Artificial intelligence computed tomography helps evaluate the severity of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study
Yi Han, Su-cheng Mu, Hai-dong Zhang, Wei Wei, Xing-yue Wu, Chao-yuan Jin, Guo-rong Gu, Bao-jun Xie,Chao-yang Tong
1 Department of Emergency Medicine, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
2 Department of Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, China
KEYWORDS: COVID-19; Artificial intelligence; Chest computed tomography
INTRODUCTION
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by a novel β-coronavirus named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).By the end of June 2021, more than 177,800,000 confirmed cases had been documented, and the number is increasing with a skyrocketing speed every day.We often use computed tomography (CT), a noninvasive imaging approach, to assist in the diagnosis of pneumonia and COVID-19.Chest CT of COVID-19 patients revealed multiple areas of consolidation and ground-glass opacity (GGO) with bilateral peripheral involvement. Progression to “crazypaving” patternsresults in the fundamental pathology of severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Therefore, early identification of the severity of this disease would help reduce mortality.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has demonstrated success in medical imaging due to its high feature extraction capability.Specifically, AI was applied to detect various features of chest CT images.Recent studies showed that a deep learning model could accurately detect COVID-19 and differentiate it from community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)and other lung conditions.Furthermore, AI assistance helped inexperienced radiologists distinguish the different types of pneumonia on chest CT.However,COVID-19 shares similar imaging features with other types of pneumonia, which makes disease severity evaluation much more difficult.
In this study, we used the intelligent evaluation system constructed by Hangzhou YITU Healthcare Technology Co., Ltd. as the CT image analysis tool to analyze chest CT images of COVID-19 patients to determine the evaluation value of this system on disease severity.
METHODS
Data collection
A total of 140 confirmed COVID-19 patients at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University were enrolled in this retrospective observational study between February 1 and April 1, 2020. A confirmed case of COVID-19 was defined as a positive result on a real-time reversetranscriptase polymerase chain reaction (real-time RTPCR) assay of nasopharyngeal swab specimens.
A trained team of physicians and medical students reviewed and collected demographic, epidemiological,clinical, physical examination findings, and laboratory data from electronic medical records. Laboratory assessments consisted of complete blood count,C-reactive protein (CRP) and cytokines, and evaluation of immunoglobulins, among other parameters. We defined the degree of severity of COVID-19 patients(severe vs. non-severe) at admission, according to American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines for CAP,and collected imaging scans of each enrolled individual. The radiologic assessments of chest CT were reviewed and rated by two attending radiologists who extracted the data using a semiquantitative rating system (Supplementary Table 1). The intelligent evaluation system developed by Hangzhou YITU Healthcare Technology Co., Ltd. was employed as the CT image analysis tool.The system combined the convolutional neural network and thresholding methods for segmented left and right lungs and detecting patchy shadows, again verified by attending radiologists. The distribution of CT values in the lungs was calculated to obtain a histogram. Subsequently, the quantitative parameters were computed, including the lung volume,inflammatory volume, proportion of the provocative book, and the mean, median, standard deviation, entropy,energy, skewness, kurtosis, peak value, Hellinger distance, and intersection over the union of the CT values.The Dice coefficient was used to evaluate the performance of this in-house built network for both the training and test sets using the previous equation.Furthermore, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II,sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA), pneumonia severity index (PSI), and confusion, urea, respiratory rate and blood pressure (CURB-65) scores were calculated based on clinical and experimental data on admission.
Patient information was confidentially protected by assigning a de-identified ID to each patient. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University (WDRY2020-K048).
