Paradoxical role of interleukin-33/suppressor of tumorigenicity 2 in colorectal carcinogenesis: Progress and therapeutic potential
INTRODUCTION
During 2020 alone, approximately 19.3 million newly diagnosed cancer cases were recorded, together with nearly 10 million global cancer mortalities[1]. Stemming from such statistics, colorectal cancer (CRC) represents the third most prevalent tumor (10%), and the second most prevalent global mortality-inducing cancer (9.4%)[1]. Approximately 10% of all CRC cases are inherited, with over 90% being sporadically randomized. In general, tumor initiation and development are primarily determined by key factors, such as genetic instability, epigenetic changes, antiapoptotic activity, immune-system circumvention, invasiveness, and metastases[2]. Three mechanisms of genetic instability in sporadic CRC have been identified: CpG-island methylation phenotype, chromosomal-based imbalances, and microsatellite instabilities. In particular, it is worth mentioning that several risk factors are related to CRC development, including lack of exercise, smoking, and red meat and alcohol consumption[3]. In addition, obesity, type 2 diabetes and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are highly linked to exacerbated CRC development. The parts played by nonneoplastic cells within tumor microenvironments (TMEs) for cancer development have been identified[2,4]. The cytokines, growth factors, and hormones secreted by these non-neoplastic cells are pivotal in cancer progression by interaction with the cellular constituents within tumor inflammation microenvironments[5]. Such cytokines include interleukin (IL)-33, a member of the IL-1 cytokine superfamily, which has been shown to mainly invoke T-helper (Th)2 immune response activities by means of its suppressor of tumorigenicity (ST)2 receptor[6]. IL-33/ST2 signal transduction is involved in IBD, maintenance of tissue homeostasis, and tumor invasion[7,8]. IL-33 can be pro- or antitumorigenic in CRC, with both activities indicating that IL-33 plays vital roles in enrolling immune-system cell types to modulate TMEs. In this review, IL-33/ST2 involvement in colorectal carcinogenesis, progress and therapeutic potential are discussed.
He followed the road that led from his father s cottage to the hill, where he sat down to rest, saying to himself: I am sure my brothers must have stopped here, and I will do the same
Yet another version of the tale--the French The Story of Grandmother --has Little Red Riding Hood rescuing herself. After she is fed a piece of her grandmother by the wolf, she announces that she needs to go to the bathroom. Since this activity is done outside--this is before the common appearance of indoor bathrooms--she goes outside and then runs away.
