Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Head and Neck Information Needs Questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer and their caregivers
Yu Li ,Lihui Liu ,Rong Yn ,Chunxing Su ,Hong Guo ,Xioyu Li ,Shujin Yue ,*
a School of Nursing,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China
b Qilu Hospital of Shandong University,Ji'nan,China
c Beijing Shijitan Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing,China
d Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute,Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences,Ji'nan,China
Keywords:Caregivers Chinese Head and neck neoplasms Needs assessment Reliability Surveys and questionnaires Validity
ABSTRACT Objectives: This study aimed to assess the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Head and Neck Information Needs Questionnaire (HaNiQ).Methods: The HaNiQ was translated into a Chinese version using internationally recognized forwardand back-translation procedures.The reliability and validity of the HaNiQ were measured using Cronbach’s α coefficient,split-half reliability,exploratory factor analysis,and Pearson correlation analysis.Results: A total of 207 patients in different head and neck cancer (HNC) stages and 174 caregivers completed the Chinese version of the HaNiQ.Internal consistencies varied between good and very well(Cronbach’s α coefficient 0.74-0.90);the split-half coefficient and the content validity index(CVI)of the questionnaire were 83.5% and 83.33%,respectively.The cumulative contribution rates of the 5 subscales in patients with HNCand their caregivers were 62.41%and 61.19%,respectively.However,there are some differences between the Chinese questionnaire for caregiver and the original questionnaire regarding the attribution of items.Items 22,23,and 27 in the Psychosocial subscale of the English version were assigned to the Survivorship subscale in the Chinese version for caregivers.Conclusions: The results demonstrated that the Chinese version of the HaNiQ is a reliable and valid instrument for measuring the information needs of patients with HNC and that of their caregivers.Though the structure of the Chinese version was different from the English version for caregivers of HNC patients,the Chinese version of the HaNiQ appears to be reliable and would benefit from further testing.
What is known ?
? Nurses offer information support in clinical practice.
? The Head and Neck Information Needs Questionnaire (HaNiQ)can measure the information needs of head and neck cancer(HNC)patients and their caregivers.
What is new ?
? This study translates the HaNiQ into a Chinese version and verifies its reliability and validity,which provides a specific instrument to measure the information needs of HNC patients and their caregivers.
1.Introduction
Head and neck cancers (HNCs) are defined according to their anatomical location and include cancers of the lip,oral cavity,larynx,nasopharynx,oropharynx,hypopharynx,nasal cavity,paranasal sinuses,thyroid gland,salivary glands,and the like [1].According to the GLOBOCAN 2020,HNCs of the lip,oral cavity,larynx,and pharynx are cumulatively in the top 10 most commonly diagnosed adult cancers worldwide,with 878,348 new cases and 444,347 deaths[2].The 2015 update of nationwide cancer statistics of the National Central Cancer Registry of China (NCCRC) [3]showed that the number of new cases and deaths for HNCs was more than 225,100 and 77,500,respectively.Among the various diseases,HNCs stand out because of the associated poor prognosis,with a lower five-year survival rate compared with other cancers,depending on the tumor site and stage.
The duration of HNC treatment ranges from 12 to 36 months and is associated with a significant decrease in the quality of life[4]and higher levels of depression and anxiety compared with other cancer patients.The increased rate of depression in patients with HNC is related to both the treatment and tumor-related physical symptoms,with two identifiable peaks of depression occurring one year after treatment [5].Furthermore,there is a significant deterioration in patients’ symptoms in the first year after treatment,while a slow recovery ensues,symptoms nevertheless persist [4].Identifying the needs of patients with HNCs is the first step in helping medical workers provide treatment and care to patients.Besides,the guidelines also list this as the first step in developing appropriate interventions[6].Owing to the particular location,HNC can cause potential profound impairments to speech,swallowing,vision,hearing,and physical appearance during treatment.Therefore,patients with HNC are more emotionally traumatized and have more information needs than other cancer patients [7].Information support is an important avenue through which medical staff can better provide health services for patients with HNC and is closely related to the treatment,prognosis,rehabilitation,and even recurrence monitoring of patients.Nursing care of patients with HNC requires a multidisciplinary and cooperative nursing approach.Thus,information support incorporated a wide range of areas,including tumor,nutrition,dentistry,speech,rehabilitation,and so on [8,9].