Statistical analysis
All analyses and figures were performed with SPSS 26.0 and GraphPad Prism 8.0. Measurement data were presented as the means with standard deviation, and significance was tested by-test and one-way ANOVA.Nonparametric variables were expressed as medians and interquartile ranges, and we used the Mann-Whitney-test or Kruskal-Wallis tests to compare differences between groups. Categorical variables were summarized as counts and percentages, and significance was detected by Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test. Correlation analysis was performed using Kendall’s tau-b correlation coefficient; a linear equation was acquired using Boxplot and Wilcoxon methods. The sensitivity and specificity of the two rating systems for patient diagnosis were represented and analyzed by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographic and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients
A total of 140 confirmed COVID-19 cases at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University were collected between February 1 and April 1, 2020. Twenty-two cases that did not have chest CT images were excluded, and one case with an unmeasurable AI-CT image was excluded. A total of 117 diagnosed cases were enrolled in this study, with 40 severe cases and 77 non-severe cases (Figure 1). The median age was 63.5 (IQR, 48.8-70.2) years, and severe patients were older than non-severe patients (69 vs. 62,=0.002,Table 1). Sixty-seven patients (57.3%) were male, and a total of 32 (27.4%) patients had a history of hypertension,diabetes (20, 17.1%), and coronary heart disease (6, 5.1%).All enrolled patients had a fever; the highest temperature was approximately 38.9 ℃, among which 25 (21.4%) had dyspnea. Severe patients had more dyspnea symptoms on admission (30.0% vs. 16.9%,=0.117), higher APACHE II (9.0 vs. 4.0,<0.001) and SOFA (3.0 vs. 1.0,<0.001)scores, higher PSI (88.63 vs. 56.03,<0.001), CURB-65(1.0 vs. 0,<0.001), CT semiquantitative rating scores (4.0 vs. 1.0,<0.001) and AI-CT rating scores (49.71 vs. 4.59,<0.001). Furthermore, severe patients required significantly more oxygen therapy, including nasal tubes, facial masks,and high-flow nasal catheters (HFNCs), and more ventilation support, including both noninvasive ventilation (NIV) and mechanical ventilation (MV) (all<0.001). Compared with non-severe patients, fewer patients were discharged (30.0% vs.92.2%,<0.001) and had longer length of stay (38 d vs. 20 d,<0.001) in the severe group, while there was no difference in the mortality rate (4 [10.0%] vs. 4 [5.2%],=0.555).
Laboratory indices of COVID-19 patients
The levels of neutrophils (<0.001), CRP (<0.001),interleukin-6 (IL-6) (=0.002), IL-10 (=0.005) and procalcitonin (PCT) (<0.001) in severe patients were higher at admission than those in non-severe patients. Lymphocytes(<0.001), CD3(<0.001), CD4(<0.001), and CD8(<0.001) lymphocytes, monocytes (=0.004), and the PiO/FiO(P/F) ratio (=0.016) in severe patients were decreased compared to those in non-severe patients at admission. No significant differences in the serum levels of white blood cells(=0.150), CD19 cells (=0.223), CD16+56 cells (=0.085),and other cytokines IL-2 (=0.646), IL-4 (=0.895), TNF-α(=0.491) and IFN-γ (=0.569) were observed between the two groups (Table 2).
Correlation between CT and AI-CT rating system
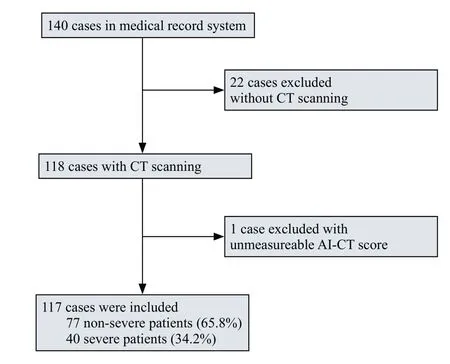
Figure 1. Flowchart of patient recruitment.
The CT semiquantitative score was perfectly linearly associated with the AI-CT rating system, except for three discrete dots (Figure 2). Further analysis of the data using Boxplot and Wilcoxon tests concluded a linear equation,which showed that AI-CT score= -11.951+12.967×CTscore,<0.001, Adj=75.5%.
Comparison of CT and AI-CT rating systems among different oxygenation levels
The CT semiquantitative rating score was significantly lower in patients who did not need oxygen therapy than in those who did; while CT score was more deficient in patients who only needed nasal tubes than in those who needed HFNC or MV (<0.001). Similarly,the AI-CT score was significantly lower in patients who did not need oxygen therapy than in those who needed a facial mask, HFNC, NIV, or MV and was lower in patients who only needed nasal tubes than in those who needed HFNC, NIV, or MV (<0.001) (Figure 3).