DISCOVERY AND STRUCTURE OF IL-33 AND ITS LIGAND ST2
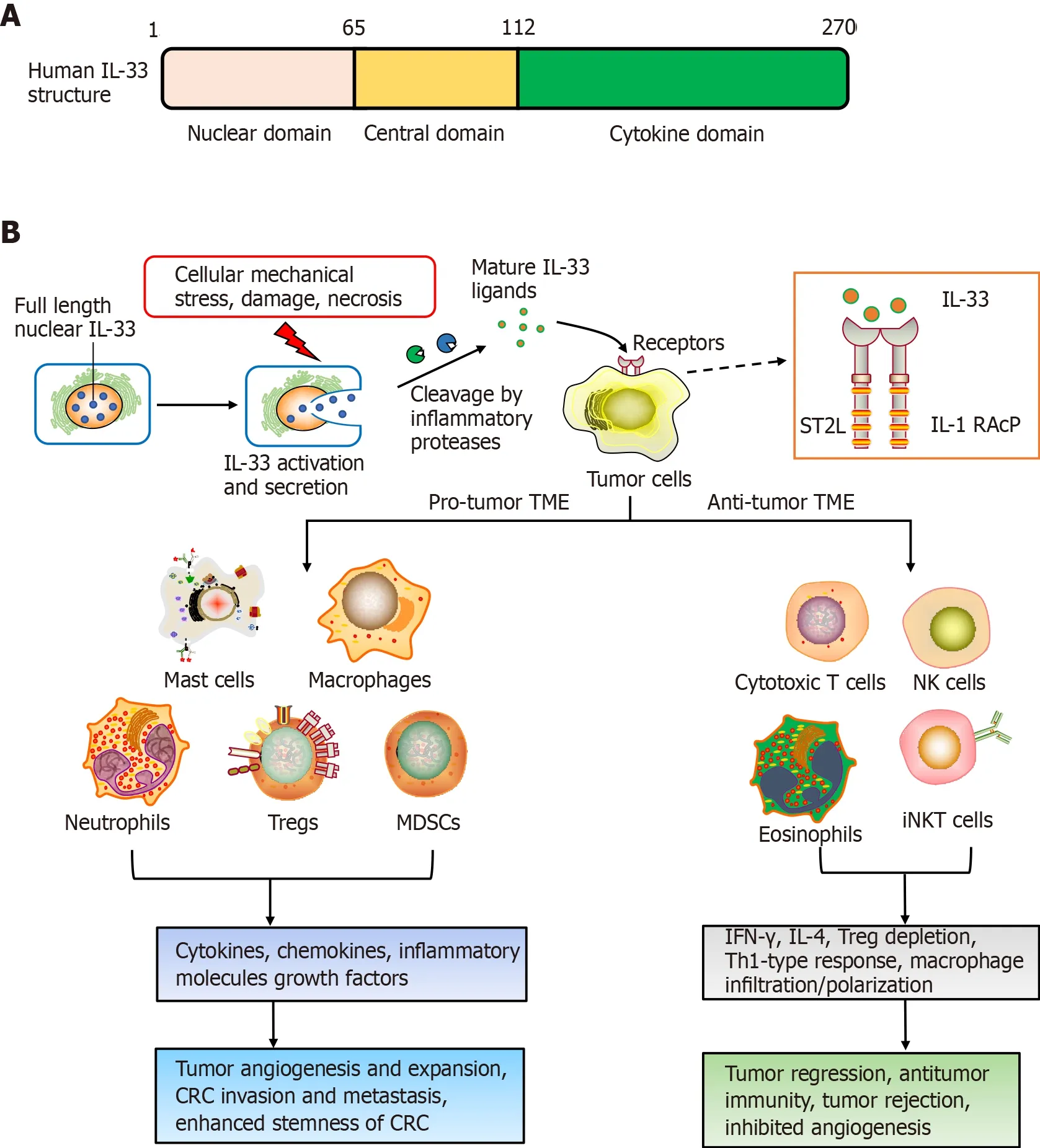
IL-33 was first identified in 2003. It is highly upregulated within hypertrophic veins as a nuclear protein, and given its first name, nuclear factor, from high endothelial venules[9]. Later in 2005, IL-33 was recognized as a member of the IL-1 cytokines family[6]. Meanwhile, IL-33 was recognized to be a ligand for ST2 receptor[6]. The molecular full-length weight for human IL-33 is 30 kDa. This cytokine has 270 amino acid residues, while murine IL-33 has only 266[6]. Human IL-33 consists of three domains: the N-terminal (aa 1-65), which is important for chromatin-binding and nuclear localization; central (aa 66-111), which interacts with nuclear factor-B; and Cterminal IL-1-like cytokine domain (aa 112-270), including the region binding to ST2[10]. After synthesis, IL-33 is passively released following cellular mechanicalstress/damage triggers[11]. Meanwhile, the precursor protein IL-33 is cleaved to produce the 10-fold-active matured version, compared to full-length IL-33, and is segmented to effectively activate group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s)[12,13].
The ST2 receptor was first recognized as an oncogene in murine fibroblasts[14,15]. It has been investigated for many years before establishment of ligand IL-33, so ST2 was previously considered to be orphan receptor. The ST2 receptor derives from IL-1RL, which is a type-1 transmembrane protein[14]. Four ST2 isoforms are produced by alternative splicing, such as ST2L (ligand), sST2, ST2V (variant), and ST2LV (ligand variant). ST2L is a membrane-anchored receptor similar to IL-1, having three immunoglobulin-like extracellular, transmembrane domains, together with IL-1R1-like intracellular domains[16,17]. sST2 is a soluble-secreted isoform of ST2 that has no transmembrane domain, although it carries an extracellular domain as ST2L, with 5-9 extra amino acids on the C terminus in humans and mice[16,18]. ST2V resembles sST2 and lacks the third extracellular domain, although it has a hydrophobic tail instead of a third immunoglobulin-like domain[19]. ST2LV is an additional soluble isoform with no transmembrane domain[20]. ST2L and sST2 have been thoroughly investigated, altthough knowledge is scarce about ST2V and ST2LV. ST2L is typically expressed on fibroblasts, mast cells, Th2 lymphocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages, and sST2 is mainly present on fibroblasts/epithelial cells[20].
