Incidental radiological findings suggestive of COVID-19 in asymptomatic patients
lNTRODUCTlON
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).Infection has a major global influence on social, health, and economic issues.COVID-19 is considered the most significant major health epidemic since the Spanish flu 100 years ago[1].It first appeared in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 and was officially declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020, extending rapidly worldwide thereafter and becoming an outbreak.By the end of 2020, more than 78 million people were infected, leading to over 1.7 million deaths[2].Unlike infections with other coronaviruses, asymptomatic COVID-19 patients are infectious, leading to the rapid spread of infection worldwide[1,3].The most common modes of transmission of the virus are person-to-person spreading during intimate contact with an infected person (or asymptomatic infected carriers), inhalation of respiratory droplets, and contact with surfaces contaminated with respiratory droplets or aerosols, which can penetrate the lungs through the nose or mouth[2,4,5].SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor for cell entry.ACE2 receptors are present in high amounts on epithelial cells, which are more predominant in oral mucosa and lungs, than in heart, blood vessels, brain, and other organs, leading to a diversity in the disease presentation[5-8].The clinical presentation of COVID-19 ranges from asymptomatic to critically ill, and the most common manifestations are mild to moderate respiratory illness, where recovery occurs without requiring special treatment[6-8].However, many nonspecific symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, shivering, anorexia, headache, olfactory dysfunction and loss of taste, shortness of breath, cough with or without expectoration, dyspnea, chest tightness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and muscle soreness, overlap with other viral infections[2,5-12].Despite most patients with COVID-19 complaining of mild symptoms, the death rate is considerable, ranging from 0.3%-13.1%, with more susceptibility to severe forms of the disease in older patients, especially those with underlying disease, such as diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, hyperlipidemia, obesity, and chronic renal and hepatic disease[4,10,11].
COVlD-19 DlAGNOSlS
A confirmed case of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is defined by World Health Organisation as a patient with a positive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test, irrespective of clinical signs and symptoms[12].This test directly assesses the viral load from a nasopharyngeal swab, sputum, or endotracheal lavage[13].It has impressive specificity of up to 100% owing to its specificity to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genome sequence, but has imperfect sensitivity of 89% (95%CI: 81%-94%)[14].A positive result denotes the presence of viable virus only, and a negative result does do not rule out COVID-19 infection[13,15].False-negative RT-PCR results may occur if the test is performed too early or late in infection course, the viral load is insufficient, or the specimen is of poor quality and also due to technical errors or inappropriate handling and shipping of the specimen.False-positive results may occasionally occur due to technical errors or reagent contamination[14,16,17].The turnaround time for an RT-PCR test ranges from 50 min to 4 h for semi- to fully automated, walk-away assays and 6-14 h for manually performed assays[12,13,18].
When Cognac reached Brad, he dropped the basket at feet and, panting, looked up at Brad for approval. As Brad reached down to pick up the rings, a suddenly quiet Cognac solemnly raised his paw to meet my almost- husband s hand-a canine19 Way to go, Brad.
More than 50% of patients with a positive RT-PCR test may be asymptomatic at the time of testing only or throughout the entire duration of the disease, leading to more spread of the virus.Accordingly, it is essential to detect COVID-19 infection at the early stage to immediately isolate the infected person from the healthy population[14,19].The need for a simple, rapid method to identify asymptomatic patients who need urgent medical or surgical intervention in an emergency and in oncology patients, patients in the intensive care unit, or those who need hospital admission is crucial to prevent the spread of infection.In cases where RT-PCR test results take some time to be available and because this test has imperfect sensitivity, chest radiography is appropriate[8,9,20-23].
CLASSlCAL lMAGlNG CRlTERlA OF COVlD-19
To prevent the spread of infection in hospital patients or healthcare workers, chest radiography is considered the first-line imaging modality to be performed in patients with suspected coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) or to exclude the presence of COVID-19 infection in patients who need to receive medical or surgical treatment[10,13,17,18,24-29].Most radiological imaging modalities are beneficial in characterizing COVID-19 infection.
Yasin
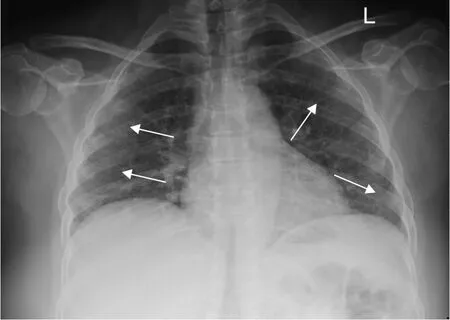
[7] studied the association of COVID-19 severity and X-ray findings among 350 positive COVID-19 patients.Of them, 62.9% had an abnormal baseline CXR, and the most common findings were consolidation opacities (81.3%), followed by reticular interstitial thickening (39.9%) and ground glass opacities (GGOs) (32.5%).An example of CXR findings in a patient with COVID-19 is presented in Figure 1.