HNCs are complex and involve a wide range of fields:oncology,surgery,dental radiation,oncology,pathology,linguistics,rehabilitation medicine,and nursing.Although nurses have been offering information support in clinical practice as an important part of multidisciplinary nursing,there is often no systematic method of information support or planning for patients with HNC,and the information support is limited[10].In a study of 93 HNC survivors,caregivers’health behaviors and self-care behaviors play a positive role in patient care,and there is a significant gap in addressing communication and informational needs between patients and caregivers [11].Due to the differences in tumor sites,treatment methods,time of complications,and course of the disease,the breadth and time of information needs are also different.Furthermore,a large number of studies have shown that both patients with HNCs and their caregivers have a large number of unmet information needs,it will harm the patient’s recovery.Effective assessment of the information needs of patients with HNCs and their caregivers is the premise of providing personalized information support,as well as the key link of optimizing nursing work to improve medical satisfaction.
In China,the tools provided to patients with cancer and their caregivers are either universal or designed specifically for a particular type of cancer,and they encompass a broad range of requirements.However,the information needs of HNC patients and their caregivers have not been appropriately measured.Currently,the Head and Neck Information Needs Questionnaire (HaNiQ)developed by the Head and Neck Cancer Research Centre of Liverpool Hospital in Australia has been validated and popularized in Australian patients[12].The questionnaire has good reliability and validity,and there are two versions,one in English and the other in Portuguese.A literature review revealed that the Chinese version of the questionnaire has not yet been developed and verified in Eastern countries,including China.Therefore,the study aims to translate the HaNiQ into a Chinese version and verify its reliability and validity.
2.Methods
2.1.Instrument
The HaNiQ,a specific tool for assessing the information needs of patients with HNC and that of caregivers,was developed in 2013 by Dr.Dall'Armi’s team from the Head and Neck Cancer Group of the Australian Institute of Oncology[12].The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the total questionnaire is 0.94,and the Cronbach’s α coefficient of each area is 0.73-0.89.Presently,there are two versions,in English and Portuguese.The HaNiQ score is based on the responses elicited in 5 topic domains that include 30 items:Disease Profile(3 items),Treatment (8 items),Side Effects (8 items),Psychosocial (8 items),and Survivorship (3 items).Based on the information needs of patients with HNC and their caregivers,each item has four response choices that are assigned different score values.Each item has four choices:“not important=1”,“a little important=2”,“important=3”,“very important=4”.In terms of percentages,a higher number represents an area of greater importance for information provision.For all subscale scores as well as the total score,increasing scores represent higher priority areas for information provision.The authors Dr.Simpson and Dr.Dall'Armi were both in agreement about the study design.
2.2.Study design
This study is a psychometric study with a cross-sectional design to verify the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of HaNiQ.The study was conducted in three stages to reach operational conceptual,semantic,and measurement equivalence between the original English version and the Chinese version [13].In the first stage,a Chinese version of the HaNiQ was created through translation and cross-cultural adaptation.In the second stage,the content validity of the HaNiQ was evaluated,and the measurement properties were examined in the third stage.
2.2.1.Translation and cross-cultural adaptation
To ensure the conceptual,semantic,measurement equivalence,and content validity,an integrative translation method was employed to translate the English version into Chinese [14,15].Forward and backward translation,developed by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer,was employed[16].
The study included 5 researchers who either had experience in relevant clinical work or were familiar with Chinese and Western culture.Initially,2 forward-translators who were native Chinese speakers and fluent in English completed the translation independently.Then,the two translations were compared and discussed by a former researcher in step 1 and another researcher who was proficient in both languages and could judge the quality of the translation.The researchers discussed some of the obvious differences,and once all the questions were resolved,a first version of the HaNiQ was translated.Following this step,the Chinese version of the HaNiQ was translated into English by two other Chinese researchers who had not seen the original version and had academic experience in English environments.A second version of the HaNiQ was then translated.The researcher in step 2 and the two researchers in step 3 discussed the two translated versions of the HaNiQ.After all the questions were resolved,the Chinese version was considered complete.Last but not least,a comparison was made of the differences between the English version and the original of the HaNiQ,and all the detailed records of each step in the process were carefully collated.