ROLES OF IL-33/ST2 IN CRC
IL-33/ST2 and CRC carcinogenesis
Many studies have shed light on IL-33 functions, whereas the literature on ST2 in CRC is scarce. Antitumorigenic functions of the IL-33 receptor have been gradually explained in CRC since 2016. Akimoto and co-workers have reported that soluble sST2 negatively correlated with colon tumor malignant growthby modifying the TME[51]. They further revealed the mechanisms: sST2 inhibited IL-33-driven angiogenesis, macrophage infiltration/polarization, and Th1 and Th2 activities. Another study by Donnell and colleagues demonstrated that ST2L downregulation in colon cancer, together with elevated tumor grade, led to ST2L downregulation. Colontumor-resident ST2 knockdown led to increased tumor expansion in animal studies, with a decrease in IL-33-driven macrophage infiltration and enrollment through antagonizing chemokine CCL2[52]. This indicates that IL-33 has an antitumor function against CRC and the IL-33/ST2 axis exerts protective functions against colon-based tumor-triggering.
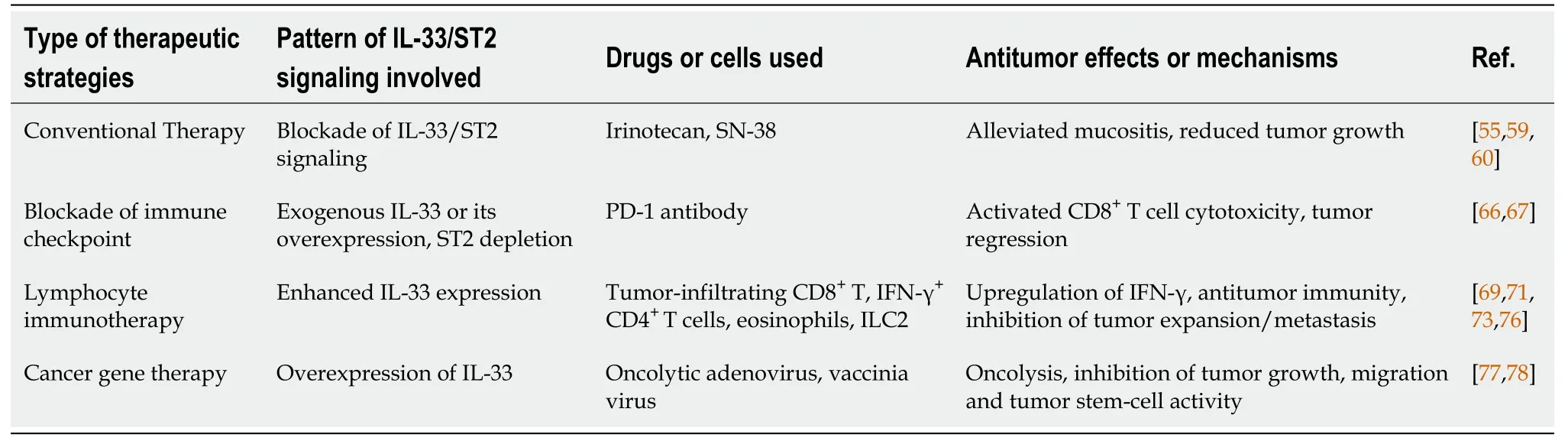
Irinotecan (CPT-11) is a topoisomerase I inhibitor, and is an antitumor drug that can be used to treat metastatic CRC[57,58]. The clinical pharmacokinetics of CPT-11 and its metabolites such as SN-38 seem to be the key factor for optimal use of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs[57]. CPT-11 systemic-based treatment causes intense mucosal disruption and diarrhea, coinciding with small intestinal IL-33 upregulation. However, the symptoms of mucositis were markedly lower within ST2mice. Recombinant IL-33 protein reinforces CPT-11-driven mucositis, and blockade of IL-33 with its complementary antibody (or soluble ST2) significantly alleviates mucositis and reduces tumor growth by CPT-11 in a mouse model of CT26 colon cancer[59]. Such results indicate that thwarting the IL-33/ST2 axis can be exploited as a novel therapy against mucositis, consequently enhancing the beneficial effect of chemotherapy against CRC.