Chest X-ray
On April 15, 2020, the Royal College of Surgeons and Royal College of Radiologists published guidelines on the use of preoperative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and chest computed tomography (CT) during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic to exclude COVID-19 infection before elective surgery.These guidelines aim to eliminate the risk of COVID-19-related complications after elective surgery and prevent the transmission of COVID-19 to other patients and healthcare workers[22].The major obstacle in the management of acute surgical conditions in both urgent and elective surgery is the increased risk of nosocomial transmission.Chetan
[58] evaluated chest CT screening for COVID-19 in a total of 439 elective and emergency surgical patients.The elective surgical cohort included 156 patients who underwent preoperative low-dose unenhanced chest CT, and the emergency surgical cohort included 283 patients with abdominal emergencies where the preoperative abdominal CT was extended cranially to include the lungs from below the carina.Of the 432 patients, 32 (7%) showed potential COVID-19-related lung changes[58].These findings changed surgical management in the elective surgical cohort only and not in the acute abdominal emergency cohort requiring surgery.On the other hand, Ap Dafydd
[22] assessed the role of chest CT in screening for asymptomatic COVID-19 infection in self-isolating patients before elective oncological surgery.They concluded that preoperative chest CT was unhelpful and might introduce an unnecessary delay.Siegel reported suspected incidental COVID-19 findings in the lung bases in abdominal CT, which raised the possibility of the transmission COVID-19 to the clinician[59].Thus, direct communication between the radiologist and the referring physician is the first step to protect both patients and healthcare workers against the spread of infection.Furthermore, the authors documented the possibility of viral pneumonia being used as a broad term that helps in decisionmaking.Hynes
[60] detected incidental peripheral GGOs in the upper lobes of both lungs, which were characteristic of COVID-19 pneumonia, in a 97-year-old female patient who presented with stroke.She underwent arch-to-vertex CT angiography, which was negative for acute stroke.Sun
[8] performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of chest imaging findings in patients with COVID-19.They concluded that chest CT had a low specificity in differentiating COVID-19 pneumonia from other types of pneumonia and recommended that COVID-19 diagnosis be confirmed by clinical and laboratory examinations.Dedeilia
[61] reported that COVID-19 had a major effect on pediatric surgery, because children with COVID-19 are usually asymptomatic or have mild symptoms.Furthermore, many upper respiratory infections in children, such as influenza virus, rhinovirus, and others, present the same symptoms as COVID-19, and coinfection of SARS-CoV-2 may also occur[4,28,62].Thus, the surgical committee must follow established guidelines to facilitate the workflow and prevent virus transmission, and every patient should be tested by RTPCR.However, if rapid intervention is crucial in an emergency and RT-PCR results are not available soon enough, the assessment can be based on clinical conditions and/or chest imaging findings [7,22,60].
So the young man departed, and went away, away, away, as well as his horse would take him, begging his living as he rode along, and, somehow or other, at last he got to the land of the sun
Chest computed tomography
