Orexins: A promising target to digestive cancers, inflammation, obesity and metabolism dysfunctions
Alain Couvineau, Thierry Voisin, Pascal Nicole, Valerie Gratio, Anne Blais
Abstract Hypothalamic neuropeptides named hypocretin/orexins which were identified in 1998 regulate critical functions such as wakefulness in the central nervous system.These past 20 years had revealed that orexins/receptors system was also present in the peripheral nervous system where they participated to the regulation of multiple functions including blood pressure regulation, intestinal motility,hormone secretion, lipolyze and reproduction functions. Associated to these peripheral functions, it was found that orexins and their receptors were involved in various diseases such as acute/chronic inflammation, metabolic syndrome and cancers. The present review suggests that orexins or the orexin neural circuitry represent potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of multiple pathologies related to inflammation including intestinal bowel disease, multiple sclerosis and septic shock, obesity and digestive cancers.
Key Words: Orexin; Neuropeptide; G-protein coupled receptor superfamily; Inflammation;Metabolic syndrome; Cancer
INTRODUCTION
Toward the end of the 1990 s, two independent groups managed respectively by J.G.Sutcliffes and M. Yanagisawa have discovered two new hypothalamic neuropeptides which are produced by the same precursor encoded by a single gene[1 ,2 ]. One of these two seminal publications co-led by Luis de Lecea and Thomas Kilduff’s was based on subtractive cDNA cloning strategy allowing the identification of the hypocretin-1 and hypocretin-2 , a contraction between “hypothalamus” corresponding to the location of orexins production and “secretin”, one hormone having a slight amino acid homology with hypocretins[1 ]. At the same time, the Takeshi Sakurai’s publication based on the identification of orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) by screening with purified unknown peptides from brain extracts has allowed the identification of both hypothalamic orexin-A (OxA) and orexin-B (OxB) referring to the Greek term meaning“appetite” because these two neuropeptides induced feeding after intraventricular brain injection[2 ]. These two neuropeptides identified by Sutcliffes’s group and Yanagisawa’s group turned out to be identical. It should be noted that the actual current use assigns the term “hypocretin” for the gene species and “orexins” for the protein species. From this discovery, the two orphans GPCRs have been identified as hypocretin (Hcrt)/orexin receptor 1 (OX1 R) and Hcrt/orexin receptor 2 (OX2 R) which belong to the large class A rhodopsin-like subfamily of GPCRs[3 ]. To elucidate the role of orexins in feeding, the Yanagisawa’s group has developed a knock out mice invalidated for the hypocretin gene. This model has revealed that the regulation of feeding and appetite were not the major physiologic role of orexins[4 ]. However, the absence of orexins secretion in this model, led to cataplectic attack symptoms[4 ].Moreover, the invalidation of OX2 R induces sleep attack whereas the OX1 R invalidation led to the sleep disturbance characterized by narcolepsy[5 ].
The role of the orexins/OXR system was firstly widely studied in the central nervous system (CNS) (Figure 1 ). Many publications have demonstrated and confirmed that the orexin main role in the CNS was to maintain wakefulness[6 ]. The absence of orexins production, associated to the loss of orexin neurons, in human CNS induce narcolepsy with cataplexy (Narcolepsy type I). The impact of orexin on sleep regulation had led to the development, by the pharmaceutical industries and the academic laboratories, of orexin receptor-targeting molecules, mainly antagonists, able to regulate the wake-sleep cycle for insomnia treatment[7 ]. A growing number of antagonists have been developed and classified into two categories: the single orexinreceptor antagonists (SORAs) including selective OX1 R antagonist (SORA1 s) and OX2 R antagonist (SORA2 s) and dual orexin-receptor antagonists (DORAs). Recently,two of these antagonists named suvorexant and lately lemborexant were approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in insomnia treatment[8 ,9 ]. Moreover, the central action of orexins regulates food intake, energy homeostasis, reward seeking,stress, motivation and drug addictions[10 ,11 ] (Figure 1 ) which included the addiction to cocaine, opioids, amphetamines, cannabis, alcohol and nicotine[12 ]. Despite the major role of orexins in CNS, these two neuropeptides were also studied, to a lesser extent, in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). In various peripheral organs including the adrenal glands, kidney, cardiovascular system, reproductive tract, adipose tissue and digestive tract, orexins also acted as regulators (Figure 1 )[13 ]. The relatively low extensive studies of the roles of orexins in the PNS support that their actions were not fully elucidated and controversial[10 ]. In the digestive tract, orexin has been detected in neurons of the enteric nervous system (ENS) and in the enteroendocrine gut cells[14 ]. The presence of orexin in enteroendocrine cells supported the idea that this neuropeptide is involved in nutrition and energy homeostasis. Moreover, the use of different antibodies directed against OxA, OxB and prepro-orexin revealed an orexinimmunoreactivity in ENS[15 ]. Orexins modulate motility and orexin level was regulated by fasting[16 ]. In the pancreas, OxA was present in pancreatic islets,immunoreactivity being detected in pancreatic beta cells and potentially in alpha cells[14 ]. In humans, OX1 R but not OX2 R was also detected in pancreatic islets[17 ].Although some studies support the role of OxA in the control of insulin secretion, this role remains conjectural[14 ]. However, the majority of these studies seemed to show that OxA directly or indirectlyviathe inhibition of glucagon release, regulated the insulin secretion[14 ]. It should be noted that OxB was also detectable in beta cells[17 ]but nothing is known about its role in the pancreas. If the presence of orexins in CNS,PNS and ENS was well established, the circulating level of these neuropeptides in healthy human blood was very low (about 2 to 50 pM) which is not enough to activate orexin receptors[18 ,19 ].