We sought to ensure that the translated version matched the original version of the HaNiQ,and that linguistic differences and expressions were clarified in the translation process.Because there were several places where direct translation was inappropriate,it was necessary to change the order of words or modify some words to match the Chinese language.The full details and questions about the translation process are summarized in an interim report.A panel of 8 experts(3 HNC experts and 3 clinical nurse specialists,2 individuals from the teaching and research staff) evaluated and validated the Chinese version.The Chinese version of the HaNiQ was finally considered ready for pilot-testing with 30 patients with HNC and their caregivers,and the results indicated that the Chinese version of HaNiQ was understandable.
2.2.2.Content validation
Content validity is primarily used to assess whether the items in the questionnaire represent the measured indicators or dimensions.This validity is usually quantified using the content validity index(CVI)and has its own rating system(not relevant=1,sometimes relevant=2,quite relevant=3,highly relevant=4).The higher the item score,the better the content reliability[17].We usually use Lawshe’s content validity index to determine the CVI[18,19].Based on this method,we selected 8 experts from relevant fields to evaluate the content validity [20].All experts were required to have more than 10 years of working experience in HNC.There were 3 HNC experts and 3 nurses,as well as 2 individuals from the teaching and research staff in head and neck oncology.
2.3.Participants,setting and procedure
A sample of patients with HNC and their caregivers was included in this study.The study was open to patients in all stages of HNC based on their diagnosis who were undergoing treatment(palliative treatment).The participants were recruited from 5 cancer hospitals in China between April and September 2018.The sample size was estimated according to the principle that the surveyed number was 5-10 times the number of items.HaNiQ contained 30 items.Thus,the total sample size was estimated to be 150-300.The inclusion criteria were patients:1) met the clinical diagnostic criteria of HNC and whose health condition was stable,2) were more than 18 years old at the time of diagnosis,3) were conscious and able to understand and respond appropriately,and 4)knew the truth about their disease and volunteered to take part in the study.Patients were excluded if they 1) had complications associated with organic lesions of important organs,such as heart,brain,kidney,etc.,or 2) had a history of mental illness and were taking psychotropic drugs.The caregivers of HNC patients were eligible to participate:1)once the patient was recruited,they were invited to identify a caregiver who could also participate,2) more than 18 years old and 3) could communicate,express themselves and write.Caregivers were excluded if they had a mental illness.All patients with HNC and their caregivers participated voluntarily in this study.
After the completion of the Chinese version,30 representative patients with HNC and their caregivers were invited to participate in a preliminary experiment.During the pilot study,a researcher asked the subjects how they felt and whether they understood the contents of the questionnaire.The participants’ suggestions and feelings were recorded,and the patients’questions and completion time were noted.For the reliability study,the HaNiQ was administered to patients with HNC and their caregivers.After the preliminary experiment,a formal investigation was conducted.
2.4.Statistical analysis
In this study,descriptive statistical methods were used to analyze the demographic data and basic clinical data.The internal consistency of the HaNiQ was measured by Cronbach’s α coefficient and Split-half reliability[21].The content validity was expressed by CVI,and the structural validity was evaluated by exploratory factor analysis(EFA)and Pearson correlation analysis.First,Bartlett’s test of Sphericity and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) were used to test whether the sample was suitable for factor analysis.Second,if the sample size was sufficient,the principal factors(PF)and maximum variance method were used to analyze the EFA of the questionnaire[22].In the process of extracting factors,eigenvalues are usually required to be greater than 1 and are regarded as a common factor.The factor rotation method of orthogonal rotation,the varimax method,was used to extract factors,and all the statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS statistical program (version 22.0).
2.5.Ethical considerations
Cancer patients and their caregivers are considered a vulnerable group due to the nature of the disease and the stress that they experience,especially in families undergoing palliative care.However,early studies suggested that this group may be grateful for the opportunity to participate in a study and may benefit from their involvement [23,24].During the validation process,an informed consent that outlines the study’s basic ethical principles,which are not considered harmful to the study participants,is obtained.Furthermore,the patients and caregivers involved are aware of the patient’s real health condition.At the same time,we emphasized the voluntary aspect of completing the questionnaire before responding,which allows researchers to terminate and withdraw from the study at any time.When analyzing and submitting data results,the participant’s identifying information is protected following the principle of confidentiality.Written informed consent was signed by all participants.This study was conducted under the approval of the hospital’s Ethics Committee and the support of the relevant department leaders.