Oncology patients are a very special group of because of their high vulnerability to infections caused by risk factors due to their impaired immune systems, such as leukopenia, long-lasting immunosuppression (steroids, antibodies), or low immunoglobulin levels[63].Oncology patients infected with COVID-19 may present as asymptomatic or with nonspecific symptoms, like fever, cough, dyspnea, fatigue, myalgia, and headache[49,64].Also, because oncology patients need to continue their treatment, especially in newly discovered cases or patients receiving their treatment as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or other forms, the benefit: risk ratio of cancer treatment may need to be reconsidered in certain patients[49,65,66].Some reports are describing the accidentally discovered COVID-19 signs in different imaging modalities performed within the context of following cancer patients.However, the most attractive data was related to the use of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography-CT (PET-CT) imaging, which demonstrates the increased uptake across a variety of pathological etiologies, including infections, inflammatory processes, and neoplasms.Thus, FDG PET-CT imaging plays a role in localizing foci of infection and inflammation in cases of fever of unknown origin.PET-CT permits detailed evaluation of both functional and anatomical/pathological processes[58,44].Albano
[65] reported a case series performed in the nuclear medicine units in Northern Italy from March 16-24, 2020.This included 65 asymptomatic patients referred for PET-CT with no suspicion of COVID-19 infection.Of them, six (9%) showed
F-FDG-avid interstitial pneumonia, suggesting COVID-19 infection.The study also included 12 patients who were admitted for whole-body
I scintigraphy followed by single photon emission CT 3-4 d after radioiodine administration, and 1 of these patients showed peripheral GGOs, suggesting COVID-19 infection, but not an increase in radioiodine uptake.All of the patients with findings suggestive of COVID-19 infection were confirmed positive upon further workup.Mo
[66] reported similar findings in another asymptomatic 60-year oncology patient in the United States with human papillomavirus, and Franceschi
[67] reported a similar scenario in an asymptomatic 61-year-old patient with treated primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Wakfie-Corieh
[68] retrospectively reviewed 1079 oncologic
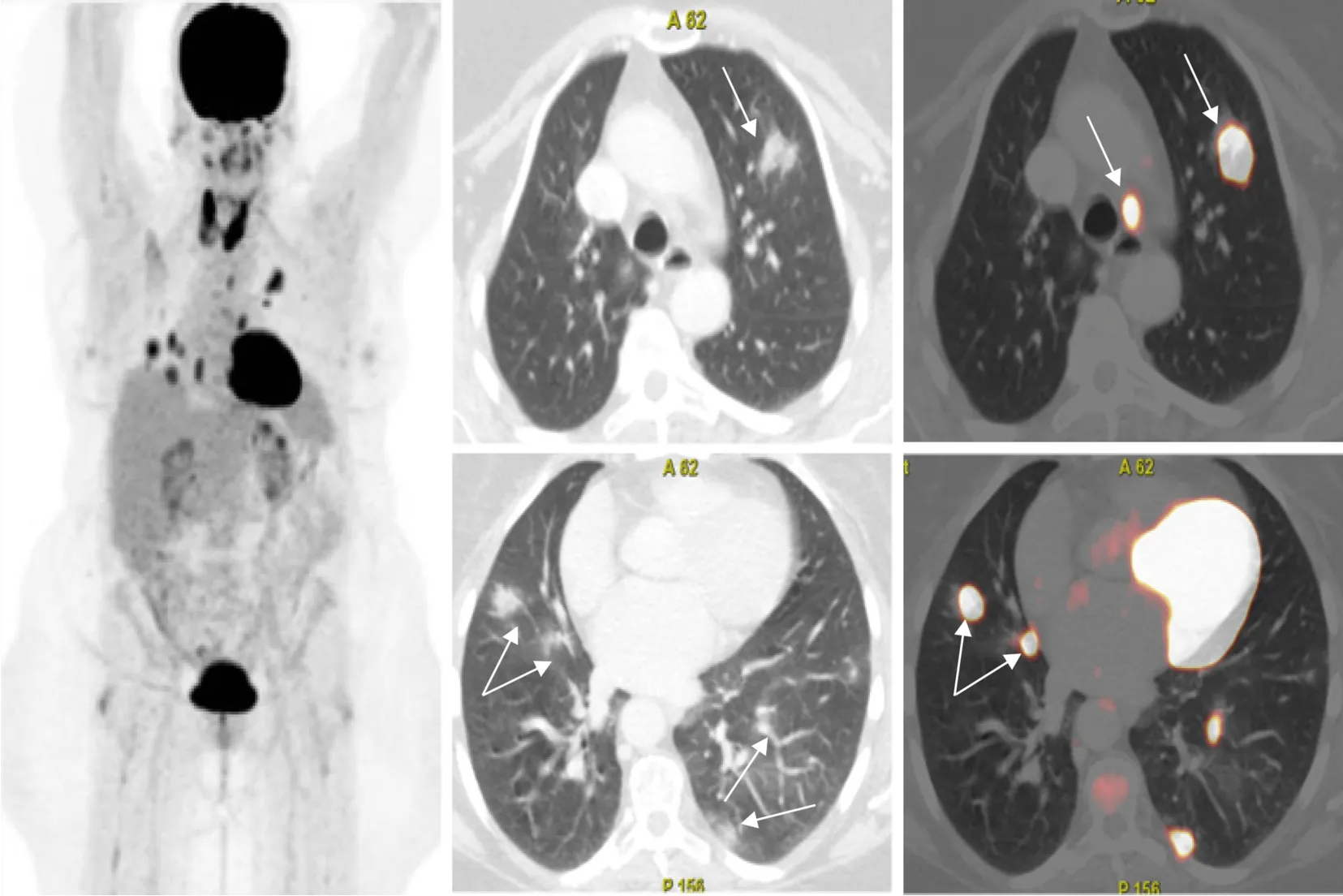
F-FDG PET-CT scans performed between February 2 and May 18, 2020 to identify lung and extraparenchymal lung involvement in asymptomatic cancer patients with COVID-19.The authors concluded that FDG PET-CT-positive findings were usually limited to thoracic structures, and silent, distant involvement was infrequent.An example of PET-CT findings in COVID-19 infection is shown in Figure 5.Another retrospective review discussed the incidental findings suggestive of COVID-19 in asymptomatic cancer patients in France who underwent
F-FDG PET-CT from January 1 to February 21, 2020, in the era before COVID-19 (
= 867 PET-CT scans) and from March 16 to April 17, 2020, in the era of socially spread COVID-19 (
= 529 PET-CT).They noticed a 1.6% increase in parenchymal lung changes during the COVID-19 era[44].
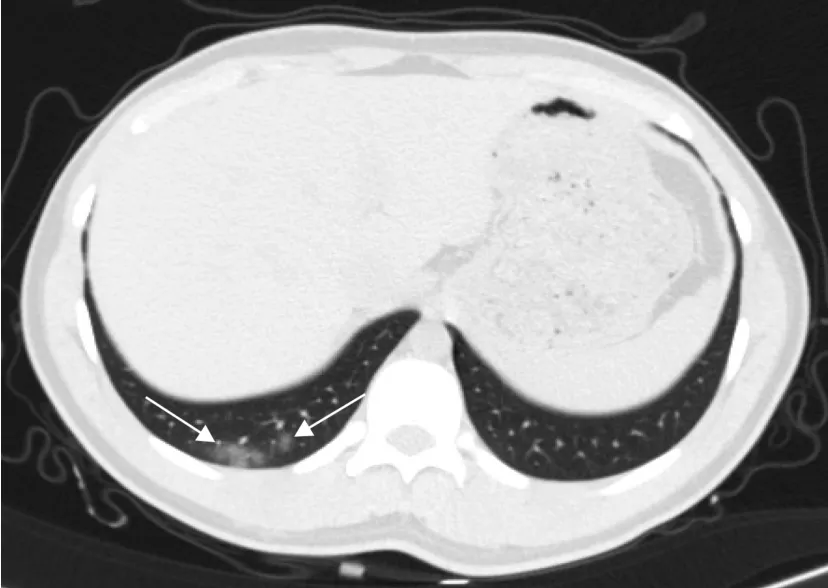
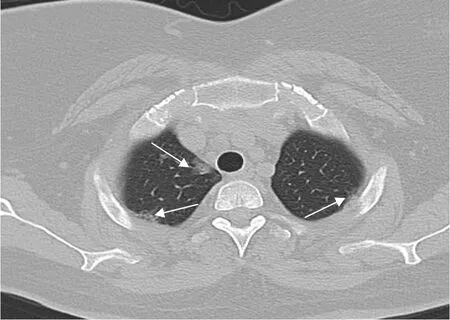
The Fleischner Society[38] recommends performing a chest CT in moderate to severe infections presenting with hypoxemia and moderate to severe dyspnea, regardless of the RT-PCR test result [39], while RT-PCR is indicated if incidental findings on CT suggest the presence of viral pneumonia[14,19,34,38,39].Chest abnormalities associated with COVID-19 may be incidentally detected in the visualized lung parenchyma in CT examinations of other body regions, such as in the lower lung base in abdominal CT (Figure 2), the lung apex in head and neck CT studies (Figure 3), and the lung tissues seen in dorso-lumbar spine CT[18,40].Several studies have been published reporting incidental chest CT findings of COVID-19 in the visualized lung parenchyma in patients with acute abdomen without respiratory manifestation who undergo abdominal CT in the scenario of an acute pandemic[41-47](Table 1).
When they drew near, Tritill killed it, Litill took out its heart for the young man to cook, and both began quickly to turn the horns into drinking cups
Lung ultrasound
So he began to work as a clerk for Tony. We never spoke7 of May anymore and neither of us ever mentioned my theory. But I noticed that Harry always saw every person who came up the stairs.