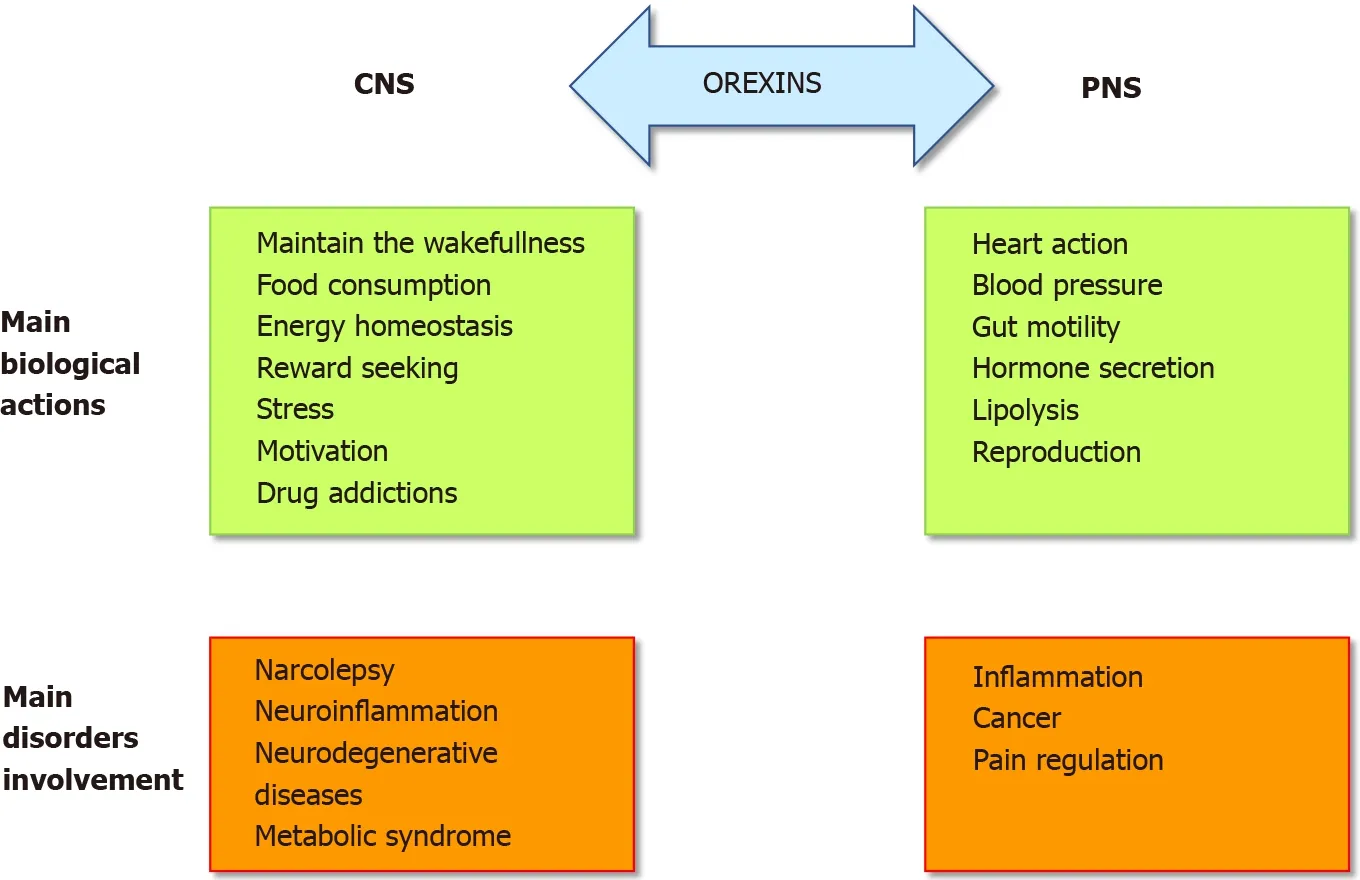
Figure 1 Pathophysiological roles of orexins/orexins receptors system. CNS: Central nervous system; PNS: Peripheral nervous system.