The TME plays important roles in triggering cancer. The alarm protein IL-33 has been shown to be involved in formation of the early TME and to influence carcinogenesis and progression. Pastille and colleagues used animal models and patient samples to suggest that IL-33/ST2 axis activity restricted effector CD8T cell functions in the CRC environment and promoted tumor growth in the colon[26]. In addition, IL-33 downregulates IL-17 and differentiation through forkhead box (FOX)P3, indicating an immunosuppressive environment during CRC tumorigenesis[26]. In murine models for colon cancer, IL-33 within tumor regions can recruit and activate macrophages into the microenvironment, leading to prostaglandin E2 upregulation, consequently exacerbating colon cancer stemness/progression[27]. IL-33/ST2 signaling can activate c-Jun and stem cell genes (,and) to induce CRC stemness, eventually to promote carcinogenesis[27]. More importantly, Taniguchi[28] reported the potential role of IL-33 in regulating tumor-initiating cells, as well as the impact on stem cell-niche interactions, which is necessary for tumor progression, and highlighted the new role of IL-33 in promoting CRC stemness and carcinogenesis.
IL-33/ST2 and CRC progression
A major hallmark for CRC progression is chronic inflammation[29]. IL-33 is upregulated within serum of ulcerative colitis cases, and consequently involved in the development and maintenance of inflammation. Meanwhile, ulcerative colitis is intimately linked to CRC progression, indicating that IL-33 has a pivotal role in triggering colon tumors[30]. Kirsten and colleagues suggested that involvement of the IL-33/ST2 axis was critical for CRC progression using bone marrow chimera investigations. This is partly because activation of the IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway damages intestinal barrier integrity, inducing immune-system cells to express protumorigenic IL-6[31]. Therefore, there is now compelling evidence that IL-6 serum level is linked to late-stage CRC in patients, together with being a predictor for poor prognosis in CRC[32].
Several studies indicated that exogenous or endogenous IL-33 is positively related to recruitment and CD8T/NK cell triggering within the TME. In melanoma or breast cancer models, exogenous application or transgenic expression of IL-33 recruits and activates (IFN-γCD107) CD8T and NK cells to orchestrate the TME, regulates xenograft tumor expansion and prevents lung metastasis of breast cancer in mice[49,67]. In the CRC model, Xia[68] found that overall antitumor responses/IFN-γ expression by tumor-infiltrating CD8T cells were impaired in IL-33-deficient mice. Conversely, IL-33 upregulated IFN-γ by activated CD4/CD8T cells, improving CD8T cell infiltrative and antitumor responses against protumor effects by Treg cells. These results imply that the balance of CD8T cells and Treg cells within the TME is a crucial factor for IL-33-mediated anticancer responses in CRC.
People ask me about tips. As far as I know, practically everyone will give you something. Come to think of it, most Americans are pretty generous. I always try to be nice to everyone, whether they tip or not. I believe in God and try to be a good member of my parish. I try to act toward others like I think God wants me to act. I have been trying this for a long time, and the longer I try, the easier it gets.
Of course I promised I would, for I was too happy to think of what my parents would say, or indeed of anything except Richard was not at our meeting place as he had arranged
IL-33 is considered to have a cancer-promoting role because IL-33/ST2 axis induction leads to CRC carcinogenesis/development. However, another concern is that IL-33 has a paradoxical role. Selected studies have indicated that IL-33 has a less-known role of tumor suppressor within many malignant tumors[44,45].
IL-33/ST2 and CRC prevention
Recently, IL-33/Treg cell interaction has attracted increasing attention. An early study showed that IL-33 can promote Treg cell function in the colorectum, where FOXP3Treg cells are abundant[41]. Treg cells can resist dysregulated inflammatory responses, and consequently acquire tissue-specific survival and function. It is well known that TME-resident IL-33 and Treg cells in the TME are individually implicated within CRC progression, albeit this is still in dispute. IL-33/ST2 signaling exacerbates CRC progression through modulation of FOXP3Treg cell phenotypic features and curtailing IL-17 differentiation[26]. Furthermore, tumor-derived IL-33 can remodel the TME through the recruitment of CD11b/GR1and CD11b/F4/80myeloid cells and promote CRC growth and liver metastasis in mice, with the potential as a therapeutic target[42]. IL-33 also has a pivotal effect on Treg cell functional stability, with genetic deletion of IL-33 improving the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies[43].
The IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway usually induces Th2-cell-derived expression of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. IL-33 is also involved in cellular immunity-related responses through upregulating IL-4 and interferon (IFN)-γ by CD8T, invariant natural killer (NK)T cells and NK cells, together with amplifying Th1-oriented immune responses[46-48]. Thus, it shows that IL-33/ST2 signaling plays two roles in tumorigenesis - stimulating tumor growth or inhibiting tumor progression.