A lung ultrasound (US) in COVID-19 pneumonia is usually performed using a portable US machine at the bedside to minimize the spread of infection to other patients and healthcare workers[48].The classical appearance is bilateral irregular pleural lines, subpleural consolidation, areas of thick white lung tissue, and thick irregular vertical artifacts suggesting interstitial alveolar damage[48-50].In the pediatric age group, lung US has an advantage over CT because it does not use ionizing radiation.Vertical artifacts (70%) and pleural irregularities (60%) were the most common abnormalities detected in 10 symptomatic pediatric patients with confirmed COVID-19 who underwent a chest US while awaiting RT-PCR results Notably, pleural effusions were absent in all 10 patients[44,50,51].The follow-up of lung US findings to monitor pulmonary involvement in symptomatic COVID-19 patients is preferable to the use of repeated CT scans, especially in critically ill patients or patients on a ventilator, owing to the difficulty in transporting such patients to the CT equipment[5,8,50].Additionally, US can detect pneumothorax and other complications.However, a major disadvantage is the prolonged close exposure of the operator to the infection and also the need for careful sterilization of the device and the use of transducer and keyboard covers[10].No reports about incidental lung US findings are available because this is not a routine examination, and it is only performed in certain circumstances.
Magnetic resonance imaging
The guidelines for preoperative COVID-19 testing for elective cancer surgery of 15 April, 2020, were updated on May 14, 2020, to document accumulating evidence that preoperative chest CT screening does not add to the detection of COVID-19 in asymptomatic, isolated, and tested patients and is not recommended for screening before elective cancer surgery[58].Thus, chest CT should only be considered for screening in preoperative planning in asymptomatic patients who are not isolated when RT-PCR test results are unavailable.
ASYMPTOMATlC COVlD-19 PATlENTS lN ELECTlVE AND EMERGENCY SURGERlES
Chest X-ray (CXR) findings in COVID-19 patients usually appear at 10-12 d from symptom onset as bilateral lower zone consolidation patches or diffuse airspace opacities with peripheral distribution[10,11,30].The CXR may be normal in up to 63% of cases, particularly in the early stages[28], and it has a great value in patients with moderate to severe disease who have acute respiratory distress syndrome, showing bilateral diffuse alveolar consolidation that may progress to white lung with or without mild pleural effusion[26,31-33].
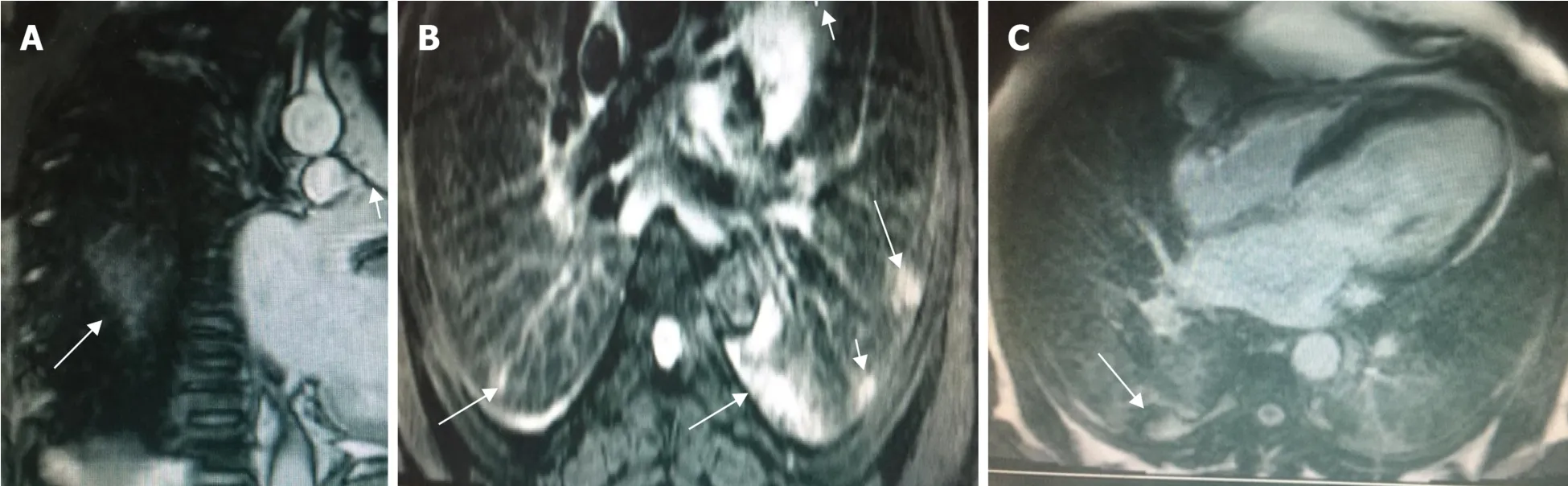
Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays no role in the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia, there are many reports of the detection of incidental COVID-19 in MRIs performed for other diagnostic purposes in asymptomatic patients[8,40,42].After an extensive review of the literature, we found many cases of reported COVID-19 findings in upper lung cuts that appear in brain, neck, and cervico-dorsal spine MRIs and in lower cuts in abdomen and liver MRI studies[4,52-55].COVID-19 infection appears as peripheral areas of high signal on T2-weighted short tau inversion recovery imaging caused by edema or alveolar opacities.A high T1 signal is observed due to higher tissue density, and partial alveolar collapse with focal areas of restricted diffusion is observed on diffusion-weighted imaging because of increased cell density from the inflammatory reaction.Partial collapse with a heterogeneous enhancement pattern is observed after contrast administration.Thus, radiologists should be alert and look carefully for these findings[34,42,54-56].Figure 4 shows an example of cardiac MRI findings in a COVID-19 patient.Ates
[52] studied thorax CT and MRI findings in 32 COVID-19 patients who underwent chest CT and then MRI within 24 h after the chest CT.They reported that MRI had a sensitivity of 91.67% and a specificityof 100%.Furthermore, rapid limited study using a T2-weighted spin echo sequence, which is widely available in all scanners and can detect GGOs or consolidative patches with no exposure to radiation, was suggested.Angelini
[42] reported a case of incidental COVID-19 pneumonia in a 60-year-old male with multiple myeloma and negative respiratory symptoms who underwent whole-body MRI as routine followup.The COVID-19 pneumonia presented as peripheral posterior GGOs in the lung in T2-weighted sequences.Deen
[57] reported the detection of incidental basal lung lesions on liver MRI in a 49-year-old woman with a negative RT-PCR result for COVID-19 who presented at the emergency department with vague symptoms.An abdominal US revealed a liver mass, and subsequent MRI examination identified it as a hemangioma, while the scanned lung base showed peripheral high T2-weighted focal areas with restricted diffusion in the left lower lobe.Consequently, the patient underwent a chest CT that confirmed presence of bilateral multiple GGOs.Di Girolamo
[43] reported a 71-year-old woman with T4a colorectal cancer who underwent an abdominal MRI for routine follow-up of hepatic metastasis that led to the incidental detection of bilateral lower lobe GGOs in the scanned lung.Thereafter, the patient underwent RT-PCR, which confirmed that they were positive for COVID-19.MRI can help in the early recognition of cases so that a rapid treatment protocol can be established, the immediate isolation to reduce community transmission, and the organization of close monitoring.Thus, it is important to both the patient and the physician that these findings are highlighted and reported.