These biological effects were mediated through two orexin receptor subtypes, OX1 R and OX2 R which were coupled to Gq protein[10 ]. The interaction of orexins with its receptors led to the intracellular calcium release involving the phospholipase C (PLC)(Figure 2 ). Some reports have revealed that orexins were also able to activate the cAMP, PI3 K/Akt, JNK and MAPK/Erk1 /2 signaling pathways (Figure 2 )[13 ]. The crystallographic structure of OX1 R and OX2 R associated to the suvorexant antagonist was reported[20 ,21 ]. Recently, the structure of OX2 R complexed with OxB has been reported, suggesting that the molecular mechanisms which govern the activation or inactivation of receptors were located in the OX2 R orthosteric site[22 ].
In pathological conditions, an abnormal expression of OX1 R was observed in human peripheral organs. The presence of an ectopic expression of OX1 R in intestinal bowel disease (IBD) including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, in pancreatitis and digestive cancers as colon, pancreas and liver cancers, has been demonstrated[3 ].The role of the orexin system in various human pathologies such as narcolepsy[23 ],neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease)[24 ], ischemia[25 ], oxidative stress[26 ], chronic inflammation including IBD[10 ], multiple sclerosis[10 ] and metabolic syndrome[27 ] but also cancers[3 ], highlighted its potential therapeutic importance(Figure 1 ). In this context, the present review summarizes the impact of orexins and their receptors in chronic inflammation (i.e.,ulcerative colitis, multiple sclerosis, septic shock and metabolic syndrome) and cancers.
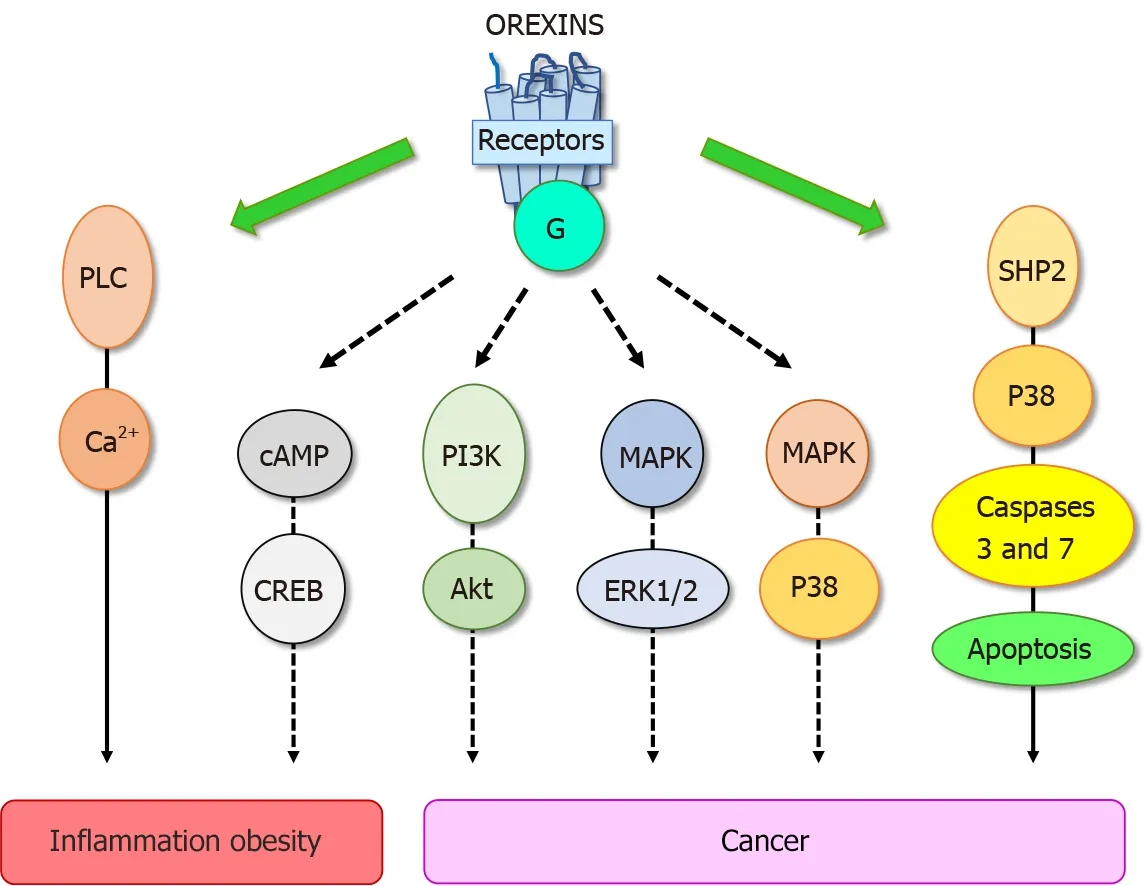
Figure 2 Main signaling pathways activated by orexins/orexins receptors system involved in peripheral diseases. PLC: Phospholipase C;cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB: C-AMP response element-binding protein; PI3 K: Phosphoinositide 3 -kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; MAPK: Mitogenactivated protein kinase; ERK1 /2 : Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 ; P38 : Mitogen-activated protein kinase; SHP2 : Src homology 2 domains of Src homology 2 -containing phosphatase 2 .