In aspects of cancer prevention, tumoral IL-33 overexpression increases antitumoral responses by the immune system, together with tumor rejection through activation of CD8T/NK cells[49]. Furthermore, Treg cell depletion synergizes with re-expression of IL-33 to contribute cancer-eliminating Th1-type immunity-related actions, implicating that IL-33 is a promising antitumor cytokine for immunotherapy[49]. Another study implied a protective role for IL-33/ST2 against CRC invasiveness and metastases, resulting in reduced colorectal tumor growth[50]. Malik[30] have demonstrated that IL-33-lacking mice are sensitive to colitis-associated cancer (CAC). Meanwhile, this study highlighted that IL-33, IgA, IL-1α and the microbiota are candidate drug targets against IBD/CAC.
Like most malignant tumors, CRC carcinogenesis involves multiple factors and processes. For most sporadic CRC, the important causes of CRC carcinogenesis are adenomas, intestinal polyp deterioration, tumor suppressor gene APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) mutation and TME formation[21]. Recently, many studies have shown that IL-33/ST2 plays a vital role in CRC occurrence and progression[22]. Cui[23] reported that the IL-33/ST2 axis promoted the neoplastic transformation of human colorectal adenoma to CRC, which is closely correlated with increased IL-33 expression in CRC tissues as compared to adjacent noncancer tissues.
Consequently, negative functions for the IL-33/ST2 axis in CRC progression depend on its involvement in the induction of angiogenesis, regulation of anti-tumor-based immunity-related responses and TME modulation[53]. Additional studies are needed to validate the precise functions adopted by IL-33/ST2 signaling in CRC (Figure 1).
DIVERSIFIED THERAPEUTICS BASED ON IL-33/ST2 SIGNALING IN CRC
IL-33 is related to carcinogenesis, progression and poor prognosis in some cancers, including CRC[40]. Due to TME-resident IL-33/ST2 variability, their overexpression/ recombinant protein inhibits CRC expansion. This suggests the potential of the IL-33/ST2 axis as a drug target for CRC. Many studies have reported possible strategies for the treatment of CRC based on the IL-33/ST2 axis (Table 1).
2. Little Red Riding Hood: The red riding hood is a popular and familiar symbol to much of Europe and North America. In the height of portraiture11 in the nineteenth century, many young daughters of wealthy families were painted wearing red capes12 or hoods13. Today, some little girls still want to wear red capes for Halloween or other imaginative play.
IL-33/ST2 and conventional therapies
Intestinal mucositis and severe diarrhea are commonly associated with cancer chemotherapy and are thus dose-limiting adverse effects. Combining radiation with conventional chemotherapy can exacerbate mucositis, leading to chemotherapeutic dose reductions or inevitable cessation of such treatments[54]. Since chemotherapy directly results in DNA damage/apoptosis through reactive oxygen species (ROS) and variation of cytokine production[55], as a proinflammatory factor, IL-33 has a pivotal part in driving inflammation/tumors through its ST2 receptor. One particular investigation highlighted that IL-33, in reduced doses, resisted chemotherapeutic platinumdrug-induced cell death and enhanced cellular invasiveness in selected tumors through JNK pathway triggering[56]. Thus, regulation of the IL-33/ST2 pathway can relieve inflammation/improve chemotherapy function.
Another study found that IL-33 acts as a mediator of intestinal polyposis and regulator of tumor stromal cell activation in Apcmice, a genetic model of intestinal tumorigenesis[24]. In the Apcpolyps, IL-33 is expressed in tumor epithelial cells, and ST2 is related to two stromal cell types, subepithelial myofibroblasts and mast cells. Stimulation of IL-33 induces stromal cells to express components of the extracellular matrix and growth factors that promote tumor development and growth[24]. He[25] reported that epithelial IL-33 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmice with transgenic expression of IL-33 in intestinal epithelial cells through the expansion of ST2T regulatory (Treg) cells, Th2 cytokine production and alternative activation of macrophages. Conversely, loss of IL-33 or ST2 in Apcmice inhibits tumorigenesis and tumor angiogenesis, and induces apoptosis in adenomatous polyps[24,25]. This suggests that IL-33 promotes the transition of adenomas and polyposis to CRC through the activation of tumor stromal cells and the formation of a protumorigenic microenvironment.