ASYMPTOMATlC COVlD-19 ONCOLOGY PATlENTS
Chest computed tomography (CT) plays a pivotal role in the early detection of COVID-19 pneumonia and has better sensitivity (98%) compared with RT-PCR (89%), particularly in the early course of the disease.However, it also has low specificity (25%) due to the overlap between COVID-19 pneumonia and other types of viral pneumonia[5,8,30,31].Radiologists must be familiar with the different imaging findings of COVID-19 pneumonia to differentiate it from other types of pneumonia[11,13,30].Early COVID-19 chest CT findings include bilateral multiple GGOs with a peripheral, subpleural, and posterior distribution, with or without consolidation.In the late phase, the consolidation patches, linear opacities, “crazy-paving” pattern, reversed halo sign, and vascular enlargement become more common[5,9,10,18,32].The pulmonary histologic findings of COVID-19 resemble those of other coronavirus infections, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)[4], which also shows similarities in chest CT findings[23,33,34].Great variability is observed in chest CT findings in COVID-19 patients according to the stage and severity of the disease[6,9,15,24,25,35,36].The Radiological Society of North America classifies the chest CT findings into four categories related to COVID-19 diagnosis: (1) Compatible with viral pneumonia; (2) Indeterminate; (3) Atypical (suggestive of other diagnoses); and (4) No evidence of pneumonia[37].
Infection with COVID-19 may remain asymptomatic and appears as incidental findings in nuclear imaging procedures performed for standard oncologic indications[63-67].PET-CT findings are considered sensitive for the detection of early COVID-19 infection, even before its detection as nasal viral carriage[41,55,66].It appears in
FFDG PET-CT as multiple areas of GGOs showing increased FDG uptake (SUV
is usually around 5.5)[41,55,66].Some theories explain the FDG activity detected in COVID-19 pulmonary lesions is the result of viral replication after the viral particles penetrate the cells.This replication starts to overwhelm the cellular structure, inciting a proinflammatory state that disrupts the infected and adjacent endothelium, leading to increased FDG uptake[67].
Petey sat and looked out over the gully. Dad would marry that girl. Yes, that girl who had kissed Petey and fussed over him, saying she d try to be a good mother to him, and all. . . .
Landete
[28] reported some correlation between the degree of FDG uptake in pulmonary lesions and COVID-19 infection, which may be used as a predictor for the recovery time because the patients with pulmonary lesions had a higher SVU
and took longer to recover.However, a larger sample size is necessary to confirm the predictive value.Many authors did not recommend the use of PET-CT as a primary diagnostic modality for investigating cases of suspected COVID-19 in the emergency setting because PET is an expensive imaging modality associated with prolonged acquisition times and increased radiation burden in comparison with conventional CXR and chest CT[18,44,56].
Nuclear medicine has no primary role in the diagnosis of COVID-19, yet awareness of the pattern of COVID-19 in this type of patient who is either asymptomatic or in the early stage of the disease before manifestations may have great implications in the further management of oncology patients with underlying immunosuppression, either by malignancy or oncologic therapeutics, because the virus is highly contagious and PET requires a much lengthier time in the unit than most other investigations.
CONCLUSlON
In some asymptomatic patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia on different radiological tools, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, the definitive test for COVID-19, may be false negative.As community transmission of the COVID-19 increases and isolation restrictions are lifted, incidental findings highly suspicious of COVID-19 pneumonia on imaging modalities of asymptomatic patients may become more common.It is crucial to be aware of such appearances and the difficulties that come with them.Radiologists must be alert to signs of COVID-19 infection in various imaging modalities because many asymptomatic patients present to the radiology department for other reasons and could be already infected with COVID.If it remains unrecognized, these patients can transmit COVID-19 to the community and to healthcare workers.
1 Pitlik SD.COVID-19 Compared to Other Pandemic Diseases.
2020; 11 [PMID: 32792043 DOI: 10.5041/RMMJ.10418]
2 Shereen MA, Khan S, Kazmi A, Bashir N, Siddique R.COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses.
2020; 24: 91-98 [PMID: 32257431 DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005]
3 Choi H, Qi X, Yoon SH, Park SJ, Lee KH, Kim JY, Lee YK, Ko H, Kim KH, Park CM, Kim YH, Lei J, Hong JH, Kim H, Hwang EJ, Yoo SJ, Nam JG, Lee CH, Goo JM.Erratum: Extension of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) on Chest CT and Implications for Chest Radiograph Interpretation.
2020; 2: e204001 [PMID: 33779627 DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020204001]
4 Singhal T.A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19).
2020; 87: 281-286 [PMID: 32166607 DOI: 10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6]
5 Revzin MV, Raza S, Warshawsky R, D'Agostino C, Srivastava NC, Bader AS, Malhotra A, Patel RD, Chen K, Kyriakakos C, Pellerito JS.Multisystem Imaging Manifestations of COVID-19, Part 1: Viral Pathogenesis and Pulmonary and Vascular System Complications.