3.Results
Participants completed a Chinese version of the questionnaire after providing informed consent during the clinical visit.A total of 220 patients with HNC and 180 caregivers participated in the study,and 207 valid questionnaires from patients with HNC and 174 valid questionnaires from their caregivers were included in this analysis.Questionnaires with a response rate of less than 70% were excluded.The effective response rates of patients and caregivers were 94.1%and 96.7%,respectively.Most patients were also willing to talk about their information needs and feelings when receiving information support.
The patients were from 18 provinces in China,and 38.1% (145/381) of the total participants were from Beijing.The average duration of care was 3 months.Clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1 and their caregivers in Table 2.
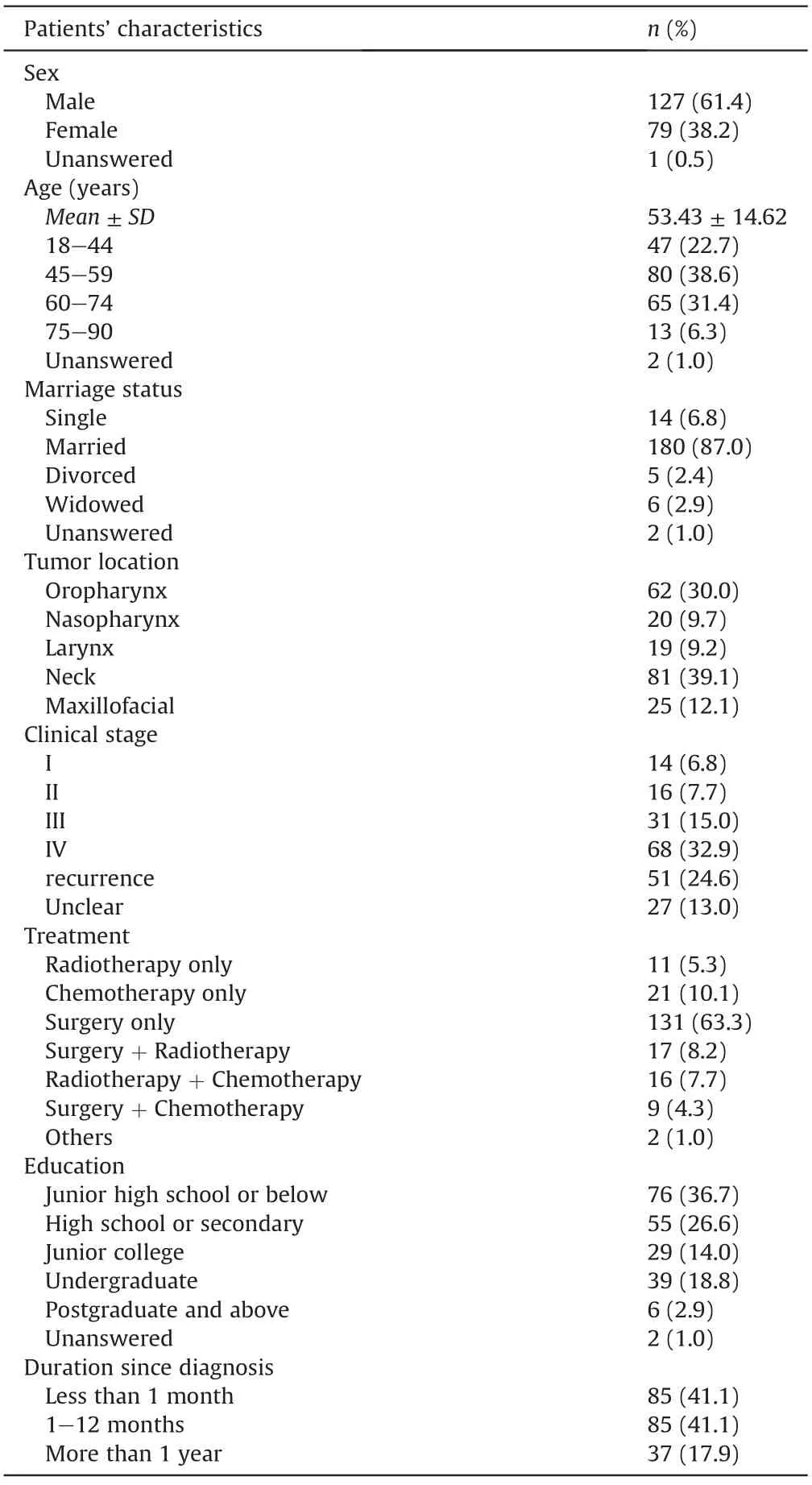
Table 1Demographic information of patients with head and neck cancer included in the study (n=207).