OREXINS AND DIGESTIVE CANCERS
Despite the constant progress of the therapeutic arsenal, cancer is still the second causes of death worldwide[28 ]. To date, the treatment range options include surgery,chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonotherapy, antibody therapy, gene therapy,immunotherapy which integrate recent treatments based on anti-PDL-1 and CAR-T cells[29 ,30 ]. Digestive cancers, including colorectal cancer (CRC), pancreas cancers(PC), liver cancer (HCC), gastric cancer and esophageal cancer represent the second cause of cancer worldwide behind lung cancer[29 ]. In addition, biliary tract cancers as cholangiocarcinoma (CCH) also belonging to digestive cancers is less frequent.However, it should be noted that the incidence of PC which is mostly depicted (94 %)by the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is constantly increasing[31 ]. The factors increasing risk of digestive cancer include not only tobacco smoke, alcohol use,low physical activity, and diet, but another high-risk factor has also been identified,chronic inflammation such as IBD, pancreatitis, liver fibrosis and metabolic syndrome[32 ]. As mentioned above, OxA displays anti-inflammatory properties in IBD and other inflammatory diseases. These data indicate that orexin could play a role in triggering cancer. In 2004 , our group tested the impact of 26 peptides including neuropeptides, hormones and orexins, on the cell growth of cancer cell line HT-29 derived from colorectal cancer[33 ]. The vast majority of these peptides had no significant effect on cell growth, only OxA and OxB inhibited the tumoral cell growth[33 ]. Analysis of this effect showed that orexins had no effect on cell cycle and cell proliferation but were able to induce a mitochondrial apoptosis in cancer cells[34 ,35 ].Apoptosis was mediated by OX1 R and OX2 R however, only OX1 R was ectopically expressed in human digestive cancers including CRC, PDAC, CHC and CCH[3 ,36 ].Moreover, we observed that OX1 R was also expressed in hepatic and lung metastasis from CRC[35 ]. It should be noted that OX1 R and OX2 R were not expressed in normal colon epithelium and in normal exocrine pancreas and liver[35 ,36 ]. However, as mentioned in the introduction, the main signaling pathway activated by orexin receptors involved the intracellular calcium release. Moreover, the inhibition of PLC enzyme which was activated by receptors in the presence of orexinsviathe Gq protein[37 ] was unable to inhibit the apoptosis process induced by orexins in cancer cells[33 ].These observations indicated that the orexins/OX1 R system triggered a new signaling pathway in cancer cells responsible of the pro-apoptotic peptide effect. Assessment of the new mechanism of action of orexins/OXR revealed that the interaction between orexins and their receptors induced phosphorylation of two immunoreceptor tyrosinebased inhibitory motifs (ITIM), present in the receptor sequences, induced by Src kinases[34 ,38 ]. Receptors phosphorylation led to the recruitment and the activation of tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 (Figure 2 ) followed by the activation of p38 mitogen-stress protein kinase, translocation of Bax protein into the mitochondria, release of cytochrome c which participates to apoptosome formation and then activation of caspase 3 and 7 inducing DNA condensation and fragmentation causing the cancer cell death[34 ,38 ]. In preclinical mice models, we reported that when cancerous cell lines,such as HT-29 or LoVo or cells obtained from human colon tumors, were subcutaneously xenografted to mice administration of OxA and OxB were able to drastically reduced the tumor volume by apoptosis[35 ]. Although, preproorexin and OxA were immuno-detectable in total colon, no detection of preproorexin was obtained in normal and dysplastic epithelium[35 ] suggesting that endogenous OxA has no impact on tumoral growth. The colon cancer treatment was based mainly on surgery and chemotherapy but the primary cause of chemotherapy failure was associated to drug resistance[39 ]. Global studies indicated that more than 90 % of patient cancer mortality was related to chemoresistance. The “gold-standard”treatment used in CRC was the 5 -fluorouracil (5 -FU). The development of HT-29 colon cancer cell line resistant to 5 -FU demonstrated that OX1 R was always expressed and orexins were able to induced pro-apoptotic effect in these cells suggesting that orexins response was conserved in drug-resistant cancer cells[35 ].