2020; 40: 1574-1599 [PMID: 33001783 DOI: 10.1148/rg.2020200149]
6 Pham TD.Classification of COVID-19 chest X-rays with deep learning: new models or fine tuning?
2021; 9: 2 [PMID: 33235710 DOI: 10.1007/s13755-020-00135-3]
7 Yasin R, Gouda W.Chest X-ray findings monitoring COVID-19 disease course and severity.
2020; 51: 193 [DOI: 10.1186/s43055-020-00296-x]
8 Sun Z, Zhang N, Li Y, Xu X.A systematic review of chest imaging findings in COVID-19.
2020; 10: 1058-1079 [PMID: 32489929 DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-564]
9 Lomoro P, Verde F, Zerboni F, Simonetti I, Borghi C, Fachinetti C, Natalizi A, Martegani A.COVID-19 pneumonia manifestations at the admission on chest ultrasound, radiographs, and CT: single-center study and comprehensive radiologic literature review.
2020; 7: 100231 [PMID: 32289051 DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2020.100231]
10 Kwee TC, Kwee RM.Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know.
2020; 40: 1848-1865 [PMID: 33095680 DOI: 10.1148/rg.2020200159]
11 Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S.COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review.
2020; 215: 108427 [PMID: 32325252 DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427]
12 World Health Organization.WHO Interim guidance 20 March 2020 - Global Surveillance for COVID-19 disease caused by human infection with novel coronavirus (COVID-19).Who 2020; 1–4.Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/global-surveillance-for-human-infectionwith-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov)
13 Sethuraman N, Jeremiah SS, Ryo A.Interpreting Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2.
2020; 323: 2249-2251 [PMID: 32374370 DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.8259]
14 Kim H, Hong H, Yoon SH.Diagnostic Performance of CT and Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction for Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Meta-Analysis.
2020; 296: E145-E155 [PMID: 32301646 DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020201343]
15 Xie X, Zhong Z, Zhao W, Zheng C, Wang F, Liu J.Chest CT for Typical Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia: Relationship to Negative RT-PCR Testing.
2020; 296: E41-E45 [PMID: 32049601 DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020200343]
16 W?lfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Müller MA, Niemeyer D, Jones TC, Vollmar P, Rothe C, Hoelscher M, Bleicker T, Brünink S, Schneider J, Ehmann R, Zwirglmaier K, Drosten C, Wendtner C.Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019.
2020; 581: 465-469 [PMID: 32235945 DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x]
17 Pu J, Leader JK, Bandos A, Ke S, Wang J, Shi J, Du P, Guo Y, Wenzel SE, Fuhrman CR, Wilson DO, Sciurba FC, Jin C.Automated quantification of COVID-19 severity and progression using chest CT images.
2021; 31: 436-446 [PMID: 32789756 DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07156-2]
18 D'Andrea A, Radmilovic J, Carbone A, Forni A, Tagliamonte E, Riegler L, Liccardo B, Crescibene F, Sirignano C, Esposito G, Bossone E.Multimodality imaging in COVID-19 patients: A key role from diagnosis to prognosis.
2020; 12: 261-271 [PMID: 33362917 DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i11.261]
19 D?hla M, Boesecke C, Schulte B, Diegmann C, Sib E, Richter E, Eschbach-Bludau M, Aldabbagh S, Marx B, Eis-Hübinger AM, Schmithausen RM, Streeck H.Rapid point-of-care testing for SARSCoV-2 in a community screening setting shows low sensitivity.
2020; 182: 170-172 [PMID: 32334183 DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.04.009]
20 Cleverley J, Piper J, Jones MM.The role of chest radiography in confirming covid-19 pneumonia.
2020; 370: m2426 [PMID: 32675083 DOI: 10.1136/bmj.m2426]
21 European Society of Radiology (ESR).The identity and role of the radiologist in 2020: a survey among ESR full radiologist members.
2020; 11: 130 [PMID: 33270175 DOI: 10.1186/s13244-020-00945-9]
22 Ap Dafydd D, O'Mahony M, Jhanji S, Devaraj A, Allum W, Nicol D, Blunt DM, Riddell AM.The role of CT chest in screening for asymptomatic COVID-19 infection in self-isolating patients prior to elective oncological surgery: findings from a UK Cancer Hub.
2021; 94: 20200994 [PMID: 33242245 DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200994]
23 Wong HYF, Lam HYS, Fong AH, Leung ST, Chin TW, Lo CSY, Lui MM, Lee JCY, Chiu KW, Chung TW, Lee EYP, Wan EYF, Hung IFN, Lam TPW, Kuo MD, Ng MY.Frequency and Distribution of Chest Radiographic Findings in Patients Positive for COVID-19.
2020; 296: E72-E78 [PMID: 32216717 DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020201160]
24 World Health Organization.Use of chest imaging in COVID-19.2020; 1–56.Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/use-of-chest-imaging-in-covid-19
25 Carotti M, Salaffi F, Sarzi-Puttini P, Agostini A, Borgheresi A, Minorati D, Galli M, Marotto D, Giovagnoni A.Chest CT features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: key points for radiologists.
2020; 125: 636-646 [PMID: 32500509 DOI: 10.1007/s11547-020-01237-4]
26 Ali RMM, Ghonimy MBI.Radiological findings spectrum of asymptomatic coronavirus (COVID-19) patients.
2020; 51: 0-5 [DOI: 10.1186/s43055-020-00266-3]
27 Kaufman AE, Naidu S, Ramachandran S, Kaufman DS, Fayad ZA, Mani V.Review of radiographic findings in COVID-19.
2020; 12: 142-155 [PMID: 32913561 DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i8.142]
28 Landete P, Quezada Loaiza CA, Aldave-Orzaiz B, Mu?iz SH, Maldonado A, Zamora E, Sam Cerna AC, Del Cerro E, Alonso RC, Cou?ago F.Clinical features and radiological manifestations of COVID-19 disease.
2020; 12: 247-260 [PMID: 33362916 DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i11.247]
29 Zhang HW, Yu J, Xu HJ, Lei Y, Pu ZH, Dai WC, Lin F, Wang YL, Wu XL, Liu LH, Li M, Mo YQ, Zhang H, Luo SP, Chen H, Lyu GW, Zhou ZG, Liu WM, Liu XL, Song HY, Chen FZ, Zeng L, Zhong H, Guo TT, Hu YQ, Yang XX, Liu PN, Li DF.Corona Virus International Public Health Emergencies: Implications for Radiology Management.