CT and Al-CT rating system for the identification of severe COVlD-19 cases
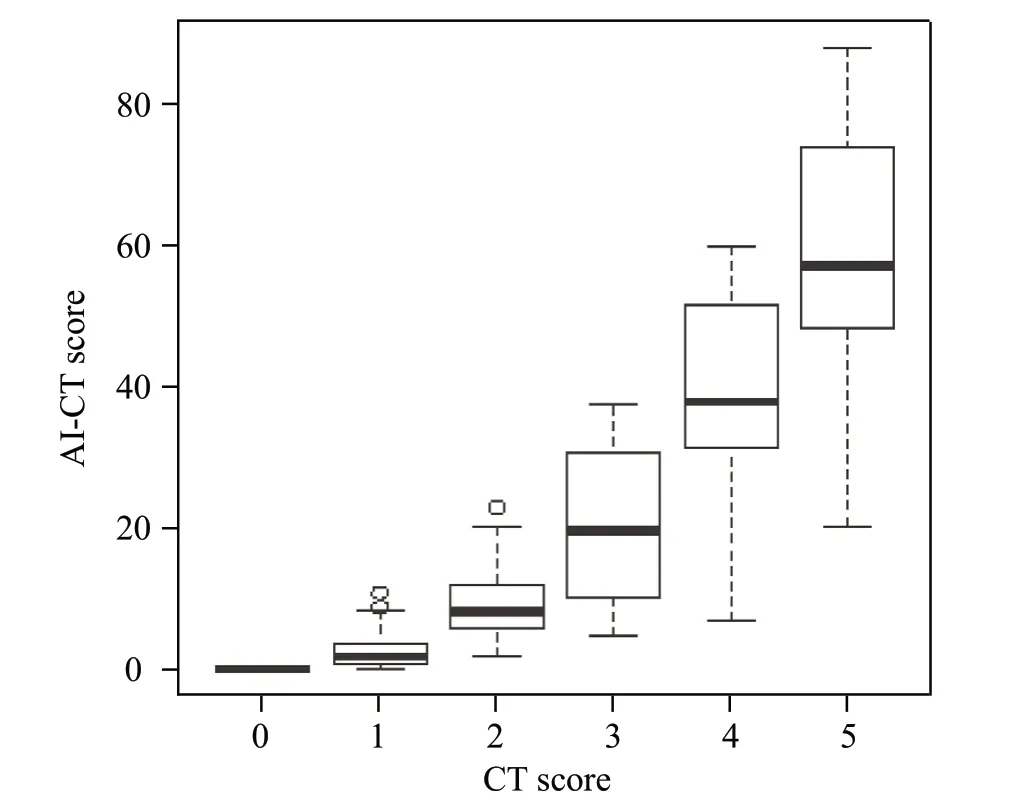
Figure 2. Correlation between CT and AI-CT rating system. AICT had a linear correlation with the CT rating score except for three discrete dots. Equation: AI-CT score=-11.951+12.967×CT score, P <0.001, Adj R2 = 75.5%.
To assess the predictive value of the two rating systems,the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the ROC curve (AUC) were calculated. As indicated in Figure 4A, the AUC 0.929 implied a perfect accuracy of AI-CT (cut-off value 32.3) in COVID-19 patients as a predictive level for the identification of severe conditions,with high specificity (94.8%) and sensitivity (77.5%).The CT rating (cut-off value 2.5) also showed relatively high accuracy with AUC=0.856 (<0.001). However,as indicated in Figure 4B, we did not see any significant difference in the predictive value between the AI-CT(AUC=0.831) and CT (AUC=0.808) rating systems for MV(>0.05). In the more in-depth analysis of the percentage of GGOs (AUC=0.836) and consolidation (AUC=0.745)in chest CT images by AI technology, the percentage of GGOs was more predictive for MV (<0.05, Figure 4C)(Supplementary Table 2).airway abnormalities (bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening).Therefore, CT helps to make a complete assessment of the severity of COVID-19. A chest CT severity score (CT-SS) summing individual scores from 20 lung regions revealed a rapid identification of severe patients with COVID-19.The prediction of severity is of great importance, which could help to estimate ICU events and lead to the clinical decision of treatment.
AI, an emerging technology in medical imaging, is considered to fight COVID-19 actively. AI has shown efficacy in differentiating COVID-19 from pneumonia of other etiology.In addition to early screening, severity
DISCUSSION
Previous studies have been proposed for CT-based COVID-19 diagnosis with generally promising results.CT manifestations of COVID-19 patients revealed abnormal lung opacities (GGOs and consolidation) andassessment was also crucial for treatment planning.Radiologists proposed AI models for COVID-19 severity assessment. A deep learning method is adopted to divide the lung into anatomical subregions based on CT values to differentiate infection volumes and ratios and is used as a quantitative approach.