IL-33/ST2 and treatment with immune-checkpoint inhibitor
Recent results showed that IL-33/ST2 act as candidate targets of checkpoint inhibitors for CRC immunotherapy, where they are secreted by lymphocytes, stromal cells and tumor cells to recruit immune cells and remodel the tolerogenic TME. A recent study reported that ST2 is specifically expressed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) of CRC, and ST2 upregulation is related to low survival odds and reduced CD8T cell cytotoxicity in CRC[66]. They also found that ST2-positive TAMs were enrolled into CRC xenograft model tumors through chemokine receptor CXCR3, promoting an immunosuppressive TME. Thus, the combined effect of ST2 depletion using ST2-knockout mice and treatment with PD-1 antibody had a significant suppressive effect on CRC growth. The use of IL-33 trap fusion protein reduced tumor-infiltrating ST2TAMs and thwarted xenograft tumor expansion in CRC preclinical models. Thus, the IL-33/ST2 axis plays a big part in CRC immuno-therapy.
Immunotherapy represents a powerful method in cancer treatment. Stemming from this, immune checkpoint modulation has been broadly applied to treat multiple cancers, following the discovery of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 and programmed cell death (PD)-1[60,61], which was awarded the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Blockade of immune checkpoint yields promising clinical results in CRC. However, only a subset of cancer patients having an elevated microsatellite instability frequency phenotype develop durable antitumor immune responses due to the complicated TME associated with PD-1 and PD ligand (PD-L)1[62,63]. It can be explained from recent data that IL-33/ST2 can regulate PD-1/PD-L1 signaling within tumors. For example, exogenous IL-33 upregulated PD-1 by CD8T cells, together with upregulated PD-L1 within murine acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells[64]. Thus, combining IL-33 with PD-1 antibody dramatically extends AML murine survival times in a CD8T-cell-based fashion, even leading to full regression within 50% of such treated mice. Another study showed that IL-33 triggered CD8T cells/ILC2s in pancreatic tumors, and activated ILC2s increased PD-1 expression. Subsequent combined treatment of IL-33 and PD-1 inhibition enhanced immunotherapy outcomes in a murine model[65].
IL-33/ST2 signaling and lymphocyte immunotherapy
Being an alarmin and immune regulation-related factor, IL-33 has a pivotal role in regulating the function of a wide range of immune cells. However, whether IL-33/ST2 signaling-regulated immune lymphocytes exert potential antitumor immunity in CRC is still a question under investigation. Recent research progress seems to suggest the positive reactivity based on Th1 cells (CD8T and NK cells) and Th2 cells (CD4T, ILC2 and eosinophils.).
It is also reported that epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a powerful signaling molecule, affecting CRC progression and intestinal epithelial cell development[33-35]. IL-33 and ST2 expression profiles can be strongly stimulated by EGF, without increasing the extracellular secretion of IL-33. Consequently, IL-33 upregulation leads to CRC triggering, thus indicating that the EGF/IL-33/ST2 axis components are novel drug targets against CRC[36]. In addition, CRC triggering/progress can be influenced through the immune microenvironment[37-39]. Multiple investigations have indicated that IL-33 thwarts host-based tumor immunity, tumor stroma modulation and exacerbation of angiogenesis, thus contributing to IL-33 receptor ST2-driven CRC[40].
But if, my dearest, you are not sure that you can face lift with me in a land strange to you, then do not take this important step, for I love you too much to wish you the smallest unhappiness
In addition to activating Th1 response, IL-33 additionally modulate Th2 functions, including CD4T cells, ILC2s and eosinophils in the TME. IL-33 can directly target conventional and regulatory CD4T cells expressing ST2, and promote the immunosuppressive functions of Treg cells, which causes tumor growth and immune evasion[69]. IL-33 preferentially promotes Th2 response to modulate tumor immunity. In murine CT26 or MC38 CRC models, recombinant IL-33 markedly reduced colon tumor expansion/metastatic activity in lungs/liver[70]. IL-33 treatment can augment IFN-γCD4T cells, together with upregulating CD40L on TILs. Moreover, IL-33 was found to be adequate for upregulating ST2 on CD4T cells, although not in CD8T/NK cells, suggesting that IL-33/ST2 signaling activates CD4T cells through positive-feedback looping.