In PDAC, which represents the tenth most common cancer and the fifth in term of mortality[40 ,41 ], OX1 R expression was detected in 96 % of adenocarcinomas[36 ]. This expression was independent of the gender, patient age and tumor size[36 ]. OxA induced SHP2 -dependent apoptosis in AsPC-1 cells derived from human PDAC as well as in PDAC slices from tumor patients maintained in culture[36 ]. The study using preclinical mouse models xenografted with AsPC-1 cells or cells isolated from patient’s tumor indicated that OxA reduced the tumor development by induction of apoptosis[36 ]. OX1 R was expressed at the early stage of development of digestive cancers including PDAC precancerous lesions named pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and dysplastic polyps in colon[3 ,36 ]. As mentioned above, various OxA antagonists such as almorexant or suvorexant have been developed for the treatment of insomnia.Surprisingly, AsPC-1 cells treatment with those antagonists showed that these two compounds inhibited PDAC cell growth by apoptosis induction[36 ]. Similarly, the intraperitoneal injection of almorexant in preclinical models led to inhibition of the tumor development indicating that this antagonist acted as OxA which was a full OX1 R agonist[36 ]. These observations indicated that almorexant which blocked the intracellular calcium release induced by orexins was fully able to activate the proapoptotic signaling pathway in cancer cells. This type of molecule, able to discriminate various signaling pathways activated by one type of receptor, was termed biased ligand[42 ]. A very recent study on cryo-electron microscopy structure of OX2 R active state revealed that one residue presents on the binding site play a central role in the receptor transition from the inactive to the active state[22 ]. This report could suggest that one or more residues in the receptor binding site drive the activation/inactivation of various signaling pathways. Moreover, this study confirmed the important role of Lys11 and Lys15 residues present in OxB, for the peptide interactions with its receptors[43 ]. OX1 R was also expressed in HCC[44 ] and many studies reported that OxA had pro-apoptotic properties in gastric cancer[45 ], cholangiocarcinoma[3 ], esophagus cancer[35 ] but also in non-digestive cancer including prostate cancer[46 ] and neuroblastoma[35 ] in which apoptosis induced in these cancers by OxA was SHP2 -dependent. Some report revealed that orexin receptors were also expressed in cortical adenomas[47 ], pheochromocytomas[48 ] and in endometrial carcinoma[49 ].Observations indicated that OX1 R was expressed in early stages of colon and pancreas cancer development[3 ,36 ] legitimately asking the following question: is the OxA/OX1 R system is involved in chronic inflammation which may represent an important risk factor in tumorigenesis?
OREXINS AND IBD
The two major phenotypes of IBD were represented by ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD). These two disorders were characterized by a chronic inflammation of the intestine mucosa mediated by the immune system[50 ]. CD may affect any part of gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus but often it concerns the part between the small intestine and the colon which can involve the deeper organ layer[51 ]. Whereas, UC affects mainly the colon and the rectum with a distal to the proximal gradient, characterized by superficial lesions having relapsing-remitting cycles[52 ]. These inflammations were characterized by persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloody stools, great fatigue, immune cell infiltration and weight loss[52 ]. To date,the etiology of these disorders remains unknown. IBD was associated to an increased risk (2 -6 times) to develop CRC as compared to the general population[32 ,53 ]. Identification of UC pathogenic factors revealed that this disease involved numerous factors:genetic predisposition, epigenetic modifications, environmental factors including diet,geography, modern lifestyle, smoking, pollution, infections, exercise…, gut microbial factors (dysbiosis), inflammasome signaling pathways, endoplasmic reticulum stress and a disruption of immune response[54 ,55 ]. The treatment of UC was based on the severity and extension of the disease, involving the use of anti-inflammatory compounds such as 5 -aminosalicylates, corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs such as azathioprine, 6 -mercaptopurine, methotrexate, cyclosporine A, etc.[56 ]. The understanding of the role of various cytokines [Interleukin (IL)-6 , IL-1 β, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα)] and other soluble mediators in UC, led to the development of therapies based on anti-TNFα, anti-IL-12 /23 , anti-integrin α4 β7 and Janus kinase inhibitors[57 ]. The use of these drugs used alone or in combination has undoubtedly been a substantial advance in UC treatment in the last few decades.Unfortunately, important progress remains to be made to obtain curative treatment of IBD patients. The discovery of new targets is a main challenge for the therapeutic treatment of UC. In that respect, GPCR family represents a potential and innovative source of new targets. Several encouraging examples of GPCRs could play this therapeutic role in IBD through interaction with cannabinoid receptors[58 ],neuropeptide receptors[59 ], histamine receptors[60 ] and chemokine receptors[61 ].Taking into account that OX1 R was expressed in colon cancer and in precancerous lesions[10 ], the question is “Is OX1 R expressed in IBD which represents a high risk to develop cancer?”. Indeed, OX1 R has been detected in inflamed mucosa from patient suffering of UC and CD[62 ]. It should be noted that OX1 R was not expressed in normal human intestinal epithelium[35 ]. An epidemiologic study revealed that narcoleptic patients presented a higher prevalence to develop IBD[63 ]. To determine the role of OxA/OX1 R system in ulcerative colitis, the classical DSS-induced colitis mouse model which reproduced the acute phase of colitis, was used. In this model,OX1 R was ectopically expressed in inflamed mucosa[62 ]. Daily intraperitoneal injections of OxA revealed on this model, an anti-inflammatory effect of the peptide on the mucosa integrity and intestinal barrier[62 ]. OxA inhibited the secretion of various cytokines including IL-6 , TNFα, IL-8 , IL-1 β, IL-1 α, IL-17 and MCP-1 cytokines in intestinal mucosa and in immune cells extracted from colon[62 ]. In contrast, these antiinflammatory effects were reverted by the SORA1 antagonist, SB-408124 demonstrating the specific effect of OxA which was fully mediated by OX1 RviaPLC signaling pathways (Figure 2 )[62 ]. A recent report also showed that OxA was able to prevent the intestinal barrier disruption caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)[64 ]. To study the role of OxA/OX1 R system on chronic inflammatory phases of UC, a genetically engineered mouse model invalidated for the IL-10 cytokine and NADPH Oxidase 1 was used. OxA peripheral injections induced the same anti-inflammatory effect compared to the DSS-induced colitis mouse model. This anti-inflammatory impact was mainly mediated by the activation of PLC that led to intracellular calcium release and inhibit Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation which plays a key role in proinflammatory cytokine secretion[65 ]. Even if only few studies have been devoted to the peripheral role of OxA in IBD, it seems clear that OxA/OX1 R system displays antiinflammatory properties in UC and may represent a promising new target in the treatment of this disease.
