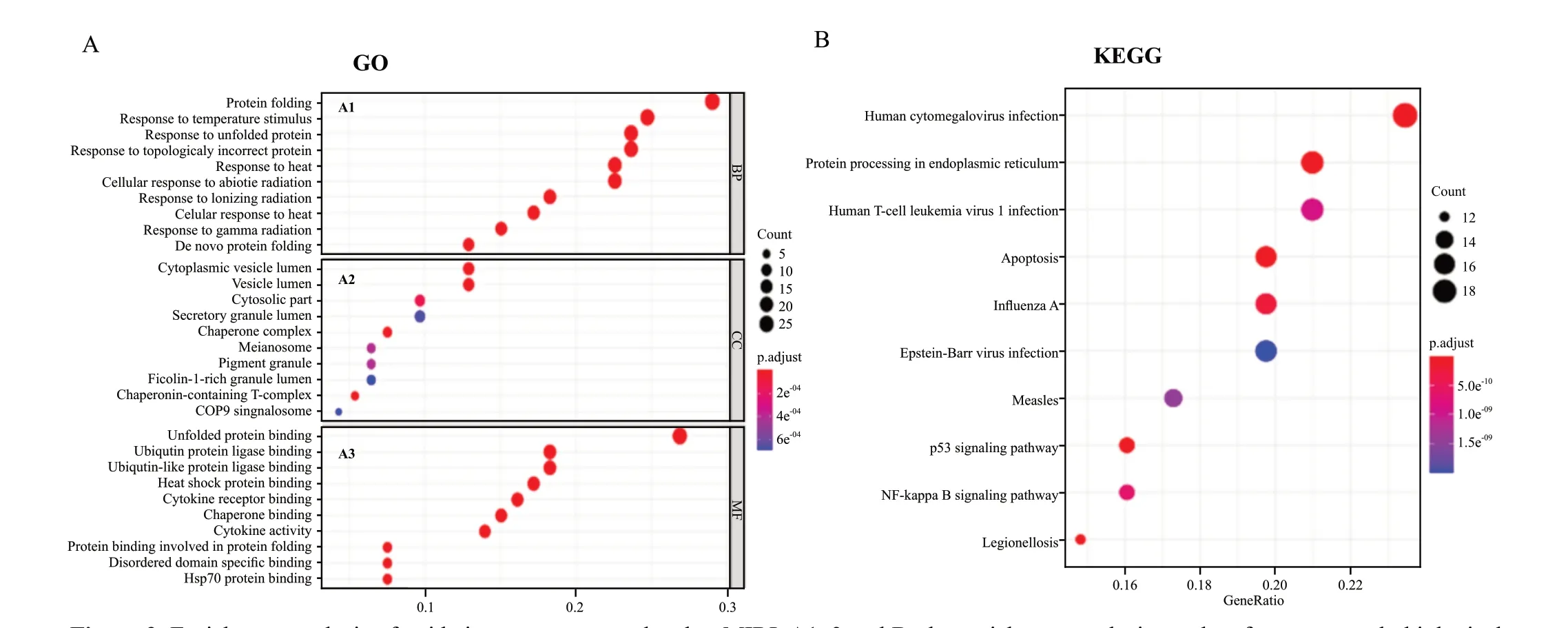
Figure 2. Enrichment analysis of oxidative stress genes related to MIRI. A1-3 and B: the enrichment analysis results of genes, namely biological processes, cellular components, molecular functions, and KEGG respectively. The main 10 results of each term are shown, and the color indicates the significant degree of enrichment and the size indicates the number of genes enriched for each result. GO: gene ontology; KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.

Figure 3. A and B: Relative expression of the TNFSF6 and CYP1A1 in each patient; C: Correlation between TNFSF6 and CYP1A1 in the AMI group (r=0.227, P<0.05). Compared with control group, #P<0.05.
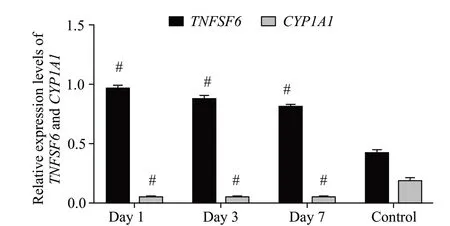
Figure 4. Relative expression levels of TNFSF6 and CYP1A1 on days 1, 3, and 7. Compared with control group, #P<0.05.
DEGs identification analysis showed that 12 of the 114 stress and toxicity-related genes in AMI patients were significantly differentially expressed compared to the control group, with eight significantly upregulated and four significantly down-regulated genes(Supplementary Figure 1 and Table 2). The up-regulated DEGs included three heat shock protein-related genes(,, and), two genes related to apoptosis signaling (and), one oxidative and metabolic stress-related gene (),one cell growth arrest/senescence gene (), and one DNA damage and repair-related gene (). Heat shock protein (HSP) is called the molecular bridesmaid,and the heat shock response is associated with cardiac IRI and repair.Therefore, in this study, it has been speculated that the heat shock response and its related factors may also have important protective effects in myocardial IRI.is a natural killer cell enhancer.In many cell systems, ROS can activate the MAPK pathway and regulate cell proliferation, differentiation,survival, and apoptosis.is involved in cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis.may play a crucial role in the DNA response induced by DNA damage; it can regulate the G/M phase of the cell cycle by interacting with Cdc2 protein, and thereby directly inhibit the regulation of Aurora-A kinase in the stability of centrosomes.also regulates G/S phase of the cell cycle. During emergency PCI in patients with myocardial infarction, up-regulation of these genes may be accompanied by an increase in oxidative stress,while the cells produce a series of genetic changes in pathological processes such as cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis. This study indicated that the upregulated DEGs during MIRI may result in genetic alterations in pathological processes such as oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis.