2020; 27: 463-467 [PMID: 32113880 DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.02.003]
30 Inui S, Kurokawa R, Nakai Y, Watanabe Y, Kurokawa M, Sakurai K, Fujikawa A, Sugiura H, Kawahara T, Yoon SH, Uwabe Y, Uchida Y, Gonoi W, Abe O.Comparison of Chest CT Grading Systems in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia.
2020; 2: e200492 [PMID: 33778648 DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020200492]
31 Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, Tao Q, Sun Z, Xia L.Correlation of Chest CT and RTPCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases.
2020; 296: E32-E40 [PMID: 32101510 DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020200642]
32 Mathew RP, Jose M, Jayaram V, Joy P, George D, Joseph M, Sleeba T, Toms A.Current status quo on COVID-19 including chest imaging.
2020; 12: 272-288 [PMID: 33510852 DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i12.272]
33 Revzin MV, Raza S, Srivastava NC, Warshawsky R, D'Agostino C, Malhotra A, Bader AS, Patel RD, Chen K, Kyriakakos C, Pellerito JS.Multisystem Imaging Manifestations of COVID-19, Part 2: From Cardiac Complications to Pediatric Manifestations.
2020; 40: 1866-1892 [PMID: 33136488 DOI: 10.1148/rg.2020200195]
34 Ng MY, Lee EYP, Yang J, Yang F, Li X, Wang H, Lui MM, Lo CS, Leung B, Khong PL, Hui CK, Yuen KY, Kuo MD.Imaging Profile of the COVID-19 Infection: Radiologic Findings and Literature Review.
2020; 2: e200034 [PMID: 33778547 DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020200034]
35 Hameed S, Elbaaly H, Reid CEL, Santos RMF, Shivamurthy V, Wong J, Jogeesvaran KH.Spectrum of Imaging Findings at Chest Radiography, US, CT, and MRI in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19.
2021; 298: E1-E10 [PMID: 32584166 DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020202543]
36 Baratella E, Crivelli P, Marrocchio C, Bozzato AM, Vito A, Madeddu G, Saderi L, Confalonieri M, Tenaglia L, Cova MA.Severity of lung involvement on chest X-rays in SARS-coronavirus-2 infected patients as a possible tool to predict clinical progression: an observational retrospective analysis of the relationship between radiological, clinical, and laboratory data.
2020; 46: e20200226 [PMID: 32965310 DOI: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20200226]
37 de Jaegere TMH, Krdzalic J, Fasen BACM, Kwee RM; COVID-19 CT Investigators South-East Netherlands (CISEN) study group.Radiological Society of North America Chest CT Classification System for Reporting COVID-19 Pneumonia: Interobserver Variability and Correlation with Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction.
2020; 2: e200213 [PMID: 33778589 DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020200213]
38 Or Caspi, Michael J.Smart RBN.The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic A Multinational Consensus Statement From the Fleischner Society.
2020; 19-21
39 Rubin GD, Ryerson CJ, Haramati LB, Sverzellati N, Kanne JP, Raoof S, Schluger NW, Volpi A, Yim JJ, Martin IBK, Anderson DJ, Kong C, Altes T, Bush A, Desai SR, Goldin J, Goo JM, Humbert M, Inoue Y, Kauczor HU, Luo F, Mazzone PJ, Prokop M, Remy-Jardin M, Richeldi L, Schaefer-Prokop CM, Tomiyama N, Wells AU, Leung AN.The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement From the Fleischner Society.
2020; 158: 106-116 [PMID: 32275978 DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.003]
40 Palmucci S, Mauro LA, Messina M, Russo B, Failla G, Milone P, Berretta M, Ettorre GC.Diffusionweighted MRI in a liver protocol: its role in focal lesion detection.
2012; 4: 302-310 [PMID: 22900131 DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i7.302]
41 Ali SA, Abdelkawi MM.Incidentally recognized COVID-19 pneumonia in routine oncologic 18FFDG PET/CT examinations: a local experience during pandemic era.
2020; 51 [DOI: 10.1186/s43055-020-00333-9]
42 Angelini V, Villanacci A, Belotti A, Castagnoli F, Frittoli B, Corvino A, Brunetti A, Grazioli L.Incidental whole-body MRI evidence of COVID-19 in an asymptomatic patient in a high prevalence region.
2020; 51 [DOI: 10.1186/s43055-020-00288-x]
43 Di Girolamo M, Muscogiuri E, Zucchelli A, Laghi A.An Incidental Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia With Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
2020; 12: e12115 [PMID: 33489530 DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12115]
44 Pallardy A, Rousseau C, Labbe C, Liberge R, Bodet-Milin C, Kraeber-Bodere F, Fleury V.Incidental findings suggestive of COVID-19 in asymptomatic cancer patients undergoing 18F-FDG PET/CT in a low prevalence region.
2021; 48: 287-292 [PMID: 32860074 DOI: 10.1007/s00259-020-05014-3]
45 Barrios-López JM, Rego-García I, Mu?oz Martínez C, Romero-Fábrega JC, Rivero Rodríguez M, Ruiz Giménez JA, Escamilla-Sevilla F, Mínguez-Castellanos A, Fernández Pérez MD.Ischaemic stroke and SARS-CoV-2 infection: a causal or incidental association?
2020; 35: 295-302 [DOI: 10.1016/j.nrleng.2020.05.008]
46 Tulchinsky M, Fotos JS, Slonimsky E.Incidental CT Findings Suspicious for COVID-19-Associated Pneumonia on Nuclear Medicine Examinations: Recognition and Management Plan.
2020; 45: 531-533 [PMID: 32502091 DOI: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003100]
47 Ferrando-Castagnetto F, Wakfie-Corieh CG, García AMB, García-Esquinas MG, Caro RMC, Delgado JLC.Incidental and simultaneous finding of pulmonary thrombus and COVID-19 pneumonia in a cancer patient derived to
F-FDG PET/CT.New pathophysiological insights from hybrid imaging.