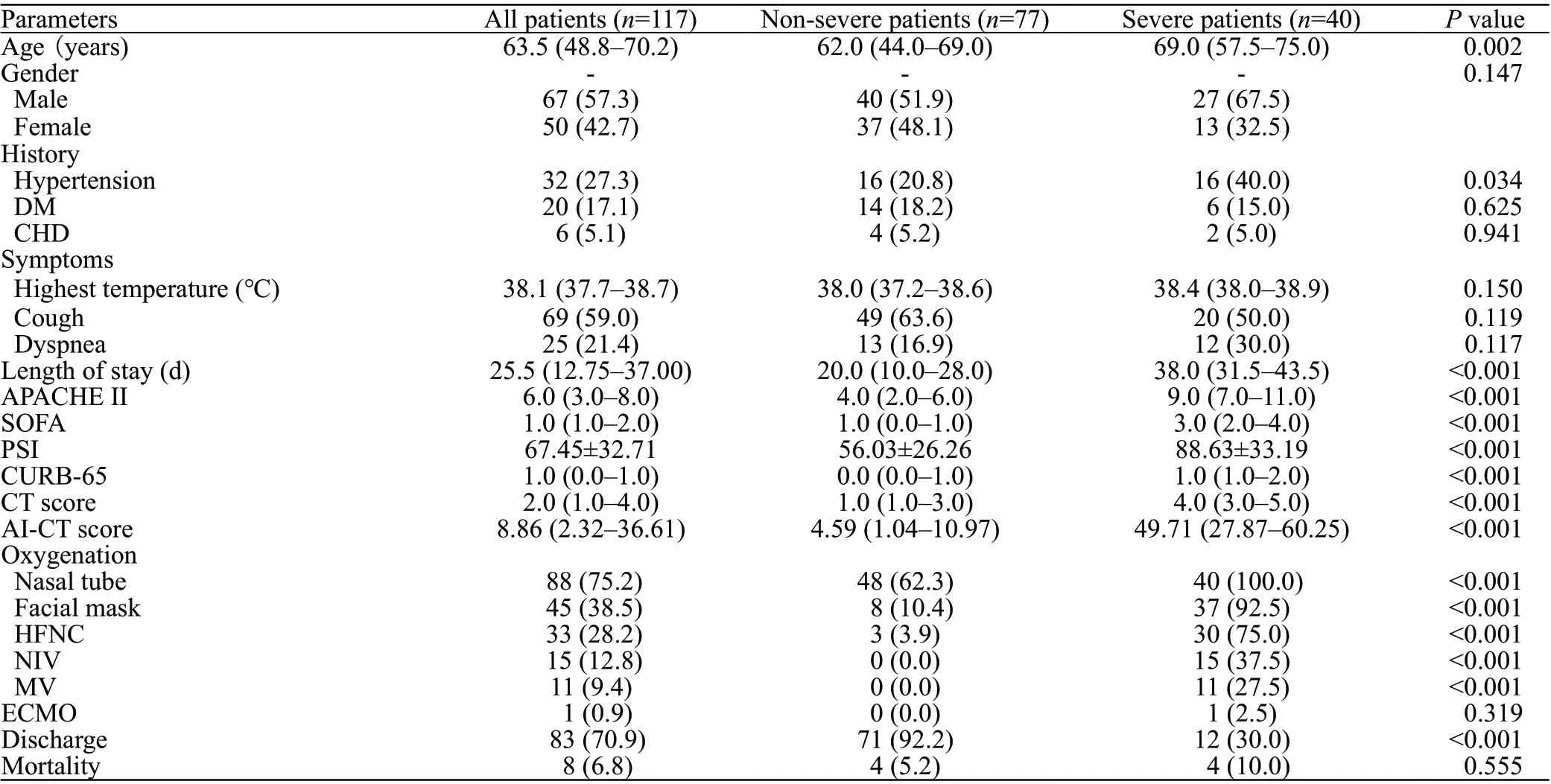
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients
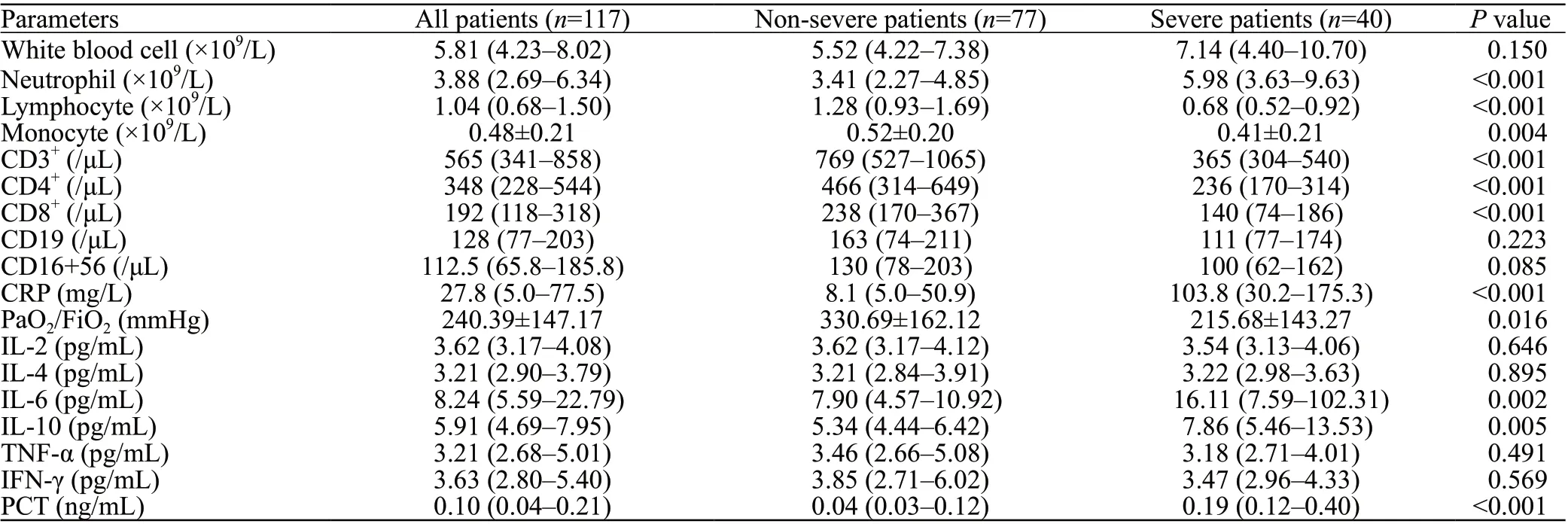
Table 2. Laboratory indices of COVID-19 patients

Figure 3. Comparison of CT and AI-CT rating systems among different oxygenation levels. A: The CT semiquantitative rating score was significantly lower in patients who did not need oxygenation therapy than in those who did, and was lower in patients who only needed nasal tubes than in those who needed HFNC or MV. B: the AI-CT score was significantly lower in patients who did not need oxygenation therapy than in those who needed a facial mask, HFNC, NIV or MV, and was lower in patients who only needed nasal tubes than in those who needed HFNC, NIV or MV. **P<0.01.

Figure 4. The predictive value of AI-CT and CT rating systems for disease severity and mechanical ventilation. A: AI-CT had better predictive value for disease severity than the CT rating system, AUC=0.929 vs. 0.856, P<0.001; B: AI-CT and CT rating systems had similar predictive value for mechanical ventilation, AUC=0.831 vs. 0.808, P>0.05; C: GGOs had better predictive value for invasive mechanical ventilation than consolidation, AUC=0.836 vs. 0.745, P<0.05). AI: artificial intelligence; GGO: ground-glass opacity.
In this study, we used both an AI evaluation system and a semiquantitative rating system to analyze the CT images of COVID-19 patients. We found a significant correlation of these two systems with lymphocytes and their subsets, P/F ratio, CRP, and PCT, which reflected the severity of this disease (Supplementary Figure 1).Furthermore, under different oxygenation conditions,the CT semiquantitative rating score and AI-CT score were significantly lower in patients who did not need oxygenation therapy than in those who did, and were lower in patients who only needed nasal tubes than in those who needed progressive supportive ventilation(e.g., HFNC, NIV or MV). It can thus be suggested that the higher the rating scores, the more progressive oxygenation conditions are needed, which might further confirm the association between the rating systems and the severity of this disease.
As indicated previously, the AI-CT rating system had perfect accuracy (AUC=0.929) in predicting the severity of COVID-19 patients, with high specificity (94.8%) and moderate sensitivity (77.5%). The CT semiquantitative rating system also showed high accuracy with an AUC of 0.856, which was lower than that of the AI-CT system.However, there was no difference in predicting the need for MV. However, surprisingly, in the more in-depth analysis of the percentage of GGOs (AUC=0.836) and consolidation (AUC=0.745) in chest CT images by AI technology, the rate of GGOs was more predictive for MV.