Experts made a conservative assessment of the contents of the Chinese version of the questionnaire.The validity of the questionnaire was 83.33% (content validity greater than 80% indicates that the questionnaire is fine) [25].The clarity and appropriateness of each item ranged from 80 to 100%.The item-level CVI (I-CVI) was 0.875(when the number of experts was more than 6,it was no less than 0.78) [25].The scale-level CVI (S-CVI) of the scale level was 0.979 (not less than 0.8),and the average S-CVI=0.925.The total number of experts in this study was 8,and 7 of them scored 3 or 4on the overall scale of the questionnaire.The I-CVI value of 0.875 and the Kappa was 0.88,indicating that the consistency of the questionnaire was fine among different experts.
The correlation between items and the total score was used to select individual items.The correlation coefficient less than 0.3 indicates the homogeneity between this item and the total score of the questionnaire is not high,that is recommended to delete.For HNC patients,the correlation coefficients ranged from 0.528 to 0.719.For the caregivers,the correlation coefficients ranged from 0.398 to 0.708.These results showed that correlations between single items and the total scale were significant,and no item was deleted.The structural validity of the Chinese version of the questionnaire was analyzed using EFA.The KMO of the scale for patients and their caregivers was 0.910 and 0.884,respectively,indicating that the questionnaire was suitable for EFA when the sample was sufficient.Bartlett’s test of Sphericity showedP<0.01,which indicated that the EFA was meaningful.The cumulativecontribution rates of the five factors in the two populations were 62.41% and 61.19%.In this study,five factors (i.e.,Disease Profile,Treatment,Side Effects,Psychosocial,and Survivorship) were represented in both the patients and caregivers.However,while the Chinese version of the questionnaire for patients had the same structure as the English version,for caregivers,the structure of the Chinese version was different from the English version.Items 22,23,and 27,which were in the Psychosocial subscale in the English version,are now in the Survivorship subscale (Table 3).

Table 2Demographic information of caregivers of patients with head and neck cancer included in the study (n=174).
Internal consistency reliability of the total HaNiQ,as calculated by Cronbach’s α coefficient and Guttman split-half coefficient,was 0.82 and 0.84 in the sacle for patients with HNC,and 0.78 and 0.81 in the sacle for the caregivers(Table 4).
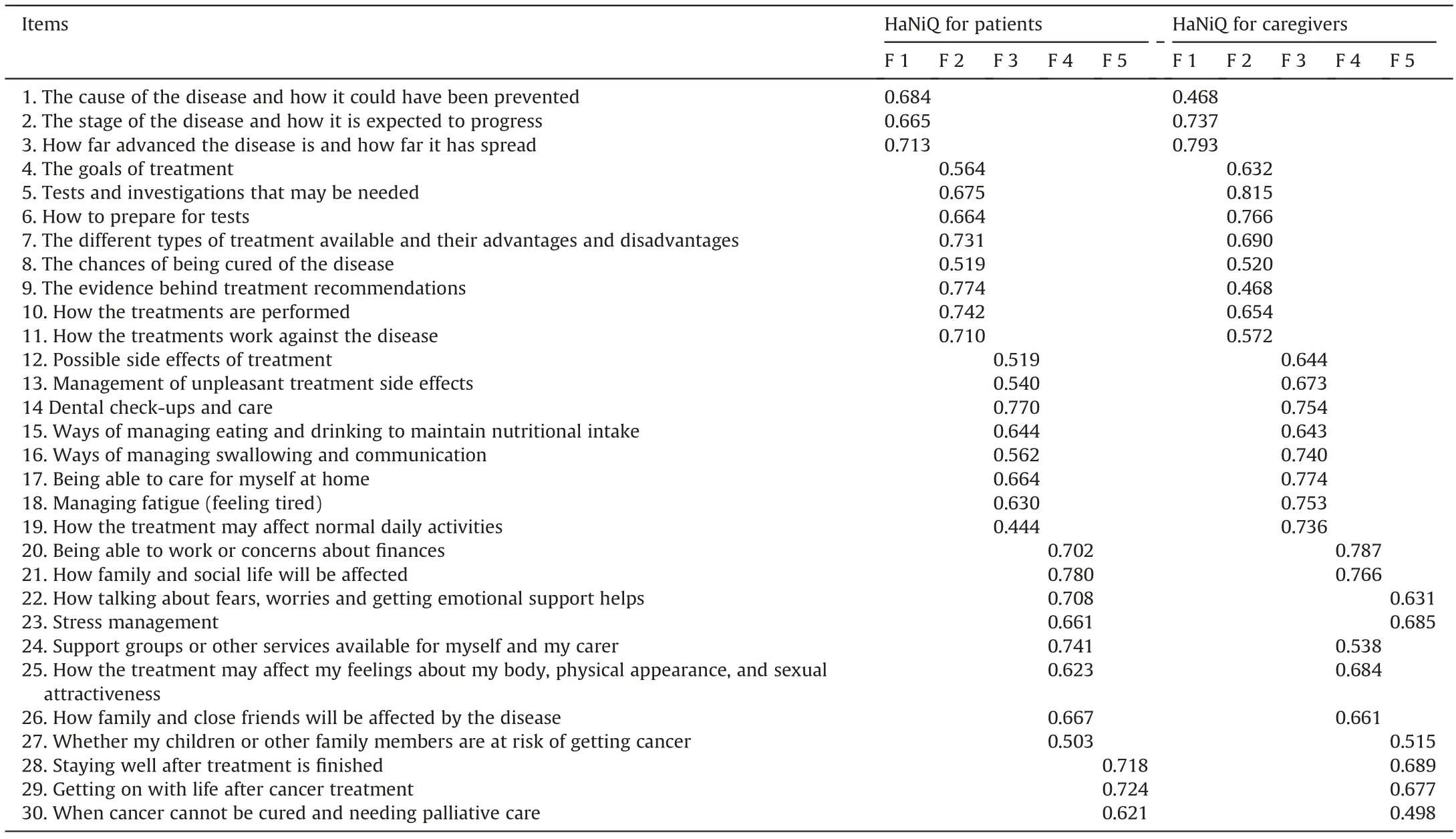
Table 3Principal component analysis of the Chinese version of the HaNiQ