2020; 15: 1803-1805 [PMID: 32788944 DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.07.032]
48 Alrifai A, El-Raey FM, Yousef AM, Zaky S.Ultrasound in Suspected Pneumonic COVID-19: Our Experience.
2020; 2: 682-689 [DOI: 10.21608/ijma.2020.43493.1176]
49 Iqbal M, Shahbaz M, Qadeer O Bin, Nazir K, Naeem M, Afzal MS, Imran MB.Nuclear medicine practices during the COVID-19 pandemic—review of some recently published protocols.
2020; 51: 1-8 [DOI: 10.1186/s43055-020-00349-1]
50 Jackson K, Butler R, Aujayeb A.Lung ultrasound in the COVID-19 pandemic.
2021; 97: 34-39 [PMID: 32895294 DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138137]
51 Haft JW, Atluri P, Ailawadi G, Engelman DT, Grant MC, Hassan A, Legare JF, Whitman GJR, Arora RC; Society of Thoracic Surgeons COVID-19 Task Force and the Workforce for Adult Cardiac and Vascular Surgery.Adult Cardiac Surgery During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Tiered Patient Triage Guidance Statement.
2020; 110: 697-700 [PMID: 32305286 DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.04.003]
52 Ates OF, Taydas O, Dheir H.Thorax Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Patients with Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).
2020; 27: 1373-1378 [PMID: 32830031 DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.08.009]
53 Kaiser Ururahy Nunes Fonseca E, Chate RC, Neto RS, Ishikawa WY, Silva MMA, Yokoo P, Szarf G.Pulmonary Findings of COVID-19 Identified at Cardiac MRI.
2020; 2: e200193 [PMID: 33778575 DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020200193]
54 Langenbach MC, Hokamp NG, Persigehl T, Bratke G.MRI appearance of COVID-19 infection.
2020; 26: 377-378 [PMID: 32352920 DOI: 10.5152/dir.2020.20152]
55 Torkian P, Rajebi H, Zamani T, Ramezani N, Kiani P, Akhlaghpoor S.Magnetic resonance imaging features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: The first preliminary case series.
2021; 69: 261-265 [PMID: 33002753 DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.09.002]
56 Fields BKK, Demirjian NL, Dadgar H, Gholamrezanezhad A.Imaging of COVID-19: CT, MRI, and PET.
2021; 51: 312-320 [PMID: 33288215 DOI: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2020.11.003]
57 Deen SS, Wetscherek M, Karia S, Godfrey EM.Diagnostic challenges of incidental lung lesions on liver MRI during the COVID-19 pandemic.
2020; 13 [PMID: 32690573 DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-237430]
58 Chetan MR, Tsakok MT, Shaw R, Xie C, Watson RA, Wing L, Peschl H, Benamore R, MacLeod F, Gleeson FV.Chest CT screening for COVID-19 in elective and emergency surgical patients: experience from a UK tertiary centre.
2020; 75: 599-605 [PMID: 32593409 DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2020.06.006]
59 Siegel A, Chang PJ, Jarou ZJ, Paushter DM, Harmath CB, Arevalo J Ben, Dachman A.Lung base findings of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) on abdominal CT in patients with predominant gastrointestinal symptoms.
2020; 215: 607-609 [DOI: 10.2214/ajr.20.23232]
60 Hynes JP, Moore P, Murray JG.Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Detected at the Lung Apices During CT Angiography in Acute Stroke Assessment.
2020; 215: W40 [PMID: 32538694 DOI: 10.2214/AJR.20.23484]
61 Dedeilia A, Esagian SM, Ziogas IA, Giannis D, Katsaros I, Tsoulfas G.Pediatric surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic.
2020; 9: 7-16 [PMID: 33014718 DOI: 10.5409/wjcp.v9.i2.7]
62 Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S.Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China.
2020; 145 [PMID: 32179660 DOI: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702]
63 Gosain R, Abdou Y, Singh A, Rana N, Puzanov I, Ernstoff MS.COVID-19 and Cancer: a Comprehensive Review.
2020; 22: 53 [PMID: 32385672 DOI: 10.1007/s11912-020-00934-7]
64 Setti L, Kirienko M, Dalto SC, Bonacina M, Bombardieri E.FDG-PET/CT findings highly suspicious for COVID-19 in an Italian case series of asymptomatic patients.
2020; 47: 1649-1656 [PMID: 32342191 DOI: 10.1007/s00259-020-04819-6]
65 Albano D, Bertagna F, Bertoli M, Bosio G, Lucchini S, Motta F, Panarotto MB, Peli A, Camoni L, Bengel FM, Giubbini R.Incidental Findings Suggestive of COVID-19 in Asymptomatic Patients Undergoing Nuclear Medicine Procedures in a High-Prevalence Region.
2020; 61: 632-636 [PMID: 32238429 DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.246256]
66 Mo A, Brodin NP, Tomé WA, Garg MK, Kabarriti R.COVID-19 Incidentally Detected on PET/CT During Work-up for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer.
2020; 34: 1681-1684 [PMID: 32503829 DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11961]
67 Franceschi AM, Clifton M, Ahmed O, Matthews R, Franceschi D.Incidental PET/CT Findings of Suspected COVID-19 in a Region of High Prevalence.
2020; 12: e9716 [PMID: 32944437 DOI: 10.7759/cureus.9716]
68 Wakfie-Corieh CG, Blanes García AM, Ferrando-Castagnetto F, Valhondo-Rama R, Ortega Candil A, Rodríguez Rey C, Cabrera Martín MN, García-Esquinas MG, Couto Caro RM, Pedrera Canal M, Carreras Delgado JL.Assessment of extra-parenc hymal lung involvement in asymptomatic cancer patients with COVID-19 pneumonia detected on
F-FDG PET-CT studies.
2021; 48: 768-776 [PMID: 32901353 DOI: 10.1007/s00259-020-05019-y]