At daybreak,17 even before the sun was up, the woman came and woke the two children: Get up, you lie-abeds, we re all going to the forest to fetch wood
Emerging studies have proved the positive role of eosinophils in mediating anticancer immunity-related counteractivity by IL-33 within several cancers, including CRC[71]. A more recent study by Kienzl and colleagues demonstrated that IL-33 can inhibit cancer expansion in CT26 engraftment/colitis-linked CRC mouse models[72]. The IL-33-induced effect was cancelled within eosinophil-lacking dblGATA-1 mice, although it was rescued through adoptive transfer of-triggered eosinophils by IL-33[72]. They further found that IL-33 treatment upregulated eosinophil biomarkers associated with triggering and homing (CD11b and Siglec-F), and with degranulation (CD63 and CD107a)and. These results implied that eosinophils are a requisite for the antitumor effect of IL-33 in CRC. Moreover, IL-33 stimulation can enrich ILC2s in the TME of many cancers, and ILC2s also constitutively express ST2[73]. Thus, IL-33 targets directly ILC2s and induces ILC2 cell expansion, enrichment and activation in tumors[74]. Thus, it was proved that, in local expression of IL-33 in murine CRC, CT26 enhanced MyD88-based antitumor ILC2 activity[75]. In this study, IL-33 promoted production of CXCL2 from ILC2s, and created a TME with CXCR2-expressing tumor cells through a dysfunctional angiogenesis/hypoxia/ROS axis, which caused tumor cell-specific apoptosis. The finding highlights the vital role of ILC2s in the IL-33-mediated antitumor effect for CRC immunotherapy.
IL-33/ST2 signaling and cancer gene therapy and other blockade strategies
Recently, gene therapy using viral or nonviral vectors to carry therapeutic genes for diseases has attracted increased attention. In particular, breakthroughs have been made in the treatment of genetic diseases. Gene therapy also shows a promising prospect in the field of human cancer treatment. In our group, cancer gene therapy using oncolytic viruses as vectors has achieved encouraging results. We have constructed multiple oncolytic viruses targeting multiple cancers, such as CD55-Smad4 for CRC[76], GD55 for liver cancer[77,78] and Ad-wnt(24) for Wnt signaling-positive cancer[79]. In CRC, tumor-disruptive adenovirus CD55-Smad4 was developed without issues and succeeded in regulating CRC cell growth, migration, and tumor stem-cell activity through reining-in of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Previous reports have demonstrated that recombinant ST2/IL-33 significantly inhibits CRC growth and enhances antitumor immune effects[72]. It additionally suggests that oncolytic viruses, targeting CRC and carryingorgene, have the potential for tumor therapy through overexpression oforgene and lysis of tumor cells mediated by oncolytic viruses. Our unpublished results showed that oncolytic adenovirus and vaccinia virus carrying thegene can effectively inhibit the growth of mouse CT26 CRC cells, and furtherexperiments are ongoing (Figure 2).

There are at least two anti-IL-33 antibodies (SAR440340 and MEDI3506) being developed to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, moderate-to-severe asthma, and chronic bronchitis in clinical phase I and II trials (NCT03387852, NCT03546907, NCT04751487, NCT04570657, NCT04701983, and NCT04631016). Thus, it suggests that the blockade strategy using anti-IL-33 antibodies has the potential for treatment of human cancer, including CRC, where IL-33 plays the protumorigenesis role.
CONCLUSION
IL-33 plays a controversial role in carcinogenesis, cancer prevention and cancer immunity, although the specific mechanism is still unclear. In CRC, the divergent roles of IL-33 may depend on the TME. Therefore, how to orchestrate the TME to design and optimize appropriate treatment strategies based on IL-33/ST2 signaling for CRC is an important question. These strategies include how to activate and recruit IFN-γsecreting CD4and CD8T cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, M1 macrophages, eosinophils and ILC2s, and how to better combine chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors and cancer gene therapy to achieve more effective treatments for CRC. Moreover, being an alarmin, IL-33 may take up the role of a potential biomarker for CRC diagnosis, therapy and prognosis.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年1期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年1期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutation, infectivity,transmission, and vaccine resistance
- Clinical manifestations and prenatal diagnosis of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy: A case report
- Lunate dislocation with avulsed triquetral fracture: A case report
- Protein-losing enteropathy caused by a jejunal ulcer after an internal hernia in Petersen's space: A case report
- Eustachian tube teratoma: A case report
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in pregnancy: A case report