Table 4The stability of the questionnaire was measured by the Cronbach’s α coefficient and Guttman split-half coefficient.
4.Discussion
Providing information support to patients with HNC and their caregivers is a key part of nurses’ daily work.Some studies have shown that too little information support is conducive to the optimal treatment and rehabilitation of patients[26,27].HNC leads to high levels of dysfunction and significant reliance on the support of their caregivers,especially in the palliative stage [28].Also,the psychological problems of patients with HNC are more serious than those of patients with other tumors,and the degree of satisfaction with information needs is closely related to the level of anxiety and depression [10,26].Therefore,it is very beneficial for healthcare providers to understand the information needs of patients obtained from the use of scientific evaluation tools,thereby enabling personalized information support for patients.
Because the psychological impact of cancer experienced by patients in China and Western countries may differ,there may be differences among patients from different cultures in their understanding and acceptance of information support that is available[29].In China and many other countries worldwide,many patients,especially those with cancer,receive less information regarding their actual condition because of stress and fear.However,many studies have shown that most cancer patients are willing to receive as much information as possible about their disease,whether good or bad[30-32].This study offers a scientific tool that can be used to provide personalized information support for patients with HNC and their caregivers.
Some patients with thyroid cancer and their caregivers were included in our study because they are frequently seen in HNC Departments.Furthermore,their information needs did not appear to be any different in this study,even though they are often thought of as representing a different population (e.g.,the patients are primarily women,with a better prognosis and are younger).However,the information needs of these patients may require additional independent inquiry.We contacted the original author before including the patients with thyroid cancer,and based on the original author’s advice,we included patients with advanced thyroid cancer as well as those with metastatic thyroid cancer.
Based on the recommendations presented in international guidelines [33,34],the adaptation of HaNiQ and the psychometric testing of the instrument achieved satisfactory results.The questionnaire shows good psychometric properties in terms of content validity [18,19] and internal consistency [35].