CT provides high-quality 3D images for evaluating COVID-19. Image segmentation facilitates radiologists to identify lung infiltration and prompts accurate quantitative analysis of COVID-19. It delineates the regions of interest, e.g., lung, lobes, bronchopulmonary segments, and infected areas or lesions. From a chest CT image, the AI was designed to detect possible pneumonia lesions quickly, measure their volume, density, and shape, and compare changes in multiple lung lesions,which provided a quantitative report of the percentage of GGOs or consolidation.While a manual read of a CT image takes up to 15 min, AI can finish reading the image in 10 s. A recent review of AI applications in COVID-19 showed that AI could be as accurate as humans. AI can also save radiologists’ time and perform the diagnosis faster along with the standard tests for COVID-19.Fast and accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 can save lives and limit the spread of the disease.
Given that not all people diagnosed with COVID-19 need intensive care, the ability to forecast disease severity can help to plan medical care. A predictive algorithm was developed to predict the mortality risk of COVID-19 and presented that it could indicate the condition of developing ARDS with 80% accuracy,which was precisely similar to our findings. Furthermore,in our study, the percentage of GGOs in chest CT images had more predictive value for invasive ventilation than consolidation. GGO was defined as an area of increased lung opacity within which vessel margins were indistinct.We considered the percentage of GGO-reflected areas of insufficient ventilation with reversible ability. Therefore,early detection of GGO in chest CT images may help with early intubation, MV, and early treatment. It may help with medical resource allocation and utilization, limit the length of hospital stay, and save lives.
In addition, the CT semiquantitative rating system was linearly correlated with the AI-CT system. However, it is worth noting that three dots were discrete and failed to present a linear dependence relation.
Inaccurate imaging interpretation makes patient management difficult. A previous study has shown that compared to an individual radiologist, AI augmentation significantly improved radiologists’ performance in distinguishing COVID-19 from pneumonia of other etiologies.We further analyzed the two discrete dots. From the acquired raw data, CT images were reconstructed for subsequent reading and diagnosis. The experienced radiologists reviewed CT images visually and rated them using the semiquantitative rating system.The extension of the lung opacification was visually rated from 0 to 5: score 1, 1%-5% involvement; score 2,6%-25% involvement; score 3; 26%-50% involvement;score 4, 51%-75% involvement; score 5, 76%-100%involvement.For the two discrete dots, the CT semiquantitative rating score was low (1-2), while AICT showed relatively high results. More than 10%(Supplementary Figure 2A) and 20% (Supplementary Figure 2B) lung areas of infiltration were observed by another radiologist for further CT images reviewing. This may be because different radiologists hold true across different lesion types. Researchers also found that AI system performance was overall superior to that of junior radiologists and was comparable to that of mid-senior radiologists.Therefore, we considered that AI could assess the scope of infiltration more accurately.
Furthermore, our study excluded one case whose CT semiquantitative rating score was 5, while AI-CT was unmeasurable. We found extensive attached lesions not restricted from surrounding tissue in both lungs by further reviewing the CT image (Supplementary Figure 3). The lesions were large and heavily infiltrated. Therefore, AI could not correctly identify and segment the structures.Some radiologists expressed concern that there were not enough data available to train AI models in COVID-19.Their concern was that most of the available COVID-19 CT images might suffer from selection bias.This might be the fundamental flaw of AI. In the next step, research on COVID-19 might be more practical to establish a model containing AI and clinical indices to assess disease severity to help with clinical decisions and treatment plans.
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have shown that the performance of AI technology trained on relatively large datasets to evaluate disease severity in COVID-19 patients is inferior to that of radiologists. Although AI could not be considered an independent way to assess disease severity,there was no doubt that GGOs displayed more predictive value for further MV.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all the patients, doctors, and nurses who participated in the study. We would also like to thank Dr. Quming Zhao from the Children’s Hospital of Fudan University for his help with practical questions and insightful discussions. His assistance was invaluable.
This research was funded by the Shanghai Pujiang Program (grant number 2020PJD011).
Patient information was confidentially protected by assigning a deidentified ID to each patient. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University (WDRY2020-K048).
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
YH collected and analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript; SCM organized, analyzed, and interpreted the data; HDZ acquired CT images and evaluated lung infiltration by a semiquantitative rating system; YH, SCM and HDZ are co-first authors, the order of the authorship was based on their contributions to this study. CYT designed the study and took responsibility for the integrity of data and the accuracy of data analysis; GRG provided administrative, technical and material support and provided essential theoretical guidance for this study;BJX offered technical support of radiology and interpreted the AI technique data. GRG, BJX and CYT are co-corresponding authors.XYW helped with statistical analysis, WW and CYJ organized data and performed the literature search.
All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