OREXINS AND SEPTIC SHOCK
Septic shock is a dramatic medical condition that represents a major health problem in response to a complex disorder arising from the dysregulation of an inflammatory response to infection that leads to low blood pressure and cellular metabolism abnormalities. Sepsis is caused not only by bacteria, but also by fungi, viruses or parasites. It could be located most frequently in the brain, lungs, urinary tract, skin or abdominal organs. It can lead to multiple organ dysfunction syndromes and death[66 ]. The pathophysiology of septic shock is not completely understood but an immune and coagulation response to the infection is the key role in the development of severe sepsis involving pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. Septic shock was characterized by a widespread inflammatory response which produced a hypermetabolic effect. This effect was manifested by an increase of protein catabolism,cellular respiration and metabolic acidosis which was compensated by respiratory alkalosis[66 ]. LPS or endotoxins are major cell wall components of Gram-negative bacteria, which induce systemic inflammatory response responsible of sepsis[67 ]. LPSinduced endotoxemia mouse model is one of the several well-studied animal models of septic shock[68 ,69 ]. Sepsis is characterized by an inflammatory cytokine secretion of TNFα, IL-6 , IL-1 β, and MCP-1 [70 ]. NF-κB represents a therapeutic target since it induces pro-inflammatory gene transcription implicated in the septic shock[71 ]. In fact, in LPS-induced septic shock murine models, NF-κB inhibitors such as parthenolide and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate[71 ], or an antagonist of toll-like receptor 4 , the FP7 [72 ] reverse sepsis effects on organ failure and hypotension. G proteincoupled receptors (GPCRs) may be potential targets for pharmacotherapy in sepsis.They could be involved in re-establishment of vascular endothelial barrier and alleviation of sepsis-induced organ dysfunctions. Several GPCRs and their associated ligands have been shown to play a role in septic shock but also in its treatment,including chemokine receptors (i.e., ACKR2 , CCR2 , CCR5 , CX3 CR1 , and CXCR1 ),neuropeptides (i.e., VIP, neuropeptide Y, ghrelin, urotensin II, ocytocin, vasopressin,neurotensin, orexins, substance P, and apelin), proteases [i.e., thrombin (PAR1 and PAR2 )], lipid derivatives (i.e., N-arachidonylglycine) and amines (i.e., catecholamines,dopamine histamine, melatonin)[73 ]. Some reports indicate that intracerebral administration of orexin regulated body temperature and heart rate and increased the adrenocorticotropic hormone level in a mouse sepsis model induced by a caecal ligation associated to perforation[74 ]. The central administration of OxA to mice with endotoxin shock was shown to increase survival[75 ]. This report indicates that the exogenous administration of OxA was able to cross the blood barrier in systemic inflammation condition and induced an inhibition of IL-17 , IFNγ, IL-6 and TNFα secretion[75 ]. Moreover, OxA restored body temperature and cardiovascular function in LPS-induced mice[75 ]. These authors hypothesized that OxA which was able to improve the survival of mice under septic shock condition, acts on the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systemviathe CNS, demonstrating a putative interest in treatment of septic shock.