The dimension and factor naming of the Chinese version was the same as the English version for patients with HNC.In the EFA,item 27 was over 0.45 in the Survivorship (factor 2=0.476) and Psychosocial (factor 4=0.503) subscales when administered to patients with HNC.Because the patient indicated a need to address genetic problems associated with the disease,no items were deleted.Based on the thinking habits of the Chinese people,this can be attributed to the social and psychological domains of information needs.However,there was a slight change in the attribution of questionnaire items among the caregivers.Item 8 of the questionnaire was over 0.45 in the Treatment (factor 2=0.520) and Survivorship (factor 3=0.467) subscales,and item 30 was over 0.45 in Survivorship (factor 3=0.498) and Disease Profile (factor 5=0.464)subscales.Because caregivers pay more attention to the disease,no items were deleted.The dimension of higher factor load is retained,that is,item 8 belongs to the Treatment dimension,and item 30 belongs to the Survivorship dimension.What’s more,items 22,23,and 27 that previously were included in the Psychosocial subscale are now in the survivorship subscale.This result is mainly because caregivers and patients have different perspectives on such issues as genetic correlation and disease-related survival stress.The reasons may be that the caregivers were under more psychological pressure in the process of care,playing a variety of social roles,while facing a heavy burden of caring patients,which have a greater impact on their own life and living conditions.Besides,having a tumor patient in the family can cause post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in caregivers;moreover,HNC has a genetic predisposition.For caregivers who are mainly immediate family members,the high demand for stress management,emotional support,and genetic information is close to the caregiver’s survival.
The questionnaire for patients with HNC was consistent with the original questionnaire with minor changes to the caregiver items.This questionnaire is acceptable and comprehensive.
Limitations.A limitation of this research is the cross-sectional study design.Moreover,the responsiveness to changes of the HaNiQ was not appropriately assessed.A longitudinal study should be used to reflect the changes in the information required at all stages of the HNC[30].Furthermore,some patients with HNC may not have responded to the questionnaire because of their poor physical state (perhaps because very few of these patients have a positive attitude towards treatment).Another limitation of our study was convenience sampling (i.e.,samples were selected only among those patients with HNC and their caregivers willing to fill out the questionnaires).
5.Conclusions
The Chinese version of the HaNiQ is a reliable and valid instrument for measuring information needs in patients with HNC and their caregivers.However,the Chinese version of the HaNiQ for caregivers has a slightly different structure from the original version.Further studies are required to verify the structure of the Chinese version of the HaNiQ for caregivers and the applicability of the tool in Chinese HNC patients and their caregivers.
Funding
This research was supported by Beijing University of Chinese Medicine [2020-JYB-ZDGG-081].
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Yu Li:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Data curation,Writing -original draft,Writing -review &editing,Project administration.Lihui Liu:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Data curation,Writing-review&editing,Supervision,Project administration.Rong Yan:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Data curation,Writing -review &editing.Chunxiang Su:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Writing -review &editing.Hong Guo:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Investigation,Resources,Writing -review &editing.Xiaoyu Li:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Writing -review &editing.Shujin Yue:Conceptualization,Methodology,Validation,Formal analysis,Funding acquisition,Writing -review&editing,Supervision,Project administration.
Declaration of competing interest
No conflict of interest has been declared by the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the patients with HNC and their caregivers who participated in this study.The authors are grateful to the directors from Nursing School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing Shijitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University,Beijing Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University,Cancer Hospital Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Peking University Cancer Hospital,and Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute for their helping with this research.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2021.06.004.
 International Journal of Nursing Sciences2021年3期
International Journal of Nursing Sciences2021年3期
- International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- The impacts of organizational culture and neoliberal ideology on the continued existence of incivility and bullying in healthcare institutions:A discussion paper
- Prevalence and correlates of lifestyle behavior,anxiety and depression in Chinese college freshman:A cross-sectional survey
- Understanding South African mothers’ challenges to adhere to exclusive breastfeeding at the workplace:A qualitative study
- Operating room nurses’ lived experiences of ethical codes:A phenomenological study in Iran
- A qualitative study on the experiences and attributions for resigned nurses with career plateau
- Sense of courage:The mediating role of courage between emotional reflexivity and work-life integration among nurses in Indian hospitals