Down-regulated DEGs consisted of one cell proliferation/carcinogenesis-related gene (),two oxidative and metabolic stress-related genes (and), and one DNA damage and repair-related gene ().regulates cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity. The CAT catalase () gene encodes an antioxidant enzyme that can catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into HO and molecular oxygen,which plays an important role in scavenging free radicals.is a cytochrome oxidase subunit and was significantly down-regulated, which is consistent with the results of Stegall et al.is a DNA repair gene whose loss prevents damaged DNA from being properly repaired, leading to abnormal cell replication and spreading of cancer cells.
Moreover, PCR was performed to further verify the significance of the expression ofand.The results ofandexpression analysis were consistent with those results from the gene chip analysis. In this study, the relative expression ofin the AMI group was significantly higher than those in the control group, while the relative expression ofwas significantly lower. Besides,was upregulated at different time points, andwas down-regulated. Correlation analysis revealed a simple negative correlation betweenand, suggesting thatandmay act antagonistically in the regulation of MIRI.
Jeremias et alrevealed that soluble FasL was released from the heart during early reperfusion, while expression of Fas and FasL was significantly increased in the ischemic myocardium in a mouse heart IRI model. At the same time,Zhang et alshowed that the serum apoptotic factors sFas and sFasL in patients with AMI were significantly higher than normal. In this study, the obvious up-regulation ofsuggested myocardial apoptosis occurred in AMI patients, and its mechanism may be associated with increased oxidative stress reactions. Oxygen free radicals are important factors in initiating apoptosis, and the use of antioxidants and free radical scavengers can effectively inhibit apoptosis. A slight increase in ROS triggers the apoptotic pathway, and a further rise of ROS may accelerate the apoptotic process. ROS may activate the apoptotic program by regulating the expression of apoptosis-related genes such as.
This study showed that thegene was significantly down-regulated during IRI in patients with AMI, which is consistent with the findings of Hou et al.The decreased cytochrome oxidase activity in the mitochondria of ischemic cardiomyocytes might be the potential reason, so that NADPH cannot be fully oxidized, leading to increased ROS generation. Studies have shown that the P450 enzyme system protects cell membranes, inhibits lipid peroxidation, and scavenges free radicals in the process of oxidative stress reactions.When ischemia/reperfusion occurs, calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 is activated by intracellular Caoverload during arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism,which promotes the metabolism of AA and weakens the expression of. AA produces a large amount of ROS through the metabolism of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase, and the massive production of ROS further promotes AA metabolism.
As many researches indicated, enormous oxidative stress related biological markers were heavily involved during MIRI, which further led to cell damage. In our study, T-AOC was performed to assess the oxidative stress between the two groups. Results showed that T-AOC was significantly lower in AMI group comparing to control (Table 1). And GO term enrichment analysis showed that the DGEs were significantly enriched in protein folding, response to unfolded protein, response to topologically incorrect protein, unfolded protein binding and ubiquitin protein ligase binding, suggesting that some of these DEGs might be involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress and protein folding. Meanwhile,KEGG pathway enrichment analysis found that the DEGs were significantly enriched in protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum and apoptosis (Figure 2).Interestingly, oxidative stress condition can interfere with protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum, resulting in endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) during MIRI.Intracellular signal transduction pathways actived by the ERS was called unfolded protein response (UPR) which was caused by the imbalance between ROS production and antioxidant response. Additionally, the endoplasmic reticulum could be a new player in the promotion of the pro- or antioxidative pathways and in such a modulation,the UPR pathways play an essential role. The UPR consists of a set of conserved signaling pathways evolved to restore the proteostasis during protein misfolding within the endoplasmic reticulum and the persistent activation of UPR leads to increased oxidative stress and cell death.Ca-mediated mitochondrial ROS production further enhances calcium release from ER,which in turn impairs Ca-dependent chaperone activity and ER homeostasis, resulting in ER stress. Moreover,ROS themselves impair the ER oxidative protein folding.At the same time, the tightening of ER-mitochondria contact sites during chronic ER stress facilitate calcium influx and ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis.Taken all together, these results implied that UPR and apoptosis induced by ERS linked to oxidative stress reaction were related to mechanism of MIRI. On this evidence, we predict that these protein folding-related pathways act as an essential bridge between oxidative stress and MIRI and are worthy of further study.
CONCLUSIONS
WBCs are important cells that mediate myocardial IRI. The gene regulation of myocardial IRI is a complex process involving multiple genes, including those related to oxidative metabolic stress, heat shock, DNA damage and repair, and apoptosis signal transduction gene. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) caused by oxidative stress can lead to UPR and apoptosis, which may be an essential signaling pathway and therapeutic target for MIRI.
National Natural Science Foundation of China(81670220, 31270992, and 30800215); Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2014A030313086);Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project(2015A020212013); Guangzhou Science and Technology Project(201804010007).
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University ([2019]176).
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
ZFM and HZ were involved in study conception,study design. QLG finished the basic experiment and drafted the paper. All others had significant input in revising the manuscript.All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