OREXINS AND MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune dysregulation of the blood-brain barrier that affects the CNS through the migration of activated inflammatory cells. In the world,2 .3 million people are diagnosed with MS. The major causes listed for MS are inflammation, demyelination, oligodendrocyte loss, axonal loss and neurodegeneration. The neurodegeneration is a consequence of the inflammation induced by the demyelination which is related to the immune system activation[76 ]. T-cell mediated destruction of myelin and the autoimmune responses induced are still conjectural.However, this chronic inflammatory process involved a Th1 /Th17 autoimmune response in the spinal cord and brain[77 ]. More recent data define MS as a primary degenerative disorder, which begins in oligodendrocytes that leads to neuroinflammation and to demyelination[78 ]. These neurodegenerative processes are present in different brain regions, including the hypothalamus and the orexinergic neurons that projected to various brain region encompassing hippocampus, cortical areas, striatum,and spinal cord[79 ]. As mentioned above, orexin neurons which represent about 70 ,000 neurons in the human brain, were involved in the regulation of sleep, pain,cognition, anxiety, alertness and motor function[80 ] and few studies proposed that orexin dysfunction could be connected to fatigue in MS[81 ]. Moreover, orexins have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties by improving experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis pathology[82 ]. In MS the T helper cell 1 cytokines are produced in large concentration by myelin activated T cells to activate microglial cells and macrophages. Then, they induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines,reactive oxygen, and reactive nitrogen species productions which are associated to demyelination and neurodegeneration. OxA inhibited reactive oxygen species production and also interleukin IL-1 β, IL-6 , and IL-8 expression. Similarly, to the inhibition of NF-κB activation by OxA in IBD[62 ], OxA was also able to reduce, in MS,the activation of NF-κB signaling pathways which leads to the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3 ) and also to a MMP13 enzyme reduction in the tissue inflammation site[83 ]. Furthermore, OxA administration was shown to be able to cross the blood-brain barrier and reach the CNS in LPS-induced septic shock murine models[75 ].
Cerebral ischemia, and neurodegeneration induced by severe oxidative stress models, have been shown to be reduced by OxA. Moreover, OxA can active glucocorticoid secretion and the sympathetic nervous system through catecholamines releases which had anti-inflammatory properties that reduces immune response[85 ]. In Parkinson’s neurodegeneration disease, OxA had a neuroprotective impact[10 ] and in Alzheimer’s disease, OXR activation also displayed a neuroprotective action[85 ].Recently, the use of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model mimicking multiple sclerosis shown that orexins were able to induce anti-inflammatory effects. The intraventricular injections of OxA reversed clinical symptoms of EAE including partial or total paralysis of the two hind legs and death[82 ]. The authors also reported that treatment of the EAE mice model with OxA induced a large reduction in demyelination, microglial activation, and astrogliosis. OxA was shown to reduce nitric oxide synthase gene expression, an oxidative stress target which controls EAE pathology in the CNS. MMP9 (an inflammation enhancer) and IL-12 (a proinflammatory cytokine) expressions were also downregulated. Otherwise, OxA treatment limited CD4 + T lymphocytes infiltration and Th1 and Th17 cytokines production induced by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG35 –55 ). OxA treatment also inhibited chemokine production as MCP-1 /CCL2 and IP-10 /CXCL10 .Moreover, OxA reduced the cytokine production including IFN-γ, IL-17 , TNF-α, IL-10 ,and TGFβ in the CNS[82 ]. Some of the common symptoms associated with MS are fatigue and sleep disturbances suggesting that MS and narcolepsy/catalepsy can share common genetic aspects[86 ]. Indeed, the physiological and psychological effects of MS are more severe in patients with sleep disorders[87 ]. To conclude, orexins which displayed immuno-modulating and neuroprotective properties reinforced by the orexinergic system involvement in the pathological development of multiple sclerosis become an interesting target as anti-inflammatory molecules for MS.
OREXINS AND METABOLIC SYNDROME
Control of Energy balance and metabolism is complex, they are monitored by the nervous and humoral systems. This section will consider the regulation of these functions by OxA and OxB or through their specific receptors. Orexins that are expressed in the lateral hypothalamus were first identified as factors that enhance feeding behavior. However, Haraet al[88 ,89 ] shown that orexin deficiency or postnatal ablation of orexin neurons induced mice obesity supporting that orexins are negative regulators of energy metabolism. Moreover, in human narcolepsy, related to orexin deficiency, is associated to a greater body mass index and to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome[90 ]. In contrast orexin overexpression protects rodents from dietinduced obesity and improves glucose control[91 ].
Orexin functions have been mainly described in the central nervous system but orexins and their receptors are also detected in various organs including the intestine,pancreas, adrenal glands, kidney, adipose tissue and reproductive tract. In peripheral tissues, orexins could affect insulin release, intestinal mobility, hormone secretion and blood pressure regulation[92 ]. Body weight and energy homeostasis are precisely controlled by many metabolic and hormonal factors including OxA. Orexins and their receptors have been located in the endocrine pancreas where they were co-located with insulin and beta cells[93 ] suggesting the role of orexin receptors in the glucose homeostasis. Some specificity of both isoforms of orexin and of each receptor in the control of energy balance have been reported but their roles remain unclear[92 ,94 ].Recently plasma OxA have been negatively associated with insulin resistance and positively with insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes suggesting a functional role of orexin in the development of correlated obesity diseases[95 ]. These data support that orexin can modulate appetite, energy expenditure and glucose and lipid metabolism.
Orexin and food intake
Intra-cerebroventricular injections of OxA was shown to increase food intake in rats,while OxB was less effective[96 ]. However, orexin infusion stimulates feeding during the light period but not at the dark phase and induces no significant increase of the total food intake over 24 h[97 ]. In a previous study we reported that chronic treatment of mice under standard diet with daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of OxA did not have any important effects on energy intake and energy expenditure, even if the i.p.OxA injections were sensed by the hypothalamus and affected the expression of several receptors and neurotransmitters in the hypothalamus[98 ]. Moreover, it has been proposed that orexin-induced feeding not simply follow the arousal state but increase the signal of low glucose and hunger[99 ].
Orexin and obesity
OxA deficiency is associated with narcolepsy and to higher risk of obesity suggesting that OxA deficiency can contribute to glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity.Transgenic mice in which orexin-containing neurons are ablated develop narcolepsy and obesity[88 ]. However, overexpression of OX2 R in rats protects them from dietinduced obesity and improves glucose control and leptin sensitivity suggesting that triggering OX1 R or OX2 R did not regulate the same pathway (Figure 3 )[91 ]. Moreover,lack of the orexins decreased energy expenditure and increase adiposity, principally through a reduction of physical activity. At the opposite exogenous OxA attenuates adiposity in rats and mice ingesting high fat diet. We also reported that i.p. injection of OxA to mice ingesting standard diet induced a small but significant reduction of visceral fat mass and adiposity but we did not observe any decrease of the subcutaneous fat, suggesting a lesser sensitivity of these fat pads to OxA[98 ]. These results support the potential anti-obesity effects of orexins. However, conflicting results have reported by different studies.In vitrostudies using 3 T3 -L1 showed that OxA stimulates preadipocytes proliferation whereas OxB suppresses. Both OxA and OxB can stimulate pig adipocytes but no convincing evidence have been reported in humans[17 ,100 ]. It has also been shown that OxA contributes to changes of the white fat morphologyviastimulation of preadipocytes proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis but OxA has no effect on lipolysis in fat tissue derived from human explants[101 ]. Moreover, OxA can raise corticosterone levels and glucocorticoids that can stimulate lipolysis in adipocytes[102 ]. In addition,in vivostudies reported that OxA potentiates physical activity and energy expenditure which reduce lipid accumulation.
Orexin and brown adipose tissue
Brown fat cell functions are different they generate heat. Many data support that OxA is required for adipogenesis of brown adipose tissue (BAT) in rodents. Activation of brown adipose tissue is controlled by environmental and hormonal factors as well as sympathetic neurons[103 ]. Ida et al[104 ] reported that cold stress stimulates the expression of preproorexin mRNA expression suggesting that orexin may be involved in body temperature control. Moreover, ablation of hypothalamic orexin neurons reduced BAT thermogenesis[105 ] and at the opposite central administration promotes thermogenesis[106 ]. A recent report, contrary to previous studies[107 ,108 ], did not show a direct effect of orexin on BAT development but a regulation of BAT by orexin signaling through the sympathetic system[109 ]. Moreover,in vivoOxA fail to stimulate the differentiation of human brown preadipocytes as well as the expression of the genes regulating thermogenesis.
Orexin and regulation of glucose homeostasis
Orexin deficiency has been associated with obesity, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in rodents and humans[110 ]. OxA i.p. injections have been shown to increase GLUT4 expression in the liver suggesting that orexin can improve glucose uptake in hepatocytes, adipocytes and skeletal muscle[111 ]. Moreover, several studies show that orexin stimulates insulin secretion[112 -114 ]. In rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM), an obesity treatment with OxA decreases fasting glucose and plasma levels of TNFα improve glucose control by increasing insulin sensitivity, increases plasma concentration of adiponectin and protects β-cells from apoptosis[114 ]. More studies are needed to better elucidate the mechanisms by which OxA modulates adipokines levels and other metabolic parameters such as the ability to reduce glucose.This effect can be a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of DM and of its complications.
To summarize, a variety of data are presented in the literature. This disparity depends if the studies presentin vitroorin vivodata and if the orexin administration was central (intraventricular) or peripheral. More studies will be needed to better define the mechanism by which the orexins regulate food intake, energy expenditure and glucose metabolism.
CONCLUSION
Since the identification of orexin peptides in hypothalamus demonstrating their crucial roles in sleep/wake regulation, the importance of their peripheral effects revealed their potential interests as therapeutic molecules in a wide range of human pathologies including also digestive diseases such as acute/chronic inflammation (IBD, septic shock, MS), metabolic syndrome and cancers.

Figure 3 Main actions of orexins and their receptors on diet-induced obesity.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年44期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年44期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Proton pump inhibitors and colorectal cancer: A systematic review
- Autosomal recessive 333 base pair interleukin 10 receptor alpha subunit deletion in very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease
- Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in the presence of penicillin allergy
- Challenges in the diagnosis of intestinal neuronal dysplasia type B: A look beyond the number of ganglion cells
- COVID-19 : Effect on gastroenterology and hepatology service provision and training: Lessons learnt and planning for the future
- Role of early transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt in acute variceal bleeding: An update of the evidence and future directions
